diff --git a/astro.config.mjs b/astro.config.mjs
index 34f59ac7..e6a3a76f 100644
--- a/astro.config.mjs
+++ b/astro.config.mjs
@@ -10,12 +10,49 @@ export default defineConfig({
starlight({
title: 'Contribute | freeCodeCamp.org',
description: 'Contribute to freeCodeCamp.org',
+ locales: {
+ root: {
+ label: 'English',
+ lang: 'en'
+ },
+ es: {
+ label: 'Español',
+ lang: 'es'
+ },
+ de: {
+ label: 'German',
+ lang: 'de'
+ },
+ it: {
+ label: 'Italian',
+ lang: 'it'
+ },
+ jp: {
+ label: 'Japanese',
+ lang: 'jp'
+ },
+ pt: {
+ label: 'Portuguese',
+ lang: 'pt'
+ },
+ uk: {
+ label: 'Ukrainian',
+ lang: 'uk'
+ },
+ zh: {
+ label: 'Chinese',
+ lang: 'zh'
+ },
+ 'zh-Tw': {
+ label: 'Chinese Traditional',
+ lang: 'zh-TW'
+ }
+ },
logo: {
src: './public/icons/icon-96x96.png',
replacesTitle: true
},
tableOfContents: true,
- defaultLocale: 'en',
editLink: {
baseUrl: 'https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/contribute/edit/main/'
},
@@ -37,6 +74,7 @@ export default defineConfig({
]
})
],
+
output: 'hybrid',
adapter: cloudflare({
imageService: 'passthrough'
diff --git a/src/components/FCCHeader.astro b/src/components/FCCHeader.astro
index 3751a527..1757f601 100644
--- a/src/components/FCCHeader.astro
+++ b/src/components/FCCHeader.astro
@@ -10,6 +10,7 @@ import FCCThemeSelect from './FCCThemeSelect.astro';
* Render the `Search` component if Pagefind is enabled or the default search component has been overridden.
*/
const shouldRenderSearch = true;
+
//config.pagefind || config.components.Search !== '@astrojs/starlight/components/Search.astro';
---
@@ -32,6 +33,7 @@ const shouldRenderSearch = true;
+
diff --git a/src/content/config.ts b/src/content/config.ts
index 414c5dac..6b1a5df8 100644
--- a/src/content/config.ts
+++ b/src/content/config.ts
@@ -1,6 +1,14 @@
-import { defineCollection } from 'astro:content';
-import { docsSchema } from '@astrojs/starlight/schema';
+import { defineCollection, z } from 'astro:content';
+import { docsSchema, i18nSchema } from '@astrojs/starlight/schema';
export const collections = {
- docs: defineCollection({ schema: docsSchema() })
+ docs: defineCollection({ schema: docsSchema() }),
+ i18n: defineCollection({
+ type: 'data',
+ schema: i18nSchema({
+ extend: z.object({
+ 'custom.label': z.string().optional()
+ })
+ })
+ })
};
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/de/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a33bb9ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Authors Analytics Manual
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Search by Language
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+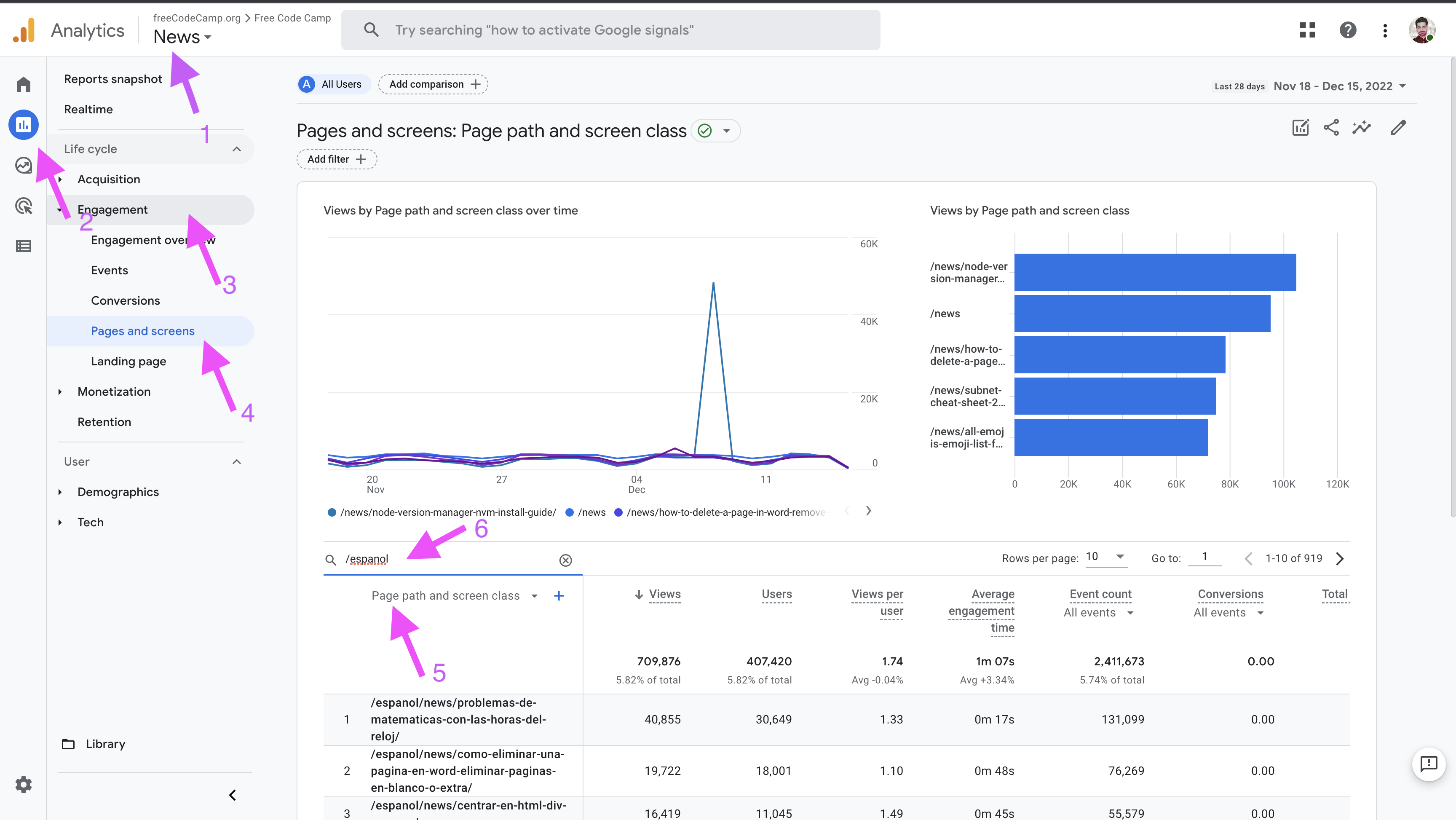
+
+1. From the top dropdown menu, select `News`.
+1. From the sidebar, click on `Reports`.
+1. From the secondary sidebar, select `Engagement`.
+1. Click on `Pages and Screens`.
+1. In the search bar, type the subpath for the desired language.
+1. From the dropdown under the search bar, choose `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filter Reports by Author
+
+After arriving at the `Pages and Screens` reports mentioned above, use the following steps to filter the results by specific authors.
+
+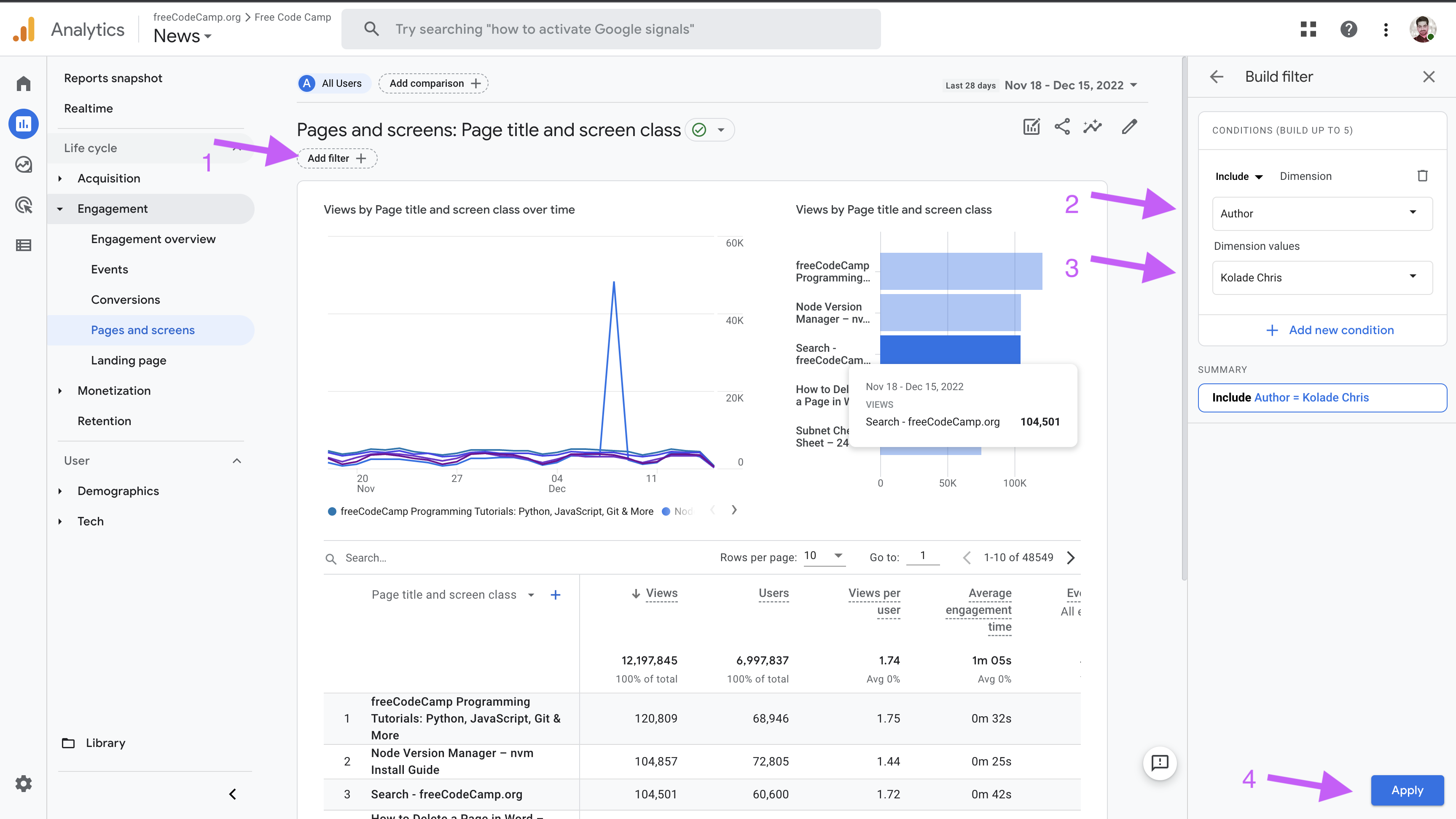
+
+1. Click on the `Add filter` button.
+1. From the side navigation include `Author`.
+1. From the `Dimensions values` dropdown, choose an author's name.
+1. Click on the `Apply` button to apply changes.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/de/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..51fd31d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
+---
+title: Best Practices für die Codebasis
+---
+
+## Styling a component
+
+We recommend styling components using our [design style guide](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+The colors are defined in [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css), and the fonts are in [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+We are strongly opinionated about adding new variables/tokens to the colors. After careful research, the colors have been chosen to respect the freeCodeCamp brand identity, developer experience, and accessibility.
+
+The `!important` keyword may be used to override values in some cases (e.g. accessibility concerns). You should add a comment describing the issue, so it doesn't get removed in future refactoring.
+
+### RTL support
+
+We are striving to support right-to-left (RTL) layout in the codebase for languages that are read in this direction. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Here are some quick rules of thumb to follow:
+
+- Don't use `float` properties
+ - Use Flexbox and Grid layouts instead, as they have RTL support already built-in, and those will be easier to maintain and review.
+- Don't define the direction while using `margin` and `padding`: it may seem harmless to use `padding-right` and `margin-left`, but these directions aren't mirrored when the layout changes to RTL, and adding counter values for them in the RTL file makes maintaining the codebase harder.
+ - Use logical properties for them: You can add the same spacing by using `padding-inline-end` and `margin-inline-start`, and you won't need to worry about RTL layout, as they follow where the line starts and ends, and you won't need to add any extra values in the RTL files, so people won't need to remember to change the same values in two files.
+- Don't use `!important` in `font-family`: RTL layout uses different fonts compared to the LTR layout, when you add `!important` in the `font-family` property it affects the RTL layout too.
+
+## General JavaScript
+
+In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
+
+It is encouraged to use functional components over class-based components.
+
+## Specific TypeScript
+
+### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
+
+#### Beibehalten des Git-Dateiverlaufs
+
+Sometimes changing the file from `.js` to `.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
+
+The best bet at achieving this is to:
+
+1. Umbenennen der Datei
+2. Commit mit dem Flag `--no-verify`, damit Husky sich nicht über die Lint-Fehler beschwert
+3. Refactoring zu TypeScript für die Migration, in einem separaten Commit
+
+:::note
+Editoren wie VSCode zeigen dir wahrscheinlich trotzdem an, dass die Datei gelöscht und eine neue erstellt wurde. Wenn du die CLI für `git add .` verwendest, zeigt VSCode die Datei als umbenannt im Stage an
+:::
+
+### Naming Conventions
+
+#### Schnittstellen und Typen
+
+For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
+
+React Component Props - suffix with `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+React Stateful Components - suffix with `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component {}
+```
+
+Default - object name in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+## Redux
+
+### Action Definitions
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### How to Reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### How to Dispatch
+
+Within a component, import the actions and selectors needed.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return ;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+
+
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [TypeScript Docs](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [TypeScript with React CheatSheet](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/de/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0271dcde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Kurse VSCode Erweiterung
+---
+
+Dies beschreibt die Wartungsrichtlinien für das [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) Repository, das den Quellcode für die [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses) Erweiterung enthält.
+
+## Veröffentlichung der Erweiterung
+
+Eine GitHub-Aktion veröffentlicht automatisch die Erweiterung im Visual Studio Marketplace bei der Veröffentlichung einer neuen GitHub-Version.
+
+1. Packe eine neue Version der Erweiterung:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack --
+```
+
+Dabei ist `` eines von: `major`, `minor`, `patch`.
+
+2. Schiebe die neue Version nach `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "(): "
+git push
+```
+
+Optional kannst du direkt zu `upstream/main` pushen, aber es wird empfohlen, einen neuen PR zu eröffnen, um die Richtigkeit zu überprüfen.
+
+3. Erstelle eine neues GitHub-Release über die GitHub-Benutzeroberfläche:
+
+- Erhöhe die Versionsnummer korrekt, wenn du einen neuen Tag erstellst.
+- Lade die `.vsix`-Datei mit dem Release hoch.
+- Veröffentliche das Release und bestätige, dass die Aktion erfolgreich war.
+
+> [!NOTE] Das Erstellen einer Version erfordert Schreibzugriff auf das `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension` Repository.
+
+## Manuelles Veröffentlichen der Erweiterung
+
+Ein manueller Upload auf den Visual Studio Marketplace kann mit den folgenden Schritten durchgeführt werden:
+
+1. Besuche https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ und melde dich an
+2. Navigiere zur [freeCodeCamp Publisher Seite](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Wähle die entsprechende Erweiterung aus und wähle `Update`
+4. Lade die Datei aus deinen lokalen Dateien hoch
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c4a01ce5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Dateistruktur des Studienplans (Curriculum)
+---
+
+Unsere wichtigsten Lehrinhalte befinden sich in dem Verzeichnis mit dem aussagekräftigen Namen `Curriculum`. Auf dieser Seite erfährst du, wie diese Dateien organisiert sind.
+
+## Terminologie
+
+Es gibt ein paar Begriffe, die wir verwenden, wenn wir über unsere Studienplaninhalte sprechen.
+
+- `certification` : Wenn in diesem Fall von einer Zertifizierung die Rede ist, geht es um das eigentliche Zertifikat, das die Nutzer/innen beantragen. Das ist unabhängig vom Namen des SuperBlocks.
+- `superBlock` : Ein Superblock ist die oberste Ebene einer Sammlung von Aufgaben. Jeder Superblock entspricht einer Zertifizierung im Lehrplan (z.B. Responsive Web Design).
+- `block` : Ein Block ist ein Abschnitt innerhalb eines Superblocks. Ein Block entspricht einer Gruppe von Aufgaben in einer bestimmten Zertifizierung (z. B. Grundlegendes HTML und HTML5)
+- `challenge` : Eine Aufgabe ist eine einzelne Lektion innerhalb des Lehrplans (z.B. Sag Hallo zu HTML-Elementen)
+
+## Dateibaum
+
+Mit diesen Begriffen würde die Dateistruktur folgendermaßen definiert werden:
+
+
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## Das `_meta` -Verzeichnis
+
+Das `_meta` -Verzeichnis ist ein besonderes Verzeichnis, welches `.json` -Dateien enthält. Diese Dateien entsprechen jedem Block im Studienplan und werden verwendet, um zu bestimmen, zu welchem SuperBlock ein Block gehört und in welcher Reihenfolge die Aufgaben innerhalb dieses Blocks bearbeitet werden.
+
+## Umbenennung von Dateien
+
+Es kann vorkommen, dass du ein Zertifikat, einen Superblock, einen Block oder eine Aufgabe umbenennen musst. In diesem Abschnitt werden die notwendigen Schritte beschrieben, um Fehler bei der Umbenennung zu vermeiden.
+
+:::danger
+Das Umbenennen von Dateien innerhalb der Studienplanstruktur führt oft dazu, dass sich der Pfad (oder die URL) des Inhalts auf der Startseite ändert. Dies sollte mit Bedacht geschehen, da für jede Änderung eine Weiterleitung eingerichtet werden muss.
+:::
+
+### Umbenennen eines Zertifikats
+
+Wenn du eine Zertifizierung umbenennst, willst du wahrscheinlich auch den zugehörigen Superblock umbenennen. Gehe wie folgt vor, um nur das Zertifikat umzubenennen:
+
+1. Benenne den Ordner `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` in den neuen Namen um.
+1. Benenne in der Datei `meta.json` dieses Ordners die Werte in `name`, `dashedName` und `challengeOrder` in den neuen Zertifikatsnamen um.
+1. Benenne den Ordner `{superBlock}-certificate` und die darin enthaltene YAML-Datei in `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate` in den neuen Namen um.
+1. Ändere den `title` in der YAML-Datei in den neuen Namen um.
+1. Benenne die Datei und den Ordner aus Schritt 3 für die übrigen Studienplansprachen um.
+1. Aktualisiere `client/src/redux/index.ts`, um den richtigen `title` zu benutzen.
+1. Optional aktualisiere den `certSlug` für den superblock in der gleichen Datei. **Beachte**, dass das Umbenennen eines `certSlug` die URL für die Zertifizierung ändern wird und sollte deshalb nur nach sorgfältiger Überlegung durchgeführt werden.
+1. Aktualisiere den `title` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` auf den neuen Wert. **Beachte**, dass das Ändern des `title` hier **die SuperBlock-Seite für die zugehörige Zertifizierung unterbricht**. Er ist darauf angewiesen, dass der SuperBlock-Titel mit dem Titel der Zertifizierung übereinstimmt. Wahrscheinlich willst du den SuperBlock gleichzeitig umbenennen.
+1. Wenn du den `certSlug` in Schritt 7 umbenannt hast, ändere ihn hier für das cert und alle verschachtelten `projects`-Werte.
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. Wenn du den `certSlug` in Schritt 7 umbenannt hast, aktualisiere den key von`certSlugTypeMap` in derselben Datei.
+1. Aktualisiere bei Bedarf den Zertifikatsnamen im `legacyCerts`-Array von `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx`.
+1. Aktualisiere die Hauptdatei `README.md` auf den neuen Namen.
+
+### Umbenennen eines Superblocks
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du einen SuperBlock umbenennst, wird der neue Ordnername als Pfad verwendet und sollte als "richtiger" Name betrachtet werden. Alle anderen Werte sollten aktualisiert sein, um diese Veränderung widerzuspiegeln.
+
+Außerdem wirst du wahrscheinlich das Zertifikat und den `{superBlock}-projects`-Block umbenennen wollen, wenn du einen superBlock umbenennst, da sie alle einen gemeinsamen Namen haben. Um nur einen superBlock umzubenennen, musst du:
+
+1. Benenne den Ordner superBlock im Verzeichnis `curriculum/challenges/english` um.
+1. Benenne den superBlock Ordner in _allen_ anderen `curriculum/challenges/{language}` Verzeichnissen um.
+1. Für jeden Block innerhalb dieses Superblocks aktualisierst du den `superBlock`-Wert in der `meta.json`-Datei auf seinen dashedName. Du musst hier keine Ordner umbenennen. Mach das, wenn du einen Block umbenennst.
+1. Benenne den Superblock-Ordner in `client/src/pages/learn` um.
+1. Aktualisiere die Datei `index.md` im oben genannten Ordner und ändere die Werte für `title` und `superBlock` auf den neuen Namen.
+1. Aktualisiere die `index.md` für jeden Blockordner, um den richtigen `superBlock`-Wert zu verwenden.
+1. In der Datei `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` aktualisierst du den Pfad für das Zertifikat(cert) am Anfang der Datei und den `title`-Wert für diesen SuperBlock. **Beachte**, dass das Ändern des `title` hier **die Möglichkeit zerstört,** die eigentliche Zertifizierung für diesen SuperBlock anzuzeigen. Er ist darauf angewiesen, dass der SuperBlock-Titel mit dem Titel der Zertifizierung übereinstimmt. Wahrscheinlich möchtest du die Zertifizierung gleichzeitig umbenennen.
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. Aktualisiere den Pfadwert in `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. Aktualisiere für jede Sprache in `client/i18n/locales` die Datei `intro.json`, um den neuen SuperBlock `dashedName` zu verwenden. In der englischen Datei aktualisierst du auch den `title`.
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. Aktualisiere alle Werte, in denen er verwendet wird.
+1. Aktualisiere die Hauptdatei `README.md` auf den neuen Namen.
+
+### Umbenennen eines Blocks
+
+Wenn du einen Studienplanblock umbenennen willst, musst du Folgendes tun:
+
+1. Ändere den Namen des Blockordners im Verzeichnis `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
+1. Ändere den Namen des gleichen Blockordners in _allen_ der anderen Sprachverzeichnisse, damit er übereinstimmt. Diese müssen alle mit der englischen Struktur übereinstimmen, sonst wird der Build nicht funktionieren.
+1. Ändere den Namen des Blockordners im `_meta`-Verzeichnis.
+1. Aktualisiere die Eigenschaften `name` und `dashedName` in der `meta.json`-Datei des Blocks.
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Umbenennen einer Aufgabe
+
+Wenn du eine einzelne Aufgaben-Datei umbenennen willst, musst du Folgendes tun:
+
+1. Ändere den Namen der Challenge-Datei im Verzeichnis `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Ändere den Namen des `title` und `dashedName` in dieser Datei.
+1. Ändere den Namen der Datei und den `dashedName` in diesen Dateien, damit _alle_ der anderen Sprachverzeichnisse übereinstimmen.
+1. Aktualisiere den Namen der Aufgabe in der entsprechenden `meta.json`-Datei. Die Namen der Aufgaben werden im Build nicht verwendet, aber sie dienen dazu, die Reihenfolge der Aufgaben benutzerfreundlich zu gestalten.
+1. Wenn es sich bei der Aufgabe um ein Zertifikatsprojekt handelt, aktualisiere die YAML-Datei in `curriculum/english/12-certificates/` auf den neuen Namen.
+1. Wenn es sich bei der Aufgabe um ein Zertifikatsprojekt handelt, aktualisiere den `title` und `link` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. Wenn es sich bei der Aufgabe um ein Zertifikatsprojekt handelt, aktualisiere die Hauptdatei `README.md` auf den neuen Namen.
+
+## Die `dashedName`-Eigenschaft
+
+Die Eigenschaft `dashedName` wird verwendet, um den URL-Pfad für den Superblock, Block oder die Aufgabe zu generieren. Diese sollten in der Regel dem entsprechen, was der `/utils/slugs.js` Helper für den Dateinamen ausgeben würde.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/devops.md b/src/content/docs/de/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3aeef4d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: Das DevOps Handbuch
+---
+
+Dieser Leitfaden wird dir helfen zu verstehen, wie unser Infrastruktur-Stack aufgebaut ist und wie wir unsere Plattformen warten. Dieses Handbuch enthält zwar nicht alle Einzelheiten zu allen Vorgängen, aber er kann als Referenz für dein Verständnis der Systeme dienen.
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+Dies umfasst drei Schritte, die nacheinander zu durchlaufen sind:
+
+1. Neue Änderungen (sowohl Fixes als auch Features) werden über Pull-Requests in unseren primären Entwicklungsbranch (`main`) eingebunden.
+2. Diese Änderungen durchlaufen eine Reihe von automatisierten Tests.
+3. Sobald die Tests bestanden sind, geben wir die Änderungen frei (oder aktualisieren sie bei Bedarf) und stellen sie in unserer Infrastruktur bereit.
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+Normalerweise wird [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (der Standard-Entwicklungsbranch) einmal am Tag in den [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging)-Branch zusammengeführt und in einer isolierten Infrastruktur freigegeben.
+
+Dies ist eine Zwischenversion für unsere Entwickler und freiwillig Mitwirkenden. Sie wird auch als unsere "Staging"- oder "Beta"-Version bezeichnet.
+
+Sie ist identisch mit unserer Live-Produktionsumgebung auf `freeCodeCamp.org`. Sie verwendet jedoch einen separaten Satz von Datenbanken, Servern, Web-Proxies, etc. Diese Isolation ermöglicht es uns, laufende Entwicklungen und Funktionen in einem "produktionsähnlichen" Szenario zu testen, ohne die regulären Benutzer der Hauptplattformen von freeCodeCamp.org zu beeinträchtigen.
+
+Sobald das Entwicklerteam [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) mit den Änderungen auf der Staging-Plattform zufrieden ist, werden diese Änderungen alle paar Tage auf den [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current)-Branch verschoben.
+
+Dies ist die finale Version, die Änderungen auf unsere Produktionsplattformen auf freeCodeCamp.org überführt.
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+Wir verwenden verschiedene Stufen von Integrations- und Abnahmetests, um die Qualität des Codes zu überprüfen. Alle unsere Tests werden durch Software wie [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) und [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp) durchgeführt.
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. Diese helfen uns, die Integration zwischen verschiedenen Komponenten zu testen.
+
+> [!NOTE] We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+
+All diese Tests helfen dabei, zu verhindern, dass sich Probleme wiederholen und stellen sicher, dass wir keinen Fehler einführen, während wir an einem anderen Fehler oder einer Funktion arbeiten.
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+Wir haben eine Continuous-Delivery-Software konfiguriert, um Änderungen auf unsere Entwicklungs- und Produktionsserver zu übertragen.
+
+Sobald die Änderungen in die geschützten Release-Branches geschoben werden, wird automatisch eine Build-Pipeline für den Branch erstellt. Die Build-Pipelines sind für die Erstellung von Artefakten und deren Aufbewahrung in einem Cold Storage zur späteren Verwendung zuständig.
+
+Die Build-Pipeline erstellt eine entsprechende Release-Pipeline, wenn sie einen erfolgreichen Lauf absolviert hat. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. Die Änderungen in den `production*`-Branches können nur per Fast-Forward-Merge im [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) landen.
+
+> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. Den Remotezugriff korrekt konfigurieren.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Ergebnisse:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Stelle sicher, dass dein `main`-Branch fehlerfrei ist und mit dem upstream synchronisiert ist.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Prüfe ob das GitHub CI den `main`-Branch für den upstream weitergibt.
+
+ Die [Continuous Integration](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions)-Tests sollten für den `main`-Branch grün und BESTANDEN (PASSING) sein. Klicke auf das grüne Häkchen neben dem Commit-Hash, wenn du den Code des `main`-Branch siehst.
+
+ Überprüfen des Status auf GitHub Actions (Screenshot)
+
+ 
+
+
+ Wenn dies fehlschlägt, solltest du anhalten und die Fehler untersuchen.
+
+4. Bestätige dass du in der Lage bist, das Repository lokal zu erstellen.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Verschieben von Änderungen von `main` nach `prod-staging` über ein Fast-Forward-Merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > Wenn dies der Fall ist, hast du möglicherweise etwas falsch gemacht und solltest noch einmal von vorn beginnen.
+
+Die obigen Schritte lösen automatisch einen Lauf in der Build-Pipeline für den `prod-staging`-Branch aus. Sobald der Build abgeschlossen ist, werden die Artefakte als `.zip`-Dateien in einem Cold Storage gespeichert, um später abgerufen und verwendet werden zu können.
+
+Die Release-Pipeline wird automatisch ausgelöst, wenn ein neues Artefakt über die angeschlossene Build-Pipeline verfügbar ist. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+Der Prozess ist meist identisch mit den Staging-Plattformen, wobei einige zusätzliche Kontrollen durchgeführt werden. Dies geschieht nur, um sicherzustellen, dass wir nichts auf freeCodeCamp.org beschädigen, das jederzeit von Hunderten von Benutzern verwendet werden kann.
+
+| Führe diese Befehle NICHT aus, bevor du nicht sichergestellt hast, dass alles auf der Staging-Plattform funktioniert. Du solltest keine Tests auf Staging umgehen oder überspringen, bevor du weiter fortfährst. |
+| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Stelle sicher, dass dein `prod-staging`-Branch fehlerfrei ist und mit dem upstream synchronisiert ist.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Verschiebe Änderungen von `prod-staging` nach `prod-current` mittels eines fast-forward Merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > Wenn dies der Fall ist, hast du vielleicht etwas falsch gemacht und solltest noch einmal von vorne beginnen.
+
+Die obigen Schritte lösen automatisch einen Lauf in der Build-Pipeline für den `prod-current`-Branch aus. Sobald ein Build-Artefakt fertig ist, löst es einen Lauf in der Release-Pipeline aus.
+
+**Zusätzliche Schritte für Mitarbeiter (Staffs)**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. Sie können den Freigabedurchlauf entweder _genehmigen_ oder _ablehnen_.
+
+Wenn die Änderungen einwandfrei funktionieren und auf der Staging-Plattform getestet wurden, kann die Freigabe erfolgen. Die Genehmigung muss innerhalb von 4 Stunden nach dem Auslösen der Veröffentlichung erteilt werden, bevor sie automatisch abgelehnt wird. Ein Mitarbeiter kann den Freigabelauf für abgelehnte Läufe manuell erneut auslösen oder auf den nächsten Freigabezyklus warten.
+
+Für Mitarbeiter bestimmt:
+
+| Prüfe deine E-Mail für einen direkten Link oder [geh zum Release Dashboard](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release), nachdem der Build-Lauf abgeschlossen ist. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Sobald einer der Mitarbeiter eine Freigabe genehmigt, schiebt die Pipeline die Änderungen live auf das Produktions-CDN und die API-Server von freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+Hier ist der aktuelle Test-, Build- und Deployment-Status der Codebasis.
+
+| Branch | Unit-Tests | Integrations-Tests | Builds & Deployments |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (experimentell, in Vorbereitung) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+Wir laden dich ein, diese Versionen in einem **"public beta testing"** Modus zu testen und frühen Zugriff auf kommende Funktionen der Plattformen zu erhalten. Manchmal werden diese Funktionen/Änderungen als **, Beta, Staging,** usw. bezeichnet.
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+Wir danken dir, dass du uns Fehler meldest, auf die du stößt und uns hilfst, freeCodeCamp.org besser zu machen. Du rockst!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| Anwendung | Sprache | URL |
+| :-------- | :--------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Lernen | Englisch | |
+| | Spanisch | |
+| | Chinesisch | |
+| News | Englisch | |
+| Forum | Englisch | |
+| | Chinesisch | |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] Der Domainname ist anders als **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. Dies ist beabsichtigt, um die Indizierung durch Suchmaschinen zu verhindern und Verwirrung bei regelmäßigen Benutzern der Plattform zu vermeiden.
+>
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**Die aktuelle Version der Plattform ist immer verfügbar unter [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+Das Entwicklerteam führt Änderungen aus dem `prod-staging`-Branch nach `prod-current` zusammen, wenn sie Änderungen veröffentlichen. Das oberste Commit sollte das sein, was du live auf der Website siehst.
+
+Du kannst die genaue Version, die eingesetzt wurde, in den Build- und Deployment-Protokollen im Statusbereich nachlesen. Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+Es gibt einige bekannte Einschränkungen und Kompromisse bei der Beta-Version der Plattform.
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **Benutzer der Beta-Version haben ein von der Produktionsversion getrenntes Konto.** Die Beta-Version verwendet eine von der Produktionsversion physisch getrennte Datenbank. So können wir versehentliche Datenverluste oder Änderungen verhindern. The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ Es wird erwartet, dass die Deployments häufig und in schnellen Iterationen erfolgen, manchmal mehrmals am Tag. As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ Die Beta-Seite ist und war immer dazu da, die lokale Entwicklung und das Testen zu unterstützen, nichts anderes. Es ist kein Versprechen auf das, was kommt, sondern ein Ausblick auf das, woran gearbeitet wird.
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ Wir verwenden einen Test-Mandanten für freeCodeCamp.dev auf Auth0 und haben daher nicht die Möglichkeit, eine benutzerdefinierte Domain einzustellen. Dies führt dazu, dass alle Weiterleitungsaufrufe und die Anmeldeseite auf einer Standarddomain erscheinen, wie z.B.: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. Dies hat keinen Einfluss auf die Funktionalität und ist so nah an der Produktion, wie wir es nur bekommen können.
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+Bitte eröffne neue Issues für Diskussionen und zum Melden von Fehlern.
+
+Du kannst eine E-Mail an `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` senden, wenn du irgendwelche Fragen hast. Wie immer sollten alle Sicherheitslücken an `security[at]freecodecamp.org` gemeldet werden, anstatt an den öffentlichen Tracker und das Forum.
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. Diese Handbuch gilt nur für die **freeCodeCamp Mitarbeiter**.
+> 2. Diese Anweisungen sollten nicht als vollständig angesehen werden, bitte sei vorsichtig.
+
+Als Mitarbeiterin oder Mitarbeiter hast du vielleicht Zugang zu unseren Cloud-Anbietern wie Azure, Digital Ocean usw. erhalten.
+
+Hier sind einige praktische Befehle, mit denen du an den virtuellen Maschinen (VM) arbeiten kannst, z. B. um Wartungsupdates durchzuführen oder allgemeine Aufgaben zu erledigen.
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+
+### Azure
+
+Installiere Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(Einmalig) Installation auf macOS mit [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(Einmalig) Login:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Abruf der Liste der VM-Namen und IP-Adressen:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Installiere Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(Einmalig) Installation unter macOS mit [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(Einmalig) Login:**
+
+Authentifizierung und Kontextwechsel: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#Authentifizierung mit-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Liste der VM-Namen und IP-Adressen abrufen:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+Wir arbeiten daran, unser IaC-Setup zu erstellen. Während das in Arbeit ist, kannst du das Azure-Portal oder die Azure CLI nutzen, um neue virtuelle Maschinen und andere Ressourcen zu starten.
+
+:::tip
+Unabhängig davon, welche Spinning-Ressourcen du wählst, haben wir ein paar [handliche Cloud-Init-Konfigurationsdateien](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init), die dir bei der grundlegenden Einrichtung helfen, z.B. bei der Installation von Docker oder dem Hinzufügen von SSH-Schlüsseln usw.
+:::
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+Du solltest die VMs auf dem neuesten Stand halten, indem du Updates und Upgrades durchführst. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Bevor du diese Befehle ausführst:
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - Wenn du Pakete auf einer VM aktualisierst, auf der bereits eine Anwendung läuft, stelle sicher, dass die Anwendung gestoppt/gespeichert wurde. Paket-Updates verursachen Netzwerkbandbreite, Speicher- und/oder CPU-Nutzungsspitzen, die zu Ausfällen bei laufenden Anwendungen führen.
+
+Paketinformationen aktualisieren
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Installierte Pakete upgraden
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Unbenutzte Pakete entfernen
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+Wir betreiben lastverteilte (Azure Load Balancer) Instanzen für unsere Webserver. Auf diesen Servern läuft NGINX, das den gesamten Datenverkehr von verschiedenen Anwendungen, die auf ihrer eigenen Infrastruktur laufen, zu freeCodeCamp.org umleitet.
+
+Die NGINX-Konfiguration ist verfügbar in [diesem Repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### Erste Installation
+
+Provisionieren der VMs mit Code
+
+1. Installiere NGINX und konfiguriere es aus dem Repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Installiere die Cloudflare-Ursprungszertifikate und die upstream Anwendungskonfiguration.
+
+ Hole die Cloudflare-Ursprungszertifikate aus dem sicheren Speicher und installiere sie an erforderlichen Stellen.
+
+ **oder**
+
+ Übertrage bestehende Zertifikate:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Aktualisiere die Upstream-Konfigurationen:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Ergänze/aktualisiere die Quell-/Herkunfts-IP-Adressen der Anwendung.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Konfiguriere die Azure Firewalls und `ufw` nach Bedarf für die ingress-Ursprungsadressen.
+
+4. Füge die VM zum Load Balancer Backend Pool hinzu.
+
+ Konfiguriere den Load Balancer und füge ihm Regeln hinzu, falls nötig. Es kann möglicherweise erforderlich sein, auch die VMs zum Load Balancer-Backend-Pool hinzufügen.
+
+### Logging und Monitoring
+
+1. Überprüfe den Status des NGINX-Dienstes mit dem folgenden Befehl:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Logging und Monitoring für die Server sind verfügbar unter:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), unser aktuelles Basis-Monitoring-Dashboard. Wir arbeiten an feineren Metriken für eine bessere Messbarkeit
+
+### Aktualisieren von Instanzen (Wartung)
+
+Konfigurationsänderungen an unseren NGINX-Instanzen werden auf GitHub gepflegt, diese sollten auf jeder Instanz wie folgt bereitgestellt werden:
+
+1. Verbinde dich per SSH mit der Instanz und gib sudo ein
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Lade den neuesten Konfigurationscode herunter.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Teste und lade die Konfiguration neu [mit Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. Installiere Build-Tools für Node-Binaries (`node-gyp`) usw.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Erste Installation
+
+Bereitstellung von VMs mit dem Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Logging und Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Aktualisieren von Instanzen (Wartung)
+
+Codeänderungen müssen von Zeit zu Zeit auf die API-Instanzen übertragen werden. Es kann ein fortlaufendes Update oder ein manuelles Update sein. The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+Automatisierte Pipelines können derzeit keine Aktualisierungen von Abhängigkeiten vornehmen. Wir müssen eine manuelle Aktualisierung durchführen, bevor die Deployment-Pipeline ausgeführt wird.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. Du solltest diese Befehle nicht ausführen müssen. Sie dienen nur der Dokumentation.
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Erstinstallation
+
+Bereitstellung von VMs mit dem Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Logging und Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Instanzen aktualisieren (Wartung)
+
+Codeänderungen müssen von Zeit zu Zeit auf die API-Instanzen übertragen werden. Es kann ein fortlaufendes Update oder ein manuelles Update sein. Letzteres ist wichtig, wenn du Abhängigkeiten ändern oder Umgebungsvariablen hinzufügen.
+
+:::danger
+Automatisierte Pipelines können derzeit keine Aktualisierungen von Abhängigkeiten vornehmen. Wir müssen eine manuelle Aktualisierung durchführen, bevor die Deployment-Pipeline ausgeführt wird.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manuelle Updates - Werden für die Aktualisierung von Abhängigkeiten und Umgebungsvariablen verwendet.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Fortlaufende (Rolling) Updates - Werden für logische Änderungen am Code verwendet.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Wir führen fortlaufende Aktualisierungen des Codes, der Logik, mittels Pipelines durch. Du sollte diese Befehle nicht ausführen müssen. Sie dienen nur der Dokumentation.
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+Unsere Chatserver sind mit einer HA-Konfiguration verfügbar, die [in den Rocket.Chat-Dokumenten empfohlen wird](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). Die Datei `docker-compose` dafür ist [hier](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config) verfügbar.
+
+Wir stellen redundante NGINX-Instanzen bereit, die ihrerseits einen Load Balancing (Azure Load Balancer) vor dem Rocket.Chat-Cluster aufweisen. Die NGINX-Konfigurationsdatei ist [hier](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config) verfügbar.
+
+### First Install
+
+Bereitstellen von VMs mit dem Code
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+Konfigurationsänderungen für unsere NGINX-Instanzen werden auf GitHub gepflegt. Diese sollten auf jeder Instanz wie folgt implementiert werden:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+ssh in die VM (gehostet auf Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+Liste die aktuell installierten node & npm Versionen auf
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Installiere die neueste Node.js LTS, und installiere alle globalen Pakete neu
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Überprüfe installierte Pakete
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Optional) Deinstalliere alte Versionen
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall
+```
+
+:::danger
+In Client-Anwendungen ist es nicht möglich, `pm2 resurrect` zu verwenden, um Shell-Skripte zwischen Node.js-Versionen wieder herzustellen. Setze stattdessen Prozesse von Grund auf neu auf. This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> Wenn du PM2 für Prozesse verwendest, musst du auch die Anwendungen aufrufen und die Prozessliste für die automatische Wiederherstellung bei Neustarts speichern.
+
+Hole die Anweisungen/Befehle zur Deinstallation mit dem Befehl `unstartup` und verwende die Ausgabe, um die systemctl Dienste zu entfernen
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Hole dir die Installationsanweisungen/Befehle mit dem `startup` Befehl und benutze die Ausgabe, um die systemctl Dienste hinzuzufügen
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Kurzbefehle für PM2, um gespeicherte Prozesse aufzulisten, wiederherzustellen usw.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. Im Großen und Ganzen kannst du die hier aufgeführten Schritte befolgen.
+
+Du benötigst einen PAT, den du hier finden kannst: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+Navigiere zu [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) und registriere den Agenten von Grund auf neu in den erforderlichen [Entwicklungsgruppen](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+> [!NOTE] Du solltest die Skripte im Home-Verzeichnis ausführen und sicherstellen, dass kein anderes `azagent` Verzeichnis existiert.
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+Derzeit müssen Agents zum Aktualisieren entfernt und neu konfiguriert werden. Dies ist erforderlich, damit sie die `PATH`-Werte und andere Systemumgebungsvariablen korrekt übernehmen können. Wir müssen dies zum Beispiel tun, um Node.js auf unseren Ziel-VMs zu aktualisieren.
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Wenn du die oben genannten Schritte abgeschlossen hast, kannst du die gleichen Schritte wie bei der Installation des Agenten wiederholen.
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+Wir verwenden [ein CLI-Tool](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast), um den wöchentlichen Newsletter zu versenden. Um dieses in Betrieb zu nehmen und den Prozess zu beginnen:
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+Wir verwenden ein eigenes [Theme](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) für unsere Nachrichtenpublikation. Wenn du die folgenden Änderungen am Theme vornimmst, können neue Sprachen hinzugefügt werden.
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Aktualisiere die Publikations-Assets, indem du zum Ghost Dashboard > Einstellungen > Allgemein gehst und die [Icon](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), das [Logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png) und das [Cover](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png) der Publikationen hochlädst.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/faq.md b/src/content/docs/de/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c84d49d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+:::tip
+**`help wanted`** Issues sind frei zugänglich und du musst nicht um Erlaubnis bitten, bevor du sie bearbeitest. Issues mit dem **`first timers only`**-Label sind jedoch spezielle Issues, die für Leute gedacht sind, die noch nicht zur freeCodeCamp Codebasis beigetragen haben.
+:::
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. Wir werden höchstwahrscheinlich den ersten Pull Request mergen, der das Problem behebt.
+2. Wenn mehrere Mitwirkende etwa zur gleichen Zeit einen Pull Request für dasselbe Problem öffnen, geben wir dem Pull Request den Vorrang, der das Problem am besten löst. Einige der Dinge, die wir berücksichtigen:
+ - Hast du auch Tests durchgeführt?
+ - Hast du alle Anwendungsfälle erfasst?
+ - Hast du sichergestellt, dass alle Tests erfolgreich waren und dass alles lokal funktioniert?
+3. Schließlich geben wir Pull Requests Vorrang, die unseren empfohlenen Richtlinien entsprechen.
+ - Hast du die Checkliste für Pull Requests befolgt?
+ - Hast du deinem Pull Request einen aussagekräftigen Titel gegeben?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- To be a **Discord/Chat** moderator, have an active presence in our chat and have positive engagements with others, while also learning and practicing how to deal with potential conflicts that may arise.
+- To be a **Forum** moderator, similar to a chat moderator, have an active presence and engage with other forum posters, supporting others in their learning journey, and even giving feedback when asked. Take a look at [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) for more information.
+- To be a **GitHub** moderator, help process GitHub issues that are brought up to see if they are valid and (ideally) try to propose solutions for these issues to be picked up by others (or yourself).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- der `Contributors` Kategorie von [unserem Community-Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- dem `#Contributors` Kanal auf [unserem Chatserver](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a7e54c55
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: Wie man Cypress Tests erstellt
+---
+
+Wenn du Änderungen an JavaScript, CSS oder HTML vornimmst, die die Funktionalität oder das Layout einer Seite verändern könnten, ist es wichtig, entsprechende [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io)-Integrationstests hinzuzufügen.
+
+Wie man Cypress-Tests oder "Specs" schreibt, erfährst du in der offiziellen [Dokumentation](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html) von Cypress.
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Cypress-Tests befinden sich im Verzeichnis `./cypress`.
+
+- Cypress-Tests für ein Studienplanmodul befinden sich im entsprechenden Studienplanverzeichnis, d.h. `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+> [!NOTE] If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Starte MongoDB und erstelle die Datenbank](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Starte die freeCodeCamp Client-Anwendung und den API-Server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+Um Tests mit Produktions-Builds durchzuführen, ersetze unten `dev` durch `prd`.
+
+- Um alle Tests im Verzeichnis `./cypress` auszuführen:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- Um einen einzelnen Test durchzuführen:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- Um einen Entwicklungs-Build zu erstellen, starte den Entwicklungsserver und führe alle vorhandenen Cypress-End-to-End-Tests aus:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Sicherstellen, dass die Entwicklungsumgebung läuft
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Richte die Datenbank ein
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Entwickle den Server und den Client
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Cypress Build Tools installieren
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- Wenn du im Terminal dazu aufgefordert wirst, wähle dein Tastaturlayout nach Sprache/Region aus
+
+Jetzt kann [Cypress ausgeführt werden](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+
+
+
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c2e0bd97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **Hinweis:** Dies ist ein **optionaler** Schritt und wird nur bei der Arbeit mit E-Mail-Workflows benötigt
+
+- [Einführung](#introduction)
+- [MailHog installieren](#installing-mailhog)
+- [MailHog verwenden](#using-mailhog)
+- [Nützliche Links](#useful-links)
+
+## Einführung
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog ist eine Alternative zur Nutzung eines E-Mail-Dienstleisters, um echte E-Mails zu versenden. Es ist ein Entwickler-Tool für E-Mail-Tests, das die von deiner freeCodeCamp-Instanz gesendeten E-Mails abfängt.
+
+## MailHog installieren
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>MailHog mit Docker installieren</summary>
+
+Wenn du Docker installiert hast, kannst du
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+eingeben, um MailHog im Hintergrund zu starten und
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+um es zu stoppen.
+
+Wenn die Installation abgeschlossen ist, kannst du [MailHog](#using-mailhog) benutzen.
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>MailHog auf macOS installieren</summary>
+
+Installiere MailHog auf macOS mit [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+Wenn die Installation abgeschlossen ist, kannst du [MailHog](#using-mailhog) benutzen.
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installation von MailHog unter Windows</summary>
+
+Lade die neueste Version von MailHog von [MailHogs offiziellem Repository](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases) herunter. Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a `.exe` file will be downloaded to your computer.
+
+Wenn der Download abgeschlossen ist, klicke auf die Datei, um sie zu öffnen. Es kann sein, dass eine Benachrichtigung der Windows-Firewall erscheint, die eine Zugriffsberechtigung für MailHog anfordert. Es öffnet sich eine Standard-Windows-Kommandozeile, in der MailHog ausgeführt wird, sobald der Firewall-Zugriff gewährt wurde.
+
+Beende MailHog, indem du das Fenster der Kommandozeile schließt. To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (`.exe`) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
+
+Starte [mit der Nutzung von MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>MailHog unter Linux installieren</summary>
+
+Installiere zuerst [Go](https://golang.org).
+
+Führe die folgenden Befehle aus, um GO auf Debian-basierten Systemen wie Ubuntu und Linux Mint zu installieren.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+Führe die folgenden Befehle aus, um GO auf RPM-basierten Systemen wie CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, etc. zu installieren.
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+Alternativ kannst du GO auch mit den folgenden Befehlen installieren.
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+Setze nun den Pfad für Go mit den folgenden Befehlen.
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+Gib schließlich die folgenden Befehle ein, um MailHog zu installieren und auszuführen.
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+Starte [mit der Nutzung von MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+## MailHog verwenden
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## Nützliche Links
+
+- Weitere Informationen zu MailHog findest du im [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) Repository. Außerdem gibt es zusätzliche Informationen über benutzerdefinierte MailHog-Konfigurationen.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..713c41ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines to contribute to the codebase. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+Ignoring these steps may soil your copy which makes the contributing, maintaining, and reviewing processes difficult.
+
+## Contributing to the Codebase
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the freeCodeCamp upstream `main` branch to your `main` fork branch:
+
+ > [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull requests that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+ >
+ > You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+ This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Update your copy of the freeCodeCamp upstream repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp main:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ The resulting output should be empty. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run freeCodeCamp to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Make a conventional commit message. This is a good practice as a developer, and you will be following standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any more time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Quick commands reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working.
+
+| command | description |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Run all JS tests in the system, including client, server, lint and challenge tests. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Run the client test suite. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Run the curriculum test suite. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific Block. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific SuperBlock. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Run the curriculum test suite, without bailing after the first error |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Run the server test suite. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Run the Cypress end to end tests. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Starts Storybook for component library development. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8c6fdcca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Neue Sprachen auf `/learn` bereitstellen
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Aktualisierung der Crowdin-Einstellungen
+
+Bevor du eine neue Sprache freigeben kannst, musst du zulassen, dass die Sprachen von Crowdin heruntergeladen werden können. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Danach scrollst du nach unten zu `Language Mapping`, wo du eine Option zum Hinzufügen eigener Sprachcodes findest. Füge einen neuen Eintrag für die Sprache hinzu, die du veröffentlichen willst, indem du `language` als `Placeholder`-Wert auswählst und eine URL-freundliche Kleinschreibung des Namens deiner Sprache für den `Custom code` einträgst. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). Der Schritt für die beiden ist der gleiche. Zum Beispiel, wenn du Dothraki-Downloads aktivieren möchtest:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Beachte, dass der Schlüssel `download_language` auf den Sprachcode festgelegt werden muss, der auf Crowdin angezeigt wird.
+
+## Eine Sprache aktivieren
+
+> [!NOTE] Der obige Abschnitt mit der Aktualisierung der Workflows sollte abgeschlossen sein, bevor du fortfährst - dies muss in getrennten Schritten geschehen, sonst schlagen die Builds fehl.
+
+Es gibt ein paar Schritte, die du unternehmen musst, damit die Codebasis in deiner gewünschten Sprache erstellt werden kann.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. Hier gibt es mehrere Objekte.
+
+- `Languages`: Add the new language to `Languages` enum, similar to the others. The string value here will be used in the `.env` file to set a build language later.
+- `availableLangs`: Add the new property from the `Languages` enum to both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays.
+- `i18nextCodes`: Dies sind die ISO-Sprachcodes für jede Sprache. Du musst den entsprechenden ISO-Code für die Sprache hinzufügen, die du aktivieren möchtest. Diese müssen für jede Sprache einzigartig sein.
+- `LangNames`: Dies sind die Anzeigenamen für die Sprachauswahl im Navigationsmenü.
+- `LangCodes`: Dies sind die Sprachcodes, die für die Formatierung von Datumsangaben und Zahlen verwendet werden. Dies sollten Unicode CLDR-Codes statt ISO-Codes sein.
+- `hiddenLangs`: Diese Sprachen werden im Navigationsmenü nicht angezeigt. Dies wird für Sprachen verwendet, die noch nicht zur Veröffentlichung bereit sind. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: These are languages that read from right to left.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `i18n.ts` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configure Search
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. Diese Daten werden für die Suchleiste verwendet, die `/news `-Artikel lädt. Es ist zwar unwahrscheinlich, dass du diese Funktion testen wirst, aber das Fehlen der Daten für deine Sprache kann zu Fehlern führen, wenn du versuchst, die Codebasis lokal zu erstellen.
+
+Füge ein Objekt für deine Sprache zum `algoliaIndices`-Objekt hinzu. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn wir bereits eine Instanz von news in deiner Zielsprache bereitgestellt haben, kannst du die Werte aktualisieren, damit sie die Live-Instanz widerspiegeln. Andernfalls verwendest du die englischen Werte.
+
+Wenn du Dothraki hinzufügen würdest:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+Du musst einen zusätzlichen Schritt unternehmen, um die Übersetzungen der Client-UI zu übernehmen.
+
+Die Crowdin-Workflows ziehen automatisch _einige_ der UI-Übersetzungen herunter, aber es gibt ein paar Dateien, die manuell verschoben werden müssen.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+Für die Videoaufgaben musst du ein paar Dinge ändern. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. Zum Beispiel, indem man Dothraki zur Abfrage hinzufügt:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Füge dann eine ID für die neue Sprache zu jeder Videoaufgabe in einem geprüften Block hinzu. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. Das Front Matter sollte dann so aussehen:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Aktualisiere das `VideoLocaleIds`-Interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types`, um die neue Sprache aufzunehmen.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+Wenn du Übersetzungen lokal testen möchtest, bevor du sie zu unserem main-Repository hinzufügst, kannst du die Änderungen am Crowdin-Workflow überspringen. Folge den Schritten zur Aktivierung einer Sprache, lade dann die Übersetzungen von Crowdin herunter und lade sie in deinen lokalen Code.
+
+Da die Sprache noch nicht für die Produktion freigegeben wurde, laden unsere Skripte die Übersetzungen noch nicht automatisch herunter. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Sobald du die Dateien hast, musst du sie im richtigen Verzeichnis ablegen. Für die Studienplanaufgaben solltest du die Zertifizierungsordner (z.B. `01-responsive-web-design`) in das Verzeichnis `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` ablegen. Für unsere Dothraki-Übersetzungen wäre dies `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. Die Client-Übersetzungsdateien `.json` werden im Verzeichnis `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` abgelegt.
+
+Aktualisiere deine `.env`-Datei, um deine neue Sprache für `CLIENT_LOCALE` und `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` zu verwenden.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `pnpm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+If you build the client in one language and then want to build it in a different language, you will need to use the command `pnpm run clean-and-develop` after changing the `.env` file, as Gatsby will cache the first language.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+Du kannst zwar lokal Übersetzungen zu Testzwecken vornehmen, aber wir erinnern alle daran, dass Übersetzungen _nicht_ über GitHub eingereicht werden sollten und nur über Crowdin erfolgen sollten. Achte darauf, dass du deine lokale Codebasis zurücksetzt, wenn du mit dem Testen fertig bist.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Neue Sprachen auf `/news` bereitstellen
+
+Um die News für eine neue Sprache bereitzustellen, musst du zwei PRs erstellen. Ein PR geht an das [CDN Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) und der andere an das [News Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News bezieht während des Builds angesagte Links und Artikeltitel aus unserem CDN und fügt sie in den Footer ein. News holt sich während des Builds auch Day.js-Dateien aus dem CDN, um Datum und Uhrzeit für jede Sprache zu lokalisieren.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Klone das [CDN Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) und erstelle einen neuen Zweig.
+
+Im Verzeichnis [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) erstellst du eine neue Datei und nennst sie `language.yaml`. Wenn du zum Beispiel Dothraki News startest, nennst du die Datei `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Kopiere dann den Inhalt der [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml)-Datei für angesagte Artikel und füge ihn in die neue YAML-Datei ein, die du gerade erstellt hast.
+
+Der Inhalt sieht dann etwa so aus:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+Standardmäßig enthält Day.js nur Englisch als Gebietsschema. Damit es mit anderen Sprachen funktioniert, musst du eine neue Day.js Gebietsschemadatei zum CDN hinzufügen.
+
+Im Verzeichnis [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) erstellst du eine neue Datei und nennst sie `isocode.min.js`. Wenn du zum Beispiel Dothraki News startest, nennst du die Datei `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Die Versionsnummer wird sich ändern, wenn die Abhängigkeiten aktualisiert werden.
+
+Dann besuche [diese Seite auf cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) mit allen verfügbaren Day.js-Dateien für die von uns verwendete Version, suche den Link `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` für die neue Sprache und öffne ihn in einem neuen Tab.
+
+> [!NOTE] Du musst nur die .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js Locale-Datei hinzufügen. Du musst keine weiteren Day.js-Dateien hinzufügen.
+
+Kopiere den Code des Gebietsschema aus Day.js von dem neuen Tab in die neue Datei, die du erstellt hast. Hier ist zum Beispiel eine ungekürzte Version des englischen Gebietsschemas für Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Erstelle dann einen PR für das CDN-Repository, um sowohl die YAML- als auch die Day.js-Dateien zur Überprüfung hinzuzufügen.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+Das [News Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) zieht die Daten von einer Ghost-Instanz, die Dateien, die du dem CDN hinzugefügt hast, erstellt die News und stellt sie bereit.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. Du solltest bei diesem Schritt nicht von einem Fork aus arbeiten.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Klone das News-Repository und erstelle einen neuen Zweig.
+
+Öffne die Datei `config/index.js`, um die neue Sprache hinzuzufügen und die notwendigen Werte zu konfigurieren. Es müssen ein paar Objekte und Arrays geändert werden:
+
+- `locales`: Dieses Array enthält die aktiven und kommenden News-Sprachen. Das sind die Werte, die in der `.env`-Datei verwendet werden, um die Ghost-Instanz und die Benutzeroberfläche für jeden Build zu wählen. Füge den Textnamen der neuen Sprache in Kleinbuchstaben zu diesem Array hinzu.
+- `localeCodes`: Dieses Objekt ist eine Übersicht der ISO-Codes für jede Sprache und wird verwendet, um i18next zu konfigurieren, bevor die Benutzeroberfläche erstellt wird. Um eine neue Sprache hinzuzufügen, verwende den Namen der Sprache in Kleinbuchstaben als _Schlüssel_ und den ISO 639-1 Sprachcode als _Wert_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: Dieses Objekt ist eine Übersicht der Algolia-Indizes für jede Sprache. Um eine neue Sprache hinzuzufügen, verwende den Namen der Sprache in Kleinbuchstaben als _Schlüssel_ und `news-` gefolgt von dem ISO 639-1 Sprachcode in Kleinbuchstaben als _Wert_.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du dir nicht sicher bist, welchen String du beim Setzen von `algoliaIndices` verwenden sollst, schicke eine Nachricht an Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo) oder eine andere Person mit Zugang zu Algolia und bitte sie, das zu überprüfen.
+
+Wenn du zum Beispiel Dothraki News startest, sollten die oben genannten Objekte / Arrays wie folgt aussehen:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. Wenn du zum Beispiel Dothraki News startest, erstelle einen neuen Ordner namens `dothraki`.
+
+Kopiere dann die JSON-Dateien aus dem Verzeichnis `english` in deinen neuen Ordner.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Dann commitest und pushst du deinen Zweig direkt in das News-Repository.
+
+> [!NOTE] Du musst zu einem der Teams gehören, die Zugriff auf das News-Repository haben, um Zweige direkt zu News zu pushen. Derzeit dürfen nur die Entwickler-, i18n- und Staff-Teams dies tun.
+
+Eröffne schließlich einen PR zur Überprüfung.
+
+Sobald die PRs für das CDN und das News Repo genehmigt wurden, können sie zusammengeführt werden.
+
+> [!NOTE] Deployment will be handled subsequently by the staff. Here is a sample PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) of how they do it and more details are available in the [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7ec6c5d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+Videoaufgaben sind eine neue Art von Aufgaben im freeCodeCamp-Studienplan.
+
+Eine Videoaufgabe ist ein kleiner Abschnitt eines Videokurses in voller Länge zu einem bestimmten Thema. Eine Videoaufgabenseite bettet ein YouTube-Video ein. Jede Aufgabenseite enthält eine Multiple-Choice-Frage zum Video. Der/die Nutzer/in muss die Frage richtig beantworten, bevor er/sie zur nächsten Videoaufgabe des Kurses übergehen kann.
+
+Die Videoaufgabenseiten werden von Mitgliedern des freeCodeCamp-Teams erstellt. YouTube-Videos werden auch von Mitgliedern des freeCodeCamp-Teams hochgeladen. Viele der Videoaufgaben sind noch nicht mit Fragen verknüpft.
+
+Du kannst helfen, indem du Multiple-Choice-Fragen zu den Videoabschnitten erstellst und die Fragen zu den Markdown-Dateien für die Videoaufgabe hinzufügst.
+
+## Vorlage für Aufgaben
+
+Unten siehst du eine Vorlage, wie die Markdown-Dateien für die Aufgaben aussehen.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+Diese Felder werden derzeit für die Multiple-Choice-Aufgaben in Python verwendet.
+
+## --text--
+
+Der Fragetext gehört hierher.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Antwort 1
+
+---
+
+Antwort 2
+
+---
+
+Mehr Antworten
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+Die Anzahl der richtigen Antworten gehört hierher.
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Überfliege das Video, das mit der Aufgabe verbunden ist, und erstelle eine Multiple-Choice-Frage.
+
+Finde zunächst die `videoId`.
+
+Im folgenden Code aus der Kopfzeile einer Video-Challenge-Markdown-Datei lautet die `videoId` beispielsweise "nVAaxZ34khk". Auf GitHub sollten die Informationen in einem Tabellenformat dargestellt werden.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Als Nächstes rufst du das YouTube-Video mit dieser Video-ID auf. Die URL für das Video lautet dann:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (Ersetze `videoId` in der URL durch die ID des Videos - ohne eckige Klammern`.)
+
+Im obigen Beispiel lautet die URL https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Überfliege das YouTube-Video mit dieser `videoId` und überlege dir eine Multiple-Choice-Frage, die auf dem Inhalt des Videos basiert.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. Um die Frage lokal hinzuzufügen, musst du [freeCodeCamp lokal einrichten](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Du kannst die Datei auch auf GitHub finden und auf den Button "Bearbeiten" klicken, um die Frage direkt in deinem Browser hinzuzufügen.
+
+Wenn eine Frage noch nicht zu einer bestimmten Videoaufgabe hinzugefügt wurde, wird sie mit der folgenden Standardfrage versehen:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## ``---text--
+
+Text der Frage
+
+## --answers--
+
+Antwort 1
+
+---
+
+Antwort 2
+
+---
+````
+
+Füge den Fragetext unter dem angezeigten Teil hinzu bzw. aktualisiere ihn:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Füge Antworten (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, und so weiter) unter `## --answers--` hinzu bzw. aktualisiere sie. Achte darauf, dass du die Nummer unter `## --video-solution--` mit der richtigen Antwortnummer aktualisierst. Du kannst weitere mögliche Antworten hinzufügen, indem du das gleiche Format verwendest. The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### Fragebeispiele
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Was wird mit diesem JavaScript-Code auf der Konsole ausgegeben?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Was wird nach der Ausführung dieses Codes ausgedruckt:
+
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+Für weitere Beispiele kannst du dir die Markdown-Dateien für den folgenden Videokurs ansehen. Zu allen Aufgaben gibt es bereits Fragen: [Python für Jedermann Kurs](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+Nachdem du eine oder mehrere Fragen erstellt hast, kannst du die Änderungen in einem neuen Branch übertragen und [einen Pull-Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) öffnen.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc19873d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: Wie man einen Pull-Request (PR) öffnet
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Wenn du mit den Änderungen am Code fertig bist, kannst du diese Richtlinien befolgen, um einen PR zu eröffnen.
+
+Wir erwarten von unseren Mitwirkenden, dass sie den für dieses Projekt spezifischen Prozess kennen. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Einige Beispiele hierfür sind:
+
+1. Bearbeite Dateien nicht direkt über GitHub - Das kannst du zwar, aber es ist keine gute Idee.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Achte darauf, dass du die PR-Checkliste befolgst und nicht nur Dinge abhakst, sonst nehmen wir dich nicht ernst.
+4. Verwende die korrekte Art der Verknüpfung von Themen in der Beschreibung des PR, indem du die `XXXXXX` aktualisierst. Füge nicht einfach überall und nach Lust und Laune Heftnummern ein.
+5. Erwähne jemanden nicht zu oft mit "@mention" oder bitte ihn nicht zu oft um Bewertungen.
+
+ Wir verstehen, dass du gerne einen Beitrag leisten möchtest. So gerne sich ein Betreuer auch bei dir melden würde, er hat alle Hände voll zu tun, um Hunderte von Anfragen wie deine zu bearbeiten. Habe Geduld, früher oder später wird sich jemand bei dir melden.
+
+6. Arbeite nicht direkt an deinem `Hauptzweig` - erstelle einen neuen Zweig für die Änderungen, an denen du arbeitest.
+
+> [!NOTE] Deine Öffentlichkeitsarbeit sollte sich nur auf Änderungen des englischen Lehrplans beziehen. Lese stattdessen [diesen Leitfaden](index#translations), um zu Übersetzungen beizutragen.
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. Die Konvention hat das folgende Format:
+
+> `<type>([optional scope(s)]): <description>`
+>
+> Zum Beispiel:
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Typ:**
+
+| Typ | Wann wählen |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | Nur wenn du neue Funktionen, Tests usw. hinzufügst. |
+| chore | Änderungen, die sich nicht auf den Code, die Tests oder den Wortlaut einer Lektion beziehen. |
+| docs | Änderungen im Verzeichnis `/docs` oder in den Mitwirkungsrichtlinien, etc. |
+
+**Geltungsbereich (Scope):**
+
+Du kannst einen Geltungsbereich aus [dieser Liste von Labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope) auswählen.
+
+**Beschreibung:**
+
+Fasse dich kurz (weniger als 30 Zeichen) und einfach; du kannst weitere Informationen im PR-Beschreibungsfeld und in den Kommentaren hinzufügen.
+
+Einige Beispiele für gute PR-Titel wären:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## Einen Pull-Request vorschlagen
+
+1. Sobald die Änderungen übertragen wurden, wirst du aufgefordert, einen Pull-Request auf der GitHub-Seite deines Forks zu erstellen.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Screenshot ansehen</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. Grundsätzlich sollten alle Pull-Requests gegen das Haupt-Repository von freeCodeCamp, den `main`-Branch, gerichtet sein.
+
+ Stelle sicher, dass dein Base Fork auf freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp eingestellt ist, wenn du einen Pull-Request einreichst.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Screenshot ansehen</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Übermittle den Pull-Request von deinem Branch an den `main`-Branch von freeCodeCamp.
+
+4. Füge eine ausführlichere Zusammenfassung der von dir vorgenommenen Änderungen und deren Nutzen in den Hauptteil deines PR-Textes ein.
+
+ - Du erhältst eine Vorlage für einen Pull-Request. Dies ist eine Checkliste, die du befolgen solltest, bevor du den Pull-Request öffnest.
+
+ - Fülle die Details so aus, wie du es für richtig hältst. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - Wenn der PR ein bestehendes GitHub Problem beheben soll, dann am Ende von der Beschreibungstext deines PR verwenden Sie das Schlüsselwort _Schließt_ mit der Ticketnummer zu [automatisch schließen, wenn der PR akzeptiert und zusammengeführt wird](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Beispiel: `Closes #123` wird Issue 123 schließen
+
+5. Gib an, ob du auf einer lokalen Kopie der Website getestet hast oder nicht.
+
+ - Das ist sehr wichtig, wenn du Änderungen vornimmst, die nicht nur Textinhalte wie die Dokumentation oder eine Aufgabenbeschreibung betreffen. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: für die Erstellung eines PR und vielen Dank, dass du dir die Zeit genommen haben, einen Beitrag zu leisten.
+
+Unsere Moderatoren werden jetzt einen Blick darauf werfen und dir ein Feedback hinterlassen. Bitte habe Geduld mit den anderen Moderatoren und respektiere ihre Zeit. Alle Pull-Requests werden zu gegebener Zeit überprüft.
+
+Und wie immer kannst du deine Fragen in der [Kategorie "Contributors" in unserem Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) oder im ["Contributors"-Chatraum](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) stellen.
+
+:::tip
+Wenn du mehr Pull-Requests beisteuern willst, empfehlen wir dir, die [Richtlinien für Änderungen und Synchronisierung](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) zu lesen, damit du deinen Fork nicht löschen musst.
+:::
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+Es kann zu Konflikten kommen, weil viele Mitwirkende an dem Repository arbeiten und Änderungen deinen PR zerstören können, der noch auf eine Überprüfung und Zusammenführung wartet.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+Wenn du an regulären Bugs und Features auf unserem Entwicklungszweig `main` arbeitest, kannst du einen einfachen Rebase durchführen:
+
+1. Rebase deiner lokalen Kopie:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Löse alle Konflikte und füge Commits hinzu / bzw. bearbeite sie
+
+ ```bash
+ # Entweder
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Oder
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Schiebe deine Änderungen in den PR zurück
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Achte darauf, dass dein Upstream mit deinem Local übereinstimmt:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Entweder löschst du deinen lokalen Branch, nachdem du ein Backup gemacht hast (wenn du ihn noch lokal hast):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # Beispiel:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # Beispiel:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # Beispiel:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Beginne mit einer weißen Weste:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # example:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80ade30d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Korrekturlesen von Übersetzungen
+---
+
+Unser Korrekturleseteam ist dafür verantwortlich, dass die Übersetzungen den Ausgangstext genau wiedergeben. Wir vertrauen darauf, dass unsere Korrekturleserinnen und -leser dafür sorgen, dass wir qualitativ hochwertige Übersetzungen erhalten.
+
+Alle unsere Übersetzungen werden von Hand erstellt, von echten Menschen. Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+Um mit dem Korrekturlesen zu beginnen, besuche [unsere Übersetzungsplattform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) und logge dich ein. Wähle "Go to console" in der oberen Navigationsleiste, um von der öffentlichen Ansicht zur Ansicht des Arbeitsbereichs zu wechseln.
+
+## Eine Datei auswählen
+
+Du solltest die Liste der Projekte sehen, auf die du Zugriff erhalten hast. Wähle das Projekt aus, das du Korrektur lesen möchtest, und wähle dann die Sprache.
+
+
+
+Du solltest jetzt die Liste der verfügbaren Dateien sehen. Wähle deine Datei aus, indem du auf den Button `Proofread` rechts neben der Datei klickst und dann `Proofreading` aus dem Dropdown-Menü wählst, das erscheint.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du dich in dieser Arbeitsbereichsansicht befindest, aber anstelle des Korrekturlesens an der [Übersetzung einer Datei](how-to-translate-files) arbeiten möchtest, kannst du stattdessen `Crowdsourcing` aus dem Dropdown-Menü auswählen.
+
+## Korrekturlesen von Übersetzungen
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Hier siehst du die Liste der Strings in der ausgewählten Datei mit den dazugehörigen Übersetzungen. Die Übersetzung, die hier angezeigt wird, ist diejenige, die von der Übersetzergemeinschaft die höchste Punktzahl (zwischen Upvotes und Downvotes) erhalten hat.
+
+Du kannst dir zwar _alle_ vorgeschlagenen Übersetzungen für einen bestimmten String ansehen, aber bei der Entscheidung, welche Übersetzung du genehmigst, solltest du die Community-Bewertungen (die durch die Upvotes und Downvotes bestimmt werden) berücksichtigen. Die Community kann die vorgeschlagenen Übersetzungen überprüfen und empfehlen, welche am genauesten und klarsten ist.
+
+1. Dies ist der Originaltext (in Englisch).
+2. Dies ist die passende übersetzte Textstelle. Der beliebteste Übersetzungsvorschlag, basierend auf positiven und negativen Bewertungen, wird hier angezeigt.
+3. Wenn du auf dieses Häkchen klickst, wird die Übersetzung genehmigt.
+4. Crowdin zeigt den Status der einzelnen Textstelle an. `Done` bedeutet, dass eine Übersetzung genehmigt wurde und bei unserem nächsten Crowdin-Pull heruntergeladen werden wird. `Todo` bedeutet, dass die Textstelle bisher nicht geprüft wurde. `Hidden` bedeutet, dass der String gesperrt ist und _nicht übersetzt werden sollte_. `Comment` bedeutet, dass der String einen zugehörigen Kommentar hat.
+5. Übersetzungen können hier mit den Checkboxen ausgewählt und in einer Sammelaktion genehmigt werden.
+6. Du kannst die von der Community vorgeschlagenen Übersetzungen, ihre Beliebtheitswerte und die von Crowdin vorgeschlagenen Übersetzungen hier einsehen.
+7. Dieser Button blendet den rechten Anzeigebereich ein/aus, in dem du Übersetzungen, Kommentare, Translation Memory und Glossarbegriffe sehen kannst.
+8. Crowdin zeigt hier Fehlermeldungen aus den Qualitätssicherungsprüfungen an. Das heißt, wenn etwas in der Übersetzung nicht korrekt erscheint, wird Crowdin dich benachrichtigen. Diese Übersetzungen sollten mit Vorsicht genehmigt werden.
+
+Nach dem Korrekturlesen einer Datei sind keine weiteren Aktionen erforderlich.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du einen String in der Korrekturansicht genehmigst, wird er als vollständig markiert und bei unserem nächsten Pull von Crowdin auf GitHub heruntergeladen.
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+Wenn du Fragen hast oder daran interessiert bist, Korrekturleser zu werden, kannst du dich gerne in unserem [Contributors Chat Room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) an uns wenden. In der Regel gewähren wir dir Zugang zum Korrekturlesen, wenn du schon eine Weile im freeCodeCamp mitarbeitest.
+
+Unser Mitarbeiterteam und unsere Community-Moderatoren sind immer auf der Suche nach freundlichen Freiwilligen wie dir, die uns dabei helfen, der Welt qualitativ hochwertige Übersetzungen zur Verfügung zu stellen.
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin ermöglicht es dir, deine Übersetzungen zu genehmigen. Im Allgemeinen ist es am besten, wenn du deine vorgeschlagenen Übersetzungen von einem anderen Korrekturleser durchsehen lässt, um sicherzugehen, dass keine Fehler enthalten sind.
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+Wenn du bereits Korrekturleser/in bist und Interesse an einem eigenen Kanal auf unseren Chatservern für eine bestimmte Sprache hast, [fülle dieses Formular aus](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82269d34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCamp. Das ist sehr empfehlenswert, wenn du regelmäßig einen Beitrag leisten willst.
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows. - You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase. - Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+ :::
+
+If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Here are some pros and cons which should help you decide which option is best for you:
+
+| Gitpod | Your own machine (local setup) |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| No minimum hardware requirements | Specific and minimum requirements |
+| No need to install any software | Additional software required |
+| Always up to date copy of repository | Need to maintain a local copy of the repository |
+| Slower and can take a few minutes to launch | Faster and can be launched in seconds |
+| Need an internet connection to work | Minimal internet connection required (once setup) |
+| Some tasks like compilation and tests can take longer to complete | Faster completion of tasks (depending on your machine's capabilities) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+We have automated the process of installing all the dependencies & tools you will need. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Fastest)** Prepend `gitpod.io/#` in front of any URL from GitHub.
+
+ For example, if you visit your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, add `gitpod.io/#` in the front of the URL in the address bar and hit enter.
+
+ That is you can navigate to `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` and you should see a workspace created for you. This works for any repository or pull-request on GitHub.
+
+2. Alternatively install one of the below extensions for your browser.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - works with Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. See the extension page for details, screenshots, etc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### Voraussetzungen:
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### Befolge diese Schritte, um deine Entwicklungsumgebung vorzubereiten:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ :::tip
+ Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+ :::
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+> [!WARNING] If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`). Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further information about this problem.
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# Erstelle eine Kopie der "sample.env" und nenne sie ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+:::tip
+Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
+:::
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+> [!NOTE] Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
+>
+> If you followed along with the [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), then you should be able to skip this step if the MongoDB server from that guide is already running. You can confirm this by checking that you can reach `http://localhost:27017` on your local machine.
+
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+> [!WARNING] Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..48407d1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp Mobile App locally
+---
+
+Folge dieser Anleitung, um die freeCodeCamp mobile App lokal auf deinem System einzurichten. Dies ist sehr empfehlenswert, wenn du regelmäßig einen Beitrag leisten willst.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Installiere zunächst die erforderliche Software für dein Betriebssystem.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Voraussetzung | Version | Notizen |
+| --------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (wird zusammen mit Flutter ausgeliefert) | `3.x` | Wir verwenden die Version, die mit Flutter ausgeliefert wird. |
+
+:::danger
+Wenn du eine andere Version hast, installiere bitte die empfohlene Version. Wir können nur Installationsprobleme für die empfohlenen Versionen unterstützen.
+:::
+
+Wenn Flutter bereits auf deinem Rechner installiert ist, führe die folgenden Befehle aus, um die Versionen zu überprüfen:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+Wir empfehlen dringend, auf die neuesten stabilen Versionen der oben aufgeführten Software zu aktualisieren.
+:::
+
+Sobald du die notwendigen Ressourcen installiert hast, musst du deine Entwicklungsumgebung vorbereiten. Dies ist bei vielen Entwicklungsabläufen üblich, und du musst dies nur einmal tun.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Installiere [Git](https://git-scm.com/) oder deinen bevorzugten Git-Client, falls du das nicht schon getan hast. Aktualisiere die neueste Version; die Version, die mit deinem Betriebssystem mitgeliefert wurde, ist möglicherweise veraltet.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. Wir empfehlen die Verwendung des Pixel 3a XL und Nexus One (für die Emulation kleinerer Bildschirme).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Optional, aber empfohlen) [Richte einen SSH-Schlüssel](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) für GitHub ein.
+
+5. Installiere einen Code-Editor deiner Wahl.
+
+ Wir empfehlen dringend die Verwendung von [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) oder Android Studio. Wir empfehlen auch die Installation der offiziellen [Erweiterungen](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) ist ein Schritt, bei dem du deine eigene Kopie des Repositorys (auch bekannt als _Repo_) auf GitHub erhältst.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Später kannst du über einen Pull Request (PR) beantragen, dass Änderungen aus deinem Fork in das Haupt-Repository gezogen werden.
+
+:::tip
+Das Haupt-Repository unter `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` wird oft als `upstream`-Repository bezeichnet.
+Dein Fork unter `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` wird oft als `origin`-Repository bezeichnet. `YOUR_USER_NAME` wird durch deinen GitHub-Benutzernamen ersetzt.
+:::
+
+**Folge diesen Schritten, um das `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile`-Repository zu forken:**
+
+1. Gehe zum freeCodeCamp mobile Repository auf GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Klicke auf den "Fork"-Button in der oberen rechten Ecke der Benutzeroberfläche ([Mehr Details hier](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Nachdem das Repository geforkt wurde, gelangst du zu deiner Kopie des Repositorys unter `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` würde durch deinen GitHub-Benutzernamen ersetzt werden)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+Beim [Klonen](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) **downloadest ** du eine Kopie eines Repositorys von einem `remote`- Ort, der entweder dir oder einer anderen Person gehört. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` wird durch deinen GitHub-Benutzernamen ersetzt.)
+
+Führe diese Befehle auf deinem lokalen Rechner aus:
+
+1. Öffne ein Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in deinem Projektverzeichnis
+
+ _z.B.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Klone deinen Fork von freeCodeCamp und ersetze `YOUR_USER_NAME` durch deinen GitHub Benutzernamen
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+Dadurch wird das gesamte freeCodeCamp mobile Repository in dein Projektverzeichnis heruntergeladen.
+
+Hinweis: `--depth=1` erstellt einen oberflächlichen Klon deines Forks, der nur den jüngsten Verlauf/Commit enthält.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Jetzt, wo du eine Kopie deines Forks heruntergeladen hast, musst du einen `upstream` zum übergeordneten Repository einrichten.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+Du benötigst eine Referenz von deinem lokalen Klon auf das `upstream`-Repository zusätzlich zum `origin`-Repository. Auf diese Weise kannst du Änderungen aus dem Haupt-Repository synchronisieren, ohne dass du wiederholt forken und klonen musst.
+
+1. Wechsle in das neue `mobile`-Verzeichnis:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Füge eine Remote-Referenz zum Haupt-Repository von freeCodeCamp mobile hinzu:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Stelle sicher, dass die Konfiguration korrekt aussieht:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ Die Ausgabe sollte in etwas so aussehen wie unten (ersetze `YOUR_USER_NAME` durch deinen GitHub Benutzernamen):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Jetzt, da du eine lokale Kopie der mobilen Anwendung hast, kannst du die folgenden Anweisungen befolgen, um sie lokal auszuführen.
+
+Wenn du auf Probleme stößt, führe zunächst eine Suche nach deinem Problem im Web durch und siehe nach, ob es bereits beantwortet wurde. Wenn du keine Lösung findest, suche bitte auf unserer [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) Seite nach einer Lösung und melde das Problem, falls es noch nicht gemeldet wurde.
+
+Und wie immer kannst du Fragen in der [Kategorie 'Contributors' in unserem Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) oder [auf unserem Chat-Server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) stellen.
+
+> [!NOTE] Das Verzeichnis `mobile` enthält zwei Ordner, nämlich `mobile-api` und `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` enthält den API-Code, der für die Bereitstellung der Podcasts verwendet wird. `mobile-app` enthält die Flutter-App. Dort solltest du dich befinden, wenn du die folgenden Schritte befolgst.
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+Die Standard-API-Schlüssel und Umgebungsvariablen sind in der Datei `sample.env` gespeichert. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Denke daran, das Verzeichnis in `mobile-app` zu ändern, bevor du die folgenden Befehle ausführst.
+
+```bash
+# Erstelle eine Kopie der "sample.env" und benenne sie ".env".
+# Trage die notwendigen API-Schlüssel und Secrets in die Datei ein:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+Die Schlüssel in der `.env` Datei müssen _nicht_ geändert werden, um die App lokal auszuführen. Du kannst die aus `sample.env` kopierten Standardwerte so belassen, wie sie sind.
+
+#### Schritt 2: Installieren von Abhängigkeiten
+
+In diesem Schritt werden die für die Ausführung der Anwendung erforderlichen Abhängigkeiten installiert:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Schritt 3: Starte die freeCodeCamp mobile App
+
+Starte den Emulator deiner Wahl (Android oder iOS) und warte, bis der Startvorgang abgeschlossen ist.
+
+Du kannst die App nun mit folgendem Befehl starten:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+Wenn du VSCode oder Android Studio verwendest, kannst du die App ganz einfach starten, ohne Terminalbefehle ausführen zu müssen. Mehr Informationen dazu [hier](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Folge diesen Schritten:
+
+1. Überprüfe, ob du dich auf dem `main`-Branch befindest:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Du solltest eine Ausgabe wie diese erhalten:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ Wenn du nicht auf main bist oder dein Arbeitsverzeichnis nicht bereinigt ist, löse alle ausstehenden Dateien/Commits auf und checke `main` aus:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Synchronisiere die letzten Änderungen aus dem Upstream `main`-Zweig mit deinem lokalen Hauptzweig:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Wenn du noch ausstehende Pull Requests aus dem `main`-Zweig deines Forks besitzt, verlierst du sie am Ende dieses Schrittes.
+ >
+ > Du solltest sicherstellen, dass dein Pull-Request von einem Moderator zusammengeführt wird, bevor du diesen Schritt ausführst. Um dieses Szenario zu vermeiden, solltest du **immer** auf einem anderen Zweig als dem `main` arbeiten.
+
+ Dieser Schritt **synchronisiert die letzten Änderungen** aus dem Haupt-Repository von freeCodeCamp mobile. Es ist wichtig, dass du deinen Zweig so oft wie möglich auf den neuesten `upstream/main` zurücksetzt, um spätere Konflikte zu vermeiden.
+
+ Aktualisiere deine lokale Kopie des freeCodeCamp mobile Upstream-Repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Führe einen Hard Reset deines Hauptzweiges mit dem freeCodeCamp mobile main durch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Schiebe deinen Hauptbranch in deinen origin, um einen sauberen Verlauf deines Forks auf GitHub zu haben:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Die resultierende Ausgabe sollte leer sein.
+
+3. Erstelle einen neuen Zweig:
+
+ Die Arbeit an einem separaten Zweig für jede Ausgabe hilft dir, deine lokale Arbeitskopie sauber zu halten. Du solltest niemals am `main` arbeiten. Dadurch wird deine Kopie von freeCodeCamp mobile verunreinigt und du musst eventuell mit einem neuen Klon oder Fork neu beginnen.
+
+ Vergewissere dich, dass du auf `main` bist, wie zuvor erklärt, und zweige von dort ab:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Dein Zweigname sollte mit `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/` usw. beginnen. Vermeide die Verwendung von Issue-Nummern in Zweigen. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Einige Beispiele für gute Zweignamen sind:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Bearbeite Seiten und arbeite am Code in deinem bevorzugten Texteditor.
+
+5. Wenn du mit den Änderungen zufrieden bist, solltest du die mobile App optional lokal ausführen, um eine Vorschau der Änderungen zu erhalten.
+
+6. Stelle sicher, dass du alle Fehler korrigierst und die Formatierung deiner Änderungen überprüfst.
+
+7. Überprüfe und bestätige die Dateien, die du aktualisierst:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Dies sollte eine Liste `unstaged`-Dateien anzeigen, die du verändert hast.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Führe die Änderungen durch und mache einen Commit:
+
+ In diesem Schritt solltest du nur Dateien markieren, die du selbst bearbeitet oder hinzugefügt hast. Bei Bedarf kannst du einen Reset durchführen und Dateien lösen, die du nicht ändern wolltest.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Oder du kannst alle `unstaged`-Dateien zum Staging-Bereich hinzufügen:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Nur die Dateien, die in den Staging-Bereich verschoben wurden, werden hinzugefügt, wenn du einen Commit durchführst.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Ausgabe:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Jetzt kannst du deine Änderungen mit einer kurzen Nachricht wie dieser übertragen:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Einige Beispiele:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Optional:
+
+ Wir empfehlen dringend eine konventionelle Commit-Nachricht zu verfassen. Dies ist eine gute Praxis, die du bei einigen der beliebten Open-Source-Repositories sehen kannst. Dies ermutigt dich als Entwickler, Standardverfahren zu befolgen.
+
+ Einige Beispiele für konventionelle Commit-Meldungen sind:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Halte sie kurz, nicht länger als 50 Zeichen. Du kannst jederzeit zusätzliche Informationen in der Beschreibung der Commit-Nachricht hinzufügen.
+
+ Das dauert nicht länger als eine unkonventionelle Meldung wie "update file" oder "add index.md"
+
+ Mehr darüber, warum du konventionelle Commits verwenden solltest, erfährst du [hier](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Wenn du feststellst, dass du eine Datei bearbeiten oder die Commit-Nachricht aktualisieren musst, nachdem du einen Commit gemacht hast, kannst du das nach der Bearbeitung der Dateien wie folgt tun:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Dies öffnet einen Standard-Texteditor wie `nano` oder `vi`, in dem du den Titel der Commit-Nachricht bearbeiten und die Beschreibung hinzufügen/bearbeiten kannst.
+
+10. Als nächstes kannst du deine Änderungen in deinen Fork schieben:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+Nachdem du deine Änderungen übertragen hast, kannst du hier nachlesen, [wie man einen Pull Request erstellt](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Probleme bei der Installation der empfohlenen Voraussetzungen
+
+Wir entwickeln regelmäßig auf den neuesten oder beliebtesten Betriebssystemen wie macOS 10.15 oder höher, Ubuntu 18.04 oder höher und Windows 10 (mit WSL2).
+
+Es wird empfohlen, dein spezifisches Problem auf Ressourcen wie Google, Stack Overflow und Stack Exchange zu untersuchen. Es besteht eine gute Chance, dass jemand mit demselben Problem konfrontiert war und bereits eine Antwort auf deine spezifische Frage gefunden hat.
+
+Wenn du mit einem anderen Betriebssystem arbeitest und/oder immer noch Probleme hast, lese bitte [Hilfe erhalten](#getting-help).
+
+### Probleme mit der Benutzeroberfläche, Build-Fehler usw.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+Wenn du nicht weiterkommst und Hilfe brauchst, kannst du deine Fragen in der [Kategorie "Contributors" in unserem Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) oder im ["Contributors "Chatraum](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) stellen.
+
+In der Konsole deines Browsers oder in der Bash / Terminal / Kommandozeile kann eine Fehlermeldung erscheinen, die dir hilft, das Problem zu identifizieren. Gib diese Fehlermeldung in deiner Problembeschreibung an, damit andere das Problem leichter identifizieren und dir bei der Suche nach einer Lösung helfen können.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1001f9bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp auf dem Windows Subsystem für Linux (WSL) einrichten
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 oder höher) - verfügbar für alle Distributionen einschließlich Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop für Windows**: Siehe entsprechende Anforderungen für [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) und [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+Dieser Leitfaden behandelt einige allgemeine Schritte bei der Einrichtung von WSL2. Sobald einige der üblichen Probleme mit WSL2 behoben sind, solltest du in der Lage sein, [diesem Leitfaden zur lokalen Einrichtung](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) zu folgen, um mit freeCodeCamp unter Windows und einer WSL-Distribution wie Ubuntu zu arbeiten.
+
+## WSL aktivieren
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Ubuntu installieren
+
+1. Wir empfehlen Ubuntu-18.04 oder höher mit WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Abhängigkeiten (Dependencies) für das Betriebssystem aktualisieren
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Git einrichten
+
+Git ist bei Ubuntu 18.04 vorinstalliert. Überprüfe deine Git-Version mit `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Optional, aber empfohlen) Du kannst jetzt mit dem [Einrichten deiner SSH-Schlüssel](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) bei GitHub fortfahren.
+
+## Installation eines Code-Editors
+
+Wir empfehlen wärmstens, [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) auf Windows 10 zu installieren. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+Im Wesentlichen bearbeitest und speicherst du deinen Code auf Ubuntu-18.04, während VS Code auf Windows installiert ist.
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Docker Desktop installieren
+
+**Docker Desktop für Windows** ermöglicht es dir, Datenbanken wie MongoDB und andere Dienste wie NGINX und mehr zu installieren und auszuführen. Dies ist nützlich, um häufige Fallstricke bei der Installation von MongoDB oder anderen Diensten direkt auf Windows oder WSL2 zu vermeiden.
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
+
+Es gibt einige Mindestanforderungen an die Hardware für das beste Erlebnis.
+
+## Docker Desktop für WSL konfigurieren
+
+Sobald Docker Desktop installiert ist, [folgst du dieser Anleitung](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) und konfigurierst es so, dass es die Ubuntu-18.04-Installation als Backend verwendet.
+
+Dadurch laufen die Container auf der WSL-Seite und nicht unter Windows. Du kannst sowohl unter Windows als auch unter Ubuntu über `http://localhost` auf die Dienste zugreifen.
+
+## MongoDB vom Docker Hub aus installieren
+
+Sobald du Docker Desktop für die Zusammenarbeit mit WSL2 konfiguriert hast, befolge diese Schritte, um einen MongoDB-Dienst zu starten:
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Starte den MongoDB-Dienst an Port `27017` und konfiguriere ihn so, dass er bei Systemneustarts automatisch ausgeführt wird
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Du kannst jetzt sowohl von Windows als auch von Ubuntu aus auf den Dienst unter `mongodb://localhost:27017` zugreifen.
+
+## Installing Node.js and pnpm
+
+Wir empfehlen dir, die LTS-Version für Node.js mit einem Node-Versionsmanager zu installieren - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. Du solltest immer noch in der Lage sein, an den meisten Teilen der Codebasis zu arbeiten.
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Häufig gestellte Fragen zu:
+ - [Windows Subsystem für Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop für Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3144772a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
+---
+title: Wie man Übersetzungen lokal testet
+---
+
+:::note
+Dieser Vorgang ist nicht erforderlich, wird aber dokumentiert, falls du eine Vorschau darauf haben möchtest, wie deine Übersetzungen aussehen werden.
+:::
+
+Wenn du deine Übersetzungen auf einer lokalen Instanz der freeCodeCamp `/learn`-Seite testen möchtest, stelle zuerst sicher, dass du die [Codebasis](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) eingerichtet hast.
+
+## Eine Sprache aktivieren
+
+Es gibt ein paar Schritte, die du unternehmen musst, damit die Codebasis in deiner gewünschten Sprache erstellt werden kann.
+
+Gehe zuerst in die Datei `config/i18n/all-langs.ts`, um die Sprache zur Liste der verfügbaren Sprachen hinzuzufügen und die Werte zu konfigurieren. Hier gibt es vier Objekte.
