diff --git "a/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.jpg" "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.jpg"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..70ade7e
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.jpg" differ
diff --git "a/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.jpg" "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.jpg"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..4737a82
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.jpg" differ
diff --git "a/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.jpg" "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.jpg"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f010701
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.jpg" differ
diff --git "a/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/4.jpg" "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/4.jpg"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9953fee
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/4.jpg" differ
diff --git "a/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_W12D1.md" "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_W12D1.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..b4b3d33
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W12D1/W12D1\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_W12D1.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+#### Review: Out-of-Order
+
+- Dynamic: $Tomasulo$
+- Static: ( via code movement ) 在编译阶段,调整顺序,防止冲突
+
+#### Distributed Computing System
+
+- Example Problem: Snoopy Protocol(总线监听协议)
+- Coherence (分布式) vs. Consistency(集中式)
+
+$SMP$ (Symmetrical Multi-Processing)
+
+
+
+#### Coherence
+
+主要内容:Lecture 12
+
+- Snoopy(snoop:窥探,调查)
+
+ - Invalid:某个数据有修改后,全部有该数据的地方的 $valid$ 位都改为 $invalid$
+
+- Directory-based
+
+#### 主要任务:看懂这张图
+
+一篇写的还挺清楚的知乎:
+
+笔记:CPU中的cache(四) - Robinson的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/145049266
+
+
+
+##### Exclusive:
+
+假设有人拥有,并只有它拥有最新的数据,那它处于 exclusive 状态,此时 memory 还没有最新的数据,当有人要访问这个数据,
+
+exclusive 听到后,就会发出 read miss,使得 memory 听不到这个访问,abort 掉,并把它拥有的唯一新数据写回memory,并将自己的数据返回给想要这个数据的人,下一步变成 shared 状态。
+
+技术上如图:
+
+
+
+##### Shared:
+
+如果 memory 有两个数据 x,y,假设 x,y 的映射都是同一行,此时x在cache中,read y miss了,这时只要把 y 读过来就行了,因此转一圈依旧回到 shared 状态。
+
+##### Invalid:
+
+exclusive 有 x',shared状态有 x,有人拥有了最新的 x’‘,此时 exclusive 状态和 shared 状态都过时了,都转变为 Invalid状态。
+
+把所有旧的都写回memory,包括 x',x,但是 x' ,x 的写回 memory 的过程会被 write miss abort 掉。
+
+#### Consistency Problem
+
+$P_i$ 程序
+
+```
+a=0;
+...
+a=1;
+if(b==0)then
+```
+
+$P_j$ 程序
+
+```
+b=0;
+...
+b=1;
+if(a==0)then
+```
+
+Q: both `a==0` & `b==0` (在 $P_i$ 和 $P_j$ 同时跑的情况下)
+
+#### 一些概念
+
+- $SMP$ / Cluster / Grid / Cloud
+
+ - **SMP**:对称多处理"(Symmetrical Multi-Processing)简称 SMP
+
+ 是指在一个计算机上汇集了一组处理器(多CPU),各CPU之间共享内存子系统以及总线结构。
+
+ - **Cluster:**
+
+ 简单的说,集群(cluster)就是一组计算机,它们作为一个总体向用户提供一组网络资源。这些单个的计算机系统就是集群的节点(node)。一个理想的集群是,用户看来,集群是一个系统,而非多个计算机系统。而且集群系统的管理员能够任意添加和删改集群系统的节点。
+
+ - **Grid**(格网计算)是一种新的高性能的分布式计算方法。
+
+ 格网计算作为新一代的分布式计算方法,有集中管理,比如要加入某某grid才行
+
+ - **Cloud:**
+
+ 也是一种分布式计算方法,里面没有集中管理
+
+- Cloud Computing
+
+ - $SaaS$(Software as a Service)
+
+ - $PaaS$(Platform as a Service)
+
+ - $IaaS$(Infrastructure as a Service)
+
+ 
