Lets contain our cdk pipeline in a new top level directory called:
cd /workspace/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023
mkdir thumbing-serverless-cdkThis is so we can use the AWS CDK CLI for anywhere.
npm install aws-cdk -gWe'll add the the install to our gitpod task file
- name: cdk
before: |
npm install aws-cdk -gWe'll initialize a new cdk project within the folder we created:
cdk init app --language typescriptAdd the following code to your thumbing-serverless-cdk-stack.ts
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3';
const bucketName: string = process.env.THUMBING_BUCKET_NAME as string;
const bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'ThumbingBucket', {
bucketName: bucketName,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});export THUMBING_BUCKET_NAME="cruddur-thumbs"
gp env THUMBING_BUCKET_NAME="cruddur-thumbs"Deploying stacks with the AWS CDK requires dedicated Amazon S3 buckets and other containers to be available to AWS CloudFormation during deployment.
cdk bootstrap "aws://$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID/$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION"-
Use
cdk synthto check cdk file before deploying it -
Run the cdk bootstrap command to configure our account for CDK
gitpod /workspace/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023/thumbing-serverless-cdk (main) $ cdk bootstrap "aws://873001202713/ca-central-1"
⏳ Bootstrapping environment aws://873001202713/ca-central-1...
Trusted accounts for deployment: (none)
Trusted accounts for lookup: (none)
Using default execution policy of 'arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess'. Pass '--cloudformation-execution-policies' to customize.
CDKToolkit: creating CloudFormation changeset...
✅ Environment aws://873001202713/ca-central-1 bootstrapped.-
Use
cdk deployto deploy the CDK stack to AWS -
Create
.env.exampleto create env variables for CDK
cp .env.example .env inside .gitpod.yml. This is because .env is ignored with our gitignore
THUMBING_BUCKET_NAME="br-assets.cruddur.com"
THUMBING_FUNCTION_PATH="/workspace/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023/aws/lambdas/process-images/"
THUMBING_S3_FOLDER_INPUT="avatars/original"
THUMBING_S3_FOLDER_OUTPUT="avatars/processed"
THUMBING_WEBHOOK_URL="api.cruddur.com/webhooks/avatar"
THUMBING_TOPIC_NAME="cruddur-assets"Working with CDK will help a lot with productivity
https://github.com/poxrud/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023
- create inside /aws/lambdas/process-images -- index.js -- test.js -- s3-image-processing.js -- example.json
initialize the folder as npm so that we could install sharpjs and run tests
cd /aws/lambdas/process-images
npm init -y
npm i sharpinstall s3 client
npm i @aws-sdk/client-s3-
deply with
cdk deploy -
build sharp libarary for production. Use instructions here: https://sharp.pixelplumbing.com/install#aws-lambda
rm -rf nodule_modules/sharp
SHARP_IGNORE_GLOBAL_LIBVIPS=1 npm install --arch=x64 --platform=linux --libc=glibc sharp- inside
/thumbing-serverless-cdk-stack.tsin the bottom of the constructor, add code to create s3 bucked event, to trigger a lambda on file uploads. Using this code:
this.createS3NotifyToLambda(folderInput, lambda, bucket)Then add the function createS3NotifyToLambda to the class.
Then try it out with cdk synth and if all is good deploy with cdk deploy.