+
+- `availableLangs`: Füge sowohl für den `client` als auch für das Studienplan(`curriculum`)-Array den Textnamen der Sprache hinzu. Dies ist der Wert, der später in der `.env`-Datei verwendet wird.
+- `auditedCerts`: Füge den Textnamen der Sprache als _Schlüssel_ und ein Array von `SuperBlocks.{cert}`-Variablen als _Wert_ hinzu. So erfährt der Client, welche Zertifikate vollständig übersetzt sind.
+- `i18nextCodes`: Das sind die ISO-Sprachcodes für jede Sprache. Du musst den entsprechenden ISO-Code für die Sprache hinzufügen, die du aktivieren willst. Diese müssen für jede Sprache einzigartig sein.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. Dies sollten Unicode CLDR-Codes statt ISO-Codes sein.
+
+Wenn du zum Beispiel Dothraki als Sprache aktivieren möchtest, sollten deine `all-langs.js`-Objekte wie folgt aussehen:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Als nächstes öffnest du die Datei `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`. Diese Daten werden für die Suchleiste verwendet, die `/news `-Artikel lädt. Es ist zwar unwahrscheinlich, dass du diese Funktion testen wirst, aber das Fehlen der Daten für deine Sprache kann zu Fehlern führen, wenn du versuchst, die Codebasis lokal zu erstellen.
+
+Füge ein Objekt für deine Sprache zum `algoliaIndices`-Objekt hinzu. You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn wir bereits eine Instanz von news in deiner Zielsprache bereitgestellt haben, kannst du die Werte aktualisieren, damit sie die Live-Instanz widerspiegeln. Andernfalls verwendest du die englischen Werte.
+
+Wenn du Dothraki hinzufügen würdest:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Schließlich stellst du in deiner `.env`-Datei `CLIENT_LOCALE` und `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` auf deine neue Sprache ein (verwende den `availableLangs` Wert).
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## Aktivieren von lokalisierten Videos
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Übersetzungen laden
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+Du kannst zwar lokal Übersetzungen zu Testzwecken vornehmen, aber wir erinnern alle daran, dass Übersetzungen _nicht_ über GitHub eingereicht werden sollten und nur über Crowdin erfolgen sollten. Achte darauf, dass du deine lokale Codebasis zurücksetzt, wenn du mit dem Testen fertig bist.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..481268e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,344 @@
+---
+title: So übersetzt du die Ressourcen von freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+## Prepare yourself for Contributions
+
+> Die freeCodeCamp Lokalisierungs-Roadmap - Es gibt keine Geschwindigkeitsbegrenzungen
+
+:::tip
+Du kannst damit beginnen, indem du [diese Ankündigung](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) liest. Wir empfehlen die Teilnahme an [unserem Community-Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) und [Discord-Chat-Server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+Du kannst so viel übersetzen, wie und wann du willst. Es kommt nur darauf an, wie viel Zeit und Energie du bereit bist, als freiwilliger Übersetzer zu investieren.
+
+Wir bitten dich nur um Verständnis für die folgenden Punkte:
+
+1. **Übersetzungen sind eine Teamleistung.**
+
+ Das Übersetzen der freeCodeCamp-Ressourcen ist eine der schönsten und lohnendsten Erfahrungen als Helfer, und es funktioniert am besten, wenn du deine Freunde und Kollegen einbeziehst, die die gleiche Weltsprache sprechen wie du.
+
+ Du kannst damit beginnen, indem du [diese Ankündigung](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) liest. Wir empfehlen dir, dich mit deinen Freunden in [unserem Community-Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) und [Discord-Chat-Server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) anzumelden und dein Interesse zu bekunden, bevor du mit den Übersetzungen beginnst. Crowdin und andere Tools machen es einfach, Übersetzungen beizusteuern, aber es ist immer noch eine Menge Arbeit.
+
+ Wir wollen, dass du Spaß am Mitmachen hast und nicht ausbrennst oder das Interesse verlierst.
+
+ Eine kleine Gruppe von 4-5 Personen ist eine gute Größe, um mit deiner eigenen Weltsprache zu starten. Du kannst dann noch mehr Freunde für dein Team gewinnen.
+
+2. **Es kostet eine ganze Menge, Server für jede Sprache zu betreiben.**
+
+ Oberflächlich betrachtet mag es nicht so kompliziert erscheinen, wie der technische Stack aufgebaut ist, aber es kostet eine ganze Menge, die Motoren am Laufen zu halten. Dazu gehört auch die Bereitstellung zusätzlicher Server und die Bereitstellung von Personal, das sich um diese kümmert.
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org verpflichtet sich, diese wie immer kostenlos zur Verfügung zu stellen, aber wir müssen die Ressourcen für diejenigen priorisieren, die sie am meisten brauchen. Das Letzte was wir wollen, ist, dass die Server für eine Sprache abgeschaltet werden, wenn die Übersetzungsaktivität nachlässt & die Inhalte veralten.
+
+ Bei der Übersetzung des Lehrplans können wir, sobald eine Sprache mindestens einige Zertifizierungen erreicht hat, damit beginnen, die Sprache auf [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn) live zu schalten, während du mit der Übersetzung der restlichen Zertifizierungen fortfährst.
+
+ Zum Beispiel würden wir zumindest die gesamte Front-End-Zertifizierungssuite bereitstellen wollen, wenn wir eine neue Weltsprache zum ersten Mal ausliefern.
+
+3. **Aber was ist mit den Sprachen, die nicht auf der Übersetzungsplattform aufgeführt sind?**
+
+ Wir haben uns unsere Benutzerbasis angesehen und die Liste der aktivierten Sprachen auf der Übersetzungsplattform um mehr als 30 der am häufigsten gesprochenen Sprachen erweitert. Einige Sprachen, wie z. B. Chinesisch und Spanisch, sind zu diesem Zeitpunkt bereits auf **"/learn"** live geschaltet.
+
+ Leider umfasst die Liste nicht alle Sprachen, die es gibt. Wir bekommen jeden Tag dutzende von Anfragen von Unterstützern wie dir, die helfen wollen, die Seite in eine Sprache zu übersetzen, die sie sprechen.
+
+ Wir freuen uns auf jeden Fall darauf, die Liste um weitere Sprachen zu erweitern, aber wie du dir vielleicht schon denken kannst, wäre das nur machbar, wenn wir genug Beteiligung für eine Weltsprache bekommen.
+
+ Wenn du möchtest, dass wir eine neue Weltsprache aufnehmen, empfehlen wir dir, deine Freunde dafür zu begeistern.
+
+ Sobald du eine kleine Gruppe von Leuten hast (mindestens 4-5), die interessiert sind und sich engagieren, können wir einen Versuch starten. Wir erklären dir alle Details und führen dich durch einige der Tools und Prozesse.
+
+## Überblick über Crowdin
+
+Unser Traum ist es, dich mit den nötigen Ressourcen auszustatten, damit du lernen kannst, egal welche Weltsprache du sprichst. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source codebase & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wir verwenden ein anderes Tool und einen anderen Arbeitsablauf für die Übersetzung von [Nachrichtenartikeln](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). Wenn du an der Übersetzung von Artikeln interessiert bist, lese [diese Ankündigung](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/news/freecodecamp-in-deine-muttersprache-uebersetzen/) und wende dich an deinen Language Lead.
+
+Der Übersetzungsworkflow ist in zwei Hauptaktivitäten unterteilt:
+
+- **Übersetzen** von Studienplandateien, Dokumentation und Elementen der Benutzeroberfläche wie Buttons, Labels, etc.:
+
+ Als Übersetzer kannst du dich auf [unserer Übersetzungsplattform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) anmelden und Übersetzungen in einer der über 30 Sprachen beisteuern, die dort aktiviert sind.
+
+- **Korrekturlesen** der Übersetzungen für alle oben genannten Punkte.
+
+ Korrekturleser überprüfen, ob die von der Community beigesteuerten Übersetzungen einen einheitlichen Ton haben und frei von üblichen Problemen wie Tippfehlern usw. sind. Kurzum, sie sorgen für eine hohe Qualität der Übersetzungen. Beachte, dass wir aus einem gutem Grund keine maschinellen Übersetzungen verwenden.
+
+> [!WARNING] Wir verwenden GitHub nicht mehr, um Dateien direkt zu übersetzen. Wenn du wieder mitarbeiten möchtest, gehe stattdessen zu unserer [Übersetzungsplattform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+## Getting Started
+
+Zuerst solltest du in unserem [Diskord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) "Hallo" sagen. Wir posten regelmäßig Updates über Übersetzungsressourcen und beantworten dort deine Fragen.
+
+Als nächstes gehst du zu unserer [Übersetzungsplattform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) und loggst dich ein (wenn du noch nie an Übersetzungen mitgewirkt hast, musst du einen Account erstellen).
+
+Nachfolgend findest du eine ausführliche Anleitung, die dir dabei hilft, die dir zur Verfügung stehenden Übersetzungswerkzeuge und Arbeitsabläufe zu verstehen.
+
+Viel Spaß beim Übersetzen.
+
+## Wähle ein Projekt und eine Datei
+
+Sobald du die Übersetzungsplattform besuchst, solltest du mehrere "Projekte" sehen, die zur Übersetzung verfügbar sind:
+
+1. [Contributing documentation](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs) - Projekt, das die Dateien für diese Dokumentationsseite enthält.
+2. [Coding Curriculum](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum) - Projekt, welches unsere Aufgabendateien für unseren Studienplan enthält.
+3. [Benutzeroberfläche](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui) - Projekt, das Zeichenfolgen für UI-Elemente wie Buttons, Labels, etc. für unsere Lernplattform enthält.
+
+Wähle ein beliebiges Projekt aus, zu dem du beitragen möchtest, und du wirst eine Liste der verfügbaren Sprachen für die Übersetzung sehen.
+
+
+
+Wähle die Sprache aus, an der du arbeiten möchtest, und du siehst den kompletten Dateibaum.
+
+
+
+Für jede Datei und jeden Ordner wird ein Fortschrittsbalken angezeigt. Der **blaue** Teil des Fortschrittsbalkens zeigt an, wie viel Prozent der Datei bereits übersetzt wurde, während der **grüne** Teil des Fortschrittsbalkens anzeigt, wie viel Prozent der Datei vom Korrekturleseteam genehmigt wurde.
+
+Wähle eine Datei aus, an der du arbeiten möchtest und Crowdin öffnet die Editor-Ansicht.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn sich die Editoransicht öffnet, musst du auf das Einstellungssymbol (dargestellt als Zahnrad) klicken und die Einstellung 'HTML-Tags anzeigen' auf 'ANZEIGEN' umstellen. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass du Tags wie `<code></code>` anstelle von `<0></0>` sehen kannst.
+
+## Lehrplan übersetzen
+
+
+
+Crowdin trennt ein Dokument in übersetzbare "Strings", normalerweise Sätze. Jeder String wird einzeln übersetzt. Siehe Bild oben:
+
+1. Eine grün hervorgehobene Zeichenfolge hat bereits eine vorgeschlagene Übersetzung.
+2. Eine rot markierte Zeichenfolge hat _keine_ vorgeschlagene Übersetzung.
+3. Ein String mit ausgegrautem Text kann nicht übersetzt werden. Dies ist der Fall bei Codeblöcken und anderen Inhalten, die nicht übersetzt werden dürfen. Du wirst diese Zeichenfolgen im Editor nicht auswählen können.
+4. Wenn ein Mitwirkender eine Übersetzung für einen String vorgeschlagen hat, zeigt Crowdin den Vorschlag hier an. Du kannst eine identische Übersetzung nicht speichern - stattdessen solltest du, wenn eine Übersetzung korrekt ist, auf das `+` Symbol klicken, um sie "hochzuvoten". Eine ungenaue Übersetzung kann mit dem `-` Icon "heruntergevoted" werden.
+5. Crowdin empfiehlt Übersetzungen, die auf Translation Memory (TM) oder Machine Translation (MT) basieren. Translation Memory bezieht sich auf ähnliche oder identische Strings, die wir in anderen Dateien übersetzt/freigegeben haben. Machine Translation bezieht sich auf Übersetzungen, die von der in Crowdin integrierten Bibliothek empfohlen werden.
+6. Dies ist der Editorbereich, in dem du deinen Übersetzungsvorschlag für den ausgewählten String schreiben kannst.
+7. Der aktuell im Editor ausgewählte String wird gelb hervorgehoben.
+8. Hier siehst du Tags, die den Zustand des Strings anzeigen. `Done` bedeutet, dass der String mindestens eine vorgeschlagene Übersetzung hat. `Todo` bedeutet, dass der String keine Übersetzungsvorschläge hat.
+9. Hier siehst du das Fenster für die Kommentare. Wenn du Fragen oder Bedenken zu einem bestimmten String hast, kannst du hier einen Kommentar zu dem String hinterlassen, den andere Übersetzer sehen können.
+10. Diese beiden Buttons blenden die linke (Dokument-) und rechte (Kommentar-) Ansicht aus.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du einen versteckten String siehst, die Übersetzungen enthält, teile uns dies bitte im [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) mit, damit wir die Übersetzung aus dem Speicher entfernen können.
+
+Wenn du eine Übersetzung für einen String fertiggestellt hast, wähle den `Save` Button, um deine Übersetzung auf Crowdin zu speichern. Andere Mitwirkende können dann über deine Übersetzung abstimmen und Korrekturleser können sie genehmigen.
+
+Du kannst so viele Strings übersetzen, wie du möchtest - es sind keine zusätzlichen Schritte erforderlich, wenn du eine vollständige Datei fertigstellst oder eine neue Übersetzung vorschlägst. Ein Klick auf den `Save` Button ist alles, was nötig ist, um eine Übersetzung zu speichern.
+
+> [!NOTE] Wenn du in der englischen Quelldatei etwas siehst, das ungenau oder falsch ist, korrigiere es bitte nicht im Rahmen des Übersetzungsprozesses. Hinterlasse stattdessen einen Kommentar zu dem String, um uns auf die Unstimmigkeit hinzuweisen, oder erstelle ein Issue auf GitHub.
+
+## Die Lernoberfläche übersetzen
+
+Unsere `/learn`-Oberfläche basiert auf JSON-Dateien, die in ein i18n-Plugin geladen werden, um übersetzten Text zu erzeugen. Diese Übersetzungsarbeit verteilt sich sowohl auf Crowdin als auch auf GitHub.
+
+### Auf GitHub
+
+Die Dateien `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json` und `trending.json` enthalten Informationen, die an deine Sprache angepasst werden müssen. Wir können diese jedoch nicht in Crowdin laden, da der Inhalt nicht eins zu eins übersetzt werden kann.
+
+Diese Dateien werden höchstwahrscheinlich von deinem Sprachverantwortlichen (Language Lead) gepflegt, aber du kannst gerne [nachlesen, wie du sie übersetzen kannst](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### Auf Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Bearbeite die folgenden Dateien nicht über einen GitHub-PR.
+:::
+
+Die Dateien `intro.json` und `translations.json` werden beide auf Crowdin im Projekt "Learn User Interface" übersetzt. Diese zu übersetzen kann etwas knifflig sein, da jeder einzelne JSON-Wert als eigener String erscheint und manchmal der Kontext fehlt.
+
+Die `Context`-Informationen, die Crowdin bereitstellt, können jedoch dabei helfen zu verstehen, wo der String in die größere Struktur eingebunden ist.
+
+
+
+Wenn du Fragen dazu hast, wo der zu übersetzende String verwendet wird, frage bitte im [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) nach.
+
+## Dokumentation übersetzen
+
+Die Übersetzung der Dokumentation für die Mitarbeit ist ein ähnlicher Prozess wie die Übersetzung der Lehrplandateien.
+
+> [!NOTE] Unsere Dokumentation wird von `docsify` unterstützt, und wir haben ein spezielles Parsing für Nachrichtenboxen wie diese hier. Wenn du Strings siehst, die mit `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]` oder `[!TIP]` beginnen, solltest du diese Wörter NICHT übersetzen.
+
+### How to Translate Documentation with Internal Links
+
+Wenn du an der Übersetzung der Dokumentation arbeitest, achte auf interne Links, die auf einen anderen Teil der Dokumentation verweisen.
+
+Achte darauf, dass du die ID des Zielabschnitts (der Teil nach `#`) durch die ID des übersetzten Dokuments ersetzt. Auf Japanisch sieht es zum Beispiel so aus:
+
+Vor der Übersetzung
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Nach der Übersetzung
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト]($1#$2)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+Die eigentlichen Dateien in der Dokumentation sind in Markdown geschrieben, aber sie erscheinen als HTML-Tags auf Crowdin.
+
+Du kannst herausfinden, wie `docsify` einen String in deiner Sprache in eine ID umwandelt, indem du dir die übersetzten Seiten ansiehst. Wenn die Übersetzung noch nicht bereitgestellt wurde, kannst du dir eine Vorschau anzeigen lassen, indem du [die Dokumentseite lokal aufrufst](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md#Lokale Bereitstellung der Dokumentationsseite).
+
+Du kannst [ hier ](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md#Wie man einen internen Link erstellt) mehr über interne Links in unserer Dokumentation erfahren.
+
+## Übersetze das LearnToCode RPG
+
+Das LearnToCode RPG läuft auf Ren'Py, das eine spezielle Syntax für übersetzte Strings verwendet: (Siehe [Ren'Py Text Dokumentation](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- Die zu übersetzenden Sätze stehen immer zwischen `""`. Dies sind Dialoge oder Strings der Benutzeroberfläche. Die Schlüsselwörter, die vor oder nach dem Dialog stehen, sind Schlüsselwörter zur Steuerung der Spiel-Engine und werden in den nachfolgenden Regeln genauer erklärt. Beachte, dass diese erste Regel für alle nachfolgenden Regeln gilt.
+- Im Falle von `new "..."` übersetze nicht das Schlüsselwort `new`.
+- Präfixe wie `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (oder Varianten wie `player happy`, `player @ happy`) sollten nicht übersetzt werden. Dies sind Steuerschlüsselwörter, um das Charakter-Sprite im Spiel korrekt anzuzeigen.
+- Postfixe wie `nointeract` sollten nicht übersetzt werden.
+- Übersetze keine Dinge zwischen `[]` und `{}`. Dies sind variable Interpolationen und Text-Tags. Diese müssen in halber Breite Klammern `[]` und `{}` bleiben, anstatt ihrer Gegenstücke in voller Breite `【】` und `「」`
+- Das Schlüsselwort `nointeract` am Ende des Satzes darf nicht übersetzt werden.
+- Wenn wir versuchen, Klammern in voller Breite `()` zu verwenden, wird eine QA-Warnung angezeigt. Um die QA-Warnung zu vermeiden, verwende Klammern mit halber Breite `()`
+
+### Beispiele
+
+---
+
+#### Vor der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- Dies ist die Zeile, die übersetzt werden muss. Siehe Übersetzung unten
+```
+
+#### Nach der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? Was für ein Zufall! Unser VIP-Teammitglied, {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} wird sich geehrt fühlen, davon zu hören."
+```
+
+Hinweis: Die Tags `[]` und `{}` sollten intakt bleiben.
+
+---
+
+#### Vor der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- übersetze diese Zeile, siehe unten
+```
+
+#### Nach der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Überspringen"
+```
+
+Hinweis: Auch hier sollten das Präfix `new` und der Tag `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` intakt bleiben.
+
+---
+
+#### Vor der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### Nach der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Ha ha, [player_name],Du bist so witzig. Ich bin sicher, dass dir die Arbeit als Entwickler Spaß machen wird."
+```
+
+Hinweis: `layla @ neutral` und `[player_name]` bleiben unverändert.
+
+---
+
+#### Vor der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### Nach der Übersetzung
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Vielleicht ist das alles nur ein Traum?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Ein Hinweis dazu, wie Crowdin einen Satz unterteilt
+
+Achte darauf, wie Crowdin eine Dialogzeile zwischen öffnenden und schließenden Anführungszeichen `""` unterteilt. Bei der Übersetzung des Dialogs müssen wir darauf achten, dass die einleitenden und abschließenden Anführungszeichen beibehalten werden, auch wenn die Anführungszeichen in verschiedenen Abschnitten vorkommen.
+
+Dies ist die zu übersetzende Zeile:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin unterteilt es in drei Teile wie unten dargestellt:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Screenshot 2022-01-23 um 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# Original
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# übersetzt, wobei die einleitenden Anführungszeichen beibehalten werden `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Screenshot 2022-01-23 um 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# Original
+What is that?
+
+# übersetzt, keine Anführungszeichen auf beiden Seiten
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Screenshot 2022-01-23 um 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# Original
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# übersetzt, wobei die abschließenden Anführungszeichen beibehalten werden `"`
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## Übersetzungen bewerten
+
+Crowdin ermöglicht es dir, die vorhandenen Übersetzungsvorschläge zu bewerten. Wenn du versuchst, eine Übersetzung zu speichern, erscheint möglicherweise die Meldung, dass du eine doppelte Übersetzung nicht speichern kannst - dies bedeutet, dass ein anderer Mitwirkender diese identische Übersetzung vorgeschlagen hat. Wenn du mit der Übersetzung einverstanden bist, dann klicke auf die Schaltfläche `+`, um die Übersetzung "hochzustufen".
+
+Wenn du eine Übersetzung siehst, die ungenau ist oder nicht die gleiche Klarheit wie das Original bietet, klicke auf den `-`-Button, um die Übersetzung "herunterzustufen".
+
+Crowdin nutzt diese Stimmen, um jeder vorgeschlagenen Übersetzung für einen String eine Punktzahl zu geben, die dem Korrekturleseteam hilft, zu entscheiden, welche Übersetzung für den jeweiligen String am besten geeignet ist.
+
+## Qualitätssicherungsprüfungen
+
+Wir haben einige Qualitätssicherungsschritte aktiviert, die sicherstellen, dass eine Übersetzung so genau wie möglich ist - dies hilft unseren Korrekturlesern bei der Überprüfung vorgeschlagener Übersetzungen.
+
+Wenn du versuchst, eine Übersetzung zu speichern, erscheint möglicherweise eine Warnmeldung mit einem Hinweis auf deine vorgeschlagene Übersetzung.
+
+
+
+Diese Meldung wird angezeigt, wenn das Qualitätssicherungssystem von Crowdin einen potenziellen Fehler in der vorgeschlagenen Übersetzung festgestellt hat. In diesem Beispiel haben wir den Text eines `<code>`-Tags geändert und Crowdin hat dies erkannt.
+
+> [!WARNING] Du hast die Möglichkeit, eine Übersetzung trotz Fehlern zu speichern. Wenn du dies tust, indem du auf "Save Anyway" klickst, solltest du auch einen Korrekturleser oder Projektmanager markieren und erklären, warum die QS-Meldung in diesem Fall ignoriert werden muss.
+
+## Bewährte Praktiken bei der Übersetzung
+
+Befolge diese Richtlinien, um sicherzustellen, dass unsere Übersetzungen so genau wie möglich sind:
+
+- Übersetze nicht den Inhalt innerhalb der `<code>`-Tags. Diese Tags kennzeichnen Text, der im Code vorkommt und in Englisch belassen werden sollte.
+- Füge keine zusätzlichen Inhalte hinzu. Wenn du der Meinung bist, dass eine Aufgabe Änderungen am Textinhalt oder zusätzliche Informationen erfordert, solltest du die Änderungen in einem Issue auf GitHub oder in einem Pull Request vorschlagen, der die englische Datei ändert.
+- Ändere nicht die Reihenfolge des Inhalts.
+
+Wenn du Fragen hast, kannst du uns gerne in unserem [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) ansprechen und wir helfen dir gerne weiter.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..86f553f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: So verwendest du Docker unter Windows Home
+---
+
+Bei der Einrichtung von Docker unter Windows Home gibt es einige Fallstricke, die du vermeiden solltest. Als erstes musst du die [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) als Administrator verwenden. Leider unterstützt Windows Home kein Docker für Windows Desktop, sodass stattdessen Toolbox verwendet werden muss. Es muss als Administrator ausgeführt werden, da die Installation Symlinks verwendet, die sonst nicht erstellt werden können.
+
+Sobald du die Toolbox installiert hast, führe das Docker Quickstart Terminal als Administrator aus. Damit wird eine `default` virtuelle Maschine erstellt, wenn sie noch nicht existiert. Wenn das geschehen ist, schließe das Terminal und öffne VirtualBox (wieder als Administrator). Du solltest die `default` Maschine sehen können. Die Website ist ziemlich ressourcenintensiv, also halte die virtuelle Maschine an und erhöhe die Einstellungen so weit wie möglich - vor allem den Arbeitsspeicher. It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Wenn du sicher bist, dass Docker funktioniert, klone das freeCodeCamp Repository in ein Verzeichnis innerhalb von `C:\Users`. Diese Verzeichnisse werden gemeinsam genutzt, so dass Docker Zugriff auf die lokalen Verzeichnisse hat, die es während der Installation benötigt.
+
+Wenn du Meldungen siehst wie
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+when you `pnpm run docker:init` this is likely the culprit.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..206e3f8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: Wie man an Programmieraufgaben arbeitet
+---
+
+Unser Ziel ist es, ein unterhaltsames und voll interaktives Lernerlebnis zu entwickeln.
+
+Sich interaktive Programmieraufgaben auszudenken ist schwierig. Es wäre viel einfacher, eine ausführliche Erklärung zu schreiben oder ein Video-Tutorial zu erstellen. Aber für unseren Hauptstudienplan bleiben wir bei dem, was für die meisten Menschen am besten funktioniert - ein vollständig interaktives, videospielähnliches Erlebnis.
+
+Wir wollen, dass die Teilnehmer einen Flow-Zustand erreichen. Wir wollen, dass sie in Schwung kommen und so schnell wie möglich Fortschritte in unserem Studienplan machen. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+Beachte, dass wir für Version 7.0 des freeCodeCamp-Studienplan zu einem [vollständig projektorientierten Modell mit viel mehr Wiederholungen](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/) übergehen.
+
+Um diese Aufgaben zu lösen, braucht es viel Kreativität und Liebe zum Detail. Es gibt viele Möglichkeiten, dir zu helfen. Du bekommst Unterstützung von einem ganzen Team von Mitwirkenden, an die du deine Ideen weitergeben und deine Aufgaben demonstrieren kannst.
+
+Und wie immer kannst du deine Fragen in der [Kategorie "Contributors" in unserem Forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) oder im ["Contributors"-Chatraum](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) stellen.
+
+Mit deiner Hilfe können wir einen interaktiven Studienplan entwickeln, der Millionen von Menschen dabei helfen wird, in den nächsten Jahren das Programmieren zu lernen.
+
+Der Inhalt jeder Aufgabe wird in einer eigenen Markdown-Datei gespeichert. Diese Markdown-Datei wird später mit unseren Tools in HTML umgewandelt, um interaktive Webseiten zu erstellen.
+
+Du kannst alle Studienplaninhalte von freeCodeCamp.org im [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges) Verzeichnis finden.
+
+## Richte die Hilfsmittel für den Studienplan ein
+
+Bevor du an dem Studienplan arbeitest, musst du einige Hilfsmittel einrichten, mit denen du deine Änderungen testen kannst. Du kannst jede der unten aufgeführten Optionen verwenden:
+
+- Du kannst [das freeCodeCamp lokal einrichten](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Das ist **sehr empfehlenswert** für regelmäßige/wiederholte Beiträge. Mit diesem Setup kannst du arbeiten und deine Änderungen testen.
+- Verwende Gitpod, eine kostenlose Online-Entwicklungsumgebung. Wenn du auf den Button unten klickst, wird eine programmierfertige Entwicklungsumgebung für das freeCodeCamp in deinem Browser gestartet. Es dauert nur wenige Minuten.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### Wie man an Praxisprojekten arbeitet
+
+Die Praxisprojekte haben einige zusätzliche Werkzeuge, die dir helfen, neue Projekte und Schritte zu erstellen. Näheres dazu findest du in [diesen Dokumenten](how-to-work-on-practice-projects).
+
+## Aufgabenvorlage
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Challenge Title'
+challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Anweisungstext für die Aufgabe, in Markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+Tests, die gegen Benutzercode laufen, in Paaren von Markdown-Text und Codeblock-Testcode.
+
+```js
+Code für den ersten Test
+```
+
+Wenn eine dynamische Ausgabe basierend auf dem Code des Benutzers erforderlich ist, werden --fcc-expected-- und --fcc-actual-- durch die erwarteten und tatsächlichen Werte der Testaussagen ersetzt. Sei vorsichtig, wenn du mehrere Aussagen hast, da die erste Aussage, bei der ein Fehler auftritt, die Werte von --fcc-expected-- und --fcc-actual-- bestimmt.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Zusätzliche Informationen für eine Aufgabe, in Markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Der Code wird vor dem Code des Nutzers ausgewertet.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Code, der nach dem Code des Nutzers und kurz vor den Tests ausgewertet wird
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Boilerplate-Code, der im Editor angezeigt wird. Dieser Abschnitt sollte nur Code innerhalb von Backticks enthalten, wie den folgenden:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Lösungen werden für die CI-Tests verwendet, um sicherzustellen, dass Änderungen an den Hinweisen (hints) weiterhin wie vorgesehen funktionieren
+
+```js
+// erste Lösung - die Sprache(n) sollte(n) mit dem Startwert übereinstimmen.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// zweite Lösung - also wenn der Startwert in HTML geschrieben ist...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// dritte Lösung usw. - Ihre Lösungen sollten in HTML geschrieben sein.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. In den obigen Abschnitten sind Beispiele für `lang`:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Nummerierung der Aufgabe
+
+Jede Aufgabe benötigt eine `id`. Wenn du keine angibst, erstellt MongoDB eine neue, zufällige ID, wenn es die Daten speichert. Das wollen wir aber nicht, denn wir wollen, dass die Aufgaben-IDs in verschiedenen Umgebungen (Staging, Produktion, viele verschiedene Entwickler usw.) konsistent sind.
+
+Um eine neue in einer Shell zu erstellen (vorausgesetzt, MongoDB wird separat ausgeführt):
+
+1. Führe den Befehl 'mongo' aus.
+2. Führe den Befehl `ObjectId()` aus.
+
+Zum Beispiel:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Aufgabentitel
+```
+
+## Aufgaben benennen
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Verwende die Uhrzeiger-Notation, um das Padding eines Elements festzulegen
+- Arrays mit .reduce komprimieren
+- Verwende die Klammer-Notation, um das erste Zeichen in einem String zu finden
+
+## Aufgabenbeschreibungen/ Instruktionen
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (Großbuchstaben bei "J" und "S" und keine Abkürzungen)
+- Node.js
+- Obwohl sie manchmal ungenau sind, sollten die nicht mit Bindestrichen versehenen Formen von "Back-End" und "Front-End" verwendet werden, da sie weiter verbreitet sind.
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- vereinfache die Aufgabe, oder
+- Teile die Aufgabe in zwei Aufgaben auf.
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- Sprachliche Schlüsselwörter stehen in `` \` `` Backticks. Zum Beispiel HTML-Tag-Namen oder CSS-Eigenschaftsnamen.
+- Verweise auf Codeteile (d. h. Funktions-, Methoden- oder Variablennamen) sollten in `` \` ``-Backticks eingeschlossen werden. Siehe untenstehendes Beispiel:
+
+```md
+Verwende `parseInt`, um die Variable `realNumber` in eine Integerzahl umzuwandeln.
+```
+
+- Verweise auf Dateinamen und Pfadverzeichnisse (z. B. `package.json`, `src/components`) sollten in `` \` ``-Backticks eingeschlossen werden.
+- Mehrzeiligen Codeblöcken **muss eine Leerzeile vorangestellt werden**. Die nächste Zeile muss mit drei Backticks beginnen, unmittelbar gefolgt von einer der [unterstützten Sprachen](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. Siehe untenstehendes Beispiel:
+- Whitespace ist in Markdown wichtig, deshalb empfehlen wir, ihn in deinem Editor sichtbar zu machen.
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+````md
+```{Sprache}
+
+[HIER DEIN CODE]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Zusätzliche Informationen in Form einer Anmerkung sollten von Leerzeilen umgeben sein und wie folgt formatiert werden: "**Note:** Rest des Anmerkungstextes...".
+- Wenn mehrere Notizen erforderlich sind, listest du alle Notizen in separaten Sätzen auf und verwendest das Format: **Notes:** Erster Text der Notiz. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## Tests schreiben
+
+Aufgaben sollten so viele Tests enthalten, wie nötig sind, um zu überprüfen, ob ein Teilnehmer ein Konzept verstanden hat.
+
+Unser Ziel ist es, den einzelnen Aspekt der Aufgabe zu vermitteln und zu prüfen, ob die Teilnehmer/innen diesen Aspekt verstanden haben.
+
+Aufgabentests können die Assertion-Bibliotheken von Node.js und Chai.js nutzen. Außerdem kann bei Bedarf auf den vom Benutzer erstellten Code in der Variable `code` zugegriffen werden. Zusätzlich stellt das Objekt `__helpers` mehrere Funktionen zur Verfügung, die das Schreiben von Tests vereinfachen. The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. Die Groß- und Kleinschreibung und die Abstände des Kommentarwörterbuchs müssen eingehalten werden. Das Kommentarwörterbuch sollte nicht ohne vorherige Absprache mit dem Entwicklungsteam erweitert werden.
+
+Die verwendeten Kommentare sollten ein Leerzeichen zwischen den Kommentarzeichen und dem eigentlichen Kommentar enthalten. Im Allgemeinen sollten Kommentare sparsam verwendet werden. Überlege dir immer, ob du die Beschreibung oder die Instruktionen einer Aufgabe umschreiben kannst, wenn du dadurch einen Kommentar im Startcode vermeiden kannst.
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Change code below this line
+
+ // Change code above this line
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Change code below this line */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Change code above this line */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+Deklariere die Variable myGlobal unterhalb dieser Zeile
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Wir arbeiten an einer Integration, die die Arbeit an i18n für das Kommentarwörterbuch ermöglicht.
+
+## Hinweise und Lösungen
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. Beginne mit den gleichen Schritten wie beim Erstellen eines neuen Themas, aber schau dir die nächsten Schritte zum Erstellen des Titels an.
+2. Der Titel des Themas sollte mit `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` beginnen und mit dem eigentlichen Titel der Studienplanaufgabe verkettet werden. Wenn die Aufgabe zum Beispiel "`Chunky Monkey`" heißt, würde der Titel des Themas lauten "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. `camperbot` sollte der Eigentümer dieser Themen/Posts sein. Du musst also einen Admin bitten, den Eigentümer des Hauptposts auf `camperbot` zu ändern.
+4. Sobald das neue Thema erstellt ist, wird eine Forenthemen-ID erstellt. Sie befindet sich am Ende der URL des Forenthemas. Diese ID muss dem Frontmatter der Studienplanaufgabendatei über den normalen Pull-Request-Prozess hinzugefügt werden, damit der `Erhalte einen Tipp` Button auf das Thema verlinkt.
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# Aufgabentitel hier eintragen
+
+---
+
+## Problemerläuterung
+
+Hier wird zusammengefasst, was zu tun ist, ohne die Aufgabenbeschreibung und/oder die Instruktionen einfach zu wiederholen. Dies ist ein optionaler Abschnitt
+
+#### relevante Links
+
+- [Linktext](Link_url_hier eintragen)
+- [Linktext](Link_url_hier eintragen)
+
+---
+
+## Hinweise
+
+### Hinweis 1
+
+Hinweis hier eintragen
+
+### Hinweis 2
+
+Hinweis hier eintragen
+
+---
+
+## Lösungen
+
+<details><summary>Lösung 1 (Klicken zum Anzeigen/Verbergen)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Erklärung des Codes
+
+- Erklärung des Codes hier eintragen
+- Erklärung des Codes hier eintragen
+
+#### Relevante Links
+
+- [Linktext](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Linktext](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Testen von Aufgaben
+
+Bevor du [einen Pull-Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) für deine Änderungen erstellst, musst du überprüfen, ob die von dir vorgenommenen Änderungen nicht versehentlich Probleme mit der Aufgabe verursachen.
+
+1. Um alle Aufgaben zu testen, führe den folgenden Befehl im Stammverzeichnis aus
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f0cd11f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. Sie wird mit [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) und [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/) in verschiedene Weltsprachen übersetzt.
+
+Du kannst mehr darüber erfahren, wie du die Client-Anwendung lokal für die Entwicklung einrichtest, indem du [unseren Leitfaden zur lokalen Einrichtung](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) liest. By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+Das kann hilfreich sein, wenn du an einem Feature arbeitest, das speziell auf die Lokalisierung abzielt und du zum Beispiel die Beschriftung eines Buttons in einer anderen Sprache validieren musst.
+
+:::tip
+You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. Lies stattdessen [diesen Leitfaden hier](how-to-translate-files).
+:::
+
+Wir wollen verstehen, wie die i18n-Frameworks und -Werkzeuge funktionieren.
+
+## Dateistruktur
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**Dateien, die auf unserer Übersetzungsplattform übersetzt wurden:**
+
+- Die Datei `translations.json` enthält den Großteil des Textes, der auf den Elementen der Benutzeroberfläche erscheint. Die Schlüssel werden in der Codebasis verwendet, um den richtigen Text für die eingestellte Sprache zu erhalten. This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- Die Datei `intro.json` enthält die Schlüssel-Werte-Paare für den Einleitungstext auf den Zertifikatseiten.
+
+ Wenn du Übersetzungen für die Schlüssel hinzufügen/aktualisieren willst, lies bitte [diesen Leitfaden hier](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Dateien, die NICHT auf unserer Übersetzungsplattform übersetzt wurden:**
+
+- Die `motivation.json` Dateien müssen nicht die gleichen Zitate, Komplimente oder Array-Längen haben. Nur die gleiche JSON-Struktur.
+
+- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
+
+ Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+Wenn du eine neue Sprache testest, erstelle einen Ordner mit dem Namen der Sprache als Titel neben den anderen Sprachen und kopiere die JSON-Dateien aus einer anderen Sprache in deinen neuen Ordner.
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+Befolge dann die Anweisungen in den Kommentaren in derselben Datei, um die restlichen Variablen nach Bedarf hinzuzufügen/zu aktualisieren.
+
+Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the string of the locale you want to build from the `Languages` enum in the above file.
+
+## Wie du Komponenten strukturierst
+
+Wenn du an einer Funktion oder einem Fehler für die Client-Webanwendung arbeitest, z. B. wenn du neue Elemente auf der Einstellungsseite hinzufügst, solltest du die folgenden Richtlinien befolgen. Sie helfen dir, die Komponenten für die Lokalisierung in alle unterstützten Weltsprachen vorzubereiten.
+
+### Funktionelle Komponente
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// in der Rendermethode:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// Aufruf der Funktion "t" mit einem Key aus der JSON-Datei:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // weitere Details unten
+```
+
+### Klassenkomponente
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation fügt die Funktion "t" zu props hinzu:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// Aufruf der Funktion "t" mit einem Key aus der JSON-Datei:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // weitere Details unten
+
+// Export ohne redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// oder mit redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Übersetzen mit Hilfe der "t"-Funktion
+
+### Grundlegende Übersetzung
+
+```js
+// in der Komponente:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// in der JSON Datei:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// Output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### Mit dynamischen Daten
+
+```js
+// in der Komponente:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// in der JSON Datei:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// Output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+Das obige Beispiel übergibt der Funktion `t` ein Objekt mit einer Variablen `username`. Die Variable wird im JSON-Wert verwendet, wo `{{username}}` steht.
+
+## Übersetzen mit der `Trans`-Komponente
+
+Generell gilt: Verwende die "t"-Funktion, wenn du kannst. Es gibt aber eine `Trans`-Komponente für den Fall, dass das nicht ausreicht, z. B. wenn du Elemente in den Text eingebettet hast. Du kannst die `Trans`-Komponente mit jeder Art von React-Komponente verwenden.
+
+### Verschachtelte Grundelemente
+
+```js
+// in der Komponente:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in der JSON Datei:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// Output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i` und `p` sind die Standardwerte, aber diese Liste kann in der i18n-Konfiguration erweitert werden.
+
+### Verschachtelte komplexe Elemente
+
+In anderen Fällen möchtest du einen bestimmten Text innerhalb eines anderen Elements platzieren, ein Anker-Tag ist ein gutes Beispiel dafür:
+
+```js
+// in der Komponente:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in der JSON Datei:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// Output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+Im obigen Beispiel wird der Schlüssel in den Attributen der `Trans`-Komponente gesetzt. Die `<0>` und `</0>` im JSON stehen für das erste Kindelement der Komponente, in diesem Fall das Ankerelement. Wenn es mehr Kindelemente gäbe, würden sie einfach von dort aus weiterzählen und dabei dieselbe Syntax verwenden. Du kannst die Kindelemente einer Komponente in den React Dev Tools finden, indem du sie inspizierst. `placeholder` ist einfach da, weil der Linter sich über leere `<a>`-Elemente beschwert.
+
+### Mit einer Variablen
+
+```js
+// in der Komponente:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in der JSON Datei:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// Output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+Im obigen Beispiel werden der Schlüssel und eine Variable in den Attributen der `Trans`-Komponente festgelegt. `{{ email }}` muss auch irgendwo in der `Trans`-Komponente stehen, es ist egal wo.
+
+## Ändern des Textes
+
+Um den Text auf der Client-Seite zu ändern, gehst du in die entsprechende `.json`-Datei, suchst den Schlüssel, der in der React-Komponente verwendet wird, und änderst den Wert in den gewünschten neuen Text. Du solltest die Codebasis nach diesem Schlüssel durchsuchen, um sicherzustellen, dass er nicht an anderer Stelle verwendet wird. Oder, falls ja, dass die Änderungen an allen Stellen sinnvoll sind.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Hinzufügen von Text
+
+Wenn der Text, den du dem Client hinzufügen möchtest, bereits in der entsprechenden `.json`-Datei vorhanden ist, verwende den vorhandenen Schlüssel. Andernfalls erstellst du einen neuen Schlüssel.
+
+Die englische Datei ist die "Quelle der Wahrheit" für alle `.json`-Dateien, die den gleichen Namen haben. Wenn du einen neuen Schlüssel hinzufügen musst, füge ihn dort ein. Dann fügst du den Schlüssel zu **allen** `translations.json`-Dateien hinzu.
+
+> [!NOTE] Verwende englischen Text für alle Sprachen, wenn die Datei über Crowdin übersetzt wird. Andernfalls werden die Tests fehlschlagen.
+
+Es wäre auch schön, wenn die Schlüssel in allen Dateien die gleiche Reihenfolge hätten. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. In der [Dokumentation](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) erfährst du, wie sie verwendet werden.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [react-i18next Dokumente](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [i18next Dokumente](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4cff3871
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: Wie man an Übungsprojekten arbeitet
+---
+
+Our practice projects use a step-based approach to teach concepts to campers. Ein Projekt besteht aus mehreren Dateien, die wir als **"Schritte"** bezeichnen. Diese Dateien werden nach der Challenge-ID benannt, um Probleme mit dem Übersetzungsablauf zu vermeiden. Das macht es leider schwierig, die zu einem bestimmten Schritt gehörende Datei zu finden.
+
+Wir haben ein Editor-Tool für Aufgaben entwickelt, das hier Abhilfe schafft. Mit diesem Tool kannst du durch die verfügbaren Projekte und die Schritte für jedes Projekt (in der richtigen Reihenfolge) navigieren. Außerdem gibt es einen eingebetteten Code-Editor, mit dem du die Dateien direkt bearbeiten kannst.
+
+## Den Aufgaben-Editor verwenden
+
+In dieser Anleitung erfährst du, wie du mit unserem Aufgaben-Editor an den Übungsprojekten arbeiten kannst.
+
+### Starten des Editors
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Then, run `pnpm run challenge-editor` to start both the client and the API that powers the editor.
+
+Der Client läuft auf Port `3300`, so dass du ihn unter `http://localhost:3300` erreichen kannst. Die API läuft auf Port `3200`, um Konflikte mit dem Lernclient und dem Server zu vermeiden. Dies ermöglicht es dir, die freeCodeCamp-Anwendung gleichzeitig mit dem Editor laufen zu lassen, so dass du deine Änderungen lokal testen kannst.
+
+### Navigating the Editor
+
+The default view will list the available `superblocks` - these are the certifications. Click on the certification link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to the list of blocks. These are the practice projects. Click on the project link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to a list of steps for the project. If you are working on an existing step, you can click on the step link to open the editor. If you are adding or removing steps, click the `Use the step tools` link to switch to the step tools for that challenge.
+
+### Editing Steps
+
+When you click on a step, you'll be taken to the editor. This is a basic text editor that offers syntax highlighting.
+
+After you have made your changes, click the `Save Changes` button to save your changes. You will get a browser alert letting you know that your changes are ready to commit. Note that you'll need to use `git` manually to stage and commit your files - this tool will not do that for you.
+
+### Step Tools
+
+When you click the `Use the step tools` link, you'll be taken to the step tools page. This allows you to add or remove steps from the project.
+
+#### Create Next Step
+
+Clicking this button will add a new step at the end of the project. This step will use the previous step's code as the seed.
+
+#### Create Empty Steps
+
+Enter the number of steps you want to add in the input. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Insert Step
+
+Enter the step number that you want to add. Then, click the `Insert Step` button to add the step. The following steps will be re-ordered.
+
+#### Delete Step
+
+Enter the step number you want to delete. Then click the `Delete Step` button to remove that step. This will automatically update the step numbers for the remaining steps.
+
+#### Update Step Titles
+
+You should not have to use this tool unless you've manually deleted or added steps. This tool will reorder the step numbers.
+
+## Using the Scripts Manually
+
+If you want to work on the steps manually, in your local IDE, you can run the step management scripts directly.
+
+The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step in the project. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Wechsle in das Verzeichnis des Projekts.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Wechsle in das Verzeichnis des Projekts.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # where X is the number of steps to create.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a new step at a specified position, incrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json). The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Wechsle in das Verzeichnis des Projekts.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # where X is the position to insert the new step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+A one-off script that deletes an existing step, decrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json)
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Wechsle in das Verzeichnis des Projekts.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # where X is the step number to be deleted.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+A one-off script that automatically updates the frontmatter in a project's markdown files so that they are consistent with the project's meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Wechsle in das Verzeichnis des Projekts.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed433453
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on the Component Library
+---
+
+Welcome to freeCodeCamp's `ui-components` library. The components are built mostly from scratch with basic HTML elements and [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp has been using Bootstrap components in the UI. However, we are moving away from it and building our own component library, which helps standardize our UX/UI patterns and improve accessibility. The project is tracked in [this GitHub issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+The following steps are recommended when working on a new component:
+
+- Research and planning
+- Implement the component
+- Display the use cases on Storybook
+- Write unit tests
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Before building a component, you need to research and document on how the existing version behaves and looks, to ensure that the new one has matching styles and supports all the current usages. In order to meet the web accessibility requirements, you should also pay attention to the accessibility aspect of the component, see which HTML elements and ARIA attributes are used under the hood.
+
+Once you have gathered enough information about the component, you can start thinking about the props interface. Ideally, the interface should be as similar to the current version as possible, to ease the adoption later on. Since we are using Bootstrap components, the simplest approach is to mimic [their implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+We prefer smaller pull requests rather than a large one, because they speed up the review time and reduce cognitive overload for the reviewers. For that reason, you should think about how you would break down the implementation and come up with a delivery plan.
+
+We recommend opening a separate GitHub issue for each component and include all the notes in the issue description. It can be used as a place to host all of your working notes, as well as a way to communicate the approach with the reviewers. We will use the issue thread for further discussion if needed. [The issue for Button component](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) can be used as a reference.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+A new component can be created using the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+The command will generate a new folder inside the `ui-components` directory, with the following files:
+
+| File name | Purpose |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | It is used for exporting the component and its types. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | It is used for demoing the component on Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | It is a test file. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | It is where we implement the component. |
+| `types.ts` | It is where we locate the component's interface and types. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Support forwarding ref
+- Be styled for both light and dark themes
+- Be styled internally based on their props (the consumers should not need to restyle the component with the `className` prop)
+- Utilize the built-in styling system from Tailwind instead of having custom styles
+
+### Using Colors
+
+There are two color "layers" in the component library:
+
+- The base layer, where the color names describe what the colors are, e.g. `gray00`, `blue50`
+- The semantic layer, where the color names describe what the colors are for, e.g. `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. There are exceptions, however, specifically when you are styling the component's states such as hover, active, disabled, etc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+> [!NOTE] Color definition can be found in the [`colors.css` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). A color is only available for use if it is added to the [`tailwind.config.js` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) under the `colors` property.
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Tailwind CSS Configuration](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [React Bootstrap v0.33 Docs](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Bootstrap 3.3.7 stylesheet](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [React Bootstrap current implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [React Bootstrap current tests](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Use cases of the component should be added to the Storybook file (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+To start Storybook, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+The Storybook page is available on [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+We use [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) to write unit tests. The tests should assert that the components behave as expected and are accessible.
+
+To run tests against the component library, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Testing for Accessibility](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Order of priority of React Testing Library's queries](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Common mistakes with React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..13d696a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+To work on the contributing guidelines, you can edit or add files in the `docs` directory [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). When your changes are merged, they will be made available automatically at the documentation site.
+
+When adding a new file to the `docs` directory, you should evaluate if the file should also be added to the sidebar navigation. We typically create a link in the [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) file for new and independent guides. Alternatively, You may follow the instructions below on creating an internal link for supporting guides.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+If you want to create a link targeting a different section of the contributing guidelines, follow this format:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// If the target section is within the same page, you can omit the file name
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Make sure you include the file extension (`.md`). Don't specify the full URL or append `/` before the file name.
+
+This is necessary to make these links work for the translated version of the document. Otherwise, they will redirect to the English version of the page regardless of the language.
+
+#### Translating docs with internal links
+
+When you work on translating docs on Crowdin, make sure to replace the `#target-section-heading-id` with the id on the translated document. [Learn more about translating docs here](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+> [!NOTE] A quick reminder that you do not need to set up anything for working on the content for the documentation site.
+>
+> To work on the contributing guidelines, see [work on the docs content](#work-on-the-docs-content) section.
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+The site is generated using [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) and served using GitHub pages.
+
+Typically you would not need to change any configuration or build the site locally. In case you are interested, here is how it works:
+
+- Der Quelltext der Homepage ist in [`docs/index.html`](index.html) zu finden.
+- Wir stellen diese Datei als SPA (Single Page Application) mit `docsify` und GitHub Pages bereit.
+- The `docsify` script generates the content of `markdown` files in the `docs` directory on demand.
+- Die Homepage wird aus der [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage) erstellt.
+- The sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dc88d705
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: Wie man am FreeCodeCamp.orgs Entwickler-News-Theme arbeitet
+---
+
+Die Entwicklernews, auch bekannt als [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) Seite, wird mit [Ghost](https://ghost.org/) betrieben. Wir verwenden ein individuelles Theme für das Erscheinungsbild der Website. Der Quellcode des Themes ist hier verfügbar: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## Das Theme
+
+Ghost verwendet eine einfache Templating-Sprache namens [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) für seine Themes. Das Theme, das auf `/news` verwendet wird, basiert auf dem Standard-Theme [casper](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
+
+Das Standard-Theme ist ziemlich ausführlich kommentiert, so dass es relativ einfach sein sollte, durch Lesen des Codes und der Kommentare herauszufinden, was vor sich geht. Wenn du dich mit der Funktionsweise vertraut gemacht hast, findest du in Ghost auch eine vollständige [Theme-API-Dokumentation](https://themes.ghost.org), in der alle möglichen Handlebars-Helfer und Vorlagen erklärt werden.
+
+**Die Hauptdateien sind:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - Die Hauptvorlagen-Datei
+- `index.hbs` - Wird für die Startseite verwendet
+- `post.hbs` - Wird für einzelne Beiträge (posts) verwendet
+- `page.hbs` - Wird für einzelne Seiten verwendet
+- `tag.hbs` - Wird für Tag-Archive verwendet
+- `author.hbs` - Wird für Autorenarchive verwendet
+
+Ein wirklich toller Trick ist, dass du auch benutzerdefinierte, einmalige Vorlagen erstellen kannst, indem du einfach den Slug einer Seite in eine Vorlagendatei einfügst. Zum Beispiel:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Benutzerdefinierte Vorlage für die `/about/` Seite
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Benutzerdefinierte Vorlage für `/tag/news/` Archiv
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Benutzerdefinierte Vorlage für `/author/ali/` Archiv
+
+## Entwicklung
+
+1. Installiere Ghost lokal.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Hinweis: Derzeit verwendet freeCodeCamp die Ghost-Version `2.9.0`, also stelle sicher, dass du eine höhere Version verwendest.
+
+ Achte darauf, dass du die `ghost`-Befehle aus dem `ghost-local-site`-Verzeichnis ausführst. Folge den zusätzlichen Anweisungen in [der offiziellen Dokumentation von Ghost](https://docs.ghost.org), wenn du mit der Benutzeroberfläche nicht vertraut bist.
+
+2. Forke und klone das Repository in deinem Theme-Verzeichnis (ersetze `YOUR_USERNAME` durch deinen GitHub Benutzernamen):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Stelle sicher, dass du alle Voraussetzungen erfüllst.
+
+ Die Stile des Themes werden mit Gulp/PostCSS kompiliert, um zukünftige CSS-Spezifikationen zu erfüllen. Du benötigst [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Stelle sicher, dass deine Node.js-Version mit `ghost` kompatibel ist.
+
+4. Abhängigkeiten (Dependencies) installieren und das Theme entwickeln
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Jetzt kannst du `/assets/css/`-Dateien bearbeiten, die automatisch zu `/assets/built/` kompiliert werden.
+
+6. Zugriff auf die Entwicklungsseite.
+
+ a. Gib `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` in deine Adressleiste ein. Fahre mit dem Setup fort, zu dem du auf der Seite aufgefordert wirst (wenn du Ghost zum ersten Mal ausführst).
+
+ b. _(Einmalig, während des Setups)_ Starte Ghost einmal an einem separaten Terminal neu, um sicherzustellen, dass das Theme verfügbar ist.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(Einmalig, während des Setups)_ Wenn du das getan hast, gehst du auf `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` und scrollst bis zum Ende. Stelle sicher, dass du auf `freecodecamp-news-theme` aktivieren klickst.
+
+7. Zippe den endgültigen Code und erstelle einen Pull-Request
+
+ Die `zip` Gulp-Aufgabe verpackt die Themedateien in `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, die wir dann auf die Produktionsseite hochladen können.
+
+ Wenn du einen PR erstellst, stelle bitte sicher, dass du das folgende Skript ausgeführt hast, bevor du den Code committest und einen PR sendest.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Andere Referenzen und Ressourcen
+
+### Verwendete PostCSS-Funktionen
+
+- Autoprefixer - Mach dir keine Gedanken über das Schreiben von Browser-Präfixen, das wird alles automatisch erledigt, mit Unterstützung für die letzten 2 Hauptversionen eines jeden Browsers.
+- Variablen - Einfache reine CSS-Variablen
+- [Farbfunktion](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### SVG-Symbole
+
+Das Theme verwendet Inline-SVG-Symbole, die über Partials von Handlebars eingebunden werden. Du kannst alle Symbole (Icons) innerhalb von `/partials/icons` finden. Um ein Icon zu verwenden, gib einfach den Namen der entsprechenden Datei an, z. B. Um das SVG-Symbol in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` einzubinden - verwende `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+Du kannst deine eigenen SVG-Icons auf dieselbe Art und Weise hinzufügen.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1026a361
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+Diese Seite beschreibt, wie du zu den freeCodeCamp-Tutorials und -Projekten beitragen kannst, die mit der CodeRoad VS Code-Erweiterung durchgeführt werden.
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. Sie beginnen alle mit `learn-`. Zum Beispiel: `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Jedes Tutorial-Repo hat einen `main`-Branch und einen „Version“-Branch, z.B. `v1.0.0`.
+
+Die beiden wichtigsten Dateien im `main`-Branch sind `TUTORIAL.md` und `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` enthält alle Anweisungen, Hinweise, Titel und so weiter für das Tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` enthält Anweisungen für CodeRoad, z.B. welche Befehle wann ausgeführt werden sollen, welche Dateien auf Änderungen zu beobachten sind und welcher Versionsbranch für die Schritte zu verwenden ist.
+
+Der „Version“-Branch enthält die Commits, die bei jedem Schritt eines Tutorials geladen werden. Die Commit-Nachrichten für diesen Branch müssen präzise sein. Der erste Commit benötigt `INIT` für seine Nachricht und enthält alle Dateien, die vor der ersten Lektion geladen werden sollen.
+
+Nachfolgende Commit-Nachrichten müssen mit der Schrittnummer in `TUTORIAL.md` aus dem `main`-Branch übereinstimmen. Zum Beispiel wird der Commit mit der Nachricht `10.1` geladen, wenn ein Benutzer zum Schritt `10.1` geht.
+
+Um Änderungen an den Commits in einem Versionsbranch vorzunehmen, musst du die Commits, die du ändern willst, rebasen und bearbeiten. Dadurch wird die Git-Historie umgeschrieben, sodass wir keine PRs für diese Art von Branch akzeptieren können. Sobald ein Versionsbranch im freeCodeCamp-Repository vorhanden ist, sollte er sich nicht mehr ändern.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Nimm niemals Änderungen an einem Versionsbranch vor, der sich in einem der freeCodeCamp-Repos befindet. Erstelle immer einen Neuen.
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### Voraussetzungen
+
+Installiere die [CodeRoad CLI Tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) mit `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+Es gab einige Probleme mit der neuesten Version. Wenn `coderoad --version` nach der Installation nicht funktioniert, mache ein Downgrade auf `0.7.0` mit `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Arbeiten an `main`
+
+Diese Anleitung ist für PRs, die nur kleine Änderungen an `main` zu **bestehenden Lektionen** vornehmen. Dabei handelt es sich hauptsächlich um Änderungen oder Korrekturen von Tippfehlern, Grammatik, Hinweisen und Anleitungen in der Datei `TUTORIAL.md`.
+
+Für alles andere, einschließlich des Hinzufügens oder Löschens von Lektionen, befolge den [Leitfaden zum Arbeiten an einem Versionsbranch](#working-on-version-branch). Du musst dafür keinen neuen Versionsbranch erstellen - du kannst einen PR erstellen, indem du den Anweisungen unten folgst.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Diese Änderungen werden den bestehenden Versionsbranch verwenden. Wenn sie besonders wichtig sind, kannst du sie gerne in die `CHANGELOG.md` aufnehmen. In den meisten Fällen sollte eine gute Commit-Nachricht ausreichen.
+
+Du musst die Datei `tutorial.json` nie direkt ändern. Diese wird mit den CLI-Tools erstellt.
+
+Wenn du nur geringfügige Änderungen vornimmst, wie z. B. das Ausbessern eines Schreib- oder Grammatikfehlers, musst du deine Änderungen nicht testen.
+
+Befolge diese Anweisungen, um einen PR zu erstellen. Beachte dabei, dass die Anweisungen normalerweise die Lektionen um sie herum als Kontext verwenden:
+
+- Erstelle eine Kopie des neuesten Versionsbranch mit `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - du musst diesen Branch nicht auschecken, er muss nur existieren.
+- Erstelle einen neuen Branch von `main` und checke ihn aus.
+- Mache deine Änderungen und führe einen **Commit** durch. Zur Erinnerung: Du musst nichts in der Datei `tutorial.json` ändern. Wahrscheinlich musst du nur Änderungen an der `TUTORIAL.md` vornehmen
+- Führe `coderoad build` aus, um die Datei `tutorial.json` neu zu erstellen
+- Übertrage deine Änderungen mit `update json` als Nachricht
+- Erstelle einen PR
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+Wenn du deine Änderungen an `main` nach den obigen Anweisungen testen willst, befolge diese Anweisungen:
+
+- Befolge die Anweisungen auf dem [rdb-alpha Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha), um einen Container zu starten
+- Starte das Tutorial mit der `tutorial.json` Datei auf dem neuen Branch
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+Wenn du einen PR überprüfst, der nur `main` ändert und dabei wie oben beschrieben didaktische oder grammatikalische Probleme behandelt, sollten die Änderungen in `TUTORIAL.md` mit den Änderungen in `tutorial.json` übereinstimmen.
+
+Die Datei `tutorial.json` sollte keine Änderungen an Commit-Hashes oder Step/Level-Ids enthalten. Start- oder Level-Befehle oder Datei-Überwachungen sollten wahrscheinlich auch nicht geändert werden. Es gibt Ausnahmen, wenn es ein Problem mit einer Stufe gibt, aber die sollten mit mehr Vorsicht behandelt werden.
+
+Denke auch daran, dass die Anleitungen in der Regel die Lektionen um sie herum als Kontext verwenden, also achte darauf, dass sie sinnvoll sind.
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Zur Erinnerung: Nimm niemals Änderungen an einem Versionsbranch vor, der sich in einem der freeCodeCamp-Repos befindet. Erstelle immer einen Neuen.
+
+Es gibt keine einfache Möglichkeit, genau zu sehen, was sich zwischen den Versionsbranches geändert hat, da die Git-Historie neu geschrieben wird. Die Verwendung neuer Versionsbranches muss sorgfältig abgewogen und getestet werden.
+
+Diese Anweisungen gelten für alle Änderungen in einem "Versions"-Branch, wie z. B. Tests, Testtexte, Zurücksetzen von Dateien, Hinzufügen und Löschen von Schritten und vieles mehr.
+
+Befolge diese Anweisungen, um eine neue Version zu erstellen:
+
+- Checke den **letzten** Versionsbranch mit `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` aus
+- Erstelle einen neuen Branch davon, indem du die Version mit `git checkout -b vX.X.Y` erhöhst
+- Nimm deine Änderungen an dem Versionsbranch vor. Weitere Informationen zur Arbeit mit Tutorials findest du in der [CodeRoad Dokumentation](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial)
+- Schiebe den neuen Branch zu deinem Fork mit `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Schau dir den `main`-Branch an
+- Erstelle einen neuen Branch von `main`. z.B. `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Ändere die `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` zu deinem Fork des Repos. So können du und die Prüfer sie testen, bevor sie in das freeCodeCamp-Repository gestellt wird. Ändere die Version auf den neuen Branch an den beiden Stellen der Datei. Füge deine Änderungen für die neue Version in die `CHANGELOG.md` ein. Nimm alle anderen Änderungen vor, die du benötigst.
+- Bestätige (Commit) deine Änderungen mit der Nachricht `Feat: Release Version X.X.Y - <optionale Beschreibung>`
+- Starte `coderoad build`, um eine neue `tutorial.json`-Datei zu erstellen
+- Füge die Datei hinzu und übertrage sie
+- Schiebe die Änderungen in deinen Fork
+- Teste deine Änderungen gemäß der [Testanweisungen unten](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Nimm weitere Änderungen vor und übertrage sie, wie du es soeben getan hast, oder befolge den Rest der Anweisungen, wenn du zufrieden bist
+- Erstelle einen PR für `main` mit deinem neuen `feat/version-X.X.Y`-Branch. Gib ihm einen Titel wie `Version X.X.Y ready for review`. Dies wird nicht zusammengeführt (merged), sondern dient nur dazu, die Prüfer wissen zu lassen, dass eine neue Version bereitsteht
+- Danach werden deine Änderungen überprüft
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- Befolge die Anweisungen auf dem [rdb-alpha Repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha), um einen Container zu starten
+- Starte das Tutorial mit der Datei `tutorial.json` in dem Fork, in dem sich die Änderungen befinden. Achte darauf, dass du die Datei im `feat: Version-X.X.Y`-Branch verwendest und nicht im `main`-Branch
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+Bevor du eine neue Version veröffentlichst, schau dir den neuen `feat/version-vX.X.Y`-Branch (wird mit `main` zusammengeführt) auf dem Fork des Benutzers an. Vergewissere dich, dass die Datei `CHANGELOG.md` um die neuen Änderungen ergänzt wurde und dass die Version an den beiden Stellen der `coderoad.yaml` mit dem neuen Versionsbranch übereinstimmt.
+
+Wenn du Schreibzugriff auf das freeCodeCamp-Repository hast, die Dateien `CHANGELOG` und `coderoad.yaml` überprüft hast, die Änderungen anhand der obigen Anweisungen getestet hast und eine neue Version eines Tutorials pushen möchtest:
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Zur Erinnerung: Nimm niemals Änderungen an einem Versionsbranch vor, der sich in einem der freeCodeCamp-Repos befindet. Erstelle immer einen Neuen.
+
+- Wenn du keinen Remote-Zugang zu dem Ort hast, an dem die neuen Änderungen existieren, erstelle einen Remote-Zugang zum Fork des Benutzers mit `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Lösche alle **lokalen** Branches, die den gleichen Namen haben wie die neuen Branches. Wahrscheinlich heißen sie entweder `vX.X.Y` oder `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Checke den neuen Versionsbranch mit `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y` aus
+- Schiebe den neuen Versionszweig mit `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y` in das freeCodeCamp Repo. Du musst den neuen Branch pushen, bevor du `main` mit der neuen `tutorial.json`-Datei aktualisierst
+- Checke den Benutzerbranch aus, der mit `main` zusammengeführt werden soll, mit `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Ändere die `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` zurück auf das freeCodeCamp Repo
+- Füge die Änderungen hinzu und übertrage sie
+- Starte `coderoad build`, um die neue `tutorial.json`-Datei zu erstellen
+- Füge die Datei hinzu und übertrage sie
+- Schiebe die Änderungen in deinen Fork mit `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Erstelle einen PR zu `main` auf dem freeCodeCamp Repo
+- Wenn du zufrieden bist, füge es zusammen oder lass es und bitte um eine Überprüfung von jemandem
+- Nachdem der PR zusammengeführt wurde, öffne das Tutorial, indem du den Anweisungen im [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) folgst, um sicherzustellen, dass es richtig geladen wird und du einige Schritte durchlaufen kannst
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Mach alle Commits in diesem Branch rückgängig, bis einschließlich des Commits der Version, die auf die Version folgt, zu der du zurückkehren willst. Du könntest zum Beispiel Commits haben, die wie folgt aussehen:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+Wenn du zu v1.0.0 zurückkehren willst, nimm alle Commits ab `Release: Version 1.0.1` und danach zurück
+
+- Erstelle einen PR. Gib ihm einen Titel wie `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/intro.md b/src/content/docs/de/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d1a4f949
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+Die [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org)-Community ist dank tausender freundlicher Freiwilliger wie dir möglich. Wenn Du deine Zeit und dein Fachwissen einbringen möchtest, würden wir uns freuen, dich an Bord begrüßen zu dürfen.
+
+> [!NOTE] Bevor du fortfährst, nimm dir bitte kurz 2 Minuten Zeit, um unseren [Verhaltenskodex (Code of Conduct)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct) zu lesen. Wir setzen Ihn in unserer Community strikt durch, damit das Mitwirken bei freeCodeCamp.org für alle eine sichere, inklusive Erfahrung ist.
+
+Du bist herzlich eingeladen, Inhalte für unseren [Studienplan](#curriculum) zu erstellen, zu aktualisieren und Fehler zu beheben. Du kannst uns helfen, Fehler in der [Lernplattform](#learning-platform) von freeCodeCamp.org zu beheben, oder uns helfen, freeCodeCamp.org in verschiedene Weltsprachen zu[ übersetzen](#translations).
+
+Wir beantworten die häufigsten Fragen zum Thema Mithilfe [ in unseren FAQ für Mitwirkende](FAQ).
+
+Fröhliches Mitmachen.
+
+---
+
+## Studienplan
+
+Unser Studienplan wird von der weltweiten freeCodeCamp-Community zusammengestellt. Auf diese Weise können wir das Fachwissen von Freiwilligen wie dir einfließen lassen.
+
+Du kannst helfen, den Studienplan zu erweitern und zu verbessern. Du kannst auch die User Stories der Projekte aktualisieren, um die Konzepte besser zu erklären. Und du kannst unsere automatisierten Tests verbessern, damit wir den Code der Teilnehmer/innen noch genauer testen können.
+
+**Wenn du daran interessiert bist, unseren Studienplan zu verbessern, erfährst du hier [wie du zum Studienplan beitragen kannst](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges).**
+
+## Übersetzungen
+
+Wir lokalisieren freeCodeCamp.org in die wichtigsten Sprachen der Welt.
+
+Die Zertifizierungen sind bereits in einigen wichtigen Weltsprachen, wie unten zu sehen, verfügbar:
+
+- [Chinesisch (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Spanisch (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italienisch (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Portugiesisch (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ukrainisch (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japanisch (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [German (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+Wir möchten dich dazu ermutigen, die [Ankündigung hier](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) zu lesen und sie an deine Freunde weiterzuleiten, um sie für dieses Thema zu begeistern.
+
+**Wenn du daran interessiert bist, zu übersetzen, findest du hier [eine Anleitung zum Übersetzen der freeCodeCamp-Ressourcen](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## Lernplattform
+
+Unsere Lernplattform läuft auf einem modernen JavaScript-Stack. Es umfasst verschiedene Komponenten, Werkzeuge und Bibliotheken. Dazu gehören Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack und mehr.
+
+Im Großen und Ganzen haben wir einen Node.js-basierten API-Server, eine Reihe von React-basierten Client-Anwendungen, Testskripte, um die von Teilnehmer:innen eingereichten Studienplanprojekten zu bewerten, und einiges mehr. Wenn du einen produktiven Beitrag zur Lernplattform leisten willst, empfehlen wir dir, dich mit diesen Werkzeugen etwas vertraut zu machen.
+
+**If you want to help us improve our codebase here's [how to set up freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/de/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..37ee0386
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: Das offizielle freeCodeCamp-Language Lead-Handbuch
+---
+
+Dieses Handbuch hilft dir dabei, die Tools für deine Lokalisierungsvorhaben einzurichten und zu nutzen.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+Die meisten Ihrer Einladungen werden für die Stufe "Contributor " sein. Auf dieser Ebene kann der Benutzer Entwürfe erstellen. Wähle diese Rolle, wenn du einen neuen Übersetzer einlädst.
+
+Die Stufe "Author" ermöglicht es dem Benutzer, Entwürfe zu erstellen und diese zu veröffentlichen.
+
+Auf der Ebene "Editor" hat der Benutzer Zugriff auf alle Entwürfe und kann sie veröffentlichen. Wähle diese Rolle, wenn du einen neuen Korrekturleser (proofreader) einlädst.
+
+Die Stufe "Administrator" ist für freeCodeCamp-Mitarbeiter und Language Leads reserviert.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+Wir verwenden einen [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack)-basierten Ansatz zur Erstellung und Bereitstellung der Artikel. Diese Strategie sorgt für eine schnelle statische Website, die von einem CDN zwischengespeichert und bereitgestellt wird.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) fungiert als unsere Content-Management-Plattform, und [11ty](https://11ty.dev) erstellt aus den Artikeln statische Inhalte - einfaches HTML, JavaScript und CSS. Nur diese statischen Inhalte werden auf unseren Servern bereitgestellt.
+
+Dieser Prozess ist automatisiert und läuft regelmäßig ab. Wenn du jetzt etwas veröffentlichst, wird es in ein paar Stunden auf der Nachrichtenseite verfügbar sein.
+
+Die aktuellen Zeitpläne und den Status kannst du hier einsehen: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+`Link` ist der Link zum Originalartikel.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+:::tip
+Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+:::
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Achte darauf, dass der Titel und der Link richtig zugeordnet sind.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Jeder Titel muss in einer einzigen Zeile bleiben und darf nicht in eine neue Zeile übergehen.
+
+Du solltest [den übersetzten Client lokal einrichten](how-to-enable-new-languages), um zu sehen, ob die Titel die richtige Länge haben. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articles that can be translated:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+The following articles should **not** be translated:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+The following links are pointing to external sites and cannot be translated:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Once you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, you can update the links in the footer for `/news` by editing the file at `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) repository.
+
+> [!NOTE] Pull requests to this repository are currently limited to staff only. If you want to update this file, ask someone on the staff team for help.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+When you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, as well as when the curriculum in your language is ready for launch, you can update the links in the footer for `/learn` by editing the file at `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) repository.
+
+> [!WARNING] Only "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", and "Code of Conduct" can be translated. Leave other URLs unchanged.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+Du findest diese Boxen überall in der Dokumentation:
+
+> [!NOTE] Ich bin eine Notizbox
+
+:::tip
+Ich bin eine Tippbox
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] Ich bin eine Warnbox
+
+:::danger
+Ich bin eine Aufmerksamkeitsbox
+:::
+
+Standardmäßig erscheinen die Kopfzeilen auch in den übersetzten Dokumenten auf Englisch.
+
+Du kannst die Kopfzeilen in den Dokumenten in deine Sprache übersetzen lassen, indem du die Datei `docs/index.html` auf diese Weise änderst:
+
+Innerhalb des `script` Elements gibt es ein Objekt, die `flexibleAlerts` Eigenschaft, die diese Form hat:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Innerhalb des Objekts der Label-Eigenschaft, vor der `'/'`-Eigenschaft, fügst du eine neue Eigenschaft für deine Sprache hinzu, wie `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+Das Hinzufügen der Übersetzungen für Portugiesisch würde zum Beispiel so aussehen:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+Die motivierenden Zitate befinden sich im [Curriculum-Repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) in der Datei `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json`.
+
+Diese Datei hat folgende allgemeine Struktur:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+Die Komplimente sind die kurzen Sätze, die am Ende einer Aufgabe erscheinen.
+
+Du musst die Sätze nicht direkt aus dem Englischen übersetzen, sondern kannst eine Reihe von kurzen Sätzen schreiben, die sich eignen, um sie am Ende einer Aufgabe zu zeigen.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Du solltest mit mindestens einem Dutzend Komplimenten beginnen, um eine gewisse Abwechslung zu schaffen, wenn die Benutzer die Aufgaben abschließen.
+:::
+
+Die Motivationszitate sind die Zitate, die auf https://freecodecamp.org/learn erscheinen.
+
+Das `motivationalQuotes`-Array ist ein Array aus Objekten. Diese Objekte sollten eine `quote`-Eigenschaft und eine `author`-Eigenschaft enthalten. Wie hier:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Du solltest mit mindestens einem Dutzend Zitaten beginnen, um eine gewisse Vielfalt zu haben. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+:::
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+In der Datei `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json` wird eine Datei mit allgemeinen Links geführt, die auf unserer [Lehrplan-Website](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) verwendet wird.
+
+Einige dieser Links werden sich nicht ändern - aber du solltest die `/news`-Artikel-Links aktualisieren, damit sie auf die übersetzte Version des Artikels in deiner Sprache verweisen, wenn er veröffentlicht wird.
+
+Du solltest auch die `help`-Kategorien aktualisieren, um auf das Unterforum deiner Sprache zu verweisen (normalerweise `language/category`, wie `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). Dies ermöglicht es freeCodeCamp-Benutzern, 'Hilfeanfragen' im richtigen Forum zu erstellen.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+Die Metadaten der Website befinden sich in der Datei `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json`. Diese Datei hat 5 Schlüssel:`title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords`, und `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+Der Wert `youre-unsubscribed` sollte direkt übersetzt werden. Die anderen Werte müssen so genau wie möglich übersetzt werden, wobei auch die in deiner Sprache üblichen Suchbegriffe und Phrasen berücksichtigt werden müssen.
+
+Wenn du dabei Hilfe benötigst, wende dich an uns im ["Contributor" Chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Vorübersetzungs-Workflow auf Crowdin
+
+Der Vorübersetzungs-Workflow kann verwendet werden, um Übersetzungen aus dem Translation Memory auf Strings anzuwenden.
+
+:::tip
+Diese Funktion ist sehr nützlich, um viele Übersetzungen aus dem Translation Memory in großen Mengen wiederherzustellen, wenn viele Dateien aktualisiert worden sind.
+:::
+
+Du findest den Vorübersetzungs-Workflow oben auf der Seite in der Konsole eines Projekts. Wenn du in der oberen rechten Ecke "Go to console" siehst, klicke zuerst darauf.
+
+
+
+
+
+Du kannst "From Machine Translation" oder "From Translation Memory" wählen. Wähle "Translation Memory", um Übersetzungen aus dem Speicher wiederherzustellen.
+
+Dann sind drei Schritte zu absolvieren:
+
+1. Dateien. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Sprachen. Stelle hier deine Sprache ein.
+3. Vorhandene Übersetzungen. Die beste Kombination ist hier "100% match" und "Apply to untranslated strings only". Genehmige nicht automatisch, denn es ist immer besser, ein menschliches Auge auf die Dinge zu werfen.
+
+
+
+Wenn du diese Einstellung abgeschlossen hast, drücke den Button Pre-Translate und warte. Sobald der Vorgang abgeschlossen ist, wirst du benachrichtigt. Wie lange das dauert, hängt davon ab, wie viele unübersetzte Strings in den ausgewählten Dateien enthalten sind.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+:::tip
+An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+:::
+
+Das Crowdin-Glossar wird im [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries)-Repository aufbewahrt.
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+Die `client.csv`-Datei ist für das Projekt "Learn User Interface", die `curriculum.csv`-Datei ist für das Projekt "Coding Curriculum", die `docs.csv`-Datei ist für das Projekt "Contributing Documentation".
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+In der `.csv`-Datei siehst du, dass die englische Sprache die ersten drei Spalten belegt, `Term:English` ist die Spalte für den englischen Begriff, `Description:English` ist die Spalte für die englische Beschreibung, und `Part:English` steht für die Wortart (z. B. Substantiv, Verb usw.) des Begriffs.
+
+Dann hat jede Zielsprache zwei Spalten. Wenn du ins Dothrakische übersetzt, wirst du an den Spalten `Term:Dothraki` und `Description:Dothraki` interessiert sein. Die Spalte `Term:Dothraki` ist für die Übersetzung des Begriffs in Dothraki, und die Spalte `Description:Dothraki` ist für die Beschreibung des Begriffs in Dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+:::
+
+Nachdem du die Änderungen vorgenommen und die Datei gespeichert hast, musst du einen PR mit den vorgeschlagenen Änderungen erstellen. Nachdem der PR angenommen wurde, musst du den GitHub Action-Workflow ausführen, um das Crowdin-Glossar zu aktualisieren. Deine Änderungen im Glossar werden sich nicht sofort auswirken, aber sie werden kommen.
+
+## Wie man einen Mitwirkenden zum Korrekturleser (Proofreader) befördert
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+Dadurch wird die Benutzerverwaltung geöffnet, in der du die Liste aller Benutzer sehen kannst.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Verwende das Menü mit den drei Punkten in der Benutzerzeile, um ein Menü zu öffnen und wähle "Add to team". Die Korrekturleserteams haben den Standardnamen `Proof Readers(<Sprache>)`, du kannst das Team über den Namen der Sprache suchen. Wenn du das Team ausgewählt hast, benutze den Button "ADD" unten auf der Seite, um den Vorgang abzuschließen.
+
+Der Benutzer ist jetzt ein Korrekturleser.
+
+:::tip
+Der neu beförderte Korrekturleser könnte vom Lesen der [Korrekturlesen von Übersetzungen](how-to-proofread-files)-Dokumentation profitieren.
+:::
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/de/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5058d67a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: Das offizielle freeCodeCamp Moderator Handbuch
+---
+
+Dieses Handbuch hilft dir, verschiedene Orte in unserer Community zu moderieren. This covers conversations and interactions in issues and pull request threads on GitHub, the community forum, the chat rooms, and other official communities that we foster.
+
+:::note
+Alle freeCodeCamp-Moderatoren sind Community-weite Moderatoren. That means we trust you to oversee any of these places.
+:::
+
+Du kannst auf jeder der Plattformen, die dich am meisten interessieren, als Moderator/in tätig sein. Einige Moderatoren helfen nur auf GitHub, während andere nur im Forum helfen. Einige Moderatoren sind überall aktiv.
+
+Unterm Strich wollen wir, dass es dir Spaß macht, Moderator/in zu sein, und dass du deine knappe Zeit in Dinge investierst, die dich interessieren.
+
+> "Mit großer Macht kommt große Verantwortung" - Uncle Ben
+
+Als Moderator/in ist das Temperament wichtiger als die technischen Fähigkeiten.
+
+Hör zu. Be helpful. Missbrauche deine Macht nicht.
+
+Das freeCodeCamp ist eine inklusive Community, und das soll auch so bleiben.
+
+We have a single [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) that governs our entire community. Je weniger Regeln, desto einfacher ist es, sich sie zu merken. Du kannst die Regeln [hier](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) lesen und sie dir einprägen.
+
+:::note
+As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+:::
+
+## GitHub moderieren
+
+Auf GitHub haben Moderatoren zwei Hauptaufgaben:
+
+1. Triaging and responding to issues.
+2. Reviewing and merging pull requests (aka QA).
+
+### GitHub Issues moderieren
+
+We use our main [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) repository as a common issue tracker for all of our repositories. We get new issues every day, all of which need to be triaged, labeled, and addressed. Das ist auch ein guter Ort, um mit Beiträgen zur Open-Source-Codebasis anzufangen.
+
+#### Triage von Issues
+
+[Triaging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) ist ein Prozess, bei dem die Aufmerksamkeit für jeden neuen Issue Report priorisiert wird. Wir haben eine umfangreiche Liste von Labels, die wir verwenden, um die Priorität, Kategorie, Status und Umfang jedes Problems zu kennzeichnen.
+
+Du kannst uns helfen, die Issues zu ordnen und einzuteilen, indem du Labels aus [dieser Liste](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels) anwendest. Normalerweise ist neben dem Label eine Beschreibung verfügbar, in der die Bedeutung erläutert wird.
+
+Bitte achte besonders auf die Label `"help wanted"` und `"first timers only"`. Diese sollen zu Threads hinzugefügt werden, von denen du denkst, dass sie für potenzielle Mitwirkende geöffnet werden können, um einen Pull-Request zu erstellen.
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### Schließen veralteter, inaktiver Issues und Pull-Requests
+
+- Veraltete Issues oder PRs sind solche, die seit 21 Tagen (3 Wochen nach der letzten Aktivität) keine Aktivität vom Autor erfahren haben, aber erst nachdem ein Moderator weitere Informationen/Änderungen angefordert hat.
+
+- Activity is defined as: Comments requesting an update on the PR and triages like `status: update needed` label, etc.
+
+- Wenn der Beitragende um zusätzliche Hilfe oder sogar Zeit bittet, kann das oben Gesagte gelockert und nach einer Antwort erneut überprüft werden. In jedem Fall sollten die Moderatoren nach bestem Wissen und Gewissen den Status der ausstehenden PR klären.
+
+:::tip
+We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+:::
+
+### Pull-Requests moderieren
+
+Pull Requests (PRs) sind die Art und Weise, wie Mitwirkende Änderungen an das freeCodeCamp-Repository übermitteln. Wir müssen eine Qualitätssicherung (QA) für Pull-Requests durchführen, bevor wir entscheiden, ob wir sie zusammenführen, Änderungen beantragen oder schließen.
+
+#### Arten von Pull Requests
+
+1. **Challenge instruction edits**
+
+ These are changes to the text of challenges - the description, instructions, or test text.
+
+ Du kannst sie auch direkt auf GitHub überprüfen und entscheiden, ob du sie zusammenführen möchtest. Wir müssen hier etwas vorsichtiger sein, denn Millionen von Menschen werden diesem Text begegnen, wenn sie den freeCodeCamp-Studienplan durcharbeiten. Macht der Pull-Request den Text klarer, ohne ihn viel länger zu machen? Sind die Änderungen relevant und nicht übermäßig pedantisch? Denke daran, dass unser Ziel ist, dass die Aufgaben so deutlich und so kurz wie möglich sind. Sie sind nicht der Ort für unklare Details. Die Mitwirkenden könnten versuchen, Links zu Ressourcen zu den Aufgaben hinzuzufügen.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me) comment. Sobald ein Pull Request mindestens zwei Genehmigungen (einschließlich deiner) von den Moderatoren oder dem Entwicklungsteam erhält, kannst du ihn zusammenführen.
+
+2. **Challenge code edits**
+
+ These are changes to the code in a challenge - the challenge seed, challenge solution, and test strings.
+
+ These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution and to make sure the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
+
+ Einige Mitwirkende werden versuchen, zusätzliche Tests hinzuzufügen, um spitzfindige Sonderfälle abzudecken. Wir müssen aufpassen, dass wir die Aufgabe nicht zu kompliziert machen. Diese Aufgaben und ihre Tests sollten so einfach und intuitiv wie möglich sein. Abgesehen von den Algorithmusaufgaben und dem Abschnitt zur Interviewvorbereitung sollten die Teilnehmer/innen in der Lage sein, jede Aufgabe innerhalb von etwa 2 Minuten zu lösen.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. Sobald ein Pull-Request mindestens zwei Genehmigungen (einschließlich deiner) von den Moderatoren oder dem Entwicklungsteam erhält, kannst du ihn zusammenführen.
+
+3. **Platform changes**
+
+ Diese Code-Bearbeitungen ändern die Funktionalität der freeCodeCamp-Plattform selbst.
+
+ Manchmal versuchen Mitwirkende, Änderungen ohne große Erklärungen vorzunehmen, aber bei Codeänderungen müssen wir sicherstellen, dass es einen echten Bedarf für die Änderung gibt. Diese Pull-Requests sollten auf ein bestehendes GitHub Issue verweisen, in dem die Gründe für die Änderung erläutert werden. Dann kannst du die Pull-Request auf deinem Computer öffnen und sie lokal testen.
+
+ Wenn du das getan hast und die Änderungen gut aussehen, solltest du sie noch nicht zusammenführen. Du kannst den Pull-Request mit "LGTM" kommentieren und dann **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** erwähnen, damit sie einen letzten Blick darauf werfen können.
+
+4. **Automatisierte PRs (Dependabot)**
+
+ Einige PRs sind automatische Aktualisierungen von Abhängigkeiten, die über eine Integration vorgenommen werden. Du solltest diese PRs nicht zusammenführen oder genehmigen. Ein Mitglied des Entwicklerteams kümmert sich um die Überprüfung und Zusammenführung solcher automatischen PRs.
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+Wenn du einen Pull-Request zum Überprüfen auswählst, solltest du dich diesem zunächst selbst zuweisen. Du kannst dies tun, indem du in der rechten Spalte der GitHub-Benutzeroberfläche auf den Link "assign yourself" unter dem Bereich "assignees" klickst.
+
+Je nachdem, um welche Art von Pull-Request es sich handelt, befolge die entsprechenden Regeln, die zuvor aufgelistet wurden.
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+Vergewissere dich vor dem Zusammenführen eines Pull Requests, dass GitHub alle Prüfungen für die Pull-Requests als bestanden meldet (grüne Häkchen). Wenn du feststellst, dass eine der Prüfungen fehlschlägt, untersuche bitte die Ursache und kläre sie. Führt die Änderung dazu, dass unsere Tests nicht mehr funktionieren? Wird die Seite korrekt aufgebaut, wenn der PR zusammengeführt wird? Diese Kontrollen sind entscheidend für die Stabilität der Plattform.
+
+:::caution
+Das Zusammenführen eines PRs, der die CI/CD-Prüfungen nicht besteht, kann für alle Beteiligten, einschließlich des Entwicklungsteams und der Mitwirkenden, zu Schwierigkeiten führen.
+:::
+
+##### Handling Merge Conflicts:
+
+Sometimes there will be a merge conflict.
+
+Das bedeutet, dass ein anderer Pull-Request eine Änderung an demselben Teil der Datei vorgenommen hat. GitHub hat ein Tool, mit dem du diese Merge-Konflikte direkt auf GitHub lösen kannst. Du kannst versuchen, diese Konflikte zu lösen. Use your best judgment.
+
+Die Änderungen des Pull-Requests stehen oben und die des main-Branch unten. Manchmal gibt es dort überflüssige Informationen, die gelöscht werden können. Bevor du fertig bist, stelle sicher, dass du die `<<<<<`, `======` und `>>>>>>` löschst, die Git hinzufügt, um Merge-Konflikte anzuzeigen.
+
+Wenn du dir unsicher bist, frag bitte einen der anderen Moderatoren oder das Entwicklerteam um Hilfe.
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+Wenn der Pull-Request so aussieht, dass er zusammengeführt werden kann (und keine weiteren Genehmigungen benötigt - denk daran, dass wir mindestens zwei benötigen), kannst du ihn zusammenführen. Achte darauf, dass du die Standardoption **"Squash and Merge"** verwendest. Dadurch werden alle Pull-Request-Commits zu einem einzigen Commit zusammengefasst, wodurch die Git-Historie viel einfacher zu lesen ist.
+
+> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way!
+
+Wenn der Autor des Pull-Requests zum ersten Mal beiträgt, solltest du ihm auch zu seinem ersten zusammengefassten Pull-Request für das Repository gratulieren. Du kannst in der oberen rechten Ecke des PR-Body nachsehen, ob es sich um einen "first-time" Mitwirkenden handelt. Es wird `First-time contributor` angezeigt, wie unten dargestellt:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ First-time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="Abzeichen für den erstmaligen Beitrag zu einem Pull-Requests" />
+</details>
+
+Wenn der Pull-Request nicht bereit zum Zusammenführen zu sein scheint, kannst du dem Autor höflich antworten und ihm sagen, was er tun sollte, um ihn fertigzustellen. Wir hoffen, dass sie antworten und ihr Pull-Request bald fertig ist.
+
+Wenn du eine zweite Meinung zu einem Pull-Request benötigst, hinterlasse deine Kommentare zu dem Pull-Request und füge dann das Label "discussing" zu dem Pull-Request hinzu.
+
+##### Closing an Invalid Pull Request:
+
+Oft ist ein Pull-Request mit wenig Aufwand verbunden. You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "Made changes" or "Update index.md".
+
+Es gibt auch Situationen, in denen der/die Mitwirkende versucht, einen Link zu seiner/ihrer Website hinzuzufügen, eine von ihm/ihr erstellte Bibliothek einzubinden oder eine unseriöse Bearbeitung vorzunehmen, die niemandem außer ihm/ihr selbst hilft.
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## Das Forum moderieren
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Deleting Forum Posts
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. Jemand hat ein pornografisches oder grafisch gewalttätiges Bild gepostet.
+2. Jemand hat einen Link oder Code gepostet, der bösartig ist und anderen Teilnehmern, die darauf klicken, schaden könnte.
+3. Someone has flooded a thread with a lot of spam messages.
+4. An account has been created, beyond a reasonable doubt, to spam.
+
+### Dealing with Spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Dealing with Off-Topic Conversations
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Dealing with Posted Solutions
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Underage Users
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per our Terms of Service.
+
+It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
+
+Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
+
+Thank you for understanding.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- When trying to include a "Canned reply" in a response, if the menu doesn't open (after clicking on the gear), click on the text area first then try it again.
+- The moderator's 'wrench' is at the bottom of the view-port but if you click it and cannot see the "Select Posts" button because it has scrolled out of view, you may need to try to scroll to it, though sometimes that doesn't work in which case moving to a desktop/laptop monitor may be needed.
+- Sometimes clicking on the three-dot menu below a post can hide the reply icon. Reload the page to get it back.
+
+## Facebook moderieren
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderating Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot serves as our moderation bot, and all of the commands use Discord's native slash command interface. You can see a list of all of the commands by typing `/` in any channel.
+
+1. **Make sure the user intended to violate the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Not all violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. In diesen Fällen kannst du sie einfach bitten, ihren Code mit Diensten wie CodePen oder Pastebin einzufügen.
+
+2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), the moderator will proceed as follows:**
+
+ For minor offences, a warning may be issued with the `/warn` command. For more egregious offences, you can remove the member from the server temporarily with the `/kick` command, or permanently with the `/ban` command. In some cases, a member may just need some time to cool off and collect their thoughts - the `/mute` command allows you to prevent them from engaging with our community for a set period of time. A muted member can see the conversation, but cannot post messages or add reactions.
+
+ All moderation commands will take a `reason` parameter, which should be a short explanation of why the action was taken. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. As such, we should avoid using Discord's built-in moderation tools, as they will not be logged.
+
+ > [!WARNING] The reason provided to a moderation command will also be included in the DM notification to the camper. Please remember to be professional here.
+
+3. **Creating a private discussion**
+
+ Es kann Situationen geben, in denen du ein Anliegen mit einem Teilnehmer unter vier Augen besprechen musst. Dies sollte nicht über DMs geschehen, da dies zu Situationen führen kann, in denen du eine Sache behauptest und der Teilnehmer eine andere. Nutze stattdessen die Funktionen des Bots, um eine private Diskussion zu führen:
+
+ - Call the `/private` command, where `target` is the camper you want to open a private channel with.
+ - The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
+ - When the conversation is complete, click the `❌ Close` button _on the first message in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
+
+4. **Deleting messages**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. If a message is not in line with our Code of Conduct, or otherwise not appropriate for our community, you are generally safe to delete it.
+
+ Note that if the message contains content that violates Discord's terms of service, you'll want to report it via https://dis.gd/report **prior to** deleting it.
+
+5. **Don’t threaten to take action**
+
+ If a camper breaks the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `/private` command, or use the bot's moderation commands.
+
+ If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant moderation action or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of their actions without making it come across as a warning.