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git "a/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.png" "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.png"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..47b5975
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/1.png" differ
diff --git "a/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.png" "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.png"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fbb8a80
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/2.png" differ
diff --git "a/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.png" "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.png"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..25dbe2b
Binary files /dev/null and "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/3.png" differ
diff --git "a/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_Review_W15D2.md" "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_Review_W15D2.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..59867a3
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W15D2/W15D2\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205/Note_Review_W15D2.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+### 一、基础考点
+
+流水+循环+跳转预测
+
+没有跳转预测:加气泡(NOP指令 软气泡)
+
+如果有跳转预测:猜得对 是什么样的(使用的是饱和计数器)
+
+### 二、冗余存储
+
+RAID 1-0 :(概念如图)
+
+RAID 0-1:落了两个RADI 的盘,位mirror
+
+
+
+### 三、事务内存
+
+transaction:数据库里的概念,完成一个事物,需要n步操作,这个操作的序列,要保证必须一口气做完,如果中间被人打断了,必须重新做
+
+一致性:怎么理解Intel TSX 指令
+
+重讲一遍一致性
+
+一致性模型:软件与memory之间的一个合同
+
+
+
+- 带同步,最weak的方式,必须大家都同意了,才能越过同步点,颗粒度较大,开销较大,保证越过同步点后都是一致的
+- 不带同步
+ - 最严格的方式:打一个绝对物理时间的标签,严格按时间顺序操作,基本不可能,只是个模型而已
+ - sequential:可以通过技术实现的。定义:所有的进程 P1 P2 对共享的存储,可以看到相同的顺序(Intel 的考点在这),利用 cache 的 coherence
+
+任何人修改,都要在总线上发 `invalid` 信号
+
+
+
+可能要有一个 jump 指令?
+
+add x2 x2 3 不对memory操作
+
+abort_handler为什么要做这件事情?
+
+- 用一个寄存器存状态,看有没有出过事(相当于在xEnd清算)
+- $x_3$ 把cache中的 $x_0$ 换掉了,还没xend,此时无条件产生abort。
+
+为什么要 sub x2, x2, 3
+
+到xend检查状态位,看看从xbegin 到 xend 有没有出过事(几次无所谓
+
+cache line:检测位 总线上发出一条 `invalid xxx` 出事了!
+
+xbegin xend 每个line 都有一个监测位
diff --git a/W5D1/Note_W5D1_HuKeya.md b/W5D1/Note_W5D1_HuKeya.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..bd3dfdb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/W5D1/Note_W5D1_HuKeya.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+# Week 5 Day 1 Note By Hu Keya
+
+### Memory Hierarchy
+
+1. Register Cache / Memory / Disk
+2. Memory Technology
+3. Interface
+4. Timing
+
+### Register Cache / Memory / Disk
+
+ +
+By Von Neumann Structure we know that
+
+- codes and data are all stored in memory Unit
+- only CPU can visit memory unit.
+
+### Memory Technology
+
+How to make a memory device?
+
+- #### Electric Way:
+
+ - During 30-50s
+ - ms level
+ - Using relay to implement self-locking
+
+- #### Electronic Way:
+
+ - $\mu s$ $ns$ level
+
+ - During 70s: Using Logic Gates to implement latch and trigger such as R-S.
+
+
+
+By Von Neumann Structure we know that
+
+- codes and data are all stored in memory Unit
+- only CPU can visit memory unit.
+
+### Memory Technology
+
+How to make a memory device?
+
+- #### Electric Way:
+
+ - During 30-50s
+ - ms level
+ - Using relay to implement self-locking
+
+- #### Electronic Way:
+
+ - $\mu s$ $ns$ level
+
+ - During 70s: Using Logic Gates to implement latch and trigger such as R-S.
