给你一个下标从 0 开始的 m x n 二进制矩阵 mat 和一个整数 cols ,表示你需要选出的列数。
如果一行中,所有的 1 都被你选中的列所覆盖,那么我们称这一行 被覆盖 了。
请你返回在选择 cols 列的情况下,被覆盖 的行数 最大 为多少。
示例 1:
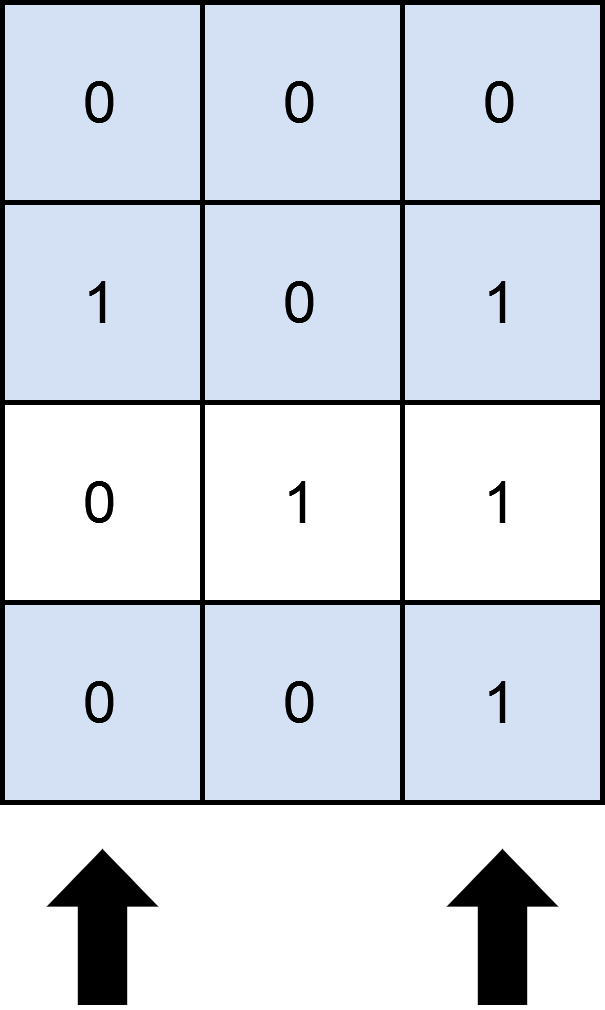
输入:mat = [[0,0,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]], cols = 2 输出:3 解释: 如上图所示,覆盖 3 行的一种可行办法是选择第 0 和第 2 列。 可以看出,不存在大于 3 行被覆盖的方案,所以我们返回 3 。
示例 2:
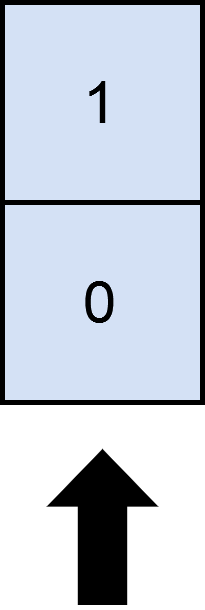
输入:mat = [[1],[0]], cols = 1 输出:2 解释: 选择唯一的一列,两行都被覆盖了,原因是整个矩阵都被覆盖了。 所以我们返回 2 。
提示:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12mat[i][j]要么是0要么是1。1 <= cols <= n
方法一:DFS 或二进制枚举
直接二进制枚举选中的列,然后判断是否覆盖所有行中的 1,若是,更新答案。
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def maximumRows(self, mat: List[List[int]], cols: int) -> int:
def dfs(mask, i):
if i > n or mask.bit_count() > cols:
return
nonlocal ans
if i == n:
t = sum((v & mask) == v for v in arr)
ans = max(ans, t)
return
dfs(mask, i + 1)
dfs(mask | 1 << i, i + 1)
arr = []
ans, n = 0, len(mat[0])
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
x = 0
for j, v in enumerate(row):
x |= v << j
arr.append(x)
dfs(0, 0)
return ansclass Solution:
def maximumRows(self, mat: List[List[int]], cols: int) -> int:
arr = []
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
x = 0
for j, v in enumerate(row):
x |= v << j
arr.append(x)
ans, n = 0, len(mat[0])
for mask in range(1, 1 << n | 1):
if mask.bit_count() > cols:
continue
t = sum((v & mask) == v for v in arr)
ans = max(ans, t)
return ansclass Solution {
private int ans;
public int maximumRows(int[][] mat, int cols) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int[] arr = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int x = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
x |= mat[i][j] << j;
}
arr[i] = x;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 1; mask <= 1 << n; ++mask) {
if (Integer.bitCount(mask) > cols) {
continue;
}
int t = 0;
for (int v : arr) {
if ((v & mask) == v) {
++t;
}
}
ans = Math.max(ans, t);
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maximumRows(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int cols) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<int> arr(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int x = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) x |= mat[i][j] << j;
arr[i] = x;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int mask = 1; mask <= 1 << n; ++mask) {
if (__builtin_popcount(mask) > cols) continue;
int t = 0;
for (int v : arr) t += (v & mask) == v;
ans = max(ans, t);
}
return ans;
}
};func maximumRows(mat [][]int, cols int) int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
arr := make([]int, m)
for i, row := range mat {
x := 0
for j, v := range row {
x |= v << j
}
arr[i] = x
}
ans := 0
for mask := 1; mask <= 1<<n; mask++ {
if bits.OnesCount(uint(mask)) != cols {
continue
}
t := 0
for _, v := range arr {
if (v & mask) == v {
t++
}
}
ans = max(ans, t)
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}