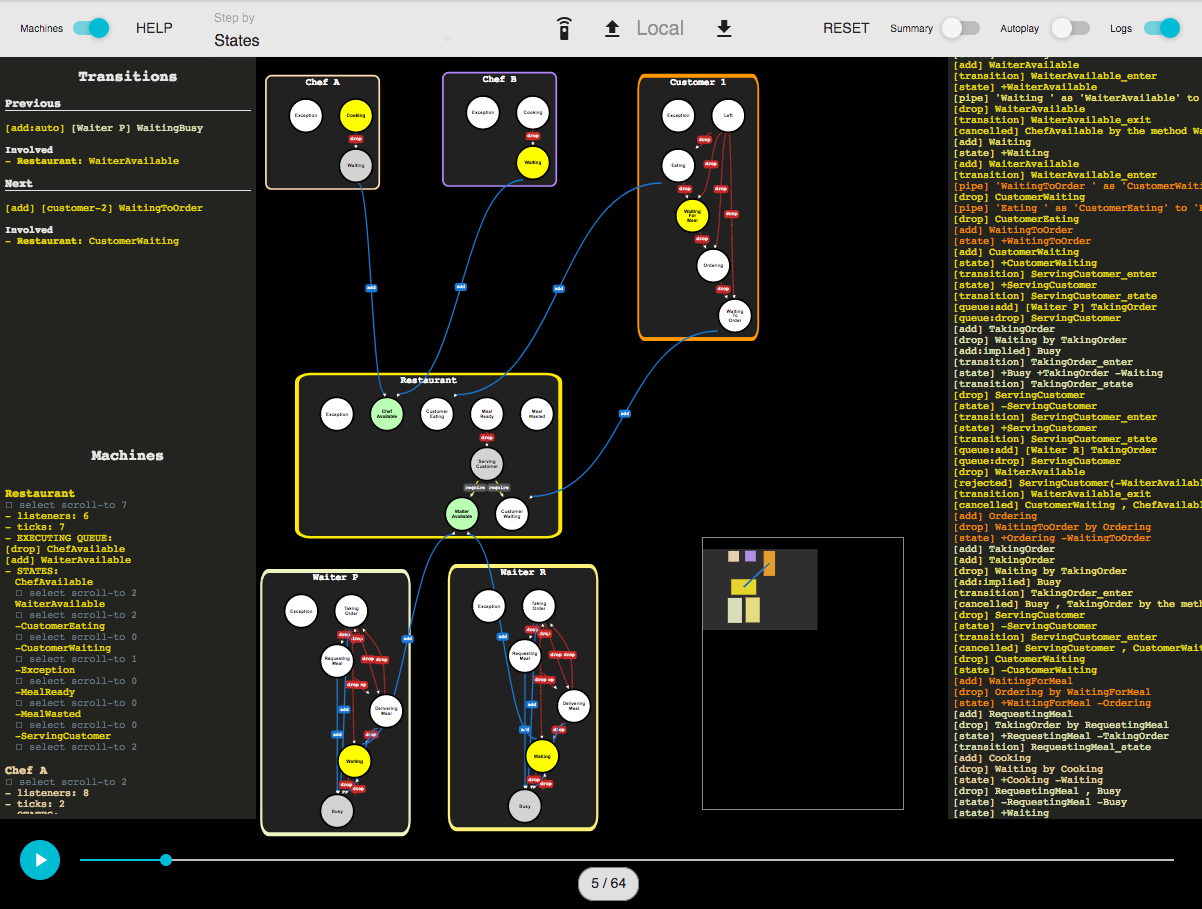
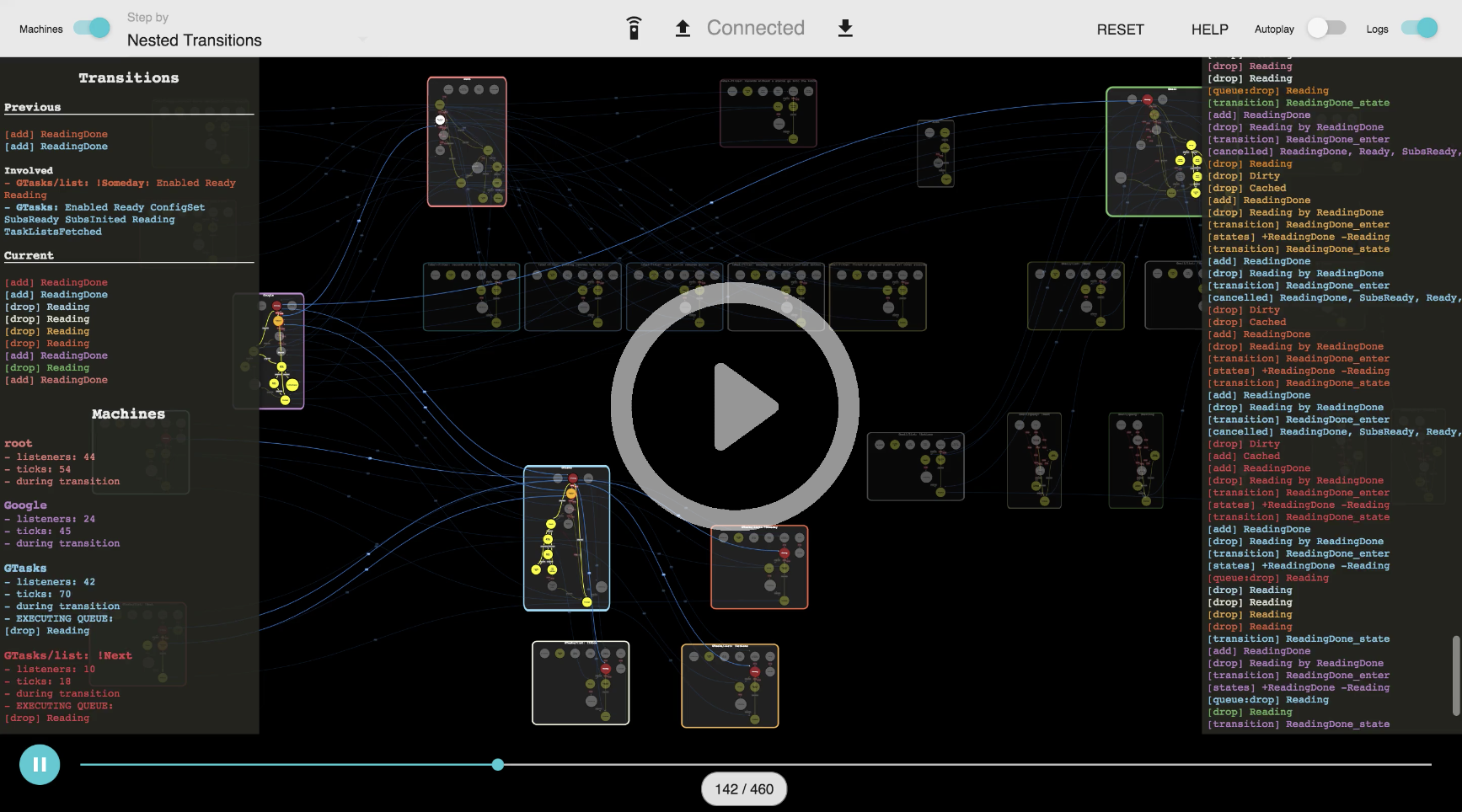
AsyncMachine is a relational state machine (dependency graph) for a declarative flow control.
Usages:
- state management
- parallel tasks
- loose coupling
- resource allocation / disposal
- exception handling
- fault tolerance
- method cancellation
It can be used as a single state machine, or a network composed of many. Gzipped code is 7.5kb.
npm i asyncmachine
- AsyncMachine - The Definitive Guide (wiki)
PDF version (25 pages, 1.5mb) - API docs (TypeScript)
- Roadmap
Components:
Features:
- synchronous mutations
- state negotiation
- cancellation
- automatic states
- exception handling
- visual inspector / debugger
This basic examples makes use of: states, transitions, relations and synchronous mutations.