+
+ For example:
+
+ - Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
+
+ - Or if you really have to explain why:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - For mild and unintentional violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Don’t brag about being a moderator**
+
+ Do not see yourself as above the community. **You are the community.** And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
+
+ If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
+
+7. **Don’t contradict other moderators**
+
+ If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their PoV (Point of View).
+
+ _Remember: We’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front._
+
+8. **Talk with other moderators**
+
+ We have a `#mod-chat` room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporarily inactive**
+
+ If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
+
+## How to Become a Moderator
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+> [!NOTE] For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
+>
+> This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- The user is guaranteed some privacy.
+- Public chat is no longer disrupted.
+- Other team members can pitch in, should you feel uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/de/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..42f86d8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Der offizielle freeCodeCamp Moderator Onboarding Leitfaden
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+:::note
+Wenn du [Das Moderatorenhandbuch](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook) noch nicht gelesen hast, solltest du dort zuerst anfangen.
+:::
+
+## Das Forum
+
+### Erste Schritte
+
+Das erste, was dir auffallen wird, nachdem du den Moderatorenstatus im Forum erhalten hast, ist, dass deine Benutzeroberfläche etwas anders aussehen wird, mit neuen Admin-Tools und Zugang zum Mod-Team-Subforum.
+
+Einige der neuen Werkzeuge werden in einem neuen Menüpunkt erscheinen, der wie ein Schraubenschlüssel aussieht. Einige werden als neue Registerkarten oder Schaltflächen erscheinen oder sogar als neue aktivierte Optionen in den Forenmenüs.
+
+Um dich mit den neuen Werkzeugen und Rechten vertraut zu machen, kannst du in deiner ersten Woche in dieser herausgehobenen Rolle eine oder mehrere der folgenden Methoden kombinieren:
+
+:::tip
+Die ersten beiden sind die wichtigsten.
+:::
+
+### Mach dich mit den Discourse Admin Tools vertraut
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. Um dich mit Discourse und der Moderatorenrolle vertraut zu machen, lies zunächst den [Leitfaden für neue Benutzer](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) und den [Leitfaden für neue Moderatoren](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116) von Discourse.
+
+### Folge einem Moderator aufmerksam
+
+Alle Aktionen der Moderatoren können in den [Aktionsprotokollen](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs) nachverfolgt werden. The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. Beiträge, die überprüft werden sollen, werden im Bereich [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) des Forums angezeigt.
+
+In der ersten Woche solltest du darauf achten, was markiert und was überprüft wird, und dies mit den Maßnahmen vergleichen, die aufgrund der markierten Beiträge ergriffen werden. Es kann vorkommen, dass das Systemkonto einen Beitrag markiert, weil der Benutzer ihn zu schnell erstellt hat. In vielen Fällen heben die Moderatoren die Markierung des Beitrags auf, indem sie auf die Schaltfläche "Approve Post" klicken oder ihn als "Not Spam" markieren (je nach Art der Markierung).
+
+In der Regel können Spam-Markierungen auch von Mitgliedern oder Moderatoren gesetzt werden. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+Vielleicht bemerkst du, dass die Moderatoren ein Verfahren namens "Split Topic" anwenden. Dies kann der Fall sein, wenn ein Moderator einen Beitrag, der fälschlicherweise in einem bestehenden Thema verfasst wurde, in ein neues Thema getrennt hat, oder wenn ein Moderator doppelte Themen zusammengeführt hat, die ein einzelner Benutzer für dieselbe Frage erstellt hat. Wenn du dir diesen Vorgang ansiehst, werden verschiedene Aktionen und ihre Ursachen deutlich.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. Dazu gehören:
+
+- Begrüßung eines neuen Forumsmitglieds, das Code ohne eine Frage gepostet hat -> " Welcome - remind question"
+- Erinnerung an Mitglieder, keine Code-Lösungen zu posten, sondern stattdessen Hinweise und Tipps zu geben -> " Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Reagiere auf eine Situation, in der der Code von jemandem bei dir funktioniert, bei ihm aber nicht -> " Browser Issues"
+- Ermutigung der Mitglieder, GitHub-Issues zu erstellen, wenn ein möglicher Fehler gefunden wird -> "Bug Report"
+
+Es gibt noch mehr, die du dir durchlesen kannst, um dich mit ihren jeweiligen Einsatzmöglichkeiten vertraut zu machen. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Lies die Beiträge des Mod-Teams im Subforum
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Wo du um Hilfe bitten kannst
+
+Wenn du Hilfe brauchst, um mit einer Situation umzugehen, die dir unangenehm ist oder bei der du unsicher bist, diskutiere mit deinen Moderationskollegen entweder im [Mod-Team Subforum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) oder im [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) auf Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/de/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/de/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..15004934
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Verantwortliche Offenlegung - Hall of Fame
+---
+
+Wir freuen uns über jede verantwortungsvolle Offenlegung von Schwachstellen, die die Integrität unserer Plattformen und Nutzer/innen beeinträchtigen könnten. Wenn du daran interessiert bist, zur Sicherheit unserer Plattform beizutragen, lies bitte unsere [Sicherheitsrichtlinien](security).
+
+Auch wenn wir im Moment keine Belohnungen oder Swags anbieten, sind wir diesen großartigen Menschen dankbar, dass sie uns helfen, die Plattform für alle sicher zu halten:
+
+- Mehul Mohan from [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Behebung von Sicherheitslücken](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) arbeitet mit IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/security.md b/src/content/docs/de/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f1234477
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp.org's Security Policy
+---
+
+Dieses Dokument beschreibt unsere Sicherheitsrichtlinien für die Codebases und Plattformen, die wir betreiben, und wie du Schwachstellen melden kannst.
+
+## Eine Schwachstelle melden
+
+> [!NOTE] If you think you have found a vulnerability, **please report it responsibly**. Do not create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, follow this guide.
+
+### Guidelines
+
+We appreciate responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. In the interest of saving everyone time, we encourage you to report vulnerabilities with these in mind:
+
+1. Ensure that you are using the **latest**, **stable**, and **updated** versions of the Operating System and Web Browser(s) available to you on your machine.
+2. We consider using tools & online utilities to report issues with SPF & DKIM configs, SSL Server tests, etc., in the category of ["beg bounties"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) and are unable to respond to these reports.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Reporting
+
+After confirming the above guidelines, please feel free to send an email to `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. You can also send us a PGP encrypted message at `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Once you report a vulnerability, we will look into it and ensure that it is not a false positive. If we need to clarify any details, we will get back to you. You can submit separate reports for each issue you find. Please note that we will not be able to respond to any issues that we think are outside the guidelines.
+
+## Platforms and Codebases
+
+Here is a list of the platforms and codebases we are accepting reports for:
+
+### Learn Platform
+
+| Version | Branch | wird unterstützt | aktive Website |
+| ----------- | -------------- | ---------------- | ------------------------ |
+| production | `prod-current` | Ja | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| staging | `prod-staging` | Ja | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| development | `main` | Nein | |
+
+### Publication Platform
+
+| Version | wird unterstützt | aktive Website |
+| ---------- | ---------------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| production | Ja | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localized | Ja | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Mobile App
+
+| Version | wird unterstützt | aktive Website |
+| ---------- | ---------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| production | Ja | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Other Platforms
+
+Apart from the above, we are also accepting reports for repositories hosted on GitHub under the freeCodeCamp organization.
+
+### Other Self-hosted Applications
+
+We self-host some of our platforms using open-source software like Ghost & Discourse. If you are reporting a vulnerability, please ensure that it is not a bug in the upstream software.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/de/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3d8984d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS or are still facing issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+:::warning
+Please avoid creating GitHub issues for problems with the prerequisite technologies. They are out of the scope of this project.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. If one of them isn't cached, run the following:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+OR
+
+Use the shortcut
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Use `git clean` in interactive mode:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to clean git untracked files (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="How to clean git untracked files" />
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+While in development, your session is stored as cookies. Clearing them will sign you out of your development account.
+
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, too. It will overwrite the development user in your local database.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+When you try to navigate to http://localhost:8000/developmentuser to view the profile page, Gatsby takes over serving the client-side pages and hence you will get a 404 page for the user profile when working.
+
+There is a "Preview Custom 404 Page" button, click it to see the profile.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+The first time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are using Apple Devices with M1 Chip to run the application locally, it is suggested to use Node v14.7 or above. You might run into issues with dependencies like Sharp otherwise.
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions in the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/de/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/de/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dfe350fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/de/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: So funktioniert der Benutzer-Token-Workflow
+---
+
+Benutzer-Tokens werden verwendet, um die Benutzer/innen gegenüber Dritten zu identifizieren, damit Aufgaben, die bei diesen Diensten erledigt werden, im Konto der Benutzer/innen gespeichert werden können.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+Im Moment werden die Token nur für die Einreichung der Aufgaben für relationale Datenbanken verwendet. A token gets created when a signed-in user clicks the "Click here to start the course" or "Click here to start the project" buttons to start one of the Relational Database courses or projects.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+Ein Benutzer-Token wird gelöscht, wenn sich ein Benutzer aus dem freeCodeCamp abmeldet, seinen Fortschritt zurücksetzt, sein Konto löscht oder den Token manuell über das Widget auf der Einstellungsseite löscht.
+
+## How they Work
+
+Token werden in einer `UserToken`-Sammlung in der Datenbank gespeichert. Jeder Datensatz hat eine eindeutige `_id`, die der Token ist, und eine `user_id`, die auf das Konto des Benutzers aus der `user`-Sammlung verweist. Das Token wird mit JWT kodiert und an den Client gesendet, wenn es erstellt wird. That encoded token is then given to third-party services that need it and sent to our API by them when a challenge is completed. Wenn unsere API sie erhält, wird sie dekodiert, damit wir den Benutzer, der eine Aufgabe einreicht, identifizieren und die abgeschlossene Aufgabe in seinem `completedChallenges` speichern können.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/es/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..109b49ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Manual para Autores de Google Analytics
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Búsqueda por Idioma
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+
+
+1. En el menú desplegable de arriba, seleccione `News`.
+1. En la barra lateral, haga clic en `Report`.
+1. En la barra lateral secundaria, seleccione `Compromiso`.
+1. Haga clic en `Pages and Screens`.
+1. En la barra de búsqueda, escriba la subruta para el idioma deseado.
+1. En el menú desplegable que esta por debajo de la barra de búsqueda, eliga `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filtrar Informes por el Autor
+
+Después de encontrar los informes de `Pages and Screens` mencionados anteriormente, utilice los siguientes pasos para filtrar los resultados de autores específicos.
+
+
+
+1. Haga clic en el botón `Add filter`.
+1. En el apartado de navegación incluyen `Author`.
+1. En el menú desplegable `Dimensions values`, eliga un nombre de autor.
+1. Haga clic en boton `Apply` para aplicar los cambios.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/es/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..aa1914c8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
+---
+title: Las mejores prácticas de la base de código
+---
+
+## Dándole estilo a un componentes
+
+Recomendamos dar estilo a los componentes usando nuestra [guía de estilo de diseño](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+Los colores están definidos en [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css)y las fuentes están en [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+Somos muy obstinados sobre la adición de nuevas variables/tokens a los colores. Después de una cuidadosa investigación, los colores han sido elegidos para respetar la identidad de la marca freeCodeCamp y la experiencia del desarrollador y accesibilidad.
+
+La palabra clave `!important` puede utilizarse para sobrescribir valores en algunos casos (por ejemplo, problemas de accesibilidad). Debería añadir un comentario describiendo el problema, para que no se elimine en futuras refactorizaciones.
+
+### Soporte RTL
+
+We are striving to support right-to-left (RTL) layout in the codebase for languages that are read in this direction. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Here are some quick rules of thumb to follow:
+
+- Don't use `float` properties
+ - Use Flexbox and Grid layouts instead, as they have RTL support already built-in, and those will be easier to maintain and review.
+- Don't define the direction while using `margin` and `padding`: it may seem harmless to use `padding-right` and `margin-left`, but these directions aren't mirrored when the layout changes to RTL, and adding counter values for them in the RTL file makes maintaining the codebase harder.
+ - Use logical properties for them: You can add the same spacing by using `padding-inline-end` and `margin-inline-start`, and you won't need to worry about RTL layout, as they follow where the line starts and ends, and you won't need to add any extra values in the RTL files, so people won't need to remember to change the same values in two files.
+- Don't use `!important` in `font-family`: RTL layout uses different fonts compared to the LTR layout, when you add `!important` in the `font-family` property it affects the RTL layout too.
+
+## General JavaScript
+
+In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
+
+It is encouraged to use functional components over class-based components.
+
+## Specific TypeScript
+
+### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
+
+#### Retención del historial de archivos Git
+
+Sometimes changing the file from `<filename>.js` to `<filename>.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
+
+The best bet at achieving this is to:
+
+1. Renombrar el archivo
+2. Comenta con la etiqueta `--no-verify` para evitar que Husky se queje de los errores de lint
+3. Refactoriza a TypeScript para la migración, en un commit separado
+
+:::note
+Es probable que los editores como VSCode te muestren que el archivo se ha eliminado y que se ha creado uno nuevo. Si utilizas CLI para `git add .`, entonces VSCode mostrará el archivo como renombrado en stage
+:::
+
+### Naming Conventions
+
+#### Interfaces y Tipos
+
+For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
+
+React Component Props - suffix with `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+React Stateful Components - suffix with `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Default - object name in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Action Definitions
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### How to Reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### How to Dispatch
+
+Within a component, import the actions and selectors needed.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [TypeScript Docs](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [TypeScript with React CheatSheet](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/es/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9565d258
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+---
+title: Cursos de extensión de VSCode
+---
+
+Esto detalla las guías de mantenimiento para el repositorio de [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extensión](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension), el cual contiene el código fuente de la extensión [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses).
+
+## Publicando la Extensión
+
+'GitHub Action' publica automáticamente la extensión en el Marketplace de Visual Studio, cada vez que se publica una nueva versión en GitHub.
+
+1. Empaquete una nueva versión de la extensión:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Donde `<tag_type>` es uno de: `mayor`, `menor`, `parchar`.
+
+2. Envía la nueva versión a `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Opcionalmente puedes empujar directamente al `upstream/main`pero abrir un nuevo PR es recomendado para mejor órden.
+
+3. Cree una nueva versión de GitHub usando la interfaz de usuario de GitHub:
+
+- Incremente correctamente el número de versión al crear una nueva etiqueta.
+- actualizar el archivo `.vsix` con la nueva versión.
+- Publique el lanzamiento y confirme que la acción se realizó correctamente.
+
+:::note
+La creación de una versión requiere acceso de escritura al repositorio `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension` repositorio.
+:::
+
+## Publicación Manual de la Extensión
+
+Se puede realizar una carga manual en Visual Studio Marketplace siguiendo estos pasos:
+
+1. Visite https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ e inicie sesión
+2. Vaya a la [página del editor de freeCodeCamp](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Seleccione la extensión relevante y seleccione `Actualizar`
+4. Sube el archivo desde tus archivos locales
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d751b9b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+---
+title: Estructura de archivos del currículo
+---
+
+Nuestro contenido instructivo principal se encuentra dentro del directorio convenientemente llamado `curriculum`. Esta página desglosará cómo están organizados estos archivos.
+
+## Terminología
+
+Hay algunos términos que utilizamos cuando hablamos del contenido de nuestro currículo.
+
+- `certification` : Cuando se hace referencia a una certificación en este caso, se está hablando del certificado real que los usuarios reclaman. Que es independiente del nombre del súper bloque.
+- `superBlock` : Un súper bloque es la colección de desafíos del nivel superior. Cada súper bloque corresponde a una certificacion en el currículo (p. ej. Diseño Web Responsivo).
+- `block` : Un bloque es una sección dentro de un súper bloque. Un bloque corresponde a un grupo de desafíos en una certificacion determinada (p. ej. HTML Básico y HTML5)
+- `challenge`: Un desafío es una sola lección dentro del currículo (p. ej. Di hola a los Elementos HTML)
+
+## Árbol de archivos
+
+Usando esos términos, así es como se definiría la estructura de archivos:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## El directorio `_meta`
+
+El directorio `_meta` es un directorio especial que contiene archivos `.json`. Estos archivos corresponden a cada bloque en el currículo y son utilizados para determinar a qué súper bloque pertenece cada bloque y el orden de los desafíos dentro de ese bloque.
+
+## Renombrando archivos
+
+Puede haber ocasiones en las que necesites renombrar un certificado, súper bloque, bloque o desafío. Esta sección describirá los pasos necesarios para evitar errores de compilación al hacerlo.
+
+:::danger
+Renombrar archivos dentro de la estructura del currículo puede cambiar a menudo la ruta (o URL) del contenido en la página web principal. Debe hacerse con cuidado, ya que se deben establecer redireccionamientos para cada cambio que se realice.
+:::
+
+### Renombrando una certificación
+
+Al renombrar una certificación, es probable que desees renombrar el súper bloque asociado junto a ella. Haz lo siguiente para renombrar sólo el certificado:
+
+1. Cambia el nombre de la carpeta `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` por el nuevo nombre.
+1. En el archivo `meta.json` de esa carpeta, cambia los valores en `name`, `dashedName` y `challengeOrder` al nuevo nombre de certificado.
+1. En `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, cambia el nombre de la carpeta `{superBlock}-certificate` y el archivo YAML dentro de ella, por el nuevo nombre.
+1. En el archivo YAML, cambia el `title` por el nuevo nombre.
+1. Renombra el archivo y la carpeta del paso 3 para el resto de los lenguajes del currículo.
+1. Actualiza `client/src/redux/index.ts` para que utilice el `title` correcto.
+1. Como alternativa, actualiza el `certSlug` para el súper bloque en el mismo archivo. **Ten en cuenta** que renombrar un `certSlug` cambiará el URL para las certificaciones y solo debe hacerse con consideración.
+1. Actualiza el `title` en `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` por el nuevo valor. **Ten en cuenta que** cambiar el `title` aquí **romperá** la página del súper bloque asociada a la certificación. Depende del título del súper Bloque para que coincida con el título de la certificación. Es probable que desees renombrar el súper bloque al mismo tiempo.
+1. Si renombraste `certSlug` en el paso 7, cámbialo aquí para el "cert" y todos los valores de `projects` anidados.
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. Si renombraste el `certSlug` en el paso 7, actualiza la clave de `certSlugTypeMap` en el mismo archivo.
+1. Actualiza el nombre del certificado en el arreglo `legacyCerts` dentro del `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx` si es necesario.
+1. Actualiza el archivo principal `README.md` al nuevo nombre.
+
+### Renombrar un súper bloque
+
+:::note
+Cuando renombras un súper bloque, el nuevo nombre de carpeta es usado como la ruta y debe considerarse el nombre "correcto". Todos los demás valores deben actualizarse para reflejar ese cambio.
+:::
+
+Además, es probable que desees renombrar el certificado y el bloque `{superBlock}-projects` cuando renombres un súper bloque, ya que todos comparten un nombre. Para renombrar solamente un súper bloque necesitas:
+
+1. Renombrar la carpeta del super bloque en el directorio `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Renombra la carpeta súper bloque en _todos_ los otros directorios `curriculum/challenges/{language}`.
+1. Para cada bloque dentro del súper bloque, actualice el valor `superBlock` en el archivo `meta.json` a su nombre con guiones. No necesitas renombrar ninguna carpeta aquí. Hazlo cuando renombres un bloque.
+1. Renombra la carpeta súper bloque en `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Actualiza el archivo `index.md` en la carpeta superior, cambiado los valores de `title` y `superBlock` al nuevo nombre.
+1. Para cada carpeta de bloque dentro de la superior, actualiza el `index.md` para que utilice el valor de `superBlock` correcto.
+1. En el archivo `cliente/src/recursos/cert-and-project-map.ts`, actualiza la ruta para certificado en la parte superior del archivo y el valor `title` para ese súper bloque. **Ten en cuenta** que cambiar el `title` aquí **interrumpirá** la capacidad de ver la certificación real para este súper bloque. Depende del título del súper Bloque para que coincida con el título de la certificación. Es probable que desees renombrar la certificación al mismo tiempo.
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. Actualiza el valor de la ruta en `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. Para cada idioma en `client/i18n/locales`, actualiza el archivo `intro.json` para que utilice el nuevo `dashedName` (nombre con guiones) del súper Bloque. En el archivo en inglés, actualiza también el `title`.
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. Actualiza todos los valores donde sea usado.
+1. Actualiza el archivo principal `README.md` al nuevo nombre.
+
+### Renombrando un bloque
+
+Cuando renombras un bloque del currículo, tienes que:
+
+1. Cambiar el nombre de la carpeta del bloque en el directorio `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
+1. Cambiar el nombre de la misma carpeta de bloque en _todos_ los demás directorios de lenguajes para que coincidan. Estos deben ser todos iguales a la estructura en inglés o se producirá un error en la compilación.
+1. Cambiar el nombre de la carpeta del bloque en el directorio `_meta`.
+1. Actualizar las propiedades `nombre` y `dashedName` (nombre con guiones) del archivo `meta.json` de ese bloque.
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renombrando un desafío
+
+Al renombras un solo archivo de desafío, tienes que:
+
+1. Cambiar el nombre del archivo del desafío en el directorio `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Cambiar el nombre del `title` y de `dashedName` (nombre con guiones) dentro de ese archivo.
+1. Cambiar el nombre del archivo y los `dashedName` en esos archivos para coincidir con _todos_ los demás directorios de idiomas.
+1. Actualizar el nombre del desafío en el archivo `meta.json` correspondiente. Los nombres de los desafíos aquí no se utilizan en la compilación, pero proveen una forma amigable al usuario de identificar el orden de los mismos.
+1. Si el desafío es un proyecto de certificado, actualizar el archivo YAML en `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` con el nuevo nombre.
+1. Si el desafío es un proyecto de certificado, actualizar el `title` y el `link` en `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. Si el desafío es un proyecto de certificado, actualizar el archivo principal `README.md` con el nuevo nombre.
+
+## La propiedad `dashedName`
+
+La propiedad `dashedName` se usa para generar la ruta URL para el súper bloque, el bloque o el desafío. Por lo general, estos deberían coincidir con los nombres que generaría el asistente `/utils/slugs.js` para el nombre del archivo.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/devops.md b/src/content/docs/es/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e3bb22a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1004 @@
+---
+title: Manual de DevOps
+---
+
+Esta guía te ayudará a comprender nuestra infraestructura y cómo le damos mantenimiento a nuestras plataformas. Si bien esta guía no contiene detalles exhaustivos de todas las operaciones, esta podría utilizarse como referencia para tu comprensión de los sistemas.
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+Esto involucra tres pasos que deben seguirse en secuencia:
+
+1. Los nuevos cambios (tanto correcciones como funcionalidades) se integran en nuestra rama principal de desarrollo (`main`) a través de pull requests.
+2. Estos cambios son ejecutados a través de una serie de pruebas automatizadas.
+3. Una vez que las pruebas se completan de forma satisfactoria, publicamos los cambios (o los actualizamos si es necesario) para desplegarlos en nuestra infraestructura.
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+Normalmente, [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (la rama de desarrollo por defecto) se integra diariamente en la rama [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) y se publica en una infraestructura aislada.
+
+Esta es una publicación intermedia para nuestros desarrolladores y colaboradores voluntarios. También es conocida como nuestra publicación "staging" o "beta".
+
+Este es idéntico a nuestro entorno de producción en `freeCodeCamp.org`, excepto que utiliza un conjunto separado de bases de datos, servidores, web-proxies, etc. Este aislamiento nos permite probar el desarrollo y las funcionalidades de manera continua en un escenario similar al de "producción", sin afectar a los usuarios regulares de las principales plataformas de freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+Una vez que el equipo de desarrolladores [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) está satisfecho con los cambios en la plataforma de "staging", estos cambios se trasladan cada ciertos días a la rama [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current).
+
+Esta es la versión final que despliega los cambios a nuestras plataformas de producción en freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+Empleamos varios niveles de pruebas de integración y aceptación para verificar la calidad del código. Todas nuestras pruebas se realizan a través de software como [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) y [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. Estas nos ayudan a probar la integración entre diferentes componentes.
+
+:::note
+We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+:::
+
+Juntas, estas pruebas ayudan a evitar que los problemas se repitan y garantizan que no introduzcamos un error mientras trabajamos en otro error o en una funcionalidad.
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+Hemos configurado un software de entrega continua para publicar los cambios en nuestros servidores de desarrollo y producción.
+
+Una vez que los cambios se envían a las ramas de publicación protegidas, se activa automáticamente un flujo de compilación para la rama. Los flujos de compilación son responsables de construir artefactos y mantenerlos en un almacenamiento en frío para su uso posterior.
+
+El flujo de compilación dispara el flujo de publicación correspondiente si este completa una ejecución exitosa. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. Los cambios en las ramas de `production-*` sólo pueden llegar a través de una fusión fast-forward al [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+:::note
+In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+:::
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. Configura tus repositorios remotos correctamente.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Resultado:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Asegúrate de que tu rama `main` sea impecable y esté sincronizada con la corriente ascendente.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Comprueba que el GitHub CI este aprobado en la rama `main` para el flujo upstream.
+
+ Las pruebas de [integración continua](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) deben estar en verde y en estado PASSING para la rama `main`. Haz clic en la marca de verificación verde junto al hash del commit si estás viendo el código de la rama `main`.
+
+ <details> <summary> Comprobando el estado en GitHub actions (captura de pantalla) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ Si esto está fallando debes detenerte e investigar los errores.
+
+4. Confirme que puede crear el repositorio localmente.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Mueve los cambios desde `main` a `prod-staging` mediante una fusión fast-forward
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+:::note
+You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+
+Si esto ocurre, es posible que hayas hecho algo incorrectamente y deberías comenzar de nuevo.
+:::
+
+Los pasos anteriores activarán automáticamente un flujo de compilación para la rama `prod-staging`. Una vez que se completa la compilación, los artefactos se guardan como archivos `.zip` en un almacenamiento en frío para ser recuperados y usados más adelante.
+
+El flujo de publicación se activa automáticamente cuando hay un nuevo artefacto disponible en el flujo de compilación conectado. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+El proceso es prácticamente el mismo que el de las plataformas de staging, con algunas comprobaciones adicionales. Esto es solo para asegurarnos de que no rompemos nada en freeCodeCamp.org, el cual puede tener a cientos de usuarios usándolo en cualquier momento.
+
+| NO ejecutes estos comandos a menos que hayas verificado que todo funciona en la plataforma de staging. No debes omitir ni evitar ninguna prueba en staging antes de continuar. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Asegúrate de que tu rama `prod-staging` este sin cambios y sincronizada con el upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Mueve los cambios de `prod-staging` a `prod-current` mediante una fusión fast-forward
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ :::note
+ You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ :::
+
+ > Si esto ocurre, es posible que hayas hecho algo incorrectamente y deberías comenzar de nuevo.
+
+Los pasos anteriores activarán automáticamente un flujo de compilación para la rama `prod-current`. Una vez que un artefacto de compilación está listo, este activará la ejecución en el flujo de publicación.
+
+**Pasos Adicionales para el Staff Action**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. Pueden _aprobar_ o _rechazar_ la publicación.
+
+Si los cambios funcionan y se han probado en la plataforma de staging, entonces se pueden aprobar. La aprobación debe darse dentro de las 4 horas posteriores a la activación de la publicación antes de sea rechazada automáticamente. Un miembro del personal puede volver a iniciar la ejecución de la publicación de manera manual para publicaciones que fueron rechazados o esperar el siguiente ciclo de publicación.
+
+Para uso del personal:
+
+| Revisa tu correo electrónico para ver si hay un enlace directo o [ve al panel de publicaciones](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) después de que la ejecución de la compilación haya terminado. |
+| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Una vez que uno de los miembros del personal apruebe una publicación, el flujo enviará los cambios a los servidores de API y CDN de producción de freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+Aquí está el estado actual de las pruebas, compilación y despliegue del código base.
+
+| Rama | Pruebas de unidad | pruebas de integración | compilación y despliegue |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (experimental, próximamente) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+Te invitamos a probar estas versiones en un modo **"prueba beta pública"** y obtener acceso anticipado a las próximas funciones de las plataformas. A veces, estas funcionalidades/cambios se denominan **next, beta, staging,** etc. indistintamente.
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+Te agradecemos por reportar los errores que encuentres y ayudar a mejorar freeCodeCamp.org. ¡Eres genial!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| Aplicación | Idioma | URL |
+| :--------- | :------ | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Aprende | Inglés | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Español | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Chino | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| Noticias | Inglés | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Foro | Inglés | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Chino | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+:::note
+El nombre de dominio es diferente a **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. Esto es intencional para evitar la indexación de los motores de búsqueda y evitar confusiones para los usuarios habituales de la plataforma.
+:::
+
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**La versión actual de la plataforma siempre está disponible en [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+El equipo de desarrollo fusiona los cambios de la rama `prod-staging` a `prod-current` cuando publican los cambios. El commit más reciente debe ser lo que ves en vivo en el sitio.
+
+Puedes identificar la versión exacta desplegada visitando los registros de compilación y despliegue disponibles en la sección de estado. Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+Existen algunas limitaciones y problemas conocidos al utilizar la versión beta de la plataforma.
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **Los usuarios de la versión beta tendrán una cuenta separada a la de producción.** La versión beta usa una base de datos físicamente separada de la de producción. Esto nos da la capacidad de prevenir cualquier pérdida accidental de datos o modificaciones. The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ Se espera que el despliegue sea frecuente y en iteraciones rápidas, a veces varias veces al día. As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ El sitio beta es y siempre ha sido para aumentar el desarrollo y las pruebas locales, nada más. No es una promesa de lo que se avecina, sino un vistazo de lo que se está trabajando.
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ Usamos un entorno de prueba para freeCodeCamp.dev en Auth0 y por lo tanto, no tenemos la capacidad de establecer un dominio personalizado. Esto hace que todas las redirecciones de peticiones y la página de inicio de sesión aparezcan en un dominio predeterminado como: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. Esto no afecta la funcionalidad y es lo más cercano a la producción que podemos conseguir.
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+Por favor abre un nuevo reporte (issue) para discusiones e informes de errores.
+
+Puedes enviar un correo electrónico a `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` si tienes alguna consulta. Como siempre, todas las vulnerabilidades de seguridad deben notificarse a `security[at]freecodecamp.org` en lugar del registro público o el foro.
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+:::!WARNING
+
+1. La guía se aplica únicamente a los **miembros del personal de freeCodeCamp**.
+2. Estas instrucciones no deben considerarse exhaustivas, por favor ten cuidado.
+ :::
+
+Como miembro del equipo interno, es posible que se te haya dado acceso a nuestros proveedores de servicios en la nube como Azure, Digital Ocean, etc.
+
+Aquí hay algunos comandos útiles que puedes usar para trabajar en las máquinas virtuales (MV), por ejemplo, realizar actualizaciones de mantenimiento o realizar tareas de limpieza general.
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+:::note
+While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+:::
+
+### Azure
+
+Instala el CLI de Azure `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(Una sola vez) Instalar en macOS con [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(Una sola vez) Inicio de sesión:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Obtener la lista de nombres de las máquinas virtuales y direcciones IP:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Instalar el CLI de Digital Ocean `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(Una sola vez) Instalar en macOS con [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(Una sola vez) Inicio de sesión:**
+
+Autenticación y cambio de contexto: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Obtener la lista de nombres de las máquinas virtuales y direcciones IP:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+Estamos trabajando para crear nuestra configuración de "laC", y mientras esta en proceso, puedes usar el portal de Azure o Azure CLI para poner en marcha nuevas maquinas virtuales y otros recursos.
+
+> [!TIP] Independientemente de tu elección de ejecución de recursos, tenemos algunos [ archivos de configuración de inicio útiles en la nube](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) para ayudarte a realizar parte del aprovisionamiento básico, como instalar docker o agregar claves SSH, etc.
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+Debes mantener las máquinas virtuales actualizadas mediante la realización de actualizaciones. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Antes de ejecutar estos comandos:
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - Si estás actualizando paquetes en una máquina virtual que ya está sirviendo una aplicación, asegúrate de que la aplicación se ha detenido / guardado. Las actualizaciones de paquetes causarán que el ancho de banda de la red, la memoria y/o CPU tengan picos que pueden ocasionar interrupciones en aplicaciones en ejecución.
+
+Actualizar la información de paquetes
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Actualizar los paquetes instalados
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Limpieza de paquetes no utilizados
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+Estamos ejecutando instancias de balanceo de cargas (Azure Load Balancer) para nuestros servidores web. Estos servidores ejecutan NGINX como proxy inverso, enrutando hacia freeCodeCamp.org el tráfico de varias aplicaciones que se ejecutan en sus propias infraestructuras.
+
+La configuración de NGINX está disponible en [este repositorio](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### Primera Instalación
+
+Aprovisionamiento de máquinas virtuales con el código
+
+1. Instala NGINX y configúralo desde el repositorio.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Instala los certificados de origen de Cloudflare y la configuración de la aplicación upstream.
+
+ Obtén los certificados de origen de Cloudflare del almacenamiento seguro e instálalos en las ubicaciones requeridas.
+
+ **O**
+
+ Mueve los certificados existentes:
+
+ ```bash
+ # En Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # En Remoto
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Actualiza las configuraciones upstream:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Agrega/actualiza las direcciones IP fuente/origen de la aplicación.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configura los firewalls de Azure y `ufw` según sea necesario para las direcciones de origen de entrada.
+
+4. Agregue la MV al grupo de backend del balanceador de carga.
+
+ Configura y agrega reglas al balanceador de carga si es necesario. Es posible que también necesites agregar las MVs al grupo de backend del balanceador de carga si es necesario.
+
+### Registro de eventos y monitoreo
+
+1. Compruebe el estado del servicio NGINX utilizando el siguiente comando:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. El registro de eventos y el monitoreo de los servidores están disponibles en:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), nuestro panel de control básico actual. Estamos trabajando en métricas más granulares para una mejor visibilidad de los datos
+
+### Actualización de las instancias (mantenimiento)
+
+Los cambios en la configuración de nuestras instancias NGINX son mantenidos en GitHub, y se deben desplegar en cada instancia de la siguiente manera:
+
+1. SSH en la instancia y entra en modo sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Obtén el código de configuración más reciente.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Prueba y recarga la configuración [con Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. Instala las herramientas de compilación para archivos binarios de Node (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Primera instalación
+
+Aprovisionamiento de MVs con el código
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Registro de eventos y monitoreo
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Actualización de las instancias (mantenimiento)
+
+Los cambios en el código deben desplegarse en las instancias de la API cada tanto. Esto puede ser una actualización continua o una actualización manual. The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+> [!ATTENTIÓN] Los flujos automáticos no están manejando actualizaciones de dependencias en el momento. Necesitamos realizar una actualización manual antes de que se ejecute cualquier flujo de despliegue.
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+:::note
+We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. No debes tener que ejecutar estos comandos. Estos están aquí para documentación.
+:::
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Primera Instala
+
+Aprovisionamiento de MVs con el código
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Registro de eventos y monitoreo
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Actualización de las instancias (mantenimiento)
+
+Los cambios en el código deben desplegarse en las instancias del API cada cierto tiempo. Esto puede ser una actualización continua o una actualización manual. La última es esencial al cambiar dependencias o al agregar variables de entorno.
+
+:::danger
+Los flujos automáticos no están manejando actualizaciones de dependencias en el momento. Necesitamos realizar una actualización manual antes de que se ejecute cualquier flujo de despliegue.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Actualizaciones Manuales: Utilizadas para actualizar dependencias, variables de entorno.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Actualizaciones continuas: Utilizadas para cambios lógicos en el código.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+:::note
+Estamos manejando actualizaciones continuas de código, lógica, a través de flujos. No necesitarás aplicar estos comandos. Estos están por la documentación.
+:::
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+Nuestros servidores de chat están disponibles con una configuración HA [recomendada en la documentación de Rocket.Chat](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). El archivo `docker-compose` para esto está [disponible aquí](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+Aprovisionamos instancias NGINX redundantes que a su vez tienen equilibrio de carga (Azure Load Balancer) frente al clúster Rocket.Chat. El archivo de configuración de NGINX está [disponible aquí](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Aprovisionamiento de MVs con el código
+
+**Clúster NGINX:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Clúster de Docker:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**Clúster NGINX:**
+
+Los cambios de configuración a nuestras instancias NGINX se mantienen en GitHub, estos se deben implementar en cada instancia de la siguiente manera:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Clúster de Docker:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+ssh en la máquina virtual (alojada en Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+Lista las versiones instaladas de node y npm
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Instala el último Node.js LTS y reinstala cualquier paquete global
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Verifica los paquetes instalados
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Opcional) Desinstalar versiones antiguas
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+Para las aplicaciones cliente, el script de shell no se puede resucitar entre las versiones de Node.js con `pm2 resurrect`. En su lugar, despliega procesos desde cero. This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> Si utilizas PM2 para procesos, también deberás abrir las aplicaciones y guardar la lista de procesos para la recuperación automática en los reinicios.
+
+Obtén las instrucciones/comandos de desinstalación con el comando `unstartup` y usa la salida para eliminar los servicios de systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Obtén las instrucciones/comandos de instalación con el comando `startup` y usa la salida para agregar los servicios de systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Comandos rápidos para que PM2 enumere, reviva procesos guardados, etc.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. En términos generales, puedes seguir los pasos que se enumeran aquí.
+
+Necesitarás una PAT, que puedes obtener desde aquí: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+Navega a [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) y registra el agente desde cero en el requisito [deployment groups](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+:::note
+Debes ejecutar los scripts en el directorio de inicio, y asegurarte de que no existe ningún otro directorio `azagent`.
+:::
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+Actualmente actualizar los agentes requiere que sean eliminados y reconfigurados. Esto es necesario para que recojan correctamente los valores `PATH` y otras variables de entorno del sistema. Necesitamos hacer esto, por ejemplo, para actualizar Node.js en nuestras MV objetivo de implemetación.
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Una vez que hayas completado los pasos de arriba, puedes repetir los mismos pasos que para instalar el agente.
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+Utilizamos [una herramienta CLI](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) para enviar el boletín semanal. Para actualizar y comenzar el proceso:
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+Utilizamos un [tema](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) personalizado para nuestra publicación de noticias. Los siguientes cambios en el tema permiten añadir nuevos idiomas.
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Actualice los recursos de la publicación yendo al panel de Ghost > ajustes > generales y subiendo el icono [de las publicaciones](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png)y [portada](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/faq.md b/src/content/docs/es/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..107c913e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions ---
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files.md) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+> [!TIP] Los temas de **`se busca ayuda`** están en marcha y no es necesario pedir permiso antes de trabajar en ellos. Sin embargo, temas con la etiqueta **`solo principiantes`** son temas especiales que están diseñados para personas que no han contribuido a la base de código de freeCodeCamp antes.
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. Lo más probable es que fusionemos el primer pull request que aborde el tema o problema.
+2. En el caso de múltiples colaboradores abriendo un pull request para el mismo problema más o menos al mismo tiempo, daremos prioridad al pull request que aborde mejor la cuestión. Algunas de las cosas que consideramos:
+ - ¿Has incluido pruebas?
+ - ¿Entendiste todos los casos de uso?
+ - ¿Te aseguraste de que pasaran todas las pruebas, y confirmaste que todo funciona localmente?
+3. Por último, damos prioridad a los pull requests que siguen nuestras directrices recomendadas.
+ - ¿Has seguido la lista de verificación de pull request?
+ - ¿Has dado a tu pull request un título significativo?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- To be a **Discord/Chat** moderator, have an active presence in our chat and have positive engagements with others, while also learning and practicing how to deal with potential conflicts that may arise.
+- To be a **Forum** moderator, similar to a chat moderator, have an active presence and engage with other forum posters, supporting others in their learning journey, and even giving feedback when asked. Take a look at [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) for more information.
+- To be a **GitHub** moderator, help process GitHub issues that are brought up to see if they are valid and (ideally) try to propose solutions for these issues to be picked up by others (or yourself).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook.md) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- La categoria de `Contributors` de [nuestro foro de comunidad](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- El canal `#Contributors` de
+
+nuestro servidor de chat<1>.</li> </ul>
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..613d253e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
+---
+title: Cómo agregar pruebas de Cypress
+---
+
+Al realizar cambios en JavaScript, CSS o HTML que podrían cambiar la funcionalidad o el diseño de una página, es importante agregar una prueba de integración de [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io) correspondiente.
+
+Para aprender como escribir pruebas de Cypress, o especificaciones, observa la [documentación](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html) oficial de Cypress.
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Las pruebas de Cypress están en el directorio `./cypress`.
+
+- Las pruebas de Cypress para un módulo curricular están en el directorio curricular correspondiente, por ejemplo: `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+:::note
+If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+:::
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Inicia MongoDB y propaga la base de Datos](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Inicia la aplicación de cliente de freeCodeCamp y el servidor API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+Para ejecutar pruebas en las compilaciones de producción, reemplaza `dev` con `prd` abajo.
+
+- Para ejecutar todas las pruebas en el directorio `./cypress`:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- Para ejecutar una sola prueba:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- Para crear una compilación de desarrollo, inicia el servidor de desarrollo y ejecuta todas las pruebas de cypress existentes de extremo a extremo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Asegúrate de que el entorno de desarrollo se esté ejecutando
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Propaga la base de datos
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Inicia el servidor de desarrollo y cliente
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Instala las herramientas de compilación de Cypress
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- Cuando se te solicite en la terminal, selecciona la distribución de tu teclado por idioma / área
+
+Ahora, [Cypress puede ser ejecutado](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..28628a2f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+:::note
+Este es un **paso opcional** y es necesario solo cuando se trabaja con flujos de trabajo de correo electrónico
+:::
+
+- [Introducción](#introduction)
+- [Instalando MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Usando MailHog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Enlaces útiles](#useful-links)
+
+## Introducción
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog es una alternativa al uso de un proveedor de servicios de correo electrónico para enviar correos electrónicos reales. Es una herramienta de desarrollo para pruebas de correo electrónico que capturará los mensajes de correo electrónico enviados por tu instancia de freeCodeCamp.
+
+## Instalando MailHog
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Instalando MailHog con Docker</summary>
+
+Si ya tienes Docker instalado puedes usar
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+Para iniciar MailHog en segundo plano y
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+Para frenarlo.
+
+Cuando la instalación finalice, puedes comenzar a [usar MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando MailHog en macOS</summary>
+
+Instalando MailHog en macOS con [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+Cuando la instalación finalice, puedes comenzar a [usar MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando MailHog en Windows</summary>
+
+Descarga la última versión de MailHog del [repositorio oficial de MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a `.exe` file will be downloaded to your computer.
+
+Cuando la descarga finalice, haz clic en el archivo para abrirlo. Puede aparecer una notificación del cortafuegos de Windows solicitando permiso de acceso para MailHog. Se abrirá una línea de comandos estándar de Windows donde se ejecutará MailHog una vez que se le otorgue el permiso del cortafuegos.
+
+Detén MailHog cerrando la ventana de comandos. To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (`.exe`) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
+
+Comienza a [usar MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando MailHog en Linux</summary>
+
+Primero, instala [Go](https://golang.org).
+
+Ejecuta los siguientes comandos para instalar GO en sistemas basados en Debian como Ubuntu y Linux Mint.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+Ejecuta los siguientes comandos para instalar GO en sistemas basados en RPM como CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+Alternativamente, ejecuta los siguientes comandos para instalar GO.
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+Ahora establece la ruta para Go con los siguientes comandos.
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+Finalmente, ingresa los siguientes comandos para instalar y ejecutar MailHog.
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+Comienza a [usar MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+## Usando MailHog
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## Enlaces útiles
+
+- Revisa el repositorio de [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) para más información relacionada con MailHog. También está disponible información adicional sobre configuraciones personalizadas de MailHog.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c5e787c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Sigue estas recomendaciones para poder contribuir a la base del código. Es recomendable que lo hagas si quieres contribuir de forma regular.
+
+Ignorar estos pasos puede empobrecer tu copia lo que hara que el proceso de contribución, revisión y mantenimiento sea dificultoso.
+
+## Contribuir a la base del código
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Sigue estos pasos:
+
+1. 1. Utiliza el siguiente comando para confirmar que estes en la rama `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ el comando debería devolverte el siguiente resultado:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Copia las ultimas modificaciones de la rama `main` del upstream de freeCodeCamp a la rama `main ` de tu bifurcación:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Si tenes alguna pull request pendiente que hiciste desde la rama `main` de tu bifurcación, cuando realices este paso se perderán.
+ >
+ > Siempre debes asegurarte que tu pull request haya sido fusionada por un moderador antes de realizar este paso. Para evitar esta situación, **siempre** deberías trabajar en una rama distinta a la `main`.
+
+ Este paso ** obtendrá los cambios más recientes** del repositorio principal de freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Actualizar tu copia del repositorio principal de freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Formatea tu rama main con la rama main de freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Hace push de tu rama main a tu bifurcación original para limpiar tu historial en GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ El resultado debería ser que el directorio de trabajo está limpio. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Crea una nueva rama:
+
+ Trabajar en una rama separada para cada incidente ayuda a que tu copia del trabajo se muestre ordenada. Nunca deberías trabajar en `main`. Esto hará que tu copia de freeCodeCamp quede desordenada y podrá ser necesario que tengas que empezar de nuevo con una copia nueva o bifurcación.
+
+ Verificá que estás en `main` siguiendo los pasos ya explicados y empezá desde ahí:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ El nombre de tu rama debería comenzar con `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Evita usar números de incidentes en las ramas. Deberían ser cortos, significativos y únicos.
+
+ Algunos ejemplos de buenos nombres para ramas son:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edita la páginas y trabaja en el código en tu editor de texto favorito.
+
+5. Una vez que estes conforme con los cambios realizados, de manera opcional, deberías ejectuar freeCodeCamp para previsualizar los cambios.
+
+6. Asegurate de corregir cualquier error que pueda aparecer y comprabar el formato de tus cambios.
+
+7. Comprobá y confirmá los archivos que estás actualizando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Este comando debería mostrar una lista de los archivos `unstaged` que editaste.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Organizar los cambios y hacer un commit:
+
+ En este paso, sólo deberías marcar los archivos que has editado o añadido tu mismo. Puede realizar un reseteo y resolver archivos que no tenías intención de cambiar si es necesario.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ O puedes añadir todos los archivos que no estén `unstaged` al área de staging:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Sólo los archivos que fueron movidos al área de staging serán añadidos cuando hagas un commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Resultado:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Ahora, puedes confirmar tus cambios con un mensaje corto así:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Algunos ejemplos:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Escribe un mensaje commit convencional. This is a good practice as a developer, and you will be following standard practices.
+
+ Algunos ejemplos de mensajes de commits convencionales son:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Manténlos cortos, no más de 50 caracteres. Siempre puedes añadir información adicional en la descripción del mensaje del commit.
+
+ Esto no toma más tiempo que un mensaje no convencional como 'actualizar archivo' o 'añadir index.md'
+
+ Puedes aprender más sobre por qué deberías usar commits convencionales [aquí](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Si te das cuenta de que necesitas editar un archivo o actualizar el mensaje de confirmación después de hacer un commit puedes hacerlo después de editar los archivos con:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Esto abrirá un editor de texto predeterminado como `nano` o `vi` donde puedes editar el título del mensaje de confirmación y añadir/editar la descripción.
+
+10. A continuación, puedes enviar tus cambios a tu bifurcación:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proponer una Pull Request (PR)
+
+Después de que hayas cofirmado tus cambios, consulta aquí sobre [cómo abrir una Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Referencia de comandos rápidos
+
+Una referencia rápida a los comandos que necesitarás cuando trabajes.
+
+| comando | descripción |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| `pnpm test` | Ejecuta todas las pruebas JS en el sistema, incluidas las pruebas de cliente, servidor, lint y pruebas de desafío. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Ejecuta el conjunto de pruebas del cliente. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Ejecuta el conjunto de pruebas del currículo. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Evalúa un bloque específico. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Evalúa un SuperBlock específico. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Ejecuta el conjunto de pruebas del currículo, sin tener que salir después del primer error |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Ejecute la suite de pruebas del servidor. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Ejecuta los tests end to end de Cypress. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Desinstala todas las dependencias y limpia las cachés. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Inicia Storybook para el desarrollo de la biblioteca de componentes. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d2b85e01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,480 @@
+---
+title: Implementando nuevos idiomas en `/learn`
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Actualizando los ajustes de Crowdin
+
+Antes de poder publicar un nuevo idioma, tendrás que permitir que los idiomas se descarguen de Crowdin. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Luego, busca la opción `Language Mapping`, donde encontrarás la opción de añadir códigos personalizados para los idiomas. Añade una nueva entrada para el idioma que publicarás: seleccionando `language` como el valor de `Placeholder` e ingresando el nombre del idioma en minúsculas para el valor de `Custom code`. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). Los pasos a seguir en los dos casos son iguales. Por ejemplo, si quisieras habilitar las descargas de Dothraki, la instrucción a añadir en los dos documentos sería:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Ten en cuenta que la opción `download_language` deberá corresponder al código del idioma que aparece en Crowdin.
+
+## Habilitando un idioma
+
+> [!NOTA] La sección anterior con la actualización de los flujos de trabajo debería estar completos antes de continuar, estos deben hacerse en pasos separados o las compilaciones fallarán.
+
+Hay algunos pasos a seguir para permitirle a la base de código compilarse a tu idioma de preferencia.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. Aquí hay varios objetos.
+
+- `Languages`: Add the new language to `Languages` enum, similar to the others. The string value here will be used in the `.env` file to set a build language later.
+- `availableLangs`: Add the new property from the `Languages` enum to both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays.
+- `i18nextCodes`: Estos son los códigos de idioma ISO para cada lenguaje. Necesitarás añadir el código ISO correspondiente para el idioma que estás activando. Estos deben ser únicos para cada lenguaje.
+- `LangNames`: Estos son los nombres mostrados para el selector de idiomas en el menú de navegación.
+- `LangCodes`: Estos son los códigos de idiomas usados para formatear fechas y números. Estos deben ser códigos Unicode CLDR en vez de los códigos ISO.
+- `hiddenLangs`: Estos idiomas no se mostrarán en el menú de navegación. Esto es usado para los idiomas que todavía no están listos para su lanzamiento. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: These are languages that read from right to left.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `i18n.ts` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+:::note
+When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+:::
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configure Search
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. Estos datos son utilizados por la barra de búsqueda que carga artículos de `/news`. Si bien es poco probable que vayas a probar esta funcionalidad, lea falta de datos para tu lenguaje puede llevarle a errores al intentar construir el código base localmente.
+
+Agrega un objeto para al objeto `algoliaIndices`. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+:::note
+Si ya hemos desplegado una instancia de noticias en tu destino de idioma, puedes actualizar los valores para reflejar la instancia real. De lo contracio, use los valores del inglés.
+:::
+
+Si tuvieras que añadir el idioma Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+Necesitará dar un paso adicional para manejar las traducciones de la interfaz de usuario del cliente.
+
+Los flujos de trabajo de Crowdin bajarán automáticamente _algunas_ traducciones de la interfaz de usuario, pero hay un par de ficheros que necesitan ser movidos manualmente.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+Para los desafìos de video, debe cambiar algunas cosas. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. Por ejemplo, agregando a Dothraki para la consulta:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Luego agregue un ID para el nuevo idioma a cualquier desafío de video en un bloque auditado. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. La parte delantera debería verse así:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Actualice la interfaz `VideoLocaleIds` en `client/src/redux/prop-types` para incluir el nuevo idioma.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+Si desea probar las traducciones localmente, antes de añadirlas a nuestro repositorio principal, salte los cambios del flujo de trabajo de Crowdin. Siga los pasos para activar un idioma, luego descargue las traducciones de Crowdin y cargue las traducciones en su código local.
+
+Como el lenguaje no ha sido aprovado para producción, nuestros scripts aún no descargan las traducciones de manera automática. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Una vez que poseas los archivos, necesitarás colocarlos en el directorio correcto. Para los desafíos de currículum, deberías colocar las carpetas de certificación (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) dentro del directorio `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Para nuestras traducciones al Dothraki, deberia ser `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. La traducción del cliente `.json` archivos irá al directorio `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Actualice su archivo `.env` para usar su nuevo idioma para `CLIENT_LOCALE` y `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `pnpm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+> [!TIP] If you build the client in one language and then want to build it in a different language, you will need to use the command `pnpm run clean-and-develop` after changing the `.env` file, as Gatsby will cache the first language.
+
+:::danger
+Si bien puedes realizar traducciones localmente con motivos de prueba, le recordamos a todos que las traducciones _no_ deben ser enviadas a través de GitHub, estas deben ser enviadas únicamente a traves de Crowdin. Asegúrate de reestablecer tu base de código local despues de que hayas finalizado con las pruebas.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Deploying New Languages on `/news`
+
+To deploy News for a new language, you'll need to create two PRs. One PR will be to the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), and the other will be to the [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News sources trending links and article titles from our CDN during the build and adds them to the footer. News also fetches Day.js files from the CDN during the build to localize dates and times for each language.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Clone the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) and create a new branch.
+
+In the [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) directory, create a new file and name it `language.yaml`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Then copy the contents of the [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) trending file and paste it into the new YAML file you just created.
+
+The contents will look something like this:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+By default, Day.js only includes English as a locale. To enable it to work with other languages, you need to add a new Day.js locale file to the CDN.
+
+In the [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) directory, create a new file and name it `isocode.min.js`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `mis.min.js`.
+
+:::note
+The version number will change as the dependencies are updated.
+:::
+
+Then, visit [this page on cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) with all available Day.js files for the version we're using, find the `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` link for the new language, and open it in a new tab.
+
+:::note
+You only need to add the .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js locale file. You do not need to add any other Day.js files.
+:::
+
+Copy the Day.js locale code from the new tab into the new file you created. For example, here is an un-minified version of the English locale code for Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Then open a PR to the CDN repo to add both the YAML and Day.js files for review.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+The [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) pulls data from a Ghost instance, the files you added to the CDN, builds News, and deploys it.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. You should not work off of a fork for this step.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Clone the News repo and create a new branch.
+
+Open the `config/index.js` file to add the new language and configure the necessary values. There are a few objects and arrays to modify:
+
+- `locales`: This array contains the active and upcoming News languages. These are the values that are used in the `.env` file to choose the Ghost instance and UI to use for each build. Add the text name of the new language in lowercase to this array.
+- `localeCodes`: This object is a map of ISO codes for each language, and is used to configure i18next before building the UI. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_ and the ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: This object is a map of Algolia indices for each language. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_, and `news-` followed by the lowercase ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+
+:::note
+If you are unsure about the string to use while setting `algoliaIndices`, send a message to Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo), or someone else with access to Algolia, and ask them to check.
+:::
+
+For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, here are what the objects / arrays above should look like:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. For example, if you're launching Dothraki News, create a new folder named `dothraki`.
+
+Then copy the JSON files from the `english` directory to your new folder.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Then commit and push your branch directly to the News repo.
+
+:::note
+You need to be on one of the teams with access to the News repo to push branches directly to News. Currently, only the dev, i18n, and staff teams are allowed to do this.
+:::
+
+Finally, open a PR for review.
+
+Once both your PRs to the CDN and News repo have been approved, they can be merged.
+
+:::note
+Deployment will be handled subsequently by the staff. Here is a sample PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) of how they do it and more details are available in the [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f8521b48
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+Los retos en vídeo son un nuevo tipo de desafío en el currículo de freeCodeCamp.
+
+Un desafío de vídeo es una pequeña sección de un curso de vídeo completo sobre un tema en particular. Una página de desafío de vídeo inserta un vídeo de YouTube. Cada página de desafío tiene una única pregunta de selección múltiple relacionada con el vídeo. El usuario deberá responder correctamente la pregunta antes de avanzar al siguiente desafío de video en el curso.
+
+Las páginas de desafío de vídeo son creadas por miembros del equipo de freeCodeCamp. Los vídeos de YouTube también son subidos por miembros del equipo de freeCodeCamp. Muchos de los desafíos de video todavía no tienen preguntas asociadas a ellos.
+
+Puedes ayudar creando preguntas de selección múltiple relacionadas con las secciones de video y agregando las preguntas a los archivos markdown para los desafíos de video.
+
+## Plantilla de desafío
+
+A continuación se muestra una plantilla de cómo se ven los archivos markdown de los desafíos.
+
+```md
+---
+id: Identificador único (alfanumérico, MongoDB_id)
+title: Título del desafío
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'Id del video de YouTube del video desafío'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --descripción--
+
+Texto de descripción del desafío, en markdown
+
+`` `html
+
+<div>código de ejemplo</div>
+```
+
+# --question--
+
+Estos campos se utilizan actualmente para los desafíos de Python de opción múltiple.
+
+## --text--
+
+El texto de la pregunta va aquí.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Respuesta 1
+
+---
+
+Respuesta 2
+
+---
+
+Más respuestas
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+El número para la respuesta correcta va aquí.
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Skim through the video associated with the challenge and create a multiple-choice question
+
+First, find the `videoId`.
+
+For example, in the following code from the header of a video challenge markdown file, the `videoId` is "nVAaxZ34khk". En GitHub, la información debe ser colocada en un formato de tabla.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+A continuación, accede al vídeo de YouTube con esa `videoId`. The URL for the video will be:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (replace `videoId` in the URL with the video's ID - without square brackets)
+
+In the example above, the URL is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Skim the YouTube video with that `videoId` and think of a multiple-choice question based on the content of the video.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. Para añadir la pregunta localmente, necesitas [configurar freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). También puede encontrar el archivo en GitHub y hacer clic en el botón Editar para añadir la pregunta directamente en su navegador.
+
+Si aún no se ha agregado una pregunta a un desafío de video en particular, tendrá la siguiente pregunta predeterminada:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Question text
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Agrega/Actualiza el texto de la pregunta debajo de la parte que dice:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Añade/Actualiza las respuestas (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, y así) debajo de `## --answers--`. Asegúrate de actualizar el número debajo de `## --video-solution--` con el número de respuesta correcto. Puede añadir más respuestas posibles usando el mismo formato. The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### Ejemplos de preguntas
+
+````md
+# --pregunta--
+
+## --texto--
+
+Qué muestra este código JavaScript en la consola?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hola _mundo_
+
+---
+
+**hola** mundo
+
+---
+
+hola mundo
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --pregunta--
+
+## --texto--
+
+¿Qué se imprimirá después de ejecutar este código?:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+Para más ejemplos, puede ver los archivos de markdown para el siguiente curso de video. Todos los desafíos ya tienen preguntas: [Curso de Python para todos](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+Después de crear una o más preguntas, puedes enviar los cambios a una nueva rama y [abrir una pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d6b031a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: Cómo abrir una Pull Request (PR)
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Una vez que haya hecho cambios en el código, puede seguir estas pautas para abrir un PR.
+
+Esperamos que nuestros colaboradores conozcan el proceso específico de este proyecto. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Algunos ejemplos de ello son:
+
+1. No edite archivos directamente a través de GitHub – mientras pueda, no es una buena idea.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Asegúrate de seguir la lista de PR y no solo marcar las cosas; de lo contrario, no te tomaremos en serio.
+4. Utilice la forma correcta de vincular problemas en la descripción del PR actualizando el `XXXXX`. No solo añada números de emisión en cualquier lugar y donde le plazca.
+5. No usar "@mention" o solicitar comentarios demasiadas veces.
+
+ Entendemos que está emocionado por contribuir. As much as a maintainer will love to get back to you, they are busy people looking after hundreds of requests just like yours. Be patient, someone will get to you sooner or later.
+
+6. Do not work directly off your `main` branch - create a new branch for the changes you are working on.
+
+:::note
+Your PR should be targeting changes to the English curriculum only. Read [this guide](index#translations) instead for contributing to translations.
+:::
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. The convention has the following format:
+
+> `<tipo>([ámbito opcional]): <descripción>`
+>
+> Por ejemplo:
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Type:**
+
+| Tipo | Cuándo seleccionar |
+| :---- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | Sólo si está añadiendo nuevas funcionalidades, pruebas, etc. |
+| chore | Cambios que no están relacionados con el código, las pruebas o la redacción de la lección. |
+| docs | Cambios al directorio `/docs` o a las pautas de contribución, etc. |
+
+**Scope:**
+
+You can select a scope from [this list of labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Description:**
+
+Keep it short (less than 30 characters) and simple; you can add more information in the PR description box and comments.
+
+Some examples of good PR titles would be:
+
+- `fix(a11y): contraste mejorado en la barra de búsqueda`
+- `feat: se agregan más test a los retos de HTML y CSS`
+- `fix(api,client): evitar errores CORS en el envío de formularios`
+- `docs(i18n): se arreglan los enlaces para que sean relativos en lugar de absolutos`
+
+## Proponer una Pull Request
+
+1. Once the edits have been committed, you will be prompted to create a pull request on your fork's GitHub Page.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. By default, all pull requests should be against the freeCodeCamp main repo, `main` branch.
+
+ Make sure that your Base Fork is set to freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp when raising a Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Submit the pull request from your branch to freeCodeCamp's `main` branch.
+
+4. Include a more detailed summary of the changes you made and how your changes are helpful in the body of your PR.
+
+ - Se le presentará una plantilla de pull request. Esta es una lista de verificación que debería haber seguido antes de abrir la solicitud de pull request.
+
+ - Rellene los detalles como considere oportuno. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - Si el PR está pensado para abordar un problema existente de GitHub entonces, al final de el cuerpo de la descripción de su PR, use la palabra clave _Cierra_ con el número de incidencia para [cerrar automáticamente ese problema si se acepta y fusionan las relaciones públicas](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Ejemplo: `Cerrar #123` cerrará el problema 123
+
+5. Indicate if you have tested on a local copy of the site or not.
+
+ - Esto es muy importante cuando se hagan cambios que no sean solo ediciones del contenido de texto como documentación o una descripción de un desafío. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: Enhorabuena por hacer una PR y muchas gracias por tomarse el tiempo para contribuir.
+
+Our moderators will now take a look and leave you feedback. Please be patient with the fellow moderators and respect their time. All pull requests are reviewed in due course.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!TIP] Si vas a contribuir con más PRs, te recomendamos que leas las directrices ["haciendo cambios y sincronizando"](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) para evitar la necesidad de borrar tu bifurcación.
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+Conflicts can arise because many contributors work on the repository, and changes can break your PR which is pending a review and merge.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+When you are working on regular bugs and features on our development branch `main`, you are able to do a simple rebase:
+
+1. Rebase your local copy:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Resolve any conflicts and add / edit commits
+
+ ```bash
+ # Either
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Or
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Push back your changes to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Make sure your upstream comes in sync with your local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Either delete your local branch after taking a backup (if you still have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Start off with a clean slate:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # example:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4b8f8714
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+---
+title: Como revisar traducciones
+---
+
+Nuestro equipo de revisión es responsable de garantizar que las traducciones reflejen con precisión el texto original. Confiamos en nuestro equipo de revisión para asegurarnos de que tenemos traducciones de muy alta calidad.
+
+Todas nuestras traducciones están hechas a mano, por humanos reales. Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+Para comenzar a revisar, visita [nuestra plataforma de traducción](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) e inicia sesión. Selecciona "Ir a la consola" en la barra de navegación superior para cambiar de la vista pública a la vista de espacio de trabajo.
+
+## Seleccionar un archivo
+
+Verás la lista de proyectos a los que se le ha otorgado acceso. Selecciona el proyecto que te gustaría revisar y luego selecciona el idioma.
+
+
+
+Ahora podrás ver la lista de archivos disponibles. Elige tu archivo seleccionando el botón `Proofread` a la derecha de ese archivo, luego elige `Proofreading` en el menú desplegable que aparece.
+
+:::note
+Si estás en la vista "workspace" pero quieres trabajar en [traducir un archivo](how-to-translate-files) en lugar de revisar, puedes seleccionar la opción `Crowdsourcing` del menú desplegable.
+:::
+
+## Revisar traducciones
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Aquí verás la lista de cadenas en el archivo seleccionado, con sus traducciones correspondientes. La traducción que se muestra aquí es la traducción que ha recibido la puntuación más alta (entre votos a favor y en contra) de la comunidad de traducción.
+
+Mientras puedas ver _todas_ las traducciones propuestas para una cadena determinada, las puntuaciones de la comunidad (determinadas por los votos a favor y en contra) deben tenerse en cuenta al elegir cuál traducción aprobar. La comunidad puede revisar las traducciones propuestas y recomendar cuál es la más clara y precisa.
+
+1. Este es el segmento original (en inglés).
+2. Este es el segmento traducido que le corresponde. Aquí se mostrará la traducción propuesta más popular, según sus votos positivos y negativos.
+3. Al hacer clic en este botón de tilde aprobarás esa traducción.
+4. Crowdin mostrará el estado de cada segmento. `Done` (listo) significa que una traducción ha sido aprobada y que será descargada en el próximo pull de Crowdin. `Todo` (por hacer o "to do") significa que el segmento aún no ha sido revisado. `Hidden` (Oculto) significa que la cadena está bloqueada y _no debe traducirse_. `Comment` significa que la cadena de texto incluye un comentario.
+5. Puedes usar las casillas de verificación para seleccionar varias traducciones y aprobarlas en un solo paso.
+6. Aquí puedes ver las traducciones propuestas por la comunidad, sus puntajes de popularidad y las traducciones sugeridas por Crowdin.
+7. Este botón muestra/oculta el panel del lado derecho, donde puedes ver traducciones, comentarios, la memoria de traducciones y el glosario de términos.
+8. Crowdin muestra aquí los mensajes de error de las verificaciones de calidad (QA / quality assurance). En otras palabras, Crowdin te notificará si algo en la traducción no parece estar correcto. Estas traducciones deberían ser aprobadas cuidadosamente.
+
+No se requieren acciones adicionales una vez que el archivo ha sido revisado.
+
+:::note
+Aprobar una cadena en la vista de revisión la marcará como completa y se descargará en nuestra próxima extracción de Crowdin a GitHub.
+:::
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+Si tiene alguna pregunta o le interesa colaborar en el equipo de revisión, sientase libre de contactarnos en nuestra [sala de chat de contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Generalmente, le concederemos acceso a la corrección si ha estado contribuyendo a freeCodeCamp durante un tiempo.
+
+Nuestro equipo de personal y de moderadores de la comunidad buscan constantemente voluntarios amables como tú que nos ayuden a poner a disposición del mundo traducciones de alta calidad.
+
+:::note
+Crowdin te permite aprobar tus propias traducciones. Sin embargo, en general suele ser mejor permitir que otro corrector revise tus traducciones propuestas como medida adicional para asegurarse que no hayan errores.
+:::
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+Si ya eres un revisor y estás interesado en tener un canal dedicado en nuestros servidores de chat para un idioma específico, [completa este formulario](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ec03797e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,297 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Sigue estas directrices para configurar un entorno de desarrollo para freeCodeCamp. Esto es altamente recomendable si desea contribuir regularmente.
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows. - You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase. - Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+ :::
+
+Si deseas hacer una contribución puntual, debes utilizar Gitpod para realizar cambios. La configuración de Gitpod lanza un entorno listo para codificar en pocos minutos en tu navegador web. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Estos son algunos pros y contras que deberían ayudarte a decidir cuál es la mejor opción para ti:
+
+| Gitpod | Su propia máquina (configuración local) |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| Sin requisitos mínimos de hardware | Requisitos específicos y mínimos |
+| No es necesario instalar ningún software | Software adicional necesario |
+| Copia del repositorio siempre actualizada | Necesidad de mantener una copia local del repositorio |
+| Más lento y puede tardar unos minutos en iniciarse | Más rápido y puede ponerse en marcha en segundos |
+| Necesita conexión a Internet para funcionar | Requiere una conexión mínima a Internet (una vez configurado) |
+| Algunas tareas, como la compilación y las pruebas, pueden llevar más tiempo | Realización más rápida de las tareas (en función de las capacidades de tu máquina) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+Hemos automatizado el proceso de instalación de todas las dependencias & herramientas que necesitarás. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Más rápido)** Añade `gitpod.io/#` a cualquier URL de GitHub.
+
+ Por ejemplo, si visitas tu fork en `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, añade `gitpod.io/#` delante de la URL en la barra de direcciones y pulsa enter.
+
+ Es decir, puedes navegar a `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` y debes ver un espacio de trabajo creado para ti. Esto funciona para cualquier repositorio o pull-request en GitHub.
+
+2. También puedes instalar una de las siguientes extensiones para tu navegador.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - funciona con navegadores basados en Chromium como Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc.
+ - [Complemento para Firefox](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. Consulta la página de la extensión para más detalles, capturas de pantalla, etc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### Pre-requisitos:
+
+| Pre-requisitos | Versión | Notas |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | Utilizamos la versión "Active LTS", Ve [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+Si tienes una versión diferente, instala la versión recomendada. Sólo podemos resolver problemas de instalación de las versiones recomendadas. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+> [!TIP] Recomendamos encarecidamente actualizar a las últimas versiones estables del software mencionado anteriormente, también conocidas como versiones de soporte a largo plazo (LTS).
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### Sigue estos pasos para dejar listo tu entorno de desarrollo:
+
+1. Instala [Git](https://git-scm.com/) o tu cliente Git favorito, si aún no lo has hecho. Actualiza a la última versión; la versión incluida con tu sistema operativo puede estar obsoleta.
+
+2. (Opcional pero recomendado) [Configura una clave SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) para GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ > [!TIP] Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+> [!TIP] The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+>
+> Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+> [!WARNING] If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`). Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further information about this problem.
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# Crear una copia de la "sample.env" y nombrarla ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+> [!TIP] Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+:::note
+Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
+
+If you followed along with the [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), then you should be able to skip this step if the MongoDB server from that guide is already running. You can confirm this by checking that you can reach `http://localhost:27017` on your local machine.
+:::
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+> [!TIP] You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+> [!WARNING] Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ef2a1cc6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,508 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp Mobile App locally
+---
+
+Siga esta guía para establecer la aplicación móvil FreeCodeCamp en su sistema. Es altamente recomentado si se quiere contribuir regularmente.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Empezar instalando el software requerido previamente para su sistema operativo.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Requisito | Versión | Notas |
+| ------------------------------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (viene junto con Flutter) | `3.x` | Usamos la versión que viene con Flutter. |
+
+> [ATENCIÓN!] Si hay una versión diferente, por favor instalar la versión recomendada. Solo daremos soporte a problemas de instalación de versiones recomendadas.
+
+Si Flutter ya está instalado en su equipo, ejecute los siguientes comandos para verificar la versión:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+> [!TIP] Pedimos encarecidamente actualizar a la última version "stable" del siguiente software.
+
+Una vez que estén instalados los requisitos previos, hay que preparar el entorno de desarrollo. Es muy común para muchos equipos de trabajo, y solo hace falta hacerlo una vez.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Instalar [Git](https://git-scm.com/) u otro cliente Git, si todavía no hay ningumo. Acualizar a la versión más reciente. La que viene con el sistema operativo puede estar desactualizada.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. Recomendamos usar Pixel 3a XL y Nexus One(para emular pantallas más pequeñas).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Opcional pero recomendado) [Configurar una clave SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) para GitHub.
+
+5. Instala un editor de código de tu elección.
+
+ Recomendamos utilizar [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) o Android Studio. También recomendamos instalar las [extensiones oficiales](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Fork](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) es un paso donde consigues tu propia copia del repositorio (conocido como _repo_) en GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Más adelant, podrás solicitar cambios para que se muestren en el repositorio principal de tu "fork" (bifurcación) a través de una "pull request" (PR).
+
+> [!TIP] El repositorio principal en `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` es frecuentemente conocido como el repositorio `upstream`.
+>
+> Tu fork en `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` suele referirse como el repositorio `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` será remplazado con tu nombre de usuario de GitHub.
+
+**Sigue estos pasos para hacer un for del repositorio `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile`:**
+
+1. Ve al repositorio freeCodeCamp móvil en GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Haz clic en el botón "Fork" en la esquina superior derecha de la interfaz ([Más detalles aquí](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Después de haber hecho fork al repositorio, serás llevado a tu copia del repositorio en `https://github. om/NOMBRE_DE_USUARIO/mobile` (`OMBRE_DE_USUARIO` sería reemplazado con tu nombre de usuario de GitHub.)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+"[Clonar](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/)" es donde tú "**descargas**" una copia de un repositorio desde una localización "`remota`" que es propiedad tuya o de alguien más. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`TU_NOMBRE_DE_USUARIO` debería ser reemplazado con tu nombre de usuario de GitHub.)
+
+Ejecuta estos comandos en tu máquina local:
+
+1. Abre una Terminal / Símbolo del sistema / Shell en el directorio de proyectos
+
+ _ejemplo: `/directoriodetusproyectos/`_
+
+2. Clona tu fork de freeCodeCamp, reemplazando `TU_NOMBRE_DE_USUARIO` por tu nombre de usuario de GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clon --depth=1 https://github.com/TU_NOMBRE_DE_USUARIO/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+Esto descargará el repositorio entero de freeCodeCamp móvil en tu directorio de proyectos.
+
+Nota: `--depth=1` crea un clon superficial de tu fork con solo la historia/commit más reciente.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Ahora que has descargado una copia de tu fork, necesitarás configurar un `upstream` remoto en el repositorio padre.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+Necesitas una referencia de tu clon local al repositorio `upstream` además del repositorio `origin`. Esto es para que puedas sincronizar los cambios desde el repositorio principal sin el requisito de hacer fork y clonar repetidamente.
+
+1. Cambiar el directorio al nuevo directorio `móvil`:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Añadir una referencia remota al repositorio principal de freeCodeCamp móvil:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Asegúrate de que la configuración se vea correcta:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ La salida debería verse parecida a como se muestra debajo (remplazando `TU_NOMBRE_DE_USUARIO` con tu usuario de GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Ahora que tienes una copia local de la app móvil de freeCodeCamp, puedes seguir estas instrucciones para ejecutarla localmente.
+
+Si tienes problemas, primero realiza una búsqueda web para tu problema y comprueba si ya ha sido respondida. Si no encuentras una solución, por favor busca en nuestra página [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) para una solución y reporta el problema si aún no ha sido reportado.
+
+Y como siempre, siéntete libre de preguntar en la categoría ['Contribuyentes' en nuestro foro](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [nuestro servidor de chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::note
+El directorio `móvil` contiene dos carpetas, por ejemplo: `mobile-api` y `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contiene el código API utilizado para ejecutar los podcasts. `mobile-app` contiene la aplicación Flutter que es donde deberías estar cuando siga los pasos siguientes.
+:::
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+Las claves de la API por defecto y las variables de entorno se almacenan en el archivo `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Recuerda cambiar el directorio a `mobile-app` antes de ejecutar los siguientes comandos.
+
+```bash
+# Crear una copia del "sample.env" y nombrarla ".env".
+# Llenarlo con las keys y secrets de la API necesarios:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+Las claves dentro del archivo `.env` _no_ requieren ser cambiadas para correr la aplicación de forma local. Puedes dejar los valores por defecto copiados desde `sample.env`.
+
+#### Paso 2: Instalar dependencias
+
+Este paso instalará las dependencias necesarias para que la aplicación se ejecute:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Paso 3: Iniciar la app móvil de freeCodeCamp
+
+Inicia el emulador de tu elección (Android o iOS) y espera a que se complete el proceso de arranque.
+
+Ahora puedes iniciar la aplicación ejecutando el siguiente comando:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+> [!TIP] Si estás utilizando VSCode o Android Studio entonces puedes iniciar fácilmente la aplicación sin tener que ejecutar ningún comando en la terminal. Más información [aquí](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Sigue estos pasos:
+
+1. Valida que estás en la rama `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Deberías obtener una salida como esta:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ Si no estás en main o tu directorio de trabajo no está limpio, resuelve cualquier archivos/commits pendientes y comprueba `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sincroniza los últimos cambios desde la rama principal `main` a tu rama local main:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Si tienes algún pull request pendiente que hayas hecho desde la rama `main` de tu fork, los perderás al final de este paso.
+ >
+ > Deberías asegurarte de que tu pull request esté hecho merge por un moderador antes de realizar este proceso. Para evitar este escenario, deberías **siempre** trabajar en una rama que no sea `main`.
+
+ Este paso **sincronizará los últimos cambios** desde el repositorio móvil de freeCodeCamp. Es importante que hagas rebase de tu rama sobre la última `principal/main` tan a menudo como sea posible para evitar conflictos más tarde.
+
+ Actualiza tu copia local del repositorio de freeCodeCamp móvil:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Restablece tu rama main con el main de freeCodeCamp móvil:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Has push de tu rama main a tu origen para tener un historial limpio en tu fork en GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ La salida resultante debería estar vacía.
+
+3. Crear una nueva rama:
+
+ Trabajar en una rama separada para cada asunto te ayuda a mantener limpia tu copia de trabajo local. Nunca deberías trabajar en `main`. Esto sumergirá tu copia de freeCodeCamp móvil y puede que tengas que empezar otra vez con un clon o un fork nuevo.
+
+ Comprueba que estás en `main` como se explicó anteriormente, y ramifica desde ahí:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Tu nombre de rama debería comenzar con `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Evita el uso de números de incidencia en las ramas. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Algunos ejemplos de buenos nombres de ramas son:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edita páginas y trabaja en el código en tu editor de texto favorito.
+
+5. Una vez que estés contento con los cambios, deberías ejecutar la aplicación móvil localmente para previsualizar los cambios (opcional).
+
+6. Asegúrate de corregir los errores y comprobar el formato de tus cambios.
+
+7. Comprueba y confirma los archivos que estás actualizando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Esto debería mostrar una lista de archivos `unstaged` que has editado.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Organizar los cambios y hacer un commit:
+
+ En este paso, sólo deberías marcar los archivos que has editado o añadido tu mismo. Puede realizar un reset y resolver archivos que no tenías intención de cambiar si es necesario.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add ruta/al/archivo/editado.ext
+ ```
+
+ O puedes añadir todos los archivos que no estén `organizados` al área de staging:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Sólo los archivos que fueron movidos al área de staging serán añadidos cuando hagas un commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Salida:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Ahora, puedes hace commit de tus cambios con un mensaje corto, así:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: mensaje corto"
+ ```
+
+ Algunos ejemplos:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Opcional:
+
+ Recomendamos encarecidamente hacer un mensaje de commit convencional. Esta es una buena práctica que verás en algunos de los repositorios de Código Abierto populares. Como desarrollador, esto te anima a seguir las prácticas estándar.
+
+ Algunos ejemplos de mensajes de commits convencionales son:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Manténlos cortos, no más de 50 caracteres. Siempre puedes añadir información adicional en la descripción del mensaje del commit.
+
+ Esto no toma más tiempo que un mensaje no convencional como 'actualizar archivo' o 'añadir index.md'
+
+ Puedes aprender más sobre por qué debes usar commits convencionales [aquí](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Si te das cuenta de que necesitas editar un archivo o actualizar el mensaje de confirmación después de hacer un commit puedes hacerlo después de editar los archivos con:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Esto abrirá un editor de texto predeterminado como `nano` o `vi` donde puedes editar el título del mensaje de commit y añadir/editar la descripción.
+
+10. A continuación, puedes enviar tus cambios a tu fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin nombre/rama-aqui
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+:::note
+You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+:::
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+Después de que hayas hecho commit de tus cambios, consulta aquí [cómo abrir una Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Problemas con la instalación de los prerrequisitos recomendados
+
+Regularmente desarrollamos en los últimos o sistemas operativos más populares como macOS 10.15 o posterior, Ubuntu 18.04 o posterior y Windows 10 (con WSL2).
+
+Se recomienda buscar tu problema específico en recursos como Google, Stack Overflow y Stack Exchange. Existe la posibilidad de que alguien haya tenido el mismo problema y ya exista una respuesta a tu pregunta específica.
+
+Si estás en un sistema operativo diferente y/o todavía tienes problemas, consulta [obtener ayuda](#getting-help).
+
+### Problemas con la interfaz de usuario, fuentes, errores de compilación, etc.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+Si estás atascado y necesitas ayuda, siéntete libre de hacer preguntas en la categoría de ['Contribuyentes' en nuestro foro](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o en [la sala de chat de contribuyentes](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Puede haber un error en la consola de tu navegador o en Bash / Terminal / Línea de comandos que te ayudará a identificar el problema. Proporciona este mensaje de error en la descripción de tu problema para que otros puedan identificar el problema más fácilmente y ayudarte a encontrar una solución.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c872707d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,233 @@
+---
+title: Configurar freeCodeCamp en el subsistema de Windows para Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+:::note
+Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+
+**WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Versión 2004, Build 19041 o superior) - disponible para todas las distribuciones incluyendo Windows 10 Home.
+
+**Docker Desktop para Windows**: Vea los requisitos correspondientes para [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) y [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+:::
+
+Esta guía cubre algunos pasos comunes con la configuración de WSL2. Una vez que algunos de los problemas habituales con WSL2 son solucionados, deberías de ser capaz de seguir [esta guía de configuración local](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)para trabajar con freeCodeCamp en Windows corriendo una distribución WSL como Ubuntu.
+
+## Habilitar WSL
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Instalar Ubuntu
+
+1. Recomendamos usar Ubuntu-18.04 o superior con WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Actualizar las dependencias del sistema operativo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Configurar Git
+
+Git viene pre-instalado con Ubuntu 18.04, verifica tu versión de Git con `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Opcional, pero recomendado) Ahora puedes proceder a [configurar tus claves ssh](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) con GitHub.
+
+## Instalar un editor de código
+
+Recomendamos encarecidamente instalar [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) en Windows 10. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+Esencialmente, editaras y almacenaras tu código en Ubuntu-18.04 con el VS Code instalado en Windows.
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Instalando Docker Desktop
+
+**Docker Desktop para Windows** te permite instalar y ejecutar bases de datos como MongoDB y otros servicios como NGNIX y más. Esto sirve para evitar trampas cuando se instala Mongo DB u otros servicios directamente desde Windows o WSL2.
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
+
+Hay unos requrimientos mínimos de hardware para una mejor experiencia.
+
+## Configurar Docker Desktop para WSL
+
+Una vez instalado Docker Desktop, [sigue estas instrucciones](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) y configúralo para usar la instalación de Ubuntu-18.04 como un backend.
+
+Esto hace que los contenedores se ejecuten del lado de WSL en vez de Windows. Serás capaz de acceder a servicios de `http://localhost` tanto en Windows como en Ubuntu.
+
+## Instalar MongoDB desde Docker Hub
+
+Una vez que hayas configurado Docker Desktop para trabajar con WSL2, sigue estos pasos para iniciar un servicio MongoDB:
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Inicia el servicio MongoDB en el puerto `27017`, y configúralo para que se ejecute automáticamente al reiniciar el sistema
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Ahora puedes acceder al servicio desde Windows o Ubuntu en `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Installing Node.js and pnpm
+
+Recomendamos que instales la versión LTS de Node.js con un gestor de versiones de node - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. Aún así deberías poder trabajar en la mayor parte del código base.
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Preguntas frecuentes sobre:
+ - [Subsistema de Windows para Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop para Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9d67360e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,225 @@
+---
+title: Cómo probar las traducciones localmente
+---
+
+:::note
+Este proceso no es requerido, pero esta documentado en caso de que quieras previsualizar como lucirán tus traducciones.
+:::
+
+En caso de que quieras probar tus traducciones en una instancia local del sitio `/learn` de freeCodeCamp, primero asegúrate de haber [configurado la base de código](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Habilitando un lenguage
+
+Hay algunos pasos a seguir para permitirle a la base de código compilar en tu lenguaje deseado.
+
+Primero, visita el archivo `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` para agregar el idioma a la lista de lenguajes disponibles y configurar los valores. Hay cuatro objetos aquí.
+
+- `avaliableLangs`: Tanto para el arreglo `client` como para el arreglo `curriculum`, añade el nombre en texto del lenguaje. Este es el valor que se utilizará en el archivo `.env` más tarde.
+- `auditedCerts`: Agrega el nombre del texto como la _clave_, y añade un arreglo de variables de `SuperBlocks.{cert}` como el _value_. Esto le dice al cliente qué certificaciones están totalmente traducidas.
+- `i18nextCodes`: Estos son los codigos de idioma ISO para cada lenguaje. Necesitarás añadir el código ISO apropiado para el idioma que estás activando. Estos deben ser únicos para cada lenguaje.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. Estos deben ser códigos CLDR Unicode en lugar de códigos ISO.
+
+Por ejemplo, si quisieras habilitar Dothraki como un lenguaje, tus objetos `all-langs.js` deberían verse así:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+A continuación, abre el archivo `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts` file. Estos datos son utilizados por la barra de búsqueda que carga artículos de `/news` (noticias). Si bien es poco probable que pruebe esta funcionalidad, la falta de datos para su idioma puede provocar errores al intentar crear la base de código localmente.
+
+Agregue un objeto para su idioma al objeto `algoliaIndices`. You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+:::note
+Si ya hemos desplegado una instancia de noticias en tu idioma de destino, puedes actualizar los valores para reflejar la instancia real. De lo contrario, utiliza los valores en inglés.
+:::
+
+Si tuvieras que agregar Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ };
+```
+
+Finalmente, en tu archivo `.env`, configura `CLIENT_LOCALE` y `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` a tu nuevo lenguaje (usa el valor `availableLangs`)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## Habilitar Videos Localizados
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Cargando traducciones
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+Si bien puedes realizar traducciones localmente con motivos de prueba, le recordamos a todos que las traducciones _no_ deben ser enviadas a través de GitHub, estas deben ser enviadas únicamente a traves de Crowdin. Asegúrate de reestablecer tu base de código local despues de que hayas finalizado con las pruebas.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d327dc61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,351 @@
+---
+title: Cómo traducir recursos de freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+## Prepare yourself for Contributions
+
+> Guía de orientación de freeCodeCamp - Sin límites de velocidad
+
+> [!TIP] Puedes comenzar leyendo [este anuncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). Recomendamos unirte a [nuestro foro de la comunidad](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) y al [servidor de Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Puedes traducir tanto como quieras, y cuando quieras. Es solo cuestión de cuánto tiempo y energía estás dispuesto a invertir como traductor voluntario.
+
+solo queremos que entiendas lo siguiente:
+
+1. **Las traducciones son un esfuerzo de equipo.**
+
+ Traducir los recursos de freeCodeCamp es una de las experiencias más divertidas y gratificantes como colaborador, y funciona mejor si involucras a tus amigos y colegas que hablan el mismo idioma que tú.
+
+ Puedes comenzar leyendo [este anuncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). Recomendamos te unas al [foro de la comunidad](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) y al [servidor de Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) con tus amigos, y muestres tu interés antes de comenzar a traducir. Crowdin y otras herramientas facilitan contribuir con traducciones, sin embargo, sigue siendo bastante de trabajo.
+
+ Queremos que disfrutes contribuyendo y no te canses o pierdas interés.
+
+ Un grupo pequeño de 4 a 5 personas es un buen tamaño para comenzar tu específico idioma. Y después puedes reclutar aún más amigos para unirse al equipo.
+
+2. **Cuesta bastante girar servidores para cada idioma.**
+
+ En la superficie puede no parecer lo complicado que es la pila técnica, pero cuesta bastante mantener los motores en funcionamiento. Esto incluye el aprovisionamiento de servidores adicionales y la dedicación de personal para cuidarlos.
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org está comprometido a ofrecerlos gratis como siempre. Sin embargo, debemos priorizar los recursos para aquellos que más lo necesitan. Lo último que queremos es cerrar los servidores de un idioma si la actividad de traducción se apaga y las cosas se vuelven obsoletas.
+
+ Al traducir el currículo, una vez que un idioma alcance al menos unas cuantas certificaciones, podremos comenzar a implementar el idioma en [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), mientras continúas traduciendo las certificaciones restantes.
+
+ Por ejemplo, nos gustaría implementar al menos toda la suite de certificaciones de front-end cuando enviamos un nuevo idioma por primera vez.
+
+3. **Pero, ¿qué pasa con los idiomas que no figuran en la plataforma de traducción?**
+
+ Hemos revisado nuestra base de usuarios y hemos añadido más de 30 idiomas más hablados a la lista de idiomas habilitados en la plataforma de traducciones. Algunos idiomas como el chino y español ya están implementados en vivo en **"/learn"** en este momento.
+
+ Desafortunadamente, la lista no incluye cientos de idiomas. Recibimos docenas de solicitudes de colaboradores como tú todos los días que quieren ayudar a traducir el sitio a un idioma que hablan.
+
+ Definitivamente estamos deseando agregar más idiomas a la lista, pero como ya puedes adivinar, solo sería factible si obtenemos suficiente impulso alrededor de un idioma.
+
+ Si deseas que incluyamos un nuevo idioma, te recomendamos que entusiasmes a tus amigos con esto.
+
+ Una vez que tengas un pequeño grupo de personas (al menos 4-5) interesadas y comprometidas, podemos llamar. Te explicaremos todos los detalles y te guiaremos a través de algunas de las herramientas y procesos.
+
+## Vista previa de Crowdin
+
+Nuestro sueño es brindate los recursos para aprender, sin importar el idioma que hables. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source codebase & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
+
+:::note
+Utilizamos una herramienta y un flujo de trabajo diferentes para traducir [artículos de noticias](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). Si te interesa traducir artículos, lee [este anuncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) y contacta al traductor lider de tu idioma.
+:::
+
+El flujo de trabajo de traducción se divide en dos actividades principales:
+
+- **Traduciendo** archivos de currículo, documentación y elementos de interfaz de usuario como botones, etiquetas, etc.:
+
+ Como traductor puedes registrarte en [nuestra plataforma de traducción](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) y contribuir con las traducciones en cualquiera de los más de 30 idiomas habilitados allí.
+
+- **Revisando** las traducciones de todo lo anterior.
+
+ Los revisores verifican que las traducciones aportadas por la comunidad sean uniformes en el tono y libres de problemas comunes como errores tipográficos, etc. En resumen, aseguran que la calidad de las traducciones sea alta. Ten en cuenta que no utilizamos traducciones automáticas por una razón.
+
+> [!WARNING] Ya no estamos usando GitHub para traducir archivos directamente. Si fuiste colaborador y estás regresando, entonces dirígete a nuestra [plataforma de traducción](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+## Getting Started
+
+Primero, asegúrate de decir "Hola" en nuestro [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Publicamos actualizaciones regulares sobre los recursos de traducción y respondemos a muchas de tus consultas allí.
+
+A continuación, dirígete a nuestro [plataforma de traducción](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) e inicia sesión (si no has contribuido a traducciones anteriormente, deberás crear una cuenta).
+
+Por último, ve a través del recorrido detallado a continuación para comprender las herramientas de traducción y los flujos de trabajo a tu disposición.
+
+Feliz traducción.
+
+## Selecciona un Proyecto y un Archivo
+
+Una vez que visites la plataforma de traducción, verás varios "proyectos" disponibles para traducción:
+
+1. [Documentación del proyecto de contribución ](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs), el cual contiene los archivos para este sitio de documentación.
+2. [Proyecto de currículo de programación](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum), el cual contiene nuestros archivos de desafío para nuestro plan de estudios.
+3. [Aprende Interfaz de usuario](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui) proyecto que contiene cadenas para elementos de interfaz de usuario como botones, etiquetas, etc. para nuestra plataforma de aprendizaje.
+
+Selecciona cualquier proyecto al que desees contribuir y verás una lista de los idiomas disponibles para la traducción.
+
+
+
+Selecciona el idioma en el que deseas trabajar y verás el árbol de archivos completo.
+
+
+
+Cada archivo y carpeta mostrará una barra de progreso. La parte **azul** de la barra de progreso indica qué porcentaje del archivo se ha traducido, mientras que la parte **verde** de la barra de progreso indica qué porcentaje del archivo ha sido aprobado por el equipo de revisión.
+
+Selecciona un archivo para trabajar y Crowdin abrirá la vista de edición.
+
+:::note
+Cuando se abra la vista de edición, deberás hacer clic en el icono de configuración (que se muestra como un engranaje) y cambiar la configuración ''HTML tags displaying (Mostrar etiquetas HTML)" por "SHOW (Mostrar)". Esto asegurará que puedas ver las etiquetas como `<code></code>` en lugar de `<0></0>`.
+:::
+
+## Traducir el Currículo
+
+
+
+Crowdin separa un documento en "cadenas" traducibles, normalmente oraciones. Cada cadena se traduce individualmente. Tomando como referencia la imagen anterior:
+
+1. Una cadena resaltada en verde ya tiene una traducción propuesta.
+2. Una cadena resaltada en rojo _no_ tiene una traducción propuesta.
+3. Una cadena con texto en gris no es traducible. Este es el caso de los bloques de código y otros contenidos que no deben traducirse. No podrás seleccionar estas cadenas en el editor.
+4. Si un contribuyente ha propuesto una traducción a una cadena, Crowdin mostrará esas propuestas aquí. No podrás guardar una traducción idéntica, en su lugar, si una traducción es precisa, debes hacer clic en el ícono `+` para votar a su favor. Puedes votar en contra de una traducción inexacta con el icono `-`.
+5. Crowdin recomendará traducciones basadas en Memoria de Traducción (TM) o Traducción Automática (MT). La memoria de traducción se refiere a cadenas similares o idénticas que hemos traducido / aprobado en otros archivos. La Machine Translation (traducción automática) remite hacia las traducciones recomendadas por su biblioteca integrada.
