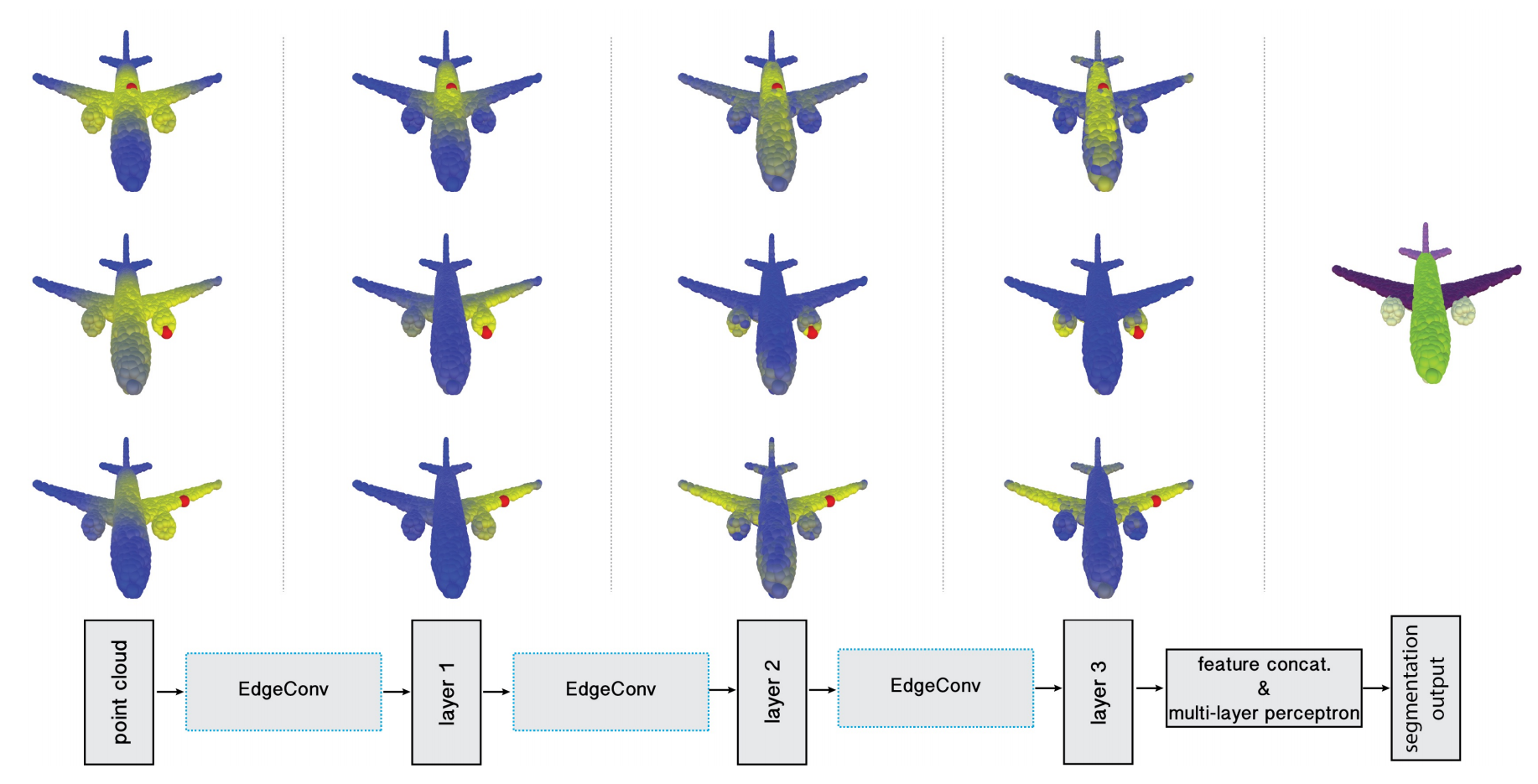
Point clouds provide a flexible geometric representation suitable for countless applications in computer graphics; they also comprise the raw output of most 3D data acquisition devices. While hand-designed features on point clouds have long been proposed in graphics and vision, however, the recent overwhelming success of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image analysis suggests the value of adapting insight from CNN to the point cloud world. Point clouds inherently lack topological information so designing a model to recover topology can enrich the representation power of point clouds. To this end, we propose a new neural network module dubbed EdgeConv suitable for CNN-based high-level tasks on point clouds including classification and segmentation. EdgeConv acts on graphs dynamically computed in each layer of the network. It is differentiable and can be plugged into existing architectures. Compared to existing modules operating in extrinsic space or treating each point independently, EdgeConv has several appealing properties: It incorporates local neighborhood information; it can be stacked applied to learn global shape properties; and in multi-layer systems affinity in feature space captures semantic characteristics over potentially long distances in the original embedding. We show the performance of our model on standard benchmarks including ModelNet40, ShapeNetPart, and S3DIS.
We implement DGCNN and provide the results and checkpoints on S3DIS dataset.
Notice: We follow the implementations in the original DGCNN paper and a PyTorch implementation of DGCNN code.
| Method | Split | Lr schd | Mem (GB) | Inf time (fps) | mIoU (Val set) | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DGCNN | Area_1 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 68.33 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | Area_2 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 40.68 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | Area_3 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 69.38 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | Area_4 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 50.07 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | Area_5 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 50.59 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | Area_6 | cosine 100e | 13.1 | 77.94 | model | log | |
| DGCNN | 6-fold | 59.43 |
Notes:
- We use XYZ+Color+Normalized_XYZ as input in all the experiments on S3DIS datasets.
Area_5Split means training the model on Area_1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and testing on Area_5.6-foldSplit means the overall result of 6 different splits (Area_1, Area_2, Area_3, Area_4, Area_5 and Area_6 Splits).- Users need to modify
train_areaandtest_areain the S3DIS dataset's config to set the training and testing areas, respectively.
Since DGCNN testing adopts sliding patch inference which involves random point sampling, and the test script uses fixed random seeds while the random seeds of validation in training are not fixed, the test results may be slightly different from the results reported above.
@article{dgcnn,
title={Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds},
author={Wang, Yue and Sun, Yongbin and Liu, Ziwei and Sarma, Sanjay E. and Bronstein, Michael M. and Solomon, Justin M.},
journal={ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
year={2019}
}