- Path Sum II
中等
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals targetSum.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
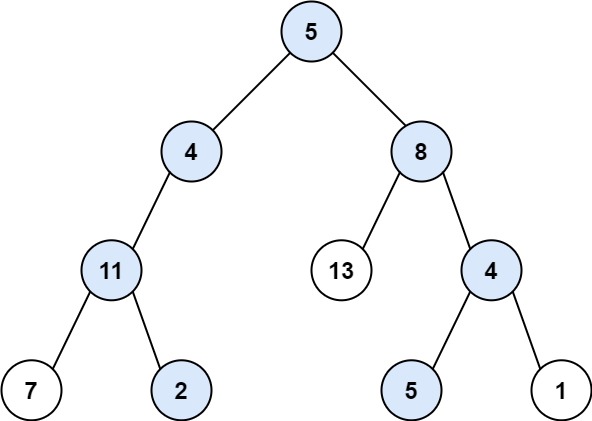
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 5000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
相关企业
- 字节跳动|11
- Facebook|7
- 亚马逊 Amazon|2
相关标签
- Tree
- Depth-First Search
- Backtracking
- Binary Tree
相似题目
- Path Sum 简单
- Binary Tree Paths 简单
- Path Sum III 中等
- Path Sum IV 中等
思路:我们采用dfs(深度优先搜索)递归遍历整棵树,在搜索的过程中要存储「经过的路径」和「最终结果」。每次对某节点处理完后,需要回溯一步,删除path中的该节点。
- 变量定义:数组path表示目前的路径;二维数组res存储所有的目标路径,即最终的返回结果。我们在dfs函数中需要传递root, target, path 和res。
- 递归条件(recursive case): 对于当前节点root,我们首先把它加入path中,然后分别对它的左右子树调用binaryTreePathSum函数,其中target值要减去root.val。只要有一个返回true,则说明存在这样的路径。
- 终止条件(base case):当前节点为空时,不做处理直接返回。当前节点为叶节点时,我们比较val与target是否相等。如果相等,说明从根节点到该节点的路径和符合要求,于是把当前path的拷贝加入我们的结果res中。
注意,我们在回溯的时候是对原数组进行inplace操作,而加入res中的是原数组的拷贝。
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n是节点的数量。我们每个节点只访问一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n)。
- 空间复杂度:取决于最终返回结果的res的空间大小。最差情况下,当树为完全二叉树且每条路径都符合要求时,空间复杂度为O(nlog(n))。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
currpath = []
result = []
self._pathSum(root, currpath, 0, targetSum, result)
return result
def _pathSum(self, currNode, currpath, currpathValueSum, targetSum, result):
if not currNode:
return
currpathValueSum += currNode.val
currpath.append(currNode.val)
# leaf
if not currNode.left and not currNode.right and currpathValueSum == targetSum:
result.append(currpath[:])
# non-leaf
self._pathSum(currNode.left, currpath, currpathValueSum, targetSum, result)
self._pathSum(currNode.right, currpath, currpathValueSum, targetSum, result)
# non-leaf go back one level
currpath.pop()
currpathValueSum -= currNode.val