+6. Este es el panel del editor, donde puedes escribir tu propuesta de traducción para la cadena seleccionada.
+7. La cadena seleccionada actualmente en el editor se resaltará en amarillo.
+8. Aquí verás etiquetas que indican el estado de la cadena. `Done` (hecho) significa que la cadena tiene al menos una traducción propuesta. `Todo` (por hacer) significa que la cadena no tiene ninguna traducción propuesta.
+9. Aquí puedes ver la ventana de comentarios. Si tienes preguntas o inquietudes sobre una cadena en particular, puedes dejar aquí un comentario sobre la cadena para que lo vean otros traductores.
+10. Estos dos botones de "panel" ocultarán las vistas izquierda (documento) y derecha (comentarios).
+
+:::note
+Si observas una cadena oculta que incluye traducciones, por favor notifícanos en el [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) para que podemos eliminar esa traducción de la memoria.
+:::
+
+Cuando hayas completado la traducción de una cadena, pulsa el botón `Save` (guardar) para almacenar tu traducción en Crowdin. Luego, otros contribuyentes podrán votar tu traducción y el equipo de revisores podrán aprobarla.
+
+Eres bienvenido a traducir tantas cadenas como desees, no se requieren pasos adicionales cuando completas todo un archivo o propones una nueva traducción. Hacer clic en el botón `Save` es todo lo que se necesita para almacenar una traducción.
+
+:::note
+Si ves algo en el archivo fuente en inglés que sea inexacto o incorrecto, por favor no lo corrijas a través del flujo de traducción. En su lugar, deja un comentario en la cadena para notificarnos que hay una discrepancia, o crea un issue en GitHub.
+:::
+
+## Traducir la Interfaz de Aprendizaje
+
+Nuestra interfaz `/learn` se basa en archivos JSON cargados en un plugin i18n para generar texto traducido. Este esfuerzo de traducción está dividido entre Crowdin y GitHub.
+
+### En GitHub
+
+Los archivos `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivación.json` y `trending.json` contienen información que necesita ser actualizada para reflejar tu idioma. Sin embargo, no podemos cargarlos en Crowdin, ya que el contenido no es algo que sea una traducción uno-a-uno.
+
+Estos archivos probablemente serán mantenidos por el líder de tu idioma, pero serás bienvenido a [leer sobre cómo traducirlos](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### En Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+No edites los siguientes archivos a través de un PR de GitHub.
+:::
+
+Los archivos `intro.json` y `translations.json` están traducidos en Crowdin, en el proyecto Learn User Interface. Traducir estos puede ser un poco complicado, ya que cada valor JSON individual aparece como su propia cadena y a veces falta contexto.
+
+Sin embargo, la información de `Contexto` proporcionada en Crowdin puede ayudar a entender dónde se ajusta la cadena a la estructura más grande.
+
+
+
+Si tienes alguna pregunta sobre donde encaja una cadena en el texto, contacta con nosotros en nuestro [chat de colaborador](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Traducir la Documentación
+
+Traducir nuestra documentación de contribución es un flujo similar a la traducción de nuestros archivos de currículum.
+
+:::note
+Nuestra documentación de contribución esta basada en `docsify`, y tenemos una forma especial de procesar los cuadros de mensaje como este. Si ves cadenas que comiencen con `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]` o ` [!TIP]`, estas palabras NO deben traducirse.
+:::
+
+### How to Translate Documentation with Internal Links
+
+Cuando trabajes en la traducción de la documentación, ten en cuenta los enlaces internos que apuntan a una sección diferente de la documentación.
+
+Asegúrate de reemplazar el id de la sección de destino (la parte después de `#`) con el id en el documento traducido. Por ejemplo, se verá así en japonés:
+
+Antes de traducir
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Después de traducir
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト]($1#$2)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+Los archivos reales de la documentación están escritos en Markdown, pero aparecerán como etiquetas HTML en Crowdin.
+
+Puedes averiguar cómo `docsify` convierte una cadena en tu idioma en un id mirando las páginas traducidas. Si la traducción no está desplegada todavía, puedes previsualizarla [ejecutar el sitio de la documentación localmente]($1#$2).
+
+Puedes obtener más información sobre [enlaces internos en nuestra documentación aquí](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#como-crear-un-enlace-interno).
+
+## Traducir el LearnToCode RPG
+
+El LearnToCode RPG se ejecuta en Ren'Py, el cual utiliza una sintaxis especial para las cadenas traducidas: (Ver [ documentación de texto Ren'Py](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- Las oraciones a traducir están siempre entre `""`. Estos son diálogos o cadenas de interfaz de usuario. Las palabras clave que vienen antes o después del diálogo son palabras clave de control del motor del juego y se explicarán en detalle en las reglas posteriores. Tenga en cuenta que esta primera regla rige todas las reglas posteriores enumeradas.
+- En el caso de `new "..."` No traduzcas la palabra clave `new`.
+- Prefijos como `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (o variantes como `player happy`, `player @ happy`) no deben traducirse. Estas son palabras clave de control para mostrar correctamente el sprite del personaje en el juego.
+- Postfixes como `nointeract` no deben ser traducidos.
+- No traduzca cosas entre `[]` y `{}`. Estas son interpolaciones variables y etiquetas de texto. Estos deben permanecer entre paréntesis de media anchura `[]` y `{}` en lugar de sus homólogos de ancho completo `【】` y `「」`
+- No traduzca la palabra clave `nointeract` al final de la oración.
+- Si intentamos usar paréntesis de ancho completo `()`, se mostrará una advertencia de QA. Para evitar la advertencia de QA, utilice paréntesis de ancho medio `()`
+
+### Ejemplos
+
+---
+
+#### Antes de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- esta es la línea que necesita traducirse. ver traducción a continuación
+```
+
+#### Después de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我们的VIP队友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}会很高兴的。"
+```
+
+Nota: Las etiquetas `[]` y `{}` deben dejarse intactas.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes de traducir
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- traducir esta línea, ver abajo
+```
+
+#### Después de traducir
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳过"
+```
+
+Nota: De nuevo, el prefijo `new` y la etiqueta `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` deben dejarse intactos.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### Después de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定会喜欢你的开发者工作的。"
+```
+
+Nota: `layla @ neutral` y `[player_name]` se quedan sin cambios.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### Después de traducir
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也许这都是一场梦?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Una observación sobre cómo Crowdin segmenta una oración
+
+Presta atención a cómo Crowdin segmenta una línea de diálogo envuelta entre comillas de apertura y cierre `""`. Cuando traducimos el diálogo, tenemos que asegurarnos de mantener las comillas de apertura y cierre, incluso si las comillas aparecen en diferentes segmentos.
+
+Esta es la línea a traducir:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin lo segmenta en tres partes como a continuación:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Captura de pantalla 2022-01-23 a las 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# traducido, manteniendo las comiilas de apertura `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Captura de pantalla 2022-01-23 a las 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+What is that?
+# traducido, sin comillas en ninguno de los lados.
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Captura de pantalla 2022-01-23 a las 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# traducido, manteniendo las comillas de cierre `"`
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## Calificar traducciones
+
+Crowdin te permite calificar las traducciones propuestas existentes. Si intentas guardar una traducción, es posible que veas un mensaje que indica que no puedes guardar una traducción duplicada, esto significa que otro contribuyente ha propuesto una traducción idéntica. Si estás de acuerdo con esa traducción, haz clic en el botón `+` para votar a favor de la traducción.
+
+Si ves una traducción que es inexacta o no proporciona la misma claridad que la cadena original, haz clic en el botón `-` para votar en contra de la traducción.
+
+Crowdin usa estos votos para dar una puntuación a cada traducción propuesta para una cadena, lo que ayuda al equipo de revisión a determinar qué traducción es la mejor para cada cadena.
+
+## Comprobaciones de aseguración de la calidad
+
+Hemos habilitado algunos pasos de control de la calidad que verificarán que una traducción sea lo más precisa posible, esto ayuda a nuestro equipo de revisión a comprobar las traducciones propuestas.
+
+Cuando intentes guardar una traducción, puede que aparezca un mensaje de advertencia con una notificación con respecto a tu traducción propuesta.
+
+
+
+Este mensaje aparece cuando el sistema de QA de Crowdin ha identificado un posible error en la traducción propuesta. En este ejemplo, hemos modificado el texto de una etiqueta `<code>` y Crowdin lo ha capturado.
+
+> [!WARNING] Tienes la opción de guardar una traducción a pesar de los errores. Si lo haces, al hacer clic en "Save Anyway (Guardar de todos modos)", también debes etiquetar a un miembro del equipo de revisión o encargado del proyecto y explicar por qué el mensaje de QA debe ignorarse en este caso.
+
+## Mejores prácticas de traducción
+
+Sigue estas pautas para asegurarte de que nuestras traducciones sean lo más precisas posible:
+
+- No traduzca el contenido con etiquetas de `<code>`. Estas etiquetas indican texto que se encuentra en código y que debe dejarse en inglés.
+- No agregues contenido adicional. Si sientes que un desafío requiere cambios en el contenido de texto o información adicional, debería proponer los cambios a través de un problema de GitHub o una pull request que modifique el archivo en inglés.
+- No cambiar el orden del contenido.
+
+Si tienes alguna duda, siéntete libre de pedir ayuda en nuestro [Discord](https://discord. gg/PRyKn3Vbay) y con gusto te ayudaremos.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..21581ba9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Cómo utilizar Docker en Windows Home
+---
+
+Hay unas cuantas dificultades que debes evitar al configurar Docker en Windows Home. En primer lugar, tienes que utilizar [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) como administrador. Desafortunadamente, Windows Home no soporta Docker para Windows Desktop, por lo que se debe utilizar Toolbox en su lugar. Tiene que ejecutarse como Administrador, ya que la instalación utiliza enlaces simbólicos, los cuales no se pueden crear de otra manera.
+
+Una vez instalado Toolbox, ejecute Docker Quickstart Terminal como Administrador. Esto creará una máquina virtual `default` (predeterminada) si no existía anteriormente. Una vez que esto haya ocurrido, cierra la terminal y abre VirtualBox (otra vez como Administrador). Debes ser capaz de ver la máquina `default`. El sitio es bastante intensivo en recursos, así que detén la máquina virtual y aumenta la configuración tanto como puedas, especialmente la memoria. It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Una vez que estés contento de que Docker está funcionando, clona el repositorio freeCodeCamp en un directorio dentro de `C:\Users`. Estos directorios son compartidos dándole acceso a Docker a los directorios locales que necesita durante la instalación.
+
+Si ves mensajes como
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+when you `pnpm run docker:init` this is likely the culprit.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..47858f80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,739 @@
+---
+title: Cómo trabajar en los desafíos de codificación
+---
+
+Nuestro objetivo es desarrollar una experiencia de aprendizaje interactiva y divertida.
+
+Diseñar desafíos de codificación interactivos es difícil. Sería mucho más fácil escribir una explicación larga o crear un tutorial en vídeo. Pero para nuestro plan de estudios, estamos aferrándonos a lo que mejor funciona para la mayoría de la gente - una experiencia totalmente interactiva y de videojuegos.
+
+Queremos que los campistas entren en un estado de flujo. Queremos que generen impulso y exploten a través de nuestro plan de estudios con el menor número de trabas posible. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+Ten en cuenta que para la versión 7.0 del plan de estudios gratuito, estamos avanzando hacia [un modelo totalmente orientado al proyecto con mucha más repetición](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+La creación de estos desafíos requiere una inmensa creatividad y atención al detalle. Hay mucha ayuda disponible. Tendrás el apoyo de todo un equipo de colaboradores a los que podrás comentar tus ideas y demostrar tus desafíos.
+
+Y como siempre, sientase libre de hacer preguntas en la [categoría de 'Contribuidores' de nuestro foro](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [en la sala de chat de contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Con tu ayuda, podemos diseñar un currículo de código interactivo que ayudará a millones de personas a aprender a programar en los próximos años.
+
+El contenido para cada desafío está guardado en su archivo de lenguaje de marcado. Este archivo de lenguaje de marcado se convierte más tarde en HTML utilizando nuestras herramientas para crear páginas web interactivas.
+
+Podrás encontrar todo el contenido curricular de freeCodeCamp.org en el directorio [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges).
+
+## Configurar las herramientas para el plan de estudios
+
+Antes de trabajar en el plan de estudios, necesitarás configurar algunas herramientas para ayudarte a probar tus cambios. Puedes utilizar cualquier opción de las siguientes:
+
+- Puedes [configurar freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) en tu máquina. Esto es **altamente recomendable** para contribuciones regulares/repetidas. Esta configuración te permite trabajar y probar tus cambios.
+- Utilice Gitpod, un entorno de desarrollo gratuito en línea. Al hacer clic en el botón de abajo se iniciará un entorno de desarrollo listo para freeCodeCamp en su navegador. Sólo toma unos minutos.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### Cómo trabajar en proyectos de práctica
+
+Los proyectos de práctica tienen algunas herramientas adicionales para ayudar a crear nuevos proyectos y pasos. Para leer más, consulta [ estos documentos ](how-to-work-on-practice-projects)
+
+## Plantilla de desafío
+
+`````md
+Esto no ha sido finalizado completamente, pero lo siguiente debería estar cerca de la estructura final:
+
+````mdx
+---
+id: Identificador único (alfanumérico, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Título del Desafío'
+challengeType: Integer, definido en `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url del video de explicación'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --descripción--
+
+Texto de descripción, en lenguaje de marcado
+
+```html
+<div>código de ejemplo</div>
+```
+````
+`````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Texto de instrucción de desafío, en lenguaje de marcado
+
+# --hints--
+
+Pruebas para ejecutar en el código del usuario, en pares de lenguaje de marcado y bloques de código de prueba.
+
+```js
+Código para prueba uno
+```
+
+Si tú buscas una salida basada en el código de usuario, --fcc-expected-- y --fcc-actual-- serán reemplazados con los valores de esperado y actual de la afirmación de la prueba. Ten cuidado si tienes múltiples afirmaciones desde la primera afirmación fallida determinará los valores de --fcc-expected-- y --fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'esto reemplazará --fcc-actual--',
+ 'esto reemplazará --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notas--
+
+Información adicional para un desafío, en markdown
+
+# --semilla-
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Código evaluado antes del código del usuario.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Código evaluado después del código del usuario, y justo antes de las pruebas
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Código repetitivo para renderizar en el editor. Esta sección deberá solo contener código dentro de comillas invertidas, como prosigue:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hola Mundo!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --soluciones--
+
+Las soluciones se utilizan para las pruebas de CI para garantizar que los cambios en las sugerencias seguirán siendo válidos según lo previsto
+
+```js
+// primera solución - la(s) lengua(s) deben coincidir con la semilla.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// segunda solución - así que si la semilla está escrita en HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// tercera solución, etc. - Sus soluciones deben estar en HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. En las secciones anteriores, los ejemplos de `lang` son:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Numeración del desafio
+
+Cada reto necesita un `id`. Si no especifica uno, MongoDB creará uno nuevo aleatorio cuando guarde los datos; sin embargo, no queremos que haga eso, ya que queremos que los id de desafío sean consistentes en diferentes entornos (puesta en escena, producción, muchos desarrolladores diferentes, etc.).
+
+Para generar una nueva en un shell (asumiendo que MongoDB se está ejecutando por separado):
+
+1. Ejecute el comando `mongo`.
+2. Ejecute el comando `ObjectId()`.
+
+
+Por ejemplo:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+título: Título del desafío
+```
+
+## Nombrando desafíos
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Utilice Notación en sentido de la derecha para especificar el relleno de un elemento
+- Condensa arreglos con ".reduce"
+- Utilice la notación de corchete para encontrar el primer carácter en una cadena
+
+## Descripciones/Instrucciones de Desafíos
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (mayúsculas en "J" y "S" y sin abreviaturas)
+- Node.js
+- Aunque a veces sea inexacto, se deben utilizar formularios no separados de 'back-end' y 'front end', ya que se usan más ampliamente.
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- Simplificar el desafío, o
+- Dividir el desafío en dos desafíos.
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- Las palabras clave del lenguaje van en etiquetas ``. Por ejemplo, nombres de etiquetas HTML o nombres de propiedades CSS.
+- Las referencias a las partes del código (es decir, funciones, métodos o nombres de variables) deben estar envueltas en etiquetas ``. Ver el ejemplo a continuación:
+
+```md
+Usa `parseInt` para convertir la variable `realNumber` en un entero.
+```
+
+- Las referencias a los nombres de archivos y directorios de rutas (por ejemplo, `package.json`, `src/components`) deben estar envueltas en etiquetas `<code>`.
+- Los bloques de código de múltiples líneas **deben estar precedidos por una línea vacía**. La siguiente línea debe comenzar con tres backticks seguidos inmediatamente por uno de los [idiomas soportados](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. Ver el ejemplo a continuación:
+- El espacio en blanco es importante en Markdown, por lo que le recomendamos que lo haga visible en su editor.
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+```md
+`` `{idioma}
+
+[TU CÓDIGO AQUÍ]
+```
+
+````
+
+- La información adicional en forma de una nota debe ser formateada `Nota: El texto restante de la nota...
+- Si se necesitan varias notas. then list all of the notes in separate sentences using the format `Note: First note text. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## Pruebas de escritura
+
+Los desafíos deben tener el número mínimo de pruebas necesarias para verificar que un campador entienda un concepto.
+
+Nuestro objetivo es comunicar el único punto que el reto está tratando de enseñar y comprobar que han comprendido ese punto.
+
+Las pruebas de desafío pueden hacer uso de las librerías de aserción de Node.js y Chai.js. Además, si es necesario, se puede acceder al código generado por el usuario en la variable `code`. Además, el objeto `__helpers` expone varias funciones que simplifican el proceso de escritura de los test. The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. El caso exacto y el espaciado del comentario del diccionario deben ser utilizados. El diccionario de comentarios no debe ser expandido sin una discusión previa con el equipo de desarrollo.
+
+Los comentarios usados deben tener un espacio entre los caracteres del comentario y los propios comentarios. En general, los comentarios deben usarse con moderación. Siempre considere reescribir la descripción o las instrucciones de un desafío si pudiera evitar usar un comentario de código de semilla.
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Cambia el código debajo de esta línea
+
+ // Cambia el código encima de esta línea
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Cambiar código debajo de esta línea */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Cambiar código sobre esta línea */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+Declara la variable myGlobal debajo de esta línea
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Estamos trabajando en una integración que permita trabajar en i18n para el diccionario de comentarios.
+
+## Consejos y soluciones
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. Comience siguiendo los mismos pasos para crear un nuevo tema pero revise el siguiente para crear el título.
+2. El título del tema debe comenzar con `Guía de Desafío gratuita:` concatenada con el título real del desafío curricular. Por ejemplo, si el desafío se llama "`Chunky Monkey`", el título del tema sería "`Guía gratuita del Desafío CodeCamp: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. `camperbot` debe ser el dueño de estos temas/posts, así que necesitarás solicitar a un administrador que cambie la propiedad de la publicación principal a `camperbot`.
+4. Una vez creado el nuevo tema, se crea un identificador del tema del foro. Se encuentra al final de la URL del tema del foro. Este id debe añadirse a la parte frontal del archivo de desafío curriculum a través del proceso normal de pull request para el botón `Obtener una pista` para vincular al tema.
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# El nombre del desafío va aquí
+
+---
+
+## Explicación del problema
+
+Esto resume lo que se debe hacer sin solo repetir la descripción del desafío y / o las instrucciones. #### Enlaces relevantes
+
+- [Texto del enlace](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## Pistas
+
+### Pista 1
+
+La pista va aquí
+
+### Pista 2
+
+La pista va aquí
+
+---
+
+## Soluciones
+
+<detalles><sumario>Solución 1 (Haga clic para mostrar/ocultar)</sumario>
+
+```js
+function miFunc() {
+ console.log('¡Hola Mundo!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Explicación del código
+
+- La explicación del código va aquí
+- La explicación del código va aquí
+
+#### Enlaces relevantes
+
+- [Texto del enlace](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Texto del enlace](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## desafios de tests
+
+Antes de que tu [hagas un pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) para tus cambios, tu necesitas validar que los cambios que has realizado no causan inadvertidamente problemas con el desafío.
+
+1. Para testear todos los desafíos, ejecuta el siguiente comando desde el directorio raíz
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d7914030
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,286 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. Se traduce a varios idiomas utilizando [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) y [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+Puedes obtener más información sobre cómo configurar la aplicación cliente localmente para su desarrollo siguiendo [nuestra guía de configuración local aquí](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+Esto podría ser útil cuando se está trabajando en una función que se dirige específicamente a algo que implica la localización, y requiere que valides, por ejemplo, la etiqueta de un botón en un idioma diferente.
+
+> [!TIP] You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. En su lugar, lee [esta guia](how-to-translate-files).
+
+Veamos cómo funcionan los marcos de trabajo y las herramientas de i18n.
+
+## Estructura de archivos
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**Archivos traducidos en nuestra plataforma de traducción:**
+
+- El archivo `translations.json` contiene la mayor parte del texto que aparece en los elementos de la interfaz de usuario. Las claves son usadas en el código base para obtener el texto correcto de cualquier lenguaje que sea seleccionado. This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- El archivo `intro.json` contiene los pares clave-valor para el texto de introducción en las páginas de certificación.
+
+ Si quieres añadir/actualizar las traducciones para las claves por favor lee [esta guía aquí.](https://freecodecamp.crowdin.com/how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Archivos que NO son traducidos en nuestra plataforma de traducciones:**
+
+- Los archivos `motivation.json` no requieren que tengan las mismas comillas, complementos o tamaños u orden. Simplemente la misma estructura JSON.
+
+- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
+
+ Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+Si estas probando un nuevo idioma, crea una carpeta con el nombre del idioma como titulo junto al otro idioma y copia los archivos JSON desde el otro idioma dentro de la nueva carpeta.
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+A continuación, sigue las instrucciones en los comentarios en el mismo archivo para agregar/actualizar el resto de las variables tanto como se necesite.
+
+Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the string of the locale you want to build from the `Languages` enum in the above file.
+
+## Como estructurar los componentes
+
+Si estás trabajando en una característica o en un error para el cliente de la app web, por ejemplo agregando unos nuevos elementos UI en la página de configuración, debes seguir las líneas de ayuda siguientes. Te ayudarán a preparar los componentes para localizarlo en todos los idiomas mundiales soportados.
+
+### Componente funcional
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// en el método de renderizado:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// llamar la función "t" con una clave del archivo JSON:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // más detalles abajo
+```
+
+### Componente de clase
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation agregar la función "t" a props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// llamar la función "t" con una clave del archivo JSON:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // más detalles abajo
+
+// exportar sin redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// o con renderizado:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Traducir utilizando la función "t"
+
+### Traducción básica
+
+```js
+// en el componente:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// en el archivo JSON:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// salida:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### Con datos dinámicos
+
+```js
+// en el componente:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// en el archivo JSON:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// salida:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+Los ejemplos de arriba pasan un objeto a la función `t` con una variable `username`. La variable deberá ser usada en el valor JSON donde está `{{username}}`.
+
+## Traduce con el Componente `Trans`
+
+La regla general es usar la función "t" cuando puedas. Pero hay un componente `Trans` para cuando eso no sea suficiente, generalmente cuando tienes un elemento insertado dentro del texto. Puedes usar el componente `Trans` con cualquier tipo de componente de react.
+
+### Elementos básicos anidados
+
+```js
+// en el componente
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// en el archivo JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// salida:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i`, and `p` están por defecto, pero esa lista puede ser extendida en la configuración i18n.
+
+### Elementos complejos anidados
+
+En otros tiempos, querrás tener cierto texto dentro de otro elemento, una etiqueta de anclaje es un buen ejemplo:
+
+```js
+// en el componente:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// en el archivo JSON:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// salida:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+En el ejemplo de arriba, la clave es colocada en los atributos del componente `Trans`. El `<0>` y `</0>` en el JSON representa el primer hijo del componente, en este caso, el elemento ancla. Si hubiera más hijos, podrían contarlos después de que usen la misma sintaxis. Puedes encontrar el hijo de un componente en las herramientas dev de react inspeccionándolos. El `placeholder` están simplemente ahí debido a que el linter busca un elemento vacío `<a>`.
+
+### Con una variable
+
+```js
+// en el componente:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// en el archivo JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// salida:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+En el ejemplo de arriba, la clave y la variable son establecidas en el atributo del componente `Trans`. El `{{ email }}` necesita estar en algún lado del componente `Trans` tan bien, no importa donde.
+
+## Cambiar texto
+
+Para cambiar el texto de las cosas del lado del cliente, ve al archivo relevante `.json`, encuentra la clave que es usada en el componente React, y cambia el valor al nuevo texto que quieras. Deberías de buscar en la base del código para que esa clave para asegurarte de que no está siendo usada en ningún otro sitio. O, si es así, que el cambio tenga sentido en todos los sitios.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Agregar texto
+
+Si el texto que quieres añadir al cliente existe en el archivo pertinente, `.json`, usa la clave existente. En el caso contrario, crea una clave nueva.
+
+El archivo English es la "fuente de la verdad" para todos los archivos `.json` que compartan el mismo nombre. Si necesitas añadir una nueva clave, añádela ahí. Después, añade la clave **all** de los archivos `translations.json`.
+
+:::note
+Utiliza texto en inglés para todos los idiomas si el archivo se traduce a través de Crowdin. La prueba se caerá si no lo haces.
+:::
+
+Sería bueno mantener la clave en el mismo orden en todos los archivos también. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+:::note
+The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. Vea [the documentation](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) de como debe ser usado.
+:::
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [Documentación de react-i18next ](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [Documentación de i18next](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f6379903
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: Cómo Trabajar en Proyectos de Práctica
+---
+
+Nuestros proyectos de práctica utilizan un enfoque basado en pasos para enseñar conceptos a los campistas. Un proyecto constará de múltiples archivos, a los que nos referimos como **"pasos"**. Estos archivos son nombrados por el ID de desafío, para evitar problemas con el flujo de traducción. Desafortunadamente, esto hace difícil encontrar el archivo asociado a un paso específico.
+
+Hemos creado una herramienta de edición de desafíos que ayuda a remediar eso. Esta herramienta permite navegar los proyectos disponibles y los pasos para cada proyecto (en orden). También hay un editor de código embebido que se puede utilizar para trabajar directamente sobre los archivos.
+
+## Utilizando el editor de desafíos
+
+Estas instrucciones le indicarán cómo utilizar nuestra herramienta de edición de desafíos para trabajar en los proyectos de práctica.
+
+### Iniciar el Editor
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Then, run `pnpm run challenge-editor` to start both the client and the API that powers the editor.
+
+El cliente se ejecutará en el puerto `3300`, por lo que puede acceder a él en `http://localhost:3300`. La API se ejecuta en el puerto `3200` para evitar conflictos con el cliente y el servidor de aprendizaje. Esto le permitirá ejecutar la aplicación freeCodeCamp al mismo tiempo que el editor, para que pueda probar sus cambios localmente.
+
+### Navegando por el Editor
+
+La vista predeterminada mostrará una lista de los `superbloques` disponibles: estas son las certificaciones. Click on the certification link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to the list of blocks. These are the practice projects. Click on the project link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to a list of steps for the project. If you are working on an existing step, you can click on the step link to open the editor. If you are adding or removing steps, click the `Use the step tools` link to switch to the step tools for that challenge.
+
+### Editing Steps
+
+When you click on a step, you'll be taken to the editor. This is a basic text editor that offers syntax highlighting.
+
+After you have made your changes, click the `Save Changes` button to save your changes. You will get a browser alert letting you know that your changes are ready to commit. Note that you'll need to use `git` manually to stage and commit your files - this tool will not do that for you.
+
+### Step Tools
+
+When you click the `Use the step tools` link, you'll be taken to the step tools page. This allows you to add or remove steps from the project.
+
+#### Create Next Step
+
+Clicking this button will add a new step at the end of the project. This step will use the previous step's code as the seed.
+
+#### Create Empty Steps
+
+Enter the number of steps you want to add in the input. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Insert Step
+
+Enter the step number that you want to add. Then, click the `Insert Step` button to add the step. The following steps will be re-ordered.
+
+#### Delete Step
+
+Enter the step number you want to delete. Then click the `Delete Step` button to remove that step. This will automatically update the step numbers for the remaining steps.
+
+#### Update Step Titles
+
+You should not have to use this tool unless you've manually deleted or added steps. This tool will reorder the step numbers.
+
+## Using the Scripts Manually
+
+If you want to work on the steps manually, in your local IDE, you can run the step management scripts directly.
+
+The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step in the project. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Redirígete al directorio del proyecto.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Redirígete al directorio del proyecto.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # where X is the number of steps to create.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a new step at a specified position, incrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json). The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Redirígete al directorio principal del proyecto.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # where X is the position to insert the new step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+A one-off script that deletes an existing step, decrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json)
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Redirígete al directorio principal del proyecto.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # where X is the step number to be deleted.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+A one-off script that automatically updates the frontmatter in a project's markdown files so that they are consistent with the project's meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Redirígete al directorio del proyecto.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5323f96e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Cómo trabajar en la biblioteca de componentes
+---
+
+Bienvenido a la librería `ui-components` de freeCodeCamp. Los componentes se construyen principalmente desde cero con elementos HTML básicos y [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp ha estado usando componentes de Bootstrap en la interfaz de usuario. Sin embargo, nos estamos alejando de ella y construyendo nuestra propia biblioteca de componentes, lo que ayuda a estandarizar nuestros patrones UX/UI y a mejorar la accesibilidad. El proyecto está rastreado en [este problema de GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+Se recomiendan los siguientes pasos al trabajar en un nuevo componente:
+
+- Investigación y planificación
+- Implementar el componente
+- Mostrar los casos de uso en el Storybook
+- Escribir pruebas unitarias
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Antes de construir un componente, necesita investigar y documentar cómo se comporta y se ve la versión existente, para asegurarse de que el nuevo tiene estilos coincidentes y soporta todos los usos actuales. Para cumplir con los requisitos de accesibilidad web, también debe prestar atención al aspecto de accesibilidad del componente, ver qué elementos HTML y atributos ARIA se utilizan bajo el capó.
+
+Una vez que haya reunido suficiente información sobre el componente, puede empezar a pensar en la interfaz de accesorios. Idealmente, la interfaz debe ser tan similar a la versión actual como sea posible, para facilitar la adopción más adelante. Puesto que estamos utilizando componentes de Bootstrap, el enfoque más simple es imitar [su implementación](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+Preferimos solicitudes de extracción más pequeñas que grandes porque aceleran el tiempo de revisión y reducen la sobrecarga cognitiva de los revisores. Por este motivo, debería pensar en cómo desglosar la aplicación y elaborar un plan de entrega.
+
+Recomendamos abrir un número separado de GitHub para cada componente e incluir todas las notas en la descripción de incidencias. Se puede utilizar como un lugar para alojar todas sus notas de trabajo, así como una forma de comunicar el enfoque con los revisores. Utilizaremos el tema para seguir debatiendo, si es necesario. [El problema para el componente Button](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) puede ser utilizado como referencia.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+Se puede crear un nuevo componente utilizando el siguiente comando desde el directorio raíz:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+El comando generará una nueva carpeta dentro del directorio `ui-components`, con los siguientes archivos:
+
+| Nombre del archivo | Propósito |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | Se utiliza para exportar el componente y sus tipos. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | Se utiliza para demostrar el componente en Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | Se trata de un archivo de prueba. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | Ahí es donde aplicamos el componente. |
+| `types.ts` | It is where we locate the component's interface and types. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Apoyar el reenvío de ref
+- Estilo tanto para temas claros como oscuros
+- Estilo internamente basado en sus accesorios (los consumidores no deben necesitar reponer el componente con el accesorio `className`)
+- Utilizar el sistema de estilo incorporado desde Tailwind, en lugar de tener estilos personalizados
+
+### Using Colors
+
+Hay dos "capas" de color en la biblioteca de componentes:
+
+- La capa base, donde los nombres de los colores describen lo que son los colores, por ejemplo, `gray00`, `blue50`
+- La capa semántica, donde los nombres de los colores describen para qué sirven, por ejemplo, `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. Sin embargo, hay excepciones, específicamente cuando se estilan los estados del componente, tales como hover, active, disabled, etc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+:::note
+La definición del color se encuentra en el [archivo `colors.css`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). Un color sólo está disponible para su uso si se añade al [archivo `tailwind.config.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) bajo la propiedad `colors`.
+:::
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Configuración del CSS de Tailwind](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [Documentación de React Bootstrap v0.33](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Hoja de estilo de Bootstrap 3.3.7](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [Implementación actual de React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [Pruebas actuales de React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Los casos de uso del componente deben añadirse al archivo Storybook (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+Para iniciar Storybook, ejecute el siguiente comando desde el directorio raíz:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+La página Storybook está disponible en [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+Usamos [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) para escribir pruebas unitarias. Las pruebas deben afirmar que los componentes se comportan como se espera y son accesibles.
+
+Para ejecutar pruebas a la biblioteca de componentes, ejecute el siguiente comando desde el directorio raíz:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Pruebas de Accesibilidad](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Orden de prioridad de las consultas de React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Errores comunes con la biblioteca de pruebas de React](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ce5daf6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+Para trabajar en las pautas de contribución, puedes editar o agregar archivos al directorio `docs`, [disponible aquí](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). Cuando tus cambios se fusionen, automáticamente estarán disponibles en el sitio de documentación.
+
+Cuando se agrega un nuevo archivo al directorio `docs`, deberías evaluar si el archivo también debe ser agregado a la barra lateral de navegación. Normalmente creamos un enlace en el archivo [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) para guías nuevas e independientes. Alternativamente, puede seguir las instrucciones de abajo en crear un link interno para guías de soporte.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+Si quieres crear un link dirigido a una sección diferente a las pautas de contribución, sigue este formato:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// Si la sección de destino está dentro de la misma página, puedes omitir el nombre del archivo
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Asegurate de incluir la extensión del archivo (`.md`). Don't specify the full URL or append `/` before the file name.
+
+Esto es necesario para hacer que estos enlaces fucionen para la versión traducida del ducumento. Otherwise, they will redirect to the English version of the page regardless of the language.
+
+#### Traduciendo archivos con enlaces internos
+
+Cuando estas traduciendo documentos en Crowdin, asegurate de reemplazar el `#target-section-heading-id` con el id en el documento traducido. [Aprende mas sobre como traducir documentos aqui](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+:::note
+Recuerda que no necesitas establecer nada para trabajar en el contenido para el sitio de documentación.
+
+Para trabajar en las directrices de contribución, consulte [trabajar en la sección de contenido de documentos](#work-on-the-docs-content).
+:::
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+El sitio esta generado usando [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) y se esta ejecutado usando Github pages.
+
+Normalmente no vas a necesitar cambiar ninguna configuración o compliar el sitio localmente. En caso de que te interese, asi es como funciona:
+
+- El código de la página de inicio para este sitio está disponible en [`docs/index.html`](index.html).
+- Servimos este archivo como SPA utilizando `docsify` y GitHub Pages.
+- El script `docsify` genera el contenido de los archivos `lenguaje de marcado` en el directorio `docs` en linea.
+- La página de inicio se genera a partir del [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage).
+- The sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fb7c2d80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: Cómo trabajar en las noticias para desarrolladores de freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Las noticias del desarrollador también conocidas como el sitio [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) funciona con [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). Utilizamos un tema personalizado para el aspecto del sitio. El código fuente del tema está disponible aquí: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## El Tema
+
+Ghost utiliza un lenguaje de plantillas sencillo llamado [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) para sus temas. El tema usado en `/news` se basa en el tema predeterminado [casper](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
+
+El tema por defecto está fuertemente comentado, por lo que debería ser bastante fácil averiguar lo que está pasando con solo leer el código y los comentarios. Una vez que te sientas cómodo con cómo funciona todo, Ghost también tiene una completa [documentación API de temas](https://themes.ghost.org) que explica todos los posibles ayudantes de Handlebars y plantillas.
+
+**Los archivos principales son:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - El archivo de plantilla principal
+- `index.hbs` - Utilizado para la página de inicio
+- `post.hbs` - Utilizado para publicaciones individuales
+- `page.hbs` - Utilizado para páginas individuales
+- `tag.hbs` - Utilizado para archivos de etiquetas
+- `author.hbs` - Utilizado para archivos de autor
+
+Un truco realmente bueno es que también puede crear plantillas personalizadas sólo añadiendo un trozo pequeño de una página a un archivo de plantilla. Por ejemplo:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - plantilla personalizada para la página `/about/`
+- `tag-news.hbs` - plantilla personalizada para `/tag/news/` archivo
+- `author-ali.hbs` - plantilla personalizada para `/author/ali/` archivo
+
+## Desarrollo
+
+1. Obtén Ghost instalado localmente.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Nota: actualmente freeCodeCamp usa la versión Ghost `2.9.0`, así que asegúrate de que estás usando una versión superior a eso.
+
+ Asegúrate de ejecutar los comandos de `ghost` desde el directorio `ghost-local-site`. Siga las instrucciones adicionales de la [documentación oficial de Ghost](https://docs.ghost.org) si no estás familiarizado con su interfaz.
+
+2. Bifurca y clona el repositorio en tu directorio de temas (reemplazando `YOUR_USERNAME` con tu nombre de usuario de GitHub):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Asegúrese de tener todos los requisitos previos.
+
+ Los estilos de los temas se compilan usando Gulp/PostCSS para polyfill las futuras especificaciones CSS. Necesitará [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Asegúrese de que su versión de Node.js es compatible con `ghost`.
+
+4. Instalar dependencias y desarrollar el tema
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Ahora puedes editar los archivos `/assets/css/`, los cuales serán compilados a `/assets/built/` automáticamente.
+
+6. Acceder al sitio de desarrollo.
+
+ a. Introduzca `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` en su barra de direcciones. Continúe con la configuración solicitada en la página (si se ejecuta Ghost por primera vez).
+
+ b. _(Solo una vez, durante la configuración)_ Reinicie Ghost, en una terminal por separado una vez para asegurarse de que el tema está disponible.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(Solo una vez, durante la configuración)_ Una vez que hayas hecho esto, ve a `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` y desplázate hacia abajo. Asegúrate de hacer clic en activar en el `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Comprime el código final y crea un pull-request
+
+ El `zip` que Gulp empaqueta son los archivos del tema en `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, los cuales podemos subir al sitio de producción.
+
+ Cuando haga un PR, por favor asegúrese de haber ejecutado el script de abajo antes de confirmar el código y enviar un PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Otros recursos y referencias
+
+### Funcionalidades utilizadas de PostCSS
+
+- Autoprefixer - No te preocupes por escribir prefijos del navegador de ningún tipo, todo se hace automáticamente con soporte para las 2 versiones más recientes de cada navegador.
+- Variables - Variables CSS simples
+- [Función de color](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### Iconos SVG
+
+El tema utiliza iconos SVG en línea, incluidos a través de parciales de Handlebars. Puedes encontrar todos los iconos dentro de `/partials/icons`. Para usar un icono simplemente incluya el nombre del archivo relevante, por ejemplo. Para incluir el icono SVG en `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - usa `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+Puedes añadir tus propios iconos SVG de la misma manera.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..24ece0f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+Esta página describe cómo contribuir a los tutoriales y proyectos de freeCodeCamp que se complementan usando la extensión CodeRoad de VS Code.
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. Todos comienzan con `learn-`. Por ejemplo, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Cada repositorio tiene una rama principal `main` y una "versión" de rama, por ejemplo. `v1.0.0`.
+
+Los dos archivos principales en la rama `main` son `TUTORIAL.md` y `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contiene todas las instrucciones, pistas, títulos y todo lo necesario para el tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contiene instrucciones para CodeRoad, tales como qué comandos correr y cuándo, qué archivos visualizar para cambios, y qué rama de versiones utilizar para los pasos.
+
+La rama de "versión" contiene los commits que serán cargados en cada paso de un tutorial. Los mensajes de commit en esta rama deben ser específicos. El primer commit necesita `INIT` para su mensaje y contiene todos los archivos a cargar antes de la primera lección.
+
+Los mensajes de commit subsecuentes deben coincidir con el número de pasos en `TUTORIAL.md` de la rama `main`. Por ejemplo, el commit con el mensaje `10.1` será cargado cuando un usuario va al paso `10.1`.
+
+Para realizar cambios a los commits en una rama de versión, necesitaría realizar un rebase y editar los commits que desea cambiar. Esto sobreescribirá la historia del Git, por lo que no podemos aceptar PRs a ese tipo de ramas. Una vez que una rama de versión está en el repositorio de freeCodeCamp, no debería cambiar nunca.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Nunca realice o envíe cambios a una rama de versión que se encuentre en uno de los repositorios de freeCodeCamp. Siempre cree una nueva
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### Requisitos previos
+
+Instala [CodeRoad CLI tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) con `npm install -g @coderoad/cl`.
+
+Ha habido algunos problemas con la última versión. Si `coderoad --version` no funciona después de instalar, baje a la versión `0.7.0` con `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Trabajando en `main`
+
+Este conjunto de instrucciones es para PRs que sólo realizan cambios minor (menores) en `main` a **lecciones existentes**. Eso se constituye principalmente de cambios de errores de tipografía, gramática, indicios e instructivos o arreglos en el archivo `TUTORIAL.md`.
+
+Para todo lo demás, incluyendo agregando y eliminando lecciones, siga las [instrucciones para trabajar en una rama de versión](#working-on-version-branch). No necesitará crear una nueva rama de versión para esto - puedes crear una PR siguiendo las instrucciones anteriores.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Estos cambios utilizarán la rama de versión existente. Si son sustanciales, siéntase libre de agregarlos a `CHANGELOG.md`. La mayor parte del tiempo, un buen mensaje de commit debería funcionar
+
+Nunca necesitas modificar directamente el archivo `tutorial.json`. Esto se creará con las herramientas CLI.
+
+Si sólo está haciendo cambios menores como corregir un error tipográfico o gramatical, no tiene que probar los cambios.
+
+Siga estas instrucciones para hacer un PR, teniendo en cuenta que las instrucciones usualmente usan las lecciones a su alrededor para el contexto:
+
+- Crea una copia de la última rama de la versión con `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - no necesitas verificarla, solo debe existir.
+- Crea y consulta una nueva bifurcación de `main`
+- Haz **y envía** tus cambios. Recordatorio: No necesitas cambiar nada en el archivo `tutorial.json`. Es probable que sólo necesite hacer cambios en `TUTORIAL.md`
+- Ejecute `coderoad build` para recrear el archivo `tutorial.json`
+- Confirme los cambios con `update json` como mensaje
+- Hacer un PR
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+Si deseas probar sus cambios en `main` después de seguir las instrucciones anteriores, sigue estas instrucciones:
+
+- Siga las instrucciones del [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para ejecutar un contenedor
+- Comienza el tutorial usando el archivo `tutorial.json` en la nueva rama
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+Si revisa un PR que solo cambia `main` con problemas de instrucción o gramática como se describe anteriormente, los cambios en `TUTORIAL.md` deberían coincidir con los cambios en `tutorial.json`.
+
+El archivo `tutorial.json` no debería tener cambios para los hash de commit, o ids de paso/nivel. Los comandos de inicio o de nivel o los monitores de archivos probablemente no deberían cambiarse. Hay excepciones si hay un problema con un paso, pero deben ser tratados con más precaución.
+
+Además, ten en cuenta que las instrucciones usualmente usan las lecciones a su alrededor para el contexto, así que asegúrate de que tienen sentido.
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+> [!ADVERTENCIA]
+>
+> Recordatorio: Nunca hacer o enviar cambios a una rama de versión que esté en uno de los repos de freeCodeCamp. Siempre crea una nueva
+
+No hay una manera fácil de ver exactamente qué cambió entre las ramas de versiones ya que la historia de Git será reescrita. Aceptar nuevas ramas de versión para usar tendrá que hacerse con una cuidadosa consideración y pruebas.
+
+Estas instrucciones son para cambiar cualquier cosa en una rama de "versión", como pruebas, texto de prueba, archivos de reinicio, añadiendo y eliminando pasos, entre otras cosas.
+
+Sigue estas instrucciones para crear una nueva versión:
+
+- Echa un vistazo a la rama de **última versión** con `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Crea una nueva rama de eso, incrementando la versión, con `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Haga sus cambios en la rama de versiones. Ver más información en la [Documentación de CodeRoad](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) para saber cómo trabajar con tutoriales
+- Empuja la nueva rama a tu bifurcación con `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Compruebe la rama `main`
+- Crea una nueva rama de `main`. ej. `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Cambia el `uri` en `coderoad.yaml` a tu bifurcación del repositorio. Esto es así que tú y los revisores pueden probarlo antes de empujarlo al repositorio freeCodeCamp. Cambie la versión a la nueva rama en los dos puntos de ese archivo. Añade tus cambios para la nueva versión a `CHANGELOG.md`. Haz cualquier otros cambios que necesites.
+- Comprueba tus cambios con el mensaje `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>`
+- Ejecute `coderoad build` para crear un nuevo archivo `tutorial.json`
+- Agregar y confirmar el archivo
+- Enviar los cambios a tu bifurcación
+- Prueba tus cambios siguiendo las [instrucciones de prueba a continuación](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Haga cualquier cambio adicional y confirme los cambios como acaba de hacer o, si está satisfecho, siga el resto de las instrucciones
+- Hacer un PR a `principal` usando su nueva rama `feat/version-X.X.Y`. Dale un título de `versión X.X.Y lista para la revisión`. Esto no se fusionará, es sólo para hacer saber a los revisores que hay una nueva versión lista
+- Déjalo aquí para revisores
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- Sigue las instrucciones en el repositorio [rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para ejecutar un contenedor
+- Comience el tutorial utilizando el archivo `tutorial.json` en cualquier bifurcación en la que estén los cambios. Asegúrate de usar el archivo en la rama `feat: version-X.X.Y` y no la rama `main`
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+Antes de empujar una nueva versión, ver la nueva `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (se fusionará a `main`) rama en el fork del usuario. Asegúrese de que hay adiciones al `CHANGELOG. d` archivo que incluye los nuevos cambios, y la versión en los dos manchas de la carga de código `. aml` coincide con la nueva rama de versión.
+
+Si tienes acceso de escritura al repo de freeCodeCamp, has verificado los archivos `CHANGELOG` y `coderoad.yaml`, has probado los cambios usando las instrucciones anteriores, y quieres empujar una nueva versión de un tutorial:
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Recordatorio: Nunca hacer o enviar cambios a una rama de versión que esté en uno de los repos de freeCodeCamp. Siempre cree una nueva
+
+- Si no tiene un control remoto a donde existen los nuevos cambios, crear un control remoto a la bifurcación del usuario con `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Elimina cualquier **ramas** locales que compartan un nombre con las nuevas ramas. Probablemente llamado `vX.X.Y` o `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Echa un vistazo a la nueva rama de versión con `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
+- Empuja la nueva rama de versión al repositorio freeCodeCamp con `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. Necesitas empujar la nueva rama antes de actualizar `main` con el nuevo archivo `tutorial.json`
+- Compruebe la rama de usuarios que se fusionará en `main` con `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Cambie el `uri` en `coderoad.yaml` de vuelta al repositorio freeCodeCamp
+- Agregar y confirmar los cambios
+- Ejecute `coderoad build` para crear el nuevo archivo `tutorial.json`
+- Añadir y confirmar el archivo
+- Empuja los cambios a su bifurcación con `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Hacer un PR a `main` en el repositorio freeCodeCamp
+- Si estás satisfecho, fusionalo o déjalo y pide una reseña a alguien
+- Después de fusionar las relaciones públicas, abra el tutorial siguiendo las instrucciones en el repositorio [rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para asegurarse de que está cargando correctamente, y que usted puede pasar unos pasos
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Revertir todos los commits en esta rama hasta e incluyendo el commit de la versión después del que desea revertir. Por ejemplo, puede haber commits que se vean así:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+Si quieres revertir a v1.0.0, revertir todos los commits de `release: version 1.0.1` y después
+
+- Crea una PR. Dale un título de `revertir: a la versión X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/intro.md b/src/content/docs/es/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f71f4994
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+La comunidad [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) es posible gracias a miles de buenos voluntarios como tú. Si quieres contribuir con tu tiempo y experiencia, estaremos encantados de darte la bienvenida.
+
+:::note
+Antes de continuar, por favor tómate 2 minutos para leer nuestro [Código de Conducta](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct). Lo hacemos cumplir estrictamente en toda nuestra comunidad para que contribuir a freeCodeCamp.org sea una experiencia segura e inclusiva para todos.
+:::
+
+Te invitamos a crear, actualizar y corregir errores en nuestro [plan curricular](#curriculum), ayúdanos a corregir errores en la [plataforma de aprendizaje](#learning-platform) de freeCodeCamp, o [ayúdanos a traducir](#translations) freeCodeCamp.org a deferentes idiomas.
+
+Respondemos a las preguntas más comunes sobre cómo contribuir [nuestras FAQ del colaborador](FAQ).
+
+Feliz contribución.
+
+---
+
+## Plan de estudios
+
+Nuestro plan de estudios está elaborado por la comunidad global de freeCodeCamp. De esta forma, podemos incorporar el conocimiento avanzado proporcionado por voluntarios como tú.
+
+Puedes ayudar a ampliar y mejorar el plan de estudios. También puedes actualizar las historias de usuario del proyecto para explicar mejor los conceptos. Y puedes mejorar nuestras pruebas automatizadas para que podamos probar con más precisión el código de las personas.
+
+**Si estás interesado en mejorar nuestro plan de estudios, aquí mostramos [cómo contribuir al plan de estudios](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges).**
+
+## Traducciones
+
+Estamos localizando freeCodeCamp.org a los principales idiomas del mundo.
+
+Las certificaciones ya están disponibles en algunos de los principales idiomas del mundo como:
+
+- [Chino (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Español](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italiano (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [portugués (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ucraniano (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japonés (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [Alemán (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+Te animamos a leer el anuncio [aquí](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) y compartirlo con tus amigos para que se sientan entusiasmados con esto.
+
+**Si estás interesado en traducir, aquí tienes [cómo traducir los recursos de freeCodeCamp](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## Plataforma de aprendizaje
+
+Nuestra plataforma de aprendizaje se ejecuta en un stack de JavaScript moderno. Tiene varios componentes, herramientas y librerías. Estos incluyen Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack y más.
+
+A grandes rasgos, tenemos un servidor API basado en Node.js, un conjunto de aplicaciones cliente basadas en React, scripts de prueba para evaluar proyectos currículo enviados por los estudiantes, y más. Si deseas contribuir de manera productiva a la plataforma de aprendizaje, te recomendamos que te familiarices un poco con estas herramientas.
+
+**Si quieres ayudarnos a mejorar nuestra base de código, puedes verlo aquí [Cómo configurar freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/es/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e6719c82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,364 @@
+---
+title: El manual oficial de liderazgo de idioma Freecodecamp
+---
+
+Este manual lo ayudará a configurar y utilizar las herramientas para sus esfuerzos de localización.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+La mayoría de tus invitaciones serán para el nivel de "Colaborador". Este nivel permite al usuario crear borradores. Selecciona este rol cuando invitas a un nuevo traductor.
+
+El nivel "autor" permite al usuario crear borradores y publicarlos.
+
+El nivel "Editor" permite al usuario acceder a todos los Borradores y publicarlos. Seleccione este rol al invitar a un nuevo revisor (proofreader).
+
+El nivel "Administrador" está reservado para el personal de freeCodeCamp y los líderes de idiomas.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+Utilizamos un método basado en [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack) para construir y desplegar los artículos. Esta estrategia permite que el sitio se almacene rápidamente en caché y se sirva desde un CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) actúa como nuestra plataforma de gestión de contenidos, y [11](https://11ty.dev) incorpora los artículos en activos estáticos - HTML, JavaScript y CSS. Sólo estos activos estáticos están desplegados en nuestros servidores.
+
+Este proceso es automatizado y se ejecuta periódicamente. Si usted publica algo ahora, estará disponible en el sitio de noticias dentro de unas pocas horas.
+
+You can find the up-to-date build schedules and status here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+Con `link` siendo el enlace del artículo original.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+> [!TIP] Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Make sure to match the title and the link correctly.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Each title must stay on a single line and not go to a new line.
+
+You will want to [build the translated client locally](how-to-enable-new-languages) to see if the titles have the right length. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articles that can be translated:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+The following articles should **not** be translated:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+The following links are pointing to external sites and cannot be translated:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Once you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, you can update the links in the footer for `/news` by editing the file at `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) repository.
+
+:::note
+Pull requests to this repository are currently limited to staff only. If you want to update this file, ask someone on the staff team for help.
+:::
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+When you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, as well as when the curriculum in your language is ready for launch, you can update the links in the footer for `/learn` by editing the file at `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) repository.
+
+> [!WARNING] Only "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", and "Code of Conduct" can be translated. Leave other URLs unchanged.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+You can find these boxes all around the documentation:
+
+:::note
+I am a note box
+:::
+
+> [!TIP] I am a tip box
+
+> [!WARNING] I am a warning box
+
+:::danger
+I am an attention box
+:::
+
+By default, their headers appear in English even in the translated docs.
+
+You can have the headers translated in the docs in your language by changing the file `docs/index.html`, in this way:
+
+Inside the `script` element there is an object, find the `flexibleAlerts` property, which has this shape:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Inside the object of the label property, before the `'/'` property, you would add a new property for your language, like `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+For example, adding the translations for Portuguese would appear like this:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+The motivational quotes can be found in the [curriculum repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json` file.
+
+Este archivo tiene una estructura general de:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+The compliments are the short sentences that appear at the completion of a challenge.
+
+You don't need to directly translate the sentences used in English, you can write a set of short sentences that are appropriate to show at the completion of a challenge.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+> [!TIP] You should start with at least a dozen compliments to have some variety when users complete challenges.
+
+The motivational quotes are the quotes that appear at https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+The `motivationalQuotes` array is an array of objects, these objects should include a `quote` property and an `author` property. like this:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+> [!TIP] You should start with at least a dozen quotes, to have some variety. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+We maintain a file of common links used throughout our [curriculum site](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json` file.
+
+Some of these links will not change - but you should update the `/news` article links to point to your language's translated version of that article when it is published.
+
+You should also update the `help` categories to point to your language's subforum (usually `language/category`, like `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). This will allow campers to create "help posts" in the correct forum location.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+The site meta-data is in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json` file. This file has five keys: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords`, and `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+The `youre-unsubscribed` value should be directly translated. The other values will need to be translated as closely as possible, while also considering common search terms and phrases used in your language.
+
+If you need help with this, reach out to us in the [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Pre-Translate Workflow on Crowdin
+
+The Pre-Translate workflow can be used to apply translations from the Translation Memory to strings.
+
+> [!TIP] Really useful to restore a lot of translations from the Translation Memory in bulk when a lot of files have been updated.
+
+You can find the Pre-Translation workflow at the top of the page in the console of a project. If you see "Go to console" in the upper right corner, click there first.
+
+
+
+
+
+You can choose "From Machine Translation" or "From Translation Memory". Choose "Translation Memory" to recover translations from memory.
+
+Then there are three steps to complete:
+
+1. Files. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Languages. Set your language here.
+3. Existing Translations. The best combination here is "100% match" and "Apply to untranslated strings only". Do not approve automatically, as it's always best to have a human eye on things.
+
+
+
+When you have finished setting this, press the Pre-Translate button and wait. It will alert you once it has finished. The time it takes depends on how many untranslated strings are in the chosen files.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+> [!TIP] An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+
+The Crowdin Glossary is kept in the [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries) repository.
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+The `client.csv` file is for the Learn User Interface project, the `curriculum.csv` file is for the Coding Curriculum project, the `docs.csv` file is for the Contributing Documentation project.
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+In the `.csv` file you will find that the English language occupies the first three columns, `Term:English` is the column for the English term, `Description:English` is the column for the English description, and `Part:English` is for the part of speech (e.g., noun, verb etc.) of the term.
+
+Then, each target language has two columns. If you translate to Dothraki, you will be interested in the columns `Term:Dothraki` and `Description:Dothraki`. The column `Term:Dothraki` is for the translation of the term in Dothraki, and the column `Description:Dothraki` is for a description of the term in Dothraki.
+
+> [!TIP] In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+
+After you have made the changes and saved the file, you will need to make a PR with the proposed changes. After the PR is accepted, you will need to run the GitHub Action workflow to update the Crowdin Glossary. Your glossary changes will not have immediate effects, but they will come.
+
+## How to Promote a Contributor to Proofreader
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+This will open the user management tools, you will be able to see the list of all the users.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Use the three dots menu on the user row to open a menu and select "Add to team". The proofreader teams have a standard name of `Proof Readers (<language>)`, you can search the team using the language name. Once you have selected the team, use the "ADD" button at the bottom of the page to finalize the thing.
+
+The user is now a proofreader.
+
+> [!TIP] The newly promoted proofreader could benefit from reading the [How to Proofread Files](how-to-proofread-files) documentation.
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/es/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74f93ba3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: El Manual Oficial del Moderador de freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Este manual te ayudará a moderar diferentes secciones dentro de nuestra comunidad. Esto cubre conversaciones e interacciones en asuntos e hilos de pull request en GitHub, el foro de la comunidad, las salas de chat y otras comunidades oficiales que proveemos.
+
+:::note
+Todos los moderadores de freeCodeCamp son moderadores de toda la comunidad. Esto significa que confiamos en ti para supervisar cualquiera de estos lugares.
+:::
+
+Puedes ser moderador en cualquiera de las plataformas que sea de mas interés para ti. Algunos moderadores solo ayudan a través de GitHub, mientras que otros solo ayudan a través del foro. Algunos moderadores son activos en todas partes.
+
+Al final, lo que queremos es que disfrutes siendo moderador, e inviertas tu tiempo en las secciones que sean de tu interés.
+
+> "Con un gran poder, viene una gran responsabilidad" - Tio Ben
+
+Como moderador, el temperamento es más importante que las habilidades técnicas.
+
+Escucha. Se servicial. No abuses de tu poder.
+
+freeCodeCamp es una comunidad inclusiva y necesitamos mantenerla de esa manera.
+
+Tenemos un solo [Código de Conducta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) que gobierna toda nuestra comunidad. Cuantas menos reglas, mas fácil serán de recordar. Puedes leerlas y memorizarlas [aquí](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+:::note
+As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+:::
+
+## Moderando GitHub
+
+Las moderadoras tienen dos responsabilidades principales en GiHub:
+
+1. Evaluar y responder a problemas.
+2. Revisión y fusión de pull requests (también conocido como QA).
+
+### Moderando conflictos (issues) de GitHub
+
+Utilizamos nuestro repositorio principal [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) como un rastreador de problemas común para todos nuestros repositorios. Todos los días recibimos nuevos problemas, que hay que clasificar, etiquetar y tratar. Hay tambien una gran seccion para empezar a ayudar con proyectos de origen-abierto (open-source).
+
+#### Problema de clasificación
+
+La clasificación (o triaging en inglés) es un proceso de priorización de atención para un nuevo reporte de problema. Tenemos una extensa lista de etiquetas que utilizamos para marcar la prioridad, categoría, estado y alcance de cada tema.
+
+Puedes ayudarnos a organizar y clasificar los reportes de problemas mediante la aplicación de etiquetas de [esta lista](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels). Por lo general, hay una descripción junto a la etiqueta que explica su significado.
+
+Por favor, presta especial atención a las etiquetas `"help wanted"` y `"first timers only"`. Estos se deben agregar a los hilos que creas que se puedan abrir a posibles contribuyentes para realizar una pull request.
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### Cierre de solicitudes de extracción y problemas obsoletos, desactualizados e inactivos
+
+- Los problemas obsoletos o RP son aquellos que no han visto ninguna actividad del autor durante 21 días (3 semanas desde la última actividad), pero solo después de que un moderador haya solicitado más información / cambios.
+
+- La actividad se define como: Comentarios que solicitan una actualización en PR y clases como `estado: actualización necesaria` etiqueta, etc.
+
+- Si el colaborador solicita ayuda adicional o incluso tiempo, lo anterior se puede relajar y revisar después de que se dé una respuesta. En cualquier caso, los mods deben usar su mejor criterio para resolver el estado de PR.
+
+> [!TIP] We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+
+### Moderación de solicitudes de extracción
+
+Las solicitudes de extracción (PRs) es la forma en que los colaboradores envían cambios a los repositorios de freeCodeCamp´s. Debemos realizar un control de calidad (QA) en los pull requests antes de decidir si, cambios de solicitud, o cerrarlos.
+
+#### Tipo de Pull Requests
+
+1. **Edición a las instrucciones del desafío**
+
+ Estos son cambios en el texto de los desafíos: la descripción, las instrucciones o el texto de prueba.
+
+ Puedes revisar las ediciones directamente en GitHub y decidir ahí si aceptar o no los cambios. Aqui debemos ser un poco mas cuidadosos, porque millones de personas leerán estos textos en la medida que vayan completando el programa de freeCodeCamp. ¿El pull request hace más claro el texto sin alargarlo demasiado? ¿Son las recomendaciones relevantes o pedantes en exceso? Recuerda que nuestro objetivo es que los retos sean lo más claro y cortos posibles. No son el lugar para detalles oscuros. Además, los colaboradores podrían intentar añadir enlaces hacia recursos en los desafíos.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Si los cambios se ven bien, por favor asegúrese de dejar una aprobación con un comentario "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me). Una vez que un Pull Request recibe al menos dos aprobaciones (incluyendo la tuya) de los moderadores o del equipo de desarrollo, puedes hacer un Merge.
+
+2. **Edición al código del desafío**
+
+ These are changes to the code in a challenge - the challenge seed, challenge solution, and test strings.
+
+ These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution and to make sure the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
+
+ Algunos colaboradores pueden intentar añadir pruebas adicionales para cubrir casos marginales. Debemos tener cuidado de no complicar demasiado el reto. Estos retos y sus pruebas deben ser tan simples e intuitivas como sea posible. Aparte de los desafíos del algoritmo y la sección de preparación de la entrevista, los estudiantes deberían ser capaces de resolver cada desafío en unos 2 minutos.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. Una vez que un Pull Request recibe al menos dos aprovaciones (incluyendo la tuya) de los moderadores o del equipo de desarrollo, puedes hacer un Merge.
+
+3. **Cambios a la Plataforma**
+
+ Estas ediciones de código cambian la funcionalidad de la propia plataforma freCodeCamp.
+
+ A veces los colaboradores tratan de hacer cambios sin mucha explicación, pero para cambios de código necesitamos asegurarnos de que alla una verdadera necesidad para los mismos. Estos Pull Request deben hacer referencia a un GitHub Issue preexistente, donde discutir las razones del cambio. Entonces puede abrir el pull request en su computadora y probarlo localmente.
+
+ Después de haberlo hecho, si los cambios se ven bien, no los fusiones todavía. Puede comentar sobre la solicitud de extracción diciendo "LGTM", luego mencionar ** "@ freeCodeCamp / dev-team" ** para que puedan echar un vistazo final.
+
+4. **Relaciones públicas automatizadas (Dependabot)**
+
+ Algunos RP son actualizaciones de dependencia automatizadas realizadas a través de una integración. Tu no debes fusionar ni aprobar estos RP. Uno de los miembros del equipo de desarrollo se encargará de revisar y fusionar dichos PRs automatizados.
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+En primer lugar, cuando elijas un pull request a QA, deberás asignarte a él. Puedes hacer esto haciendo clic en el enlace "assign yourself" debajo de la parte "assignees" en la columna derecha de la interfaz de GitHub.
+
+Dependiendo del tipo de pull request que sea, siga las reglas indicadas arriba.
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+Antes de hacer Merge a cualquier Pull Request, asegúrate que Github está tomando todos los Checks (las marcas verdes de aprobación) y que están pasando correctamente en los Pull Request. Si ves que falla alguna de las comprobaciones, investiga y obtén alguna aclaración sobre la causa raíz. ¿Se está realizando el cambio rompiendo nuestras pruebas? ¿El sitio compilará correctamente si el PR hace Merge? Estos controles son fundamentales para la estabilidad de la plataforma.
+
+> [!ALERTA] Al fusionar un PR que no cumple con las comprobaciones de CI/CD puede causar dificultades a todas las partes interesadas, incluido el equipo de desarrollo y los colaboradores.
+
+##### Handling Merge Conflicts:
+
+Sometimes there will be a merge conflict.
+
+Esto significa que otro pull request ha hecho un cambio a esa parte exacta del mismo archivo. GitHub tiene una herramienta para abordar estos conflictos de fusión en GitHub. Puedes tratar de resolver estos conflictos. Utilice su mejor criterio.
+
+Los cambios del pull request estarán en la parte superior, y los cambios de la rama principal estarán en la parte inferior. A veces habrá información redundante que se puede eliminar. Antes de que finalices, cerciórate de eliminar el `<<<<<<`, `======`, y `>>>>>>` que Git añade para indicar áreas de conflicto.
+
+Si no está seguro, pida ayuda a uno de los compañeros moderadores o al equipo de desarrollo.
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+Si el pull request parece estar listo para fusionarse (y no requiere la aprobación de @raisedadead), puedes seguir adelante y fusionarlo. Asegúrese de utilizar la opción predeterminada ** "Squash and Merge" **. Esto juntará todos los commits de las solicitudes de extracción en un solo commit, lo que hará que el historial de Git sea mucho más fácil de leer.
+
+> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way!
+
+Si el autor del pull request es un "colaborador por primera vez" también deberias felicitarlos por su primera fusión de pull request en el repositorio. Puedes mirar la esquina superior derecha del cuerpo del PR, para determinar un colaborador de primera vez. Mostrará `First-time contributor` como se muestra a continuación:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ First-time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="Insignia de colaborador por primera vez en solicitudes de extracción (captura de pantalla" />
+</details>
+
+Si el pull request no parece listo para fusionarse, puedes responder amablemente al autor que debe hacer para prepararlo. Con suerte, responderán y prepararán sus pull request.
+
+Si necesitas una segunda opinión sobre un pull request, sigue adelante y deja tus comentarios sobre el pull request, luego agregue la etiqueta "discussing" al pull request.
+
+##### Closing an Invalid Pull Request:
+
+A menudo, una pull request requiere poco esfuerzo. You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "Made changes" or "Update index.md".
+
+También hay situaciones en las que el colaborador está tratando de agregar un enlace a su sitio web, incluir una librería que creó o realizar una edición frívola que no ayuda a nadie más que a ellos mismos.
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## Moderando el foro
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Eliminando mensajes del foro
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. Alguien ha publicado una imagen pornográfica o gráficamente violenta.
+2. Alguien ha publicado un enlace o código que es de naturaleza maliciosa y podría dañar a otros usuarios que hagan clic en él.
+3. Alguien ha inundado un hilo con muchos mensajes de spam.
+4. An account has been created, beyond a reasonable doubt, to spam.
+
+### Tratando con Spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Dealing with Off-Topic Conversations
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Dealing with Posted Solutions
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Underage Users
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Los usuarios menores de 13 años no pueden utilizar el foro según nuestras Condiciones de Servicio.
+
+Nos hemos enterado de que usted es menor de 13 años. Por los [Términos de servicio de freeCodeCamp](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), debes tener al menos 13 años para usar el sitio o el foro. Eliminaremos tu cuenta de freeCodeCamp y tu cuenta del foro. Esta restricción nos mantiene en cumplimiento de las leyes estadounidenses.
+
+Por favor, vuelva a unirse una vez que haya alcanzado al menos 13 años de edad.
+
+Gracias por su entendimiento.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- When trying to include a "Canned reply" in a response, if the menu doesn't open (after clicking on the gear), click on the text area first then try it again.
+- The moderator's 'wrench' is at the bottom of the view-port but if you click it and cannot see the "Select Posts" button because it has scrolled out of view, you may need to try to scroll to it, though sometimes that doesn't work in which case moving to a desktop/laptop monitor may be needed.
+- Sometimes clicking on the three-dot menu below a post can hide the reply icon. Reload the page to get it back.
+
+## Moderando Facebook
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderando Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+:::note
+Camperbot serves as our moderation bot, and all of the commands use Discord's native slash command interface. You can see a list of all of the commands by typing `/` in any channel.
+:::
+
+1. **Asegúrese de que el usuario ha querido violar el [Código de Conducta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Not all violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. En estos casos, puedes pedir que copien su código en aplicaciones como CodePen o Pastebin.
+
+2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), the moderator will proceed as follows:**
+
+ For minor offences, a warning may be issued with the `/warn` command. For more egregious offences, you can remove the member from the server temporarily with the `/kick` command, or permanently with the `/ban` command. In some cases, a member may just need some time to cool off and collect their thoughts - the `/mute` command allows you to prevent them from engaging with our community for a set period of time. A muted member can see the conversation, but cannot post messages or add reactions.
+
+ All moderation commands will take a `reason` parameter, which should be a short explanation of why the action was taken. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. As such, we should avoid using Discord's built-in moderation tools, as they will not be logged.
+
+ > [!WARNING] The reason provided to a moderation command will also be included in the DM notification to the camper. Please remember to be professional here.
+
+3. **Creando una discusión privada**
+
+ Puede haber situaciones en las que necesites abordar una inquietud con un usuario en privado. Esto no debe hacerse a través de Mensajes Directos, lo que puede llevar a situaciones en las que reclamas una cosa y el campista reclama otra. En su lugar, use la funcionalidad del bot para crear una discusión privada:
+
+ - Call the `/private` command, where `target` is the camper you want to open a private channel with.
+ - The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
+ - When the conversation is complete, click the `❌ Close` button _on the first message in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
+
+4. **Deleting messages**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. If a message is not in line with our Code of Conduct, or otherwise not appropriate for our community, you are generally safe to delete it.
+
+ Note that if the message contains content that violates Discord's terms of service, you'll want to report it via https://dis.gd/report **prior to** deleting it.
+
+5. **Don’t threaten to take action**
+
+ If a camper breaks the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `/private` command, or use the bot's moderation commands.
+
+ If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant moderation action or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of their actions without making it come across as a warning.
+
+ Por ejemplo:
+
+ - Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
+
+ - Or if you really have to explain why:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - For mild and unintentional violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **No se preocupe de ser un moderador**
+
+ Do not see yourself as above the community. **You are the community.** And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
+
+ If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
+
+7. **No contradigas a otros moderadores**
+
+ If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their PoV (Point of View).
+
+ _Remember: We’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front._
+
+8. **Habla con otros moderadores**
+
+ We have a `#mod-chat` room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporalmente inactivo**
+
+ If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
+
+## Cómo convertirse en moderador
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+:::note
+For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
+:::
+
+> This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- The user is guaranteed some privacy.
+- Public chat is no longer disrupted.
+- Other team members can pitch in, should you feel uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/es/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..52f87586
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: Guía oficial de incorporación de moderadores de freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+:::note
+Si aún no ha leído el [Manual del moderador](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook), deberia empezar por ahí primero.
+:::
+
+## Nuestro foro
+
+### Primeros pasos
+
+Lo primero que puede notar después de recibir el estado de moderador en el foro, es que su interfaz se verá algo diferente, con nuevas herramientas de administración para explorar y, acceder al subforo Mod-Team.
+
+Algunas de las nuevas herramientas aparecerán dentro de un nuevo elemento de menú que parece una llave inglesa. Algunos aparecerán como nuevas pestañas o botones, o incluso nuevas opciones habilitadas dentro de los menús del foro.
+
+Para familiarizarse con las nuevas herramientas y poderes, puede combinar uno o más de los siguientes métodos durante su primera semana con este rol elevado:
+
+> [!TIP] Los dos primeros son los más importantes.
+
+### Familiarícese con las herramientas de administración de discord
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. Para comenzar a familiarizarse con Discord y la función de moderación, comience leyendo la [nueva guía del usuario](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) de Discord y la [nueva guía del moderador](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116) de Discord.
+
+### Shadow a Mod
+
+Todas las acciones del moderador se pueden seguir revisando los [registros de acciones](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. Posts to be reviewed will show up in the [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) area of the forum.
+
+For the first week or so you will want to pay attention to what is getting flagged and what is being reviewed, and compare that to the actions being taken upon the flagged posts. You may see the system account flag a post because the user created it too quickly. In many cases, the moderators will unflag the post by clicking on the "Approve Post" button or mark it as "Not Spam" (depending on the flag type).
+
+Commonly, spam flags can also be raised by members or moderators. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+You may notice moderators performing a procedure called 'split topic'. This may be a case where a moderator has split a post that was made erroneously on an existing topic into a new topic, or a moderator merged duplicate topics that a single user has created for the same question. Watching this procedure will highlight different actions and their causes.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. These include:
+
+- Welcoming a new forum member who has posted code without a question -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Reminding members not to post code solutions but to provide hints and tips instead -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Responding to a situation where someone's code works for you but not for them -> "Browser Issues"
+- Encouraging members to open GitHub issues when a possible bug is found -> "Bug Report"
+
+There are more, which you can read through to become familiar with their respective uses. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Read Mod-Team Subforum Posts
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Where to Ask for Help
+
+To get help dealing with a situation that you are either uncomfortable with or unsure of how to handle, discuss with your fellow moderators on either the [Mod-Team Subforum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) or the [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) on Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/es/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/es/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9a3017b7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Divulgación responsable - Salón de la Fama
+---
+
+Apreciamos cualquier divulgación responsable de vulnerabilidades que puedan afectar la integridad de nuestras plataformas y usuarios. Si está interesado en contribuir a la seguridad de nuestra plataforma, lea nuestra política de [seguridad descrita aquí](security).
+
+Si bien no ofrecemos ninguna recompensa o botín en este momento, estamos agradecidos con estas personas increíbles por ayudarnos a mantener la plataforma segura para todos:
+
+- Mehul Mohan de [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Vulnerability Fix](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) trabajando con IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/security.md b/src/content/docs/es/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bab914bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+---
+title: Política de Seguridad de freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Este documento describe nuestra política de seguridad para los códigos, plataformas que operamos, y cómo reportar vulnerabilidades.
+
+## Informar una vulnerabilidad
+
+:::note
+Si crees que has encontrado una vulnerabilidad, **por favor, informa de ella de forma responsable**. No cree propuestas de GitHub para problemas de seguridad. En su lugar, siga esta guía.
+:::
+
+### Directrices
+
+Agradecemos la divulgación responsable de las vulnerabilidades que puedan afectar a la integridad de nuestras plataformas y usuarios. En aras de ahorrar tiempo a todo el mundo, le animamos a informar de las vulnerabilidades teniendo en cuenta esto:
+
+1. Asegúrese de que está utilizando las versiones **más recientes**, **estables** y **actualizadas** del sistema operativo y del navegador o navegadores web disponibles en su máquina.
+2. Consideramos que el uso de herramientas y utilidades en línea para informar de problemas con las configuraciones de SPF y DKIM, las pruebas del servidor SSL, etc., entra en la categoría de ["mendigar recompensas"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) y no podemos responder a estos informes.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Reportando
+
+Después de confirmar las directrices anteriores, no dude en enviar un correo electrónico a `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. También puede enviarnos un mensaje cifrado con PGP a `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Una vez que nos informe de una vulnerabilidad, la investigaremos y nos aseguraremos de que no sea un falso positivo. Si necesitamos aclarar algún detalle, nos pondremos en contacto con usted. Puede enviar informes separados para cada problema que encuentre. Tenga en cuenta que no podremos responder a las cuestiones que consideremos que están fuera de las directrices.
+
+## Plataformas y Bases de Código
+
+Esta es una lista de las plataformas y bases de código para las que aceptamos informes:
+
+### Plataforma de Aprendizaje
+
+| Versión | Rama | Soportado | Sitio web activo |
+| ---------- | -------------- | --------- | ------------------------ |
+| producción | `prod-current` | Sí | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| escenario | `prod-staging` | Sí | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| desarrollo | `principal` | No | |
+
+### Plataforma de Publicación
+
+| Versión | Soportado | Sitio web activo |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| producción | Sí | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localizado | Sí | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Aplicación Móvil
+
+| Versión | Soportado | Sitio web activo |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| producción | Sí | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Otras Plataformas
+
+Aparte de lo anterior, también aceptamos informes para los repositorios alojados en GitHub bajo la organización de freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Otras Aplicaciones Autoalojadas
+
+Algunas de nuestras plataformas las alojamos nosotros mismos utilizando software de código abierto como Ghost y Discourse. Si está informando de una vulnerabilidad, asegúrese de que no se trata de un error en el software de origen.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/es/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4155ebec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+Regularmente desarrollamos en los últimos o más populares sistemas operativos como macOS 10.15 o posterior, Ubuntu 18.04 o posterior, y Windows 10 (con WSL2).
+
+Se recomienda buscar tu problema específico en recursos como Google, Stack Overflow y Stack Exchange. Existe la posibilidad de que alguien haya enfrentado el mismo problema y que ya exista una respuesta a tu pregunta específica.
+
+Si estás en un sistema operativo diferente o todavía estas encontrandote con problemas, consulta [obtener ayuda](#getting-help).
+
+:::warning
+Por favor, evite crear asuntos de GitHub para problemas con las tecnologías previas. Están fuera del alcance de este proyecto.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. Si uno de ellos no fue almacenado en caché, ejecute lo siguiente:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+O
+
+Use el atajo
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Use `git clean` en modo interactivo:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Cómo limpiar archivos sin el seguimiento de git (captura de pantalla)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="Cómo limpiar archivos sin el seguimiento de git" />
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+Mientras estás en desarrollo, tu sesión es almacenado como cookies. Limpiarlos cerrará la sesión de tu cuenta de desarrollo.
+
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, too. Pero sobrescribirá al usuario de desarrollo en tu base de datos local.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+Cuando intenta navegar a http://localhost:8000/developmentuser para ver la página de perfil, Gatsby se encarga de servir las páginas del lado del cliente y por lo tanto obtendrá una página 404 para el perfil de usuario cuando este trabajando.
+
+Hay un botón de "Vista previa de página 404 personalizada", haga clic en él para ver el perfil.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+Si tienes errores mientras instalas dependencias, por favor asegúrate de que no estes en una red restringida o tu configuración de firewall no te impida acceder a los recursos.
+
+La primera configuración puede tardar un rato dependiendo del ancho de banda de tu red. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+:::note
+Si estás utilizando dispositivos de Apple con el chip M1 para iniciar la aplicación localmente, es sugerido usar Node v14.7 or superior. De lo contrario, podrías tener problemas con dependencias como Sharp.
+:::
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+Si estás atascado y necesitas ayuda, sientete libre de hacer preguntas en ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Puede haber un error en la consola de tu navegador o en el Bash / Terminal / Línea de comandos que te ayudará a identificar el problema. Proporciona este mensaje de error en la descripción de tu problema para que otros puedan identificar el problema fácilmente y ayudarte a encontrar una solución.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/es/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/es/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9fd1421c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/es/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Cómo funciona el flujo de trabajo de los tokens de usuario
+---
+
+Los tokens de usuario se utilizan para identificar usuarios a terceros de modo que los desafíos completados con esos servicios pueden ser guardados en la cuenta de usuario.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+Por el momento, los tokens sólo se utilizan para presentar los retos de la base de datos relacional. A token gets created when a signed-in user clicks the "Click here to start the course" or "Click here to start the project" buttons to start one of the Relational Database courses or projects.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+Se eliminará un token de usuario cuando un usuario se desconecte de freeCodeCamp, restablezca su progreso, borra su cuenta, o borra manualmente el token usando el widget de la página de configuración.
+
+## How they Work
+
+Los tokens se almacenan en una colección de `UserToken` en la base de datos. Cada registro tiene un único `_id`, que es el token, y un `user_id` que enlaza a la cuenta del usuario desde la colección `user`. El token se codifica usando JWT y se envía al cliente cuando se crea. That encoded token is then given to third-party services that need it and sent to our API by them when a challenge is completed. Cuando nuestro API lo recibe, está decodificado para que podamos identificar al usuario que envía un desafío y guardar el desafío completado en sus `Desafíos completos`.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/FAQ.md b/src/content/docs/faq.md
similarity index 100%
rename from src/content/docs/FAQ.md
rename to src/content/docs/faq.md
diff --git a/src/content/docs/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
index 1dd5a78a..ebf6f8f9 100644
--- a/src/content/docs/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
+++ b/src/content/docs/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -2,7 +2,9 @@
title: Catching emails locally
---
-**Note:** This is an **optional** step and is required only when working with email workflows
+:::note
+This is an **optional** step and is required only when working with email workflows
+:::
- [Introduction](#introduction)
- [Installing MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
index 2cc9cc98..4bc73267 100644
--- a/src/content/docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+++ b/src/content/docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -11,7 +11,8 @@ Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCam
- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows.
- You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase.
- Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
- :::
+
+:::
If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/it/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c50cee47
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Manuale Analytics per gli autori
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Cercare per lingua
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+
+
+1. Dal menu a discesa in alto, seleziona `News`.
+1. Nella barra laterale, clicca su `Reports`.
+1. Dalla barra laterale secondaria, seleziona `Engagement`.
+1. Clicca su `Pages and Screens`.
+1. Nella barra di ricerca, digita il sotto-percorso per la lingua desiderata.
+1. Dal menu a discesa sotto la barra di ricerca, scegli `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filtrare i report per autore
+
+Dopo essere arrivati ai report `Pages and Screens` menzionati sopra, utilizza i seguenti passaggi per filtrare i risultati in base all'autore.
+
+
+
+1. Clicca sul pulsante `Add filter`.
+1. Dalla barra di navigazione laterale includi `Author`.
+1. Dal menu a discesa `Dimensions values`, scegli il nome dell'autore.
+1. Clicca sul pulsante `Apply` per applicare le modifiche.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/it/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c0757e52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: Buone pratiche per il codebase
+---
+
+## Definire lo stile di un componente
+
+Consigliamo di definire lo stile dei componenti seguendo la nostra [guida di stile](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+I colori sono definiti in [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css) e i font in [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+Siamo estremamente categorici circa l'aggiunta di nuove variabili/token ai colori. Dopo un'attenta ricerca, i colori sono stati scelti per rispettare l'identità del marchio freeCodeCamp, l'esperienza dello sviluppatore e l'accessibilità.
+
+La parola chiave `!important` può essere usata per sovrascrivere i valori in alcuni casi (per esempio: problemi di accessibilità). È necessario aggiungere un commento che descriva il problema, in modo che non venga rimosso in un futuro refactoring.
+
+### Supporto RTL
+
+Stiamo cercando di supportare il layout da destra a sinistra (right-to-left, RTL) nel codebase per le lingue che sono lette in questa direzione. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Ecco alcune rapide regole pratiche da seguire:
+
+- Non utilizzare le proprietà `float`
+ - Invece, utilizza i layout Flexbox e Grid poiché hanno già integrato il supporto RTL e saranno più facili da gestire e revisionare.
+- Non definire la direzione usando `margin` e `padding`: potrebbe sembrare innocuo usare `padding-right` e `margin-left`, ma queste direzioni non sono rispecchiate quando il layout cambia in RTL e l'aggiunta di valori contatori per loro nel file RTL rende il mantenimento del codebase più difficile.
+ - Usa le proprietà logiche per loro: puoi aggiungere la stessa spaziatura usando `padding-inline-end` e `margin-inline-start` e non dovrai preoccuparti del layout RTL, dato che segue l'inizio e la fine della riga e non è necessario aggiungere alcun valore aggiuntivo nei file RTL, così le persone non dovranno ricordarsi di cambiare gli stessi valori in due file.
+- Non usare `!important` in `font-family`: il layout RTL utilizza caratteri diversi rispetto al layout LTR, aggiungendo `!important` alla proprietà `font-family` si influisce anche sul layout RTL.
+
+## JavaScript generale
+
+Nella maggior parte dei casi, il nostro [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) darà un avvertimento nel caso di un format che va contro le preferenze del nostro codebase.
+
+Si incoraggia l'utilizzo di componenti funzionali invece di componenti basati su classi.
+
+## TypeScript specifico
+
+### Migrare un file da JavaScript a TypeScript
+
+#### Mantenere la cronologia del file con Git
+
+A volte cambiare il file da `<filename>.js` a `<filename>.ts` (o `.tsx`) fa sì che il file originale venga cancellato e ne venga creato uno nuovo, altre volte è solo il nome del file a cambiare - per quanto riguarda Git. Idealmente, vogliamo che la cronologia dei file sia conservata.
+
+Il modo migliore per assicurarsene è:
+
+1. Rinominare il file
+2. Fare un commit con il flag `--no-verify` per prevenire gli avvertimenti di Husky per errori di lint
+3. Fare il refactoring per la migrazione a TypeScript in un commit separato
+
+> [!NOTE] Un editor come VSCode ha buona probabilità di mostrare comunque che un file è stato eliminato e uno nuovo è stato creato. Se usi la CLI (Command Line Interface) per eseguire `git add .`, allora VSCode mostrerà che il file è stato rinominato
+
+### Convenzioni per i nomi
+
+#### Interfacce e Tipi
+
+Per la maggior parte, incoraggiamo l'uso di dichiarazioni di interfaccia piuttosto che di tipo.
+
+Props di componenti React - suffissi con `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+Componenti React stateful - suffissi con `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Default - nomi di oggetti in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Definizione di azioni
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### Come usare Reducer
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### Come fare il dispatch
+
+Dentro un componente, importa le azioni e i selettori necessari.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [Documentazione di TypeScript](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [CheatSheet di TypeScript con React](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/it/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..957eb0c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Estensione di VSCode per i corsi
+---
+
+Questo dettaglia le linee guida della manutenzione del repo [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) che contiene il codice sorgente per l'estensione [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses).
+
+## Pubblicazione dell'estensione
+
+Una GitHub Action pubblica automagicamente l'estensione nel Visual Studio Marketplace, al rilascio di un nuovo GitHub Release.
+
+1. Impacchetta una nuova versione dell'estensione:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Dove `<tag_type>` è uno dei seguenti: `major`, `minor`, `patch`.
+
+2. Fai il push della nuova versione a `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Facoltativamente, puoi fare il push direttamente a `upstream/main`, ma aprire una PR è raccomandato per un sanity check.
+
+3. Crea una nuova GitHub Release usando la GitHub UI:
+
+- Implementa correttamente il numero di versione, quando crei una nuova tag.
+- Fai l'upload del file `.vsix` con la nuova release.
+- Pubblica la release, e conferma che l'azione ha avuto successo.
+
+> [!NOTE] Creare una release richiede permessi di scrittura sul repository `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension`.
+
+## Pubblicare l'estensione manualmente
+
+Un upload manuale al Visual Studio Marketplace può essere fatto, seguendo questi step:
+
+1. Visita https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ e fai log in
+2. Naviga alla [pagina freeCodeCamp Publisher](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Seleziona l'estensione rilevante, e seleziona `Update`
+4. Carica il file dai tuoi file locali
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..907c26ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Struttura dei file del curriculum
+---
+
+Il nostro contenuto educativo centrale è situato nella cartella chiamata convenientemente `curriculum`. Questa pagina analizzerà come questi file sono organizzati.
+
+## Terminologia
+
+Questi sono alcuni termini che usiamo quando discutiamo il contenuto del nostro curriculum.
+
+- `certification` : Quando riferito a una certificazione in questa istanza, sta parlando del certificato che gli utenti richiedono. Che è separato dal nome del superBlock.
+- `superBlock` : Un superblock è il raggruppamento superiore di sfide. Ogni superblock corrisponde ad una certificazione nel curriculum (p.e. Responsive Web Design).
+- `block` : Un block è una sezione in un superblock. Un blocco corrisponde a un gruppo di sfide in una certa certificazione (per esempio Basic HTML e HTML5)
+- `challenge`: Una sfida è una singola lezione nel curriculum (p. e. Saluta gli elementi HTML)
+
+## Albero dei file
+
+Usando quei termini, ecco come la struttura dei file viene definita:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## La cartella `_meta`
+
+La cartella `_meta` è una cartella speciale che contiene dei file `.json`. Questi file corrispondono ad ogni blocco nel curriculum e sono usati per determinare a quale superblocco corrisponde un certo blocco, e l'ordine delle sfide in quel blocco.
+
+## Rinominare i file
+
+Ci potrebbero essere volte in cui devi rinominare un certificato, superblocco, blocco o sfida. Questa sezione delinea gli step necessari per evitare errori di build nel farlo.
+
+:::danger
+Rinominare i file nella struttura del curriculum spesso cambia il percorso (o l'URL) del contenuto sulla pagina web principale. Questo è da fare con cura, poiché bisogna configurare reindirizzamenti per ogni cambiamento che viene fatto.
+:::
+
+### Rinominare una certificazione
+
+Quando rinomini una certificazione, vorrai probabilmente rinominare il superblocco associato. Fai quanto segue per rinominare solo il certificato:
+
+1. Rinomina la cartella `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` con il nuovo nome.
+1. Nel file `meta.json` di quella cartella, rinomina i valori in `name`, `dashedName`, e `challengeOrder` con il nuovo nome.
+1. In `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, rinomina la cartella `{superBlock}-certificate`, e il file YAML dentro di essa, con il nuovo nome.
+1. Nel file YAML, cambia il titolo (`title`) con il nuovo nome.
+1. Rinomina il file e la cartella dello step 3 nel resto delle lingue del curriculum.
+1. Aggiorna `client/src/redux/index.ts` con il corretto `title`.
+1. Facoltativamente, aggiorna il `certSlug` per il superblocco nello stesso file. **Nota** che rinominare un `certSlug` cambia l'URL della certificazione ed è da fare con attenta considerazione.
+1. Aggiorna il `title` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` al nuovo valore. **Nota** che cambiare `title` qui **romperà** la pagina superBlock per la certificazione associata. Fa affidamento sul titolo del superblocco per combaciare il titolo del certificato. Vorrai probabilmente rinominare il superblocco allo stesso tempo.
+1. Se hai rinominato `certSlug` allo step 7, cambialo qui per il certificato e tutti i valori dei progetti annidati `projects`.
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. Se hai rinominato `certSlug` allo step 7, aggiorna la key di `certSlugTypeMap` nello stesso file.
+1. Se necessario aggiorna il nome del certificato nell'array `legacyCerts` di `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx`.
+1. Aggiorna il file `README.md` principale al nuovo nome.
+
+### Rinominare un superblocco
+
+> [!NOTE] Quando rinomini un superblocco, il nuovo nome della cartella è usato come percorso e dovrebbe essere considerato il nome "corretto". Tutti gli altri valori devono essere aggiornati per riflettere il cambiamento.
+
+Inoltre, probabilmente vorrai rinominare il certificato e il blocco `{superBlock}-projects` quando rinomini un superblocco visto che condividono tutti un nome. Per rinominare solo un superblocco devi:
+
+1. Rinominare la cartella del superblocco nella cartella `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Rinominare la cartella del superblocco in _tutte_ le altre cartelle `curriculum/challenges/{language}`.
+1. Per ogni blocco dentro quel superblocco, aggiorna il valore `superBlock` nel file `meta.json` al suo nome a trattini. Non hai bisogno di rinominare alcuna cartella qui. Fallo quando rinomini un blocco.
+1. Rinomina la cartella del superblocco in `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Aggiorna il file `index.md` nella cartella qui sopra, cambiando i valori `title` e `superBlock` al nuovo nome.
+1. Per ogni cartella di un blocco all'interno della precedente, aggiorna `index.md` affinché usi il valore corretto di `superBlock`.
+1. Nel file `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`, aggiorna il percorso per il certificato in cima al file, e il valore di `title` per quel superblocco. **Nota** che cambiare `title` qui **romperà** l'abilità di vedere la certificazione per questo superblocco. Fa affidamento sul titolo del superblocco per abbinare il titolo del certificato. Vorrai probabilmente rinominare la certificazione allo stesso tempo.
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. Aggiorna il valore del percorso in `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. Per ogni lingua in `client/i18n/locales`, aggiorna il file `intro.json` file affinché usi il nuovo `dashedName` del superblocco. Nel file inglese aggiorna anche `title`.
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. Aggiorna il valore dove è usato.
+1. Aggiorna il file principale `README.md` con il nuovo nome.
+
+### Rinominare un blocco
+
+Quando rinomini un blocco del curriculum, devi:
+
+1. Cambiare il nome della cartella nella directory `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
+1. Cambiare il nome della cartella dello stesso blocco in _tutte_ le directory delle altre lingue. Queste devono tutte essere uguali alla struttura inglese o il build avrà errori.
+1. Cambia il nome della cartella del blocco nella directory `_meta`.
+1. Aggiorna le proprietà `name` e `dashedName` per il `meta.json` di quel blocco.
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Rinominare una sfida
+
+Quando rinomini il file di una singola sfida, devi:
+
+1. Cambiare il nome del file della sfida nella directory `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Cambiare i valori di `title` e `dashedName` in quel file.
+1. Cambia il nome del file e il valore di `dashedName` in quei file per _tutte_ le directory delle altre lingue.
+1. Cambiare il nome della sfida nel file `meta.json` rilevante. I nomi delle sfide qui non sono usati nel build, ma forniscono un metodo user-friendly per identificare l'ordine delle sfide.
+1. Se la sfida è un progetto di un certificato, aggiorna il file YAML in `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` con il nuovo nome.
+1. Se la sfida è un progetto di un certificato, aggiorna `title` e `link` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. Se la sfida è un progetto di un certificato, aggiorna il file `README.md` principale con il nuovo nome.
