- Word Search
中等
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search/
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
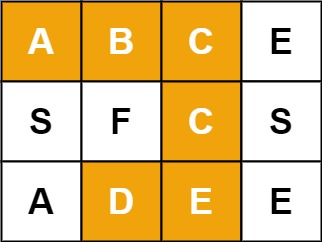
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
Output: true
Example 2:
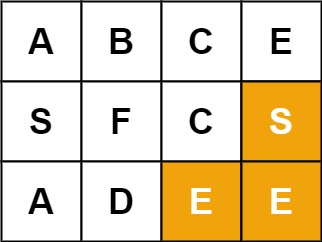
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
Output: true
Example 3:
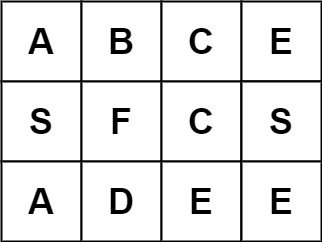
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
Output: false
Constraints:
m == board.length
n = board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 6
1 <= word.length <= 15
board and word consists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Follow up: Could you use search pruning to make your solution faster with a larger board?
相关企业
- 亚马逊 Amazon|34
- 微软 Microsoft|23
- 优步 Uber|17
- 彭博 Bloomberg|16
- Indeed|11
- Facebook|10
- 字节跳动|7
- 思科 Cisco|6
- 苹果 Apple|5
- 谷歌 Google|3
相关标签
- Array
- Backtracking
- Matrix
相似题目
- Word Search II 困难
深度优先搜索
遍历board每个点,看它是否和word开头字母相同,如果相同就就进入dfs过程
在dfs过程中 上下左右四个方向去找能匹配word里下个字符的位置
注意事项:visited:
- 一定要标记走过的点,避免重复使用,因为每个点只能用一次。
-
- dfs递归回溯时,还要把不去走的点标记为可用
$O(nm*3^length)
O(nm)是由于我们要遍历board每个点,判断它是否和word相同
O(3^length) 是由于我们dfs过程,四个方向都要去试,但有一个方向是从上一个位置过来的方向,过来的方向是不用去搜索的了
例如
abcd,先到达(0,0)位置的a,又走到(0,1)位置的b,不用回头再走a
但因为有剪枝,所以实际状态量要比这个小不少
class Solution:
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
if not board:
return False
visited = []
for i in range(len(board)):
visited.append([])
for j in range(len(board[0])):
visited[i].append(False)
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
visited[i][j] = True
found = self.dfs(board, i, j, word, 1, [board[i][j]], visited)
if found:
return True
visited[i][j] = False # backtracking
return False
def dfs(self, board, i, j, word, wordindex, currsubset, visited):
# print("".join(currsubset), word)
if "".join(currsubset) == word:
return True
for offsetx, offsety in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
newx, newy = i + offsetx, j + offsety
if not (0 <= newx <= len(board) - 1 and 0 <= newy <= len(board[0]) - 1) or visited[newx][newy]:
continue # invalid
currletter = board[newx][newy]
if currletter == word[wordindex]:
currsubset.append(currletter)
visited[newx][newy] = True
found = self.dfs(board, i+offsetx, j+offsety, word, wordindex+1, currsubset, visited)
currsubset.pop() # backtracking
visited[newx][newy] = False # backtracking
if found:
return True
return False