+
+ 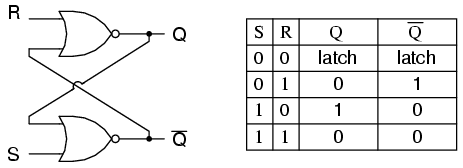 +
+ - During 80s~ : Using Capacitor, a dynamic way, such as DRAM
+
+### Interface
+
+Suppose that we have a chip with 1-bit width and $2^{10}$ length, we want to construct a memory of 8-bit width and $2^{16}$ length
+
+- make eight of chip in a row, that we get a module of 8-bit width and $2^{10}$ length
+- that make 64 of the module in a line, finally we get the memory.
+
+We have address $A [ 15: 0 ]$ for interface.
+
+- First we use $A [15:10]$ to determine which module ( from module 0 to module 63)
+- Then we use $A[9:0]$ to determine which chip to go ( from chip 0 to chip 7)
+
+### DRAM Read Timing
+
+For larger Memory there will be too many address wires, resulting in too many
+
+chip pins to place on the chip. To solve the problem, we transmit the address twice by column address and row address.
+
+**The process is as follows.**
+
+
+
+ - During 80s~ : Using Capacitor, a dynamic way, such as DRAM
+
+### Interface
+
+Suppose that we have a chip with 1-bit width and $2^{10}$ length, we want to construct a memory of 8-bit width and $2^{16}$ length
+
+- make eight of chip in a row, that we get a module of 8-bit width and $2^{10}$ length
+- that make 64 of the module in a line, finally we get the memory.
+
+We have address $A [ 15: 0 ]$ for interface.
+
+- First we use $A [15:10]$ to determine which module ( from module 0 to module 63)
+- Then we use $A[9:0]$ to determine which chip to go ( from chip 0 to chip 7)
+
+### DRAM Read Timing
+
+For larger Memory there will be too many address wires, resulting in too many
+
+chip pins to place on the chip. To solve the problem, we transmit the address twice by column address and row address.
+
+**The process is as follows.**
+
+ +
+- CAS_L: Column Address Select
+
+- A: Address
+
+- WE_L: Write Enable
+
+- OE_L: Output Enable
+
+- D: Data
+
+**Some Interpretation of process:**
+
+- Junk: Uncertain signal
+
+- High Z: high-impedance state with no signal
+
+- _L: Low level works
+
+**Reasons for asynchrony:**
+
+- Different signals sent should be given sufficient time to arrive.
+- Sufficient delay is required to detect capacitance levels
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f1fd0d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f92ba7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d057a29
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aa71cb3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e0a3eab
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png differ
diff --git "a/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md" "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c53d5b6
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+Cache (Cont.)
+
+....
+
+- Virtual vs Physics Cache ( Lecture 2)
+
+Memory ( Lecture 4 )
+
+- Organization (internal)
+- Interface (Bus)
+- Multi-Bank
+
+**两种virtual Page与Cache组合的方案:**
+
+
+
+访问所需的clock:$AMAT=T_{hit}+\eta\cross T_{penalty}$
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table in memory(+100)(Cache of page table,ex: $TLB$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+方案一:
+
+- if hit :+100+1
+- if miss:+100+1+100(miss率小于3%)
+
+方案二:
+
+- if hit:+1
+- if miss:+1+100+100
+
+此时方案二的效率显然更好
+
+> Q: what is tag?