+
+## La proprietà `dashedName`
+
+La proprietà `dashedName` è usata per generare il percorso URL del superblocco, del blocco o della sfida. Questi devono in genere combaciare con ciò che l'aiutante `/utils/slugs.js` restituirebbe per il nome del file.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/devops.md b/src/content/docs/it/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c6404364
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: Manuale di DevOps
+---
+
+Questa guida ti aiuterà a capire lo stack della nostra infrastruttura e come gestiamo le nostre piattaforme. Anche se questa guida non ha dettagli esaustivi per tutte le operazioni, può essere utilizzata come riferimento per la comprensione dei sistemi.
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+Questo prevede tre fasi da seguire in sequenza:
+
+1. I nuovi cambiamenti (sia risoluzioni di bug che nuove caratteristiche) sono aggiunti al branch principale di sviluppo (`main`) tramite pull requests.
+2. Queste modifiche sono testate da una serie di test automatizzati.
+3. Una volta che i test sono superati, rilasciamo le modifiche (o aggiornamenti se necessario) alle distribuzioni sulla nostra infrastruttura.
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+In genere, si fa un merge di [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (il ramo di sviluppo di default) nel branch [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) una volta al giorno, e questo è rilasciato in una infrastruttura isolata.
+
+Questa è una release intermedia per i nostri sviluppatori e collaboratori volontari. È anche noto come il nostro rilascio di "staging" o "beta".
+
+È identico al nostro ambiente di produzione live su `freeCodeCamp.org`, a parte il fatto che utilizza un set separato di database, server, web-proxies, ecc. Questo isolamento ci permette di testare lo sviluppo continuo e le caratteristiche in uno scenario come quello di "produzione", senza influenzare gli utenti regolari delle principali piattaforme di freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+Una volta che il team di sviluppo [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) è soddisfatto dei cambiamenti nella piattaforma di staging, questi cambiamenti sono spostati ogni pochi giorni al branch [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current).
+
+Questa è la versione finale che sposta le modifiche alle nostre piattaforme di produzione su freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+Adottiamo vari livelli di integrazione e test di accettazione per verificare la qualità del codice. Tutti i nostri test sono fatti con software come [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) e [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. Questi ci aiutano a testare l'integrazione tra i diversi componenti.
+
+> [!NOTE] We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+
+Tutti questi test aiutano a evitare che i problemi si ripetano e assicurano di non introdurre dei bug mentre si lavora su un altro bug o una nuova funzionalità.
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+Abbiamo configurato un software di consegna continua per inviare modifiche ai nostri server di sviluppo e produzione.
+
+Una volta che le modifiche sono inviate ai branch di rilascio protetti, una pipeline di build viene attivata automaticamente per il branch. Le pipeline di build sono responsabili della compilazione degli artefatti e di conservarli in un deposito di stoccaggio per un uso successivo.
+
+La pipeline di build continua ad attivare una corrispondente pipeline di rilascio se completa un'esecuzione riuscita. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. Le modifiche ai branch `production-*` possono avvenire solo tramite il merge fast-forward all'[`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. Configura correttamente i tuoi remotes.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Risultati:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Assicurati che il tuo branch `main` sia pulito e sincronizzato con la fonte (upstream).
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Controlla che i test GitHub CI siano superati nel branch `main` dell'upstream.
+
+ I test di [integrazione continua](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) dovrebbero essere verdi ed essere superati per il branch `main`. Clicca sulla spunta verde vicino all'hash del commit guardando il codice del branch `main`.
+
+ <details> <summary> Controllare lo stato sulle GitHub Actions (screenshot) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ Se questo fallisce, dovresti fermarti e investigare gli errori.
+
+4. Conferma di essere in grado di fare il build del repository localmente.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Sposta cambiamenti da `main` a `prod-staging` con un merge fast-forward
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > Se lo fanno, potresti aver fatto qualcosa in modo errato e dovresti solo ricominciare da capo.
+
+Gli step precedenti attiveranno automaticamente l'esecuzione della pipeline di build per il ramo `prod-staging`. Una volta completata la build, gli artefatti vengono salvati come file `.zip` in un archivio per essere recuperati e utilizzati in seguito.
+
+La pipeline di rilascio viene attivata automaticamente quando un nuovo artefatto è disponibile dalla pipeline di build connessa. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+Il processo è per lo più lo stesso delle piattaforme di staging, con la messa in atto di alcuni controlli aggiuntivi. Questo è solo per essere sicuri: non possiamo permetterci di rompere nulla su freeCodeCamp.org dato che può vedere centinaia di utenti che lo utilizzano in qualsiasi momento.
+
+| NON eseguire questi comandi a meno che non sia stato verificato che tutto funziona sulla piattaforma di staging. Non dovresti bypassare o saltare alcun test di staging prima di procedere ulteriormente. |
+| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Assicurati che il tuo ramo `prod-staging` sia pulito e sincronizzato con la fonte.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Sposta cambiamenti da `prod-staging` a `prod-current` con un merge fast-forward
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > Se lo fanno, potresti aver fatto qualcosa in modo errato e dovresti solo ricominciare da capo.
+
+Gli step precedenti attiveranno automaticamente l'esecuzione della pipeline di build per il ramo `prod-current`. Una volta che un artefatto di build è pronto, attiverà un avvio della pipeline di rilascio.
+
+**Misure supplementari per le azioni dello Staff**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. Possono _approvare_ o _rifiutare_ l'esecuzione del rilascio.
+
+Se le modifiche funzionano bene e sono state testate sulla piattaforma di staging, allora possono essere approvate. L’approvazione deve essere rilasciata entro 4 ore dall’attivazione del rilascio prima di essere respinta automaticamente. Un membro dello staff può riattivare il rilascio manualmente per gli avvi rifiutati, o attendere il prossimo ciclo di rilascio.
+
+Per uso dello staff:
+
+| Controlla la tua email per un link diretto o [vai alla dashboard di rilascio](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) dopo che la build è completata. |
+| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Una volta che uno dei membri dello staff approva una release, la pipeline porterà i cambiamenti live ai CDN di produzione e ai server API di freecodecamp.org.
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+Ecco lo stato attuale di test, build e deployment del codebase.
+
+| Ramo | Test unitari | Test di integrazione | Build & rilasci |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (sperimentale, futuro) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+Ti diamo il benvenuto al test di queste versioni in modalità **"public beta testing"** e all'accesso anticipato alle funzionalità imminenti delle piattaforme. A volte queste funzionalità/modifiche sono indicate come **next, beta, staging,** ecc. in modo intercambiabile.
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+Ti ringraziamo se vorrai segnalare i bug che incontrerai aiutandoci a migliorare freeCodeCamp.org. Sei un grande!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| Applicazione | Lingua | URL |
+| :----------- | :------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Learn | Inglese | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Spagnolo | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Cinese | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| News | Inglese | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Forum | Inglese | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Cinese | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] Il nome del dominio è diverso da **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. Questo è intenzionale per prevenire l'indicizzazione dai motori di ricerca e creare confusione per i normali utenti della piattaforma.
+>
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**La versione attuale della piattaforma è sempre disponibile su [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+Il team di sviluppo fa un merge dei cambiamenti dal ramo `prod-staging` a `prod-current` quando rilascia dei cambiamenti. Il commit superiore dovrebbe essere quello che si vede live sul sito.
+
+È possibile identificare la versione esatta distribuita visitando i registri di compilazione e distribuzione disponibili nella sezione stato. Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+Ci sono alcune limitazioni e compromessi noti quando si utilizza la versione beta della piattaforma.
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **Gli utenti nella versione beta avranno un account separato dalla produzione.** La versione beta utilizza un database fisicamente separato dalla produzione. Questo ci dà la possibilità di prevenire qualsiasi perdita accidentale di dati o modifiche. The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ Il deploy dovrebbe essere frequente e in iterazioni rapide, talvolta più volte al giorno. As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ Il sito beta ha il solo scopo di supportare lo sviluppo locale e il testing, nient'altro. Non è una promessa di ciò che sta arrivando, ma un assaggio di ciò a cui si sta lavorando.
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ Usiamo un test tenant per freeCodeCamp.dev su Auth0, e quindi non abbiamo l'abilità di impostare un dominio personalizzato. Questo fa sì che tutte le callback di reindirizzamento e la pagina di login appaiano su un dominio predefinito come: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. Questo non ha effetto sulle funzionalità ed è quanto più vicino possiamo arrivare alla produzione.
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+Per favore apri nuove issue per discutere e segnalare bug.
+
+Puoi inviare un'email a `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` se hai domande. Come sempre tutte le vulnerabilità di sicurezza dovrebbero essere segnalate a `security[at]freecodecamp.org` invece che al tracker pubblico o nel forum.
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. Questa guida è rivolta solo ai **membri dello staff di freeCodeCamp**.
+> 2. Queste istruzioni non devono essere considerate esaustive, per favore usa cautela.
+
+Come membro dello staff, potrebbe esserti stato dato accesso ai nostri fornitori di servizi cloud come Azure, Digital Ocean, ecc.
+
+Ecco alcuni utili comandi che puoi usare per lavorare sulle Virtual Machine (VM), per fare manutenzione o faccende generali.
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+
+### Azure
+
+Installa Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(Una volta sola) Installa su macOS con [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(Una volta sola) Login:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Ottieni una lista dei nomi delle VM e degli indirizzi IP:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Installa Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(One volta sola) Installa su macOS con [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(Una Volta) Login:**
+
+Autenticazione e cambio di contesto: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Ottieni una lista dei nomi delle VM e degli indirizzi IP:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+Stiamo lavorando per creare il nostro setup IaC, e mentre stiamo lavorando su quello puoi usare il portale di Azure o il CLI di Azure per creare nuove macchine virtuali e altre risorse.
+
+:::tip
+Non importa cosa usi per creare nuove risorse, abbiamo alcuni [utili file di configurazione cloud-init](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) per aiutarti a fare provisioning di base, come installare docker o aggiungere le chiavi SSH, ecc.
+:::
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+Dovresti tenere aggiornate le VM eseguendo update e upgrade. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Prima di eseguire questi comandi:
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - Se stai aggiornando pacchetti su una VM che sta già servendo una applicazione, assicurati che l'app sia stata fermata e salvata. L'aggiornamento dei pacchetti causerà picchi di utilizzo di banda, memoria e/o CPU portando a malfunzionamenti di applicazioni in esecuzione.
+
+Aggiorna informazioni sul pacchetto
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Aggiorna i pacchetti installati
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Pulisci i pacchetti inutilizzati
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+Stiamo eseguendo istanze di carico bilanciate (Azure Load Balancer) per i nostri server web. Questi server eseguono NGINX che inverte il proxy di tutto il traffico a freeCodeCamp.org da varie applicazioni in esecuzione sulle proprie infrastrutture.
+
+La configurazione di NGINX è disponibile su [questo repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### Prima Installazione
+
+Provisioning delle VM con il codice
+
+1. Installa NGINX e configuralo dal repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Installa i certificati di origine di Cloudfire e la configurazione dell'applicazione di upstream.
+
+ Ottieni il certificati di origine di Cloudflare dallo storage sicuro e installa nelle posizioni richieste.
+
+ **O**
+
+ Sposta i certificati esistenti:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Aggiorna le configurazioni di upstream:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Aggiungi/aggiorna gli indirizzi IP di sorgente/origine dell'applicazione.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configura i firewall di Azure e `ufw` come necessario per indirizzi di origine d'ingresso.
+
+4. Aggiungi la VM al pool del load balancer del backend.
+
+ Configura e aggiungi regole al load balancer se necessario. Potresti anche aver bisogno di aggiungere le VM al pool del load balancer del backend.
+
+### Log e monitoraggio
+
+1. Controlla lo stato dei servizi NGINX usando i comandi seguenti:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. I log e il monitoraggio dei server sono disponibili su:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), l'attuale dashboard per il monitoraggio. Stiamo lavorando a metriche più granulari per una osservabilità migliore
+
+### Aggiornamento Istanze (Manutenzione)
+
+Le modifiche di configurazione alle nostre istanze NGINX sono mantenute su GitHub, queste dovrebbero essere distribuite su ogni istanza in questo modo:
+
+1. SSH nell'istanza e inserisci sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Ottieni l'ultimo codice di configurazione.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Prova e ricarica la configurazione [con i segnali](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. Installa strumenti di generazione per i binari di node (`node-gyp`) ecc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Prima Installazione
+
+Fare il provisioning delle VM con il codice
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Aggiornamento Istanze (Manutenzione)
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Aggiornamento Istanze (Manutenzione)
+
+Ogni tanto devono essere fatti dei deployment dei cambiamenti al codice alle istanze delle API. Può essere un update continuo o un update manuale. The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+Le pipeline automatizzate al momento non gestiscono l'aggiornamento delle dipendenze. Dobbiamo fare un aggiornamento manuale prima dell'avvio di qualsiasi pipeline di deployment.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. Non dovresti aver bisogno di eseguire questi comandi. Sono qui per documentazione.
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Prima installazione
+
+Fare provisioning delle VM con il codice
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Logging e monitoraggio
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Aggiornamento istanze (Manutenzione)
+
+Ogni tanto devono essere fatti dei deployment dei cambiamenti al codice alle istanze delle API. Può essere un update continuo o un update manuale. Il secondo è essenziane quando si cambiando dipendenze o si aggiungono variabili ambientali.
+
+:::danger
+Le pipeline automatizzate al momento non gestiscono l'aggiornamento delle dipendenze. Dobbiamo fare un aggiornamento manuale prima di ogni esecuzione della pipeline di deployment.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Aggiornamenti manuali - Usati per aggiornare dipendenze, variabili env.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Aggiornamenti continui - usati per cambiamenti logici al codice.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Gli update continui a codice e logica sono gestiti dalle pipeline. Non dovresti aver bisogno di eseguire questi comandi. Sono qui per documentazione.
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+I nostri chat server sono disponibili con una configuratione HA [raccomandata nella documentazione di Rocket.Chat](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). Il file `docker-compose` per questo è [disponibile qui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+Avviamo istanze ridondanti di NGINX che sono loro stesse con bilanciamento di carico (Azure Load Balancer) sul cluster di Rocket.Chat. I file di configurazione NGINX sono [disponibili qui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Fare provisioning delle VM con il codice
+
+**Cluster NGINX:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Cluster Docker:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**Cluster NGINX:**
+
+Le modifiche di configurazione alle nostre istanze NGINX sono mantenute su GitHub, queste dovrebbero essere distribuite su ogni istanza in questo modo:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Cluster Docker:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+Fai ssh nella VM (hosted su Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+Visualizza le versioni installate di node & npm
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Installa l'ultima versione di Node.js LTC, e reinstalla i pacchetti globali
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Verifica i pacchetti installati
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Facoltativo) Disinstalla vecchie versioni
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+Per applicazioni client, lo script della shell non può essere fatto risorgere tra versioni di Node.js con `pm2 resurrect`. Fai il deploy dei processi da zero. This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> Se stai usando PM2 per processi dovresti anche richiamare le applicazione e salvare la lista di processo per un recupero automatico al riavvio.
+
+Ottieni le istruzioni/comandi di deinstallazione con il comando `unstartup` e usa l'output per rimuovere i servizi systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Ottieni le istruzioni/comandi di installazione con il comando `startup` e usa l'output per aggiungere i servizi systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Comandi veloci per PM2 per elencare, far ripartire processi salvati, ecc.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. Approssimativamente puoi seguire gli step elencati qui.
+
+Avrai bisogno di un PAT, che puoi ottenere da: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+Vai su [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) e registra l'agente dall'inizio nei requisiti [deployment groups](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+> [!NOTE] Dovresti eseguire gli script nella home directory, e assicurati che nessun'altra directory `azagent` esista.
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+Attualmente aggiornare gli agent richiede che siano rimossi e riconfigurati. Questo è richiesto perché possano ottenere valori `PATH` e altre variabili d'ambiente di sistema. Dobbiame farlo per aggiornare Node.js sulle VM target di deployment.
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Una volta completati gli step precedenti potrai ripetere gli stesi passi per installare l'agente.
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+Usiamo uno [strumento CLI](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) per inviare la nostra newsletter settimanale. Per avviare e iniziare il processo:
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+Utilizziamo un [tema](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) personalizzato per la nostra pubblicazione. L'aggiunta delle seguenti modifiche al tema consente l'aggiunta di nuove lingue.
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Cambia gli asset della pubblicazione andando alla dashboard di ghost > settings > general e caricando l'[icona](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), il [logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png), e la [copertina](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png) della pubblicazione.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/faq.md b/src/content/docs/it/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..692c1a50
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+:::tip
+Le issue **`help wanted`** sono a disposizione e non devi chiedere permessi per poterci lavorare. Tuttavia, le issue con l'etichetta **`first timers only`** sono problemi speciali che sono stati progettati per le persone che non hanno contribuito al codice di freeCodeCamp prima d'ora.
+:::
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. Abbiamo maggiori probabilità di fare il merge della prima pull request che affronta il problema.
+2. Nel caso di più contributori che aprono una pull request per lo stesso problema all'incirca allo stesso tempo, daremo la priorità alla pull request che affronta al meglio la questione. Alcune delle cose che consideriamo:
+ - Hai incluso dei test?
+ - Hai coperto tutti i casi d'uso?
+ - Ti sei assicurato che tutti i test siano superati e confermi che tutto funziona localmente?
+3. Infine, diamo la priorità alle pull request che seguono le nostre linee guida raccomandate.
+ - Hai seguito la checklist delle pull request?
+ - Hai dato alla tua pull request un titolo esplicativo?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- Per essere un moderatore per **Discord/Chat**, abbi una presenza attiva nella nostra chat e interazioni positive con gli altri, e intanto impara come gestire i potenziali conflitti che possono verificarsi.
+- Per essere un moderatore del **Forum**, in maniera simile ai moderatori della chat, abbi una presenza attiva e interagisci con gli utenti, supportando gli altri nel loro percorso di crescita e dando feedback quando richiesto. Dai un occhiata al [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) per maggiori informazioni.
+- Per essere un moderatore su **GitHub**, aiuta a processare le issue create su GitHub per vedere se sono valide e (idealmente) prova a proporre soluzioni per queste issue che possono essere applicate da altri (o da te stesso).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- La categoria `Contributors` del [forum della nostra community](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- Il canale `#Contributors` sul nostro [chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ccc15ef1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: Come aggiungere test Cypress
+---
+
+Quando si fanno cambiamenti a JavaScript, CSS o HTML che possono cambiare le funzionalità o il layout di una pagina è importante aggiungere corrispondenti test di integrazione [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io).
+
+Per imparare come scrivere test Cypress, o specs, per favore vedi la [dcoumentazione](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html) ufficiale di Cypress.
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- I test Cypress sono nella directory `./cypress`.
+
+- I test Cypress per un modulo del curriculum sono nella corrispondente cartella del curriculum, per esempio `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+> [!NOTE] If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Fai partire MongoDB e fai il seed del database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Avvia l'applicazione del client di freeCodeCamp e il server API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+Per eseguire i test su build di produzione, sostituisci `dev` con `prd` nella parte seguente.
+
+- Per eseguire tutti i test nella cartella `./cypress`:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- Per eseguire un singolo test:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ Ad esempio:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- Per creare una build di sviluppo, avvia il server di sviluppo e esegui tutti i test cypress end-to-end esistenti:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Assicurati che l'ambiente di sviluppo sia in esecuzione
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Fai il seed del database
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Sviluppa il server e il client
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Installa Cypress Build Tools
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- Quando chiesto dal terminale, seleziona il layout della tua tastiera per lingua/area
+
+Ora, [puoi eseguire Cypress](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-esegui-i-test-cypress)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bddff56c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **Nota:** Questo è un **passaggio opzionale** ed è richiesto solo quando si lavora con flussi di lavoro sulle email
+
+- [Introduzione](#introduction)
+- [Installare MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Usare Mailhog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Link Utili](#useful-links)
+
+## Introduzione
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog è una alternativa ad usare un provider di un servizio email per mandare messagi email. È uno strumento per lo sviluppo per testare le email che catturerà i messaggi email mandati dalla tua istanza di freeCodeCamp.
+
+## Installare MailHog
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Installare MailHog con Docker</summary>
+
+Se hai Docker installato puoi usare
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+per avviare MailHog in background e
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+per arrestarlo.
+
+Quando l'installazione è completa, puoi iniziare a [usare MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installare MailHog su macOS</summary>
+
+Installa MailHog su macOS con [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+Quando l'installazione è completa, puoi iniziare a [usare MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installare MailHog su Windows</summary>
+
+Scarica l'ultima versione di MailHog dalla [repository ufficiale di MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Trova e clicca sul link per la tua versione di Windows (32 o 64 bit) e un file `.exe` sarà scaricato sul tuo computer.
+
+Quando il download è stato completato, clicca per aprire il file. Potrebbe comparire una notifica del firewall di Windows, chiedendo i permessi di accesso per MailHog. Dopo aver consentito l'accesso nel firewall, si aprirà un prompt standard della riga di comando di Windows con MailHog in esecuzione.
+
+Chiudi MailHog chiudendo la finestra del prompt dei comandi. Per riaprire MailHog, clicca sul file eseguibile (`.exe`) di MailHog che è stato scaricato all'inizio; non è necessario scaricare un nuovo file di installazione.
+
+Inizia a [usare MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installare MailHog su Linux</summary>
+
+Come prima cosa, installa [Go](https://golang.org).
+
+Usa i seguenti comandi per installare GO su sistemi basati su Debian come Ubuntu e Linux Mint.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+Usa i seguenti comandi per installare GO su sistemi basati su RPM come CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, ecc.
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+In alternativa, esegui i seguenti comandi per installare GO.
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+Ora imposta il path per Go con i seguenti comandi.
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+In fine, esegui i comandi seguenti per installare ed eseguire MailHog.
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+Inizia a [usare MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+## Usare Mailhog
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## Link Utili
+
+- Controlla il repository [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) per ulteriori informazioni relative a MailHog. Ulteriori informazioni sono disponibili anche per quanto riguarda le configurazioni personalizzate di MailHog.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c506c33
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Seguire queste linee guida per contribuire al codebase. È altamente raccomandato se vuoi contribuire regolarmente.
+
+Ignorare questi passaggi può sporcare la tua copia, rendendo difficoltosi i processi di contribuzione, manutenzione e revisione.
+
+## Contribuire al codebase
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Segui questi passaggi:
+
+1. Controlla di essere sul branch `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Dovresti ottenere un output come questo:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sincronizza il tuo ramo `main` del tuo fork con gli ultimi aggiornamenti dal ramo `main` dell'upstream di freeCodeCamp:
+
+:::danger
+Se hai delle pull request in sospeso fatte dal branch `main` del tuo fork, le perderai alla fine di questi passaggi.
+
+Prima di eseguire questo passaggio, dovresti assicurarti che un moderatore abbia eseguito il merge della tua pull request. Per evitare questa situazione, dovresti **sempre** lavorare su un branch che non sia `main`.
+:::
+
+Questo passaggio **sincronizzerà le ultime modifiche** dal repository principale di freeCodeCamp.
+
+Aggiorna la tua copia del repository upstream freeCodeCamp:
+
+```bash
+git fetch upstream
+```
+
+Fai un hard reset del tuo ramo main con il ramo main di freeCodeCamp:
+
+```bash
+git reset --hard upstream/main
+```
+
+Fai un push del ramo main al tuo origin per avere una cronologia pulita nel tuo fork su GitHub:
+
+```bash
+git push origin main --force
+```
+
+You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+```bash
+git diff upstream/main
+```
+
+L'output risultante dovrebbe essere vuoto. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Crea un nuovo branch:
+
+ Lavorare su un branch separato per ogni issue ti aiuta a mantenere pulita la tua copia di lavoro locale. Non dovresti mai lavorare su `main`. Comprometteresti la tua copia di freeCodeCamp e potrebbe essere necessario ricominciare da capo con un nuovo clone o fork.
+
+ Controlla di essere su `main`, come spiegato in precedenza, e crea un branch da lì:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Il nome del branch dovrebbe iniziare con un `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, ecc. Evita di utilizzare i numeri delle issue nei branch. Tienili brevi, significativi e unici.
+
+ Alcuni esempi di nomi buoni per un branch sono:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Modifica le pagine e lavora sul codice nel tuo editor di testo preferito.
+
+5. Una volta che sei soddisfatto delle modifiche, dovresti opzionalmente eseguire freeCodeCamp per visualizzarle in anteprima.
+
+6. Assicurati di correggere eventuali errori e controlla la formattazione delle modifiche.
+
+7. Controlla e conferma i file che stai aggiornando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Questo dovrebbe mostrare un elenco di file `unstaged` che hai modificato.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Fai lo staging delle modifiche e crea un commit:
+
+ In questo passaggio, dovresti contrassegnare solo i file che hai modificato o aggiunto tu stesso. Se necessario è possibile eseguire un reset e risolvere i file che non hai intenzione di modificare.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Oppure puoi aggiungere tutti i file `unstaged` all'area di staging:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Solo i file che sono stati spostati nell'area di staging verranno aggiunti quando effettui un commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Ora, è possibile eseguire il commit delle modifiche con un breve messaggio come questo:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: breve messaggio di commit"
+ ```
+
+ Alcuni esempi:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Crea un messaggio di commit convenzionale. Questa è una buona pratica come sviluppatore, e seguirai le pratiche standard.
+
+ Alcuni esempi di messaggi di commit convenzionali sono:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Mantieni questi messaggi brevi, non più di 50 caratteri. È sempre possibile aggiungere ulteriori informazioni nella descrizione del messaggio di commit.
+
+ Questo non richiede più tempo rispetto a un messaggio non convenzionale come 'update file' o 'add index.md'
+
+ Puoi sapere di più sul perché dovresti usare i commit convenzionali [qui](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Se ti accorgi di dover modificare un file o aggiornare il messaggio del commit dopo aver fatto un commit puoi farlo dopo aver modificato i file con:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Questo aprirà un editor di testo predefinito come `nano` o `vi` dove potrai modificare il titolo del messaggio di commit e aggiungere/modificare la descrizione.
+
+10. Successivamente, è possibile inviare le modifiche al fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proporre una Pull Request (PR)
+
+Dopo aver fatto il commit delle tue modifiche, controlla qui [come aprire una Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Comandi rapidi
+
+Un rapido richiamo ai comandi di cui avrai bisogno lavorando.
+
+| comando | descrizione |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Esegue tutti i test JS del sistema inclusi client, server, lint e test delle sfide. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Esegue la test suite del client. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Esegue la test suite del curriculum. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Esegue i test di uno specifico blocco. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Esegue i test di uno specifico superblocco. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Esegue la suite di test del curriculum, senza arrestarsi dopo il primo errore |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Esegue la suite di test del server. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Esegue i test di Cypress end to end. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Disinstalla tutte le dipendenze e pulisce la cache. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Esegue Storybook per sviluppo dei componenti di library. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..790e5d1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Rilasciare nuove lingue su `/learn`
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Aggiornare le impostazioni di Crowdin
+
+Prima di poter rilasciare una nuova lingua, è necessario consentire alle lingue di fare il download da Crowdin. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Poi scorri fino a `Language Mapping`, dove vedrai un'opzione per aggiungere dei codici personalizzati per le lingue. Aggiungi una nuova voce per la lingua che vuoi rilasciare, selezionando `language` come valore `Placeholder` e inserendo il nome della lingua in minuscolo e in un formato adatto a un URL per il `Custom code`. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). Lo step sarà lo stesso per entrambi. Ad esempio, se vuoi abilitare il download per il Dothraki:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Nota che la chiave `download_language` deve essere impostata sul codice della lingua mostrato su Crowdin.
+
+## Attivare una lingua
+
+> [!NOTE] Prima di procedere dovresti completare la sezione precedente aggiornando i processi automatici - devono essere effettuate in step separati o il build fallirà.
+
+Ci sono alcuni step da svolgere per consentire il build del codebase nella lingua scelta.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. Qui ci sono diversi oggetti.
+
+- `Languages`: Aggiunge la nuova lingua all'enum `Languages` simile agli altri. Il valore della stringa qui sarà usato nel file `.env` per impostare un build della lingua in seguito.
+- `availableLangs`: Aggiunge la nuova proprietà dall'enum `Languages` a entrambi gli array `client` e `curriculum`.
+- `i18nextCodes`: Questi sono i codici ISO per le varie lingue. Dovrai aggiungere il codice ISO appropriato per la lingua che stai attivando. Devono essere unici per ogni lingua.
+- `LangNames`: Questi sono i nomi delle lingue visualizzati nel menu di navigazione.
+- `LangCodes`: Questi sono i codici delle lingue usati per formattare date e numeri. Questi devono essere codici Unicode CLDR invece di codici ISO.
+- `hiddenLangs`: Queste lingue non saranno mostrate nel menu di navigazione. Viene usato per le lingue che non sono ancora pronte per il rilascio. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: Sono le lingue che si leggono da destra a sinistra.
+
+Per esempio, se vuoi attivare la lingua Dothraki, il tuo oggetto `i18n.ts` dovrebbe essere come segue:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configurare la ricerca
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. Questi dati sono usati dalla barra di ricerca che carica gli articoli in `/news`. Anche se è poco probabile che tu stia testando questa funzione, se questi dati mancano per la tua lingua possono esserci degli errori nel costruire il codebase localmente.
+
+Aggiungi un oggetto per la tua lingua all'oggetto `algoliaIndices`. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se abbiamo già distribuito un'istanza della pubblicazione nella tua lingua target, puoi aggiornare i valori così da rispecchiare le istanze live. Altrimenti, usa i valori della pubblicazione inglese.
+
+Se volessi aggiungere Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+Dovrai fare un ulteriore passo per gestire le traduzioni dell'interfaccia utente client.
+
+I processi automatici scaricano da Crowdin _una parte_ delle traduzioni dell'interfaccia, ma ci sono alcuni file che devono essere creati manualmente.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+Per le sfide video, devi cambiare alcune cose. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. Per esempio, in questo modo aggiungeresti Dothraki alla query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Quindi aggiungi un id per la nuova lingua ogni sfida video in un blocco verificato (`auditedCerts`). Per esempio, se `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` include `scientific-computing-with-python` per `dothraki`, allora devi aggiungere l'elemento `dothraki` in `videoLocaleIds`. Il frontespizio dovrebbe essere simile a questo:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: nuovo-id-qui
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Aggiorna l'interfaccia `VideoLocaleIds` in `client/src/redux/prop-types` così che includa la nuova lingua.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+Se desideri testare le traduzioni localmente, prima di aggiungerle al nostro repository principale - salta i cambiamenti delle procedure di Crowdin. Segui i passaggi per abilitare una lingua, quindi scarica le traduzioni da Crowdin e caricale nel tuo codice locale.
+
+Poiché la lingua non è ancora stata approvata per la produzione, i nostri script non scaricheranno automaticamente le traduzioni. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Una volta che avrai i file, li dovrai mettere nelle cartelle giuste. Per le sfide del curriculum, dovresti mettere le cartelle dei certificati (ad esempio `01-responsive-web-design`) nella cartella `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Per la nostra traduzione in Dothraki, sarebbe `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. I file `.json` con le traduzioni del client vanno nella cartella `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Aggiorna il file `.env` in modo da poter utilizzare la tua lingua per `CLIENT_LOCALE` e `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Una volta che questi saranno in posizione, dovresti essere in grado di eseguire `pnpm run develop` per vedere la versione tradotta di freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+Se costruisci il client in una lingua e poi vuoi costruirlo in una lingua diversa, dovrai usare il comando `pnpm run clean-and-develop` dopo aver cambiato il file `.env`, dato che Gatsby memorizzerà nella cache la prima lingua.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+Anche se puoi farei delle traduzioni localmente per i test, ricordiamo che le traduzioni _non_ devono essere inviate attraverso GitHub ma solo tramite Crowdin. Assicurati di resettare il tuo codebase locale dopo che avrai finito con i test.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Rilasciare nuove lingue su `/learn`
+
+Per distribuire News per una nuova lingua, dovrai creare due PR. Una Pr sarà al [repo CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), e l'altra sarà al [repo News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News ottiene i link di tendenza e i titoli degli articoli dal nostro CDN durante il build e li aggiunge al piè di pagina. News recupera anche i file Day.js dal CDN durante il build per localizzare date e orari per ogni lingua.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Clona il [repo CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) e crea un nuovo branch.
+
+Nella cartella [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending), crea un nuovo file e chiamalo `language.yaml`. Ad esempio, se stai lanciando le News in Dothraki, chiama il file `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Quindi copia il contenuto del file con gli articoli di tendenza [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) e incollalo nel nuovo file YAML che hai appena creato.
+
+Il suo contenuto assomiglierà a questo:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+Per impostazione predefinita, Day.js include solo l'inglese come locale. Per abilitarlo a lavorare con altre lingue, è necessario aggiungere un nuovo file locale Day.js al CDN.
+
+Nella cartella [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale), crea un nuovo file e chiamalo `isocode.min.js`. Ad esempio, se stai lanciando le News in Dothraki, chiama il file `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Il numero della versione cambierà in quanto le dipendenze vengono aggiornate.
+
+Quindi, visita [questa pagina su cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) con tutti i file Day.js disponibili per la versione che stiamo usando, trova il link `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` per la nuova lingua e aprilo in una nuova scheda.
+
+> [!NOTE] Devi soltanto aggiungere il file .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js locale. Non è necessario aggiungere altri file Day.js.
+
+Copia il codice locale Day.js dalla nuova scheda nel nuovo file che hai creato. Per esempio, ecco una versione non minificata del codice locale inglese per Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Quindi apri una PR al repo CDN per aggiungere i file YAML e Day.js per la revisione.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+Il [repo News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) prende i dati da un'istanza di Ghost, i file che hai aggiunto al CDN, fa il build di News e il deployment.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. Non dovresti lavorare da un fork per questo passaggio.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Clona il repo News e crea un nuovo branch.
+
+Apri il file `config/index.js` per aggiungere la nuova lingua e configurare i valori necessari. Ci sono alcuni oggetti e array da modificare:
+
+- `locales`: Questo array contiene le lingue attive e le prossime lingue di News. Sono i valori che vengono usati nel file `.env` per scegliere l'istanza di Ghost e l'interfaccia utente da usare in ogni build. Aggiungi il nome della nuova lingua in minuscolo a questo array.
+- `localeCodes`: Questo oggetto è una mappa dei codici ISO per ogni lingua, e viene usato per configurare i18next prima del build dell'interfaccia utente. Per aggiungere una nuova lingua, usa il nome della lingua minuscolo come _chiave_ e il codice ISO 639-1 della lingua come _valore_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: Questo oggetto è una mappa degli indici Algolia per ogni lingua. Per aggiungere una nuova lingua, usa il nome della lingua minuscolo come _chiave_ e `news-`, seguito dal codice minuscolo ISO 639-1 della lingua come _valore_.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se non sei sicuro della stringa da usare per impostare `algoliaIndices`, manda un messaggio a Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo), o qualcun altro con accesso ad Algolia, e chiedigli di controllare.
+
+Ad esempio, se stai lanciando News in Dothraki, ecco come dovrebbero apparire gli oggetti / array sopra:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. Ad esempio, se stai lanciando le News in Dothraki, crea una nuova cartella chiamata `dothraki`.
+
+Quindi copia i file JSON dalla cartella `english` nella tua nuova cartella.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Quindi fail il commit e il push del tuo branch direttamente dal repo News.
+
+> [!NOTE] Hai bisogno di essere in uno dei team con l'accesso al repo News per fare il push direttamente a News. Attualmente, solo i team dev, i18n e staff sono autorizzati a farlo.
+
+Infine, apri una PR per la revisione.
+
+Una volta che entrambe le PR per i repo CDN e News sono state approvate, è possibile effettuare il merge.
+
+> [!NOTE] Il deployment sarà successivamente gestito dallo staff. Ecco una PR di esempio: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) su come si fa e altri dettagli disponibili in [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..07045f08
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,215 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+Le sfide video sono un nuovo tipo di sfida nel programma di studi freeCodeCamp.
+
+Una sfida video è una piccola sezione di un corso interamente su video su un argomento particolare. Una pagina di sfida video incorpora un video di YouTube. Ogni pagina di sfida ha una singola domanda a scelta multipla relativa al video. Un utente deve rispondere alla domanda correttamente prima di poter passare alla sfida video successiva nel corso.
+
+Le pagine della sfida video sono create dai membri del team freeCodeCamp. Anche i video di YouTube sono caricati dai membri del team freeCodeCamp. Molte delle sfide video non hanno ancora domande ad esse associate.
+
+Puoi aiutare creando domande a scelta multipla legate a sezioni del video e aggiungendo le domande ai file markdown per le sfide video.
+
+## Template delle sfide
+
+Di seguito è riportato un modello di come appaiono i file markdown delle sfide.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+Questi campi sono usati attualmente per le domande a scelta multipla nelle sfide di Python.
+
+## --text--
+
+Il testo della domanda va qui.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Risposta 1
+
+---
+
+Risposta 2
+
+---
+
+Altre risposte
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+Il numero della risposta corretta va qui.
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Guarda velocemente il video associato alla sfida e crea una domanda a scelta multipla
+
+Come prima cosa, trova `videoId`.
+
+Ad esempio, nel seguente codice preso dall'intestazione di un file di markdown di una sfida video, `videoId` è "nVAaxZ34khk". Su GitHub, le informazioni dovrebbero essere visibili in una tabella.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Come cosa successiva, accedi al video YouYube con quel `videoId`. L'URL di quel video sarà:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (sostituisci `videoId` nell'URL con l'ID del video - senza parentesi quadre)
+
+Nell'esempio sopra, l'URL è
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Guarda velocemente il video YouTube con quel `videoId` e pensa a una domanda a crocette basata sul contenuto del video.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. Per aggiungere la domanda localmente, è necessario [impostare freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Puoi anche trovare il file su GitHub e fare clic sul pulsante Modifica per aggiungere la domanda nel tuo browser.
+
+Se una domanda non è ancora stata aggiunta a una sfida video, avrà la seguente domanda di default:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Question text
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Aggiungi/Cambia il testo della domanda sotto la parte che dice:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Add/Update answers (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, and so on) sotto `## --answers--`. Assicurati di aggiornare il numero sotto `## --video-solution--` con il numero della risposta corretta. Puoi aggiungere altre possibili domande seguendo lo stesso formato. The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### Esempi di domande
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+What does this JavaScript code log to the console?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Cosa verrà visualizzato dopo l'esecuzione di questo codice:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+Per altri esempi, puoi guardare i file markdown dei seguenti corsi video. Tutte le sfide che hanno già domande: [Corso Python per tutti](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+Dopo aver creato una o più domande, puoi fare un commit delle tue modifiche su un nuovo ramo e [aprire una pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0bf2b568
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: Come aprire una Pull Request (PR)
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Una volta che hai fatto delle modifiche al codice, puoi seguire queste linee guida per aprire una PR.
+
+Ci aspettiamo che i nostri contributori siano consapevoli del processo specifico di questo progetto. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Alcuni esempi di ciò sono:
+
+1. Non modificare i file direttamente attraverso GitHub – nonostante sia possibile, non è una buona idea.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Assicurati di seguire la checklist della PR e non solo spuntare le cose; altrimenti, non ti prenderemo sul serio.
+4. Usa il modo corretto per linkare le issue nella descrizione della PR aggiornando `XXXXXX`. Non basta aggiungere numeri di issue dappertutto o ovunque ti pare.
+5. Non "@menzionare" o richiedere qualcuno per la revisione troppe volte.
+
+ Sappiamo che sei entusiasta di contribuire. Per quanto a un manutentore faccia piacere risponderti, si tratta di una persona impegnata che si occupa di centinaia di richieste proprio come la tua. Sii paziente, qualcuno ti risponderà prima o poi.
+
+6. Non lavorare direttamente sul ramo (branch) `main` - crea un nuovo ramo per le modifiche su cui stai lavorando.
+
+> [!NOTE] La tua PR dovrebbe essere rivolta a modifiche del solo curriculum inglese. Per contribuire alle traduzioni invece, leggi [questa guida](index#traduzioni).
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. La convenzione ha il seguente formato:
+
+> `<tipo>([ambito/i opzionale/i]): <descrizione>`
+>
+> Per esempio:
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Tipo:**
+
+| Tipo | Quando selezionare |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | Solo se si aggiungono nuove funzionalità, test, ecc. |
+| chore | Cambiamenti che non sono legati a codice, test, o testo di una lezione. |
+| docs | Modifiche alla directory `/docs` o alle linee guida per i contributi, ecc. |
+
+**Ambito:**
+
+Puoi selezionare un ambito da [questo elenco di etichette](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Descrizione:**
+
+Mantienila breve (meno di 30 caratteri) e semplice; puoi aggiungere ulteriori informazioni nella casella di descrizione PR e nei commenti.
+
+Alcuni esempi di buoni titoli di PR sono:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## Proporre una Pull Request
+
+1. Una volta che le modifiche sono state effettuate, ti verrà chiesto di creare una pull request sulla pagina GitHub del tuo fork.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Vedi screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. Di default, tutte le pull request dovrebbero essere sul repository principale di freeCodeCamp, nel ramo `main`.
+
+ Assicurati che il tuo Base Fork sia impostato su freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp quando sollevi una Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Vedi screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Fai la pull request dal tuo ramo al ramo `main` di freeCodeCamp.
+
+4. Includi un riassunto più dettagliato delle modifiche apportate e di come sono d'aiuto nel corpo della tua PR.
+
+ - Ti sarà presentato un modello di pull request. Questa è una lista di controllo che avresti dovuto seguire prima di aprire la pull request.
+
+ - Compila i dettagli come ritieni opportuno. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - Se la PR ha lo scopo di affrontare un'issue GitHub esistente, alla fine del corpo della descrizione della tua PR, usa la parola chiave _Closes_ con il numero dell'issue per [chiudere automaticamente questa issue se la PR è accettata](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Esempio: `Closes #123` chiuderà l'issue 123
+
+5. Indica se hai testato i tuoi cambiamenti su una copia locale del sito oppure no.
+
+ - Questo è molto importante quando si fanno cambiamenti che non sono solo modifiche a contenuto testuale come documentazione o descrizioni di sfide. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: Congratulazioni per avere creato un PR e grazie mille per aver dedicato il tuo tempo a contribuire.
+
+I nostri moderatori ora daranno un'occhiata e ti lasceranno un feedback. Ti preghiamo di essere paziente con i colleghi moderatori e di rispettare il loro tempo. Tutte le pull request sono riviste a tempo debito.
+
+E come sempre, poni liberamente le tue domande [nella categoria 'Contributors' sul nostro forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [nella chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+Se vuoi contribuire a più di una PR, ti raccomandiamo di leggere la [guida su fare modifiche e sincronizzare](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) per evitare di dover cancellare il tuo fork.
+:::
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+I conflitti possono sorgere perché molti contributori lavorano sul repository e le modifiche possono interrompere la tua PR in attesa di una revisione e di un merge.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+Quando stai lavorando su normali bug e funzionalità sul nostro ramo di sviluppo `main`, puoi fare un semplice rebase:
+
+1. Esegui un rebase della tua copia locale:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Risolvi eventuali conflitti e aggiungi / modifica i commit
+
+ ```bash
+ # O
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # O
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Fai il push dei tuoi cambiamenti alla PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Assicurati che il tuo upstream sia sincronizzato con il tuo repository locale:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Elimina il ramo locale dopo aver effettuato un backup (se lo hai ancora localmente):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # esempio:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # esempio:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # esempio:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Inizia con una slate pulita:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # esempio:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..90c22d1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Come revisionare le traduzioni
+---
+
+Il nostro team di revisione è responsabile di controllare che le traduzioni riflettano accuratamente il testo originale. Ci affidiamo ai revisori per avere delle traduzioni di alta qualità.
+
+Tutte le nostre traduzioni sono fatte a mano, da veri esseri umani. Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+Per iniziare a revisionare visita [la nostra piattaforma di traduzione](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) e fai il login. Seleziona "Go to console" nella barra di navigazione in alto per passare da public view a workspace view.
+
+## Selezionare un file
+
+Dovresti vedere la lista di progetti a cui ti è stato dato accesso. Seleziona il progetto che vorresti revisionare, poi seleziona la lingua.
+
+
+
+Ora dovresti vedere la lista dei file disponibili. Scegli il file selezionando il pulsante `Proofread` a destra del file, e scegliendo quindi `Proofreading` dal menu che compare.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se sei in workspace view, ma vuoi lavorare sulla [traduzione di un file](how-to-translate-files) invece di revisionare, puoi selezionare `Crowdsourcing` dal menu.
+
+## Revisionare le traduzioni
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Qui vedrai la lista delle stringhe nel file selezionato con le relative traduzioni. La traduzione che è mostrata qui è la traduzione che ha ricevuto il maggior punteggio (tra voti positivi e negativi) dalla comunità di traduttori.
+
+Anche se puoi vedere _tutte_ le traduzioni proposte per una certa stringa, il punteggio della comunità (determinato da voti positivi e voti negativi) dovrebbe essere preso in considerazione quando scegli quale traduzione approvare. La comunità può rivedere le traduzioni proposte e raccomandare quale è la più chiara e accurata.
+
+1. Questa è la stringa originale (in inglese).
+2. Questa è la corrispondente stringa tradotta. La proposta di traduzione più popolare, basata su voti positivi e negativi, sarà mostrata qui.
+3. Cliccando il pulsante di spunta approverai la traduzione.
+4. Crowdin mostrerà lo stato di ogni stringa. `Done` significa che una traduzione è stata approvata e sarà scaricata nel prossimo aggiornamento delle traduzioni. `Todo` significa che la stringa non è stata revisionata. `Hidden` significa che la stringa è bloccata e _non deve essere tradotta_. `Comment` significa che la stringa è relativa a un commento.
+5. Le traduzioni possono essere selezionate con i checkbox e approvate in un'azione cumulativa.
+6. Qui puoi vedere le traduzioni proposte dalla comunità, i punteggi di popolarità e le traduzioni suggerite da Crowdin.
+7. Questo pulsante mostra/nasconde la scheda a destra, dove puoi vedere traduzioni, commenti, traduzioni in memoria e termini del glossario.
+8. Crowdin mostra qui i messaggi di errore dai controlli di qualità. In altre parole, se qualcosa non sembra corretto nella traduzione, Crowdin te lo dirà. Queste traduzioni devono essere approvate con attenzione.
+
+Non sono necessarie altre azioni una volta che un file è stato revisionato.
+
+> [!NOTE] Approvare una stringa in modalità di revisione la segnerà come completata e farà sì che sia scaricata nel prossimo pull da Crowdin a GitHub.
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+Se hai domande o sei interessato a diventare proofreader, puoi contattarci nella [chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). In genere diamo i permessi di revisore se è da un po' che contribuisci a freeCodeCamp.
+
+Il nostro staff e i moderatori della community sono sempre alla ricerca di volontari come te che ci aiutino a rendere disponibili al mondo traduzioni di alta qualità.
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin ti permette di approvare le tue traduzioni. In genere, è meglio permettere ad un altro proofreader di rivedere le tue proposte di traduzione per maggior sicurezza che non ci siano errori.
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+Se sei un proofreader e sei interessato ad avere un canale dedicato sul server di chat per una specifica lingua, [compila questo modulo](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5a7f39f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,306 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCamp. Te lo raccomandiamo caldamente se desideri contribuire regolarmente.
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows. - You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase. - Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+
+:::
+
+If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Here are some pros and cons which should help you decide which option is best for you:
+
+| Gitpod | Your own machine (local setup) |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| No minimum hardware requirements | Specific and minimum requirements |
+| No need to install any software | Additional software required |
+| Always up to date copy of repository | Need to maintain a local copy of the repository |
+| Slower and can take a few minutes to launch | Faster and can be launched in seconds |
+| Need an internet connection to work | Minimal internet connection required (once setup) |
+| Some tasks like compilation and tests can take longer to complete | Faster completion of tasks (depending on your machine's capabilities) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+We have automated the process of installing all the dependencies & tools you will need. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Fastest)** Prepend `gitpod.io/#` in front of any URL from GitHub.
+
+ For example, if you visit your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, add `gitpod.io/#` in the front of the URL in the address bar and hit enter.
+
+ That is you can navigate to `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` and you should see a workspace created for you. This works for any repository or pull-request on GitHub.
+
+2. Alternatively install one of the below extensions for your browser.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - funziona con browser basati su Chromium come Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, ecc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. Vedi la pagina delle estensioni per i dettagli, screenshot, ecc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### Prerequisiti:
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### Segui questi passaggi per preparare il tuo ambiente di sviluppo:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ :::tip
+ Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+ :::
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+> [!WARNING] Se stai lavorando su una Distro di Linux su WSL2, potresti avere problemi di performance e stabilità eseguendo il progetto in una cartella che è condivisa tra Windows e WSL2 (per esempio `/mnt/c/Users/`). Quindi ti raccomandiamo di clonare il repo in una cartella che è usata principalmente dalla Distro di Linux su WSL2 e non condivisa direttamente con Windows (per esempio `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> Vedi [questa issue su GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) per ulteriori informazioni su questo problema.
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Apri un terminale / prompt dei comandi / Shell nella directory dei progetti
+
+ _cioè: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clona il tuo fork di freeCodeCamp, sostituendo `YOUR_USER_NAME` con il tuo nome utente GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Aggiungi un riferimento remoto al repository freeCodeCamp principale:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Assicurati che la configurazione sia corretta:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ L'output dovrebbe apparire simile al seguente (sostituendo `YOUR_USER_NAME` con il tuo username di GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# Creare una copia del "sample.env" e denominarlo ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+:::tip
+Tieni a mente che se vuoi usare servizi come Auth0 o Algolia, dovrai ottenere delle chiavi API per questi servizi per conto tuo e modificare gli elementi nel file `.env` di conseguenza.
+:::
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+> [!NOTE] A meno che tu non abbia MongoDB in esecuzione in un setup differente da quello predefinito, l'URL salvato come `MONGOHQ_URL` nel file `.env` dovrebbe andare bene. Se usi una configurazione personalizzata, modifica il valore come necessario.
+>
+> Se hai seguito la [Guida di configurazione Windows 10 via WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl), allora dovresti essere in grado di saltare questo passaggio se il server MongoDB di quella guida è già in esecuzione. Puoi averne conferma controllando di poter raggiungere `http://localhost:27017` sulla tua macchina locale.
+
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+Puoi evitare di dover avviare MongoDB ogni volta se lo installi come servizio in background. Puoi [saperne di più nella loro documentazione per il tuo sistema operativo](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+> [!WARNING] Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..129dadbf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Segui questa guida per impostare l'app mobile di freeCodeCamp localmente sul tuo sistema. È altamente raccomandato se vuoi contribuire regolarmente.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Inizia installando i prerequisiti software per il tuo sistema operativo.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Prerequisito | Versione | Note |
+| --------------------------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (viene fornito in dotazione con Flutter) | `3.x` | Usiamo la versione in dotazione con Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+Se hai una versione diversa, per favore installa la versione raccomandata. Possiamo supportare solo i problemi di installazione per le versioni consigliate.
+:::
+
+Se Flutter è già installato sulla macchina, eseguire i seguenti comandi per convalidare le versioni:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+Raccomandiamo vivamente di eseguire gli aggiornamenti all'ultima versione stabile dei software elencati qui sopra.
+:::
+
+Una volta che avrai installato i prerequisiti, dovrai preparare il tuo ambiente di sviluppo. Questo è comune a molti flussi di lavoro di sviluppo, e si dovrà fare solo una volta.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Installa [Git](https://git-scm.com/) o il tuo client Git preferito, se non lo hai già. Aggiorna alla versione più recente; la versione fornita con il tuo sistema operativo potrebbe essere obsoleta.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. Consigliamo di utilizzare Pixel 3a XL e Nexus One(per simulare schermi più piccoli).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Opzionale ma raccomandato) [Imposta una chiave SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) per GitHub.
+
+5. Installa un editor di codice di tua scelta.
+
+ Consigliamo vivamente di utilizzare [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) o Android Studio. Consigliamo anche di installare le [estensioni](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode) ufficiali.
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+Fare il [fork](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) è il passaggio grazie a cui ottieni la tua copia del repository (_repo_) su GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Più tardi, potrai richiedere che le tue modifiche siano integrate (pull) nel repository principale dal tuo fork tramite una pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+Il repository principale su `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` è spesso indicato come il repository `upstream`.
+Il tuo fork che si trova a `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` è spesso chiamato il repository `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` è sostituito dal tuo nome utente GitHub.
+:::
+
+**Segui questi passaggi per effettuare il fork del repository `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile`:**
+
+1. Vai al repository freeCodeCamp mobile su GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Fai clic sul pulsante "Fork" nell'angolo in alto a destra dell'interfaccia ([Maggiori dettagli qui](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Dopo che è stato creato un fork del repository, sarai portato alla tua copia del repository su `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` è sostituito dal tuo nome utente GitHub.)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+La [Clonazione](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) consiste nello **scaricare** una copia di un repository da una `posizione remota` che è di proprietà tua o di qualcun altro. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` è sostituito dal tuo nome utente GitHub.)
+
+Esegui questi comandi sulla tua macchina locale:
+
+1. Apri un terminale / prompt dei comandi / Shell nella directory dei progetti
+
+ _cioè: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clona il tuo fork di freeCodeCamp, sostituendo `YOUR_USER_NAME` con il tuo nome utente GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+Questo scaricherà l'intero repository mobile freeCodeCamp nella directory dei tuoi progetti.
+
+Nota: `--depth=1` crea un clone superficiale del fork, con la sola cronologia dei commit più recente.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Ora che hai scaricato una copia del fork, dovrai configurare un `upstream` remoto che punti al repository genitore.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+Hai bisogno di un riferimento dal tuo clone locale al repository `upstream` oltre che al repository `origin`. In questo modo potrai sincronizzare le modifiche dal repository principale senza bisogno di fare ripetuti fork e clonazioni.
+
+1. Spostati nella directory `mobile`:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Aggiungi un riferimento remoto al repository freeCodeCamp mobile:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Assicurati che la configurazione sia corretta:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ L'output dovrebbe apparire simile al seguente (sostituendo `YOUR_USER_NAME` con il tuo username di GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Ora che disponi di una copia locale dell'app mobile, potrai seguire queste istruzioni per eseguirla localmente.
+
+Se incontri un problema, fai prima una ricerca del problema sul web per vedere se ha già una risposta. Se non riesci a trovare una soluzione, ti preghiamo di fare una ricerca nelle nostra pagina delle [Issues su GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) per trovare una soluzione o segnalare il problema se non è ancora stato fatto.
+
+E come sempre, fai liberamente le tue domande nella [categoria 'Contributors' sul forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [sul server di chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] La directory `mobile` contiene le cartelle `mobile-api` e `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contiene il codice delle API utilizzate per i podcast. `mobile-app` contiene l'app Flutter ed è dove dovresti trovarti per seguire i passaggi successivi.
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+Le chiavi API predefinite e le variabili d'ambiente sono memorizzate nel file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Ricordati di spostarti nella directory `mobile-app` prima di eseguire i seguenti comandi.
+
+```bash
+# Crea una copia di "sample.env" e chiamalo ".env".
+# Popolalo con le chiavi API e i segreti necessari:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+_Non_ è necessario cambiare le chiavi nel file `.env` per eseguire l'applicazione localmente. Puoi lasciare i valori predefiniti copiati da `sample.env` così come sono.
+
+#### Step 2: Installare le dipendenze
+
+Questo passaggio installerà le dipendenze richieste per l'esecuzione dell'applicazione:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Avviare l'app mobile freeCodeCamp
+
+Avvia un emulatore di tua scelta (Android o iOS) e aspetta il processo di avvio per completare.
+
+Ora puoi avviare l'app eseguendo il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+Se stai usando VSCode o Android Studio puoi avviare facilmente l'app senza eseguire comandi dal terminale. Maggiori informazioni [qui](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Segui questi passaggi:
+
+1. Controlla di essere sul branch `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Dovresti ottenere un output come questo:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ Se non sei sul branch main o la directory su cui stai lavorando non è pulita, risolvi file e commit in sospeso e fai il checkout da `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sincronizza il tuo branch main locale con gli ultimi aggiornamenti dal branch upstream `main`:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Se hai delle pull request in sospeso fatte dal branch `main` del tuo fork, le perderai alla fine di questi passaggi.
+ >
+ > Prima di eseguire questo passaggio, dovresti assicurarti che un moderatore abbia eseguito il merge della tua pull request. Per evitare questa situazione, dovresti **sempre** lavorare su un branch che non sia `main`.
+
+ Questo passaggio **sincronizzerà le ultime modifiche** dal repository principale di freeCodeCamp mobile. È importante che tu faccia un rebase del tuo branch utilizzando l'ultima versione di `upstream/main` quanto più spesso possibile per evitare conflitti successivamente.
+
+ Aggiorna la tua copia locale del repository upstream freeCodeCamp mobile:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Fai un hard reset del tuo branch main con il branch main di freeCodeCamp mobile:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Fai un push del branch main al tuo origin per avere una cronologia pulita nel tuo fork su GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ L'output risultante dovrebbe essere vuoto.
+
+3. Crea un nuovo branch:
+
+ Lavorare su un branch separato per ogni problema ti aiuta a mantenere pulita la tua copia di lavoro locale. Non dovresti mai lavorare su `main`. Questo sporcherebbe la tua copia di freeCodeCamp mobile e potrebbe essere necessario ricominciare da capo con un nuovo clone o fork.
+
+ Controlla di essere su `main`, come spiegato in precedenza, e crea un branch da lì:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Il nome del branch dovrebbe iniziare con un `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, ecc. Evita di utilizzare i numeri delle issue nei branch. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Alcuni esempi di nomi buoni per un branch sono:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Modifica le pagine e lavora sul codice nel tuo editor di testo preferito.
+
+5. Una volta che sei soddisfatto delle modifiche, dovresti opzionalmente eseguire l'app mobile localmente per visualizzarle in anteprima.
+
+6. Assicurati di correggere eventuali errori e controlla la formattazione delle modifiche.
+
+7. Controlla e conferma i file che stai aggiornando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Questo dovrebbe mostrare un elenco di file `unstaged` che hai modificato.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Fai lo stage delle modifiche e crea un commit:
+
+ In questo passaggio, dovresti contrassegnare solo i file che hai modificato o aggiunto tu stesso. Se necessario è possibile eseguire un reset e risolvere i file che non hai intenzione di modificare.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Oppure puoi aggiungere tutti i file `unstaged` all'area di staging:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Solo i file che sono stati spostati nell'area di staging verranno aggiunti quando effettui un commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Ora, è possibile eseguire il commit delle modifiche con un breve messaggio come questo:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: breve messaggio di commit"
+ ```
+
+ Alcuni esempi:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Facoltativo:
+
+ Raccomandiamo caldamente di creare un messaggio di commit convenzionale. Questa è una buona pratica che vedrai su alcuni dei più popolari repository Open Source. Come sviluppatore, questo ti incoraggia a seguire le pratiche standard.
+
+ Alcuni esempi di messaggi di commit convenzionali sono:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Mantieni questi messaggi brevi, non più di 50 caratteri. È sempre possibile aggiungere ulteriori informazioni nella descrizione del messaggio di commit.
+
+ Questo non richiede tempo aggiuntivo rispetto a un messaggio non convenzionale come 'update file' o 'add index.md'
+
+ Puoi sapere di più sul perché dovresti usare i commit convenzionali [qui](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Se ti accorgi di dover modificare un file o aggiornare il messaggio del commit dopo aver fatto un commit puoi farlo dopo aver modificato i file con:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Questo aprirà un editor di testo predefinito come `nano` o `vi` dove potrai modificare il titolo del messaggio di commit e aggiungere/modificare la descrizione.
+
+10. Successivamente, è possibile inviare le modifiche al fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+Dopo aver fatto il commit delle tue modifiche, controlla qui per [come aprire una Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Problemi con l'installazione dei prerequisiti raccomandati
+
+Sviluppiamo regolarmente sui sistemi operativi più nuovi o più popolari come macOS 10.15 o successivi, Ubuntu 18.04, e Windows 10 con WSL2.
+
+Ti raccomandiamo di fare ricerche sui tuoi problemi specifici usando risorse come Google, Stack Overflow e Stack Exchange. C'è una buona probabilità che qualcuno abbia incontrato lo stesso problema e ci sia già una risposta alla tua domanda specifica.
+
+Se sei su un sistema operativo diverso e/o continui ad avere dei problemi, visita [ottenere aiuto](#ottenere-aiuto).
+
+### Problemi con UI, errori di build, ecc.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+Se sei bloccato e hai bisogno di aiuto, poni liberamente le tue domande nella [categoria 'Contributors' sul nostro forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [nella chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Potrebbe esserci un errore nella console del browser o in Bash / Terminal / Linea di comando che ti aiuterà a identificare il problema. Fornisci questo messaggio di errore nella descrizione del problema in modo che gli altri possano identificare più facilmente il problema e aiutarti a risolverlo.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..74d6ad04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Impostare freeCodeCamp sul sottosistema Windows per Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 a 64 bit (Versione 2004, Build 19041 o superiore) - disponibile per tutte le distribuzioni tra cui Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop per Windows**: Vedi i rispettivi requisiti per [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) e [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+Questa guida copre alcuni passi comuni con la configurazione di WSL2. Una volta che i problemi più comuni con WSL2 sono stati considerati, dovresti essere in grado di seguire [questa guida per settare freeCodeCamp in locale](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) per lavorare su Windows usando una distribuzione WSL come Ubuntu.
+
+## Abilita WSL
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Installare Ubuntu
+
+1. Si consiglia l'uso di Ubuntu-18.04 o superiore con WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Aggiorna le dipendenze per il sistema operativo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Imposta Git
+
+Git è preinstallato in Ubuntu 18.04, verifica la versione di git con `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Facoltativo ma consigliato) Ora puoi procedere alla [impostazione delle tue chiavi ssh](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) con GitHub.
+
+## Installazione di un editor di codice
+
+Consigliamo vivamente di installare [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) su Windows 10. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+Essenzialmente, modificherai e memorizzerai il tuo codice su Ubuntu-18.04 con Visual Studio Code installato su Windows.
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Installazione di Docker Desktop
+
+**Docker Desktop per Windows** ti permette di installare e eseguire database come MongoDB e altri servizi come NGINX. Questo è utile per evitare problemi comuni con l'installazione di MongoDB o altri servizi direttamente su Windows o WSL2.
+
+Segui le istruzioni nella [documentazione ufficiale](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) e installa Docker Desktop per la tua distribuzione Windows.
+
+Ci sono dei requisiti hardware minimi per un'esperienza migliore.
+
+## Configura Docker Desktop per WSL
+
+Una volta che Docker Desktop sarà installato, [segui queste istruzioni](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) e configuralo per usare l'installazione di Ubuntu 18.04 come Backend.
+
+Questo fa si che i container siano eseguiti su WSL invece che su Windows. Sarai in grado di accere ai servizi da `http://localhost` sia su Windows che su Ubuntu.
+
+## Installa MongoDB da Docker Hub
+
+Una volta che hai configurato Docker Desktop per lavorare con WSL2, segui questi step per avviare un servizio MongoDB:
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Avvia il servizio MongoDB sulla porta `27017` e configuralo perché sia eseguito automaticamente al riavvio del sistema
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Ora puoi accedere al servizio sia da Windows che da Ubuntu da `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Installazione di Node.js e pnpm
+
+Raccomandiamo di installare la release LTS di Node.js con un gestore di versioni di node (node version manager): [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. Dovresti essere comunque in grado di lavorare sulla maggior parte del codebase.
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Domande frequenti su:
+ - [Sottosistema Windows per Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop per Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f4095137
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: Come testare le traduzioni in locale
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Questo processo non è richiesto, ma documentato nel caso tu voglia vedere la preview delle tue traduzioni.
+
+Se vuoi testare le tue traduzioni in una istanza locale della piattaforma `/learn` di freeCodeCamp, assicurati prima di aver [preparato il codebase](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Attivare una lingua
+
+Ci sono alcuni step da fare per avere una build del codebase nella lingua di tua scelta.
+
+Prima, visita il file `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` per aggiungere la lingua alle lingue disponibili nella lista e configurare i valori. Ci sono quattro oggetti qui.
+
+- `availableLangs`: Aggiungi il nome testuale della lingua agli array `client` e `curriculum`. Questo è il valore che sarà usato nel file `.env` più tardi.
+- `auditedCerts`: Aggiungi il nome testuale della lingua come _chiave_, e aggiungi un array di variabili `SuperBlocks.{cert}` come _valori_. Questo dice al client quali certificazioni sono completamente tradotte.
+- `i18nextCodes`: questi sono i codici ISO per le varie lingue. Dovrai aggiungere il codice ISO appropriato per la lingua che stai attivando. Questi devono essere unici per ogni lingua.
+- `LangNames`: Questi sono i nomi delle lingue visualizzati nel menù di navigazione.
+- `LangCodes`: Questi sono i codici delle lingue usati per formattare date e numeri. Questi devono essere codici Unicode CLDR invece di codici ISO.
+
+Per esempio, se vuoi attivare la lingua Dothraki, il tuo oggetto `all-langs.js` dovrebbe essere come segue:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Poi, apri il file `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`. Questi dati sono usati dalla barra di ricerca che carica gli articoli in `/news`. Anche se è poco probabile che tu stia testando questa funzione, se questi dati mancano per la tua lingua possono esserci degli errori nel costruire il codebase localmente.
+
+Aggiungi un oggetto per la tua lingua all'oggetto `algoliaIndices`. Dovresti usare gli stessi valori dell'oggetto `english` per testare in locale, sostituendo la chiave `english` con il valore della tua lingua in `availableLangs`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se abbiamo già distribuito un'istanza della pubblicazione nella tua lingua target, puoi aggironare i valori per riflettere le istanze live. Altrimenti, usa i valori della pubblicazione inglese.
+
+Se volessi aggiungere Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Infinine, nel file `.env`, dai a `CLIENT_LOCALE` e `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` il valore della tua nuova lingua (usando il valore in `availableLangs`.)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### RIlasciare un superblocco
+
+Dopo che un superblocco è stato completamente tradotto in una lingua, ci sono due step per rilasciarlo. Come prima cosa aggiungi il superblocco enum all'array `auditedCerts` di quella lingua. Quindi, se vuoi rilasciare il nuovo superblocco Web Design Responsivo per Dothraki, l'array dovrebbe essere così:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Infine, l'array `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` dovrebbe essere aggiornato per includere la nuova lingua in questo modo:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+Questo sposterà il nuovo superblocco nel posto corretto nella mappa del curriculum su `/learn`.
+
+## Attivare video localizzati
+
+Per le sfide video, devi cambiare alcune cose. Come prima cosa aggiungi la nuova lingua alla query per GraphQL nel file `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`. Per esempio, in questo modo aggiungeresti Dothraki alla query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Quindi aggiungi un id per la nuova lingua ogni sfida video in un blocco verificato (`auditedCerts`). Per esempio, se `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` include `scientific-computing-with-python` per `dothraki`, allora devi aggiungere `dothraki` in `videoLocaleIds`. Il frontespizio dovrebbe essere simile a questo:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: nuovo-id-qui
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Aggiorna l'interfaccia `VideoLocaleIds` in `client/src/redux/prop-types` così che includa la nuova lingua.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+Infine aggiorna lo schema delle sfide in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Caricare le traduzioni
+
+Poiché la lingua non è ancora stata approvata per la produzione, i nostri script ancora non scaricheranno automaticamente le traduzioni. Solo lo staff ha accesso al download diretto delle traduzioni - sei il benvenuto a rivolgerti a noi attraverso la [chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), o puoi tradurre i file markdown inglesi per le esigenze di test.
+
+Una volta che avrai i file, li dovrai mettere nelle cartelle giuste. Per le sfide del curriculum, dovresti mettere le cartelle dei certificati (ad esempio `01-responsive-web-design`) nella cartella `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Per la nostra traduzione in Dothraki, questo sarebbe `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. I file `.json` con le traduzioni del client vanno nella cartella `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Una volta che questi saranno in posizione, dovresti essere in grado di eseguire `npm run develop` per vedere la versione tradotta di freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+Anche se puoi farei delle traduzioni localmente per i test, ricordiamo che le traduzioni _non_ devono essere inviate attraverso GitHub ma solo tramite Crowdin. Assicurati di resettare il tuo codebase locale dopo che avrai finito con i test.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d7805578
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: Come tradurre le risorse di freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+## Prepare yourself for Contributions
+
+> Il piano d'azione per la localizzazione di freeCodeCamp – Non ci sono limiti di velocità
+
+:::tip
+Puoi iniziare a leggere [questo articolo](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-aiutare-a-tradurre-freecodecamp-nella-tua-lingua/). Ti raccomandiamo di unirti al [forum della nostra comunità](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) e alla [chat Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+Puoi tradurre quanto vuoi e quando vuoi. È solo una questione di quante energie e quanto tempo desideri impiegare come traduttore volontario.
+
+Ti chiediamo soltanto di comprendere che:
+
+1. **Le traduzioni sono uno sforzo di gruppo.**
+
+ Tradurre le risorse di freeCodeCamp è una delle esperienze più divertenti e gratificanti come contributore, e funziona meglio se coinvolgi i tuoi amici e colleghi che parlano la tua stessa lingua.
+
+ Puoi iniziare leggendo [questo articolo](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-aiutare-a-tradurre-freecodecamp-nella-tua-lingua/). Ti raccomandiamo di unirti al [forum della nostra community](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) e alla [chat Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) insieme ai tuoi amici e di manifestare il tuo interesse prima di iniziare con la traduzione. Crowdin e altri strumenti renderanno più semplice contribuire alla traduzione, ma c'è comunque tanto lavoro da fare.
+
+ Vogliamo che tu ti diverta a contribuire e non che ti annoi e perda interesse.
+
+ Un piccolo gruppo di 4-5 persone è una buona dimensione per iniziare la nicchia per la tua lingua. Poi, puoi reclutare ancora più amici perché si uniscano alla squadra.
+
+2. **Costa un sacco creare i server per ogni lingua.**
+
+ In superficie lo stack tecnico può non sembrare complicato, ma costa un sacco tenere i motori in funzione. Questo include avere dei server aggiuntivi e il personale incaricato di controllarli.
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org si impegna a offrire queste cose gratuitamente come sempre, ma dobbiamo dare priorità alle risorse per chi ne ha più bisogno. L'ultima cosa che vogliamo è dover disattivare i server per una lingua se l'attività di traduzione si ferma e il materiale diventa obsoleto.
+
+ Per tradurre il curriculum, una volta che la lingua raggiunge almeno qualche certificazione tradotta, possiamo iniziare a metterle live su [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), mentre continui a tradurre le certificazioni rimanenti.
+
+ Per esempio, vorremmo fare il deploy almeno di tutte le certificazioni front-ent quando attiviamo una nuova lingua per la prima volta.
+
+3. **E per le lingue non elencate sulla piattaforma di traduzione?**
+
+ Abbiamo analizzato la nostra user base e aggiunto le 30+ lingue più usate alla lista delle lingue disponibili sulla piattaforma di traduzione. Al momento alcune lingue come cinese, spagnolo e italiano sono già disponibili live su **"/learn"**.
+
+ Sfortunatamente, la lista non include centinaia di lingue esistenti. Abbiamo dozzine di richieste da contributori come te ogni giorno che vogliono aiutare a tradurre il sito in una lingua che parlano.
+
+ Vogliamo decisamente aggiungere più lingue alla lista, ma come puoi già indovinare, questo è fattibile soltanto se raggiungiamo un coinvolgimento sufficiente per una certa lingua.
+
+ Se vuoi includere una nuova lingua, ti raccomandiamo di entusiasmare i tuoi amici.
+
+ Una volta che avrai un piccolo gruppo di persone (almeno 4-5) interessate e volenterose a impegnarsi, potremo fare una videochiamata. Spiegheremo tutti i dettagli e vi guideremo nell'uso degli strumenti e sui processi.
+
+## Panoramica di Crowdin
+
+Il nostro sogno è fornirti le risorse per imparare, indipendentemente dalla lingua che parli. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source codebase & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
+
+> [!NOTE] Utilizziamo uno strumento e una procedura differenti per la traduzione degli [articoli](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). Se sei davvero interessato a tradurre articoli, leggi [questo articolo](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) e rivolgiti al leader della tua lingua.
+
+La procedura di traduzione è divisa in due attività principali:
+
+- **Tradurre** i file del curriculum, la documentazione e gli elementi dell'interfaccia come pulsanti, etichette, ecc.:
+
+ Come traduttore puoi iscriverti alla [nostra piattaforma di traduzione](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) e contribuire a tradurre in una qualsiasi delle oltre 30 lingue disponibili sulla piattaforma.
+
+- **Revisionare** (Proofread) le traduzioni per gli elementi nominati in precedenza.
+
+ I revisori verificano che le traduzioni dei volontari della community abbiano un tono uniforme e non abbiano problemi comuni come errori di spelling, ecc. In breve, si occupano di assicurare un'alta qualità della traduzione. Nota che non usiamo traduzioni automatiche per una ragione.
+
+> [!WARNING] Se hai contribuito in passato e non conosci le novità, sappi che non stiamo utilizzando più GitHub per tradurre file direttamente, quindi dirigiti alla nostra [piattaforma di traduzione](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+## Getting Started
+
+Prima di tutto, passa a salutarci sul nostro [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Lì postiamo aggiornamenti regolari sulla traduzione delle risorse e rispondiamo a un sacco delle vostre domande.
+
+Poi, vai alla nostra [piattaforma di traduzione](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) e fai login (se è la prima volta che contribuisci alle traduzioni, dovrai creare un account).
+
+Infine, segui la guida dettagliata qua sotto per capire come funzionano gli strumenti di traduzione e il workflow a tua disposizione.
+
+Buona traduzione.
+
+## Selezionare un progetto e un file
+
+Quando visiti la piattaforma di traduzione, dovresti vedere vari "progetti" disponibili per la traduzione:
+
+1. Il progetto della [documentazione per contribuire (Contributing documentation)](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs) che contiene i file per questo sito di documentazione.
+2. Il progetto del [Coding Curriculum](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum), che contiene i file delle sfide del curriculum per programmatori.
+3. Il progetto dell'[interfaccia della piattaforma di apprendimento (Learn User Interface)](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui), che contiene le stringhe per gli elementi dell'interfaccia come pulsanti, etichette, ecc.
+
+Seleziona il progetto a cui vuoi contribuire, e vedrai una lista con le lingue disponibili per la traduzione.
+
+
+
+Seleziona la lingua su cui vuoi lavorare, e vedrai l'albero dei file completo.
+
+
+
+Ogni file e cartella mostrerà una barra di avanzamento. La parte **blu** della barra di avanzamento indica che percentuale del file è stata tradotta, mentre la parte **verde** indica quale percentuale del file è stata approvata dal team di revisione.
+
+Seleziona un file su cui lavorare e Crowdin aprirà l'editor.
+
+> [!NOTE] Quando l'editor si apre, dovrai cliccare sull'icona delle impostazioni (settings, mostrata come un ingranaggio) e impostare 'HTML tags displaying' sull'opzione 'SHOW'. Così sarai in grado di vedere i tag come `<code></code>` invece di `<0></0>`.
+
+## Tradurre il Curriculum
+
+
+
+Crowdin separa un documento in "stringhe" (strings) da tradurre, in genere frasi. Ogni stringa è tradotta individualmente. Con riferimento all'immagine sopra:
+
+1. Una stringa evidenziata in verde ha già una traduzione proposta.
+2. Una stringa evidenziata in rosso _non_ ha una traduzione proposta.
+3. Una stringa con testo in grigio non è traducibile. Questo è il caso per blocchi di codice e altro contenuto che non deve essere tradotto. Non sarai in grado di selezionare queste stringhe nell'editor.
+4. Se un contributore ha già proposto una traduzione per una stringa, Crowdin mostrerà qui queste proposte. Non sarai in grado di salvare una traduzione identica, invece se una traduzione è accurata dovresti usare l'icona `+` per darle un voto positivo. Una traduzione inaccurata può ricevere un voto negativo con l'icona `-`.
+5. Crowdin proporrà delle traduzioni basate sulla Memoria di Traduzione (Translation Memory - TM) e Traduzioni Automatiche (Machine Translation - MT). La Memoria di Traduzione si riferisce a stringhe simili o identiche che sono state tradotte/approvate in altri file. Le Traduzioni Automatiche si riferiscono a traduzioni raccomandate dalla loro libreria integrata.
+6. Questo è il pannello di modifica, dove puoi scrivere la tua proposta di traduzione per la stringa selezionata.
+7. La stringa attualmente selezionata nell'editor è evidenziata in giallo.
+8. Qui vedrai dei tag indicanti lo stato della stringa. `Done` significa che la stringa ha almeno una traduzione proposta. `Todo` significa che la stringa non ha alcuna proposta di traduzione.
+9. Qui puoi vedere la finestra dei commenti. Se hai domande o dubbi su una particolare stringa, puoi lasciare un commento sulla stringa qui perché altri traduttori li vedano.
+10. Questi due pulsanti dei pannelli nasconderanno i pannelli a sinistra (documento) e a destra (commenti).
+
+> [!NOTE] Se vedi una stringa nascosta che include delle traduzioni, per favore, faccelo sapere su [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), così potremo rimuovere la traduzione dalla memoria.
+
+Quando hai finito la traduzione per una stringa, usa il pulsante `Save` per salvare la tua traduzione in Crowdin. Altri contributori potranno quindi votare la tua traduzione e i revisori potranno approvarla.
+
+Sentiti libero di tradurre quante stringhe vuoi, non ci sono step addizionali richiesti quando completi un intero file o proponi una nuova traduzione. Usare il pulsante `Save` è tutto quello che serve per memorizzare una traduzione.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se vedi qualcosa nel file originale inglese che è inaccurato o non corretto, per favore non aggiustarlo con il processo di traduzione. Invece lascia un commento sulla stringa per farci sapere che c'è una discrepanza o crea una issue su GitHub.
+
+## Tradurre l'interfaccia di apprendimento
+
+La nostra interfaccia `/learn` si basa su dei file JSON caricati nel plugin i18n per generare il testo tradotto. Questo processo di traduzione è diviso tra Crowdin e GitHub.
+
+### Su GitHub
+
+I file `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json` e `trending.json` contengono informazioni che devono essere aggiornate per rispecchiare la tua lingua. Tuttavia, non possiamo caricarle su Crowdin, dato che il contenuto non è adatto per traduzioni individuali.
+
+Questi file verranno probabilmente gestiti dal leader della tua lingua ma sei vuoi puoi [leggere qui come tradurli](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### Su Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Non modificare i seguenti file con una PR su GitHub.
+:::
+
+I file `intro.json` e `translations.json` sono tradotti entrambi su Crowdin, nel progetto Learn User Interface. La traduzione di questi file può essere complicata, dato che ogni singolo valore JSON appare come una singola stringa e a volte manca di contesto.
+
+Tuttavia, le informazioni fornite da `Context` su Crowdin possono aiutarti a capire il ruolo della stringa all'interno della struttura che la contiene.
+
+
+
+Se hai domande sul ruolo di una stringa, puoi chiedere informazioni nella nostra [chat per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Tradurre la documentazione
+
+La traduzione della documentazione per la contribuzione si svolge in modo simile alla traduzione dei file del curriculum.
+
+> [!NOTE] La nostra documentazione per la contribuzione sfrutta `docsify` e abbiamo delle regole particolari per riquadri informativi come questo. Se vedi stringhe che iniziano con `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]` o `[!TIP]`, queste parole NON devono essere tradotte.
+
+### How to Translate Documentation with Internal Links
+
+Quando lavori sulla traduzione della documentazione per la contribuzione, stai attento ai link esterni che rimandano a sezioni diverse della documentazione.
+
+Assicurati di sostituire l'id della sezione (la parte dopo `#`) con l'id del documento tradotto. Ad esempio, in giapponese:
+
+Prima della traduzione
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Dopo la traduzione
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト]($1#$2)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+I file reali in docs sono scritti in Markdown, ma appaiono come tag HTML su Crowdin.
+
+Puoi scoprire come `docsify` converte una stringa nella tua lingua in un id guardando le pagine tradotte. Se la traduzione non è stata ancora distribuita, puoi avere una preview [eseguendo il sito della documentazione in locale](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#sservire-localmente-il-sito-di-documentazione).
+
+Puoi avere più informazioni sui [link esterni in docs qui](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#howcome-creare-un-link-interno).
+
+## Tradurre LearnToCode RPG
+
+LearnToCode RPG gira su Ren'Py, che utilizza una sintassi speciale per le stringhe tradotte: (Vedi [Ren'Py Text documentation](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- Le frasi da tradurre sono sempre tra virgolette `""`. Queste sono dialoghi o stringhe di UI. Le parole chiave che vengono prima o dopo i dialoghi sono parole chiave di controllo del game engine e saranno spiegate in regole seguenti. Nota che questa prima regola governa le seguenti regole elencate.
+- Nel caso di `new "..."`, non tradurre la parola chiave `new`.
+- Prefissi come `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (o varianti come `player happy`, `player @ happy`) non devono essere tradotti. Questi sono le parole chiave per visualizzare correttamente gli sprite dei personaggi nel gioco.
+- Suffissi come `nointeract` non devono essere tradotti.
+- Non tradurre stringhe tra `[]` e `{}`. Queste sono variabili interpolate e tag di testo. Queste devono rimanere parentesi a mezza larghezza `[]` e `{}` invece delle loro controparti a larghezza intera `【】` e `「」`
+- Non tradurre la parola chiave `nointeract` alla fine di una frase.
+- Se proviamo a usare parentesi a larghezza intera `()` ci sarà un avviso QA. Per evitarlo, usa parentesi a mezza larghezza `()`
+
+### Esempi
+
+---
+
+#### Prima della traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- questa è la riga da tradurre. vedi la traduzione sotto
+```
+
+#### Dopo la traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我们的VIP队友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}会很高兴的。"
+```
+
+Nota: I tag `[]` e `{}` non devono essere modificati.
+
+---
+
+#### Prima della traduzione
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- traduci questa riga, vedi sotto
+```
+
+#### Dopo la traduzione
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳过"
+```
+
+Nota: Di nuovo, il prefisso `new` e il tag `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` non devono essere modificati.
+
+---
+
+#### Prima della traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### Dopo la traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定会喜欢你的开发者工作的。"
+```
+
+Nota: `layla @ neutral` e `[player_name]` restano inalterati.
+
+---
+
+#### Prima della traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### Dopo la traduzione
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也许这都是一场梦?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Nota sulla segmentazione delle frasi in Crowdin
+
+Fai attenzione a come Crowdin segmenta le frasi dei dialoghi circondate da virgolette `""`. Quando stiamo traducendo un dialogo, dobbiamo essere sicuri di mantenere le virgolette di apertura e di chiusura, anche se appaiono in segmenti diversi.
+
+Ecco la riga che deve essere tradotta:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin la divide in tre parti:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# originale
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# tradotta, mantenendo le virgolette di apertura `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# originale
+What is that?
+# tradotta, nessuna virgoletta
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# originale
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# tradotta, mantenendo le virgolette di chiusura `"`
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## Votare le traduzioni
+
+Crowdin ti permette di votare le traduzioni esistenti. Se tenti di salvare una traduzione, potresti vedere un messaggio che ti avverte che non puoi il duplicato di una traduzione - questo significa che un altro contributore ha già proposto una traduzione identica. Se sei d'accordo con quella traduzione, clicca il pulsante `+` per darle un voto positivo.
+
+Se vedi una traduzione che non è accurata o non fornisce la stessa chiarezza della stringa originale, clicca il pulsante `-` per darle un voto negativo.
+
+Crowdin utilizza questi voti per dare un punteggio a ogni traduzione proposta per una stringa, facilitando il team di revisori che sceglie la traduzione che si adatta meglio a ogni stringa.
+
+## Controlli di Qualità
+
+Abbiamo abilitato alcuni passaggi relativi ai controlli di qualità che verificheranno che una traduzione sia la più accurata possibile - questo aiuta i nostri revisori a valutare le traduzioni proposte.
+
+Quando stai cercando di salvare una traduzione, potresti veder apparire un messaggio di avvertimento con una notifica circa la traduzione proposta.
+
+
+
+Questo messaggio appare quando il sistema QA di Crowdin identifica un potenziale errore nella traduzione proposta. In questo esempio, abbiamo modificato il testo di un tag `<code>` e Crowdin lo ha notato.
+
+> [!WARNING] Sei in grado di salvare una traduzione nonostante gli errori. Se lo fai, cliccando su "Save Anyway", dovresti anche taggare un revisore o un responsabile del progetto e spiegare perché il messaggio QA deve essere ignorato in questo caso.
+
+## Buone pratiche di traduzione
+
+Segui le linee guida per far sì che le traduzioni siano le più accurate possibile:
+
+- Non tradurre il contenuto dei tag `<code>`. Questi tag indicano testo trovato nel codice e dovrebbero essere lasciati in inglese.
+- Non inserire contenuto aggiuntivo. Se pensi che una sfida richieda delle modifiche nel testo o informazioni aggiuntive dovresti proporre i cambiamenti tramite una issue su GitHub o una pull request che modifica i file inglesi.
+- Non cambiare l'ordine del contenuto.
+
+Se hai delle domande, puoi contattarci su [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) e saremo felici di aiutarti.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1a34efb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Come usare Docker su Windows Home
+---
+
+Ci sono alcuni pericoli da evitare quando si setta Docker su Windows Home. Per prima cosa devi usare [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) come amministratore. Purtroppo Windows Home non supporta Docker per Windows Desktop, quindi deve essere usata la Toolbox. Essa deve essere eseguita come Amministratore in quanto l'installazione utilizza collegamenti simbolici che non possono essere creati altrimenti.
+
+Dopo aver installato la toolbox, esegui Docker Quickstart Terminal come amministratore. Questo creerà una virtual machine di `default`, se ancora non esiste. Dopo averlo fatto, chiudi il terminale e apri VirtualBox (ancora come Amministratore). Dovresti essere in grado di vedere la macchina di `default`. Il sito richiede molte risorse, quindi ferma la virtual machine e alza le impostazioni per quanto puoi, soprattutto la memoria. It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Una volta che sarai felice perché Docker sta funzionando, clona il repository di freeCodeCamp in una directory all'interno di `C:\Users`. Queste directory sono condivise dando a Docker accesso alle directory locali, di cui ha bisogno durante l'installazione.
+
+Se vedi messaggi come
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+quando usi `pnpm run docker:init` questa è molto probabilmente la causa.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e21415fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: Come lavorare sulle sfide di programmazione
+---
+
+Il nostro obiettivo è quello di sviluppare un'esperienza di apprendimento interattiva divertente e chiara.
+
+Progettare le sfide di programmazione interattiva è difficile. Sarebbe molto più facile scrivere una spiegazione lunga o creare un video tutorial. Ma per il nostro curriculum di base, ci atteniamo a ciò che funziona meglio per la maggior parte delle persone - un'esperienza completamente interattiva, come il videogioco.
+
+Vogliamo che i camper raggiungano uno stato di flusso. Vogliamo che costruiscano slancio e sfondino attraverso il nostro curriculum con il minor numero di intoppi possibile. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+Nota che per la versione 7.0 del curriculum freeCodeCamp, ci stiamo muovendo verso [un modello interamente orientato al progetto con molta più ripetizione](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+La creazione di queste sfide richiede un'immensa creatività e attenzione ai dettagli. C'è un sacco di aiuto disponibile. Avrai il supporto di un intero team di collaboratori a cui puoi rimbalzare le idee e mostrare le tue sfide.
+
+E come sempre, poni liberamente le tue domande [nella categoria 'Contributors' sul nostro forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [nella chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Con il tuo aiuto possiamo creare un curriculum interattivo di programmazione che aiuterà milioni di persone a imparare a programmare per gli anni a venire.
+
+Il contenuto di ogni sfida è immagazzinato nel suo file markdown. Questo file markdown viene successivamente convertito in HTML utilizzando i nostri strumenti per creare pagine web interattive.
+
+Puoi trovare tutto il contenuto del curriculum di freeCodeCamp nella directory [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges).
+
+## Imposta lo strumento per il curriculum
+
+Prima di lavorare sul curriculum, è necessario impostare alcuni strumenti per aiutarti a testare le modifiche. È possibile utilizzare qualsiasi opzione delle seguenti:
+
+- È possibile [impostare freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Questo è **altamente raccomandato** per contributi regolari/ripetuti. Questa configurazione ti permette di lavorare e testare le modifiche.
+- Usa Gitpod, un ambiente di sviluppo online gratuito. Facendo clic sul pulsante qui sotto si avvierà un ambiente di sviluppo ready-to-code per freeCodeCamp nel tuo browser. Ci vogliono solo pochi minuti.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### Come lavorare sui progetti di pratica
+
+I progetti di pratica hanno degli strumenti addizionali per aiutare a creare i nuovi progetti e gli step. Per saperne di più, leggi [questa documentazione](how-to-work-on-practice-projects)
+
+## Template delle sfide
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Challenge Title'
+challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Testo di itroduzione alla sfida, in markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+I test da eseguire sul codice scritto dall'utente, in coppie di testo markdown e blocco di codice col codice del test.
+
+```js
+Codice per test uno
+```
+
+Se vuoi output dinamico basato sul codice dell'utente --fcc-expected-- e --fcc-actual-- saranno sostituiti con i valori aspettati e i valori veri dell'asserzione del test. Fai attenzione se hai più di una asserzione, visto che la prima asserzione fallita determinerà i valori di --fcc-expected-- e fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Ulteriori informazioni per una sfida, in markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Codice eseguito prima del codice dell'utente.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Codice eseguito dopo il codice dell'utente, ma prima dei test
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Codice di partenza da far apparire nell'editor. Questa sezione deve contenere solo codice in backtick, come il seguente:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Le soluzioni sono usate dai test CI per assicurarsi che i cambiamenti alla sezione hints facciano eseguire i test correttamente
+
+```js
+// prima soluzione - il linguaggio deve combaciare con il seed.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// seconda soluzione - quindi se il seed è scritto in HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// terza soluzione ecc. - La tua soluzione deve essere in HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. Nella sezione sopra, esempi di `lang` sono:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Numerare le sfide
+
+Ogni sfida ha bisogno di un `id`. Se non ne specifichi uno, MongoDB creerà un nuovo id casuale salvando i dati; ma non vogliamo che questo accada, visto che vogliamo che gli id delle sfide siano consistenti su tutti i diversi ambienti (staging, production, diversi sviluppatori, ecc.).
+
+Per generarne un nuovo in una shell (assumendo che MongoDB sia eseguito separatamente):
+
+1. Esegui il comando `mongo`.
+2. Esegui il comando `ObjectId()`.
+
+Per esempio:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Challenge Title
+```
+
+## Dare un nome alle sfide
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Usare la notazione in senso orario per specificare il padding di un elemento
+- Condensare array usando .reduce
+- Usare la notazione a parentesi per trovare il primo carattere in una stringa
+
+## Istruzioni e descrizione di una sfida
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (lettere maiuscole in "J" e "S" e senza abbreviazioni)
+- Node.js
+- Anche se a volte inaccurate, le forme senza trattino di "back end" e "front end" dovrebbero essere usate, poiché sono le forme più comuni.
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- Semplificare la sfida, o
+- Dividere la sfida in due sfide.
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- Le parole chiave del linguaggio vanno in `` \` `` backtick. Per esempio i nomi dei tag HTML o i nomi delle proprietà CSS.
+- Riferimenti a parti di codice (come nomi di funzioni, metodi o variabili) dovrebbero essere in `` \` `` backtick. Vedi gli esempi seguenti:
+
+```md
+Usa `parseInt` per convertire la variabile `realNumber` a un numero intero.
+```
+
+- I riferimenti a nomi di file o percorsi di cartelle (come `package.json`, `src/components`) dovrebbero essere in `` \` `` backtick.
+- I blocchi di codice multi-riga **devono essere preceduti da una riga vuota**. La riga successiva deve iniziare con tre backticks seguiti immediatamente da uno dei [linguaggi supportati](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. Vedi l'esempio seguente:
+- Gli spazi bianchi hanno significato in Markdown, raccomandiamo di renderli visibili nel tuo editor.
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[IL TUO CODICE QUI]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Informazioni aggiuntive nella forma di una nota dovrebbero essere circondate da linee vuote, e formattate così: `**Note:** Resto del testo della nota...`
+- Se è necessaria più di una nota, elencale in frasi separate usando il formato: `**Notes:** Testo della prima nota. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## Scrivere i test
+
+Le sfide dovrebbero avere il numero minimo di test per verificare che un camper abbia compreso il concetto della sfida.
+
+Il nostro obbiettivo è comunicare il singolo punto che la sfida sta cercando di insegnare, e testare che abbiano capito il punto.
+
+I test delle sfide possono fare uso delle librerie di asserzioni Node.js e Chai.js. E, se necessario, il codice generato dall'utente può essere acceduto dalla variabile `code`. In aggiunta, l'oggetto `__helpers` mette a disposizione diverse funzioni che semplificano il processo di scrittura dei test. The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. I commenti devono essere usati esattamente in quel modo, ricopiando maiuscole, minuscole, e spazi. Il dizionario dei commenti non deve essere allargato senza previa discussione con il team di sviluppo.
