在装完Ubuntu20.04后,配置团队相关的东西的配置文档
Ubuntu20.04的安装在b站有许多教程,跟着来就好
-
先搞个系统盘然后进入bios更改启动顺序为USB驱动第一
-
重启按esc进入启动引导界面将Ubuntu调为第一
-
按照提示选择到分配磁盘
- /swap 分电脑运存那么多
- /efi 分4G 用来放启动引导
- / 其他的都放这里
- 打开终端:ctrl+alt+T(之后输入的命令都是输入到终端里面)
- 终端就是输入命令的窗口,Windows的cmd一样
- ==在终端内ctrl+shift+c才是复制,ctrl+shift+v粘贴==
- 基础命令
- cd 进入一个文件夹
- mkdir 创建一个文件夹
- Tab可以在输入命令时补全命令,可以增加敲命令的速度,也可以在忘记命令的时候起到提示的作用
- 按键盘上键可以重复上一条命令
sudo apt install vim
sudo chmod u+w /etc/sudoers
sudo vim /etc/sudoers
//在最后一行代码后加入
user ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
(user 为用户名)
用来翻墙的
http://101.34.95.10:8081/?platform=linux_x86_64&cur_version=1672215479
.deb文件的安装
dpkg -i xxx.deb
写.md文档
wget http://fishros.com/install -O fishros && . fishros
这是运行这个脚本的命令,按照他提示就好,它会提醒你需要换源(换源是为了更快更好的安装一些东西),输入的全部为11211(==注意一定要安装ROS1,notice版本==)
同时把rosdepc也下好
用于之后的下载用的
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
用于之后运行代码
sudo pip3 install -U catkin_tools
用来运行代码
sudo apt install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-rosmon
用于拉取团队代码和版本管理
- Git是一个工具用来管理代码的管理
- 工作空间是ROS下一种类似文件夹的东西,规定了里面的包含的最基本的东西
- ssh是用来安全连接的,用来登nuc和拉代码的
- 设置git的user name和email
git config --global user.name "LSY"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
-
检查是否存在SSH Key
cd ~/.ssh ls //看是否存在 id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub文件,如果存在,说明已经有SSH Key -
没有就生成一个
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "[email protected]"
一直按回车
-
然后拷贝密钥
cat id_rsa.pub //拷贝秘钥 ssh-rsa开头 -
去github添加SSH Key
- 点头像setting
http://wiki.ros.org/cn/ROS/Tutorials/InstallingandConfiguringROSEnvironment(官方教程,下面是具体操作的命令)
mkdir -p ~/rm_ws/src
cd ~/rm_ws/src
catkin_init_workspace
cd ..
catkin built
sudo apt install git
先把仓库的代码fork到自己仓库,然后再用ssh克隆到工作空间
cd rm_ws/src
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_control.git
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_controllers.git
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_manual.git
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_config.git
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_description.git
git clone [email protected]:L-SY/rm_bringup.git
直接复制多个就可以帮你一次性git完
在编译前先使用rosdepc(在rm_ws下)
rosdepc install -r --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro $ROS_DISTRO -y
vim .bashrc
==vim是一个编辑工具进去之后先按任意键就可以进入编辑模式,编辑完之后按ESC退出编辑模式,按 :wq(这是保存退出的意思)==
进去之后全删了复制粘贴下面的
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files (in the package bash-doc)