+>
+> A: tag=where the “block” come from
+
+但是采用方案二,会引发一些问题
+
+- virtual-cache
+
+- synonymous/ Alias
+
+- solution
+
+ - $Q_1$:切换进程时,所有进程的虚地址都是一样的,切换时新的进程可能会使用y的虚地址,找到了y,同时tag也符合,但是y不是它要的,因为在这个进程可能相同的虚地址放的是z不是y
+
+ $x\in P_A$ , $y\in P_B$ , but $vm(x)=vm(y)$
+
+ solution:加个进程标签
+
+ - $PID+tag\Rightarrow tag_{new}$
+
+ - $Q_2$:同一个进程里,同一个进程的两个不同的虚地址被映射到同一个物理地址上,那么来自物理内存的某个数据会在cache中出现两个备份。
+
+ 用一个虚地址去修改的话,可能会造成数据不一致,即造成逻辑问题
+
+ $vm_1,vm_2\in P_A$ , but $f(vm_1)=f(vm_2)=P_{mx}$
+
+ solution:不让它存在两个备份
+
+ - 任意两个映射到相同$vp$ 的 $vm$ 它们的$vp$ 可能不同,但是 $dis$ (图中 $offset$ ) 一定相同。
+
+ 原理:virtual memory size > physical memory size,不同的 virtual page 的翻译可能会都对应同一个物理page的地址,但 page 的偏移量 $offset$ 一定都一样
+
+
+
+- CAS_L: Column Address Select
+
+- A: Address
+
+- WE_L: Write Enable
+
+- OE_L: Output Enable
+
+- D: Data
+
+**Some Interpretation of process:**
+
+- Junk: Uncertain signal
+
+- High Z: high-impedance state with no signal
+
+- _L: Low level works
+
+**Reasons for asynchrony:**
+
+- Different signals sent should be given sufficient time to arrive.
+- Sufficient delay is required to detect capacitance levels
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f1fd0d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f92ba7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d057a29
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aa71cb3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e0a3eab
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png differ
diff --git "a/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md" "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c53d5b6
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+Cache (Cont.)
+
+....
+
+- Virtual vs Physics Cache ( Lecture 2)
+
+Memory ( Lecture 4 )
+
+- Organization (internal)
+- Interface (Bus)
+- Multi-Bank
+
+**两种virtual Page与Cache组合的方案:**
+
+
+
+访问所需的clock:$AMAT=T_{hit}+\eta\cross T_{penalty}$
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table in memory(+100)(Cache of page table,ex: $TLB$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+方案一:
+
+- if hit :+100+1
+- if miss:+100+1+100(miss率小于3%)
+
+方案二:
+
+- if hit:+1
+- if miss:+1+100+100
+
+此时方案二的效率显然更好
+
+> Q: what is tag?
+>
+> A: tag=where the “block” come from
+
+但是采用方案二,会引发一些问题
+
+- virtual-cache
+
+- synonymous/ Alias
+
+- solution
+
+ - $Q_1$:切换进程时,所有进程的虚地址都是一样的,切换时新的进程可能会使用y的虚地址,找到了y,同时tag也符合,但是y不是它要的,因为在这个进程可能相同的虚地址放的是z不是y
+
+ $x\in P_A$ , $y\in P_B$ , but $vm(x)=vm(y)$
+
+ solution:加个进程标签
+
+ - $PID+tag\Rightarrow tag_{new}$
+
+ - $Q_2$:同一个进程里,同一个进程的两个不同的虚地址被映射到同一个物理地址上,那么来自物理内存的某个数据会在cache中出现两个备份。
+
+ 用一个虚地址去修改的话,可能会造成数据不一致,即造成逻辑问题
+
+ $vm_1,vm_2\in P_A$ , but $f(vm_1)=f(vm_2)=P_{mx}$
+
+ solution:不让它存在两个备份
+
+ - 任意两个映射到相同$vp$ 的 $vm$ 它们的$vp$ 可能不同,但是 $dis$ (图中 $offset$ ) 一定相同。
+
+ 原理:virtual memory size > physical memory size,不同的 virtual page 的翻译可能会都对应同一个物理page的地址,但 page 的偏移量 $offset$ 一定都一样
+
+  +
+ - 修改 size,使得红线移到蓝线左边,由于 $disp$ 一致,使得 $index$ 一致
+
+
+
+ - 修改 size,使得红线移到蓝线左边,由于 $disp$ 一致,使得 $index$ 一致
+
+  +
+ $pagesize=2^d\ (d=disp\ size)$
+ $cachesize=2^{i+b}\ (i=index\ size,b=bs\ size)$
+
+ 可以减小 cache size 或者增大 page size,使得不会存在$v_{m1}\neq v_{m2}$
+
+如何确定 $P_{mx}$ :
+
+- by Compiler
+
+- $malloc$ :$mmap$(Va,Pa)
+
+
+
+**$TLB$:(Translation Look-Aside buffer)**
+
