Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
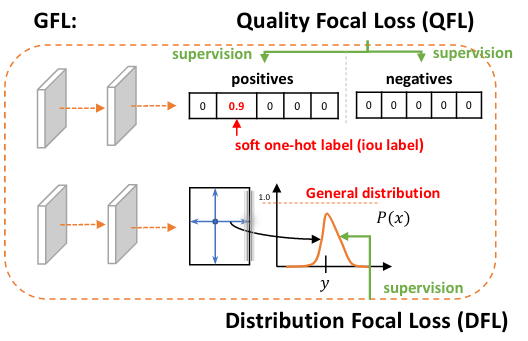
One-stage detector basically formulates object detection as dense classification and localization. The classification is usually optimized by Focal Loss and the box location is commonly learned under Dirac delta distribution. A recent trend for one-stage detectors is to introduce an individual prediction branch to estimate the quality of localization, where the predicted quality facilitates the classification to improve detection performance. This paper delves into the representations of the above three fundamental elements: quality estimation, classification and localization. Two problems are discovered in existing practices, including (1) the inconsistent usage of the quality estimation and classification between training and inference and (2) the inflexible Dirac delta distribution for localization when there is ambiguity and uncertainty in complex scenes. To address the problems, we design new representations for these elements. Specifically, we merge the quality estimation into the class prediction vector to form a joint representation of localization quality and classification, and use a vector to represent arbitrary distribution of box locations. The improved representations eliminate the inconsistency risk and accurately depict the flexible distribution in real data, but contain continuous labels, which is beyond the scope of Focal Loss. We then propose Generalized Focal Loss (GFL) that generalizes Focal Loss from its discrete form to the continuous version for successful optimization. On COCO test-dev, GFL achieves 45.0% AP using ResNet-101 backbone, surpassing state-of-the-art SAPD (43.5%) and ATSS (43.6%) with higher or comparable inference speed, under the same backbone and training settings. Notably, our best model can achieve a single-model single-scale AP of 48.2%, at 10 FPS on a single 2080Ti GPU.
| Backbone | Style | Lr schd | Multi-scale Training | Inf time (fps) | box AP | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-50 | pytorch | 1x | No | 19.5 | 40.2 | config | model | log |
| R-50 | pytorch | 2x | Yes | 19.5 | 42.9 | config | model | log |
| R-101 | pytorch | 2x | Yes | 14.7 | 44.7 | config | model | log |
| R-101-dcnv2 | pytorch | 2x | Yes | 12.9 | 47.1 | config | model | log |
| X-101-32x4d | pytorch | 2x | Yes | 12.1 | 45.9 | config | model | log |
| X-101-32x4d-dcnv2 | pytorch | 2x | Yes | 10.7 | 48.1 | config | model | log |
[1] 1x and 2x mean the model is trained for 90K and 180K iterations, respectively.
[2] All results are obtained with a single model and without any test time data augmentation such as multi-scale, flipping and etc..
[3] dcnv2 denotes deformable convolutional networks v2.
[4] FPS is tested with a single GeForce RTX 2080Ti GPU, using a batch size of 1.
We provide config files to reproduce the object detection results in the paper Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection
@article{li2020generalized,
title={Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection},
author={Li, Xiang and Wang, Wenhai and Wu, Lijun and Chen, Shuo and Hu, Xiaolin and Li, Jun and Tang, Jinhui and Yang, Jian},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04388},
year={2020}
}