importBucket(bucketName: string): s3.IBucket {
const bucket = s3.Bucket.fromBucketName(this, "AssetsBucket", bucketName);
return bucket;
}Here is the stack running:
-
setup CloudFront distribution
-
Point it to S3 bucket
-
Give bucket permission policy to allow CloudFront to access it
-
Point R53 assets.mycruddur.net to point to the CloudFront distribution
-
Manually create s3 bucket
assets.mycruddur.net
- Give our Lambda permissions to write to s3
createPolicyBucketAccess(bucketArn: string){
const s3ReadWritePolicy = new iam.PolicyStatement({
actions: [
's3:GetObject',
's3:PutObject',
],
resources: [
`${bucketArn}/*`,
]
});
return s3ReadWritePolicy;
}- attach the policy to our lambda
lambda.addToRolePolicy(s3ReadWritePolicy);- manually upload a large photo and check that a processed version was correctly placed in
avatars/processed
-
create SNS Topic, SNS Subscription, for webhook, on processed images by modifying
thumbing-serverless.cdk-stack.ts -
Change architecture to use a different bucket for uploads, and another for processed images
UPLOADS_BUCKET_NAME="mycruddur-uploaded-avatars"
ASSETS_BUCKET_NAME="assets.mycruddur.net"
ASSETS_FUNCTION_PATH="/workspace/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023/aws/lambdas/process-images/"
THUMBING_S3_FOLDER_INPUT="avatars/original"
THUMBING_S3_FOLDER_OUTPUT="avatars/processed"
THUMBING_WEBHOOK_URL="https://api.mycruddur.net/webhooks/avatar"
THUMBING_TOPIC_NAME="cruddur-assets"Here is the upload bucket firing event:
R53 entry for assets.mycruddur.net
Finally here is the image served from CloudFront
#app.py
@app.route("/api/profile/update", methods=['POST','OPTIONS'])
@cross_origin()
def data_update_profile():
auth_header = request.headers.get('Authorization')
if (auth_header == None):
LOGGER.debug("auth token not provided")
return {}, 401
bio = request.json.get('bio',None)
display_name = request.json.get('display_name',None)
try:
claims = CognitoJwtToken.verify(auth_header)
cognito_user_id = claims['sub']
model = UpdateProfile.run(
cognito_user_id=cognito_user_id,
bio=bio,
display_name=display_name
)
if model['errors'] is not None:
return model['errors'], 422
else:
return model['data'], 200
except TokenVerifyError as e:
# unauthenicatied request
LOGGER.debug(e)
return {}, 401- make backend-flask/db/sql/users/update.sql
UPDATE public.users
SET
bio = %(bio)s,
display_name= %(display_name)s
WHERE
users.cognito_user_id = %(cognito_user_id)s
RETURNING handle;- add db migration generator in order to add a new "bio" field to our users table in the db
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.schema_information (
id integer UNIQUE,
last_successful_run text
);
INSERT INTO
public.schema_information (id, last_successful_run)
VALUES(1, '0') ON CONFLICT (id) DO NOTHING;export UPLOADS_BUCKET_NAME="mycruddur-uploaded-avatars"
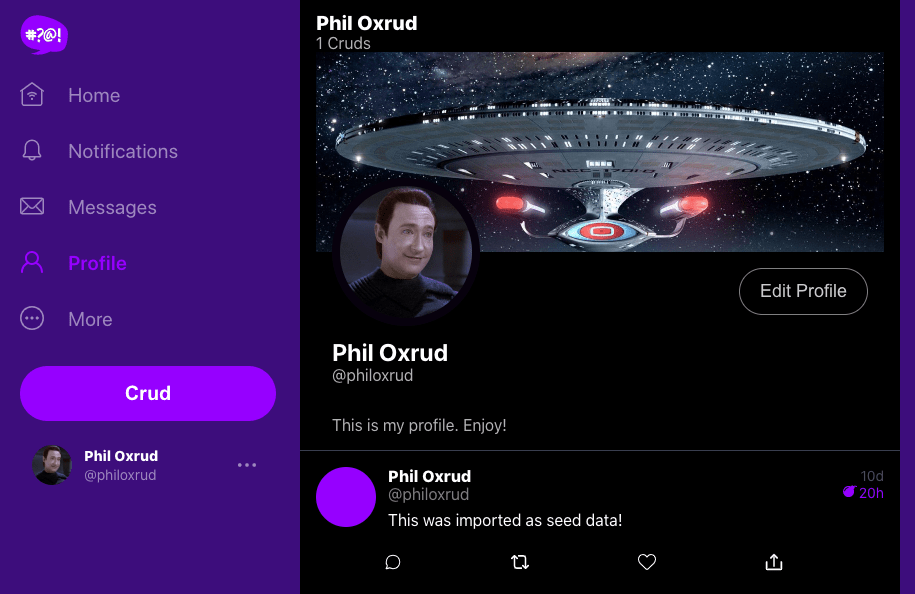
gp env UPLOADS_BUCKET_NAME="mycruddur-uploaded-avatars"Here is the profile editing screen:

Here is the updated and saved new profile

- Implemented in
bin/db/migrateandbin/db/rollback - Required the creation of a new table in the db called
schema_information
-
add Lambda code to create presigned PUT url's for uploading
-
add Lambda code for the JWT verificaiton and authorization
- in aws/lambdas/lambda-authorizer
"use strict";
const { CognitoJwtVerifier } = require("aws-jwt-verify");
const jwtVerifier = CognitoJwtVerifier.create({
userPoolId: process.env.USER_POOL_ID,
tokenUse: "access",
clientId: process.env.CLIENT_ID
});
exports.handler = async (event) => {
console.log("request:", JSON.stringify(event, undefined, 2));
const jwt = event.headers.authorization;
try {
const payload = await jwtVerifier.verify(jwt);
console.log("Access allowed. JWT payload:", payload);
} catch (err) {
console.error("Access forbidden:", err);
return {
isAuthorized: false,
};
}
return {
isAuthorized: true,
};
};also need to install jwt npm package
npm i aws-jwt-verify- zip up the lambda-authorizer folder
gitpod /workspace/aws-bootcamp-cruddur-2023/aws/lambdas (main) $ zip -r lambda-authorizer.zip lambda-authorizer/
