(Exported from code.google.com/p/eazy-photoz, April 20, 2015.)
EAZY is a photometric redshift code designed to produce high-quality redshifts for situations where complete spectroscopic calibration samples are not available. Details of the algorithm and tests of the code on public multi-wavelength photometric datasets are presented by Brammer, van Dokkum & Coppi (2008).
Please include a citation to "Brammer, van Dokkum & Coppi, 2008, ApJ, 686, 1503" in the bibliography of any published work that makes use of EAZY.
For a summary of recent changes see also Updates.md.
In the terminal:
### If you have the Github SSH key enabled
git clone [email protected]:gbrammer/eazy-photoz.git eazy-photoz
### Otherwise just use https
git clone https://github.com/gbrammer/eazy-photoz.git eazy-photoz
cd eazy-photoz/src
makeRun the example HDF-N catalog Fernandez-Soto et al. 1999:
cd ../inputs
mkdir OUTPUT
../src/eazy # generates param file
../src/eazy -p zphot.param.defaultTo get updates to the repository committed since you checked out the code:
cd [path-to-eazy-photoz]
git pullSome scripts to interact with the EAZY input/outputs are available in the threedhst module, specifically eazyPy.
"""
Demo of the Eazy python helpers in threedhst/eazyPy
https://github.com/gbrammer/threedhst/blob/master/eazyPy.py
"""
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import threedhst.eazyPy as eazy
################################################
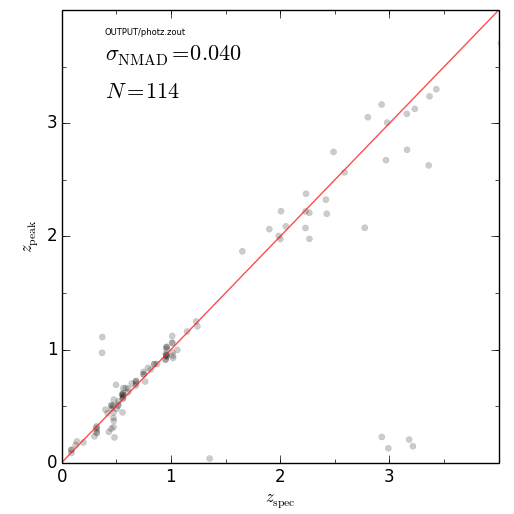
#### z_phot vs z_spec
################################################
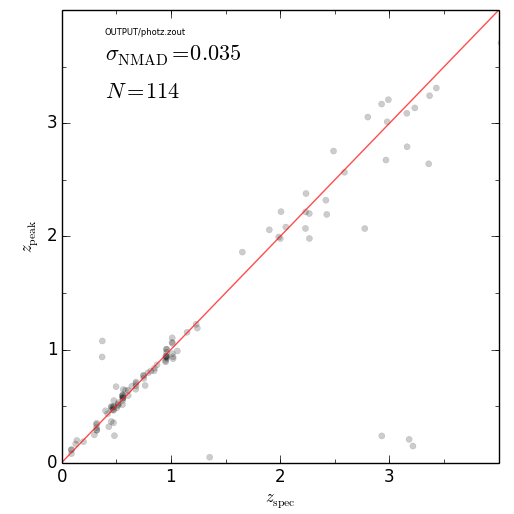
eazy.zPhot_zSpec('OUTPUT/photz.zout')
plt.savefig('zphot_zspec.png'); plt.close()################################################
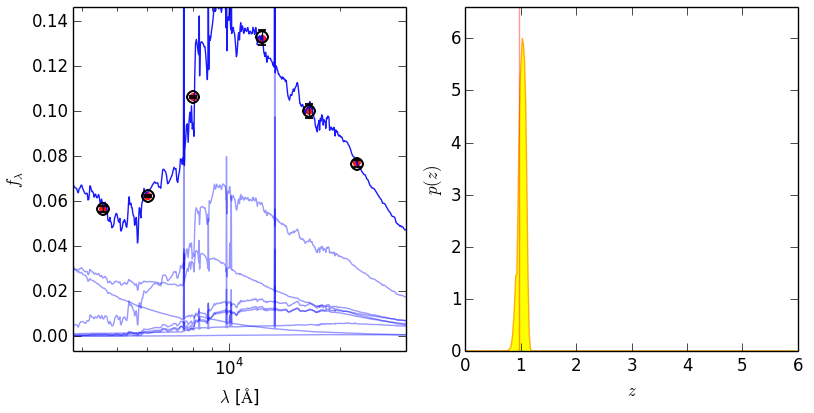
#### Example object. `idx` is zero-indexed
################################################
axes = eazy.plotExampleSED(idx=17, writePNG=False, MAIN_OUTPUT_FILE='photz',
