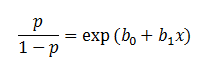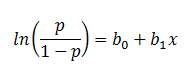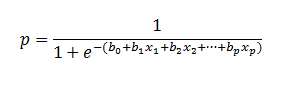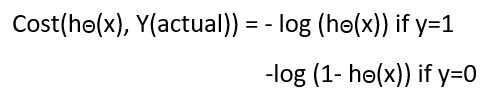Its a simplest yet widely used algorithm used in Machine Learning used for binary predictions.
Logistic regression is a classification algorithm used to assign observations to a discrete set of classes.
It is a statistical method for predicting binary classes. The outcome or target variable is dichotomous in nature. Dichotomous means there are only two possible classes. For example, it can be used for problems like: whether the loan of an individual gets approved or not, predicting whether a student passes or fails in his/her SAT exam . It computes the probability of an event occurrence.
- It is a special case of linear regression where the target variable is categorical in nature. It uses a log of odds as the dependent variable. Logistic Regression predicts the probability of occurrence of a binary event utilizing a logit function.
A linear regression is a linear approximation of a casual relationship between two or more variables. In more simpler words,
In linear model, we have a dependent variable or target variable and xn dependent varaibles or features from which we predict our target variable.
In general, these methods are used to predict the value of a response (dependent) variable from one or more predictor (independent) variables, where the variables are numeric."
Logistic regression predicts the probability of an outcome that can only have two values (i.e. a dichotomy). The prediction is based on the use of one or several predictors (numerical and categorical). A linear regression is not appropriate for predicting the value of a binary variable for two reasons:
- A linear regression will predict values outside the acceptable range (e.g. predicting probabilities outside the range 0 to 1)
- Since the dichotomous experiments can only have one of two possible values for each experiment, the residuals will not be normally distributed about the predicted line.
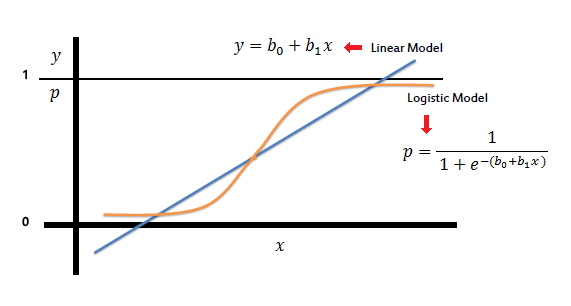
On the other hand, a logistic regression produces a logistic curve, which is limited to values between 0 and 1.
In Logistic Regression, the curve is constructed using the natural logarithm of the “odds” of the target variable, rather than the probability. Moreover, the predictors do not have to be normally distributed or have equal variance in each group.
Let's see the linear regression equation...
y= bo + b1 * x1
In the logistic regression the constant (b0) moves the curve left and right and the slope (b1) defines the steepness of the curve. By simple transformation, the logistic regression equation can be written in terms of an odds ratio.
Finally, taking the natural log of both sides, we can write the equation in terms of log-odds (logit) which is a linear function of the predictors. The coefficient (b1) is the amount the logit (log-odds) changes with a one unit change in x.
Logistic regression can handle any number of numerical and/or categorical variables.
Visualization of Linear and Logisic Regression
Model
Output = 0 or 1
Hypothesis => Y = WX + B
hΘ(x) = sigmoid (Z)
The cost function is calculated as an average of loss functions.The loss function is a value which is calculated at every instance. The loss function maps the model output of a single training example to their associated costs. It takes as input the model prediction and ground truth and outputs a numerical value.
Loss-function L: P*T -> R
where,
P = set of all predictions
T = ground truths
R = real numbers set.
Instead of Mean Squared Error, we use a cost function called Cross-Entropy, also known as Log Loss. Cross-entropy loss can be divided into two separate cost functions: one for y=1 and one for y=0.
Just as ordinary least square regression is the method used to estimate coefficients for the best fit line in linear regression, logistic regression uses maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) to obtain the model coefficients that relate predictors to the target. After this initial function is estimated, the process is repeated until LL (Log Likelihood) does not change significantly.
So, all we have the output value in a boundary between 0 and 1.
Maximizing the (log) likelihood is equivalent to minimizing the binary cross entropy. There is literally no difference between the two objective functions, so there can be no difference between the resulting model or its characteristics.