adding: lambda-authorizer/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/index.js (deflated 44%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/package.json (deflated 35%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/LICENSE (deflated 65%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/asn1.js (deflated 74%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/assert.js (deflated 76%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/cognito-verifier.js (deflated 71%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/error.js (deflated 77%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/https-common.js (deflated 52%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/https-node.js (deflated 60%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/https.js (deflated 62%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/index.js (deflated 53%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/jwk.js (deflated 74%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/jwt-model.js (deflated 30%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/jwt-rsa.js (deflated 78%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/jwt.js (deflated 74%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/node-web-compat-node.js (deflated 62%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/node-web-compat-web.js (deflated 59%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/node-web-compat.js (deflated 40%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/safe-json-parse.js (deflated 52%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/typing-util.js (deflated 19%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/cjs/package.json (deflated 34%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/ (stored 0%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/asn1.js (deflated 74%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/assert.js (deflated 76%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/cognito-verifier.js (deflated 71%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/error.js (deflated 71%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/https-common.js (deflated 50%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/https-node.js (deflated 60%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/https.js (deflated 61%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/index.js (deflated 27%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/jwk.js (deflated 73%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/jwt-model.js (deflated 18%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/jwt-rsa.js (deflated 78%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/jwt.js (deflated 73%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/node-web-compat-node.js (deflated 63%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/node-web-compat-web.js (deflated 60%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/node-web-compat.js (deflated 41%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/safe-json-parse.js (deflated 50%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/typing-util.js (deflated 16%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/dist/esm/package.json (deflated 34%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/package.json (deflated 71%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/README.md (deflated 75%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/asn1.d.ts (deflated 59%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/assert.d.ts (deflated 75%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/cognito-verifier.d.ts (deflated 72%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/error.d.ts (deflated 76%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/https-common.d.ts (deflated 41%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/https-node.d.ts (deflated 48%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/https.d.ts (deflated 63%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/index.d.ts (deflated 33%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/jwk.d.ts (deflated 74%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/jwt-model.d.ts (deflated 72%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/jwt-rsa.d.ts (deflated 77%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/jwt.d.ts (deflated 63%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/safe-json-parse.d.ts (deflated 48%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/aws-jwt-verify/typing-util.d.ts (deflated 65%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/node_modules/.package-lock.json (deflated 35%)
adding: lambda-authorizer/package-lock.json (deflated 46%)- upload the zip file to the Lambda
- add the following IAM inline policy to the Lambda Authorizer
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "logs:CreateLogGroup",
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:ca-central-1:632626636018:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:ca-central-1:632626636018:log-group:/aws/lambda/CruddurApiGatewayLambdaAuthorizer:*"
]
}
]
}- create an API Gateway with the POST
/avatars/key_uploadroute. Assign the above Authorizer Lambda to this route.