import { machine } from 'asyncmachine'
// define
const state = {
// state Wet when activated, requires state Water to be active
Wet: {
require: ['Water']
},
// state Dry when activated, will drop (de-activate) state Wet
Dry: {
drop: ['Wet']
},
// state Water when activated, will add (activate) state Wet and
// drop (de-activate) state Dry
Water: {
add: ['Wet'],
drop: ['Dry']
}
}
// initialize
const example = machine(state)
// initially the machine has no active states
example.is() // -> []
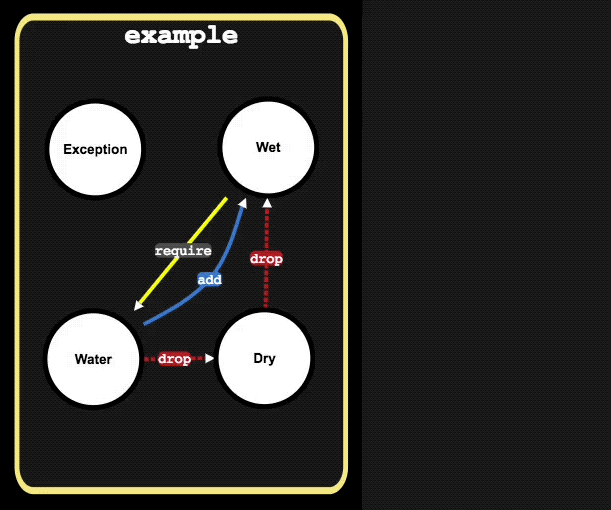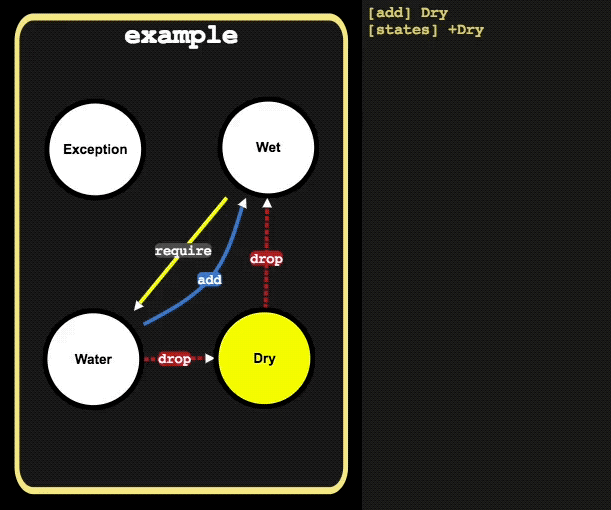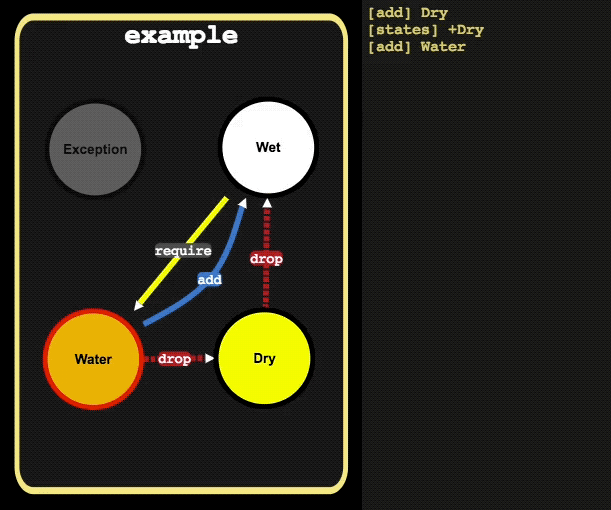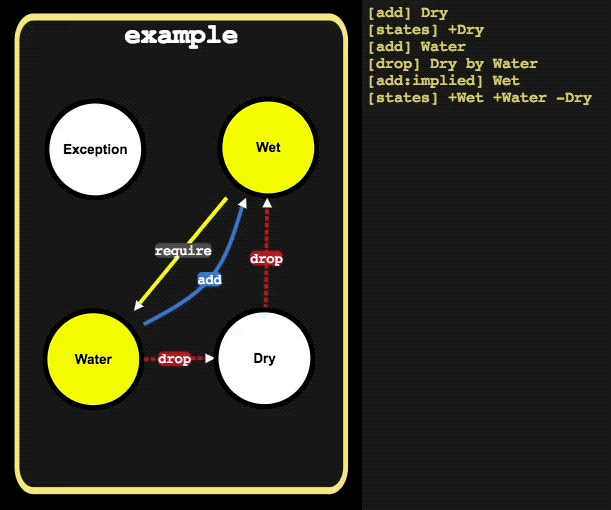
// activate state Dry
example.add('Dry')
example.is() // -> [ 'Dry' ]
// activate state Water, which will resolve the relations:
// 1. Water activates Wet
// 2. Wet requires Water
// 3. Dry de-activates Wet
// 4. Water de-activates Dry
// 5. Water activates Wet
example.add('Water')
example.is() // -> [ 'Wet', 'Water' ]Presents how the state negotiation works.
Presents the following concepts: automatic states, synchronous mutations, delayed mutations and loose coupling.
A simple fault tolerance (retrying) using the Exception state.
Shows how pipes forward states between machines.
Shows various types of transition handlers and the way params get passed to them.
Classic TodoMCV example using AsyncMachine as the controller and React as the view.
Observe state changes and navigate through specific paths with RxJS, then feed the result back as a state.
- Comming soon!
A complex example showing how to solve the producer / consumer problem using AsyncMachine.
For a real world example check TaskBot - a real-time sync engine for Google APIs.
MIT