+方案一:Virtual Addressing Cache
+
+
+
+ $pagesize=2^d\ (d=disp\ size)$
+ $cachesize=2^{i+b}\ (i=index\ size,b=bs\ size)$
+
+ 可以减小 cache size 或者增大 page size,使得不会存在$v_{m1}\neq v_{m2}$
+
+如何确定 $P_{mx}$ :
+
+- by Compiler
+
+- $malloc$ :$mmap$(Va,Pa)
+
+
+
+**$TLB$:(Translation Look-Aside buffer)**
+
+方案一:Virtual Addressing Cache
+
+ +
+方案二:Physical Addressing Cache
+
+
+
+方案二:Physical Addressing Cache
+
+ +
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table($1+\eta\cross 100$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+By using TLB,此时方案一也可以有很好的效率。
\ No newline at end of file
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table($1+\eta\cross 100$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+By using TLB,此时方案一也可以有很好的效率。
\ No newline at end of file
 +
+By Von Neumann Structure we know that
+
+- codes and data are all stored in memory Unit
+- only CPU can visit memory unit.
+
+### Memory Technology
+
+How to make a memory device?
+
+- #### Electric Way:
+
+ - During 30-50s
+ - ms level
+ - Using relay to implement self-locking
+
+- #### Electronic Way:
+
+ - $\mu s$ $ns$ level
+
+ - During 70s: Using Logic Gates to implement latch and trigger such as R-S.
+
+
+
+By Von Neumann Structure we know that
+
+- codes and data are all stored in memory Unit
+- only CPU can visit memory unit.
+
+### Memory Technology
+
+How to make a memory device?
+
+- #### Electric Way:
+
+ - During 30-50s
+ - ms level
+ - Using relay to implement self-locking
+
+- #### Electronic Way:
+
+ - $\mu s$ $ns$ level
+
+ - During 70s: Using Logic Gates to implement latch and trigger such as R-S.
+
+  +
+ - During 80s~ : Using Capacitor, a dynamic way, such as DRAM
+
+### Interface
+
+Suppose that we have a chip with 1-bit width and $2^{10}$ length, we want to construct a memory of 8-bit width and $2^{16}$ length
+
+- make eight of chip in a row, that we get a module of 8-bit width and $2^{10}$ length
+- that make 64 of the module in a line, finally we get the memory.
+
+We have address $A [ 15: 0 ]$ for interface.
+
+- First we use $A [15:10]$ to determine which module ( from module 0 to module 63)
+- Then we use $A[9:0]$ to determine which chip to go ( from chip 0 to chip 7)
+
+### DRAM Read Timing
+
+For larger Memory there will be too many address wires, resulting in too many
+
+chip pins to place on the chip. To solve the problem, we transmit the address twice by column address and row address.
+
+**The process is as follows.**
+
+
+
+ - During 80s~ : Using Capacitor, a dynamic way, such as DRAM
+
+### Interface
+
+Suppose that we have a chip with 1-bit width and $2^{10}$ length, we want to construct a memory of 8-bit width and $2^{16}$ length
+
+- make eight of chip in a row, that we get a module of 8-bit width and $2^{10}$ length
+- that make 64 of the module in a line, finally we get the memory.
+
+We have address $A [ 15: 0 ]$ for interface.
+
+- First we use $A [15:10]$ to determine which module ( from module 0 to module 63)
+- Then we use $A[9:0]$ to determine which chip to go ( from chip 0 to chip 7)
+
+### DRAM Read Timing
+
+For larger Memory there will be too many address wires, resulting in too many
+
+chip pins to place on the chip. To solve the problem, we transmit the address twice by column address and row address.