The API Gateway has a Lambda Authorizer, that will validate the passed in JWT and then return a success or failed validation.
If the validation is successful the anther Lambda will run that will create a signed url, that will be used to upload a profile image directly to the s3 profile uploads bucket. The ruby Lambda will assume that the request is authorized and will create a signed URL for profile image uploads.
-inside lambdas/cruddur-upload-avatar/function.rb
require 'aws-sdk-s3'
require 'json'
require 'jwt'
def handler(event:, context:)
puts "EVENT: #{event}"
token = event['headers']['authorization'].split(' ')[1]
puts({step: 'presignedurl', access_token: token}.to_json)
body_hash = JSON.parse(event["body"])
extension = body_hash["extension"]
decoded_token = JWT.decode token, nil, false
cognito_user_uuid = decoded_token[0]['sub']
s3 = Aws::S3::Resource.new
bucket_name = ENV["UPLOADS_BUCKET_NAME"]
object_key = "#{cognito_user_uuid}.#{extension}"
puts({object_key: object_key}.to_json)
obj = s3.bucket(bucket_name).object(object_key)
url = obj.presigned_url(:put, expires_in: 60 * 5)
body = {url: url}.to_json
{
headers: {
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "*, Authorization",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "OPTIONS,PUT,POST"
},
statusCode: 200,
body: body
}
end # def handleralso add a Gemfile with the following:
source "https://rubygems.org"
gem "aws-sdk-s3"
gem "ox"
gem "jwt"- install ruby Gemfiles dependencies, zip it up and upload to AWS Lambda
rbenv install 2.7.7
rbenv local 2.7.7
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install
zip -r function.zip function.rb vendor-
configure API Gateway to use this Lambda
-
configure S3 CORS settings, so that uploads to the bucket would be possible
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": [
"*"
],
"AllowedMethods": [
"PUT"
],
"AllowedOrigins": [
"*"
],
"ExposeHeaders": []
}
]- add IAM permissions to the CruddurUploadAvatar Lambda ruby function. This is needed to be able to generate signed URL.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:PutObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::mycruddur-uploaded-avatars/*"
}
]
}To fix Lambda CORS issue, setup API Gateway CORS settings as below:
I have found that creating a Layer was not necessary. Instead it is possible to run bundle install and ask it to include
all the packages (gems) in the local folder. This folder can then be zipped up and sent to AWS Lambda.
rbenv install 2.7.7
rbenv local 2.7.7
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install
zip -r function.zip function.rb vendor-
First we need to update the frontend to point to the API gateway. Grab the API Gateway URL and update our .env frontend files with this.
- in /frontend-react-js/Dockerfile.prod add:
ARG REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL ENV REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL=$REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL
-
also add this to the .erb file:
REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL=<%= ENV['REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL']%> - inside gitpod cli
$ export REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL="https://hx6xrw3sta.execute-api.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com"
gp env REACT_APP_API_GATEWAY_ENDPOINT_URL="https://hx6xrw3sta.execute-api.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com"-
edit
ProfileForm.jsto use the API Gateway endpoint to get a signed url for profile image upload -
serve the uploaded image from cloudfront
// ProfileAvatar.js
export default function ProfileAvatar(props) {
import './ProfileAvatar.css';
export default function ProfileAvatar(props) {
const backgroundImage = `url("https://assets.mycruddur.net/avatars/${props.id}.jpg")`;
const styles = {
backgroundImage: backgroundImage,
backgroundSize: 'cover',
backgroundPosition: 'center',
};
return (
<div
className="profile-avatar"
style={styles}
></div>
);
}Here is the final result, we can see the profile image after a profile update.