# for examples
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
# don't put duplicate lines or lines starting with space in the history.
# See bash(1) for more options
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
# append to the history file, don't overwrite it
shopt -s histappend
# for setting history length see HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in bash(1)
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
# check the window size after each command and, if necessary,
# update the values of LINES and COLUMNS.
shopt -s checkwinsize
# If set, the pattern "**" used in a pathname expansion context will
# match all files and zero or more directories and subdirectories.
#shopt -s globstar
# make less more friendly for non-text input files, see lesspipe(1)
[ -x /usr/bin/lesspipe ] && eval "$(SHELL=/bin/sh lesspipe)"
# set variable identifying the chroot you work in (used in the prompt below)
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
# set a fancy prompt (non-color, unless we know we "want" color)
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
# uncomment for a colored prompt, if the terminal has the capability; turned
# off by default to not distract the user: the focus in a terminal window
# should be on the output of commands, not on the prompt
#force_color_prompt=yes
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
# If this is an xterm set the title to user@host:dir
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
# enable color support of ls and also add handy aliases
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
# colored GCC warnings and errors
#export GCC_COLORS='error=01;31:warning=01;35:note=01;36:caret=01;32:locus=01:quote=01'
# some more ls aliases
alias ll='ls -alF'
alias la='ls -A'
alias l='ls -CF'
# Add an "alert" alias for long running commands. Use like so:
# sleep 10; alert
alias alert='notify-send --urgency=low -i "$([ $? = 0 ] && echo terminal || echo error)" "$(history|tail -n1|sed -e '\''s/^\s*[0-9]\+\s*//;s/[;&|]\s*alert$//'\'')"'
# Alias definitions.
# You may want to put all your additions into a separate file like
# ~/.bash_aliases, instead of adding them here directly.
# See /usr/share/doc/bash-doc/examples in the bash-doc package.
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
# enable programmable completion features (you don't need to enable
# this, if it's already enabled in /etc/bash.bashrc and /etc/profile
# sources /etc/bash.bashrc).
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
source ~/rm_ws/devel/setup.bash
export PATH=/home/lsy/snap/clion/198/bin:$PATH
export ROS_IP=`ifconfig | grep -Eo 'inet (addr:)?([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -Eo '([0-9]*\.){3}[0-9]*' | grep -v '127.0.0.1' | grep -v '172.17.0.1'`
if test -z "${ROS_IP}"
then
export ROS_IP=`dig +short localhost`
fi
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://192.168.2.220:11311
echo "ROS IP: ${ROS_IP}
ROS Master URI: ${ROS_MASTER_URI}"
alias setcan0='sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000'
alias setcan1='sudo ip link set can1 up type can bitrate 1000000'
alias setcan2='sudo ip link set can2 up type can bitrate 1000000'
alias setcan3='sudo ip link set can3 up type can bitrate 1000000'
alias engineer='ssh [email protected]'
alias balance='ssh [email protected]'
alias hero='ssh [email protected]'
alias standar4='ssh [email protected]'
alias standar5='ssh [email protected]'
alias standar3='ssh [email protected]'
alias sentry='ssh [email protected]'
export ROBOT_TYPE=engineer
alias engineer_client='rosrun actionlib_tools axclient.py /engineer_middleware/move_steps'
alias note='typora rm_note/rm_clion/rm_manual.md'
alias rqt_joint='rosrun rqt_joint_trajectory_controller rqt_joint_trajectory_controller'
export filepath="/etc/apt/"
alias load_ros='mon launch engineer_arm_config start.launch'
alias load_controller='. load.sh'
alias bringup="mon launch rm_bringup engineer.launch "
alias use_current="rosrun moveit_commander moveit_commander_cmdline.py"
export MVCAM_SDK_PATH=/opt/MVS
export MVCAM_COMMON_RUNENV=/opt/MVS/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/MVS/lib/64:/opt/MVS/lib/32:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
用于看代码写代码
https://www.jetbrains.com/zh-cn/clion/download/download-thanks.html?platform=linux
(可能有点久)
解压
tar -xzvf CLion-2022.3.2.tar.gz
以上基本配置就完成了!!!