+
+**The process is as follows.**
+
+ +
+- CAS_L: Column Address Select
+
+- A: Address
+
+- WE_L: Write Enable
+
+- OE_L: Output Enable
+
+- D: Data
+
+**Some Interpretation of process:**
+
+- Junk: Uncertain signal
+
+- High Z: high-impedance state with no signal
+
+- _L: Low level works
+
+**Reasons for asynchrony:**
+
+- Different signals sent should be given sufficient time to arrive.
+- Sufficient delay is required to detect capacitance levels
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f1fd0d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f92ba7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d057a29
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aa71cb3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e0a3eab
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png differ
diff --git "a/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md" "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c53d5b6
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+Cache (Cont.)
+
+....
+
+- Virtual vs Physics Cache ( Lecture 2)
+
+Memory ( Lecture 4 )
+
+- Organization (internal)
+- Interface (Bus)
+- Multi-Bank
+
+**两种virtual Page与Cache组合的方案:**
+
+
+
+访问所需的clock:$AMAT=T_{hit}+\eta\cross T_{penalty}$
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table in memory(+100)(Cache of page table,ex: $TLB$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+方案一:
+
+- if hit :+100+1
+- if miss:+100+1+100(miss率小于3%)
+
+方案二:
+
+- if hit:+1
+- if miss:+1+100+100
+
+此时方案二的效率显然更好
+
+> Q: what is tag?
+>
+> A: tag=where the “block” come from
+
+但是采用方案二,会引发一些问题
+
+- virtual-cache
+
+- synonymous/ Alias
+
+- solution
+
+ - $Q_1$:切换进程时,所有进程的虚地址都是一样的,切换时新的进程可能会使用y的虚地址,找到了y,同时tag也符合,但是y不是它要的,因为在这个进程可能相同的虚地址放的是z不是y
+
+ $x\in P_A$ , $y\in P_B$ , but $vm(x)=vm(y)$
+
+ solution:加个进程标签
+
+ - $PID+tag\Rightarrow tag_{new}$
+
+ - $Q_2$:同一个进程里,同一个进程的两个不同的虚地址被映射到同一个物理地址上,那么来自物理内存的某个数据会在cache中出现两个备份。
+
+ 用一个虚地址去修改的话,可能会造成数据不一致,即造成逻辑问题
+
+ $vm_1,vm_2\in P_A$ , but $f(vm_1)=f(vm_2)=P_{mx}$
+
+ solution:不让它存在两个备份
+
+ - 任意两个映射到相同$vp$ 的 $vm$ 它们的$vp$ 可能不同,但是 $dis$ (图中 $offset$ ) 一定相同。
+
+ 原理:virtual memory size > physical memory size,不同的 virtual page 的翻译可能会都对应同一个物理page的地址,但 page 的偏移量 $offset$ 一定都一样
+
+
+
+- CAS_L: Column Address Select
+
+- A: Address
+
+- WE_L: Write Enable
+
+- OE_L: Output Enable
+
+- D: Data
+
+**Some Interpretation of process:**
+
+- Junk: Uncertain signal
+
+- High Z: high-impedance state with no signal
+
+- _L: Low level works
+
+**Reasons for asynchrony:**
+
+- Different signals sent should be given sufficient time to arrive.
+- Sufficient delay is required to detect capacitance levels
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f1fd0d3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/595bc3b6f9f06679f45e898b928eade.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f92ba7a
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/b1a0c72b1144e30b06bd59520846e51.jpg differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d057a29
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031112522466.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..aa71cb3
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113202349.png differ
diff --git a/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e0a3eab
Binary files /dev/null and b/W8D2/asset/image-20221031113224088.png differ
diff --git "a/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md" "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..c53d5b6
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/W8D2/note_20221102_\350\203\241\347\217\202\351\233\205.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+Cache (Cont.)
+
+....
