| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two cells sharing a common edge is 1.
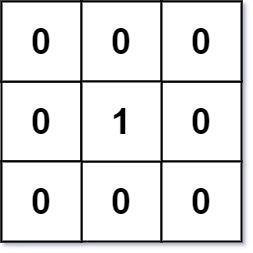
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
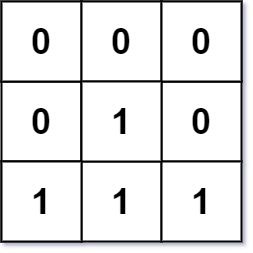
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]] Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1041 <= m * n <= 104mat[i][j]is either0or1.- There is at least one
0inmat.
Note: This question is the same as 1765: https://leetcode.com/problems/map-of-highest-peak/
We create a matrix
Then, we traverse
Next, we use Breadth-First Search (BFS), removing an element
Finally, we return
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
ans = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque()
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
if x == 0:
ans[i][j] = 0
q.append((i, j))
dirs = (-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in pairwise(dirs):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and ans[x][y] == -1:
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1
q.append((x, y))
return ansclass Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int[] row : ans) {
Arrays.fill(row, -1);
}
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[] {i, j});
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
ans[i][j] = 0;
q.emplace(i, j);
}
}
}
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int x = p.first + dirs[i];
int y = p.second + dirs[i + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
ans[x][y] = ans[p.first][p.second] + 1;
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func updateMatrix(mat [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = -1
}
}
type pair struct{ x, y int }
var q []pair
for i, row := range mat {
for j, v := range row {
if v == 0 {
ans[i][j] = 0
q = append(q, pair{i, j})
}
}
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
x, y := p.x+dirs[i], p.y+dirs[i+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1 {
ans[x][y] = ans[p.x][p.y] + 1
q = append(q, pair{x, y})
}
}
}
return ans
}function updateMatrix(mat: number[][]): number[][] {
const [m, n] = [mat.length, mat[0].length];
const ans: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => -1));
const q: [number, number][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (mat[i][j] === 0) {
q.push([i, j]);
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
const dirs: number[] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
for (const [i, j] of q) {
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const [x, y] = [i + dirs[k], j + dirs[k + 1]];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] === -1) {
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1;
q.push([x, y]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn update_matrix(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut ans = vec![vec![-1; n]; m];
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if mat[i][j] == 0 {
q.push_back((i, j));
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
let dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
while let Some((i, j)) = q.pop_front() {
for k in 0..4 {
let x = i as isize + dirs[k];
let y = j as isize + dirs[k + 1];
if x >= 0 && x < m as isize && y >= 0 && y < n as isize {
let x = x as usize;
let y = y as usize;
if ans[x][y] == -1 {
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1;
q.push_back((x, y));
}
}
}
}
ans
}
}