https://dynamic-x-docs.netlify.app/
- ssh免密
ssh-copy-id dynamicx@host
- 配置CLion
- 配置deployment
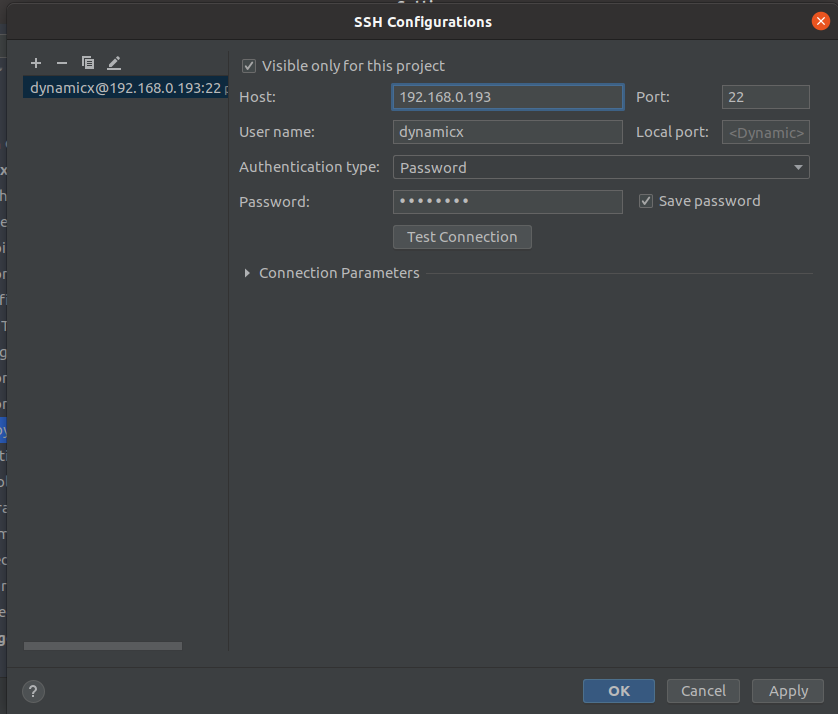
- 首先,在deployment处点击添加符号,文件类型选择SFTP,并命名为engineer
- 接下来是配置connection,点击SSH configuration处的省略号配置SSH
- 接下来在Mapping里配置
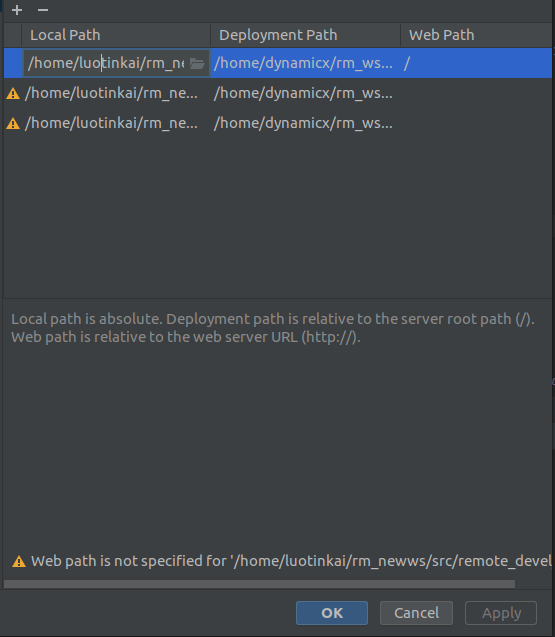
现在这一步是把本地的路径映射到目标主机上去
本地路径分别是:/home/username/工作空间名/src 对应的deployment path为/home/dynamicx/rm_ws/src(固定的)
/home/username/工作空间名/src/remote_devel/lib 对应的deployment path为/home/dynamicx/rm_ws/src/devel/lib
/home/username/工作空间名/src/remote_devel/include 对应的deployment path为/home/dynamicx/rm_ws/devel/include
配置好之后应用再点击OK
最后一步是配置Excluded path
同样是点击添加符号,然后输入路径为/home/username/工作空间名/src/remote_build
然后配置好SSH之后退出到deployment界面,同样点击Apply,再点击OK,完成上述流程之后就完全配置好了,如果需要进行远程传输,则进行如下
- Clion配置(为了兼容catkin build和catkin_make)
- 打开 File | Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | CMake
- 将 CMake options 的值更改为 -DCATKIN_DEVEL_PREFIX=../devel
- 将 Build directory 的值更改为
../build