+
+- Virtual vs Physics Cache ( Lecture 2)
+
+Memory ( Lecture 4 )
+
+- Organization (internal)
+- Interface (Bus)
+- Multi-Bank
+
+**两种virtual Page与Cache组合的方案:**
+
+
+
+访问所需的clock:$AMAT=T_{hit}+\eta\cross T_{penalty}$
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table in memory(+100)(Cache of page table,ex: $TLB$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+方案一:
+
+- if hit :+100+1
+- if miss:+100+1+100(miss率小于3%)
+
+方案二:
+
+- if hit:+1
+- if miss:+1+100+100
+
+此时方案二的效率显然更好
+
+> Q: what is tag?
+>
+> A: tag=where the “block” come from
+
+但是采用方案二,会引发一些问题
+
+- virtual-cache
+
+- synonymous/ Alias
+
+- solution
+
+ - $Q_1$:切换进程时,所有进程的虚地址都是一样的,切换时新的进程可能会使用y的虚地址,找到了y,同时tag也符合,但是y不是它要的,因为在这个进程可能相同的虚地址放的是z不是y
+
+ $x\in P_A$ , $y\in P_B$ , but $vm(x)=vm(y)$
+
+ solution:加个进程标签
+
+ - $PID+tag\Rightarrow tag_{new}$
+
+ - $Q_2$:同一个进程里,同一个进程的两个不同的虚地址被映射到同一个物理地址上,那么来自物理内存的某个数据会在cache中出现两个备份。
+
+ 用一个虚地址去修改的话,可能会造成数据不一致,即造成逻辑问题
+
+ $vm_1,vm_2\in P_A$ , but $f(vm_1)=f(vm_2)=P_{mx}$
+
+ solution:不让它存在两个备份
+
+ - 任意两个映射到相同$vp$ 的 $vm$ 它们的$vp$ 可能不同,但是 $dis$ (图中 $offset$ ) 一定相同。
+
+ 原理:virtual memory size > physical memory size,不同的 virtual page 的翻译可能会都对应同一个物理page的地址,但 page 的偏移量 $offset$ 一定都一样
+
+  +
+ - 修改 size,使得红线移到蓝线左边,由于 $disp$ 一致,使得 $index$ 一致
+
+
+
+ - 修改 size,使得红线移到蓝线左边,由于 $disp$ 一致,使得 $index$ 一致
+
+  +
+ $pagesize=2^d\ (d=disp\ size)$
+ $cachesize=2^{i+b}\ (i=index\ size,b=bs\ size)$
+
+ 可以减小 cache size 或者增大 page size,使得不会存在$v_{m1}\neq v_{m2}$
+
+如何确定 $P_{mx}$ :
+
+- by Compiler
+
+- $malloc$ :$mmap$(Va,Pa)
+
+
+
+**$TLB$:(Translation Look-Aside buffer)**
+
+方案一:Virtual Addressing Cache
+
+
+
+ $pagesize=2^d\ (d=disp\ size)$
+ $cachesize=2^{i+b}\ (i=index\ size,b=bs\ size)$
+
+ 可以减小 cache size 或者增大 page size,使得不会存在$v_{m1}\neq v_{m2}$
+
+如何确定 $P_{mx}$ :
+
+- by Compiler
+
+- $malloc$ :$mmap$(Va,Pa)
+
+
+
+**$TLB$:(Translation Look-Aside buffer)**
+
+方案一:Virtual Addressing Cache
+
+ +
+方案二:Physical Addressing Cache
+
+
+
+方案二:Physical Addressing Cache
+
+ +
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table($1+\eta\cross 100$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+By using TLB,此时方案一也可以有很好的效率。
\ No newline at end of file
+
+- visit cache+1
+- visit memory+100
+- visit page table($1+\eta\cross 100$)
+- More, n×100(if n-level page table) 多级页表
+
+By using TLB,此时方案一也可以有很好的效率。
\ No newline at end of file