+
+I commenti dovrebbero avere uno spazio tra il carattere del commento e il testo del commento. In generale, i commenti dovrebbero essere usati raramente. Considera sempre la possibilità di riscrivere la descrizione o le istruzioni di una sfida se questo ti permetterebbe di evitare l'uso di un commento nel codice seed.
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Change code below this line
+
+ // Change code above this line
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Change code below this line */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Change code above this line */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+Declare the myGlobal variable below this line
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Stiamo lavorando su un'integrazione per rendere possibile lavorare su i18n per il dizionario dei commenti.
+
+## Suggerimenti e soluzioni
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. Inizia seguendo gli stessi passaggi per creare un nuovo argomento, ma rivedi il successivo per creare il titolo.
+2. Il titolo dell'argomento dovrebbe iniziare con `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` concatenato con il titolo effettivo della sfida del curriculum. Ad esempio, se la sfida è chiamata "`Chunky Monkey`", il titolo dell'argomento sarebbe "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. `camperbot` dovrebbe essere il proprietario di questi argomenti/post, quindi dovrai chiedere a un amministratore di cambiare la proprietà del post principale a `camperbot`.
+4. Una volta creato il nuovo argomento, verrà creato un id del topic nel forum. Esso si trova alla fine dell'URL dell'argomento del forum. Questo id deve essere aggiunto alla parte frontale del file di sfida del curriculum tramite il normale processo di pull request per il pulsante `Ottieni un suggerimento` in modo da collegarlo all'argomento.
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# [Qui il nome della sfida]
+
+---
+
+## Spiegazione del problema
+
+Qui un riassunto di cosa deve essere fatto senza includere semplicemente le istruzioni e la descrizione della sfida. [This is an optional section]
+
+#### Relevant Links
+
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## Hints
+
+### Hint 1
+
+[Suggerimento 1 va qui]
+
+### Hint 2
+
+[Suggerimento va qui]
+
+---
+
+## Solutions
+
+<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Spiegazione Del Codice
+
+- La spiegazione del codice va qui
+- La spiegazione del codice va qui
+
+#### Collegamenti utili
+
+- [Testo del collegamento](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Testo Collegamento](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Testare le sfide
+
+Prima di [creare una pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request), devi verificare che i cambiamenti che hai fatto non causino inavvertitamente problemi con la sfida.
+
+1. Per testare tutte le sfide esegui il comando seguente nella directory root
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dba8a919
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. È tradotta in varie lingue internazionali usando [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) e [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+Puoi scoprire di più su come configurare l'applicazione client localmente per lo sviluppo seguendo [la nostra guida alla configurazione in locale](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+Questo può essere utile quando stai lavorando su una caratteristica che riguarda specificatamente qualcosa che coinvolge la localizzazione e ti richiede ad esempio l'etichetta di un bottone in una lingua diversa.
+
+:::tip
+You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. Invece, leggi [questa guida](how-to-translate-files).
+:::
+
+Andiamo a vedere come funzionano il framework e gli strumenti.
+
+## Struttura dei file
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**File tradotti con la nostra piattaforma di traduzione:**
+
+- Il file `translations.json` contiene la maggior parte del testo che compare sugli elementi dell'interfaccia utente. Le chiavi sono usate nel codice per ottenere i testo corretto per qualunque lingua sia impostata. This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- Il file `intro.json` contiene le coppie chiave-valore relative al testo introduttivo sulle pagine delle certificazioni.
+
+ Se vuoi aggiungere/aggiornare le traduzioni per le chiavi, per favore [leggi questa guida](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**File NON tradotti con la nostra piattaforma di traduzione:**
+
+- I file `motivation.json` non devono avere per forza le stesse frasi, complimenti o lunghezze degli array. Basta che abbiano la stessa struttura JSON.
+
+- Il file `meta-tags.json` contiene le informazioni per il tag meta del nostro sito.
+
+ I cambiamenti su questi file sono tipicamente fatti dallo staff. Se vedi qualcosa fuori dall'ordinario, ti raccomandiamo di metterti in contatto con noi sulla [chat dei contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+Se stai testando una nuova lingua, crea una cartella con il nome della lingua come titolo accanto alle altre lingue e copia i file JSON da un'altra lingua alla tua cartella.
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+Successivamente, segui le istruzioni nei commenti nello stesso file per aggiungere/aggiornare il resto delle variabili secondo necessità.
+
+Infine, imposta la variabile `CLIENT_LOCALE` nel tuo file `.env` con la stringa della lingua di cui vuoi eseguire il build dall'enum `Languages` nel file qui sopra.
+
+## Come strutturare i componenti
+
+Se stai lavorando su una caratteristica o un bug per la client web app, ad esempio aggiungendo nuovi elementi di interfaccia utente sulla pagina delle impostazioni, dovresti seguire le linee guida qui sotto. Ti aiuteranno a preparare i componenti per la localizzazione in tutte le lingue supportate.
+
+### Componenti funzionali
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// nel metodo render:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// chiama la funzione "t" con una chiave dal file JSON:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // altri dettagli sotto
+```
+
+### Componenti classe
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation aggiunge la funzione "t" alle props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// chiama la funzione "t" con una chiave dal file JSON:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // più dettagli sotto
+
+// esporta senza redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// o con redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Tradurre usando la funzione "t"
+
+### Traduzione di base
+
+```js
+// nel componente:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// nel file JSON:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### Con dati dinamici
+
+```js
+// nel componente:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// nel file JSON:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+L'esempio qui sopra passa alla funzione `t` un oggetto con una variabile `username`. La variabile verrà usata nel valore JSON al posto di `{{username}}`.
+
+## Traduci con il componente `Trans`
+
+La regola generale è usare la funzione "t" quando puoi. Ma c'è un componente `Trans` per quando questo non basta, solitamente quando hai elementi incorporati nel testo. Puoi usare il componente `Trans` con ogni tipo di componente react.
+
+### Elementi di base annidati
+
+```js
+// nel componente:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// nel file JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i`, e `p` sono quelli predefiniti, ma la lista può essere ampliata nel file i18n config.
+
+### Elementi complessi annidati
+
+Altre volte, vorrai avere un certo testo all'interno di un altro elemento, un buon esempio è il tag anchor:
+
+```js
+// nel componente:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// nel file JSON:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+Nell'esempio sopra, la chiave è impostata negli attributi del componente `Trans`. I tag `<0>` e `</0>` nel JSON rappresentano il primo figlio del componente, in questo caso l'elemento anchor. Se ci fossero più elementi figli, verrebbero contati a partire da lì, usando la stessa sintassi. Puoi trovare i figli di un componente negli strumenti per sviluppatori react ispezionandolo. `placeholder` è lì semplicemente perché il linter protesterebbe per un elemento `<a>` lasciato vuoto.
+
+### Con una variabile
+
+```js
+// nel componente:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// nel file JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+Nell'esempio sopra, la chiave e una variabile sono impostate negli attributi del componente `Trans`. Anche `{{ email }}` deve essere da qualche parte nel componente `Trans`, non importa dove.
+
+## Cambiare il testo
+
+Per cambiare il testo sul lato client, vai al relativo file `.json`, trova la chiave che viene usata nel componente React e cambiane il valore con il nuovo testo che vuoi. Dovresti cercare quella chiave nel codice, per assicurarti che non venga usata da qualche altra parte. O, se lo è, che il cambiamento abbia senso ovunque.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Aggiungere testo
+
+Se il testo che vuoi aggiungere al client esiste nel relativo file `.json`, usa la chiave esistente. Altrimenti, crea un'altra chiave.
+
+Il file in inglese è la "fonte della verità" per tutti i file `.json` che condividono lo stesso nome. Se hai bisogno di aggiungere una nuova chiave, aggiungila lì. Dopodiché, aggiungi la chiave a **tutti** i file `translations.json`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Usa del testo in inglese per tutte le lingue se il file è tradotto tramite Crowdin. Se non lo fai, i test falliranno.
+
+Sarebbe utile anche tenere tutte le chiavi nello stesso ordine in tutti i file. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. Vedi [la documentazione](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) per il suo utilizzo.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [Documentazione react-i18next ](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [Documentazione i18next](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d45477a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: Come lavorare sui progetti di pratica
+---
+
+I nostri progetti di pratica utilizzano un approccio graduale per insegnare concetti agli studenti. Un progetto consisterà in vari file, ai quali ci riferiamo come **"step"**. Questi file sono identificati dall'ID della sfida, per evitare problemi con il processo di traduzione. Sfortunatamente, questo rende difficile trovare il file associato a uno step specifico.
+
+Abbiamo costruito uno strumento editor per le sfide per rimediare a questo problema. Questo strumento consente di navigare nei progetti disponibili e negli step di ogni progetto (in ordine). Inoltre è presente un editor di codice incorporato che puoi utilizzare per lavorare direttamente sui file.
+
+## Usare l'editor per le sfide
+
+Queste istruzioni ti diranno come utilizzare il nostro strumento editor per le sfide per lavorare sui progetti per fare pratica.
+
+### Avviare l'editor
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Poi esegui `pnpm run challenge-editor` per avviare sia il client che l'API di cui fa uso l'editor.
+
+Il client verrà avviato sulla porta `3300`, così puoi accedervi su `http://localhost:3300`. L'API gira sulla porta `3200`, per evitare conflitti con il client learn e con il server. Questo ti permetterà di eseguire l'applicazione freeCodeCamp contemporaneamente all'editor, in modo che tu possa testare le tue modifiche localmente.
+
+### Navigare nell'editor
+
+La visualizzazione predefinita elencherà i `superblocks` disponibili - ovvero le certificazioni. Clicca sul link della certificazione sulla quale vuoi lavorare.
+
+Verrai portato all'elenco dei blocchi. Questi sono i progetti per fare pratica. Clicca sul link del progetto sul quale vuoi lavorare.
+
+Verrai indirizzato alla lista con gli step del progetto. Se stai lavorando su uno step esistente puoi cliccare sul link dello step per aprire l'editor. Se stai aggiungendo o rimuovendo step clicca il link `Use the step tools` per passare agli strumenti degli step per quella sfida.
+
+### Modificare gli step
+
+Quando clicchi sullo step verrai portato sull'editor. Questo è un editor di testo di base che permette la colorazione della sintassi.
+
+Dopo aver apportato le modifiche, clicca sul pulsante `Save Changes` per salvarle. Riceverai un avviso dal browser che ti comunica che le tue modifiche sono pronte per il commit. Nota che dovrai utilizzare manualmente `git` per aggiungere i file all'area di staging e per fare commit - questo strumento non lo farà per te.
+
+### Strumenti degli step
+
+Quando fai clic sul link `Use the step tools`, sarai portato sulla pagina degli strumenti degli step. Da qui potrai aggiungere o rimuovere gli step dal progetto.
+
+#### Creare uno step successivo
+
+Cliccando questo pulsante aggiungerai un nuovo step alla fine del progetto. Questo step utilizzerà il precedente step come seed.
+
+#### Creare step vuoti
+
+Inserisci nell'input il numero di step che vuoi aggiungere. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Inserire uno step
+
+Inserisci il numero dello step che vuoi eliminare. Poi, clicca sul pulsante `Insert Step` per aggiungere lo step. Gli step successivi verranno riordinati.
+
+#### Eliminare uno step
+
+Inserisci il numero dello step che vuoi eliminare. Poi clicca il pulsante `Delete Step` per eliminarlo. In questo modo, il numero degli step rimanenti verrà aggiornato automaticamente.
+
+#### Aggiornare i titoli degli step
+
+Non dovresti usare questo strumento a meno che tu non abbia manualmente cancellato o aggiunto degli step. Questo strumento riordinerà i numeri degli step.
+
+## Usare gli script manualmente
+
+Se desideri lavorare sugli step manualmente, nel tuo IDE locale, puoi eseguire direttamente gli script di gestione degli step.
+
+La cartella `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` contiene strumenti per aiutare a facilitare la creazione e il mantenimento del curriculum basato su progetti di freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Una volta finito, dovrebbe esserci una nuova sfida nel curriculum inglese che puoi usare come primo passo del progetto. Ad esempio, se hai creato un progetto chiamato `test-project` nella certificazione Web Design Responsivo, sarebbe in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+Se vuoi creare nuovi step, i seguenti strumenti semplificano il processo.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+Uno script una tantum che aggiungerà automaticamente lo step successivo in base all'ultimo step del progetto. Il codice seed della sfida userà il codice seed di quella precedente.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Vai alla directory del progetto.
+2. Esegui il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+Uno script eseguito una sola volta che aggiunge automaticamente un determinato numero di step. Il codice seed della sfida per tutti gli step creati sarà vuoto.
+
+**Nota:** Questo script esegue anche [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Vai alla directory del progetto.
+2. Esegui il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # dove X è il numero di step da creare.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+Uno script una tantum che aggiunge automaticamente un nuovo step in una posizione specificata, incrementando tutti gli step successivi (sia i loro titoli che in meta.json). Il codice seed della sfida userà il codice seed di quella precedente, rimuovendo i marcatori delle regioni editabili (MRE).
+
+**Nota:** Questo script esegue anche [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Vai alla directory del progetto.
+2. Esegui il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # dove X è la posizione in cui inserire il nuovo step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+Uno script una tantum che rimuove uno step esistente, decrementando tutti gli step successivi (sia i loro titoli che in meta.json)
+
+**Nota:** Questo script esegue anche [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Vai alla directory del progetto.
+2. Esegui il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # dove X è il numero dello step da eliminare.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+Uno script una tantum che aggiorna automaticamente il frontmatter nei file di markdown di un progetto in modo che siano coerenti con il progetto meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Vai alla directory del progetto.
+2. Esegui il seguente comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1aca07a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Come lavorare sulla libreria dei componenti
+---
+
+Benvenuti nella libreria `ui-components` di freeCodeCamp. I componenti sono principalmente creati da zero con elementi HTML base e [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp stava utilizzando componeti Bootstrap nell'UI. Ma, ci stiamo pian piano allontanando da ciò e creando la nostra libreria componenti, il che aiuta a standardizzare i pattern UI/UX e a migliorare l'accessibilità. Teniamo traccia del progetto in [questa issue su GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+I seguenti step sono raccomandati quando lavori su un nuovo componente:
+
+- Ricerca e pianificazione
+- Implementazione del componente
+- Visualizzazione degli use case in Storybook
+- Scrittura dei test unitari
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Prima di creare un componente, devi ricercare e documentare il comportamento e l'aspetto della versione esistente, per assicurarti che il nuovo componente combaci in stile e supporti tutti gli usi correnti. In modo da soddisfare tutti i requisiti di accessibilità web, dovresti prestare attenzione all'aspetto di accessibilità del componente, vedere quali elementi HTML e attributi ARIA sono usati.
+
+Una volta che hai raccolto abbastanza informazioni sul componente, puoi iniziare a pensare alle proprietà dell'interfaccia. Idealmente, l'interfaccia dovrebbe essere quanto più simile possibile alla versione corrente, per renderne più semplice l'adozione in futuro. Visto che stiamo usando componenti Bootstrap, l'approccio più semplice è mimare [la loro implementazione](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+Preferiamo pull request piccole piuttosto che grandi, perché riducono la velocità di revisione e il carico cognitivo per i revisori. Per questa ragione dovresti pensare a come dividere l'implementazione in pezzi più piccoli e creare un piano di delivery.
+
+Raccomandiamo di aprire una issue su GitHub separata per ogni componente e includere tutte le note nella descrizione della issue. Può essere usato come posto per ospitare tutte le tue note di lavoro, come pure un modo per comunicare l'approccio con i revisori. Useremo i commenti dell'issue per discussioni ulteriori se necessario. [La issue per il componente Button](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) può essere usata come referenza.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+Un nuovo componente può essere creato usando i seguenti comandi dalla root directory:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+Il comando genererà una nuova cartella dentro la directory `ui-components`, con i seguenti file:
+
+| Nome file | Scopo |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | Usato per esportare il componente e i suoi tipi. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | Usato per fare la demo del componente con Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | file di test. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | Dove implementiamo il componente. |
+| `types.ts` | Dove mettiamo l'interfaccia e i tipi del componente. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Supportare l'invio a ref
+- Essere stilizzato sia per il tema chiaro che scuro
+- Essere stilizzato internamente basato sulle proprietà (Il consumatore non dovrebbe avere bisogno di stilizzare il componente con la proprietà `className`)
+- Utilizzare il sistema integrato di stilizzazione di Tailwind invece di usare stili personalizzati
+
+### Using Colors
+
+Ci sono due strati di colori nella libreria dei componenti:
+
+- Lo strato base, dove i nomi dei colori descrivono cosa sono i colori, per esempio `gray00`, `blue50`
+- Lo strato semantico, dove i nomi dei colori descrivono lo scopo de colori, per esempio `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. Però ci sono eccezioni, specialmente quando stai dando uno stile agli stati del componente, tipo hover, attivo, disabilitato, ecc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+> [!NOTE] Le definizioni dei colori possono essere trovate nel [file `colors.css`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). Un colore è disponibile per l'uso solo se è aggiunto al [file `tailwind.config.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) sotto la proprietà `colors`.
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Tailwind CSS Configuration](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [React Bootstrap v0.33 Docs](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Bootstrap 3.3.7 stylesheet](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [Implementazione corrente di React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [Test attuali di React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Gli use case di un componente dovrebbero essere aggiunti al file Storybook (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+Per far partire Storybook, esegui i seguenti comandi dalla directory root:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+La pagina Storybook è disponibile a [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+Usiamo [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) per scrivere i test dell'unità. I test dovrebbero verificare che i componenti si comportano come previsto e sono accessibili.
+
+Per eseguire i test sulla libreria componenti, esegui il seguente comando dalla directory root:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Testare per accessibilità](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Ordine di priorità delle query di React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Errori comuni con React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80457319
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+Per lavorare sulle linee guida per i contributori, puoi modificare o aggiungere file nella cartella `docs` [disponibile qui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). Quando i tuoi cambiamenti sono accettati, saranno resi disponibili automaticamente nel sito della documentazione.
+
+Quando aggiungi un nuovo file alla cartella `docs`, dovresti valutare se il file dovrebbe essere aggiunto anche alla barra laterale di navigazione. Generalmente creiamo un link nel file [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) per guide nuove e indipendenti. In alternativa, è possibile seguire le istruzioni qui sotto sulla creazione di un link interno per le guide di supporto.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+Se vuoi creare un link che punta a una sezione diversa delle linee guida per contribuire, segui questo formato:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// Se la sezione target è nella stessa pagina puoi omettere il nome del file
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Assicurati di includere l'estensione del file (`.md`). Non specificare l'URL completo o aggiungere `/` prima del nome del file.
+
+È necessario fare così per rendere questi link funzionanti anche nella versione tradotta del documento. Altrimenti, punterebbero alla versione inglese della pagina a discapito della lingua.
+
+#### Tradurre documentazione con link interni
+
+Quando lavori per tradurre la documentazione su Crowdin, assicurati di sostituire la parte `#target-section-heading-id` con l'id del documento tradotto. [Impara di più su come tradurre la documentazione qui](how-to-translate-files#tradurre-la-documentazione).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+> [!NOTE] Non devi impostare nulla per lavorare sul contenuto della documentazione.
+>
+> Per lavorare sulle linee guida per la contribuzione, vedi [la sezione su come lavorare sul contenuto della documentazione](#work-on-the-docs-content).
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+Il sito viene generato utilizzando [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) e servito utilizzando le pagine di GitHub.
+
+In genere non è necessario modificare alcuna configurazione o costruire il sito localmente. Nel caso in cui tu sia interessato, ecco come funziona:
+
+- La sorgente della homepage per questo sito è disponibile in [`docs/index.html`](index.html).
+- Serviamo questo file come SPA (Single Page Application) usando `docsify` e GitHub Pages.
+- Lo script `docsify` genera il contenuto del `file markdown` nella directory `docs` su richiesta.
+- La homepage è generata dal file [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage).
+- La barra laterale di navigazione è generata da [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> Il sito di documentazione dovrebbe essere disponibile su <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1068eaca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: Come lavorare sul tema delle news degli sviluppatori di freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Le notizie degli sviluppatori conosciute anche come il sito [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) è alimentato da [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). Usiamo un tema personalizzato per l'aspetto del sito. Il codice sorgente del tema è disponibile qui: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## Il Tema
+
+Ghost utilizza un semplice linguaggio di modellazione chiamato [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) per i suoi temi. Il tema utilizzato su `/news` è basato sul [tema casper](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper) predefinito.
+
+Il tema di default ha molti commenti così è abbastanza facile capire cosa sta succedendo semplicemente leggendo il codice e i commenti. Una volta che ti senti a tuo agio con il funzionamento del tutto, Ghost ha anche una completa [documentazione API per i temi](https://themes.ghost.org) che spiega ogni possibile helper Handlebars e modello.
+
+**I file principali sono:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - Il file del modello principale
+- `index.hbs` - Utilizzato per la home page
+- `post.hbs` - Utilizzato per singoli post
+- `page.hbs` - Utilizzato per singole pagine
+- `tag.hbs` - Utilizzato per archivi di tag
+- `author.hbs` - Utilizzato per archivi d'autore
+
+Uno trucco davvero pulito è che è anche possibile creare modelli una tantum personalizzati solo aggiungendo lo slug di una pagina a un file di modello. Per esempio:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Modello personalizzato per la pagina `/about/`
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Modello personalizzato per l'archivio `/tag/news/`
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Modello personalizzato per l'archivio `/author/ali/`
+
+## Sviluppo
+
+1. Installare Ghost localmente.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Nota: Attualmente freeCodeCamp utilizza la versione Ghost `2.9.0`, quindi assicurati di usare una versione superiore.
+
+ Assicurati di eseguire i comandi `ghost` dalla directory `ghost-local-site`. Segui le istruzioni aggiuntive sulla documentazione ufficiale di [Ghost](https://docs.ghost.org) se non ha familiarità con la sua interfaccia.
+
+2. Forka e clona il repository nella directory del tuo tema (sostituendo `YOUR_USERNAME` con il tuo username di GitHub):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Assicurati di avere tutti i prerequisiti.
+
+ Gli stili del tema sono compilati usando Gulp/PostCSS per rispettare le future specifiche CSS. Avrai bisogno di [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Assicurati che la tua versione Node.js sia compatibile con `ghost`.
+
+4. Installa le dipendenze e sviluppa il tema
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Ora puoi modificare automaticamente i file `/assets/css/`, che saranno compilati in `/assets/built/`.
+
+6. Accedi al sito di sviluppo.
+
+ a. Inserisci `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` nella barra degli indirizzi. Continua con la configurazione richiesta sulla pagina (se stai eseguendo ghost per la prima volta).
+
+ b. _(Una sola volta durante la configurazione)_ Riavvia Ghost in un terminale separato per garantire che il tema sia disponibile.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(Una sola volta durante l'installazione)_ Una volta fatto, vai su `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` e scorri verso il basso. Assicurati di cliccare attiva su `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Zippa il codice finale e fai una pull request
+
+ Il task `zip` di Gulp impacchetta i file del tema in `dist/<theme-name>. ip`, che potremo poi caricare sul sito di produzione.
+
+ Quando fai una PR, assicurati di aver eseguito lo script sottostante prima di effettuare il commit del codice e di inviare una PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Altri riferimenti e risorse
+
+### Funzionalità PostCSS Utilizzate
+
+- Autoprefixer - Non preoccuparti di scrivere prefissi del browser di alcun tipo, è tutto fatto automaticamente con il supporto per le ultime 2 versioni principali di ogni browser.
+- Variabili - Semplici variabili CSS pure
+- [Funzione Color](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### Icone SVG
+
+Il tema utilizza icone SVG in linea, incluse tramite dei partial di Handlebars. Puoi trovare tutte le icone all'interno di `/partials/icons`. Per usare un'icona basta includere il nome del file pertinente, ad es. Per includere l'icona SVG in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - usa `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+È possibile aggiungere le proprie icone SVG nello stesso modo.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2dcaad01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+Questa pagina descrive come contribuire ai tutorial e progetti di freeCodeCamp che sono completati usando l'estensione di VS Code chiamata CodeRoad.
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. Il nome inizia sempre con `learn-`. Per esempio, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Ogni repo di un tutorial ha un branch principale `main` e un branch di versione, per esempio `v1.0.0`.
+
+I due file principali sul branch `main` sono `TUTORIAL.md` e `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contiente tutte le istruzioni, suggerimenti, titoli, ecc, per il tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contiene istruzioni per CodeRoad, tipo quali comandi eseguire e quando, quali file sorvegliare per cambiamenti e quale branch di versione usare per gli step.
+
+Il branch " di versione" contiene i commit che vengono caricati per ogni step del tutorial. I messaggi di commit di questo branch devono essere specifici. Il primo commit deve avere come messaggio `INIT` e contiene tutti i file da caricare prima della prima lezione.
+
+I seguenti messaggi di commit devono combaciare con il numero dello step in `TUTORIAL.md` dal branch `main`. Per esempio, il commit con messaggio `10.1` sarà caricato quando un utente raggiunge lo step `10.1`.
+
+Per fare cambiamenti ai commit di un branch di versione, dovresti fare un rebase e cambiare i commit che vuoi cambiare. Questo riscrive la storia di Git, quindi non possiamo accettare PR a questo tipo di branch. Una volta che un branch di versione è sul repo di GitHub non deve mai cambiare.
+
+:::caution
+Non fare mai cambiamenti a un branch di versione che si trova su un repo di freeCodeCamp. Creane sempre uno nuovo
+:::
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### Prerequisiti
+
+Installa [CodeRoad CLI tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) con `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+Ci sono stati alcuni problemi con l'ultima versione. Se `coderoad --version` non funziona dopo aver installato, fai un downgrade a `0.7.0` con `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Lavorare su `main`
+
+Queste istruzioni sono per PR che fanno solo piccoli cambiamenti su `main` a **lezioni esistenti**. Che consistono principalmente in errori di spelling e grammatica, suggerimenti, cambiamenti alle struzioni e aggiustamenti nel file `TUTORIAL.md`.
+
+Per qualsiasi altra cosa, incluso aggiungere o cancellare lezioni, segui le istruzioni [per lavorare su un branch di versione](#working-on-version-branch). Avrai bisogno di creare un nuovo branch di versione per questo - puoi creare un PR seguendo le istruzioni seguenti.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Questi cambiamenti useranno il branch di versione esistente. Se sono sostanziali, aggiungili a `CHANGELOG.md`. La maggior parte delle volte, un buon messaggio di commit dovrebbe essere sufficiente
+
+Non hai mai bisogno di cambiare il file `tutorial.json` direttamente. Quello sarà creato con gli strumenti di CLI.
+
+Se stai facendo solo cambiamenti minori come sistemare un errore di spelling o grammatica, non hai bisogno di testare i tuoi cambiamenti.
+
+Segui queste istruzioni per creare un PR, tenendo a mente che le istruzioni usando in genere le lezioni attorno a loro per contesto:
+
+- Crea una copia dell'ultimo branch di versione con `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - non hai bisogno di aprire questo branch, ha solo bisogno di esistere.
+- Crea e muoviti su un nuovo branch ramificato da `main`
+- Fai e **commit** i tuoi cambiamenti. Promemoria: non devi cambiare nulla nel file `tutorial.json`. Probabilmente devi solo fare cambiamenti a `TUTORIAL.md`
+- Esegui `coderoad build` per ricreare il file `tutorial.json`
+- Fai un commit con i tuoi cambiamenti con `update json` come messaggio
+- Crea un PR
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+Se vuoi testare i tuoi cambiamenti a `main` dopo aver usato le istruzioni precedenti, segui queste istruzioni:
+
+- Segui le istruzioni nel repo [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) per creare un contenitore
+- Inizia il tutorial usando `tutorial.json` nel nuovo branch
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+Se stai revisionando un PR che fa cambiamenti a `main`solo con istruzioni o errori di grammatica come descritto sopra, i cambiamenti in `TUTORIAL.md` devono combaciare con i cambiamenti in `tutorial.json`.
+
+Il file `tutorial.json` non deve avere cambiamenti agli hash di commit, o agli id degli step/livelli. E pure i comandi di startup o di livello o gli osservatori dei file probabilmente non dovrebbero essere cambiati. Ci sono eccezioni se c'è un problema con uno step, ma dovrebbero essere trattati con più cautela.
+
+Inoltre, tieni a mente che le istruzioni usano in genere le lezioni attorno a loro come contesto, quindi assicurati che abbiano senso.
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Promemoria: Non fare mai cambiamenti a un branch di versione che si trova su un repo di freeCodeCamp. Creane sempre uno nuovo
+
+Non c'è un modo semplice per vedere esattamente cosa cambia tra i branch di versione visto che la storia di Git sarà riscritta. Accettare un nuovo branch di versione dovrà essere fatto con attenta considerazione e testing.
+
+Queste istruzioni sono per cambiare qualunque cosa su un branch di versione, come test, testo dei test, file di reset, aggiungere e eliminare step, tra le altre cose.
+
+Segui queste istruzioni per creare una nuova versione:
+
+- Vai sull'**ultimo** branch di versione con `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Crea un nuovo branch da quel branch, incrementando la versione, con `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Fai i tuoi cambiamenti al branch di versione. Puoi trovare maggiori informazioni su come lavorare con i tutorial nella [documentazione di CodeRoad](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial)
+- Invia il nuovo branch al tuo fork con `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Vai sul branch `main`
+- Crea un nuovo branch da `main`. Per esempio `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Cambia l'`uri` in `coderoad.yaml` al tuo fork del repo. Questo è per far si che tu e i tuoi revisori possono testare prima di spingere i cambiamenti al repo di freeCodeCamp. Cambia la versione al nuovo branch nei due punti di quel file. Aggiungi i tuoi cambiamenti per la nuova versione in `CHANGELOG.md`. Fai qualsiasi altro cambiamento di cui hai bisogno.
+- Fai un commit dei tuoi cambiamenti con il messaggio `feat: release version X.X.Y - <descrizione opzionale>`
+- Esegui `coderoad build` per creare un nuovo file `tutorial.json`
+- Aggiungi il file e fai un commit
+- Spingi i cambiamenti al tuo fork con push
+- Testa i tuoi cambiamenti seguendo le [istruzioni di testing più sotto](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Fai i cambiamenti aggiuntivi necessari e fai un commit con loro come hai apena fatto, o se sei soddisfatto, segui il resto delle istruzioni
+- Fai un PR a `main` usando il tuo nuovo branch `feat/version-X.X.Y`. Dagli un titolo di `version X.X.Y ready for review`. Questo non sarà unito al database, è solo per far sapere ai revisori che c'è una nuova versione pronta
+- Lascialo qui per i revisori
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- Segui le istruzioni nel repo [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) per creare un contenitore
+- Inizia il tutorial usando il file `tutorial.json` nel fork in cui sono i cambiamenti. Assicurati di usare il file nel branch `feat: version-X.X.Y` e non nel branch `main`
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+Prima del push di una nuova versione, visualizza il nuovo branch `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (di cui sarà fatto il merge con `main`) sul fork dell'utente. Assicurati che ci siano cambiamenti al file `CHANGELOG.md` che includono i nuovi cambiamenti, e che la versione nei due punti del file `coderoad.yaml` corrisponda al nuovo branch di versione.
+
+Se hai permessi di scrittura al repo di freeCodeCamp, hai verificato i file `CHANGELOG` e `coderoad.yaml`, hai testato i cambiamenti seguendo le istruzioni qua sopra, e vuoi fare il push di una nuova versione del tutorial:
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Promemoria: Non fare mai cambiamenti a un branch di versione che si trova su un repo di freeCodeCamp. Creane sempre uno nuovo
+
+- Se non hai un remote a dove esistono i cambiamenti, crea un remote al fork dell'utente con `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Elimina qualsiasi branch **locale** che condivide un nome con i nuovi branch. Probabilmente denominato `vX.X.Y` o `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Vai sul nuovo branch di versione con `git checkout -b vX.X.X remote/vX.X.X`
+- Fai il push del nuovo branch di versione al repo di freeCodeCamp con `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. Devi fare il push del nuovo branch prima di aggiornare `main` con il nuovo file `tutorial.json`
+- Vai su il ramo degli utenti di cui sarà fatto il merge in `main` con `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Cambia l'`uri` in `coderoad.yaml` di nuovo al repo di freeCodeCamp
+- Aggiungi i cambiamenti e fai un commit
+- Esegui `coderoad build` per creare il nuovo file `tutorial.json`
+- Aggiungi il file e fai un commit
+- Fai il push dei cambiamenti al tuo fork con `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Fai un PR a `main` sul repo di freeCodeCamp
+- Se sei soddisfatto, fai il merge, o lascialo e chiedi una review da parte di qualcun altro
+- Dopo che è stato fatto il merge del PR, apri il tutotial seguendo le istruzioni nel [repo rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) per assicurarti che si carichi come si deve e che puoi procedere per qualche step
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Fai il revert di tutti i commit di questo branch fino a e includendo il commit della versione successiva a quella a cui vuoi tornare. Per esempio, se hai dei commit tipo questi:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+E vuoi tornare a v1.0.0, fai il revert di tutti i commit a partire da `release: version 1.0.1`
+
+- Crea un PR. Dagli un titolo tipo `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/intro.md b/src/content/docs/it/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9ec51fb8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+La comunità [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) è composta da migliaia di volontari come te. Se vuoi contribuire con il tuo tempo e le tue competenze, saremo entusiasti di darti il benvenuto a bordo.
+
+:::note
+Prima di procedere, prenditi due minuti per leggere il nostro [Codice di condotta](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct). Lo applichiamo rigorosamente in tutta la nostra comunità in modo che contribuire a freeCodeCamp.org sia un'esperienza sicura e inclusiva per tutti.
+:::
+
+Siete invitati a creare, aggiornare e correggere i bug nel nostro [curriculum](#curriculum), aiutarci a correggere i bug nella [piattaforma di apprendimento](#piattaforma-di-apprendimento) di freeCodeCamp.org, o [aiutarci a tradurre](#traduzioni) freeCodeCamp.org nelle diverse lingue del mondo.
+
+Rispondiamo alle domande più comuni su come contribuire [nelle nostre FAQ per i contributori](FAQ).
+
+Buon lavoro.
+
+---
+
+## Curriculum
+
+Il nostro curriculum è curato dalla comunità globale freeCodeCamp. In questo modo, siamo in grado di incorporare le utili conoscenze di volontari come te.
+
+Puoi aiutare ad espandere e migliorare il curriculum. Puoi anche aggiornare le user story del progetto per spiegare meglio i concetti. E puoi migliorare i nostri test automatici in modo da poter testare più accuratamente il codice degli studenti.
+
+**Se sei interessato a migliorare il nostro curriculum, ecco [come contribuire al curriculum](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges).**
+
+## Traduzioni
+
+Stiamo traducendo freeCodeCamp.org nelle maggiori lingue del mondo.
+
+Le certificazioni sono già disponibili in alcuni delle principali lingue, come:
+
+- [Cinese (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Spagnolo (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italiano](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Portoghese (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ucraino (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Giapponese (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [Tedesco (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+Ti incoraggiamo a leggere l'[annuncio qui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-aiutare-a-tradurre-freecodecamp-nella-tua-lingua/) e a condividerlo con i tuoi amici.
+
+**Se sei interessato a tradurre, ecco [come tradurre le risorse di freeCodeCamp](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## Piattaforma di apprendimento
+
+La nostra piattaforma di apprendimento esegue uno stack JavaScript moderno. Ha vari componenti, strumenti e librerie. Questi comprendono Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack e altro.
+
+In generale, abbiamo un server API basato su Node.js, un set di applicazioni client basate su React, script per i test di valutazione dei progetti degli utenti del curriculum e altro. Se vuoi contribuire produttivamente alla piattaforma di apprendimento, raccomandiamo di avere familiarità con questi strumenti.
+
+**Se vuoi aiutarci a migliorare il nostro codebase, ecco [come impostare freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/it/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..81da7139
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: La guida ufficiale dei Leader di lingua di freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Questa guida ti aiuterà a configurare e utilizzare gli strumenti per la localizzazione dei contenuti nella tua lingua.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+La maggior parte dei tuoi inviti sarà per il livello "Contributor". Questo livello consente all'utente di creare bozze. Seleziona questo ruolo quando inviti un nuovo traduttore.
+
+Il livello "Author" consente all'utente di creare bozze e pubblicarle.
+
+Il livello "Editor" consente all'utente di accedere a tutte le bozze e pubblicarle. Seleziona questo ruolo quando inviti un nuovo revisore (proofreader).
+
+Il livello "Administrator" è riservato allo staff di freeCodeCamp e ai leader di lingua.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+Usiamo un approccio basato su [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack) per il build e il deployment degli articoli. Questa strategia rende un rapido sito statico memorizzato nella cache e servito da un CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) costituisce la nostra piattaforma di gestione dei contenuti e [11ty](https://11ty.dev) si occupa del build degli articoli in risorse statiche – semplice HTML, JavaScript e CSS. Solo queste risorse statiche sono distribuite sui nostri server.
+
+Questo processo è automatizzato e viene eseguito periodicamente. Se pubblichi qualcosa ora, sarà disponibile sul sito di notizie in poche ore.
+
+Qui puoi trovare gli orari di build aggiornati e lo stato: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+`link` è il link all'articolo originale.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+:::tip
+Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+:::
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Assicurati di abbinare correttamente il titolo e il link.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Ogni titolo deve rimanere su una sola riga e non andare sulla successiva.
+
+Dovrai [fare il build in locale del client tradotto](how-to-enable-new-languages) per vedere se i titoli hanno la giusta lunghezza. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articoli che possono essere tradotti:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+I seguenti articoli **non** dovrebbero essere tradotti:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+I seguenti link puntano a siti esterni e non possono essere tradotti:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Una volta che hai tradotto e pubblicato gli articoli elencati come "possono essere tradotti", puoi aggiornare i link a piè di pagina per `/news` modificando il file `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` nel repository [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+> [!NOTE] Le pull request a questo repository sono attualmente limitate allo staff. Se vuoi aggiornare questo file, chiedi aiuto a qualcuno del team dello staff.
+
+Aggiorna la seguente parte nel file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+Una volta che hai tradotto e pubblicato gli articoli elencati come "possono essere tradotti", così come quando il curriculum è pronto per il rilascio nella tua lingua, puoi aggiornare i link a piè di pagina per `/learn` modificando il file `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` nel repository [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!WARNING] Solo "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", e "Code of Conduct" possono essere tradotti. Lascia gli altri URL invariati.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+Puoi trovare questi riquadri in tutta la documentazione:
+
+> [!NOTE] Sono una nota
+
+:::tip
+Sono un suggerimento
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] Sono un avvertimento
+
+:::danger
+Sono un avviso per richiamare la tua attenzione
+:::
+
+Di default, le loro intestazioni appaiono in inglese anche nella documentazione tradotta.
+
+Puoi avere le intestazioni tradotte nella documentazione nella tua lingua cambiando il file `docs/index.html`, in questo modo:
+
+All'interno dell'elemento `script` c'è un oggetto, trova la proprietà `flexibleAlerts`, che ha questa struttura:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+All'interno dell'oggetto della proprietà label, prima della proprietà `'/'`, dovrai aggiungere una nuova proprietà per la tua lingua, come `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+Ad esempio, per aggiungere le traduzioni in portoghese:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+Le citazioni motivazionali possono essere trovate nel [repository del curriculum](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) nel file `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json`.
+
+Il file ha questa struttura generale:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+I complimenti sono brevi frasi che appaiono al termine di una sfida.
+
+Non è necessario tradurre direttamente le frasi usate in inglese, è possibile scrivere una serie di frasi corte che sono appropriate per essere mostrate al completamento di una sfida.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Dovresti iniziare almeno con una dozzina di complimenti per avere un po' di varietà quando gli utenti completano le sfide.
+:::
+
+Le citazioni motivazionali sono le frasi che appaiono su https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+`motivationalQuotes` è un array di oggetti, i quali includono una proprietà `quote` e una proprietà `author`. Come questo:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Dovresti iniziare con almeno una dozzina di citazioni, per avere un po' di varietà. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+:::
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+Gestiamo un file di link comuni usati in tutto il [curriculum](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) nel file `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json`.
+
+Alcuni di questi link non cambieranno - ma dovresti aggiornare gli articoli in `/news` per rimandare alla versione tradotta nella tua lingua di un articolo, una volta pubblicato.
+
+Dovresti anche aggiornare le categorie `help` in modo che rimandino nel subforum nella tua lingua (di solito `language/category`, come `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). Questo permetterà agli utenti di freeCodeCamp di creare delle "richieste di aiuto" nella posizione corretta del forum.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+I meta-dati del sito si trovano nel file `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json`. Questo file ha cinque chiavi: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords` e `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+Il valore `youre-unsubscribed` dovrebbe essere tradotto direttamente. Gli altri valori dovranno essere tradotti nel miglior modo possibile, tenendo conto anche dei termini e delle frasi di ricerca comunemente utilizzati nella tua lingua.
+
+Se hai bisogno di aiuto, contattaci nella chat per i [contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Effettuare il Pre-Translate su Crowdin
+
+La funzionalità Pre-Translate può essere usata per applicare le traduzioni da Translation Memory alle stringhe.
+
+:::tip
+È molto utile per ripristinare le traduzioni da Translation Memory in blocco quando sono stati aggiornati molti file.
+:::
+
+Puoi trovare il Pre-Translate nella parte superiore della pagina nella console di un progetto. Se vedi "Go to console" nell'angolo in alto a destra, clicca prima lì.
+
+
+
+
+
+Puoi scegliere "From Machine Translation" o "From Translation Memory". Scegli "Translation Memory" per recuperare le traduzioni dalla memoria.
+
+Poi ci sono tre passaggi da completare:
+
+1. Files. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Languages. Imposta qui la tua lingua.
+3. Existing Translations. La migliore combinazione è "100% match" e "Apply to untranslated strings only". Non approvare automaticamente, in quanto è sempre meglio che ci sia una persona a effettuare la revisione.
+
+
+
+Quando hai finito con le impostazioni, premi il pulsante Pre-Translate e attendi. Ti avviserà al termine. Può richiedere più o meno tempo a seconda di quante stringhe non tradotte sono presenti nei file scelti.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+:::tip
+An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+:::
+
+Puoi trovare il glossario di Crowdin nel repository [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries).
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+Il file `client.csv` è per il progetto Learn User Interface, il file `curriculum.csv` è per il progetto Coding Curriculum, il file `docs.csv` è per il progetto Contributing Documentation.
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+Nel file `.csv` troverai che la lingua inglese occupa le prime tre colonne, `Term:English` è la colonna per i termini inglesi, `Description:English` è la colonna per le descrizioni inglesi, `Part:English` è la parte del discorso (sostantivo, verbo, ecc.).
+
+Poi, ogni lingua ha due colonne. Se traduci in Dothraki, sarai interessato alle colonne `Term:Dothraki` e `Description:Dothraki`. La colonna `Term:Dothraki` è per la traduzione dei termini dothraki e la colonna `Description:Dothraki` è per la descrizione dei termini dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+:::
+
+Dopo aver apportato le modifiche e salvato il file, dovrai effettuare una PR con le modifiche proposte. Una volta che la PR è stata accettata, dovrai eseguire le procedure GitHub Action per aggiornare il glossario. I cambiamenti apportati al glossario non saranno immediati.
+
+## Come Promuovere un Contributore a Revisore
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+Aprirà gli strumenti di gestione degli utenti e sarai in grado di vedere la lista di tutti gli utenti.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Utilizzare il menu a tre punti nella riga dell'utente per aprire un menu e selezionare "Add to team". I team di revisori hanno il nome standard di `Proof Readers (<language>)`, puoi cercare il team usando il nome della lingua. Una volta selezionato il team, utilizza il pulsante "ADD" in fondo alla pagina per finalizzare il processo.
+
+L'utente ora è un revisore.
+
+:::tip
+I revisori appena promossi possono trarre vantaggio dalla lettura della documentazione [Come revisionare le traduzioni](how-to-proofread-files).
+:::
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/it/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5ab31ae3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+---
+title: Il manuale ufficiale del moderatore di freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Questo manuale ti aiuterà a moderare diversi luoghi nella nostra comunità. Questo comprende le conversazioni e le interazioni nei thread delle issue e delle pull request su GitHub, nel forum della community, nelle chat room e nelle altre comunità ufficiali che ospitiamo.
+
+> [!NOTE] Tutti i moderatori di freeCodeCamp sono moderatori di tutta la comunità. Cioè confidiamo che tu supervisioni uno di questi posti.
+
+Puoi fare da moderatore su qualunque piattorma ti interessi di più. Alcuni moderatori aiutano solo su GitHub, mentre altri aiutano solo sul forum. Alcuni sono attivi ovunque.
+
+L'idea di fondo è che vogliamo che ti diverta ad essere un moderatore, e che tu investa il tuo poco tempo in luoghi che sono di tuo interesse.
+
+> "Da grandi poteri derivano grandi responsabilità." - Zio Ben
+
+Come moderatore, il carattere è più importante dell'abilità tecnica.
+
+Ascolta. Sii utile. Non abusare del tuo potere.
+
+freeCodeCamp è una comunità inclusiva ed è necessario lasciarla così.
+
+Abbiamo un singolo [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) per gestire tutta la nostra comunità. Meno sono le regole, più facile sarà ricordarle. Puoi leggere queste regole e impegnarti a ricordarle [qui](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+> [!NOTE] As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## Moderare GitHub
+
+I moderatori hanno due responsabilità principali su GitHub:
+
+1. Fare lo smistamento e rispondere alle issue.
+2. Verificare e fare il merge delle pull request (cioè controllo qualità).
+
+### Moderare gli issue di Github
+
+Usiamo il repository principale [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) per tenere traccia delle issue su tutti i nostri repository. Riceviamo nuove issue ogni giorno e per tutte occorre fare lo smistamento, assegnare un'etichetta e indirizzarle. Questo è anche un ottimo posto per iniziare ad aiutare contribuendo al codice open source.
+
+#### Smistamento delle issue
+
+[Lo smistamento (triage)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) è un processo in cui si decide con quale priorità rivolgere l'attenzione ad ogni nuovo problema riportato. Abbiamo una lunga lista di etichette che usiamo per contrassegnare priorità, categoria, status e scopo di ogni issue.
+
+Puoi aiutarci ad organizzare e fare lo smistamento delle issue riportate applicando etichette da [questa lista](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels). Solitamente, è disponibile una descrizione accanto all'etichetta che ne spiega il significato.
+
+Per favore, fai particolare attenzione alle etichette `"help wanted"` e `"first timers only"`. Queste devono essere aggiunte ai thread che pensi possano essere aperti a potenziali contributori per creare una pull request.
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### Chiudere issues e pull request stantii, obsoleti e inattivi
+
+- Le issue e le pull request stantie sono quelli che non hanno visto alcuna attività dall'autore per 21 giorni (3 settimane dall'ultima attività), ma solo dopo che un moderatore ha richiesto più informazioni/modifiche.
+
+- L'attività è definita come: Commenti che richiedono un aggiornamento sulla PR e sullo smistamento come l'etichetta `status: update needed` etc.
+
+- Se il contributore chiede ulteriore assistenza o anche del tempo, quanto sopra può essere rilassato e rivisitato dopo che è stata data una risposta. In ogni caso, i moderatori dovrebbero usare il loro buon senso per prendere una decisione sullo status in sospeso della PR.
+
+:::tip
+We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+:::
+
+### Moderare le pull request
+
+Le pull request (PR) sono il modo in cui i contributori sottopongono cambiamenti al repository di freeCodeCamp. Dobbiamo eseguire il Controllo Qualità sulle pull request prima di decidere se fare il merge, richiedere delle modifiche o chiuderle.
+
+#### Tipi di Pull Request
+
+1. **Modifiche alle istruzioni delle sfide**
+
+ Queste sono le modifiche ai testi delle sfide - la descrizione, le istruzioni o il testo dei test.
+
+ Puoi anche farne la revisione direttamente su GitHub e decidere se fare il merge. Dobbiamo fare un po' attenzione su questo perché milioni di persone incontreranno questo testo lavorando sul curriculum di freeCodeCamp. La pull request rende il testo più chiaro senza allungarlo troppo? Le modifiche sono rilevanti e non troppo pedanti? Ricorda che il nostro obbiettivo è che le sfide siano più chiare e più corte possibile. Non sono il luogo per dettagli incomprensibili. I contributori possono provare ad aggiungere link e risorse alle sfide.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Se la modifica va bene, assicurati di lasciare un'approvazione con un commento "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me). Una volta che una pull request riceve almeno due approvazioni (inclusa la tua) dai moderatori o dal dev-team, puoi procedere e farne il merge.
+
+2. **Modifiche al codice delle sfide**
+
+ Queste sono modifiche al codice in una sfida - il seed della sfida, la soluzione della sfida e le stringhe di test.
+
+ Queste pull request devono essere scaricate (pull) da GitHub e testate nel tuo computer locale o su Gitpod per assicurarti che i test della sfida possano essere superati con la soluzione corrente, e il nuovo codice non introduca errori.
+
+ Alcuni contributori potrebbero provare ad aggiungere test addizionali per coprire casi limite pedanti. Dobbiamo fare attenzione a non rendere le sfide troppo complicate. Queste sfide e i loro test dovrebbero essere più semplici e intuitivi possibile. Ad eccezione delle sfide sugli algoritmi e della sezione di preparazione al colloquio di lavoro, gli studenti dovrebbero essere in grado di risolvere ogni sfida entro due minuti.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. Una volta che una pull request ha ricevuto almeno due approvazioni (inclusa la tua) dai moderatori o dal dev-team, puoi procedere e farne il merge.
+
+3. **Modifiche alla piattaforma**
+
+ Queste modifiche al codice cambiano la funzionalità della piattaforma freeCodeCamp stessa.
+
+ A volte i contributori cercano di apportare cambiamenti senza troppe spiegazioni, ma per le modifiche al codice, dobbiamo essere sicuri che ci sia un'autentica necessità di cambiamento. Queste pull request dovrebbero fare riferimento a un'issue esistente su GitHub dove vengono discusse le ragioni della modifica. Quindi puoi aprire la pull request sul tuo computer e testarla localmente.
+
+ Dopo averlo fatto, se le modifiche funzionano, non farne ancora il merge. Puoi commentare le pull request scrivendo "LGTM", quindi menzionando **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** in modo che possano dare un'occhiata finale.
+
+4. **PR automatizzate (Dependabot)**
+
+ Alcune PR sono aggiornamenti di dipendenze automatizzati fatti attraverso un'integrazione. Non dovresti fare il merge o approvare queste PR. Uno dei membri del dev-team si prenderà carico di rivedere queste PR automatizzate e di farne il merge.
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+Prima di tutto, quando scegli una pull request da rivedere, dovresti assegnarla a te stesso. Puoi farlo facendo clic sul collegamento "assign yourself" sotto la parte "assegnatari" nella colonna di destra dell'interfaccia di GitHub.
+
+A seconda del tipo di pull request, segui le regole corrispondenti elencate in precedenza.
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+Prima di fare il merge di qualsiasi pull request, assicurati che GitHub contrassegni come superati tutti i controlli da fare (segni di spunta verdi) sulle pull request. Se noti che uno dei controlli non va a buon fine, indaga e chiarisci la causa principale. La modifica che viene apportata blocca i nostri test? Il sito verrà creato correttamente se la PR sarà unita? Questi controlli sono fondamentali per la stabilità della piattaforma.
+
+> [!WARNING] L'unione di una PR che non supera i controlli CI/CD può causare difficoltà a tutte le parti interessate, incluso il team di sviluppo e i contributori.
+
+##### Gestire i conflitti di merge:
+
+A volte ci sarà un conflitto di merge.
+
+Ciò significa che un'altra pull request ha apportato una modifica alla stessa parte di quello stesso file. GitHub ha uno strumento per affrontare questi conflitti di unione direttamente su GitHub. Puoi provare ad affrontare questi conflitti. Giudica al meglio.
+
+Le modifiche della pull request saranno in alto e le modifiche del ramo main saranno in basso. A volte ci saranno informazioni ridondanti che possono essere cancellate. Prima di finire, assicura di cancellare i simboli `<<<<<<`, `======`, e `>>>>>>` che Git aggiunge per indicare le aree in conflitto.
+
+Se non sei sicuro, chiedi assistenza a uno degli altri moderatori o al team di sviluppo.
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+Se la pull request sembra pronta per il merge (e non richiede ulteriori approvazioni, ricorda che ne servono almeno due), puoi procedere e unirla. Assicurati di utilizzare l'opzione predefinita **"Squash and Merge"**. Questo ridurrà tutti i commit della pull request a un singolo commit, rendendo la cronologia di Git molto più facile da leggere.
+
+> Dovresti quindi commentare la pull request, ringraziando il contributore in modo personale!
+
+Se l'autore della pull request è un "contributore per la prima volta" dovresti anche congratularti con lui per la sua prima pull request unita al repository. Puoi guardare nell'angolo in alto a destra nel corpo della PR per determinare chi ha contribuito per la prima volta. Mostrerà `First-time contributor` come nella figura:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Badge first-time contributor sulle pull request (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="Badge first time contributor sulle pull request" />
+</details>
+
+Se la pull request non sembra pronta per il merge, puoi rispondere educatamente dicendo all'autore cosa dovrebbe fare per prepararla. Si spera che rispondano e che la loro pull request sia più vicina ad essere pronta.
+
+Se hai bisogno di una seconda opinione su una pull request, vai avanti e lascia i tuoi commenti sulla pull request, quindi aggiungi l'etichetta "discussing".
+
+##### Chiudere una pull request invalida:
+
+Spesso una pull request avrà richiesto uno sforzo minimo. Puoi capirlo immediatamente quando il contributore non si è preoccupato di selezionare le caselle di spunta nel template per le Pull Request o ha utilizzato un titolo generico per la Pull Request come "made changes" o "Update index.md".
+
+Ci sono anche situazioni in cui il contributore sta cercando di aggiungere un collegamento al proprio sito Web, includere una libreria che ha creato o apportare una modifica frivola che non aiuta nessuno tranne se stesso.
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## Moderazione del Forum
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Eliminare dei post del forum
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. Qualcuno ha postato immagini pornografiche o graficamente violente.
+2. Qualcuno ha postato un link o del codice di natura malevola e che potrebbe danneggiare altri camper che ci cliccano sopra.
+3. Qualcuno ha inondato un thread con un sacco di spam.
+4. Un account è stato creato, oltre ogni ragionevole dubbio, per spammare.
+
+### Affrontare lo spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Affrontare conversazioni off-topic
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Affrontare le soluzioni postate
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Utenti Minorenni
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+OGGETTO: Gli utenti al di sotto dei 13 anni di età non possono utilizzare il forum per i nostri Termini di Servizio.
+
+Ci è stato fatto notare che hai un età inferiore ai 13 anni. Secondo i [termini di servizio di freeCodeCamp](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), devi avere almeno 13 anni per utilizzare il sito o il forum. Elimineremo sia il tuo account freeCodeCamp che il tuo account del forum. Questa restrizione ci mantiene in conformità con le leggi degli Stati Uniti.
+
+Per favore, iscriviti nuovamente una volta compiuti 13 anni di età.
+
+Grazie per la comprensione.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- Quando provi a includere una "risposta pronta" in una risposta, se il menu non si apre (dopo aver cliccato sull'ingranaggio), clicca sull'area del testo e poi riprova.
+- La 'chiave inglese' del moderatore è nella parte inferiore del viewport ma se ci clicchi su e non riesci a vedere il pulsante "Select Posts" perché è fuori dal campo visivo, potresti aver di scorrere le opzioni, ma a volte ciò non funziona e in tal caso potrebbe essere necessario spostarsi su un monitor fisso o di un portatile.
+- A volte cliccare sul menu con tre puntini sotto un post può nascondere l'icona reply. Ricarica la pagina per recuperarla.
+
+## Moderazione di Facebook
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderare Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot agisce come bot di moderazione e tutti i comandi utilizzano l'interfaccia di comando di Discord con la barra obliqua (slash). Puoi vedere la lista dei comandi digitando `/` in qualsiasi canale.
+
+1. **Assicurati che l'utente abbia violato intenzionalmente il [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Non tutte le violazioni del [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) sono intenzionali. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. In questi casi puoi chiedergli di incollare il codice tramite servizi come CodePen o Pastebin.
+
+2. **Se un utente viola chiaramente e intenzionalmente il [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), il moderatore procederà come segue:**
+
+ Per violazioni minori, può essere emesso un avviso con il comando `/warn`. Per violazioni più importanti, puoi rimuovere un membro dal server temporaneamente con il comando `/kick`, o permanentemente con il comando `/ban`. In alcuni casi, un membro potrebbe aver solo bisogno di tempo per calmarsi e riflettere - il comando `/mute` ti permette di impedirgli di dialogare con la community per un determinato periodo. Un membro su cui è stato usato il comando mute può vedere le conversazioni, ma non può pubblicare messaggi o aggiungere reazioni.
+
+ Tutti i comandi di moderazione richiederanno un parametro `reason`, che dovrebbe essere una breve spiegazione del perché l'azione è stata intrapresa. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. Dovremmo evitare di utilizzare gli strumenti di moderazione integrati di Discord, in quanto non saranno registrati.
+
+ > [!WARNING] La ragione fornita al comando di moderazione sarà anche inclusa nel messaggio di notifica all'utente. Per favore, ricorda di essere professionale.
+
+3. **Creare una discussione privata**
+
+ Potrebbero esserci situazioni in cui hai bisogno di rivolgerti a un camper in privato. Questo non dovrebbe essere fatto tramite messaggi diretti, che possono portare a situazioni in cui tu sostieni una cosa e il camper ne sostiene un'altra. Invece, usa la funzione del bot per creare una discussione privata:
+
+ - Chiama il comando `/private`, dove `target` è l'utente con cui vuoi aprire un canale privato.
+ - Il bot creerà un nuovo canale, e vi aggiungerà l'utente menzionato e tutti i moderatori con il ruolo `Your Friendly Moderator`. Anche se vengono aggiunti al canale tutti i moderatori per trasparenza, il moderatore che ha chiamato il comando dovrebbe essere l'unico ad interagire con l'utente a meno che non abbia bisogno di assistenza.
+ - Quando la conversazione è conclusa, clicca il pulsante `❌ Close` _sul primo messaggio nel canale privato_ per fare in modo che il bot chiuda e cancelli il canale.
+
+4. **Cancellare i messaggi**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. Se un messaggio non è in linea con il nostro Codice di Condotta o non appropriato per la nostra comunità, in genere puoi eliminarlo con certezza.
+
+ Nota che se il messaggio contiene contenuti che violano i termini di servizio di Discord, dovrai segnalarlo tramite https://dis.gd/report **prima** di eliminarlo.
+
+5. **Non minacciare di prendere provvedimenti**
+
+ Se un utente infrange il [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), non minacciarlo di intraprendere un'azione da moderatore e non avvertirlo mai in pubblico. Invece, parlagli privatamente usando il comando `/private` del bot o usa i comandi di moderazione del bot.
+
+ Se una violazione era chiaramente involontaria e non richiede una sospensione o una conversazione privata, rendi l'utente consapevole delle sue azioni senza farlo sembrare un ammonimento.
+
+ Per esempio:
+
+ - Un utente posta un muro di testo per chiedere aiuto:
+
+ Moderatore: **@username** Per favore usa CodePen o Pastebin quando posti una grande quantità di codice.
+
+ - O se devi proprio spiegare il perché:
+
+ Moderatore: **@username** Per favore usa CodePen o Pastebin quando riporti grandi quantità di codice, perché disturba la chat per tutti e può essere considerato spam secondo il nostro [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - Per violazioni minori e non intenzionali del [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderatore: Questo è un promemoria amichevole per invitare tutti a seguire il [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Non vantarti di essere un moderatore**
+
+ Non vederti come se fossi al di sopra della comunità. **Fai parte della community.**E la community si è affidata a te per proteggere qualcosa di raro che tutti condividiamo: un luogo _accogliente_ per i nuovi sviluppatori.
+
+ Se ti vanti di essere un moderatore, le persone potrebbero sentirsi a disagio intorno a te, nello stesso modo in cui si sentono a disagio accanto a un agente di polizia, anche quando non hanno fatto niente di male. Questa è semplicemente la natura umana.
+
+7. **Non contraddire gli altri moderatori**
+
+ Se sei in disaccordo con l'azione di un moderatore, parla con loro in privato o faglielo presente nel canale #mod-chat. Non scavalcare mai l'azione di un moderatore e non contraddire mai gli altri moderatori pubblicamente. Invece, discuti a mente fredda su `#mod-chat` e convinci il moderatore che egli stesso dovrebbe annullare il ban o cambiare il proprio punto di vista.
+
+ _Ricorda: siamo tutti nella stessa squadra. Vogliamo dare dignità al ruolo dei moderatori ed essere un fronte unito._
+
+8. **Parla con gli altri moderatori**
+
+ Abbiamo una stanza `#mod-chat` solo per i moderatori. Usala! Se ti senti a disagio nel gestire una determinata situazione, chiedi aiuto ad altri moderatori. Se pensi che qualcosa dovrebbe essere discusso, fallo. Fai parte di una squadra, e noi apprezziamo il contributo di ogni membro! Anche se sei totalmente in disaccordo con qualcosa presente in queste linee guida o nel [Codice di Condotta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Inattività temporanea**
+
+ Se non sarai attivo come Moderatore per un po' a causa di vacanze, malattia o qualsiasi altro motivo, assicurati di farlo sapere agli altri nel canale `#mod-chat`. In questo modo sapremo se possiamo contare sul fatto che sei regolarmente attivo sul server oppure no.
+
+## Come diventare un moderatore
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+> [!NOTE] Per GitHub: Dopo essere stato accettato come moderatore, riceverai l'invito a un repository Github. Dovrai andare all'[invito all'Organizzazione GitHub di freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) per essere in grado di accettare l'invito.
+>
+> Questo è necessario per consentirci di darti i permessi di scrittura su alcuni dei nostri repository.
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- All'utente viene garantita privacy.
+- La chat pubblica non è più interrotta.
+- Altri membri del team possono contribuire, nel caso tu sia a disagio nell'affrontare la situazione da solo.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/it/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9be367cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: La guida di onboarding ufficiale del moderatore di freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se non hai ancora letto [Il manuale del moderatore](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/i18n/italian/moderator-handbook) dovresti iniziare da lì.
+
+## Il Forum
+
+### Primi Passi
+
+La prima cosa che puoi notare dopo aver ricevuto lo status di moderatore sul forum è che la tua interfaccia sarà un po' diversa, con nuovi strumenti da admin per esplorare e accedere al subforum Mod-Team.
+
+Alcuni dei nuovi strumenti appariranno all'interno di una nuova voce di menu che assomiglia a una chiave inglese. Alcuni appariranno come nuove schede o pulsanti, o anche nuove opzioni abilitate nei menu del forum.
+
+Per acquisire familiarità con i nuovi strumenti e poteri, puoi combinare uno o più dei seguenti metodi durante la prima settimana con questo ruolo elevato:
+
+:::tip
+I primi due sono i più importanti.
+:::
+
+### Acquisisci familiarità con gli strumenti admin di Discourse
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. Per iniziare a prendere confidenza con il ruolo di moderatore di Discourse, inizia a leggere la [guida per i nuovi utenti](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) di Discourse e la[guida per i nuovi moderatori](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116) di Discourse.
+
+### Seguire un moderatore
+
+Tutte le azioni da moderatore possono essere seguite rivedendo gli [action log](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. I post da revisionare appariranno nell'area [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) del forum.
+
+Per la prima settimana o giù di lì, presta attenzione a ciò che viene contrassegnato e ciò che è in fase di revisione, e confrontalo con le azioni intraprese sui post contrassegnati. Potresti vedere l'account di sistema contrassegnare un post perché l'utente lo ha creato troppo rapidamente. In molti casi, i moderatori cancelleranno il flag del post cliccando sul pulsante "Approve Post" o contrassegnandolo come "Not Spam" (a seconda del tipo di flag).
+
+Comunemente, i flag di spam possono anche essere usati da membri o moderatori. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+Puoi notare moderatori che eseguono una procedura chiamata 'split topic'. Questo può essere un caso in cui un moderatore ha smistato un post che è stato fatto erroneamente su un argomento esistente in un nuovo argomento, o un moderatore ha unito argomenti duplicati che un singolo utente ha creato per la stessa domanda. Guardare questa procedura metterà in evidenza le diverse azioni e le loro cause.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. Questi comprendono:
+
+- Accogliere un nuovo membro del forum che ha postato del codice senza una domanda -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Ricordare ai membri di non postare il codice delle soluzioni ma di fornire indizi e suggerimenti -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Rispondere a una situazione in cui il codice di qualcuno funziona per te ma non per lui -> "Browser Issues"
+- Incoraggiare i membri ad aprire una issue su GitHub quando viene trovato un possibile bug -> "Bug Report"
+
+Ce ne sono altre, che puoi leggere per acquisire familiarità con i rispettivi utilizzi. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Leggere i post del subforum Mod-Team
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Dove chiedere aiuto
+
+Per ottenere aiuto con delle situazioni con cui non ti senti a tuo agio o che non sei sicuro di come gestire, discuti con i tuoi compagni moderatori nel [Subforum Mod-Team](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) o nella [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) su Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/it/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/it/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bd350992
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Report responsabile - Hall of Fame
+---
+
+Apprezziamo qualsiasi notifica responsabile di vulnerabilità che possa impattare l'integrità delle nostre piattaforme e i nostri utenti. Se sei interessato a contribuire alla sicurezza della nostra piattaforma, leggi la nostra [politica di sicurezza descritta qui](security).
+
+Anche se al momento non offriamo ricomplete, siamo grati a queste fantastiche persone che ci aiutano a mantenere la piattaforma al sicuro per tutti:
+
+- Mehul Mohan da [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Vulnerability Fix](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) lavorando con IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/security.md b/src/content/docs/it/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..54473f6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Politica di sicurezza di freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Questo documento delinea la nostra politica di sicurezza per i codebase, le piattaforme su cui operiamo e come riportare delle vulnerabilità.
+
+## Segnalare una vulnerabilità
+
+> [!NOTE] Se pensi di aver trovato una vulnerabilità, **per favore riportala responsabilmente**. Non creare una issue su GitHub per problemi di sicurezza. Invece, segui questa guida.
+
+### Linee guida
+
+Apprezziamo la notifica responsabile di vulnerabilità che possa impattare l'integrità delle nostre piattaforme e i nostri utenti. Nell'interesse di risparmiare il tempo di tutti, ti incoraggiamo a riportare vulnerabilità tenendo i seguenti punti a mente:
+
+1. Assicurati di star usando l'**ultima** versione **aggiornata** e **stabile** del tuo sistema operativo e del browser web che sono disponibili sulla tua macchina.
+2. Consideriamo l'ultilizzo di strumenti e utility online per riportare problemi con le configurazioni SPF & DKIM, o test SSL Server, nella categoria ["beg bounties"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) e non siamo in grado di rispondere a questi report.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Segnalare
+
+Dopo aver confermato le linee guida di qui sopra, sentiti libero di mandare una mail a `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. Puoi anche mandare un messaggio crittografato PGP a `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Una volta che riporti una vulnerabilità, la investigheremo e ci assicureremo che non sia un falso positivo. Se abbiamo bisogno di chiarimenti e dettagli, ti ricontatteremo. Puoi fare segnalazioni separate per ogni problema che trovi. Per favore nota che non saremo in grado di rispondere a qualsiasi problema che pensiamo sia al di fuori delle linee guida.
+
+## Platforms and Codebases
+
+Ecco una lista delle piattaforme e codebase per cui accettiamo segnalazioni:
+
+### Piattaforma di apprendimento
+
+| Versione | Branch | Supportata | Website attivo |
+| ---------- | -------------- | ---------- | ------------------------ |
+| production | `prod-current` | Sì | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| staging | `prod-staging` | Sì | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| sviluppo | `main` | No | |
+
+### Piattaforma di pubblicazione
+
+| Versione | Supportata | Website attivo |
+| ----------- | ---------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| production | Sì | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localizzata | Sì | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### App mobile
+
+| Versione | Supportata | Website attivo |
+| ---------- | ---------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| production | Sì | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Altre Piattaforme
+
+Oltre queste, accettiamo report per repository ospitate su GitHub sotto l'organizzazione freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Altre Applicazioni self-hosted
+
+Facciamo l'host noi stessi di alcune delle nostre piattaforme usando software open-source come Ghost & Discourse. Se stai riportando una vulnerabilità per favore assicurati che non sia un bug nel software a monte.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/it/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3cf8ea62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+Sviluppiamo regolarmente sui sistemi operativi più nuovi o più popolari come macOS 10.15 o successivi, Ubuntu 18.04 e Windows 10 (con WSL2).
+
+Ti raccomandiamo di fare ricerche sui tuoi problemi specifici usando risorse come Google, Stack Overflow e Stack Exchange. C'è una buona probabilità che qualcuno abbia incontrato lo stesso problema e ci sia già una risposta alla tua domanda specifica.
+
+Se sei su un sistema operativo diverso o continui ad avere dei problemi, visita [ottenere aiuto](#ottenere-aiuto).
+
+:::caution
+Per favore, evita di creare issue su GitHub per problemi con i prerequisiti. Sono al di fuori dell'ambito di questo progetto.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. Se uno di loro non è memorizzato nella cache, esegui quanto segue:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+O
+
+Usa la scorciatoia
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Usa `git clean` in modalità interattiva:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Come pulire i file git non tracciati (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="Come pulire i file git non tracciati" />
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+Durante lo sviluppo, la sessione viene memorizzata come cookie. Cancellarli ti farà uscire dal tuo account di sviluppo.
+
+Ti disconnetterai anche eseguendo `pnpm run seed:certified-user`. Sovrascriverà l'utente di sviluppo nel database locale.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+Quando provi a navigare su http://localhost:8000/developmentuser per visualizzare la pagina del profilo, Gatsby prende in consegna le pagine lato client, quindi otterrai una pagina 404 per il profilo utente quando lavori.
+
+C'è un pulsante "Preview Custom 404 Page", cliccalo per vedere il profilo.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+Se incontri degli errori durante l'installazione delle dipendenze, assicurati di non essere in una rete ristretta o che le impostazioni del tuo firewall non ti impediscano di accedere alle risorse.
+
+La prima configurazione può richiedere un po' di tempo a seconda della larghezza di banda della rete. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se stai usando un dispositivo Apple con Chip M1 per eseguire l'applicazione in locale, suggeriamo di usare Node v14.7 o superiore. Altrimenti potresti avere problemi con dipendenze come Sharp.
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+Se sei bloccato e hai bisogno di aiuto, poni liberamente le tue domande nella [categoria 'Contributors' sul nostro forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) o [nella chat room per i contributori](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Potrebbe esserci un errore nella console del browser o in Bash / Terminale / Linea di comando che ti aiuterà a identificare il problema. Fornisci questo messaggio di errore nella descrizione del problema in modo che gli altri possano identificarlo più facilmente e aiutarti a risolverlo.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/it/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/it/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bf11980e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/it/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Come funziona il flusso di lavoro con i token utente
+---
+
+I token utente sono utilizzati per identificare gli utenti con terze parti in modo tale che le sfide completate usando tali servizi possano essere salvate nell'account dell'utente.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+Al momento, i token sono utilizzati solo per completare le sfide della certificazione Database Relazionale. Un token viene creato quando un utente loggato clicca sui pulsanti "Clicca qui per iniziare il corso" o "Clicca qui per iniziare il progetto" per iniziare uno dei corsi o progetti della certificazione Database Relazionali.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+Un token utente viene cancellato quando un utente fa log out da freeCodeCamp, resetta i propri progressi, cancella il proprio account, o cancella manualmente il token usando il widget nella pagina delle impostazioni.
+
+## How they Work
+
+I token sono memorizzati in una raccolta `UserToken` nel database. Ogni record ha un `_id` unico, che è il token, e un `user_id` che collega all'account dell'utente dalla collezione `user`. Il token è codificato usando JWT e inviato al client quando viene creato. Questo token codificato viene quindi dato a servizi di terze parti che ne hanno bisogno e inviato alla nostra API da loro quando una sfida è completata. Quando la nostra API lo riceve, è decodificato in modo da poter identificare l'utente che presenta una sfida e salvare la sfida completata nella lista delle sfide completate `completedChallenges` dell'utente.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/jp/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a33bb9ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Authors Analytics Manual
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Search by Language
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+
+
+1. From the top dropdown menu, select `News`.
+1. From the sidebar, click on `Reports`.
+1. From the secondary sidebar, select `Engagement`.
+1. Click on `Pages and Screens`.
+1. In the search bar, type the subpath for the desired language.
+1. From the dropdown under the search bar, choose `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filter Reports by Author
+
+After arriving at the `Pages and Screens` reports mentioned above, use the following steps to filter the results by specific authors.
+
+
+
+1. Click on the `Add filter` button.
+1. From the side navigation include `Author`.
+1. From the `Dimensions values` dropdown, choose an author's name.
+1. Click on the `Apply` button to apply changes.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/jp/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2c334ee7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: コードベースのベストプラクティス
+---
+
+## Styling a component
+
+We recommend styling components using our [design style guide](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+The colors are defined in [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css), and the fonts are in [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+We are strongly opinionated about adding new variables/tokens to the colors. After careful research, the colors have been chosen to respect the freeCodeCamp brand identity, developer experience, and accessibility.
+
+The `!important` keyword may be used to override values in some cases (e.g. accessibility concerns). You should add a comment describing the issue, so it doesn't get removed in future refactoring.
+
+### RTL support
+
+We are striving to support right-to-left (RTL) layout in the codebase for languages that are read in this direction. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Here are some quick rules of thumb to follow:
+
+- Don't use `float` properties
+ - Use Flexbox and Grid layouts instead, as they have RTL support already built-in, and those will be easier to maintain and review.
+- Don't define the direction while using `margin` and `padding`: it may seem harmless to use `padding-right` and `margin-left`, but these directions aren't mirrored when the layout changes to RTL, and adding counter values for them in the RTL file makes maintaining the codebase harder.
+ - Use logical properties for them: You can add the same spacing by using `padding-inline-end` and `margin-inline-start`, and you won't need to worry about RTL layout, as they follow where the line starts and ends, and you won't need to add any extra values in the RTL files, so people won't need to remember to change the same values in two files.
+- Don't use `!important` in `font-family`: RTL layout uses different fonts compared to the LTR layout, when you add `!important` in the `font-family` property it affects the RTL layout too.
+
+## General JavaScript
+
+In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
+
+It is encouraged to use functional components over class-based components.
+
+## Specific TypeScript
+
+### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
+
+#### Git のファイル履歴を保持する
+
+Sometimes changing the file from `<filename>.js` to `<filename>.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
+
+The best bet at achieving this is to:
+
+1. ファイル名を変更する
+2. フラグ `--no-verify` でコミットして、Husky がリントエラーについて不平を言うことを防ぐ
+3. 別のコミットで、移行のために TypeScript にリファクタリングする
+
+> [!NOTE] VScode 等のエディターは、ファイルが削除され新しいファイルが作成されたことを表示する可能性があります。 `git add .` に CLI を使用すると、VSCode はファイル名が変更されたものとしてステージに表示します。
+
+### Naming Conventions
+
+#### インターフェースと型
+
+For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
+
+React Component Props - suffix with `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+React Stateful Components - suffix with `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Default - object name in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Action Definitions
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### How to Reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### How to Dispatch
+
+Within a component, import the actions and selectors needed.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [TypeScript Docs](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [TypeScript with React CheatSheet](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/jp/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a1a52f87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: VSCode 拡張機能「Courses」について
+---
+
+ここでは、[freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) リポジトリのメンテナンス方針について説明します。このリポジトリには、[freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses) 拡張機能のソースコードが含まれています。
+
+## 拡張機能を公開する
+
+新たな GitHub リリースが公開されると、自動的に GitHub Action が拡張機能を Visual Studio Marketplace へ公開します。
+
+1. 新しいバージョンの拡張機能をパッケージ化します。
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+`<tag_type>` は `major`, `minor`, `patch` のいずれかになります。
+
+2. `main` へ新しいバージョンをプッシュします。
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Optionally, you can push directly to `upstream/main`, but opening a new PR is recommended for a sanity check.
+
+3. Create a new GitHub Release using the GitHub UI:
+
+- Correctly increment the version number, when creating a new tag.
+- Upload the `.vsix` file with the release.
+- Publish the release, and confirm the action succeeded.
+
+> [!NOTE] Creating a release requires write access to the `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension` repository.
+
+## 拡張機能を手動で公開する
+
+A manual upload to the Visual Studio Marketplace can be achieved, by following these steps:
+
+1. Visit https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ and sign in
+2. Navigate to the [freeCodeCamp Publisher page](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Select the relevant extension, and select `Update`
+4. Upload the file from your local files
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cd1ec652
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: カリキュラムファイルの構造
+---
+
+名前が付けられた `curriculum` ディレクトリ内に、コア教育コンテンツがあります。 このページでは、それらのファイルがどのように整理されているのかを説明します。
+
+## 用語
+
+カリキュラム内容を説明する際に使用する用語がいくつかあります。
+
+- `certification`: この場合、ユーザーが求める実際の認定講座を意味します。 これは、スーパーブロック名とは別のものです。
+- `superBlock`: スーパーブロックは、チャレンジの最上位レベルのコレクションです。 Each superblock corresponds to a certification in the curriculum (e.g. Responsive Web Design).
+- `block`: ブロックは、スーパーブロック内のセクションです。 A block corresponds to a group of challenges in a given certification (e.g. Basic HTML and HTML5)
+- `challenge` : A challenge is a single lesson within the curriculum (e.g. Say Hello to HTML Elements)
+
+## ファイルツリー
+
+これらの用語を使用して、以下のようにファイル構造が定義されます。
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## `_meta` ディレクトリ
+
+`_meta` ディレクトリは、`.json` ファイルを含む特別なディレクトリです。 これらのファイルは、カリキュラム内の各ブロックに相当します。ブロックが属するスーパーブロックと、そのブロック内のチャレンジの順序を決めるために使用されます。
+
+## ファイル名を変更する
+
+認定講座、スーパーブロック名、ブロック名、もしくはチャレンジ名を変更する必要がある場合があります。 このセクションでは、ビルドエラーを避けるために必要な手順を概説します。
+
+:::danger
+カリキュラム構造内のファイル名を変更すると、メインの Web ページ上のコンテンツパス (または URL) が変更されることがあります。 変更ごとにリダイレクトを設定する必要があるため、注意して行ってください。
+:::
+
+### 認定講座名を変更する
+
+認定講座名を変更する際、関連付けられているスーパーブロック名も一緒に変更することも検討するでしょう。 以下は、認定講座名のみを変更するための手順です。
+
+1. `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` フォルダ名を変更します。
+1. フォルダの `meta.json` ファイル内で、`name`、`dashedName`、`challengeOrder` の値を新しい認定講座名に変更します。
+1. `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate` 内で、`{superBlock}-certificate` フォルダ名と、その中の YAML ファイル名を変更します。
+1. YAML ファイルの `title` 名を変更します。
+1. Rename the file and folder from step 3 for the rest of the curriculum languages.
+1. `client/src/redux/index.ts` を更新して、正しい `title` を使用してください。
+1. 必要に応じて、同じファイル内のスーパーブロックの `certSlug` を更新します。**注:** `certSlug` 名を変更すると、認定講座の URL が変更されるため、慎重に変更します。
+1. `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` 内の `title` を新しい値に更新してください。**注:** ここで `title` を変更すると、関連する認定講座のスーパーブロックのページ が **壊れます**。 そのページは、スーパーブロックのタイトルに依存しており、認定講座タイトルと一致します。 スーパーブロック名も同時に変更したい場合があるからです。
+1. 手順 7 で、`certSlug` 名を変更した場合は、認定講座とネストされた `projects` の値を変更します。
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. 手順 7 で `certSlug` を変更した場合、同じファイル内の `certSlugTypeMap` のキーを更新します。
+1. 必要に応じて、`client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx` の `legacyCerts` 配列内の認定講座名を更新します。
+1. メイン `README.md` ファイル名を新しい名前に更新します。
+
+### スーパーブロック名を変更する
+
+> [!NOTE] スーパーブロック名を変更すると、新しいフォルダ名がパスとして使用され、「正しい」フォルダ名とみなされます。 その変更を反映するために、その他のすべての値を更新する必要があります。
+
+Also, you will likely want to rename the certificate and the `{superBlock}-projects` block when you rename a superBlock since they all share a name. 以下は、スーパーブロック名のみを変更するための手順です。
+
+1. スーパーブロックのフォルダ名を `curriculum/challenges/english` ディレクトリに変更します。
+1. _他の_ すべての `curriculum/challenges/{language}` ディレクトリのスーパーブロックフォルダ名を変更します。
+1. スーパーブロック内の各ブロックについて、`meta.json` ファイル内の `superBlock` の値をその dashedName に更新します。 ここでは、フォルダ名を変更する必要はありません。 ブロック名変更時に、フォルダ名を変更します。
+1. `client/src/pages/learn` 内のスーパーブロックのフォルダ名を変更します。
+1. 上記フォルダの `index.md` ファイルを更新し、`title` と `superBlock` の値を新しい名前に変更します。
+1. 上記の各ブロックフォルダで、`index.md` を更新して、正しい `superBlock` の値を使用します。
+1. `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` ファイルで、ファイルの先頭にある認定講座パスと、スーパーブロックの `title` 値を更新します。**注:** ここで `title` を変更すると、スーパーブロックの実際の認定講座を表示する機能が **壊れます**。 表示機能は、スーパーブロックのタイトルに依存しており、認定講座タイトルと一致します。 認定講座名も同時に変更したいものです。
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx` のパス値を更新します。
+1. `client/i18n/locales` の言語ごとに、`intro.json` ファイルを更新して新しいスーパーブロック `dashedName` を使用します。英語のファイルの `title` も更新します。
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. 使用しているすべての値を更新します。
+1. メイン `README.md` ファイルを新しい名前に更新します。
+
+### ブロック名を変更する
+
+以下の手順に従い、カリキュラムブロック名を変更します。
+
+1. `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}` ディレクトリ内のブロックフォルダ名を変更します。
+1. 他の言語ディレクトリ _すべて_ において、同じブロックフォルダの名前を一致させます。 これらすべてが英語の構造と同じでないと、ビルドエラーになります。
+1. `_meta` ディレクトリ内のブロックフォルダ名を変更します。
+1. ブロックの `meta.json` ファイルの `name` と `dashedName` プロパティを更新します。
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### チャレンジ名を変更する
+
+以下の手順に従い、単一のチャレンジファイル名を変更します。
+
+1. `urriculum/challenges/english` ディレクトリのチャレンジファイル名を変更します。
+1. ファイル内の `title` 名と `dashedName` 名を変更します。
+1. ファイル名と他の言語ディレクトリ _すべて_ のファイルの `dashedName` を変更して一致させます。
+1. 該当する `meta.json` ファイルのチャレンジ名を更新します。 ここでのチャレンジ名は、ビルドでは使用されませんが、チャレンジの順序を識別するためのユーザーフレンドリーな方法を提供します。
+1. チャレンジが認定講座プロジェクトの場合、 `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` 内の YAML ファイルを新しい名前に更新します。
+1. チャレンジが認定講座プロジェクトの場合、`client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` の `title` と `link` を更新します。
+1. チャレンジが認定講座プロジェクトの場合、メイン `README.md` ファイルを新しい名前に更新します。
+
+## `dashedName` プロパティ
+
+`dashedName` プロパティは、スーパーブロック、ブロック、またはチャレンジの URL パスを生成するために使用されます。これらは通常 `/utils/slugs.js` ヘルパーがファイル名に対して出力するものと一致します。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/devops.md b/src/content/docs/jp/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..18e69501
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: DevOps ハンドブック
+---
+
+このガイドは、インフラストラクチャスタックとプラットフォームをどのように維持するかを理解するのに役立ちます。 このガイドで、すべての操作について詳しく説明しているわけではありませんが、システムを理解する上での参考になります。
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+これには 3 つのステップが含まれます。
+
+1. 新規変更 (修正および機能変更の両方を含む) は、プルリクエストによりプライマリ開発ブランチ (`main`) にマージされます。
+2. これらの変更は、一連の自動テストで実行されます。
+3. テストに合格すると、インフラストラクチャ上でのデプロイメントに対して変更をリリースします(または必要に応じて更新します)。
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+通常、[`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (デフォルトの開発ブランチ) は、[`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) ブランチに 1 日 1 回マージされ、分離されたインフラストラクチャにリリースされます。
+
+これは開発者とボランティアのコントリビューター用の中間リリースです。 「ステージング」または「ベータ」リリースとも呼ばれます。
+
+それは `freeCodeCamp.org` のライブプロダクション環境と同じで、データベース、サーバー、Web プロキシなどの別々のセットを使用しています。 この分離により、freeCodeCamp.org の main プラットフォームの正規ユーザーに影響を与えることなく、「本番」のようなシナリオで継続的な開発と機能をテストすることができます。
+
+開発者チーム [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) が、ステージングプラットフォームでの変更に満足したら、これらの変更は数日ごとに [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) ブランチに移されます。
+
+これが freeCodeCamp.org で本番プラットフォームに変更を加えた最終リリースです。
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+私たちは、コードの品質を確認するために、様々なレベルの統合と受け入れテストを採用しています。 すべてのテストは、[GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) や [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp) のようなソフトウェアにより実行されます。
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. これらは、異なるコンポーネント間の統合をテストするのに役立ちます。
+
+> [!NOTE] We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+
+これらのテストを組み合わせることで、問題が繰り返されるのを防ぎ、別のバグや機能の作業中にバグが発生しないようにします。
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+開発サーバーと本番サーバーに変更をプッシュする継続的デリバリーソフトウェアを設定しています。
+
+保護されたリリースブランチに変更がプッシュされると、そのブランチに対してビルドパイプラインが自動的にトリガーされます。 ビルドパイプラインは、アーティファクトを構築し、後で使用するためにコールドストレージに保管する責任があります。
+
+実行が正常に完了すると、ビルドパイプラインは対応するリリースパイプラインをトリガーします。 The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. `production-*` ブランチへの変更は、[`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) への早送りマージによってのみ可能です。
+
+> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. リモートを正しく構成します。
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **結果:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. `main` ブランチが初期状態であり、アップストリームと同期していることを確認してください。
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. GitHub CI がアップストリームの `main` ブランチを渡していることを確認してください。
+
+ [継続的インテグレーション](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) テストは、`main` ブランチに関して、緑色であり PASSING でなければなりません。 `main` ブランチコードを表示する際、コミットハッシュの横にある緑色のチェックマークをクリックします。
+
+ <details> <summary> GitHub Actionsでステータスを確認する (スクリーンショット) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ これに失敗した場合は、停止してエラーの確認をします。
+
+4. リポジトリをローカルにビルドできることを確認します。
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. 早送りマージにより、変更を `main` から `prod-staging` に移行します。
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > エラーになったとしたら、誤った操作をしたかもしれませんので、やり直します。
+
+上記手順では、`prod-staging` ブランチのビルドパイプラインで自動的に実行がトリガーされます。 ビルドが完了すると、アーティファクトは `.zip` ファイルとしてコールドストレージで保存され、後で取り出され使用されます。
+
+接続されたビルドパイプラインから新たなアーティファクトが利用可能になると、リリースパイプラインが自動的にトリガーされます。 For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+プロセスはほとんどステージングプラットフォームと同じですが、いくつかの追加のチェックが行われます。 これは、何百人ものユーザーが常に使用している freeCodeCamp.org 上で何も壊さないようにするためです。
+
+| すべてがステージングプラットフォームで動作していることを確認しない限り、これらのコマンドを実行しないでください。 先に進む前に、ステージング上のテストを回避またはスキップしないでください。 |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| |
+
+1. `prod-staging` ブランチが初期状態であり、アップストリームと同期していることを確認してください。
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. 早送りマージにより、変更を `prod-staging` から `prod-current` に移行します。
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > エラーになったとしたら、誤った操作をしたかもしれませんので、やり直します。
+
+上記手順では、`prod-current` ブランチのビルドパイプラインで自動的に実行がトリガーされます。 ビルドアーティファクトの準備が完了すると、リリースパイプラインで実行がトリガーされます。
+
+**スタッフアクションの追加手順**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. 彼らはリリース実行を _承認_、または _拒否_ することができます。
+
+変更がうまく動作し、ステージングプラットフォームでテストされている場合は、承認することができます。 承認は、自動的に拒否される前に、リリースがトリガーされてから 4 時間以内に行われる必要があります。 拒否された実行が拒否された場合、スタッフは手動でリリース実行を再トリガーするか、リリースの次のサイクルを待つことになります。
+
+スタッフ用:
+
+| ビルドの実行が完了したら、直接リンクについて E メールを確認するか、[リリースダッシュボードにアクセス](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) してください。 |
+| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+スタッフがリリースを承認すると、パイプラインは freeCodeCamp.org の本番用 CDN および API サーバーにその変更を反映させます。
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+ここでは、コードベースの現在のテスト、ビルド、およびデプロイの状況を示します。
+
+| ブランチ | 単体テスト | 統合テスト | ビルド & デプロイ |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (試験的、予定) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+皆さんがこれらのリリースを **"パブリックベータテスト"** モードでテストし、プラットフォームの今後の機能に早期アクセスできるようにします。 これらの機能 / 変更は、**ネクスト、ベータ、ステージング** などと呼ばれます。
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+見つけたバグの報告や、freeCodeCamp.org をより良くする支援に感謝します。 素晴らしい皆さんです!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| アプリケーション | 言語 | URL |
+| :--------------- | :--------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| 学習 | 英語 | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | スペイン語 | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | 中国語 | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| ニュース | 英語 | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| フォーラム | 英語 | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | 中国語 | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] ドメイン名は **`freeCodeCamp.org`** とは異なります。 これは、検索エンジンのインデックス作成を防止し、プラットフォームの通常ユーザーの混乱を避けるための、意図的なものです。
+>
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**プラットフォームの現在のバージョンは [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org) で常に利用できます。**
+
+開発者チームは、リリース変更時に、`prod-staging` ブランチから `prod-current` への変更をマージします。 トップコミットは、サイト上で表示されるもののはずです。
+
+ステータスセクションにあるビルド & デプロイログにアクセスして、デプロイされた正確なバージョンを確認できます。 Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+プラットフォームのベータ版を使用する場合、いくつかの既知の制限とトレードオフがあります。
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **ベータ版のユーザーは本番とは異なるアカウントを持つことになります。** ベータ版は本番と物理的に分離されたデータベースを使用します。 これにより、偶発的なデータ損失や変更を防ぐことができます。 The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ デプロイは頻繁に行われ、時には非常に速いペースで 1 日に複数回行われることになります。 As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ ベータサイトは、ローカルの開発とテストを強化するためのものでしたし、今もそうです。 それはこれから起こることを約束するものではありませんが、取り組まれていることを垣間見るものです。
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ Auth0 上で freeCodeCamp.dev にはテストテナントを使用しているため、カスタムドメインを設定することはできません。 そのため、すべてのリダイレクトコールバックとログインページが `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/` のようなデフォルトドメインに表示されます。 これが機能に影響を与えることはありませんし、本番環境に近いものです。
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+ディスカッションやバグ報告をする場合、新しい Issue を開いてください。
+
+ご質問があれば、`dev[at]freecodecamp.org` にメールをご送信ください。 セキュリティ脆弱性は、公開トラッカーやフォーラムではなく、`security[at]freecodecamp.org` に報告する必要があります。
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. ガイドは、**freeCodeCamp スタッフのみ** に適用されます。
+> 2. インストラクションは包括的なものではありませんので、ご注意ください。
+
+スタッフの一員として、Azure、Digital Ocean などのクラウドサービスプロバイダーへのアクセスが許可されている可能性があります。
+
+仮想マシン (VM) で作業するために使用できる便利なコマンドをいくつか紹介します。例えばメンテナンスの更新や一般的なハウスキーピングの実行です。
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+
+### Azure
+
+Azure CLI のインストール `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(一回のみ) [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh) で macOS にインストールします。**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(一回のみ) ログインします。**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **VM 名と IP アドレスのリストを取得します。**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Digital Ocean CLI `doctl` のインストール: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(一回のみ) [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh) で macOS にインストールします。**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(一回のみ) ログインします。**
+
+認証とコンテキストの切り替え: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **VM 名と IP アドレスのリストを取得します。**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+私たちは IaC 設定の作成に取り組んでいます。そして、その作業中は Azure ポータルまたは Azure CLI を使用して、新しい仮想マシンやその他のリソースをスピンさせることができます。
+
+:::tip
+スピニングリソースの選択に関係なく、docker のインストールや SSH キーの追加など基本的なプロビジョニングを行うのに役立つ [便利な cloud-init 設定ファイル](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) がいくつかあります。
+:::
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+アップデートとアップグレードを行うことで、VM を最新の状態に保つ必要があります。 This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] これらのコマンドを実行する前に下記を実行します。
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - アプリケーションを既に提供している VM 上で、パッケージを更新する場合は、アプリが停止 / 保存されていることを確認してください。 パッケージ更新により、ネットワーク帯域幅や、メモリ、CPU の使用率が急増し、 実行中のアプリケーションが停止します。
+
+パッケージ情報を更新します。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+インストール済みパッケージをアップグレードします。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+未使用のパッケージをクリーンアップします。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+Web サーバーのために、負荷分散 (Azure Load Balancer) インスタンスを実行しています。 これらのサーバーは NGINX を実行しています。NGINX は、独自インフラストラクチャで実行される様々なアプリケーションから freeCodeCamp.org へと、トラフィックを中継するリバースプロキシとして使用されます。
+
+NGINX 設定は [このリポジトリ](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config) で確認できます。
+
+### 最初のインストール
+
+コードを使用して VM をプロビジョニング
+
+1. NGINX をインストールし、リポジトリから設定します。
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Cloudflare のオリジン証明書とアップストリームアプリケーション設定をインストールします。
+
+ 安全なストレージから Cloudflare のオリジン証明書を取得し、 必要な場所にインストールします。
+
+ **または**
+
+ 既存の証明書を移動させます。
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ アップストリーム設定を更新します。
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ ソース / オリジンアプリケーションの IP アドレスを追加 / 更新します。
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ 必要に応じて、イングレスオリジンアドレスに Azure ファイアウォールと `ufw` を設定します。
+
+4. VM をロードバランサーバックエンドプールに追加します。
+
+ 必要に応じて、ロードバランサーにルールを設定し追加します。 バランサーバックエンドプールをロードするために、VM を追加する必要があるかもしれません。
+
+### ログとモニタリング
+
+1. 以下のコマンドを使用して NGINX サービスのステータスを確認します。
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. サーバーのログとモニタリングは以下で行います。
+
+ 現行の基本的なモニタリングダッシュボードは、NGINX Amplify ([https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com')) です。 監視向上のため、より細かいメトリックに取り組んでいます。
+
+### インスタンスの更新 (メンテナンス)
+
+NGINX インスタンスへの設定変更は、GitHub 上でメンテナンスされています。これらは、以下のように各インスタンスにデプロイされる必要があります。
+
+1. SSH でインスタンスに接続し、sudo と入力します。
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. 最新の設定コードを取得します。
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. 設定 [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx) をテストして再度読み込みます。
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. ノードバイナリのビルドツール (`node-gyp`) をインストールします。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### 最初のインストール
+
+コードを使用して VM をプロビジョニング
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### ログとモニタリング
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### インスタンスの更新 (メンテナンス)
+
+コードの変更は、適宜 API インスタンスにデプロイする必要があります。 ローリング更新または手動更新により実行できます。 The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+自動パイプラインは、分単位で依存関係の更新を処理していません。 デプロイパイプラインが実行される前に、手動で更新する必要があります。
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. これらのコマンドを実行する必要はありません。 ドキュメント用として、ここに記載されているだけです。
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### 最初のインストール
+
+コードを使用して VM をプロビジョニング
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### ログとモニタリング
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### インスタンスの更新 (メンテナンス)
+
+コードの変更は、適宜 API インスタンスにデプロイする必要があります。 ローリング更新または手動更新により実行できます。 依存関係を変更したり、環境変数を追加したりする場合は、後者が必須です。
+
+:::danger
+自動パイプラインは、分単位で依存関係の更新を処理していません。 デプロイパイプラインが実行される前に、手動で更新する必要があります。
+:::
+
+#### 1. 手動更新 - 依存関係や env 変数の更新に使用します。
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. ローリング更新 - コードの論理的な変更に使用されます。
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] パイプライン経由で、コードやロジックの更新をロールリング処理しています。 これらのコマンドを実行する必要はありません。 ドキュメント用として、ここに記載されているだけです。
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+チャットサーバーは、[Rocket.Chat ドキュメントで推奨されている](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install) HA 構成で利用可能です。 そのために使用する `docker-compose` ファイルは、[こちらで入手可能](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config) です。
+
+Rocket.Chat クラスタの前で、負荷分散型 (Azure ロードバランサー) の冗長 NGINX インスタンスを提供します。 NGINX 設定ファイルは、[こちらで入手可能](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config) です。
+
+### First Install
+
+コードを使用して VM をプロビジョニング
+
+**NGINX クラスタ:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Docker クラスタ:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**NGINX クラスタ:**
+
+NGINX インスタンスへの設定変更は、GitHub 上でメンテナンスされています。これらは、以下のように各インスタンスにデプロイされる必要があります。
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Docker クラスタ:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+(Digital Ocean 上でホストされている) VM に ssh で接続します。
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+現在インストールされている node と npm のバージョンをリストアップします。
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+最新の Node.js LTS をインストールし、グローバルパッケージを再インストールします。
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+インストールされたパッケージを確認します。
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(オプション) 旧バージョンをアンインストールします。
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+クライアントアプリケーションでは、`pm2 resurrect` を使用して、Node.js バージョン間でシェルスクリプトを復元することはできません。 ゼロからプロセスをデプロイします。 This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> プロセスに PM2 を使用する場合は、アプリケーションを起動し、再起動時に自動リカバリを行うためのプロセスリストを保存する必要があります。
+
+`unstartup` コマンドでアンインストールの手順 / コマンドを取得し、出力を使用して systemctl サービスを削除します。
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+`startup` コマンドでインストールの手順 / コマンドを取得し、出力を使用して systemctl サービスを追加します。
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+以下は、PM2 からリストへのクイックコマンド、保存されたプロセスの復元などです。
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. 一般的には、ここに記載されている手順に従います。
+
+https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens から入手できる PAT が必要です。
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+[Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) に移動し、必要な [デプロイグループ](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup) でエージェントをゼロから登録します。
+
+> [!NOTE] スクリプトをホームディレクトリで実行し、他の `azagent` ディレクトリが存在しないことを確認します。
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+現在、エージェントを更新するには、エージェントを削除して再設定する必要があります。 これは、`PATH` の値や他のシステム環境変数を正しく取り出すために必要です。 デプロイターゲット VM 上で、Node.js を更新する場合は、以下を実行する必要があります。
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+上記の手順を完了したら、エージェントのインストールと同じ手順を繰り返すことができます。
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+[CLI ツール](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) で、ウィークリーニュースレターを送信します。 プロセスは次のとおりです。
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+ニュースの掲載には、カスタム [テーマ](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) を使用します。 テーマに以下の変更を加えることで、新しい言語の追加が可能になります。
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Ghost ダッシュボード > 設定 > 一般と進み、出版物の [アイコン](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png)、[ロゴ](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png) および [カバー](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png) をアップロードすることで、出版物アセットを更新します。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/faq.md b/src/content/docs/jp/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..90d9e6c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+:::tip
+**`help wanted`** の Issue は誰でも作業が可能であり、作業前に許可を求める必要はありません。 ただし、 **`first timers only`** ラベルが付けられた Issue は、初めて freeCodeCamp コードベースに貢献する人用の特別な Issue です。
+:::
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. Issue に対処する最初のプルリクエストをマージする可能性が最も高いです。
+2. 複数のコントリビューターが同じ Issue に対してプルリクエストを同時にオープンした場合、 最善の対処をするプルリクエストを優先します。 考慮事項:
+ - テストを含めましたか?