OUTPUT_DIRECTORY='OUTPUT', CACHE_FILE='Same', lrange=[3800, 3.e4],
axes=None, individual_templates=True, fnu=False)
plt.savefig('eazy_fit.png'); plt.close()################################################
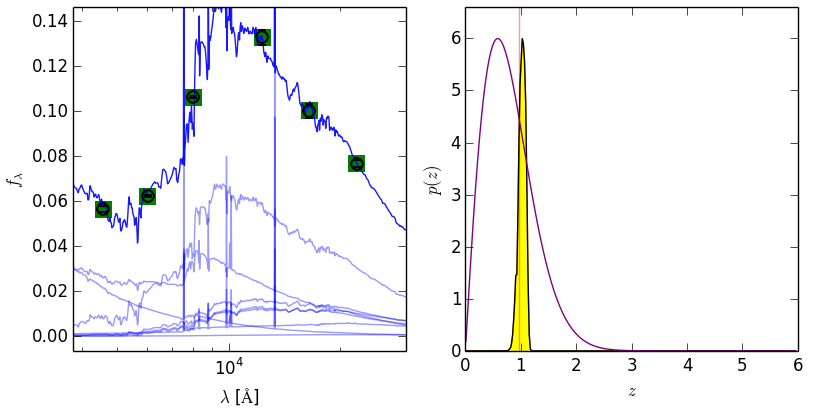
#### Pull out data from the BINARY_OUTPUTS files
################################################
## SED, data & fit
sed = eazy.getEazySED(17, MAIN_OUTPUT_FILE='photz', OUTPUT_DIRECTORY='./OUTPUT',
CACHE_FILE='Same', scale_flambda=True, verbose=False,
individual_templates=False)
lambdaz, temp_sed, lci, obs_sed, fobs, efobs = sed
axes[0].scatter(lci, obs_sed, color='orange', zorder=2)
axes[0].scatter(lci, fobs, color='green', marker='s', s=150, zorder=2)
## p(z)
zgrid, pzi, prior = eazy.getEazyPz(17, MAIN_OUTPUT_FILE='photz', OUTPUT_DIRECTORY='./OUTPUT',
CACHE_FILE='Same', binaries=None, get_prior=True)
axes[1].plot(zgrid, pzi, color='black')
axes[1].plot(zgrid, prior/prior.max()*pzi.max(), color='purple')
plt.savefig('eazy_fit_2.png')################################################
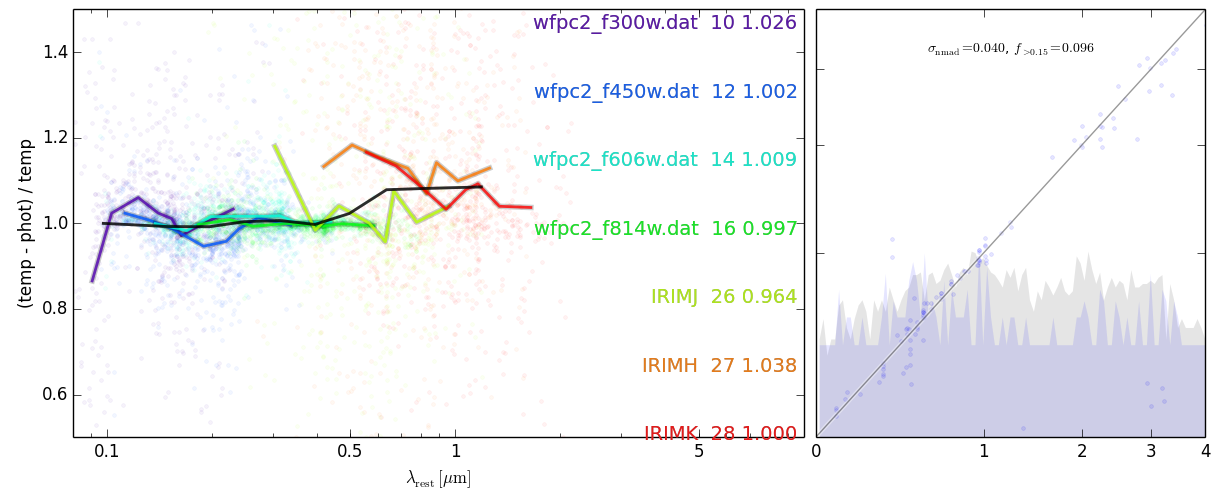
#### Investigate template fit residuals for zeropoints
################################################
eazy.show_fit_residuals(root='photz', PATH='./OUTPUT/', savefig='fit_residuals.png', adjust_zeropoints='zphot.zeropoint', fix_filter=None, ref_filter=28, get_resid=False, wclip=[1200, 30000.0])## Run again using the zphot.zeropoint file you just made, this can be done iteratively
params = eazy.EazyParam('zphot.param.default')
params['GET_ZP_OFFSETS'] = 'y'
params.write('zphot.param')
os.system('../src/eazy -p zphot.param -z zphot.zeropoint')
## Check z_phot vs z_spec again. Improves though modificaton was done with *all* objects in the
## catalog, not just (biased) subsample with z_spec.
eazy.zPhot_zSpec('OUTPUT/photz.zout')
plt.savefig('zphot_zspec_2.png'); plt.close()