class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
low = float("inf")
result = 0
for i in range(len(prices)):
low = min(low, prices[i]) #取最左最小价格
result = max(result, prices[i] - low) #直接取最大区间利润
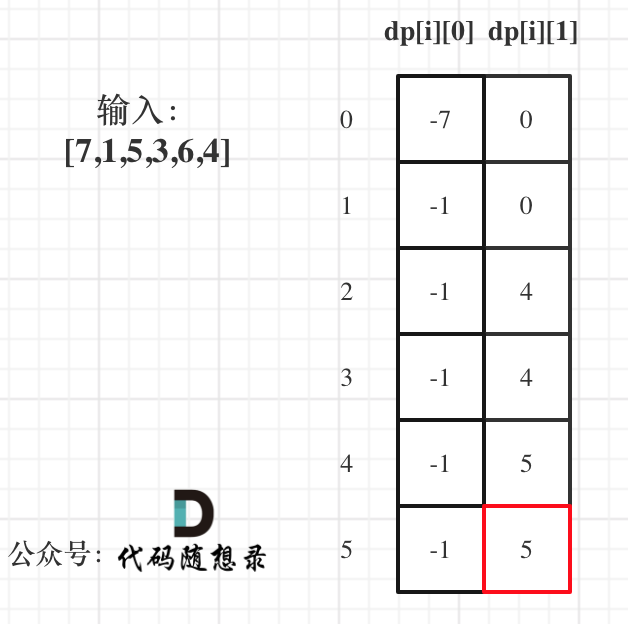
return resultdp[i][0]: max $ if hold a stock on day i
dp[i][0]: max $ if hold no stock on day i
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0],-prices[i] )
-
dp[i-1][0]: hold a stack oni-1, remain the same on day i -
-prices[i]: buy a stack on dayi
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], prices[i] + dp[i-1][0])
-
dp[i-1][1]: hold no stack on dayi-1, remain the same -
prices[i] + dp[i-1][0]: throw the stack today (dayi).
dp[0][0]: Because we hold a stock on day 0, therefore we must buy on day 0, so it will be -prices[0]
dp[0][1]: No stack on day 0, therefore 0.
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [[0,0] for _ in range(len(prices))]
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], -prices[i])
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i][0]+prices[i])
return dp[len(prices) - 1][1]Sum:
Using DP axtually do exactlly the same with greedy. we can see dp[i][0] maintain the min to buy, and dp[i][1] maintain the max_profit.
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
result = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
profit = prices[i] - prices[i-1]
if profit > 0 :
result += profit
return resultclass Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [[0,0] for _ in range(len(prices))]
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i])
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i])
return dp[len(prices) - 1][1]class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
if len(prices) == 0:
return 0
dp = [0] * 5
dp[1] = -prices[0]
dp[3] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
dp[1] = max(dp[1], dp[0] - prices[i])
dp[2] = max(dp[2], dp[1] + prices[i])
dp[3] = max(dp[3], dp[2] - prices[i])
dp[4] = max(dp[4], dp[3] + prices[i])
return dp[4]New: k times limitation of buying/selling stock.
Challenge: Initialization when i is 0. When j is even, we can see it as it bought and sold in the same day, therefore we have the status of not holding a stock the kth time.
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, k: int, prices: List[int]) -> int:
dp = [[0]*2*k for _ in range(len(prices))]
for j in range(0, 2*k, 2):
dp[0][j] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
for j in range(0, 2*k, 2): # j is even, stand for holding a stock
if j==0:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], -prices[i])
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1] - prices[i])
dp[i][j+1] = max(dp[i-1][j+1], dp[i-1][j] + prices[i])
return dp[len(prices)-1][2*k-1]Several different status:
-
Hold a stock
-
Do not hold a stock
- All other day
- Sold a stock today
- Cooldown day today (sold a stock yesterday)
To achieve these four status:
-
Hold a stock:
- hold a stock yesterday (keep the same status with yesterday)
- buy a stock today
- Yesterday is Cooldown day
- Yester is normal hold no stock day
Therefore,
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][3] - prices[i], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i]) -
All other day hold no stock: Hold no stock yesterday, cooldown day yesterday.
Therefore,
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][3]) -
Sold a stock today: Hold a stock yesterday.
dp[i][2] = dp[i-1][0] + prices[i] -
Cooldown day today: Sold a stock yesterday.
dp[i][3] = dp[i-1][2]
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(prices)
dp = [[0] * 4 for _ in range(n)]
dp[0][0] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1,n):
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][3] - prices[i], dp[i-1][1] - prices[i])
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][3])
dp[i][2] = dp[i-1][0] + prices[i]
dp[i][3] = dp[i-1][2]
return max(dp[n-1][3], dp[n-1][1], dp[n-1][2])Same with Problem 122, just add the transaction fee.
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int:
n = len(prices)
hold, free = [0] * n, [0] * n
hold[0] = -prices[0]
for i in range(1, n):
hold[i] = max(hold[i - 1], free[i - 1] - prices[i])
free[i] = max(free[i - 1], hold[i - 1] + prices[i] - fee)
return free[-1]