+ - Did you catch all use cases?
+ - すべてのテストに合格し、すべてがローカルで動作することを確認しましたか?
+3. 最後に、推奨ガイドラインに従ったプルリクエストを優先します。
+ - プルリクエストのチェックリストに従って確認しましたか?
+ - プルリクエストに意味のあるタイトルを付けましたか?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- To be a **Discord/Chat** moderator, have an active presence in our chat and have positive engagements with others, while also learning and practicing how to deal with potential conflicts that may arise.
+- To be a **Forum** moderator, similar to a chat moderator, have an active presence and engage with other forum posters, supporting others in their learning journey, and even giving feedback when asked. Take a look at [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) for more information.
+- To be a **GitHub** moderator, help process GitHub issues that are brought up to see if they are valid and (ideally) try to propose solutions for these issues to be picked up by others (or yourself).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- [コミュニティフォーラム](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) の `Contributors` カテゴリ
+- [チャットサーバーの ](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) `#Contributors` チャンネル
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..44c5c700
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: Cypress テストを追加する方法
+---
+
+ページの機能やレイアウトを変更する可能性がある JavaScript、CSS、または HTML を変更する際には、対応する [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io) 統合テストを追加することが重要です。
+
+Cypress テストもしくは「specs」の書き方については、Cypress の公式 [ドキュメント](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html) をご覧ください。
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Cypress テストは `./cypress` ディレクトリにあります。
+
+- カリキュラムモジュールの Cypress テストは、対応するカリキュラムディレクトリ、すなわち `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js` にあります。
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+> [!NOTE] If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [MongoDB を起動し、データベースをシードします。](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [freeCodeCamp クライアントアプリケーションと API サーバーを起動します。](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+`dev` を `prd` に置き換えて本番ビルドに対するテストを実行します。
+
+- `./cypress` ディレクトリで、すべてのテストを実行します。
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- 単一のテストを実行します。
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- 開発ビルドを作成するには、開発サーバーを起動し、既存の cypress エンドツーエンドテストをすべて実行します。
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. 開発環境が稼働していることを確認する
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- データベースをシードします。
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- サーバーとクライアントを構築します。
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Cypress ビルドツールをインストールする
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- 端末でプロンプトが表示されたら、言語/エリアでキーボードのレイアウトを選択してください。
+
+これで、[Cypress を実行することができます]($1#$2)。
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8565d680
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **注:** これは **オプション** ステップであり、メールワークフローを使用する場合にのみ必要です。
+
+- [はじめに](#introduction)
+- [MailHog のインストール](#installing-mailhog)
+- [MailHog の使用](#using-mailhog)
+- [有用なリンク](#useful-links)
+
+## はじめに
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog は、実際のメールメッセージを送信する電子メールサービスプロバイダの代わりになります。 これは、freeCodeCamp インスタンスから送信されたメールメッセージをキャッチするメールテスト用の開発ツールです。
+
+## MailHog のインストール
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Dockerで MailHog をインストールする</summary>
+
+Docker がインストールされていれば、次のコマンドが使用できます。
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+上記コマンドによりバックグラウンドで MailHog を起動できます。
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+上記コマンドにより MailHog を停止できます。
+
+インストールが完了すると、[MailHog の使用](#mailhog-の使用) を開始できます。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>macOS に MailHog をインストールする</summary>
+
+[Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) を使用して macOS に MailHog をインストールします。
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+インストールが完了すると、[MailHog の使用](#mailhog-の使用) を開始できます。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Windows に MailHog をインストールする</summary>
+
+[MailHog の公式リポジトリ](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases) から最新バージョンの MailHog をダウンロードします。 Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a `.exe` file will be downloaded to your computer.
+
+ダウンロードが完了したら、クリックしてファイルを開きます。 Windows ファイアウォールの通知が表示され、MailHog のアクセス許可を要求する場合があります。 ファイアウォールへのアクセスが許可されると、標準の Windows コマンドラインプロンプトが開き、MailHog が実行されます。
+
+コマンドプロンプトウィンドウを閉じて、MailHog を閉じます。 To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (`.exe`) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
+
+[MailHog の使用](#mailhog-の使用) を開始します。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Linux に MailHog をインストールする</summary>
+
+まず、[GO](https://golang.org) をインストールします。
+
+次のコマンドを実行して、Ubuntu や Linux Mint などの Debian ベースのシステムに GO をインストールします。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+次のコマンドを実行して、CentOS、Fedora、Red Hat Linux などの RPM ベースのシステムに GO をインストールします。
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+代わりに、次のコマンドを実行して GO をインストールすることもできます。
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+次のコマンドで GO のパスを設定します。
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+最後に、以下のコマンドを入力して MailHog をインストールして実行します。
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+[MailHog の使用](#mailhog-の使用) を開始します。
+
+</details>
+
+## MailHog の使用
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## 有用なリンク
+
+- MailHog に関連する詳細情報については、 [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) リポジトリを参照してください。 カスタム MailHog 設定に関する追加情報も入手できます。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a18642b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines to contribute to the codebase. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+Ignoring these steps may soil your copy which makes the contributing, maintaining, and reviewing processes difficult.
+
+## Contributing to the Codebase
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the freeCodeCamp upstream `main` branch to your `main` fork branch:
+
+:::warning
+If you have any outstanding pull requests that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+
+You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+:::
+
+This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp.
+
+Update your copy of the freeCodeCamp upstream repository:
+
+```bash
+git fetch upstream
+```
+
+Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp main:
+
+```bash
+git reset --hard upstream/main
+```
+
+Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+```bash
+git push origin main --force
+```
+
+You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+```bash
+git diff upstream/main
+```
+
+The resulting output should be empty. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run freeCodeCamp to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Make a conventional commit message. This is a good practice as a developer, and you will be following standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any more time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Quick commands reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working.
+
+| command | description |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Run all JS tests in the system, including client, server, lint and challenge tests. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Run the client test suite. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Run the curriculum test suite. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific Block. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific SuperBlock. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Run the curriculum test suite, without bailing after the first error |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Run the server test suite. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Run the Cypress end to end tests. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Starts Storybook for component library development. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7af7f0dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Deploying New Languages on `/learn`
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Updating Crowdin Settings
+
+Before you can release a new language, you will need to allow the languages to download from Crowdin. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Then scroll down to `Language Mapping`, where you will see an option to add custom language codes. Add a new entry for the language you are releasing, selecting `language` as the `Placeholder` value, and entering a URL-friendly lower-case spelling of your language's name for the `Custom code`. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). The step for these will be the same. For example, if you want to enable Dothraki downloads:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Note that the `download_language` key needs to be set to the language code displayed on Crowdin.
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+> [!NOTE] The above section with updating the workflows should be completed before proceeding - these need to be done in separate steps or the builds will fail.
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. There are several objects here.
+
+- `Languages`: Add the new language to `Languages` enum, similar to the others. The string value here will be used in the `.env` file to set a build language later.
+- `availableLangs`: Add the new property from the `Languages` enum to both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays.
+- `i18nextCodes`: These are the ISO language codes for each language. You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+- `hiddenLangs`: These languages will not be displayed in the navigation menu. This is used for languages that are not yet ready for release. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: These are languages that read from right to left.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `i18n.ts` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configure Search
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+You will need to take an additional step to handle the client UI translations.
+
+The Crowdin workflows will automatically pull down _some_ of the UI translations, but there are a couple of files that need to be moved manually.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+If you would like to test translations locally, before adding them to our main repository - skip the Crowdin workflow changes. Follow the steps for enabling a language, then download the translations from Crowdin and load them into your local code.
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Update your `.env` file to use your new language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `pnpm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+If you build the client in one language and then want to build it in a different language, you will need to use the command `pnpm run clean-and-develop` after changing the `.env` file, as Gatsby will cache the first language.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Deploying New Languages on `/news`
+
+To deploy News for a new language, you'll need to create two PRs. One PR will be to the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), and the other will be to the [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News sources trending links and article titles from our CDN during the build and adds them to the footer. News also fetches Day.js files from the CDN during the build to localize dates and times for each language.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Clone the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) and create a new branch.
+
+In the [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) directory, create a new file and name it `language.yaml`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Then copy the contents of the [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) trending file and paste it into the new YAML file you just created.
+
+The contents will look something like this:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+By default, Day.js only includes English as a locale. To enable it to work with other languages, you need to add a new Day.js locale file to the CDN.
+
+In the [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) directory, create a new file and name it `isocode.min.js`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] The version number will change as the dependencies are updated.
+
+Then, visit [this page on cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) with all available Day.js files for the version we're using, find the `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` link for the new language, and open it in a new tab.
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to add the .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js locale file. You do not need to add any other Day.js files.
+
+Copy the Day.js locale code from the new tab into the new file you created. For example, here is an un-minified version of the English locale code for Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Then open a PR to the CDN repo to add both the YAML and Day.js files for review.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+The [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) pulls data from a Ghost instance, the files you added to the CDN, builds News, and deploys it.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. You should not work off of a fork for this step.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Clone the News repo and create a new branch.
+
+Open the `config/index.js` file to add the new language and configure the necessary values. There are a few objects and arrays to modify:
+
+- `locales`: This array contains the active and upcoming News languages. These are the values that are used in the `.env` file to choose the Ghost instance and UI to use for each build. Add the text name of the new language in lowercase to this array.
+- `localeCodes`: This object is a map of ISO codes for each language, and is used to configure i18next before building the UI. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_ and the ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: This object is a map of Algolia indices for each language. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_, and `news-` followed by the lowercase ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are unsure about the string to use while setting `algoliaIndices`, send a message to Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo), or someone else with access to Algolia, and ask them to check.
+
+For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, here are what the objects / arrays above should look like:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. For example, if you're launching Dothraki News, create a new folder named `dothraki`.
+
+Then copy the JSON files from the `english` directory to your new folder.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Then commit and push your branch directly to the News repo.
+
+> [!NOTE] You need to be on one of the teams with access to the News repo to push branches directly to News. Currently, only the dev, i18n, and staff teams are allowed to do this.
+
+Finally, open a PR for review.
+
+Once both your PRs to the CDN and News repo have been approved, they can be merged.
+
+> [!NOTE] Deployment will be handled subsequently by the staff. Here is a sample PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) of how they do it and more details are available in the [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4473a6fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+ビデオチャレンジは、freeCodeCamp カリキュラムの新しいタイプのチャレンジです。
+
+ビデオチャレンジは、特定のトピックに関するノーカットビデオコースの小さなセクションです。 ビデオチャレンジページには、YouTube 動画が埋め込まれています。 各チャレンジページには、動画に関連する多肢選択問題があります。 コース内で次のビデオチャレンジに進む前に、ユーザーは質問に正しく答える必要があります。
+
+ビデオチャレンジのページは、freeCodeCamp チームのメンバーによって作成されます。 YouTube 動画も、freeCodeCamp チームのメンバーによってアップロードされます。 しかし、多くのビデオチャレンジは、まだ関連する質問がありません。
+
+ビデオセクションに関連する多肢選択式の質問を作成し、ビデオチャレンジマークダウンファイルに質問を追加する作業を手伝うことができます。
+
+## チャレンジテンプレート
+
+以下はチャレンジマークダウンファイルのテンプレートです。
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+チャレンジの説明 (マークダウンで記入)
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+現在、このフィールドは多肢選択式 Python チャレンジが使用しています。
+
+## --text--
+
+質問のテキストをここに記述します。
+
+## --answers--
+
+回答 1
+
+---
+
+回答 2
+
+---
+
+他の回答
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+正解の番号をここに記述します。
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Skim through the video associated with the challenge and create a multiple-choice question
+
+First, find the `videoId`.
+
+For example, in the following code from the header of a video challenge markdown file, the `videoId` is "nVAaxZ34khk". GitHub では、情報はテーブル形式で表示されます。
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+次に、その `videoId` で YouTube の動画にアクセスします。 The URL for the video will be:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (replace `videoId` in the URL with the video's ID - without square brackets)
+
+In the example above, the URL is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Skim the YouTube video with that `videoId` and think of a multiple-choice question based on the content of the video.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. ローカルで質問を追加するには、[freeCodeCamp をローカルに設定する](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) 必要があります。 GitHub でファイルを見つけて、編集ボタンをクリックして、ブラウザで質問を追加することもできます。
+
+特定のビデオチャレンジに質問がまだ追加されていない場合は、次のデフォルトの質問があります。
+
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+質問のテキスト
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+---
+
+他の回答
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+下記項目の下に質問テキストを追加 / 更新してください。
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+`## --answers--` の下に回答を追加 / 更新してください (`Answer 1`、`Answer 2` など)。 `## -video-solution--` の下にある番号を正解の番号に更新してください。 同じ形式で、他の回答も追加できます。 The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### 質問の例
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+この JavaScript コードは、コンソールに何を記録しますか?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+以下のコードを実行すると何が出力されますか?
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+以下のビデオコースのマークダウンファイルで、その他の例も参照できます。 すべてのチャレンジには既に質問があります: [Python for Everybody コース](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+1 つ以上の質問を作成した後、新しいブランチに変更をコミットすると、[プルリクエストをオープンする](how-to-open-a-pull-request) ことができます。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7c207a09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: プルリクエストを開く方法 (PR)
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. コードを変更したら、以下のガイドラインに従って PR を開くことができます。
+
+We expect our contributors to be aware of the process specific to this project. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Some examples of this are:
+
+1. Do not edit files directly through GitHub – while you can, it's not a good idea.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Make sure you follow the PR checklist and not just tick things off; otherwise, we won't take you seriously.
+4. Use the correct way to link issues in the description of the PR by updating the `XXXXXX`. Do not just add issue numbers everywhere and anywhere you feel like.
+5. Do not "@mention" or request someone for reviews too many times.
+
+ We understand you are excited about contributing. As much as a maintainer will love to get back to you, they are busy people looking after hundreds of requests just like yours. Be patient, someone will get to you sooner or later.
+
+6. Do not work directly off your `main` branch - create a new branch for the changes you are working on.
+
+> [!NOTE] Your PR should be targeting changes to the English curriculum only. Read [this guide](index#translations) instead for contributing to translations.
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. The convention has the following format:
+
+> `<type>([optional scope(s)]): <description>`
+>
+> 例えば、次のようになります。
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Type:**
+
+| 種類 | 選択するタイミング |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | 新しい機能、テストなどの追加時のみ |
+| chore | レッスンのコード、テスト、または検証に関連しない変更時 |
+| docs | `/docs` ディレクトリまたは貢献ガイドラインなどへの変更時 |
+
+**Scope:**
+
+You can select a scope from [this list of labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Description:**
+
+Keep it short (less than 30 characters) and simple; you can add more information in the PR description box and comments.
+
+Some examples of good PR titles would be:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## プルリクエストを提案する
+
+1. Once the edits have been committed, you will be prompted to create a pull request on your fork's GitHub Page.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. By default, all pull requests should be against the freeCodeCamp main repo, `main` branch.
+
+ Make sure that your Base Fork is set to freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp when raising a Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Submit the pull request from your branch to freeCodeCamp's `main` branch.
+
+4. Include a more detailed summary of the changes you made and how your changes are helpful in the body of your PR.
+
+ - プルリクエストテンプレートが表示されます。 これはプルリクエストを開く前に行うべきチェックリストです。
+
+ - 必要に応じて詳細を記入します。 Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - PR が既存の GitHub Issue に対処するものである場合、PR 説明本文の最後に、キーワード _Closes_ と Issue 番号を使用して、[ PR が承認されマージされたら、その Issue が自動的にクローズされるようにします](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords)。
+
+ > 例: `Closes #123` と記入すると、Issue 123 がクローズされます。
+
+5. Indicate if you have tested on a local copy of the site or not.
+
+ - これは、ドキュメントやチャレンジの説明のようなテキストコンテンツを編集するだけでなく、変更を加える場合に、非常に重要です。 Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: PR の作成おめでとうございます。時間をかけて貢献してくださったことに心から感謝します。
+
+Our moderators will now take a look and leave you feedback. Please be patient with the fellow moderators and respect their time. All pull requests are reviewed in due course.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+他のプルリクエストも提供する場合は、フォークの削除を避けるため、[変更と同期]($1#$2) のガイドラインをご覧になることを推奨します。
+:::
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+Conflicts can arise because many contributors work on the repository, and changes can break your PR which is pending a review and merge.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+When you are working on regular bugs and features on our development branch `main`, you are able to do a simple rebase:
+
+1. Rebase your local copy:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Resolve any conflicts and add / edit commits
+
+ ```bash
+ # Either
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Or
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Push back your changes to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Make sure your upstream comes in sync with your local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Either delete your local branch after taking a backup (if you still have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Start off with a clean slate:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # example:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0d28789f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: 翻訳校正の手順
+---
+
+校正チームは、翻訳文が原文を正確に反映するようにする責任があります。 私たちは、非常に高い品質の翻訳文を提供してくれる校正者を信頼しています。
+
+翻訳はすべて実際の人間が作業しています。 Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+校正を始めるには、[翻訳プラットフォーム](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) にアクセスしてログインします。 上部ナビゲーションバーで「コンソールに移動」を選択し、パブリックビューからワークスペースビューに切り替えます。
+
+## ファイルの選択
+
+アクセスが許可されたプロジェクトの一覧が表示されます。 校正を行うプロジェクトを選択し、言語を選択します。
+
+
+
+利用可能なファイルのリストが表示されます。 ファイルを選ぶには、ファイルの右側にある `Proofread` ボタンを押し、表示されるドロップダウンメニューから `Proofread` を選択します。
+
+> [!NOTE] このワークスペースビューで、校正ではなく [ファイルの翻訳](how-to-translate-files)を行いたい場合は、ドロップダウンメニューから `Crowdsourcing` を選択します。
+
+## 翻訳文の校正
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+ここでは、選択したファイル内の文字列のリストと関連する翻訳文が表示されます。 ここで表示される翻訳は、翻訳コミュニティから (賛成票と反対票の間で) 最高得点を得た翻訳です。
+
+指定された文字列の _すべての_ 翻訳候補を見ることができます。承認する翻訳文を選択する際に、(賛成票と反対票によって決定される) コミュニティのスコアを考慮します。 コミュニティは翻訳候補をレビューし、最も正確で明確な翻訳を推奨します。
+
+1. 原文の文字列 (英語) を確認します。
+2. 翻訳された文字列を確認します。 賛成票と反対票に基づいて、最も人気のある翻訳案がここに表示されます。
+3. このチェックマークボタンをクリックすると、その翻訳が承認されます。
+4. Crowdin は各文字列のステータスを表示します。 `Done` は翻訳が承認されたことを意味し、次の Crowdin プルにダウンロードされます。 `Todo` は文字列が校正されていないことを意味します。 `Hidden` は文字列がロックされており、_翻訳すべきではない_ ことを意味します。 `Comment` は、その文字列に関連するコメントがあることを意味します。
+5. 翻訳文をチェックボックスで選択し、一括して承認することもできます。
+6. コミュニティが提案した翻訳、その人気度のスコア、Crowdin が提案した翻訳をここで参照できます。
+7. このボタンで、右側の表示ペインの表示 / 非表示を切り替えます。ここでは、翻訳、コメント、翻訳メモリ、および用語集を見ることができます。
+8. 品質保証チェックにエラーがあった際に、ここにメッセージが表示されます。 つまり、翻訳文が正しくないと思われる場合に、Crowdin から通知があります。 これらの翻訳は慎重に承認します。
+
+ファイルが校正されると、追加のアクションは必要ありません。
+
+> [!NOTE] 校正ビューで文字列を承認すると完成とマークされ、Crowdin から GitHub への次のプルでダウンロードされます。
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+質問がある場合、または校正者になることに興味がある場合は、[コントリビューターチャットルーム](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) でお気軽にお問い合わせください。 一定期間 freeCodeCamp に貢献している場合は、通常、校正へのアクセスを許可します。
+
+スタッフチームとコミュニティモデレータチームは、世界中で高品質の翻訳を利用できるようにするための親切なボランティアを常に探しています。
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin では、自身の翻訳を承認することを許可します。 一般的には、エラーがないことを確認するための安全策として、他の校正者が翻訳案を見直すことをお勧めしています。
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+既に校正者であり、特定の言語のためのチャットサーバーに専用チャンネルを持つことに興味がある場合、[このフォーム](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA) に記入します。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c2db2149
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,306 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCamp. 定期的に貢献したい場合に、強くお勧めします。
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows. - You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase. - Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+
+:::
+
+If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Here are some pros and cons which should help you decide which option is best for you:
+
+| Gitpod | Your own machine (local setup) |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| No minimum hardware requirements | Specific and minimum requirements |
+| No need to install any software | Additional software required |
+| Always up to date copy of repository | Need to maintain a local copy of the repository |
+| Slower and can take a few minutes to launch | Faster and can be launched in seconds |
+| Need an internet connection to work | Minimal internet connection required (once setup) |
+| Some tasks like compilation and tests can take longer to complete | Faster completion of tasks (depending on your machine's capabilities) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+We have automated the process of installing all the dependencies & tools you will need. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Fastest)** Prepend `gitpod.io/#` in front of any URL from GitHub.
+
+ For example, if you visit your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, add `gitpod.io/#` in the front of the URL in the address bar and hit enter.
+
+ That is you can navigate to `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` and you should see a workspace created for you. This works for any repository or pull-request on GitHub.
+
+2. Alternatively install one of the below extensions for your browser.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - works with Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. See the extension page for details, screenshots, etc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### 必要条件:
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### 以下の手順に従って、開発環境を準備してください。
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ :::tip
+ Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+ :::
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+> [!WARNING] If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`). Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further information about this problem.
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# "sample.env" のコピーを作成し、".env" という名前を付けます。
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+:::tip
+Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
+:::
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+> [!NOTE] Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
+>
+> If you followed along with the [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), then you should be able to skip this step if the MongoDB server from that guide is already running. You can confirm this by checking that you can reach `http://localhost:27017` on your local machine.
+
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+> [!WARNING] Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8b0bb9de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow this guide for setting up the freeCodeCamp mobile app locally on your system. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (comes bundled with Flutter) | `3.x` | We use the version bundled with Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions.
+:::
+
+If Flutter is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. We recommend using the Pixel 3a XL and Nexus One(for emulating smaller screens).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+5. Install a code editor of your choice.
+
+ We highly recommend using [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) or Android Studio. We also recommend installing the official [extensions](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of the repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp mobile repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp mobile repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change directory to the new `mobile` directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp mobile repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of the mobile app, you can follow these instructions to run it locally.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] The `mobile` directory contains two folders ie. `mobile-api` and `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contains the API code used for serving the podcasts. `mobile-app` contains the Flutter app which is where you should be when you follow the below steps.
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Remember to change the directory to `mobile-app` before running the following commands.
+
+```bash
+# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+#### Step 2: Install dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start the freeCodeCamp mobile app
+
+Start the emulator of your choice(Android or iOS) and wait for the bootup process to complete.
+
+You can now start the app by running the following command:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+If you're using VSCode or Android Studio then you can easily start the app without having to execute any terminal commands. More information [here](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you are not on main or your working directory is not clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the upstream `main` branch to your local main branch:
+
+ > [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull request that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+ >
+ > You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+ This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp mobile. It is important that you rebase your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+ Update your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile upstream repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp mobile main:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ The resulting output should be empty.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your local work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp mobile and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run the mobile app locally to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Optional:
+
+ We highly recommend making a conventional commit message. This is a good practice that you will see on some of the popular Open Source repositories. As a developer, this encourages you to follow standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any additional time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Issues with installing the recommended prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS and/or are still running into issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+### Issues with the UI, build errors, etc.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d12d1d35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) で freeCodeCamp 開発環境を構築する
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+>
+> **WSL2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 以上) - Windows 10 Home を含むすべてのディストリビューションで利用可能です。
+>
+> **Docker Desktop for Windows**: [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) および [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements) の各要件を参照してください。
+
+このガイドでは、WSL2 のセットアップに関する一般的な手順について説明します。 WSL2 に関する一般的な問題に対処したら、[ローカルセットアップガイド](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) に従い、Ubuntu のように WSL ディストリビューションを実行している Windows 上で freeCodeCamp を起動できるようになります。
+
+## WSL を有効化する
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Ubuntu をインストールする
+
+1. WSL2 で Ubuntu-18.04 またはそれ以降を使用することをお勧めします。
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. OS の依存関係を更新します。
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Git を設定する
+
+Git は Ubuntu 18.04 でプリインストールされています。Git バージョンを `git --version` で確認してください。
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(任意ですが推奨) GitHub で [ssh キー設定](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) を実行します。
+
+## コードエディターをインストールする
+
+Windows 10 に [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) をインストールすることを強くお勧めします。 It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+基本的には、Windows にインストールされている VS Code を使用して、Ubuntu-18.04 上でコードを編集して保存します。
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Docker Desktop をインストールする
+
+**Docker Desktop for Windows** を使用すると、MongoDB のようなデータベースや NGINX などのサービスをインストールして実行できます。 MongoDB やその他のサービスを Windows または WSL2 に直接インストールする際の一般的な落とし穴を避けることができます。
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
+
+最高の体験を得るための最低限のハードウェア要件があります。
+
+## Docker Desktop for WSL を構成する
+
+Docker Desktop がインストールされたら、[この手順に従って](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) Ubuntu-18.04 をバックエンドとして使用するように設定します。
+
+これにより、コンテナは Windows 上ではなく WSL 側で実行されます。 Windows と Ubuntu の両方で `http://localhost` からサービスにアクセスできます。
+
+## Docker Hub から MongoDB をインストールする
+
+WSL2 で動作するように Docker Desktop を設定したら、次の手順に従って MongoDB サービスを起動します。
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. MongoDB サービスをポート `27017` で起動し、システム再起動時に自動的に実行するように設定します。
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Windows または Ubuntu から `mongodb://localhost:27017` でサービスにアクセスできるようになりました。
+
+## Installing Node.js and pnpm
+
+Node バージョンマネジャー - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating) を使用して、Node.js 用の LTS リリースをインストールすることを推奨します。
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. それでも、ほとんどのコードベースで作業できるはずです。
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- よくある質問:
+ - [Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop for Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5c4c1bd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: 翻訳文をローカルでテストする方法
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] このプロセスは必須ではありませんが、翻訳文がどのように見えるかをプレビューしたいという場合に備えて文書化されました。
+
+翻訳文を freeCodeCamp の `/learn` サイトでテストしたい場合は、まず [コードベースが設定済み](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) であることを確認してください。
+
+## 言語を有効にする
+
+コードベースをご希望の言語で構築するために、いくつかのステップがあります。
+
+まず、`config/i18n/all-langs.ts` ファイルにアクセスして、利用可能な言語リストに言語を追加し、値を設定します。 ここには 4 つのオブジェクトがあります。
+
+- `availableLangs`: `client` と `curriculum` 両方の配列で、言語のテキスト名を追加します。 これは `.env` ファイルで使用される値です。
+- `auditedCerts`: 言語のテキスト名を _key_ として追加し、`SuperBlocks.{cert}` 変数の配列を _value_ として追加します。 これは、クライアントにどの認定講座の翻訳が完了しているのかを伝えます。
+- `i18nextCodes`: これらは各言語の ISO の言語コードです。 有効にしようとしている言語に適切な ISO コードを追加する必要があります。 言語コードは、各言語に固有のものである必要があります。
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. ISO コードではなく、Unicode CLDR コードである必要があります。
+
+一例を挙げると、Dothraki という言語を有効にしたい場合、`all-langs.js` の各オブジェクトは次のようになります。
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+次に、`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts` ファイルを開きます。 このデータは、`/news` 記事を読み込む検索バーに使用されます。 この機能をテストする可能性は低いですが、 言語のデータがないと、ローカルでコードベースを構築しようとする際にエラーが発生する可能性があります。
+
+`algoliaIndices` オブジェクトに言語のオブジェクトを追加します。 You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] 既に対象言語でニュースのインスタンスをデプロイしている場合は、値を更新してライブインスタンスを反映することができます。 それ以外の場合は、英語の値を使用します。
+
+Dothraki を追加する場合は、次のとおりです。
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+最後に、`.env` ファイルの中で、`CLIENT_LOCALE` と `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` を新しい言語 (`availableLangs` 値を使用) に設定します。
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## ローカライズされた動画を有効にする
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## 翻訳内容を読み込む
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+テスト目的でローカルで翻訳を実行することもできますが、翻訳は GitHub を介して送信 _するのではなく_ 、Crowdin を介してのみ送信する必要があることをご承知おきください。 テストが終了したら、必ずローカルコードベースをリセットしてください。
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2b4c0e40
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp のリソースを翻訳する方法
+---
+
+## コントリビューションの心構え
+
+> freeCodeCamp ローカリゼーションのロードマップ – 進められるだけ進めてください。
+
+:::tip
+まず[こちらのお知らせ](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/)をお読みください。 [freeCodeCamp コミュニティのフォーラム](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3)や [Discord チャットサーバー](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) にも参加することをおすすめします。
+:::
+
+あなたはいつでも好きな時に、好きなだけ翻訳することができます。 あなたがボランティアの翻訳者として使える時間と労力がどれだけあるかだけの問題です。
+
+以下のことをご了承ください:
+
+1. **翻訳はチームでの活動です。**
+
+ freeCodeCamp のリソースの翻訳は、コントリビューターとして最も楽しくやりがいのある経験の一つであり、あなたと同じ言語を話す友人や同僚を巻き込むとよりうまくいくでしょう。
+
+ まず[こちらのお知らせ](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/)をお読みください。 実際の翻訳作業に入る前に、[freeCodeCamp コミュニティのフォーラム](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3)や [Discord チャットサーバー](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)に参加して、翻訳に参加したいことを仲間の翻訳者たちに伝えることを推奨します。 Crowdin などのツールによって貢献しやすくなっていますが、それでも翻訳は大変な作業です。
+
+ 私達はあなたが楽しんで貢献できること、燃え尽きたり興味を失ったりしないことを望んでいます。
+
+ ある言語の翻訳を始めるには 4、5 人の小さなグループで始めるのが良いでしょう。 その後、さらに多くの仲間を募集することもできます。
+
+2. **各言語ごとのサーバーを運用するには多くのコストがかかります。**
+
+ 表面的には複雑な技術スタックに見えないかもしれませんが、エンジンを動かし続けるにはかなりのコストがかかります。 これには追加のサーバーを準備することやスタッフをその管理に専念させることも含まれます。
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org はいつも通りこれらを無料で提供することをお約束しますが、最も必要としている人々に優先的にリソースを割り当てる必要があります。 私達が最も避けたいのは、翻訳の活動が停止して内容が古くなってしまい、その言語のサーバーをシャットダウンしなければならなくなることです。
+
+ カリキュラムの翻訳の場合、ある言語について少なくとも 2、3 の認定講座の翻訳が完了すれば、その言語を [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn) にデプロイし始めることができます。残りの認定講座の翻訳はそのまま続けられます。
+
+ 例えば、新しい言語を初めて公開するときには、少なくとも全てのフロントエンドの認定講座を揃えてデプロイしたいと考えています。
+
+3. **翻訳プラットフォームのリストにない言語はどうしたらいいですか?**
+
+ 私達はユーザー層を調査し、最も広く使われている言語を 30 以上翻訳プラットフォームに追加しました。 中国語、スペイン語などいくつかの言語はすでに **"/learn"** にデプロイされています。
+
+ 残念ながら、リストにない言語も多数あります。 コントリビューターの皆さんから、彼らの言語への翻訳を手伝いたいというリクエストが毎日たくさんあります。
+
+ もちろん更に多くの言語をリストに追加したいと思っていますが、ご想像の通り、その言語に十分な勢いがなければ実現できません。
+
+ 新しい言語を追加したい場合、あなたの友人を誘って興味を持ってもらうことをお勧めします。
+
+ 興味を持ってコミットできる少人数 (最低 4、5 人) のグループが集まったら、電話会議でお話させていただきます。 そこで詳細と、いくつかのツールやプロセスについてご説明します。
+
+## Crowdin の概要
+
+あなたが何語を話すかに関わらず、学習リソースを提供することが私達の夢です。 この大規模な取り組みのため、私達はオープンソースのコードおよびカリキュラムを、ローカライズ支援ツール [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) と一体化しました。
+
+> [!NOTE] [ニュース記事](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) の翻訳には別のツールとワークフローを使用します。 記事の翻訳に関心がある場合には、[こちらのお知らせ](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/)をお読みいただき、各言語の担当者 (ランゲージリード) までご連絡ください。
+
+翻訳のワークフローは大きく二つに分かれています。
+
+- カリキュラム、ドキュメント、UI 要素 (ボタン、ラベル等) の**翻訳**
+
+ [私達の翻訳プラットフォーム](https://translate.freecodecamp.org)にサインアップすると、翻訳者として 30 種類以上の言語の翻訳に貢献することができるようになります。
+
+- 上記全ての翻訳の**校正**
+
+ 校正者は、コミュニティによって提供された翻訳のトーンが統一されていること、誤字脱字等の一般的な問題がないことを確認します。 要するに、翻訳が高品質であることを保証します。 理由があって私達は機械翻訳を使用していません。
+
+> [!WARNING] 現在、GitHub を使用してファイルを直接翻訳することはなくなりました。以前コントリビューターだった方は、代わりに[翻訳プラットフォーム](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/)を使用してください。
+
+## はじめに
+
+まず、[Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)で挨拶をしましょう。 私達はここでリソースの翻訳に関する最新情報を投稿したり、多くの質問に答えたりしています。
+
+次に、私達の[翻訳プラットフォーム](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/)にアクセスし、ログインしてください (初めての場合、アカウントを作成する必要があります)。
+
+最後に、翻訳ツールとワークフローについて理解するため、以下の詳しい説明をお読みください。
+
+それでは翻訳をお楽しみください!
+
+## プロジェクトとファイルを選択する
+
+翻訳プラットフォームにアクセスすると、翻訳可能な「プロジェクト」が複数表示されます。
+
+1. [Contributing documentation](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs) プロジェクトには、このドキュメンテーションサイトのファイルが入っています。
+2. [Coding Curriculum](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum) プロジェクトには、カリキュラムのチャレンジのファイルが入っています。
+3. [Learn User Interface](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui) プロジェクトには、学習プラットフォームのボタン、ラベル等の UI 要素の文言が入っています。
+
+貢献したいプロジェクトを選択してください。翻訳可能な言語の一覧が表示されます。
+
+
+
+作業したい言語を選択すると、ファイル一覧がツリー状に表示されます。
+
+
+
+それぞれのファイル、フォルダに対しプログレスバーが表示されます。 プログレスバーの**青色**はファイルがどれだけ翻訳されたかを示しています。**緑色**は校正チームによってどれだけ承認されたかを示しています。
+
+作業するファイルを選択すると、Crowdin のエディター画面が表示されます。
+
+> [!NOTE] エディター画面を開いた後、設定アイコン (歯車のアイコン) をクリックし、「HTML tags displaying」の設定を「SHOW」に変更する必要があります。 この設定により、`<0></0>` ではなく `<code></code>` のようにタグが表示されます。
+
+## カリキュラムを翻訳する
+
+
+
+Crowdin はドキュメントを翻訳可能な文字列 (通常は文単位) に分割しています。 それぞれの文字列を個別に翻訳します。 上記の画像を参照してください。
+
+1. 緑でハイライトされた文字列は、既に翻訳案が提出されています。
+2. 赤でハイライトされた文字列は、まだ翻訳案が _ありません_ 。
+3. グレーアウトされている文字列は翻訳することができません。 これはコードブロックなど、翻訳すべきではない内容が該当します。 この文字列はエディター上で選択できません。
+4. 既にコントリビューターが翻訳を提案している場合、Crowdin はその翻訳案をこちらに表示します。 あなたは全く同じ翻訳案を保存することはできません。代わりに、翻訳内容が正確であれば `+` アイコンをクリックし、賛成票を投じてください。 不正確な翻訳の場合、`-` アイコンで反対票を投じることができます。
+5. Crowdin は Translation Memory (TM) もしくは Machine Translation (MT) に基づいて翻訳案を推薦します。 Translation Memory とは、他のファイルにおいて翻訳・承認された、類似または同一の文字列を指します。 Machine Translation とは、Crowdin の統合ライブラリーによって推薦された翻訳を指します。
+6. こちらがエディター領域です。選択した文字列に対する翻訳案を記述することができます。
+7. 現在エディター上で選択されている文字列は黄色でハイライトされます。
+8. こちらには文字列の状態を表すタグが表示されます。 `Done` は、文字列に対し少なくとも 1 つ翻訳案があることを意味します。 `Todo` は、文字列に対しまだ翻訳案がないことを意味します。
+9. こちらはコメントウィンドウです。 もし特定の文字列に対し疑問や懸念があれば、ここにコメントを残して他の翻訳者に見てもらうことができます。
+10. この 2 つのボタンで左側 (ドキュメント部分) と右側 (コメント部分) を隠すことができます。
+
+> [!NOTE] もし隠し文字列に翻訳が含まれているのを見つけたら、[Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) にてお知らせください。翻訳をメモリーから削除します。
+
+文字列の翻訳が終わったら、`Save` ボタンを押して翻訳を Crowdin に保存してください。 これで他のコントリビューターが翻訳内容に対し投票したり、校正者が承認したりできるようになります。
+
+翻訳を行う文字列の数に制限はありません。1 つのファイルをすべて翻訳し終わったあとや、新しい翻訳を提案する際に追加で必要になる手順もありません。 `Save` ボタンをクリックするだけで、翻訳を保存できます。
+
+> [!NOTE] もし英語の原文ファイルの中に不正確な内容を見つけた場合、それを翻訳で修正することはお控えください。 代わりに、不正確な点があることをその文字列に対するコメントでお知らせいただくか、GitHub issue を作成してください。
+
+## 学習プラットフォームの UI を翻訳する
+
+私達のサイト内 `/learn` の UI は、元となる JSON ファイルを i18n (多言語化) プラグインに読み込むことで翻訳されたテキストを生成しています。 この翻訳作業は Crowdin と GitHub に分かれています。
+
+### GitHub 上の作業
+
+`links.json`、`meta-tags.json`、`motivation.json`、`trending.json` のファイルには、言語に応じて変更されるべき内容が含まれます。 しかし、これらのファイルは Crowdin にアップロードすることができません。内容が翻訳と一対一で対応するようなものではないためです。
+
+これらのファイルは通常、各言語のランゲージリードが管理しますが、[翻訳方法の詳細を知りたい場合こちらでお読みいただけます](language-lead-handbook)。
+
+### Crowdin 上の作業
+
+:::danger
+以下のファイルは GitHub のプルリクエストで変更しないでください。
+:::
+
+`intro.json` と `translations.json` のファイルはどちらも Crowdin 上の Learn User Interface プロジェクトで翻訳します。 この作業では JSON の個々の値がその部分だけで文字列として表示され、文脈が分からないことが多いため、翻訳が難しい場合があります。
+
+しかし、Crowdin 上で `Context` として表示される情報を手掛かりに、その文字列がより大きな構造のどこに含まれるかを理解することができます。
+
+
+
+翻訳対象の文字列がどこで使われるかについて質問があれば、[コントリビューターチャット](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)にてお尋ねください。
+
+## ドキュメントを翻訳する
+
+コントリビューションドキュメントの翻訳も、カリキュラムのファイルの翻訳と同じような流れです。
+
+> [!NOTE] コントリビューションドキュメントは `docsify` によって提供されており、このようなメッセージボックス用に特別な構文解析機能があります。 `[!NOTE]`、`[!WARNING]` または `[!TIP]` などで始まる文字列を見かけたら、これらの単語は翻訳しないようにしてください。
+
+### 内部リンクのあるドキュメントの翻訳方法
+
+コントリビューションドキュメントを翻訳する際には、ドキュメント内の別のセクションをリンク先とする内部リンクに注意してください。
+
+必ず、リンク先セクションの id (`#` 以降の部分) を翻訳後のドキュメントの id に置き換えてください。 例えば、日本語の場合は以下のようになります。
+
+翻訳前
+
+```
+// HTML の場合
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// Markdown の場合
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+翻訳後
+
+```
+// HTML の場合
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// Markdown の場合
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト]($1#$2)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+ドキュメント内の実際のファイルは Markdown で書かれていますが、Crowdin では HTML タグとして表示されます。
+
+`docsify` があなたの言語の文字列をどのような id へと変換するかは、翻訳後のページを見て確認してください。 翻訳がまだデプロイされていない場合は、[ドキュメントサイトをローカルで実行]($1#$2)してプレビューできます。
+
+[ドキュメントの内部リンクについて詳しくはこちら]($1#$2)を参照してください。
+
+## LearnToCode RPG を翻訳する
+
+LearnToCode RPG は Ren'Py 上で動作します。Ren'Py では翻訳の際に独自の構文が使用されます ([Ren'Py の Text のドキュメント](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html) を参照してください)。
+
+- `""`で囲まれた文章が翻訳対象です。 ダイアログまたは UI (ユーザーインターフェース) 文字列です。 ダイアログの前後に表示されるキーワードは、ゲームエンジンを制御するキーワードです。詳細は後続のルールにて説明します。 このルールは、後続で説明する全ルールの基本であり、最も重要です。
+- `new "..."` のように表示される場合、接頭辞 `new` の部分はキーワードなので翻訳しないでください。
+- `player`、`annika`、`layla`、`marco` が先頭にて付く用語 (`player happy` や `player @ happy` などの複合形も含む) は、翻訳しないでください。 これらは、ゲーム内のキャラクターのスプライトを正しく表示し制御するためのキーワードです。
+- `nointeract` のような接尾辞も翻訳しないでください。
+- `[]` と `{}` で囲まれた部分は翻訳しないでください。 これらは補間機能とテキストタグです。 半角の `[]` と `{}` は翻訳文章にも残し、全角の `【】` や `「」`に置き換えることはしないでください。
+- 文末の `nointeract` キーワードは翻訳しないでください。
+- 全角括弧 `()`を使用しようとすると、品質保証に関する警告が表示されます。 品質保証に関する警告を避けるためには、半角括弧 `()` を使用してください。
+
+### 例
+
+---
+
+#### 翻訳前
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- こちらが翻訳を必要とする行です。 以下をご参照ください。
+```
+
+#### 翻訳後
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我们的VIP队友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}会很高兴的。"
+```
+
+注: `[]` と `{}` のタグは半角のまま残す必要があります。
+
+---
+
+#### 翻訳前
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- この行を翻訳します。以下をご参照ください。
+```
+
+#### 翻訳後
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳过"
+```
+
+注: 接頭辞 `new` と `{icon=icon-fast}` タグはそのまま残す必要があります。
+
+---
+
+#### 翻訳前
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### 翻訳後
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定会喜欢你的开发者工作的。"
+```
+
+注: `layla @ neutral` と `[player_name]` はそのまま残します。
+
+---
+
+#### 翻訳前
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### 翻訳後
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也许这都是一场梦?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Crowdin による文章の分割についての注意点
+
+Crowdin は引用符 (`""`) で囲まれたダイアログ行を分割することがあるため注意してください。 ダイアログを翻訳する際は、引用符の開始・終了が変更されていないことを確認する必要があります。引用符が別のセグメントに表示されたとしてもです。
+
+このような翻訳対象の行があったとします。
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin は以下のような 3 つのセグメントに分割します。
+
+<img width="836" alt="スクリーンショット 2022-01-23 (10 36 43)" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# 原文
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# 訳文。引用符の開始側 `"` はそのままにする
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="スクリーンショット 2022-01-23 (10 36 49)" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# 原文
+What is that?
+# 訳文。引用符はなし
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="スクリーンショット 2022-01-23 (10 36 54)" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# 原文
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# 訳文。引用符の終了側 `"` はそのままにする
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## 翻訳を評価する
+
+Crowdin では投稿済みの翻訳案を評価することができます。 翻訳内容を保存しようとした際、同じ翻訳は保存できないというメッセージが表示されることがあります。これは、すでに他のコントリビューターが全く同じ翻訳を提案していることを意味しています。 既存の翻訳に賛成であれば `+` ボタンをクリックして賛成票を投じてください。
+
+もし、翻訳が不正確であったり、原文の意味が正しく翻訳されていない翻訳を発見した場合は、`-` ボタンをクリックして反対票を投じて下さい。
+
+Crowdin はそれらの投票結果を元に各翻訳案の点数を算出します。この点数は校正チームが最適な翻訳文を選ぶための判断材料となります。
+
+## 品質保証チェック
+
+翻訳内容が可能な限り正確であることを確認し、校正チームによる翻訳文レビューに役立てるため、品質保証ステップを設けています。
+
+翻訳内容を保存しようとする際、翻訳内容に対する警告文が表示されることがあります。
+
+
+
+このメッセージは、Crowdin の品質保証システムが投稿内容に間違いが含まれている可能性があると判断した場合に表示されます。 上の例では `<code>` タグ内のテキストが変更されており、Crowdin がそれを検出しました。
+
+> [!WARNING] エラーが検出されても翻訳内容を保存することは可能です。 「Save Anyway」をクリックして保存できますが、その場合は校正者かプロジェクトマネージャー宛てにコメントし、なぜ品質保証メッセージを無視する必要があったかを説明するようにしてください。
+
+## 翻訳のベストプラクティス
+
+翻訳をできる限り正確なものとするため、以下のガイドラインに従って下さい。
+
+- `<code>` タグの中身を翻訳しないでください。 これらのタグはコードの一部であり、英語のまま残しておかなければなりません。
+- コンテンツを追加しないで下さい。 チャレンジを翻訳する際、テキスト内容の変更や追加の情報が必要だと感じた場合は、GitHub Issue を通して提案するか、提案内容を反映した英語のファイルをプルリクエストして下さい。
+- コンテンツの順番を変えないで下さい。
+
+質問があれば、[Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) にてお気軽にお尋ねください。喜んでサポートいたします。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ba187156
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Windows Home で Docker を使用する方法
+---
+
+Windows Home で Docker を設定する際に避けるべき落とし穴がいくつかあります。 まず、[Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) を管理者として使用する必要があります。 残念ながら、Windows Home は Docker for Windows Desktop をサポートしていないため、代わりに Toolbox を使用する必要があります。 インストールでシンボリックリンクを使用するため、管理者として実行する必要があります。
+
+Toolbox をインストールしたら、管理者として Docker Quickstart Terminal を実行します。 既存の仮想マシンが存在しない場合は、`default` 仮想マシンが作成されます その後、ターミナルを閉じて (再び管理者として) VirtualBox を開きます。 `default` マシンが表示されます。 サイトはかなりリソースが多いので、仮想マシンを停止し、できるだけメモリの容量を増やしてください。 It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Docker が正常に動作していることを確認したら、freeCodeCamp リポジトリを `C:\Users` 内のディレクトリにクローンします。 これらのディレクトリは共有され、インストール中に必要なローカルディレクトリに Docker アクセスを提供します。
+
+次のようなメッセージが表示される場合
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+when you `pnpm run docker:init` this is likely the culprit.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8d49e9a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: コーディングチャレンジに貢献する方法
+---
+
+私たちの目標は、楽しく明確なインタラクティブ学習体験を開発することです。
+
+インタラクティブなコーディングチャレンジの設計は難しいです。 長い説明を書いたり、ビデオチュートリアルを作成したりする方がはるかに簡単です。 しかし、私たちのコアカリキュラムは、多くの人にとって最適なものに固執しています。完全にインタラクティブでビデオゲームのような体験です。
+
+私たちはキャンパーにフロー状態を体験してほしいのです。 勢いをつけて大きな支障なくカリキュラムを突破してほしいと思っています。 We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+freeCodeCamp カリキュラムのバージョン 7.0 では、[多くの繰り返しを伴うプロジェクトに焦点を当てたモデル](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/) に移行しています。
+
+これらのチャレンジを生み出すには、大きな創造性と細部へのこだわりが必要です。 たくさんの助けを得ることができます。 アイデアを出し合ったりチャレンジを実演したりできる貢献者チーム全体がサポートしてくれます。
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+皆さんのご支援により、今後何百万もの人々がコーディングを学ぶのに役立つインタラクティブなコーディングカリキュラムを設計することができます。
+
+各チャレンジのコンテンツは、マークダウンファイルに保存されます。 このマークダウンファイルは、インタラクティブな Web ページを作成するためのツールを使用して、後で HTML に変換されます。
+
+[`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges) ディレクトリに、freeCodeCamp.org のカリキュラムコンテンツのすべてがあります。
+
+## カリキュラムのツールを設定する
+
+カリキュラムを作成する前に、変更をテストするためのツールを設定する必要があります。 以下から任意のオプションを使用できます。
+
+- [freeCodeCamp をローカル設定](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) することができます。 これは定期的 / 繰り返しの貢献に **強く推奨** します。 このセットアップで、作業と変更テストができます。
+- 無料のオンライン開発環境である Gitpod を使用します。 下のボタンをクリックすると、ブラウザで freeCodeCamp のコーディング開発準備ができている環境が起動されます。 かかる時間はほんの数分です。
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### プラクティスプロジェクトに貢献する方法
+
+プラクティスプロジェクトには、新しいプロジェクトやステップの作成に役立つ追加ツールがあります。 詳細については、[これらのドキュメント](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) をご参照ください。
+
+## チャレンジテンプレート
+
+````md
+---
+id: ユニーク ID (アルファベットと数字の MongoDB_id)
+title: 'チャレンジのタイトル'
+challengeType: `client/utils/challenge-types.js` に定義されている整数
+videoUrl: '説明動画のURL'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+チャレンジの説明 (マークダウンで記入)
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+チャレンジの指示内容 (マークダウンで記入)
+
+# --hints--
+
+ユーザコードに対して実行するテスト。マークダウンテキストと、テストコードのコードブロックをペアにして記入。
+
+```js
+Code for test one
+```
+
+ユーザーのコードに基づいて動的な出力が必要な場合、--fcc-expected-- と --fcc-actual-- は、テストのアサーションの期待値と実際の値に置き換えられます。 最初のアサーションの失敗により --fcc-expected-- と --fcc-actual-- の値が決まるので、複数のアサーションがある場合は注意してください。
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+チャレンジの追加情報 (マークダウンで記入)
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+ユーザーコードの前に評価されるコード。
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+ユーザーコードの後およびテスト直前に評価されるコード。
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+エディターにレンダリングするボイラープレートコード。 このセクションには、以下のようなバックティック内のコードのみを含める必要があります。
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+ソリューションは、ヒントの変更が意図した通りに合格するようにするために CI テストに使用されます。
+
+```js
+// 最初のソリューション - 言語はシードに一致する必要があります。
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// 2 番目のソリューション - シードが HTML で書かれている場合...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// 3番目のソリューション等 - ソリューションは HTML でなければなりません。
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. 上記セクションで、`lang` の例は、次のとおりです。
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## チャレンジの採番
+
+すべてのチャレンジには `id` が必要です。 指定されていない場合、MongoDB はデータを保存する際に新しいランダムな id を作成します。しかしながら、チャレンジ id を異なる環境 (ステージング、本番環境、多くの様々な開発者など) において一貫性のあるものにしたいので、ランダムなものは作成したくありません。
+
+シェル内で新しい id を生成するには、次のとおり実行します (MongoDB は別途実行されていると仮定)。
+
+1. `mongo` コマンドを実行します。
+2. `ObjectId()` コマンドを実行します。
+
+例:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Challenge Title
+```
+
+## チャレンジ名の決定
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Padding of an Element
+- Condense arrays with .reduce
+- Use Bracket Notation to Find the First Character in a String
+
+## チャレンジの説明 / 指示
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (「J」と「S」が大文字、省略形なし)
+- Node.js
+- 不正確な場合もありますが、より広く使われているため、ハイフンなしの 'back end' と 'front end' を使用します。
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- チャレンジを簡素化する
+- チャレンジを 2 つのチャレンジに分ける
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- 言語キーワードは `` \` `` のバックティックに入ります。 例えば、HTML タグ名や CSS プロパティ名です。
+- コード部品 (すなわち、関数、メソッド、変数名) への参照は、`` \` `` バックティックで囲みます。 下記の例を参照してください。
+
+```md
+変数 `realNumber` を整数に変換するには、`parseInt` を使用します。
+```
+
+- ファイル名とパスディレクトリへの参照 (例: `package.json`、`src/components`) は `` \` `` バックティックで囲みます。
+- 複数行コードブロック **の前に空行** が必要です。 次の行は、3 つのバックティックに続いて [対応言語](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages) の 1 つで始まります。 To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. 下記の例を参照してください。
+- 空白はマークダウンでも重要ですので、エディターで表示させることをお勧めします。
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[ここに、コードを記述してください]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- 注意書き形式の追加情報は空白行で囲みます。例: `**Note:** Rest of note text...`
+- 複数の注意書きが必要な場合は、すべての注意書きを別々の文章でリスト化します。例: `**Notes:** First note text. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## テストの記述
+
+チャレンジには、キャンパーがコンセプトを理解していることを確認するために最小限のテストが必要です。
+
+私たちの目標は、チャレンジが教えようとしている単一のポイントを伝え、そのポイントを理解していることをテストすることです。
+
+チャレンジテストでは、Node.js と Chai.js アサーションライブラリを使用できます。 また、必要に応じて、`code` 変数からユーザーが生成したコードにアクセスすることもできます。 さらに、 `__helpers` オブジェクトは、テストを記述するプロセスを簡略化するいくつかの関数を公開します。 The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. 辞書のコメントに記載されている正確な大文字と小文字の区別および語間を使用します。 コメント辞書は、開発チームとの事前議論なしに増やしてはいけません。
+
+使用するコメントは、コメント文字とコメントそのものの間にスペースを入れる必要があります。 一般的に、コメントは控えめに使用します。 シードコードコメントの使用を避けられるのであれば、チャレンジの説明や指示を書き換えることを常に検討してください。
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // この行より下にあるコードを変更してください。
+
+ // この行より上にあるコードを変更してください。
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Change code below this line */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Change code above this line */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+この行の下に myGlobal 変数を宣言してください。
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 現在、コメント辞書の i18n 作業ができるようにするためのインテグレーションに取り組んでいます。
+
+## ヒントとソリューション
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. 新しいトピックの作成と同じ手順からスタートします。タイトルを作成するために以下を確認します。
+2. トピックのタイトルは、`freeCodeCamp チャレンジガイド:` にカリキュラムチャレンジの実際のタイトルを連結します。 例えば、チャレンジに「`Chunky Monkey`」という名前が付けられている場合、トピックのタイトルは、「`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`」になります。
+3. `camperbot` はトピック / 投稿のオーナーである必要があるので、管理者に、メイン投稿のオーナーを `camperbot` に変更するようにリクエストします。
+4. 新しいトピックを作成すると、フォーラムのトピック id が作成されます。 これは、フォーラムのトピック URL の末尾にあります。 この id は、トピックにリンクするために、`ヒントを入手` ボタン用の標準プルリクエストプロセスを介して、カリキュラムチャレンジファイルのフロントマターに追加する必要があります。
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# ここにチャレンジ名を記述します。
+
+---
+
+## 問題説明
+
+チャレンジの説明や指示を再記述するのではなく、実行すべきことを要約します。 ここは任意のセクションです。
+
+#### 関連リンク
+
+- [リンクテキスト](link_url_goes_here)
+- [リンクテキスト](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## ヒント
+
+### ヒント 1
+
+ヒントを記述
+
+### ヒント 2
+
+ヒントを記述
+
+---
+
+## ソリューション
+
+<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### コードの説明
+
+- コードの説明を記述
+- コードの説明を記述
+
+#### 関連リンク
+
+- [リンクテキスト](link_url_goes_here)
+- [リンクテキスト](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## チャレンジのテスト
+
+変更のために [プルリクエストを作成する](how-to-open-a-pull-request) 前に、行った変更が誤ってチャレンジに問題を引き起こさないことを確認する必要があります。
+
+1. すべてのチャレンジをテストするには、ルートディレクトリから以下のコマンドを実行してください。
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..be23b50b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) と [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/) を使用して、様々な世界の言語に翻訳されています。
+
+開発用クライアントアプリケーションのローカル設定については、こちらの [ローカル設定ガイド](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)をご覧ください。 By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+これは、ローカライゼーションを含むものを対象にし、例えば別の言語でボタンラベルを検証する必要がある機能に関して作業している場合に役立ちます。
+
+:::tip
+You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. 代わりに、[このガイド](how-to-translate-files) をお読みください。
+:::
+
+i18n フレームワークとツールがどのように機能するかを理解しましょう。
+
+## ファイル構成
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**翻訳プラットフォーム上で翻訳されたファイル:**
+
+- `translations.json` ファイルは、ユーザーインターフェース要素に表示されるテキストの大部分を含んでいます。 キーは、設定されるすべての言語で正しいテキストが取得できるように、コードベースで使用されます。 This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- `intro.json` ファイルには、認定講座ページの紹介テキスト用に、キーと値のペアが含まれています。
+
+ キーの翻訳を追加 / 更新したい場合は、[こちらのガイド](how-to-translate-files) をご覧ください。
+
+**翻訳プラットフォーム上で翻訳されていないファイル:**
+
+- `motivation.json` ファイルは、同じ引用符、賛辞、配列の長さを含む必要はありません。 JSON 構造だけは同じです。
+
+- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
+
+ Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+新しい言語をテストするには、言語名をタイトルとしたフォルダを他の言語の隣に作成し、JSON ファイルを別の言語から新しいフォルダにコピーします。
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+次に、同じファイルのコメント指示に従って、必要に応じて残りの変数を追加 / 更新します。
+
+Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the string of the locale you want to build from the `Languages` enum in the above file.
+
+## コンポーネントの構築方法
+
+クライアント Web アプリの機能やバグの作業をしていて、例えば、設定ページに新しい UI アイテムを追加する場合は、以下のガイドラインに従ってください。 これらは、サポートされている世界言語へのローカライゼーションで、コンポーネントを準備するのに役立ちます。
+
+### 関数コンポーネント
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// in the render method:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // more details below
+```
+
+### クラスコンポーネント
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation adds the "t" function to props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // more details below
+
+// export without redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// or with redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## 「t」関数を使って翻訳する
+
+### 基本的な翻訳
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### 動的データの使用
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+上の例では、 `username` 変数を使用して `t` 関数にオブジェクトを渡します。 変数は、`{{username}}` の JSON 値で使用されます。
+
+## `Trans` コンポーネントを使用した翻訳
+
+一般的なルールは、「t」関数を使うことです。 しかし、それだけでは不十分な場合のための `Trans` コンポーネントがあります。通常、テキストに要素が埋め込まれている場合に使用されます。 どんな型の React コンポーネントでも `Trans` コンポーネントを使用できます。
+
+### ネストされた基本要素
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`、`strong`、`i`、および `p` がデフォルトですが、そのリストは、i18n config で拡張できます。
+
+### ネストされた複雑な要素
+
+別の要素内に特定のテキストを持たせたい場合、アンカータグが良い例です。
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+上記の例では、キーは `Trans` コンポーネントの属性に設定されています。 JSON の `<0>` と `</0>` はコンポーネントの最初の子要素を表します。 この場合、アンカー要素です。 もっと多くの子要素がある場合、同じ構文を使ってそこから数えるだけです。 React 開発ツールで調べることにより、コンポーネントの子要素を見つけることができます。 `placeholder` は単にそこにあるだけです。なぜなら、リンターが空の `<a>` 要素について不平を言うからです。
+
+### 変数の使用
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+上記の例では、キーと変数は `Trans` コンポーネントの属性に設定されています。 `{{ email }}` は、`Trans` コンポーネントのどこかにある必要がありますが、どこであっても問題はありません。
+
+## テキストの変更
+
+クライアント側でテキストを変更するには、関連する `.json ` ファイルで、React コンポーネントで使用されているキーを見つけて、値を新しいテキストに変更します。 そのキーが他の場所で使用されていないことを確認するために、コードベースを検索する必要があります。 他の場所で使用されていた場合、そのすべての場所で変更が実行されます。
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## テキストの追加
+
+クライアントに追加するテキストが、関連する `.json` ファイルに存在する場合は、既存のキーを使用します。 それ以外の場合は、新しいキーを作成します。
+
+英語ファイルは、同じ名前を共有する `.json` ファイルすべてにとって、「真実を語る資料」です。 新しいキーを追加する必要がある場合は、そこに追加します。 そして、そのキーを **すべて** の `translations.json` ファイルに追加します。
+
+> [!NOTE] ファイルが Crowdin で翻訳されている場合は、すべての言語に英語のテキストを使用してください。 そうしないと、テストは失敗します。
+
+すべてのファイルで、キーを同じ順序に保つことをお勧めします。 Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. 使用方法については、 [ドキュメント](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) を参照してください。
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [react-i18next docs](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [i18next docs](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..58592a81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: プラクティスプロジェクトに貢献する
+---
+
+Our practice projects use a step-based approach to teach concepts to campers. A project will consist of multiple files, which we refer to as **"steps"**. These files are named by the challenge ID, to avoid issues with the translation flow. Unfortunately, this makes it difficult to find the file associated with a specific step.
+
+We've built a challenge editor tool that helps remedy this. This tool allows you to navigate the available projects, and the steps for each project (in order). There's also an embedded code editor you can use to work on the files directly.
+
+## Using the Challenge Editor
+
+These instructions will tell you how to use our challenge editor tool to work on the practice projects.
+
+### Starting the Editor
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Then, run `pnpm run challenge-editor` to start both the client and the API that powers the editor.
+
+The client will run on port `3300`, so you can access it at `http://localhost:3300`. The API runs on port `3200`, to avoid conflicts with the learn client and server. This will allow you to run the freeCodeCamp application at the same time as the editor, so you can test your changes locally.
+
+### Navigating the Editor
+
+The default view will list the available `superblocks` - these are the certifications. Click on the certification link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to the list of blocks. These are the practice projects. Click on the project link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to a list of steps for the project. If you are working on an existing step, you can click on the step link to open the editor. If you are adding or removing steps, click the `Use the step tools` link to switch to the step tools for that challenge.
+
+### Editing Steps
+
+When you click on a step, you'll be taken to the editor. This is a basic text editor that offers syntax highlighting.
+
+After you have made your changes, click the `Save Changes` button to save your changes. You will get a browser alert letting you know that your changes are ready to commit. Note that you'll need to use `git` manually to stage and commit your files - this tool will not do that for you.
+
+### Step Tools
+
+When you click the `Use the step tools` link, you'll be taken to the step tools page. This allows you to add or remove steps from the project.
+
+#### Create Next Step
+
+Clicking this button will add a new step at the end of the project. This step will use the previous step's code as the seed.
+
+#### Create Empty Steps
+
+Enter the number of steps you want to add in the input. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Insert Step
+
+Enter the step number that you want to add. Then, click the `Insert Step` button to add the step. The following steps will be re-ordered.
+
+#### Delete Step
+
+Enter the step number you want to delete. Then click the `Delete Step` button to remove that step. This will automatically update the step numbers for the remaining steps.
+
+#### Update Step Titles
+
+You should not have to use this tool unless you've manually deleted or added steps. This tool will reorder the step numbers.
+
+## Using the Scripts Manually
+
+If you want to work on the steps manually, in your local IDE, you can run the step management scripts directly.
+
+The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step in the project. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. プロジェクトのディレクトリに変更します。
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. プロジェクトのディレクトリに変更します。
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # where X is the number of steps to create.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a new step at a specified position, incrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json). The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. プロジェクトのディレクトリに変更します。
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # where X is the position to insert the new step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+A one-off script that deletes an existing step, decrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json)
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. プロジェクトのディレクトリに変更します。
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # where X is the step number to be deleted.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+A one-off script that automatically updates the frontmatter in a project's markdown files so that they are consistent with the project's meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. プロジェクトのディレクトリに変更します。
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed433453
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on the Component Library
+---
+
+Welcome to freeCodeCamp's `ui-components` library. The components are built mostly from scratch with basic HTML elements and [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp has been using Bootstrap components in the UI. However, we are moving away from it and building our own component library, which helps standardize our UX/UI patterns and improve accessibility. The project is tracked in [this GitHub issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+The following steps are recommended when working on a new component:
+
+- Research and planning
+- Implement the component
+- Display the use cases on Storybook
+- Write unit tests
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Before building a component, you need to research and document on how the existing version behaves and looks, to ensure that the new one has matching styles and supports all the current usages. In order to meet the web accessibility requirements, you should also pay attention to the accessibility aspect of the component, see which HTML elements and ARIA attributes are used under the hood.
+
+Once you have gathered enough information about the component, you can start thinking about the props interface. Ideally, the interface should be as similar to the current version as possible, to ease the adoption later on. Since we are using Bootstrap components, the simplest approach is to mimic [their implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+We prefer smaller pull requests rather than a large one, because they speed up the review time and reduce cognitive overload for the reviewers. For that reason, you should think about how you would break down the implementation and come up with a delivery plan.
+
+We recommend opening a separate GitHub issue for each component and include all the notes in the issue description. It can be used as a place to host all of your working notes, as well as a way to communicate the approach with the reviewers. We will use the issue thread for further discussion if needed. [The issue for Button component](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) can be used as a reference.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+A new component can be created using the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+The command will generate a new folder inside the `ui-components` directory, with the following files:
+
+| File name | Purpose |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | It is used for exporting the component and its types. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | It is used for demoing the component on Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | It is a test file. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | It is where we implement the component. |
+| `types.ts` | It is where we locate the component's interface and types. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Support forwarding ref
+- Be styled for both light and dark themes
+- Be styled internally based on their props (the consumers should not need to restyle the component with the `className` prop)
+- Utilize the built-in styling system from Tailwind instead of having custom styles
+
+### Using Colors
+
+There are two color "layers" in the component library:
+
+- The base layer, where the color names describe what the colors are, e.g. `gray00`, `blue50`
+- The semantic layer, where the color names describe what the colors are for, e.g. `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. There are exceptions, however, specifically when you are styling the component's states such as hover, active, disabled, etc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+> [!NOTE] Color definition can be found in the [`colors.css` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). A color is only available for use if it is added to the [`tailwind.config.js` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) under the `colors` property.
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Tailwind CSS Configuration](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [React Bootstrap v0.33 Docs](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Bootstrap 3.3.7 stylesheet](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [React Bootstrap current implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [React Bootstrap current tests](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Use cases of the component should be added to the Storybook file (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+To start Storybook, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+The Storybook page is available on [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+We use [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) to write unit tests. The tests should assert that the components behave as expected and are accessible.
+
+To run tests against the component library, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Testing for Accessibility](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Order of priority of React Testing Library's queries](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Common mistakes with React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d08f1368
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+コントリビューションガイドラインを編集するには、`docs` [ディレクトリ](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs) のファイルを編集または追加します。 When your changes are merged, they will be made available automatically at the documentation site.
+
+When adding a new file to the `docs` directory, you should evaluate if the file should also be added to the sidebar navigation. We typically create a link in the [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) file for new and independent guides. Alternatively, You may follow the instructions below on creating an internal link for supporting guides.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+If you want to create a link targeting a different section of the contributing guidelines, follow this format:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// リンク先セクションが同じページ内にある場合、ファイル名を省略できます
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Make sure you include the file extension (`.md`). Don't specify the full URL or append `/` before the file name.
+
+This is necessary to make these links work for the translated version of the document. Otherwise, they will redirect to the English version of the page regardless of the language.
+
+#### 内部リンクのあるドキュメントを翻訳する
+
+When you work on translating docs on Crowdin, make sure to replace the `#target-section-heading-id` with the id on the translated document. [Learn more about translating docs here](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+> [!NOTE] A quick reminder that you do not need to set up anything for working on the content for the documentation site.
+>
+> コントリビューションガイドラインを編集するには、[ドキュメントの内容に貢献する](#ドキュメントの内容に貢献する) セクションを参照してください。
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+The site is generated using [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) and served using GitHub pages.
+
+Typically you would not need to change any configuration or build the site locally. In case you are interested, here is how it works:
+
+- このサイト向けのホームページのソースは、[`docs/index.html`](index.html) にあります。
+- `docsify` と GitHub Pages を使用して、このファイルを SPA として提供します。
+- The `docsify` script generates the content of `markdown` files in the `docs` directory on demand.
+- ホームページは [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage) から生成されます。
+- The sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..15488410
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp.org の開発者ニュースのテーマに貢献する方法
+---
+
+開発者ニュースは [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) サイトとも呼ばれ、[Ghost](https://ghost.org/) によって提供されます。 サイトのルックアンドフィールにカスタムテーマを使用しています。 テーマのソースコードは <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme> です。
+
+## テーマ
+
+Ghost は、テーマに [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) と呼ばれる単純なテンプレート言語を使用します。 `/news` で使用されるテーマは、デフォルトの [casper テーマ](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper) に基づいています。
+
+デフォルトのテーマには多くのコメントがあるので、コードやコメントを読むだけで何が起こっているのかを簡単に把握できます。 どのように動作するかを理解したら、 [テーマ API ドキュメント](https://themes.ghost.org) で、Handlebars ヘルパーとテンプレートの詳細をお読みください。
+
+**主なファイルは次のとおりです。**
+
+- `default.hbs` - メインテンプレートファイル
+- `index.hbs` - ホームページに使用
+- `post.hbs` - 個々の投稿に使用
+- `page.hbs` - 個々のページに使用
+- `tag.hbs` - タグアーカイブに使用
+- `author.hbs` - 著者アーカイブに使用
+
+1 つの巧妙なトリックは、テンプレートファイルにページのスラグを追加するだけで、カスタムのワンオフテンプレートを作成することもできることです。 例:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - `/about/` ページのカスタムテンプレート
+- `tag-news.hbs` - `/tag/news/` アーカイブのカスタムテンプレート
+- `author-ali.hbs` - `/author/ali/` アーカイブのカスタムテンプレート
+
+## 開発
+
+1. ゴーストをローカルにインストールします。
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > 注: freeCodeCamp は現在、バージョン `2.9.0` を使用しているため、それ以降のバージョンであることを確認してください。
+
+ `ghost-local-site` ディレクトリから `ghost` コマンドを実行します。 インターフェースに慣れていない場合は、[Ghost 公式ドキュメント](https://docs.ghost.org) の追加指示に従ってください。
+
+2. テーマディレクトリにあるリポジトリをフォークしてクローンします ( `YOUR_USERNAME` を GitHub ユーザー名に置き換えてください)。
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. 前提条件がすべて揃っていることを確認します。
+
+ テーマのスタイルは Gulp/PostCSS を使用してコンパイルされ、将来の CSS 仕様をポリフィルします。 [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/) が必要です。 Node.js のバージョンが `ghost` と互換性があることを確認してください。
+
+4. 依存関係をインストールしてテーマを開発します。
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. これで `/assets/css/` ファイルを編集できるようになりました。これは `/assets/built/` に自動的にコンパイルされます。
+
+6. 開発サイトにアクセスします。
+
+ a. アドレスバーに `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` を入力します。 ページに表示されたセットアップを続行します (ghost の初回実行時)。
+
+ b. _(セットアップ時に一度だけ)_ テーマが利用可能であることを確認するために、別の端末で Ghost を再起動します。
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(セットアップ時に一度だけ)_ これが完了したら、 `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` に行き、一番下までスクロールします。 `freecodecamp-news-theme` をクリックしてアクティブ化します。
+
+7. 最終コードを Zip してプルリクエストを作成します。
+
+ `zip` Gulp タスクは、テーマファイルを `dist/<theme-name>.zip` にパッケージ化し、本番サイトにアップロードできるようにします。
+
+ PR を行う場合は、コードをコミットして PR を送信する前に、以下のスクリプトを実行していることを確認してください。
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## その他の参照とリソース
+
+### PostCSS 機能の使用
+
+- Autoprefixer - あらゆる種類のブラウザのプレフィックスも書く必要がありません。すべてのブラウザにおいて、最新の 2 つのメジャーバージョンをサポートして自動的に行われます。
+- 変数 - シンプルな純粋な CSS 変数
+- [カラー関数](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### SVG アイコン
+
+このテーマは、Handlebars パーシャルを介して組み込まれたインライン SVG アイコンを使用しています。 すべてのアイコンは `/partials/icons` 内にあります。 アイコンを使用するには、関連ファイルの名前を含めます。例えば、 SVG アイコンを `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` に含めるには、`{{> "icons/rss"}}`を使用します。
+
+独自の SVG アイコンを同じ方法で追加できます。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4c371870
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+このページでは、CodeRoad VS Code 拡張機能を使用して作成された freeCodeCamp チュートリアルやプロジェクトに貢献する方法を説明します。
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. それらはすべて `learn-` から始まります。 例えば、`https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/` です。
+
+各チュートリアルリポジトリには、`main` ブランチと「バージョン」ブランチがあります。例えば、 `v1.0.0` です。
+
+`main` ブランチには、`TUTORIAL.md` と `coderoad.yaml` 2 つのメインファイルがあります。 `TUTORIAL.md` には、チュートリアルのすべての手順、ヒント、タイトルなどが含まれています。 `coderoad.yaml` には、どのコマンドを実行するか、どのファイルの変更を監視するか、どのブランチバージョンをステップに使用するかなど CodeRoad に対する指示が含まれています。
+
+「バージョン」ブランチには、チュートリアルの各ステップにロードされるコミットが含まれています。 このブランチのコミットメッセージは特定のものでなければなりません。 最初のコミットには、メッセージに `INIT` が必要であり、初回レッスン前にロードするファイルがすべて含まれています。
+
+後続のコミットメッセージは、`main` ブランチの `TUTORIAL.md` のステップ数と一致する必要があります。 例えば、ユーザーがステップ `10.1` に行くと、メッセージ `10.1` を含むコミットがロードされます。
+
+バージョンブランチでコミットに変更を加えるには、変更したいコミットをリベースして編集する必要があります。 これにより Git の履歴が書き換えられるので、これらの種類のブランチには PR を受け入れられません。 バージョンブランチが freeCodeCamp リポジトリ上にある場合は、変更しないでください。
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp リポジトリにあるバージョンブランチに、変更を加えたりプッシュしたりしないでください。 常に新しいものを作成してください。
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### 必要条件
+
+[CodeRoad CLI ツール](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) を `npm install -g @coderoad/cli` でインストールします。
+
+最新バージョンにはいくつかの問題があります。 `coderoad --version` がインストール後に動作しない場合は、`npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0` を使用して `0.7.0` にダウングレードしてください。
+
+### `main` に貢献する
+
+この一連の手順は、`main` で **既存のレッスン** に軽微な変更を加える PR のためのものです。 これは主に `TUTORIAL.md` ファイルのタイプミス、文法、ヒント、指示の変更または修正で構成されています。
+
+レッスンの追加や削除を含むその他すべてについては、[バージョンブランチの手順](#working-on-version-branch) に従ってください。 このために新しいバージョンブランチを作成する必要はありません。以下の手順に従って PR を作成できます。
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> これらの変更には既存のバージョンブランチを使用します。 相当量のものであれば、自由に `CHANGELOG.md` に追加してください。 ほとんどの場合、良いコミットメッセージで動作するはずです。
+
+`tutorial.json` ファイルを直接変更する必要はありません。 これは、CLI ツールで作成されます。
+
+タイプミスや文法上のエラー修正等の軽微な変更の場合は、その変更をテストする必要はありません。
+
+以下の手順に従って PR を作成します。この手順は、通常、周りのレッスンをコンテキストに使用していることを覚えておいてください。
+
+- `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` を使用して、最新バージョンのブランチのコピーを作成します。このブランチをチェックする必要はありませんが、存在している必要があります。
+- `main` の新しいブランチを作成してチェックアウトします。
+- 変更を行い **コミット** します。 注意: `tutorial.json` ファイルを変更する必要はありません。 `TUTORIAL.md` に変更を加える必要があります。
+- `coderoad build` を実行して、`tutorial.json` ファイルを再作成します。
+- `update json` でメッセージとして変更をコミットします。
+- PR を作成します。
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+上記手順の後、`main` の変更をテストしたい場合は、次の手順に従います。
+
+- [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) の手順に従ってコンテナを実行します。
+- 新しいブランチの `tutorial.json` ファイルを使用してチュートリアルを開始します。
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+上述のように、指示もしくは文法問題に関わる `main` のみを変更する PR をレビューする場合、`TUTORIAL.md` の変更は、`tutorial.json` の変更と一致する必要があります。
+
+`tutorial.json` ファイルには、コミットハッシュやステップ / レベル ID の変更を含めないでください。 起動コマンドや、レベルコマンド、ファイルウォッチャーも変更すべきではありません。 例外はありますが、ステップに問題があれば、注意深く処理する必要があります。
+
+通常、周りのレッスンをコンテキストに使用していることを覚えておいてください。指示が理にかなっていることを確認してください。
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 注: freeCodeCamp リポジトリにあるバージョンブランチに、変更を加えたりプッシュしたりしないでください。 常に新しいものを作成してください。
+
+Git の履歴が書き換えられるため、バージョンブランチ間で何が変更されたかを簡単に確認する方法はありません。 新しいバージョンブランチの使用を承諾するには、慎重な検討とテストが必要です。
+
+これらの手順は、テスト、テストテキスト、ファイルのリセット、ステップの追加や削除など、「バージョン」ブランチを変更するためのものです。
+
+新しいバージョンを作成するには、次の手順に従います。
+
+- **最新の** バージョンブランチを `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` でチェックアウトします。
+- `git checkout -b vX.X.Y` で、そこから新しいブランチを作成し、バージョンをインクリメントします。
+- バージョンブランチを変更します。 チュートリアルの使い方については、[CodeRoad ドキュメント](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) を参照します。
+- `git push -u origin vX.X.Y` で、新しいブランチをフォークにプッシュします。
+- `main` ブランチをチェックアウトします。
+- `main` から新しいブランチを作成します。 例: `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- `coderoad.yaml` の `uri` をリポジトリのフォークに変更します。 これにより、あなたとレビュアーが freeCodeCamp リポジトリにプッシュする前に、テストできるようになります。 バージョンを、そのファイルの 2 つのスポットにある新しいブランチに変更します。 新しいバージョンの変更を `CHANGELOG.md` に追加します。 その他必要な変更を行います。
+- メッセージ `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>` で、変更をコミットします。
+- `coderoad build` を実行して、新しい `tutorial.json` ファイルを作成します。
+- ファイルを追加してコミットします。
+- フォークに変更をプッシュします。
+- 以下の [テスト手順](#バージョンブランチの変更をテストする) に従って変更をテストします。 追加の変更を行い、先ほどと同様にコミットします。追加の変更がなければ、残りの手順に進みます。
+- 新しい `feat/version-X.X.Y` ブランチを使用して `main` に PR を作成します。 `version X.X.Y ready for review` のタイトルを付けます。 これはマージされません。新しいバージョンが準備ができていることをレビューアーに知らせるためのものです。
+- レビュアーのためにそこに残してください。
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) の手順に従ってコンテナを実行します。
+- 変更があるフォークの `tutorial.json` ファイルを使用してチュートリアルを開始します。 `main` ブランチ ではなく、`feat: version-X.X.Y` ブランチのファイルを使用します。
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+新しいバージョンをプッシュする前に、ユーザーのフォークで新しい `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (`main` にマージされる) ブランチを表示してください。 新規変更を含む `CHANGELOG.md` ファイルに追加があり、`coderoad.yaml` の 2 つのスポットのバージョンが新しいバージョンブランチと一致していることを確認してください。
+
+freeCodeCamp リポジトリへの書き込みアクセス権を有しており、`CHANGELOG` と `coderoad.yaml` ファイルが検証済で、上記手順を使用して変更もテスト済みであり、チュートリアルの新しいバージョンをブッシュしたい場合は、下記を実行してください。
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 留意点: freeCodeCamp リポジトリにあるバージョンブランチに変更を加えたりプッシュしたりしないでください。 常に新しいものを作成してください。
+
+- 新しい変更が存在する場所へのリモートがない場合、`git remote add <users_fork>` を使用してユーザーのフォークへのリモートを作成します。
+- 新しいブランチと同じ **local** ブランチ名を削除します。 おそらく、 `vX.X.Y` または `feat/version-X.X.Y` いずれかの名前です。
+- 新しいバージョンブランチを `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y` でチェックアウトします。
+- `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y` で freeCodeCamp リポジトリに新しいバージョンのブランチをプッシュします。 新しい `tutorial.json` ファイルで `main` を更新する前に、新しいブランチをプッシュする必要があります。
+- `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y` で、`main` にマージされるユーザーブランチをチェックアウトします。
+- `coderoad.yaml` の `uri` を freeCodeCamp リポジトリに戻します。
+- 変更を追加してコミットします。
+- `coderoad build` を実行して、新しい `tutorial.json` ファイルを作成します。
+- ファイルを追加してコミットします。
+- `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y` でフォークに変更をプッシュします。
+- freeCodeCamp リポジトリで `main` にPRを作成します。
+- 問題がない場合は、それをマージするか残して、レビューを依頼します。
+- PR がマージされた後、[rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) の指示に従ってチュートリアルを開き、正しく読み込まれていることと、いくつかのステップが実行できることを確認します。
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- このブランチにおいて、元に戻したいバージョン以降のコミットをすべて元に戻します。 例えば、次のようなコミットです。
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+v1.0.0 に戻したい場合は、 `release: version 1.0.1` 以降からすべてのコミットを元に戻します。
+
+- PR を作成します。 `revert: to version X.X.X` のタイトルを付けます。
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/intro.md b/src/content/docs/jp/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50566172
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+[freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) コミュニティは、皆さんのような親切な何千人ものボランティアのおかげで成り立っています。 貴重な時間や専門知識を提供してくださる方々を、喜んで歓迎しています。
+
+:::note
+
+先に進まれる前に、私たちの [行動規範](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/news/code-of-conduct/) をご一読ください。2 分ほどでお読みいただけます。 freeCodeCamp.org に貢献することが誰にとっても安全でインクルーシブな体験になるよう、コミュニティ全体でこの規範を厳守します。
+:::
+
+私たちの [カリキュラム](#カリキュラム) の作成、更新、バグの解消や、freeCodeCamp.org の [学習プラットフォーム](#学習プラットフォーム) のバグの解消、freeCodeCamp.org の世界言語への [翻訳](#翻訳) にご協力いただけると助かります。
+
+貢献に関する一般的なご質問には、[コントリビューターのよくある質問](FAQ) でお答えします。
+
+貢献をお楽しみください。
+
+---
+
+## カリキュラム
+
+私たちのカリキュラムは、世界中の freeCodeCamp コミュニティによってキュレーションされています。 こうすることで、皆さんのようなボランティアから専門的な知識を取り入れることができます。
+
+皆さんは、カリキュラムを拡張したり改善したりする支援ができます。 プロジェクトのユーザーストーリーをより良い概念の説明に更新することもできます。 また、より正確にコードをテストするために、テスト自動化を改善することができます。
+
+**カリキュラムの改善にご興味があれば、[カリキュラムに貢献する方法](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges) をご覧ください。**
+
+## 翻訳
+
+私たちは freeCodeCamp.org を世界中の主要言語へローカライズしています。
+
+Certifications are already live in some major world languages like below:
+
+- [Chinese (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Spanish (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italian (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Portuguese (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ukrainian (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japanese (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [German (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+We encourage you to read the [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) and share it with your friends to get them excited about this.
+
+**If you're interested in translating, here's [how to translate freeCodeCamp's resources](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## 学習プラットフォーム
+
+Our learning platform runs on a modern JavaScript stack. It has various components, tools, and libraries. These include Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack, and more.
+
+Broadly, we have a Node.js based API server, a set of React-based client applications, testing scripts to evaluate camper-submitted curriculum projects, and more. If you want to productively contribute to the learning platform, we recommend some familiarity with these tools.
+
+**If you want to help us improve our codebase here's [how to set up freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/jp/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..92a50b5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Language Lead Handbook
+---
+
+This handbook will help you set up and use the tools for your localization efforts.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+Most of your invites will be for the "Contributor" level. This level allows the user to create drafts. Select this role when inviting a new translator.
+
+The "Author" level allows the user to create Drafts and publish them.
+
+The "Editor" level allows the user to access all Drafts and publish them. Select this role when inviting a new proofreader.
+
+The "Administrator" level is reserved for freeCodeCamp staff and Language Leads.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+We use a [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack)-based approach to build and deploy the articles. This strategy makes for a speedy static site cached and served from a CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) acts as our content management platform, and [11ty](https://11ty.dev) builds the articles into static assets – plain HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. Only these static assets are deployed to our servers.
+
+This process is automated and runs periodically. If you publish something now, it will be available on the news site in a few hours.
+
+You can find the up-to-date build schedules and status here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+With `link` being the link of the original article.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+:::tip
+Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+:::
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Make sure to match the title and the link correctly.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Each title must stay on a single line and not go to a new line.
+
+You will want to [build the translated client locally](how-to-enable-new-languages) to see if the titles have the right length. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articles that can be translated:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+The following articles should **not** be translated:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+The following links are pointing to external sites and cannot be translated:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Once you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, you can update the links in the footer for `/news` by editing the file at `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) repository.
+
+> [!NOTE] Pull requests to this repository are currently limited to staff only. If you want to update this file, ask someone on the staff team for help.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+When you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, as well as when the curriculum in your language is ready for launch, you can update the links in the footer for `/learn` by editing the file at `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) repository.
+
+> [!WARNING] Only "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", and "Code of Conduct" can be translated. Leave other URLs unchanged.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+You can find these boxes all around the documentation:
+
+> [!NOTE] I am a note box
+
+:::tip
+I am a tip box
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] I am a warning box
+
+:::danger
+I am an attention box
+:::
+
+By default, their headers appear in English even in the translated docs.
+
+You can have the headers translated in the docs in your language by changing the file `docs/index.html`, in this way:
+
+Inside the `script` element there is an object, find the `flexibleAlerts` property, which has this shape:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Inside the object of the label property, before the `'/'` property, you would add a new property for your language, like `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+For example, adding the translations for Portuguese would appear like this:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+The motivational quotes can be found in the [curriculum repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json` file.
+
+This file has a general structure of:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+The compliments are the short sentences that appear at the completion of a challenge.
+
+You don't need to directly translate the sentences used in English, you can write a set of short sentences that are appropriate to show at the completion of a challenge.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen compliments to have some variety when users complete challenges.
+:::
+
+The motivational quotes are the quotes that appear at https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+The `motivationalQuotes` array is an array of objects, these objects should include a `quote` property and an `author` property. like this:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen quotes, to have some variety. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+:::
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+We maintain a file of common links used throughout our [curriculum site](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json` file.
+
+Some of these links will not change - but you should update the `/news` article links to point to your language's translated version of that article when it is published.
+
+You should also update the `help` categories to point to your language's subforum (usually `language/category`, like `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). This will allow campers to create "help posts" in the correct forum location.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+The site meta-data is in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json` file. This file has five keys: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords`, and `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+The `youre-unsubscribed` value should be directly translated. The other values will need to be translated as closely as possible, while also considering common search terms and phrases used in your language.
+
+If you need help with this, reach out to us in the [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Pre-Translate Workflow on Crowdin
+
+The Pre-Translate workflow can be used to apply translations from the Translation Memory to strings.
+
+:::tip
+Really useful to restore a lot of translations from the Translation Memory in bulk when a lot of files have been updated.
+:::
+
+You can find the Pre-Translation workflow at the top of the page in the console of a project. If you see "Go to console" in the upper right corner, click there first.
+
+
+
+
+
+You can choose "From Machine Translation" or "From Translation Memory". Choose "Translation Memory" to recover translations from memory.
+
+Then there are three steps to complete:
+
+1. Files. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Languages. Set your language here.
+3. Existing Translations. The best combination here is "100% match" and "Apply to untranslated strings only". Do not approve automatically, as it's always best to have a human eye on things.
+
+
+
+When you have finished setting this, press the Pre-Translate button and wait. It will alert you once it has finished. The time it takes depends on how many untranslated strings are in the chosen files.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+:::tip
+An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+:::
+
+The Crowdin Glossary is kept in the [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries) repository.
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+The `client.csv` file is for the Learn User Interface project, the `curriculum.csv` file is for the Coding Curriculum project, the `docs.csv` file is for the Contributing Documentation project.
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+In the `.csv` file you will find that the English language occupies the first three columns, `Term:English` is the column for the English term, `Description:English` is the column for the English description, and `Part:English` is for the part of speech (e.g., noun, verb etc.) of the term.
+
+Then, each target language has two columns. If you translate to Dothraki, you will be interested in the columns `Term:Dothraki` and `Description:Dothraki`. The column `Term:Dothraki` is for the translation of the term in Dothraki, and the column `Description:Dothraki` is for a description of the term in Dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+:::
+
+After you have made the changes and saved the file, you will need to make a PR with the proposed changes. After the PR is accepted, you will need to run the GitHub Action workflow to update the Crowdin Glossary. Your glossary changes will not have immediate effects, but they will come.
+
+## How to Promote a Contributor to Proofreader
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+This will open the user management tools, you will be able to see the list of all the users.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Use the three dots menu on the user row to open a menu and select "Add to team". The proofreader teams have a standard name of `Proof Readers (<language>)`, you can search the team using the language name. Once you have selected the team, use the "ADD" button at the bottom of the page to finalize the thing.
+
+The user is now a proofreader.
+
+:::tip
+The newly promoted proofreader could benefit from reading the [How to Proofread Files](how-to-proofread-files) documentation.
+:::
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1dbe3221
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+---
+title: 公式 freeCodeCamp モデレーターハンドブック
+---
+
+このハンドブックは、私たちのコミュニティの様々な場所をモデレートするのに役立ちます。 This covers conversations and interactions in issues and pull request threads on GitHub, the community forum, the chat rooms, and other official communities that we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] すべての freeCodeCamp モデレーターは、コミュニティ全体のモデレーターです。 That means we trust you to oversee any of these places.
+
+最も興味のあるプラットフォームのモデレーターになることができます。 GitHub を支援するモデレーターもいれば、フォーラムを支援するモデレーターもいます。 すべての場所においてご活躍いただくモデレーターもいます。
+
+モデレーターであることを楽しんでください。 興味のある場所に皆さんの時間を投資してください。
+
+> 「大いなる力には大いなる責任が伴う」 - ベンおじさん
+
+モデレーターにとって、気質は技術的スキルよりも重要です。
+
+聞きましょう。 Be helpful. 権力を乱用してはいけません。
+
+freeCodeCamp は包括的なコミュニティであり、それを維持する必要があります。
+
+We have a single [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) that governs our entire community. ルールは少ないほど、覚えやすいものです。 [こちら](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) にあるルールを読み、記憶に留めておいてください。
+
+> [!NOTE] As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## GitHub をモデレートする
+
+モデレーターは、GitHub 上で 2 つの主要な責任を負います。
+
+1. Triaging and responding to issues.
+2. Reviewing and merging pull requests (aka QA).
+
+### GitHub Issue をモデレートする
+
+We use our main [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) repository as a common issue tracker for all of our repositories. We get new issues every day, all of which need to be triaged, labeled, and addressed. オープンソースコードベースの貢献を始めるのに最適な場所です。
+
+#### Issue のトリアージ
+
+[トリアージ](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) は、新しい Issue の各報告に対して優先順位を付けるプロセスです。 それぞれの Issue の優先順位、カテゴリ、ステータス、スコープにマークを付けるために使用する広範なラベルリストがあります。
+
+[このリスト](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels) のラベルを使用して、Issue 報告を整理しトリアージすることができます。 通常、ラベルにはその説明書きがあります。
+
+`"help wanted"` と `"first timers only"` のラベルに特に注意してください。 これらは、プルリクエストを行う潜在的なコントリビューターが入る可能性があるスレッドに追加されます。
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### 古く、期限切れで、不活発な Issue とプルリクエストをクローズする
+
+- 古い Issue または 古い PR とは、作成者が過去 21 日間 (最後の活動から 3 週間) アクティビティを行っていないものを指しますが、具体的にはモデレーターが作成者に対して追加情報 / 変更を要求してから上記既定の日数を経過したものを指します。
+
+- Activity is defined as: Comments requesting an update on the PR and triages like `status: update needed` label, etc.
+
+- コントリビューターから支援もしくは時間の追加要求があった場合、それに対する回答を返し、該当する Issue または PR を後日改めて確認することができます。 いずれの場合でも、モデレーターは、未解決の PR を解決するために最善の判断を下す必要があります。
+
+:::tip
+We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+:::
+
+### プルリクエストをモデレートする
+
+プルリクエスト (PR) とは、コントリビューターが freeCodeCamp のリポジトリに変更を送信する方法です。 プルリクエストをマージするか、変更をリクエストするか、もしくはクローズするかを決定する前に、Quality Assurance (QA) を実行しなければなりません。
+
+#### プルリクエストの種類
+
+1. **Challenge instruction edits**
+
+ These are changes to the text of challenges - the description, instructions, or test text.
+
+ GitHub で確認し、マージするかどうかを決定することもできます。 しかし、これについては少し注意する必要があります。 なぜなら、freeCodeCamp カリキュラムを通して何百万人もの方がこのテキストを見るからです。 テキストは、プルリクエストにより、冗長になることなく明確になっていますか? 編集内容は、過度に知識をひけらかすものではなく、関連性の高いものになっていますか? 可能な限り明確かつ短文のチャレンジにすることが目標であることを忘れないでください。 曖昧であってはなりません。 コントリビューターが、チャレンジにリソースへのリンクを追加しようとする場合もあります。
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me) comment. プルリクエストがモデレーターまたは開発チームから少なくとも 2 つの承認 (あなたを含む) を得たら、マージすることができます。
+
+2. **Challenge code edits**
+
+ These are changes to the code in a challenge - the challenge seed, challenge solution, and test strings.
+
+ These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution and to make sure the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
+
+ コントリビューターの中には、衒学的で厄介なケースも網羅するために、追加テストを含めようとする人もいるかもしれません。 チャレンジがあまり複雑にならないように注意しなければなりません。 チャレンジとそのテストは可能な限りシンプルで直感的なものにします。 アルゴリズムチャレンジとインタビュー準備セクションは別として、学習者は約 2 分以内に各チャレンジを解決する必要があります。
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. プルリクエストがモデレーターまたは開発チームから少なくとも 2 つの承認 (あなたを含む) を得たら、マージすることができます。
+
+3. **Platform changes**
+
+ このコード編集により、freeCodeCamp プラットフォーム自体の機能を変更します。
+
+ コントリビューターは、説明せずに変更しようとすることがありますが、コードの変更については、その変更が間違いなく必要であることを確認する必要があります。 説明の無いプルリクエストについては、変更理由が説明されている既存の GitHub の問題を参照する必要があります。 その後、コンピュータでプルリクエストをオープンし、ローカルでテストすることができます。
+
+ 上記完了後、正しく変更されていても、まだマージしないでください。 「LGTM」とプルリクエストにコメントを残し、**"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** と記述することで、開発チームが最終的な確認を行います。
+
+4. **自動 PR (Dependabot)**
+
+ 一部の PR は、インテグレーションにより自動的に依存関係を更新します。 これらの PR をマージまたは承認してはなりません。 開発チームメンバーの 1 人が、このような自動化された PR のレビューとマージを行います。
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+まず最初に、レビューするプルリクエストを選択するときには、それを自分自身にアサインする必要があります。 GitHub インターフェースの右側の列にある「assignees」の下にある「assign yourself」リンクをクリックします。
+
+プルリクエストの種類に応じて、対応する上述のルールに従ってください。
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+プルリクエストをマージする前に、GitHub で、プルリクエストのすべてのチェックが合格 (緑色のチェックマーク) となっていることを確認してください。 チェックが不合格の場合は、原因を調べて明確にしてください。 テストに不合格となるような変更ですか? PR がマージされる場合、サイトは正しく構築されますか? これらのチェックはプラットフォームの安定性に不可欠です。
+
+> [!WARNING] CI/CD チェックが不合格の PR をマージすると、開発チームやコントリビューターを含むすべてのステークホルダーに問題を引き起こす可能性があります。
+
+##### Handling Merge Conflicts:
+
+Sometimes there will be a merge conflict.
+
+これは、別のプルリクエストがその同じファイルの同じ部分に変更を加えたことを意味します。 GitHub には、GitHub 上でこれらのマージ競合に対処するためのツールがあります。 皆さんはこれらの競合に対処することができます。 Use your best judgment.
+
+プルリクエストの変更は一番上にあり、main ブランチの変更は一番下にあります。 次のような、削除可能な冗長な情報がある場合もあります。 終了する前に、Git が競合エリアを表すために追加する `<<<<<<`、`======` および `>>>>>>` を削除してください。
+
+ご不明な点がある場合は、モデレーターまたは開発チームにお問い合わせください。
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+プルリクエストにマージの準備ができている (そして、少なくとも 2 人が承認済みで追加承認が必要ない) 場合、マージすることができます。 デフォルトの **"Squash and Merge"** オプションを使用してください。 これにより、すべてのプルリクエストがコミットされて単一のコミットにスカッシュされ、Git の履歴がより読みやすくなります。
+
+> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way!
+
+プルリクエストの作成者が、「新規コントリビューター」である場合、リポジトリに初めてマージされたプルリクエストに対しても祝意を伝える必要があります。 PR ボディの右上隅を見ると、新規コントリビューターであるかどうかを判断することができます。 以下のように、`First-time contributor` が表示されています。
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ First-time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="プルリクエストの新規コントリビューターバッジ" />
+</details>
+
+プルリクエストにマージの準備ができていない場合は、準備するために何をすべきかを作成者に伝えるために丁寧に返信します。 上手くいけば、作成者から返信があり、プルリクエストの準備に近づけるでしょう。
+
+プルリクエストにセカンドオピニオンが必要な場合は、プルリクエストにコメントを残してください。そして、プルリクエストに 「discussing」ラベルを追加します。
+
+##### Closing an Invalid Pull Request:
+
+大抵の場合、プルリクエストには手間がかかりません。 You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "Made changes" or "Update index.md".
+
+コントリビューターが Web サイトへのリンクを追加しようとしたり、彼らが作成したライブラリを含めようとしたり、彼ら以外の誰にも役に立たない自由な編集をしようとする状況もあります。
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## フォーラムをモデレートする
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Deleting Forum Posts
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. ポルノやグラフィカルに暴力的な画像を投稿している
+2. 本質的に悪意のあるリンクやコードを投稿し、それをクリックする他のキャンパーに害を与える可能性がある
+3. Someone has flooded a thread with a lot of spam messages.
+4. An account has been created, beyond a reasonable doubt, to spam.
+
+### Dealing with Spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Dealing with Off-Topic Conversations
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Dealing with Posted Solutions
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Underage Users
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per our Terms of Service.
+
+It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
+
+Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
+
+Thank you for understanding.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- When trying to include a "Canned reply" in a response, if the menu doesn't open (after clicking on the gear), click on the text area first then try it again.
+- The moderator's 'wrench' is at the bottom of the view-port but if you click it and cannot see the "Select Posts" button because it has scrolled out of view, you may need to try to scroll to it, though sometimes that doesn't work in which case moving to a desktop/laptop monitor may be needed.
+- Sometimes clicking on the three-dot menu below a post can hide the reply icon. Reload the page to get it back.
+
+## Facebook をモデレートする
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderating Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot serves as our moderation bot, and all of the commands use Discord's native slash command interface. You can see a list of all of the commands by typing `/` in any channel.
+
+1. **Make sure the user intended to violate the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Not all violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. この場合、CodePen や Pastebin のようなサービスを使用してコードを貼り付けるようにキャンパーに依頼することができます。
+
+2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), the moderator will proceed as follows:**
+
+ For minor offences, a warning may be issued with the `/warn` command. For more egregious offences, you can remove the member from the server temporarily with the `/kick` command, or permanently with the `/ban` command. In some cases, a member may just need some time to cool off and collect their thoughts - the `/mute` command allows you to prevent them from engaging with our community for a set period of time. A muted member can see the conversation, but cannot post messages or add reactions.
+
+ All moderation commands will take a `reason` parameter, which should be a short explanation of why the action was taken. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. As such, we should avoid using Discord's built-in moderation tools, as they will not be logged.
+
+ > [!WARNING] The reason provided to a moderation command will also be included in the DM notification to the camper. Please remember to be professional here.
+
+3. **Creating a private discussion**
+
+ キャンパーに関わる懸念事項に対して個人的に対処する必要のある場合があるかもしれません。 これは、DM を通じて行うべきではありません。あなたがあることを主張し、キャンパーがそれとは別のことを主張する状況につながる可能性があります。 代わりに、bot の機能を使用してプライベートディスカッションを作成してください。
+
+ - Call the `/private` command, where `target` is the camper you want to open a private channel with.
+ - The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
+ - When the conversation is complete, click the `❌ Close` button _on the first message in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
+
+4. **Deleting messages**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. If a message is not in line with our Code of Conduct, or otherwise not appropriate for our community, you are generally safe to delete it.
+
+ Note that if the message contains content that violates Discord's terms of service, you'll want to report it via https://dis.gd/report **prior to** deleting it.
+
+5. **Don’t threaten to take action**
+
+ If a camper breaks the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `/private` command, or use the bot's moderation commands.
+
+ If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant moderation action or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of their actions without making it come across as a warning.
+
+ For example:
+
+ - Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
+
+ - Or if you really have to explain why:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - For mild and unintentional violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Don’t brag about being a moderator**
+
+ Do not see yourself as above the community. **You are the community.** And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
+
+ If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
+
+7. **Don’t contradict other moderators**
+
+ If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their PoV (Point of View).
+
+ _Remember: We’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front._
+
+8. **Talk with other moderators**
+
+ We have a `#mod-chat` room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporarily inactive**
+
+ If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
+
+## How to Become a Moderator
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+> [!NOTE] For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
+>
+> This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- The user is guaranteed some privacy.
+- Public chat is no longer disrupted.
+- Other team members can pitch in, should you feel uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ddbc367d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Moderator Onboarding Guide
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you haven't read [The Moderator Handbook](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook) yet, you should start there first.
+
+## The Forum
+
+### First Steps
+
+The first thing you may notice after being given moderator status on the forum is that your interface will look somewhat different, with new admin tools to explore and access to the Mod-Team subforum.
+
+Some of the new tools will appear inside a new menu item that looks like a wrench. Some will appear as new tabs or buttons, or even new enabled options within the forum menus.
+
+To get familiar with the new tools and powers, you can combine one or more of the following methods during your first week with this elevated role:
+
+:::tip
+The first two are the most important.
+:::
+
+### Become Familiar with the Discourse Admin Tools
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. To begin to get familiar with Discourse and the moderation role, start by reading Discourse's [new user guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) and Discourse's [new moderator guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116).
+
+### Shadow a Mod
+
+All moderator actions can be followed by reviewing the [action logs](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. Posts to be reviewed will show up in the [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) area of the forum.
+
+For the first week or so you will want to pay attention to what is getting flagged and what is being reviewed, and compare that to the actions being taken upon the flagged posts. You may see the system account flag a post because the user created it too quickly. In many cases, the moderators will unflag the post by clicking on the "Approve Post" button or mark it as "Not Spam" (depending on the flag type).
+
+Commonly, spam flags can also be raised by members or moderators. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+You may notice moderators performing a procedure called 'split topic'. This may be a case where a moderator has split a post that was made erroneously on an existing topic into a new topic, or a moderator merged duplicate topics that a single user has created for the same question. Watching this procedure will highlight different actions and their causes.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. These include:
+
+- Welcoming a new forum member who has posted code without a question -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Reminding members not to post code solutions but to provide hints and tips instead -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Responding to a situation where someone's code works for you but not for them -> "Browser Issues"
+- Encouraging members to open GitHub issues when a possible bug is found -> "Bug Report"
+
+There are more, which you can read through to become familiar with their respective uses. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Read Mod-Team Subforum Posts
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Where to Ask for Help
+
+To get help dealing with a situation that you are either uncomfortable with or unsure of how to handle, discuss with your fellow moderators on either the [Mod-Team Subforum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) or the [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) on Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/jp/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/jp/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e2720a76
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: 責任ある開示 - 殿堂入り
+---
+
+私たちのプラットフォームおよびユーザーの整合性に影響を与える可能性のある脆弱性について、責任ある開示をお願いします。 私たちのプラットフォームのセキュリティに貢献したい方は、[セキュリティポリシー](security) をお読みください。
+
+現時点ではいかなる報奨金も報酬も提供していませんが、プラットフォームの安全性を守ってくださる皆さんに心から感謝しています。
+
+- Mehul Mohan ([codedamn](https://codedamn.com) 所属) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [脆弱性修正](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) working with IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/security.md b/src/content/docs/jp/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4f368015
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp.org's Security Policy
+---
+
+このドキュメントでは、コードベース、運用プラットフォーム、および脆弱性の報告方法に関するセキュリティポリシーについて概説します。
+
+## 脆弱性の報告
+
+> [!NOTE] If you think you have found a vulnerability, **please report it responsibly**. Do not create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, follow this guide.
+
+### Guidelines
+
+We appreciate responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. In the interest of saving everyone time, we encourage you to report vulnerabilities with these in mind:
+
+1. Ensure that you are using the **latest**, **stable**, and **updated** versions of the Operating System and Web Browser(s) available to you on your machine.
+2. We consider using tools & online utilities to report issues with SPF & DKIM configs, SSL Server tests, etc., in the category of ["beg bounties"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) and are unable to respond to these reports.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Reporting
+
+After confirming the above guidelines, please feel free to send an email to `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. You can also send us a PGP encrypted message at `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Once you report a vulnerability, we will look into it and ensure that it is not a false positive. If we need to clarify any details, we will get back to you. You can submit separate reports for each issue you find. Please note that we will not be able to respond to any issues that we think are outside the guidelines.
+
+## Platforms and Codebases
+
+Here is a list of the platforms and codebases we are accepting reports for:
+
+### Learn Platform
+
+| バージョン | ブランチ | サポート | 有効な Web サイト |
+| ------------ | -------------- | -------- | ------------------------ |
+| 本番 | `prod-current` | 有 | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| ステージング | `prod-staging` | 有 | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| 開発 | `main` | 無 | |
+
+### Publication Platform
+
+| バージョン | サポート | 有効な Web サイト |
+| ------------ | -------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| 本番 | 有 | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| ローカライズ | 有 | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Mobile App
+
+| バージョン | サポート | 有効な Web サイト |
+| ---------- | -------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| 本番 | 有 | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Other Platforms
+
+Apart from the above, we are also accepting reports for repositories hosted on GitHub under the freeCodeCamp organization.
+
+### Other Self-hosted Applications
+
+We self-host some of our platforms using open-source software like Ghost & Discourse. If you are reporting a vulnerability, please ensure that it is not a bug in the upstream software.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/jp/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..120928c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS or are still facing issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+:::caution
+Please avoid creating GitHub issues for problems with the prerequisite technologies. They are out of the scope of this project.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. If one of them isn't cached, run the following:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+OR
+
+Use the shortcut
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Use `git clean` in interactive mode:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to clean git untracked files (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="How to clean git untracked files">
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+While in development, your session is stored as cookies. Clearing them will sign you out of your development account.
+
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, too. It will overwrite the development user in your local database.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+When you try to navigate to http://localhost:8000/developmentuser to view the profile page, Gatsby takes over serving the client-side pages and hence you will get a 404 page for the user profile when working.
+
+There is a "Preview Custom 404 Page" button, click it to see the profile.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+The first time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+:::note
+If you are using Apple Devices with M1 Chip to run the application locally, it is suggested to use Node v14.7 or above. You might run into issues with dependencies like Sharp otherwise.
+:::
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions in the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/jp/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/jp/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1531334c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/jp/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: How the User Token Workflow Works
+---
+
+User tokens are used to identify users to third parties so challenges completed using those services can be saved to a user's account.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+At the moment, the tokens are only used to submit the Relational Database challenges. A token gets created when a signed-in user clicks the "Click here to start the course" or "Click here to start the project" buttons to start one of the Relational Database courses or projects.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+A user token will be deleted when a user signs out of freeCodeCamp, resets their progress, deletes their account, or manually deletes the token using the widget on the settings page.
+
+## How they Work
+
+Tokens are stored in a `UserToken` collection in the database. Each record has a unique `_id`, which is the token, and a `user_id` that links to the user's account from the `user` collection. The token is encoded using JWT and sent to the client when it's created. That encoded token is then given to third-party services that need it and sent to our API by them when a challenge is completed. When our API gets it, it is decoded so we can identify the user submitting a challenge and save the completed challenge to their `completedChallenges`.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/pt/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..73b7395a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Manual de análise dos autores
+---
+
+Se você é um autor com acesso à Propriedade do Google Analytics da publicação (editorial), pode usar este guia para visualizar o engajamento do seu artigo e pesquisar artigos no idioma da publicação.
+
+## Pesquisar por idioma
+
+Para procurar relatórios de engajamento em um idioma específico:
+
+
+
+1. No menu suspenso na parte superior, selecione `News`.
+1. Na barra lateral, clique em `Reports`.
+1. Na barra lateral secundária, selecione `Engagement`.
+1. Clique em `Pages and Screens`.
+1. Na barra de pesquisa, digite o subcaminho para o idioma desejado.
+1. Na lista suspensa da barra de pesquisa, escolha `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filtrar relatórios por autor
+
+Depois de chegar aos relatórios de `Pages and Screens` mencionados acima, use as seguintes etapas para filtrar os resultados por autores específicos.
+
+
+
+1. Clique no botão `Add filter`.
+1. A partir da navegação lateral, inclua `Author`.
+1. A partir do menu suspenso `Dimensions values`, escolha o nome de um autor.
+1. Clique no botão `Apply` para aplicar as alterações.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/pt/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..42955182
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: Práticas recomendadas da base de código
+---
+
+## Estilizando um componente
+
+Recomendamos estilizar componentes usando nosso [guia de estilo de design](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+As cores são definidas no arquivo [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css) e as fontes estão em [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+Temos uma opinião forte sobre a adição de novas variáveis/tokens às cores. Após uma pesquisa cuidadosa, as cores foram escolhidas para respeitar a identidade da marca freeCodeCamp, a experiência do desenvolvedor e a acessibilidade.
+
+A palavra-chave `!important` pode ser usada para substituir valores em alguns casos (por exemplo, questões de acessibilidade). Você deve adicionar um comentário descrevendo a questão para que ela não seja removida em futura refatoração.
+
+### Suporte a RTL
+
+Estamos nos esforçando para apoiar o layout da direita para a esquerda (do inglês, right-to-left, ou RTL) na base de código para os idiomas que são lidos nessa direção. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Seguem aqui algumas dicas práticas para isso:
+
+- Não use as propriedades `float`
+ - Em vez disso, use layouts com Flexbox e Grid, pois eles já têm incorporado o suporte a esses idiomas e serão mais fáceis de manter e revisar.
+- Não defina a direção ao usar `margin` e `padding`: pode parecer inofensivo usar `padding-right` e `margin-left`, mas essas direções não são espelhadas quando o layout muda para RTL. Adicionar valores opostos para eles no arquivo RTL torna a manutenção da base de código mais difícil.
+ - Use as propriedades lógicas para eles: você pode adicionar o mesmo espaço, usando `padding-inline-end` e `margin-inline-start`. Você não precisará se preocupar com o layout RTL, já que ele seguirá onde a linha começa e termina. Além disso, você não precisará adicionar valores a mais nos arquivos RTL. Então, não será necessário lembrar de alterar os mesmos valores em dois arquivos.
+- Não use `!important` em `font-family`: o layout RTL usará fontes diferentes daquelas do layout da esquerda para a direita (do inglês, left-to-right, ou LTR). Se você adicionar `!important` na propriedade `font-family`, isso afetará o layout RTL também, o que causa um bug de UI.
+
+## JavaScript em geral
+
+Na maioria dos casos, nosso [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) avisará sobre qualquer formatação que contradiga as práticas recomendadas desta base de código.
+
+Recomendamos o uso de componentes funcionais em vez de componentes baseados em classes.
+
+## TypeScript em específico
+
+### Migração de um arquivo JavaScript para TypeScript
+
+#### Manutenção do histórico de arquivos do Git
+
+Algumas vezes, alterar o arquivo de `<filename>.js` para `<filename>.ts` (ou `.tsx`) faz com que o arquivo original seja excluído e que um novo arquivo seja criado. Em outras situações simplesmente muda – nos termos do Git. O ideal é preservarmos o histórico dos arquivos.
+
+A melhor maneira de conseguir isso é:
+
+1. Renomear o arquivo
+2. Fazer o commit com a flag `--no-verify` para evitar que o Husky reclame de erros de lint
+3. Refatorar o TypeScript para migração em um commit em separado
+
+> [!NOTE] Editores como o VSCode provavelmente mostrarão a você que o arquivo foi excluído e que um novo arquivo foi criado. Se você utilizar a CLI para `git add .`, o VSCode mostrará o arquivo como renomeado na fase de stage
+
+### Convenções de nomes
+
+#### Interfaces e tipos
+
+Na maioria dos casos, recomendamos usar declarações de interface em vez de declarações de tipo.
+
+Props de componentes do React – sufixo com `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+Componentes stateful do React – sufixo com `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Padrão – nome do objeto em PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Definições de ações
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### Como fazer a redução
+
+```typescript
+// Ação de redução de base sem payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Lógica para lidar com os payloads opcionais
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Trocar o redutor exportado pelos combineReducers do Redux
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### Como fazer o dispatch
+
+Em um componente, importe as ações e os seletores necessários.
+
+```tsx
+// Adicione a definição de tipo
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Conecte à store do Redux
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Exemplo de componente do React conectado à store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Função de dispatch
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testes
+
+Os testes `api/` são divididos em duas partes:
+
+1. Teste de unidade
+2. Testes de integração
+
+#### Teste de unidade
+
+Testes de unidade isolam uma única função ou componente. Os testes não precisam de simulação (mocking, em inglês), mas exigirão instalações.
+
+Os testes de unidade estão localizados em um novo arquivo adjacente ao arquivo que exporta que está sendo testado:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Testes de integração
+
+Testes de integração testam a API como um todo. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Normalmente, cada arquivo de teste de integração estará diretamente relacionado a uma rota. Os testes de integração estão localizados no diretório `api/tests/`:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Mais informações
+
+- [Documentação do TypeScript](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [Ficha informativa de TypeScript com React](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/pt/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..addb0fe2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Extensão do VSCode Courses
+---
+
+Aqui detalharemos as diretrizes de manutenção para o [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) repositório que contém o código-fonte para a extensão [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses).
+
+## Publicando a extensão
+
+Uma GitHub Action publica automaticamente a extensão no Visual Studio Marketplace, no lançamento de uma nova GitHub Release.
+
+1. Pacote de uma nova versão da extensão:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Onde `<tag_type>` é: `major`, `minor` ou `patch`.
+
+2. Faça o push da nova versão para `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Como opção, você pode fazer o push diretamente para `upstream/main`, mas abrir um novo PR é recomendado para fins de verificação de sanidade.
+
+3. Crie uma GitHub Release usando a UI do GitHub:
+
+- Incremente corretamente o número da versão ao criar uma nova tag.
+- Faça o upload do arquivo `.vsix` com a release.
+- Publique a release e confirme que a action foi um sucesso.
+
+> [!NOTE] Criar uma release exige acesso de escrita ao repositório `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension`.
+
+## Publicando a extensão manualmente
+
+Um upload manual para o Visual Studio Marketplace pode ser feito seguindo estes passos:
+
+1. Visite https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ e faça login
+2. Navegue até a [página do editor do freeCodeCamp](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Selecione a extensão relevante e selecione `Update`
+4. Faça o upload do arquivo a partir de seus arquivos locais
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5ab4934d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Estrutura de arquivos do currículo
+---
+
+Nosso conteúdo principal de instrução está localizado dentro de um diretório convenientemente chamado de `curriculum`. Esta página descreverá como esses arquivos estão organizados.
+
+## Terminologia
+
+Existem alguns termos que usamos quando discutimos o conteúdo do nosso currículo.
+
+- `certification` : Quando nos referimos a uma certificação neste caso, estamos falando de um certificado factual que os usuários podem solicitar. Não estamos falando do nome do superBlock específico.
+- `superBlock` : Um superbloco é a coleção de desafios em nível superior. Cada superbloco corresponde a uma certificação no currículo (por exemplo, Design responsivo para a web).
+- `block` : Um bloco é uma seção dentro de um superbloco. Um bloco corresponde a um grupo de desafios em uma certificação determinada (por exemplo, HTML e HTML5 básico)
+- `challenge` : um desafio é uma lição única dentro do currículo (por exemplo, Conhecer os elementos HTML)
+
+## Árvore de arquivos
+
+Ao usarmos esses termos, é assim que a estrutura de arquivos deve ser definida:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## O diretório `_meta`
+
+O diretório `_meta` é um diretório especial que contém arquivos `.json`. Esses arquivos correspondem a cada bloco do currículo. Eles são usados para determinar a qual superbloco um bloco pertence, além da ordem dos desafios dentro daquele bloco.
+
+## Renomear arquivos
+
+Pode haver situações em que você precise renomear um certificado, superbloco, bloco ou desafio. Esta seção delineará os passos necessários para evitar erros na build ao fazer isso.
+
+:::danger
+Renomear arquivos dentro da estrutura do currículo geralmente mudará o caminho (ou o URL) do conteúdo na página principal da web. Isso deve ser feito com cuidado, já que os redirecionamentos precisam ser configurados para cada mudança que é realizada.
+:::
+
+### Renomear uma certificação
+
+Ao renomear uma certificação, você provavelmente vai querer renomear o superbloco associado a ela. Faça o seguinte para renomear somente o certificado:
+
+1. Renomeie a pasta `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` com o novo nome.
+1. No arquivo `meta.json` daquela pasta, renomeie os valores em `name`, `dashedName` e `challengeOrder` para o novo nome do certificado.
+1. Em `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, renomeie a pasta `{superBlock}-certificate` e o arquivo YAML dentro dela com o novo nome.
+1. No arquivo YAML, altere o `title` para o novo nome.
+1. Renomeie o arquivo e a pasta da etapa 3 para o resto dos idiomas do currículo.
+1. Atualize `client/src/redux/index.ts` para que ele use o `title` correto.
+1. Como opção, atualize o `certSlug` para o superbloco do mesmo arquivo. **Note** que renomear um `certSlug` mudará o URL para as certificações e somente deverá ser feito depois de se pensar muito sobre o assunto.
+1. Atualize o `title` em `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` com o novo valor. **Note** que mudar o `title` aqui **quebrará** a página do superbloco da certificação associada. Ela depende do título do superbloco para encontrar fazer a correspondência com o título da certificação. Você provavelmente vai querer renomear o superbloco ao mesmo tempo.
+1. Se você renomeou o `certSlug` na etapa 7, altere aqui para o cert e para todos os valores de `projects` aninhados.
+1. Em `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, atualize o valor de `certTypeTitleMap` para o novo nome.
+1. Se você renomeou o `certSlug` na etapa 7, atualize a chave de `certSlugTypeMap` no mesmo arquivo.
+1. Atualize o nome do certificado no array `legacyCerts` de `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx`, se necessário.
+1. Atualize o arquivo `README.md` principal com o novo nome.
+
+### Renomear um superbloco
+
+> [!NOTE] Ao renomear um superbloco, o novo nome de pasta é usado como o caminho e deve ser considerado o nome "correto". Todos os outros valores deverão ser atualizados para refletir essa mudança.
+
+Além disso, você provavelmente vai querer renomear o certificado e o bloco `{superBlock}-projects` quando renomear um superbloco, já que todos compartilham um mesmo nome. Faça o seguinte para renomear somente um superbloco:
+
+1. Renomeie a pasta do superbloco no diretório `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Renomeie a pasta do superbloco em _todos_ os outros diretórios `curriculum/challenges/{language}`.
+1. Para cada bloco naquele superbloco, atualize o valor de `superBlock` no arquivo `meta.json` até seu dashedName. Você não precisa renomear as pastas aqui. Faça isso ao renomear um bloco.
+1. Renomeie a pasta do superbloco em `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Atualize o arquivo `index.md` na pasta acima, alterando os valores de `title` e `superBlock` com o novo nome.
+1. Para cada pasta de bloco que estiver dentro daquela citada acima, atualize o `index.md` para que use o valor `superBlock` correto.
+1. No arquivo `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`, atualize o caminho para a certificação na parte superior do arquivo, bem como o valor de `title` para aquele superbloco. **Note** que mudar o `title` aqui **quebrará** a capacidade de ver a certificação real deste superbloco. Ela depende do título do superbloco para fazer a correspondência com o título da certificação. Você provavelmente vai querer renomear a certificação ao mesmo tempo.
+1. Atualize a chave `superBlockCertTypeMap` em `shared/config/certification-settings.js` para o novo nome do superbloco.
+1. Atualize o valor do caminho em `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. Para cada idioma em `client/i18n/locales`, atualize o arquivo `intro.json` para que use o novo `dashedName` do superbloco. No arquivo em inglês, atualize também o `title`.
+1. Verifique o arquivo `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` para ver se o superbloco está habilitado para as builds do i18n. Atualize todos os valores onde ele for utilizado.
+1. Atualize o arquivo `README.md` principal com o novo nome.
+
+### Renomear um bloco
+
+Faça o seguinte para renomear um bloco do currículo:
+
+1. Mude o nome da pasta do bloco no diretório `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
+1. Mude o nome da mesma pasta do bloco em _todos_ os outros diretórios de idioma para que correspondam. Eles devem ter a mesma estrutura que a do inglês ou haverá um erro na build.
+1. Mude o nome da pasta do bloco no diretório `_meta`.
+1. Atualize as propriedades `name` e `dashedName` para aquele arquivo `meta.json` do bloco.
+1. Atualize a pasta do bloco em `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. No arquivo `index.md` da pasta acima, atualize o valor de `block` no frontmatter.
+1. Nos arquivos `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json`, atualize o nome do bloco com o novo nome para todos os idiomas. No arquivo `intro.json` do inglês, atualize também o `title`.
+1. Atualize o arquivo `README.md` principal com o novo nome.
+
+### Renomear um desafio
+
+Faça o seguinte para renomear um único arquivo de desafio:
+
+1. Mude o nome do arquivo do desafio no diretório `curriculum/challenges/english/`.
+1. Mude o nome de `title` e de `dashedName` naquele arquivo.
+1. Mude o nome do arquivo e o `dashedName` naqueles arquivos para _todos_ os outros diretórios de idiomas para que correspondam.
+1. Atualize o nome do desafio no arquivo `meta.json` relevante. Os nomes dos desafios não são usados na build, mas fornecem uma alternativa mais fácil de identificar a ordem dos desafios.
+1. Se o desafio for um projeto de certificado, atualize o arquivo YAML em `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` para o novo nome.
+1. Se o desafio for um projeto de certificação, atualize o `title` e o `link` em `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. Se o desafio for um projeto de certificação, atualize o arquivo `README.md` principal com o novo nome.
+
+## A propriedade `dashedName`
+
+A propriedade `dashedName` é usada para gerar o caminho do URL para o superbloco, bloco, ou desafio. Ela deve corresponder em geral ao que o assistente `/utils/slugs.js` daria como resultado para o nome do arquivo.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..56524ca2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Usar os auxiliares do currículo
+---
+
+O executor dos testes tem acesso a alguns auxiliares que podem ajudar com o código dos campers.
+
+## Auxiliar do CSS
+
+Para instanciar o auxiliar dentro de um bloco de teste, use isto:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+Nesse exemplo, a variável `document` refere-se ao objeto do documento do iframe do executor do teste.
+
+### Métodos
+
+Existem alguns métodos disponíveis para analisar e testar o CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+O método `.getStyle()` recebe um seletor do CSS e retorna um objeto de declaração de estilo do CSS.
+
+Por exemplo, se o camper escreveu o seguinte CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+Você receberá um objeto que se parece com isto:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+Esse método permite testar se as propriedades específicas foram definidas:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+O auxiliar atribui um método `.getPropVal()` ao objeto de declaração de estilo que permite que você obtenha o valor de uma propriedade específica:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+O método `.getCSSRules()` recebe um tipo de regra da união entre `media | fontface | import | keyframes` e retorna um array de regras do CSS correspondentes a essa regra.
+
+Por exemplo, se o camper escreveu o seguinte código:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+O valor retornado por `helper.getCSSRules('media')` seria este array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+Você, então, pode testar se o camper escreveu a media query correta:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+O método `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` recebe um texto de mídia (por exemplo, `("max-width: 200")`) e retorna as regras de CSS dentro dessa media query.
+
+O resultado retornado é o equivalente da propriedade da regra de mídia `cssRules` a partir do valor de retorno de `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Métodos menos frequentes
+
+Estes métodos não são tão comumente utilizados, mas estão disponíveis, se forem necessários.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+O método `.getStyleDeclarations()` recebe um seletor de CSS e retorna um array de objetos de declaração de estilo do CSS (vindos do método `.getStyle()`).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+O método `.isPropertyUsed()` recebe uma **propriedade** do CSS e confere se ela foi definida/usada em algum lugar do CSS do camper.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+O método `.getStyleRule()` recebe um seletor do CSS e retorna a declaração do estilo em CSS, de modo semelhante a `.getStyle()`. No entanto, a declaração retornada desse método inclui um método `.isDeclaredAfter()` adicional, que recebe um seletor e retorna se essa regra é declarada após o seletor ter sido passado.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+O método `.getStyleSheet()` retorna o CSS do camper analisado em uma folha de estilo do CSS.
+
+## Remover conteúdo
+
+Existem alguns métodos no objeto `__helpers` para remover conteúdo do código do camper.
+
+Eles NÃO precisam ser instanciados. Eles são métodos estáticos.
+
+### Removendo comentários
+
+Usar `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()` ou `__helpers.removeJSComments()` permite a você passar o código do camper (por meio da variável `code`) para remover comentários correspondentes à sintaxe de comentário da linguagem.
+
+### Removendo os espaços em branco
+
+Usar `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` permite que você passe o código do camper (através da variável `código`) para remover todos os espaços em branco.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/devops.md b/src/content/docs/pt/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e52e2e15
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: Manual do DevOps
+---
+
+Este guia irá ajudá-lo a entender nossas ferramentas de infraestrutura e como mantemos nossas plataformas. Embora este guia não tenha muitos detalhes para todas as operações, ele pode ser usado como referência para a compreensão dos sistemas.
+
+Fale com a gente se tiver algum comentário ou dúvidas e teremos prazer em esclarecê-las.
+
+## Manual de Voo – Implementação de código
+
+Este repositório é continuamente construído, testado e implementado em **conjuntos separados de infraestrutura (servidores, base de dados, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+Isto implica três passos a serem seguidos em sequência:
+
+1. Novas alterações (sejam consertos ou funcionalidades) são mergeadas na nossa branch principal de desenvolvimento (`main`) por meio de pull requests.
+2. Estas alterações são executadas por uma série de testes automatizados.
+3. Uma vez que os testes passem, liberamos as alterações (ou as atualizamos se necessário) para implementações na nossa infraestrutura.
+
+### Compilando a base de código - mapeando branches do Git para implementações
+
+Normalmente, é feito um merge de [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (branch padrão de desenvolvimento) na branch [`production-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) uma vez ao dia e liberada em uma infraestrutura isolada.
+
+Esta é uma versão intermediária para nossos desenvolvedores e colaboradores voluntários. É também conhecida como a nossa versão de "preparo" (staging) ou "beta".
+
+Ela é idêntica ao nosso ambiente de produção em `freeCodeCamp.org`, tirando o fato de ela usar um conjunto separado de bancos de dados, servidores, web-proxies, etc. Este isolamento nos permite testar o desenvolvimento e as funcionalidades de forma contínua em um cenário semelhante ao de "produção", sem que os usuários regulares da plataforma principal do freeCodeCamp.org sejam afetados.
+
+Uma vez que a equipe de desenvolvedores [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) esteja feliz com as mudanças na plataforma de preparo, essas alterações são movidas a cada poucos dias para a branch [`production-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current).
+
+Esta é a versão final que move as mudanças para as nossas plataformas de produção no freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Testando alterações - Teste de integração e de aceitação do usuário
+
+Empregamos vários níveis de testes de integração e aceitação para verificar a qualidade do código. Todos os nossos testes são feitos através de software como [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) e [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+Temos testes unitários para nossas soluções de desafio, APIs do servidor e interfaces de usuário e cliente. Eles nos ajudam a testar a integração entre diferentes componentes.
+
+> [!NOTE] Também estamos escrevendo testes de usuário finais que ajudarão a replicar cenários do mundo real, como atualizar um e-mail ou fazer uma chamada para a API ou serviços de terceiros.
+
+Juntos, esses testes ajudam a evitar que problemas se repitam e garantem que não introduzimos um erro enquanto trabalhamos em outra falha ou recurso.
+
+### Implementando alterações - Enviando alterações para os servidores
+
+Nós configuramos software de entrega contínua para fazer push de mudanças no nosso servidor de desenvolvimento e produção.
+
+Uma vez que as alterações são enviadas para as branches de lançamento protegidas, um pipeline de construção é automaticamente acionado para a branch. Os pipelines de compilação são responsáveis pela compilação de artefatos e os guardam em um armazenamento de longo prazo para uso posterior.
+
+O pipeline de compilação aciona um correspondente pipeline de lançamento se ele completar uma execução bem-sucedida. Os pipelines de lançamento são responsáveis por coletar os artefatos de compilação, movendo-os para os servidores e deixando-os disponíveis para acesso.
+
+O estado das compilações e lançamentos está [disponível aqui](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Acione uma compilação, um teste e uma implantação
+
+Atualmente, somente membros da equipe de desenvolvedores podem dar push nas branches de produção. As alterações nas branches `production-*` podem ser enviadas para [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) apenas por meio de um fast-forward merge.
+
+> [!NOTE] Nos próximos dias, vamos melhorar este fluxo a ser feito por meio de pull-requests, para melhor gerenciamento de acesso e transparência.
+
+### Enviando alterações para aplicações em fase de preparo
+
+1. Configure seus remotes corretamente.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Resultados:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Certifique-se de que a sua branch `main` está intacta e sincronizada com a upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Verifique se a IC do GitHub está passando a branch `main` para o upstream.
+
+ Os testes de [integração contínua](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) devem estar verdes e PASSANDO para a branch `main`. Clique na marca de verificação verde próximo ao hash do commit quando estiver visualizando o código da branch `main`.
+
+ <details> <summary> Verificando o status no GitHub Actions (captura de tela) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ Se houver falhas, você deve parar e investigar os erros.
+
+4. Confirme se você consegue compilar o repositório localmente.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Mova as alterações da `main` para a `production-staging` através de um fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] Você não será capaz de dar um force push, e se houver reescrito o histórico de alguma forma, esses comandos vão falhar.
+ >
+ > Se isso acontecer, pode ser que você tenha feito algo errado e você deve simplesmente começar de novo.
+
+As etapas acima vão disparar automaticamente uma execução no pipeline de compilação para a branch `production-staging`. Quando a compilação estiver completa, os artefatos são salvos como arquivos `.zip` em um armazenamento de longo prazo para serem recuperados e usados mais tarde.
+
+O pipeline de lançamento é acionado automaticamente quando um novo artefato estiver disponível a partir do pipeline de compilação conectado. Para plataformas de staging, este processo não envolve aprovação manual e os artefatos são empurrados para os servidores de CDN do cliente e API.
+
+### Enviando alterações para aplicações de produção
+
+O processo é quase o mesmo das plataformas de preparo, com algumas verificações extras. Só para garantir, não quebramos nada no freeCodeCamp.org que possa ver centenas de usuários usá-lo a qualquer momento.
+
+| NÃO execute esses comandos a menos que tenha verificado que tudo está funcionando na plataforma de preparo. Você não deve ignorar qualquer teste na fase de preparo antes de prosseguir. |
+| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Garanta que sua branch `prod-staging` esteja impecável e sincronizada com a upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Mova as alterações da `prod-staging` para a `prod-current` através de um fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] Você não será capaz de dar um force push, e se houver reescrito o histórico de alguma forma, esses comandos vão falhar.
+ >
+ > Se falharem, você pode ter feito algo errado e deve começar de novo.
+
+As etapas acima vão disparar automaticamente uma execução no pipeline de compilação para a branch `prod-current`. Assim que um artefato de compilação estiver pronto, ele acionará uma execução no pipeline de lançamento.
+
+**Etapas adicionais para a equipe**
+
+Quando um release run é acionado, membros da equipe de desenvolvedores receberão um e-mail manual de intervenção automático. Eles podem _aprovar_ ou _rejeitar_ o release run.
+
+Se as alterações estão funcionando bem e foram testadas na plataforma de preparo, então podem ser aprovadas. A aprovação deve ser dada no prazo de 4 horas após a liberação ser acionada antes de ser automaticamente rejeitada. Uma equipe pode acionar novamente a execução de lançamento manualmente para execuções rejeitadas ou esperar pelo próximo ciclo de lançamento.
+
+Para uso de funcionários:
+
+| Verifique seu e-mail para obter um link direto ou [vá para o painel de liberação](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) depois que a execução da compilação estiver concluída. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Uma vez que um dos membros da equipe aprovar o lançamento, as mudanças serão feitas nos servidores CDN e API da produção do freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+## Estado de compilação, teste e implantação
+
+Aqui está o estado atual de teste, compilação e implantação do código.
+
+| Branch | Teste de unidade | Testes de integração | Compilações & implantações |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Pipelines da Azure](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Pipelines da Azure](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (experimental, ainda está por vir) | - | - | - |
+
+## Acesso antecipado e teste beta
+
+Você é bem-vindo para testar estes lançamentos em um modo **de "beta testing público"** e obter acesso antecipado às funcionalidades que estão por vir. Às vezes, esses recursos/mudanças são referidos como **next, beta, staging,** etc. interligadamente.
+
+Suas contribuições por meio de comentários e issues nos ajudarão a fazer as plataformas de produção do `freeCodeCamp.org` mais **resilientes**, **consistentes** e **estáveis** para todos.
+
+Agradecemos por relatar erros que encontra e ajuda para melhorar o freeCodeCamp.org. Você é demais!
+
+### Identificando a próxima versão das plataformas
+
+Atualmente, uma versão pública de testes beta está disponível em:
+
+| Aplicação | Linguagem | URL |
+| :-------- | :-------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Aprenda | Inglês | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Espanhol | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Chinês | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| Novidades | Inglês | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Fórum | Inglês | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Chinês | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] O nome do domínio é diferente de **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. Isso é intencional para evitar que ferramentas de busca indexem e evitar confusões da parte dos usuários regulares da plataforma.
+>
+> A lista (não muito longa) abaixo contém todos os aplicativos que fornecemos. Nem todas as variantes das linguagens são implantadas na fase de preparação para conservar recursos.
+
+### Identificando a versão atual das plataformas
+
+**A versão atual da plataforma está sempre disponível em [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+O time de desenvolvimento faz o merge nas mudanças da branch `prod-staging` para `prod-current` quando lançam mudanças. O commit principal deve ser o que você vê no site.
+
+Você pode identificar a versão exata implantada visitando os registros de compilação e implantação disponíveis na seção de estado. Alternativamente, você também pode entrar em contato na [sala de bate-papo dos contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Limitações conhecidas
+
+Existem algumas limitações e desvantagens conhecidas ao usar a versão beta da plataforma.
+
+- **Todos os dados/progresso pessoal nessas plataformas beta NÃO serão salvos ou transferidos para a produção**
+
+ **Os usuários na versão beta terão uma conta separada da produção.** A versão beta usa um banco de dados fisicamente separado da produção. Isso nos dá a capacidade de evitar qualquer perda acidental de dados ou modificações. A equipe de desenvolvimento pode limpar o banco de dados nesta versão beta conforme necessário.
+
+- **As plataformas beta não oferecem nenhuma garantia com relação a tempo de atividade e confiabilidade**
+
+ Espera-se que a implantação seja frequente e em iterações rápidas, às vezes várias vezes ao dia. Como resultado, haverá tempos de inatividade inesperados ou funcionalidades quebradas na versão beta.
+
+- **Para garantir a eficácia da correção, é aconselhável não direcionar usuários regulares para este site para fins de verificação.**
+
+ O site beta é e sempre foi para melhorar o desenvolvimento e os testes locais, nada mais. Não é uma promessa do que está por vir, mas um vislumbre do que está sendo trabalhado.
+
+- **O login na página pode parecer diferente da produção**
+
+ Nós utilizamos um locatário de teste para o freeCodeCamp.dev no Auth 0 e, portanto, não temos a capacidade de definir um domínio personalizado. Isso faz com que todas as callbacks de redirecionamento e a página de login apareçam em um domínio padrão como: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. Isso não afeta a funcionalidade e é o mais próximo da produção que conseguimos.
+
+## Relatar problemas e deixar comentário
+
+Abra novas issues para discussões e informações sobre erros.
+
+Você pode enviar um e-mail para `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` se você tiver alguma dúvida. Como sempre, todas as vulnerabilidades de segurança devem ser relatadas à `security[at]freecodecamp.org` em vez do rastreador público e fórum.
+
+## Manual de voo - Mantendo o servidor
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. O guia se aplica aos **membros da equipe freeCodeCamp apenas**.
+> 2. Não se deve considerar que essas instruções cubram todas as possibilidades. Tenha cuidado.
+
+Como membro da equipe, você pode ter acesso aos nossos provedores de serviços em nuvem, como Azure, Digital Ocean, etc.
+
+Aqui estão alguns comandos úteis que você pode usar ao trabalhar com máquinas virtuais (VM), por exemplo, realizando atualizações de manutenção ou limpezas em geral.
+
+## Obtenha a lista de VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] Talvez você já tenha acesso SSH às VMs. Só isso não permitirá que você liste VMs, a menos que você tenha acesso aos portais de nuvem também.
+
+### Azure
+
+Instale o Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(Apenas uma vez) Instale no macOS com [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(Apenas uma vez) Login:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Obtenha a lista de nomes de VM e endereços IP:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Instale Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(Apenas uma vez) Instale no macOS com [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(Apenas uma vez) Login:**
+
+Autenticação e troca de contexto: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Obtenha a lista de nomes de VM e endereços IP:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Rodar novos recursos
+
+Nós estamos trabalhando na criação da configuração do IaC. Enquanto isso está ocorrendo, você pode usar o portal Azure ou o Azure CLI para criar uma nova VM e outros recursos.
+
+:::tip
+Não importa sua escolha de como gastar os recursos, nós temos alguns [arquivos de configuração úteis cloud-init](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) para ajudar você a fazer provisionamento básico de como instalar o docker ou adicionar chaves SSH, etc.
+:::
+
+## Mantenha as VMs atualizadas
+
+Você deve manter as VMs atualizadas realizando atualizações e atualizações. Isto vai garantir que a máquina virtual está corrigida com as correções de segurança mais recentes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Antes de executar estes comandos:
+>
+> - Certifique-se de que a MV foi completamente fornecida e que não há etapas pós-instalação sendo executadas.
+> - Se você estiver atualizando pacotes em uma MV que já está servindo uma aplicação, certifique-se de que a aplicação está parada/salva. Atualizações de pacotes causarão picos no uso da banda larga, memória e/ou CPU levando à falhas nas aplicações que estão sendo executadas.
+
+Atualize informações do pacote
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Atualize pacotes instalados
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Limpe pacotes não utilizados
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Trabalhe em servidores web (Proxy)
+
+Estamos executando instâncias equilibradas (Azure Load Balancer) para nossos servidores na web. Esses servidores estão executando NGINX, que reverte o proxy de todo o tráfego para freeCodeCamp.org a partir de várias aplicações em execução em suas próprias infraestruturas.
+
+A configuração do NGINX está disponível neste [repositório](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### Primeira instalação
+
+Provisionando VMs com o código
+
+1. Instale o NGINX e configure a partir do repositório.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Instale os certificados de origem Cloudflare e a configuração de aplicativos upstream.
+
+ Obtenha os certificados de origem Cloudflare a partir do armazenamento seguro e instale nos locais requiridos.
+
+ **OU**
+
+ Mova os certificados existentes:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Localmente
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remotamente
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Atualize as configurações upstream:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Adicione/atualize os endereços IP do aplicativo fonte/origem.
+
+3. Configure a rede e os firewalls.
+
+ Configure o firewall da Azure e `ufw` conforme o necessário para entrar os endereços de origem.
+
+4. Adicione a MV ao pool de back-end do balanceador de carga.
+
+ Configure e adicione as regras ao balanceador de carga, se necessário. Você também pode precisar adicionar as MVs ao pool do balanceador de cargas, se necessário.
+
+### Registro e monitoramento
+
+1. Verifique o estado do serviço NGINX usando o comando abaixo:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Registro e monitoramento para os servidores estão disponíveis em:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), nosso painel básico para monitoração atual. Estamos melhorando as observações com mais métricas granulares
+
+### Atualizando instâncias (Manutenção)
+
+Configure as mudanças das instâncias do NGINX que são mantidas no GitHub, estas devem ser implantadas em cada instância assim:
+
+1. SSH na instância e digite sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Obtenha o código de configuração mais recente.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Teste e recarregue a configuração [com Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Trabalhe nas instâncias de API
+
+1. Instale ferramentas de compilação para binários node (`node-gyp`), etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Primeira instalação
+
+Provisionando MVs com o código
+
+1. Instale o Node LTS.
+
+2. Instale o pnpm globalmente.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Instale o pm2 globalmente.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Faça a clonagem do freeCodeCamp, configure env e as chaves.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # ou qualquer outra branch a ser implementada
+```
+
+5. Crie o `.env` a partir do armazenamento seguro de credenciais.
+
+6. Instale as dependências
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Configure o pm2 `logrotate` e inicialize no boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Compile o servidor
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Inicie as instâncias
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Registro e monitoramento
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Atualizando instâncias (Manutenção)
+
+Mudanças no código devem ser implementadas na instância da API de tempos em tempos. Pode ser uma atualização contínua ou manual. A data posterior é essencial quando estão sendo realizadas mudanças nas dependências ou variáveis de ambiente estão sendo adicionadas.
+
+:::danger
+Os pipelines automatizados não estão manipulando atualizações de dependências no momento. É necessário fazer uma atualização manual antes que qualquer desenvolvimento nas pipelines seja executado.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Atualizações manuais - Usadas para atualizar dependências, variáveis de ambiente.
+
+1. Pare todas as instâncias
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Instale as dependências
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Compile o servidor
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Inicie as instâncias
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Atualizações contínuas - Usadas para mudanças lógicas no código.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Estamos lidando com atualizações contínuas no código e com a lógica por meio de pipelines. Você não deve executar estes comandos. Eles estão aqui para a documentação.
+
+#### 3. Atualizando o Node
+
+1. Instale a nova versão do Node
+
+2. Atualize o pm2 para que ele use a nova versão
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Trabalhe em instâncias de client
+
+1. Instale ferramentas de compilação para os binários do node (`node-gyp` e outros).
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Primeira instalação
+
+Provisionando MVs com o código
+
+1. Instale o Node LTS.
+
+2. Atualize o `npm` e instale o PM2 e configure `logrotate` e inicie quando reiniciar
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Faça a clonagem do client, configure env e as chaves.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Inicie instâncias placeholder para o cliente web, elas serão atualizadas com artefatos do Azure pipeline.
+
+ > A fazer: Esta configuração precisa ser movida para S3 ou armazenamento Azure Blob
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Registro e monitoramento
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Atualizando instâncias (Manutenção)
+
+As alterações no código precisam ser implementadas para as instâncias de API de vez em quando. Pode ser uma atualização contínua ou manual. A data posterior é essencial quando estão sendo realizadas mudanças ou adições variáveis de ambiente.
+
+:::danger
+Os pipelines automatizados não estão manipulando atualizações de dependências no momento. É necessário fazer uma atualização manual antes que qualquer deploy nas pipelines seja executado.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Atualizações manuais - Usado para atualizar dependências, variáveis de ambiente.
+
+1. Pare todas as instâncias
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Instale ou atualize as dependências
+
+3. Inicie as instâncias
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Atualizações contínuas - Usado par mudanças lógicas no código.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Nós estamos lidando com atualizações contínuas no código, lógico, via pipelines. Você não deve ter a necessidade de executar esses comandos. Eles estão aqui para documentação.
+
+## Trabalhando nos servidores do chat
+
+Nossos servidores de chat estão disponíveis com uma configuração HA [recomendada na documentação Rocket.Chat](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). O arquivo `docker-compose` para isso está [disponível aqui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+Fornecemos instâncias NGINX redundantes com balanceamento de carga (Azure Load Balancer) na frente do cluster Rocket.Chat. O arquivo de configuração NGINX está [disponível aqui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### Primeira instalação
+
+Provisionando MVs com código
+
+**Cluster do NGINX:**
+
+1. Instale o NGINX e configure a partir do repositório.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Instale os certificados de origem Cloudflare e a configuração de aplicativos upstream.
+
+ Obtenha os certificados de origem Cloudflare a partir do armazenamento seguro e instale nos locais requiridos.
+
+ **OU**
+
+ Mova os certificados existentes:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remoto
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Atualize as configurações upstream:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Adicione/atualize os endereços IP do aplicativo fonte/origem.
+
+3. Configure a rede e os firewalls.
+
+ Configure os firewalls da Azure e `ufw` conforme necessário para entrar os endereços de origem.
+
+4. Adicione a MV ao pool de back-end do balanceador de carga.
+
+ Configure e adicione as regras ao balanceador de carga, se necessário. Você também pode precisar adicionar as MVs ao pool do balanceador de cargas, se necessário.
+
+**Cluster do Docker:**
+
+1. Instale o Docker e configure a partir do repositório
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure as variáveis de ambiente necessárias e as instâncias dos endereços de IP.
+
+3. Execute o servidor do rocket-chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Registro e monitoramento
+
+1. Verifique o estado do serviço NGINX usando o comando abaixo:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Verifique o estado das instâncias do Docker que estão sendo executadas com:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Atualizando instâncias (Manutenção)
+
+**Cluster do NGINX:**
+
+As alterações na configuração das nossas instâncias NGINX são mantidas no GitHub, elas devem ser implantadas em cada instância assim:
+
+1. Use o SSH na instância e digite sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Obtenha o código de configuração mais recente.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Teste e recarregue a configuração [com Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Cluster do Docker:**
+
+1. Use SSH na instância e vá para onde está o arquivo de configuração do chat
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Obtenha o código de configuração mais recente.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Obtenha a imagem docker mais recente do Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Atualize as instâncias que estão executando
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Veja se as instâncias estão executando
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Limpe recursos estranhos
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Resultado:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Selecione yes (y) para remover tudo que não está sendo usado. Isso vai remover todos os contêineres parados, todas as redes e volumes não usados por pelo menos um contêiner e imagens pendentes e caches de compilação.
+
+## Trabalho com as ferramentas do colaborador
+
+### Implantar atualizações
+
+ssh na VM (hospedada na Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Atualize as versões do Node.js nas MVs
+
+Liste as versões do node e do npm instaladas
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Instale a versão LTS Node.js mais recente e reinstale qualquer pacote global
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Verifique os pacotes instalados
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Coloque um alias na versão `default` do Node.js para que seja a LTS atual (marcada como a versão major mais recente)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Opcional) Desinstale versões antigas
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <versão>
+```
+
+:::danger
+Para aplicações de client, o shell script não pode ser revivido entre versões do Node.js com `pm2 resurrect`. Implante processos de zero ao invés disso. Isso deve melhorar quando mudarmos para uma configuração baseada em docker.
+:::
+
+> Se estiver usando PM2 para os processos você também vai precisar executar as aplicações e salvar a lista de processos para restaurações automáticas quando reiniciar.
+
+Obtenha as instruções/comandos de desinstalação com o comando `unstartup` e use a saída para remover os serviços systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Obtenha as instruções/comandos de instalação com o comando `startup` e use a saída para adicionar os serviços systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Comandos rápidos PM2 para listar, reviver processos salvos, etc.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Instalando e atualizando agentes do Azure Pipeline
+
+Veja: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops e siga as instruções para parar, remover e reinstalar os agentes. Em resumo, você pode seguir as etapas listadas aqui.
+
+Você vai precisar de um PAT, que você pode pegar nesse link: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Instalando agentes em alvos de implantação
+
+Vá para [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) e registre o agente do zero nos [grupos de implantação](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup) necessários.
+
+> [!NOTE] Você deve executar os scripts no diretório raiz e certificar-se de que nenhum outro diretório `azagent` existe.
+
+### Atualizando agentes
+
+Atualmente, atualizar os agentes requer que sejam removidos e reconfigurados. Isso é necessário para que eles tenham os valores do `PATH` e de outras variáveis de ambiente corretos. Precisamos fazer isso, por exemplo, para atualizar Node.js em nossas MVs de implantação.
+
+1. Vá e verifique o estado do serviço
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Pare o serviço
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Desinstale o serviço
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remova o agente do pool do pipeline
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remova os arquivos de configuração
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Quando você completar as etapas acima, você pode repetir as mesmas etapas na instalação do agente.
+
+## Manual de Vôo - Disparo de e-mail
+
+Nós usamos [uma ferramenta de linha de comando](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) para enviar a newsletter semanal. Para começar o processo:
+
+1. Se inscreva na DigitalOcean, e inicie o use de novas droplets sob o projeto `Sendgrid`. Use uma snapshot da Sendgrid no Ubuntu com a data mais recente. Isso vem pré-instalado com a ferramenta da linha de comando para pegar e-mails da base de dados. Com o volume atual, três droplets são suficientes para enviar emails de forma oportuna.
+
+2. Configure o script para pegar a lista de email.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ Você vai precisar substituir os valores padrão dentro do arquivo `.env` com suas credenciais.
+
+3. Rode o script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ Isso vai salvar a lista de email em um arquivo `emails.csv`.
+
+4. Divida os e-mails em vários arquivos, dependendo do número de droplets que você precisa. Isso fica mais fácil usando `scp` para baixar a lista de e-mails localmente e usar seu editor de texto favorito para dividi-los em múltiplos arquivos. Cada arquivo precisará do cabeçalho `email,unsubscribeId`.
+
+5. Mude para o diretório CLI com `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` e configure a ferramenta [conforme a documentação](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Execute a ferramenta para enviar os e-mails, seguindo a [documentação](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. Quando o disparo de email estiver completo, verifique se nenhum e-mail falhou antes de destruir os droplets.
+
+## Manual de Voo - adicionando instâncias de notícias aos novos idiomas
+
+### Alterações nos temas
+
+Usamos um [tema personalizado](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) para nossa publicação de notícias. Adicionar as seguintes alterações ao tema permite a inserção de novos idiomas.
+
+1. Inclua a instrução `else if` para o novo [código de idioma ISO](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) em [`setup-local.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Crie uma pasta inicial de configuração duplicando a pasta [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) e alterando seu nome para o novo código de idioma. (`en` —> `es` para espanhol)
+3. Dentro da pasta do novo idioma, altere os nomes das variáveis no `main.js` e no `footer.js` para o código curto de idioma relevante (`enMain` —> `esMain` para o espanhol)
+4. Duplique o [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) e renomeie-o para o código do novo idioma.
+5. Em [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), adicione scripts para arquivos de configuração recém-criados.
+6. Adicione o script `day.js` do idioma relacionado [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) ao [CDN do freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Alterações do painel do Ghost
+
+Atualize os itens de publicação indo no painel do Ghost > Settings > General e atualizando o [ícone](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [logotipo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png) e a [capa](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/faq.md b/src/content/docs/pt/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..80b19019
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Perguntas frequentes
+---
+
+Respostas para perguntas frequentes.
+
+## Eu sou novo no GitHub e em código aberto. Por onde devo começar?
+
+Leia nosso ["Guia de como contribuir com código aberto"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). É uma referência ampla para quem contribui com projetos pela primeira vez. E inclui muitas dicas de como contribuir para código aberto.
+
+## O que eu preciso saber para contribuir com a base de código?
+
+O freeCodeCamp é executado em uma stack de JavaScript moderna. Se estiver interessado em contribuir com a nossa base de código, você precisará ter alguma familiaridade com JavaScript e com algumas das tecnologias que usamos como o Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby e Webpack.
+
+## Posso traduzir os recursos do freeCodeCamp?
+
+Sim. Você pode contribuir com qualquer um dos mais de 30 idiomas disponíveis em nossa plataforma de tradução.
+
+Temos traduções enviadas por usuários ao vivo em alguns idiomas. Pretendemos traduzir o freeCodeCamp para vários idiomas. Você pode ler mais sobre isso em nosso [anúncio aqui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-ajudar-a-traduzir-o-freecodecamp-para-seu-idioma/).
+
+Se você está interessado em contribuir com as traduções, certifique-se de [ler este guia](how-to-translate-files) primeiro.
+
+## Posso contribuir com artigos para o editorial do freeCodeCamp ou com vídeos para o canal do YouTube do CodeCamp?
+
+Sim - você pode contribuir com o nosso blog de publicação e com o canal do YouTube.
+
+Se estiver interessado em escrever artigos para o editorial do freeCodeCamp, visite este [guia de publicação](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). Além disso, leia nosso [guia de estilo](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) pois ele ajudará você a escrever artigos mais sólidos e eficazes.
+
+Para nos ajudar a fazer vídeos educacionais para nosso canal do YouTube, você pode seguir o [guia do canal do YouTube aqui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## Como posso relatar um novo erro?
+
+Se você acha que encontrou um erro, primeiro leia o artigo ["Como relatar um erro"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) e siga suas instruções.
+
+Se você está confiante de que é um novo erro, vá em frente e crie uma nova issue no GitHub. Certifique-se de incluir o máximo de informações possível para que possamos reproduzir o erro. Temos um modelo predefinido de issue para ajudar você.
+
+Observe que essas issues do GitHub são para discussões e questões relacionadas ao código – não para obter ajuda sobre como aprender a programar. Sempre que houver dúvidas, você deve [procurar por assistência no fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) antes de criar uma issue no GitHub.
+
+## Como posso relatar um problema de segurança?
+
+Não crie issues no GitHub para problemas de segurança. Em vez disso, [siga nossa política de segurança](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## Eu sou estudante. Posso trabalhar em um recurso para créditos acadêmicos?
+
+Sim. Note, porém, que não podemos nos comprometer com nenhum cronograma ou documentação que possa ser um requisito da sua faculdade ou universidade. Recebemos muitos pull-requests e contribuições em código de desenvolvedores voluntários e respeitamos o tempo e esforço deles. Em respeito a todos os outros contribuidores, não daremos nenhuma prioridade especial a nenhum PR só por ser relacionado à escola.
+
+Pedimos que você planeje com antecedência e que trabalhe em suas contribuições de código tendo isso em mente.
+
+## O que significam estas etiquetas diferentes marcadas nas issues?
+
+Os responsáveis pelo código fazem a [triagem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) das issues e pull requests tendo como base a prioridade, importância e outros fatores. Você pode [encontrar um glossário completo dos significados aqui](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Por onde começar se quero ajudar em uma issue?
+
+Você deve consultar issues [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) ou [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) para saber o que está disponível para ajuda.
+
+:::tip
+Você não precisa pedir permissão para ajudar com issues marcadas como **`help wanted`**. No entanto, issues com a etiqueta **`first timers only`** são issues especiais projetadas para pessoas que não contribuíram antes para a base de código freeCodeCamp.
+:::
+
+## Encontrei um erro de digitação. Devo relatar uma issue antes de poder fazer um pull request?
+
+Para erros de digitação e outras mudanças em palavras, você pode diretamente abrir pull requests sem criar uma issue antes. Certifique-se de mencionar detalhes na descrição do pull request para nos ajudar a entender e revisar sua contribuição – mesmo se for uma mudança pequena.
+
+Crie uma issue se quiser discutir grandes aspectos da base do código ou currículo.
+
+## Como posso receber uma issue atribuída a mim?
+
+Tipicamente, não atribuímos issues para ninguém além de contribuidores de longo prazo. Ao invés disso, seguimos a política abaixo para sermos justos com todos:
+
+1. É muito provável que façamos o merge do primeiro pull request que resolve a issue.
+2. No caso de vários colaboradores abrindo um pull request para a mesma issue, ao mesmo tempo, daremos prioridade ao pull request que melhor resolve a issue. Algumas coisas que consideramos:
+ - Você incluiu testes?
+ - Você usou todos os casos de uso?
+ - Você garantiu que todos os testes passaram e confirmou que tudo está funcionando localmente?
+3. Por último, damos prioridade aos pull requests que seguem as nossas orientações recomendadas.
+ - Você seguiu a checklist do pull request?
+ - Você deu um título significativo ao seu pull request?
+
+## Tenho interesse em ser um moderador no freeCodeCamp. Por onde devo começar?
+
+Os moderadores da nossa comunidade são nossos heróis. Suas contribuições voluntárias fazem do freeCodeCamp uma comunidade segura e receptiva.
+
+Primeiro e mais importante, precisamos que você seja um participante ativo da comunidade e que siga à risca o nosso [código de conduta](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (não se limite apenas a aplicá-lo).
+
+Aqui estão alguns caminhos recomendados para algumas de nossas plataformas:
+
+- Para ser um moderador do **Discord/Chat**, tenha uma presença ativa em nosso chat e compromissos positivos com os outros, ao mesmo tempo em que aprende e pratica como lidar com conflitos em potencial que possam surgir.
+- Para ser um moderador do **fórum**, similar a um moderador de chat, tenha uma presença ativa e interaja com as outras pessoas que publicam no fórum, apoie-os em sua jornada de aprendizado e dê feedback quando perguntarem. Dê uma olhada no [Manual do líder do subfórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) para obter mais informações.
+- Para ser um moderador do **GitHub**, ajude a processar as issues levantadas no GitHub para ver se elas são válidas e (idealmente) tente propor soluções para essas issues a serem resolvidas por outras pessoas (ou por você mesmo).
+
+No conjunto, seja respeitoso com os outros. Somos seres humanos de todo o mundo. Tendo isso em mente, considere também usar uma linguagem de incentivo ou de apoio e esteja atento à comunicação intercultural.
+
+Se você praticar o que foi dito acima **consistentemente por algum tempo** e se nossos companheiros moderadores recomendarem você, um membro da equipe entrará em contato e fará sua inclusão na equipe de moderadores. O trabalho em código aberto é trabalho voluntário e nosso tempo é limitado. Reconhecemos que isso é provavelmente também é verdade no seu caso. Por isso, enfatizamos a importância de ser **consistente** em vez de se envolver na comunidade em tempo integral.
+
+Dê uma olhada no nosso [Manual do Moderador](moderator-handbook) para obter uma lista mais completa de outras responsabilidades e expectativas que temos nossos moderadores.
+
+## Estou com dificuldade em algo que não está incluído na documentação.
+
+**Fique à vontade para pedir ajuda em:**
+
+- A categoria `Contributors` do [fórum da nossa comunidade](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- O canal `#Contributors` em nosso [servidor](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Estamos animados em ajudar você a contribuir com qualquer tópico que desejar. Se você nos perguntar algo relacionado às issues, vamos ficar felizes em esclarecer. Certifique-se de pesquisar sua pergunta antes de postar uma nova.
+
+Agradecemos antecipadamente por ser educado(a) e paciente. Lembre-se – esta comunidade é feita principalmente de voluntários.
+
+## Assistência adicional
+
+Se você tiver dúvidas sobre a stack, a arquitetura do código, as traduções ou qualquer outra coisa, pode entrar em contato com nossa equipe [no fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**Você pode enviar um e-mail para nossa equipe de desenvolvimento: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f247d4d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: Como adicionar testes Cypress
+---
+
+Quando estiver realizando alterações em JavaScript, CSS ou HTML que podem mudar a funcionalidade ou aparência de uma página, é importante incluir os testes de integração [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io) correspondentes.
+
+Para aprender como escrever testes Cypress ou 'specs', por favor confira a [documentação](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html) oficial do Cypress.
+
+## Onde adicionar um teste
+
+- Testes Cypress estão no diretório `./cypress`.
+
+- Testes do Cypress para um módulo do currículo estão no diretório do currículo correspondente, ou seja, `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## Como executar testes
+
+> [!NOTE] Se estiver usando Gitpod, veja essa [configuração sobre Cypress-Gitpod](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Veja se as aplicações de cliente e MongoDB estão executando
+
+- [Inicie o MongoDB e crie o banco de dados](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Inicie também a aplicação de cliente freeCodeCamp e o servidor API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Execute os testes do Cypress
+
+Para executar testes usando compilações de produção, substitua `dev` por `prd` abaixo.
+
+- Para executar todos os testes no diretório `./cypress`:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- Para executar um único teste:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<caminho_para_o_arquivo_de_teste>
+ ```
+
+ Por exemplo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- Para criar uma versão de compilação, inicie o servidor de desenvolvimento e execute todos os testes cypress contínuos e funcionais existentes:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Configuração do Cypress-Gitpod
+
+### 1. Certifique-se que o ambiente de desenvolvimento está em execução
+
+Se o ambiente Gitpod não foi criado automaticamente:
+
+- Siga o [guia de instalação do MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Crie um arquivo de configuração.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Crie a base de dados
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Desenvolva o servidor e o client
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Instale as ferramentas de compilação do Cypress
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- Quando solicitado no terminal, selecione o layout do seu teclado por idioma/área
+
+Agora, [o Cypress pode ser executado](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a26c40f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: Como adicionar testes do Playwright
+---
+
+## Instalação
+
+Para instalar o Playwright, execute:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Como alternativa, você pode seguir a documentação oficial referenciada abaixo:
+
+Para instalar e configurar o Playwright na sua máquina, confira a [documentação](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+Para aprender a escrever testes do Playwright ou 'specs', confira a [documentação](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests) oficial.
+
+## Onde adicionar um teste
+
+- Os testes do Playwright estão no diretório `./e2e`.
+
+- Os arquivos de teste do Playwright têm sempre uma extensão `.spec.ts`.
+
+## Melhores práticas para a escrita de testes E2E
+
+Esta seção explicará em detalhes as melhores práticas para escrever e documentar testes E2E com base na documentação do Playwright e no nosso estilo de código comunitário.
+
+### - Importações
+
+Sempre comece com as importações necessárias no início do arquivo.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identificando um elemento do DOM
+
+O Playwright vem com [vários localizadores integrados](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), mas recomendamos a priorização dos seguintes localizadores:
+
+- `getByRole` para consultar elementos semânticos de função importante e que permitam que a tecnologia assistiva perceba a página corretamente.
+- `getByText` para consultar elementos não semânticos, como `div`, `span` ou `p`.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+Nos casos em que os elementos não podem ser consultados usando os localizadores mencionados acima, você pode usar o atributo `data-playwright-test-label` como último recurso. Esse atributo é usado para identificar elementos no DOM para testes somente com o playwright. Ele não é usado para estilização ou para qualquer outra finalidade.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+No arquivo de teste, você pode usar o método `getByTestId` para identificar o elemento.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constantes
+
+Defina quaisquer elementos constantes, conjuntos de dados ou configurações usadas durante seus testes para fácil referência.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Contexto compartilhado
+
+Se os testes dependem de um contexto compartilhado (como uma página da web carregada), use os hooks beforeAll e afterAll para configurar e encerrar esse contexto.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Nomes de testes descritivos
+
+Cada bloco de teste deve ter um nome claro e conciso descrevendo exatamente o que ele está testando.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Declarações legíveis
+
+Cada declaração deve ser o mais legível possível. Isso torna mais fácil entender o que o teste está fazendo e o que está esperando.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Evite repetições
+
+Certifique-se de que os testes não estão repetindo o mesmo código várias vezes. Se você estiver repetindo o mesmo código, considere refatorá-lo como um laço ou uma função.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Testes para telas de dispositivos móveis
+
+Use o argumento `'isMobile'` para executar testes que incluam lógica que varia para telas de dispositivos móveis.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Agrupamento de testes relacionados
+
+Agrupe testes relacionados em conjunto usando blocos "descrite". Isso torna mais fácil entender o que os testes estão fazendo e o que estão testando.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## Como executar testes
+
+### 1. Veja se as aplicações de client e do MongoDB estão em execução
+
+- [Inicie o MongoDB e crie o banco de dados](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). Para que os testes do Playwright funcionem, certifique-se de usar o comando `pnpm run seed:certified-user`.
+
+- [Inicie também a aplicação de client do freeCodeCamp e o servidor da API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Execute os testes do Playwright
+
+Para executar testes com o Playwright, verifique o seguinte
+
+- Não se esqueça de navegar primeiro para o repositório e2e
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- Para executar testes no modo auxiliar de UI:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- Para executar um único teste:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <nome_do_arquivo>
+ ```
+
+ Por exemplo:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Para executar um conjunto de arquivos de teste nas respectivas pastas:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <caminho_da_pasta1> <caminho_da_pasta2>
+ ```
+
+ Por exemplo:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Para executar o teste com o título:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <título>
+ ```
+
+ Por exemplo:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Depuração dos testes
+
+Como o Playwright é executado no Node.js, você pode depurá-lo com seu depurador preferido – por exemplo, usando console.log ou em seu IDE
+
+- Depuração de todos os testes:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Depuração de um arquivo de teste:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Geração de relatórios de teste
+
+O HTML Reporter mostra um relatório completo de seus testes, que permite filtrar o relatório por navegadores, testes que passaram, testes que falharam, testes ignorados e testes não confiáveis.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Solução de problemas
+
+O Playwright, geralmente, é uma ferramenta com pouquíssimas chances de erro. O colaborador já configurou os testes para serem executados em máquinas com todos os sistemas operacionais, incluindo as distribuições mais significativas do Windows, MacOS e Linux.
+
+- (MacOs e Linux) Se executar o Playwright resultar em um erro devido a dependências do kernel, execute o seguinte comando:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- Um erro comum visto no Playwright é o seguinte:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ Você pode corrigir o erro acima com os seguintes passos:
+
+ 1. **Verifique o URL:** confira se o URL que você está tentando navegar está certo e formatado corretamente. Certifique-se de que não há erros de digitação no URL.
+
+ 2. **Status do servidor:** confira se o servidor no URL está em execução e acessível. Você pode encontrar esse erro se o servidor não estiver em execução ou se não estiver acessível.
+
+ 3. **Disponibilidade da porta:** verifique se a porta mencionada no URL (8000, neste caso) é a porta correta e está disponível para uso. Certifique-se de que nenhum outro processo já esteja usando essa porta.
+
+ 4. **Firewall ou software de segurança:** às vezes, firewalls ou software de segurança podem bloquear conexões em portas específicas. Verifique as configurações do firewall para garantir que a porta seja permitida.
+
+ 5. **Conectividade de rede:** certifique-se de que seu sistema tenha uma conexão de rede ativa e possa acessar recursos externos.
+
+- Outro erro comum visto no Playwright é o seguinte:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. A solicitação de rede foi feita usando um método que não inclui um corpo de resposta, como HEAD ou CONNECT.
+ 2. A solicitação de rede foi feita através de uma conexão segura (HTTPS) e o corpo da resposta não está disponível por razões de segurança.
+ 3. A solicitação de rede foi feita por um recurso de terceiros (como um anúncio ou um pixel de rastreamento) que não é controlado pelo script.
+ 4. A solicitação de rede foi feita por um script que foi pausado ou interrompido antes de a resposta ser recebida.
+
+**Para mais informações sobre essas questões, confira a documentação oficial.**
+
+## Configuração do Playwright no Gitpod
+
+### 1. Certifique-se que o ambiente de desenvolvimento está em execução
+
+Se, ao iniciar o ambiente do Gitpod, o ambiente não foi desenvolvido automaticamente:
+
+- Siga o [guia de instalação do MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Criar o arquivo .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Crie um arquivo de configuração.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Crie o banco de dados
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Desenvolva o servidor e o client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Instale as ferramentas de compilação do Playwright
+
+Para instalar as dependências necessárias para executar o Playwright, execute o seguinte comando:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Execute os testes do Playwright no Gitpod
+
+Para executar todos os testes do Playwright, execute o seguinte comando:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8934f881
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **Observação:** esta é uma etapa **opcional** e é necessária somente quando trabalhando com fluxos de e-mail
+
+- [Introdução](#introduction)
+- [Instalando o MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Usando o MailHog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Links úteis](#useful-links)
+
+## Introdução
+
+Alguns fluxos de e-mail, como atualizar o e-mail de um usuário, requerem que o servidor da API do back-end envie e-mails de saída. O MailHog é uma alternativa para quem não quer usar um provedor de serviços de e-mail para enviar mensagens de e-mail de verdade. Ele é uma ferramenta de desenvolvedores para o teste de e-mails que receberá mensagens de e-mail de sua instância do freeCodecamp.
+
+## Instalando o MailHog
+
+O MailHog pode ser instalado no macOS, Windows e Linux ou usado via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Instalando o MailHog no Docker</summary>
+
+Se você tem o Docker instalado, então você pode usar
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+para iniciar o MailHog em segundo plano e
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+para para-lo.
+
+Quando a instalação for concluída, você pode começar a [usar o MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando o MailHog no macOS</summary>
+
+Instale o MailHog no macOS com [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+Os comandos acima iniciarão um serviço do MailHog em segundo plano.
+
+Quando a instalação for concluída, você pode começar a [usar o MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando o MailHog no Windows</summary>
+
+Baixe a versão mais recente do MailHog no [repositório oficial do MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Localize e clique no link para a sua versão do Windows (32 ou 64 bits) e um arquivo `.exe` será baixado no seu computador.
+
+Quando o download terminar, clique para abrir o arquivo. Uma notificação de firewall do Windows pode aparecer, solicitando permissão de acesso para MailHog. Um prompt de linha de comando padrão do Windows abrirá onde o MailHog será executado quando o acesso ao firewall for concedido.
+
+Feche o MailHog fechando a janela do prompt. Para iniciar o MailHog novamente, clique no executável do MailHog (`.exe`) arquivo que foi baixado inicialmente - não é necessário baixar um novo arquivo de instalação do MailHog.
+
+Comece a [usar o MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Instalando o MailHog no Linux</summary>
+
+Primeiro, instale o [Go](https://golang.org).
+
+Execute os seguintes comandos para instalar GO em sistemas baseados em Debian, como o Ubuntu e o Linux Mint.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+Execute os seguintes comandos para instalar GO em sistemas baseados em RPM, como CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+Como alternativa, execute os seguintes comandos para instalar o GO.
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+Agora defina o caminho para o Go com os seguintes comandos.
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+Finalmente, digite os comandos abaixo para instalar e executar MailHog.
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+Comece a [usar o MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+## Usando o MailHog
+
+Abra uma nova guia ou janela do navegador e navegue até [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) para abrir sua caixa de entrada do MailHog quando a instalação do MailHog for concluída e o MailHog estiver em execução.
+
+## Links úteis
+
+- Confira o repositório [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) para mais informações relacionadas ao MailHog. Informações adicionais também estão disponíveis sobre configurações personalizadas do MailHog.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..52d29068
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Siga estas orientações para contribuir para o código. Isso é altamente recomendado se você quer contribuir regularmente.
+
+Ignorar essas etapas pode causar problemas à sua cópia, o que dificulta os processos daqueles que contribuem, mantêm e revisam.
+
+## Contribuindo para a base de código
+
+Agora, você pode fazer alterações nos arquivos e fazer o commit das alterações no seu fork, que você pode preparar lendo [Como configurar o freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Siga estes passos:
+
+1. Certifique-se que está no branch `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Você deve ver um resultado como este:
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch main
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'origin/main'.
+
+ nada para enviar no commit, diretório de trabalho limpo
+ ```
+
+ Se você receber uma mensagem diferente, você não está em main ou seu diretório de trabalho não está limpo. Resolva quaisquer arquivos/commits pendentes e saia de `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sincronize as últimas mudanças da branch `main` upstream do freeCodeCamp para sua branch `main` do fork:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Se você possui qualquer pull request feito a partir da branch `main`, você os perderá ao fim desta etapa.
+ >
+ > Certifique-se de que foi feito um merge no seu pull request por um moderador antes de executar este passo. Para evitar essa situação, você **sempre** deve trabalhar em uma brach que não seja a `main`.
+
+ Este passo **irá sincronizar as últimas alterações** do repositório principal do freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Atualize sua cópia do repositório upstream do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Faça um hard reset na sua branch main com a main do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Faça um push da sua branch main para a origin para obter um histórico claro em seu fork do GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ Você pode validar se sua main atual combina com upstream/main fazendo um diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ O resultado deve mostrar vazio. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Crie uma branch novinha em folha:
+
+ Trabalhar em uma branch separada para cada issue ajuda a manter sua cópia de trabalho limpa. Você nunca deve trabalhar na `main`. Isso vai sujar sua cópia do freeCodeCamp e você pode ter que começar de novo com um clone ou fork.
+
+ Veja se você está na `main` como explicado antes e crie uma branch a partir dela:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Seu nome de branch deve começar com `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Evite usar números de issues em branches. Mantenha-os curtos, significativos e únicos.
+
+ Alguns exemplos de bons nomes para branches são:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edite páginas e trabalhe no código em seu editor de texto favorito.
+
+5. Quando estiver satisfeito com as alterações, você deve opcionalmente executar o freeCodeCamp para visualizar as alterações.
+
+6. Certifique-se de corrigir quaisquer erros e verificar a formatação de suas alterações.
+
+7. Verifique e confirme os arquivos que você está atualizando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Isso deve mostrar uma lista dos arquivos `unstaged` que você editou.
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch feat/documentation
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ As mudanças não estão organizadas para commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." para atualizar o que será enviado)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." para descartar as mudanças do diretório)
+
+ modificado: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modificado: docs/README.md
+ modificado: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modificado: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Organize as alterações e faça um commit:
+
+ Nesta etapa, você só deve marcar arquivos que você editou ou adicionou. Você pode executar um reset e resolver arquivos que você não pretendeu mudar se necessário.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add caminho/para/meu/arquivo/alterado.ext
+ ```
+
+ Ou você pode adicionar todos os arquivos `unstaged` para a área de preparação:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Apenas os arquivos que foram movidos para a área de staging serão adicionados quando você fizer um commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Resultado:
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch feat/documentation
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Mudanças para as quais devemos fazer um commit:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." para descartar as mudanças do diretório)
+
+ modificado: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modificado: docs/README.md
+ modificado: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modificado: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Agora, você pode fazer o commit das alterações com uma pequena mensagem assim:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Alguns exemplos:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: adicionado teste para JavaScript - passo do laço for
+ feat: adicionado link para o artigo de habilidades em alexa
+ ```
+
+ Faça uma mensagem de commit convencional. Essa é uma boa prática. Como desenvolvedor, você estará seguindo as práticas padrão.
+
+ Alguns exemplos de mensagens convencionais de commit são:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: melhorar o passo do HTML
+ fix: consertar scripts de build para o Travis-CI
+ feat: adicionar o link para o artigo de hoisting do JavaScript
+ docs: atualizar as diretrizes de colaboração
+ ```
+
+ Escreva pouco, não mais do que 50 caracteres. Você sempre pode adicionar informações extras na descrição da mensagem de commit.
+
+ Isso não leva mais tempo do que uma mensagem não convencional como 'atualizar arquivo' ou 'adicionar index.md'
+
+ Você pode aprender mais sobre o motivo de usar commits convencionais [aqui](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Se você se deu conta que precisa editar um arquivo ou atualizar a mensagem de commit você pode fazer isso assim:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Isso abrirá um editor de texto padrão, como `nano` ou `vi` onde você pode editar o título da mensagem de commit e adicionar/editar a descrição.
+
+10. Em seguida, você pode fazer push das suas alterações no seu fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/nome-aqui
+ ```
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Referência de comandos rápidos
+
+Uma rápida referência aos comandos que você precisará ao trabalhar.
+
+| comando | descrição |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Executa todos os testes JS no sistema, incluindo cliente, servidor, lint e testes dos desafios. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Executa o conjunto de testes do cliente. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Execute o conjunto de testes do client, atualizando os snapshots do Jest que estão fora de sincronia. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Executa o conjunto de teste de currículo. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Testa um bloco específico. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Testa um super bloco específico. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Executa o ocnjunto de teste de currículo, sem parar após o primeiro erro |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Executa o conjunto de testes de servidor. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Executa os testes de ponta a ponta do Cypress. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Desinstala todas as dependências e limpa os caches. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Inicia o Storybook para o desenvolvimento da biblioteca de componentes. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1a31048a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Implantar novos idiomas no `/learn`
+---
+
+Para habilitar um novo idioma em `/learn` (currículo), você precisa completar os seguintes passos:
+
+- Traduzir e aprove por completo as três primeiras certificações no Crowdin. (Design responsivo para a web novo, Algoritmos e estruturas de dados em JavaScript e Bibliotecas de desenvolvimento de front-end)
+- Complete a tradução e aprove todas as frases no projeto LearnUI (interface do usuário) no Crowdin.
+- Atualize as configurações do Crowdin para adicionar um código de idioma personalizado para o novo idioma.
+- Abra o primeiro PR para configurar o GitHub Actions. Você precisa atualizar 2 arquivos:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Abra o 2nd PR para adicionar outras configurações. Você precisa atualizar/adicionar os seguintes arquivos:
+ - Atualize `i18n.ts`
+ - Atualize `superblocks.ts`
+ - Atualize `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Adicione `links.json`
+ - Adicione `meta-tags.json`
+ - Adicione `motivation.json`
+- Peça à equipe da infraestrutura para colocar a VM para funcionar para o novo idioma.
+- Quando a VM estiver pronta, abra o terceiro PR para mostrar o novo idioma no menu de navegação.
+
+Explicaremos cada passo nas seções seguintes.
+
+## Atualizar as configurações do Crowdin
+
+Antes de lançar um novo idioma, você precisará permitir que os idiomas sejam baixados do Crowdin. Para configurar isso, você precisa adicionar um código de idioma personalizado para seu idioma.
+
+Nos projetos `Curriculum` e `Learn UI` no Crowdin, você precisará selecionar `Settings` > `Languages`, na barra lateral. Em seguida, desça até `Language Mapping`, onde você verá uma opção para adicionar códigos de idioma personalizados. Adicione uma nova entrada para o idioma que você está liberando, selecionando `language` como o valor de `Placeholder` e digitando um URL amigável em letras minúsculas do nome do seu idioma para o `Custom code`. Se você não tem certeza do que usar, ou se você não tem uma função de administrador e não pode ver as configurações entre em contato pelo nosso chat de colaboradores e nós o ajudaremos.
+
+## Atualizando os fluxos de trabalho para o GitHub Actions
+
+Em seguida, você precisa configurar a sincronização entre Crowdin e GitHub.
+
+Você precisará adicionar um passo para o [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) e para o [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). O passo para ambos será o mesmo. Por exemplo, se você quiser habilitar os downloads de Dothraki:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Observe que a chave `download_language` precisa ser definida como código do idioma exibido no Crowdin.
+
+## Habilitar um idioma
+
+> [!NOTE] A seção acima com a atualização dos fluxos de trabalho deve ser concluída antes de prosseguir - isso precisa ser feito em etapas separadas. Caso contrário, as compilações falharão.
+
+Existem algumas etapas a serem seguidas para permitir que a base de código seja compilada no idioma desejado.
+
+Primeiro, visite o arquivo [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) para adicionar o idioma à lista de idiomas disponíveis e configurar os valores. Existem vários objetos aqui.
+
+- `Languages`: adiciona o novo idioma no enum `Languages`, do mesmo modo que com os outros. O valor da string aqui será usado no arquivo `.env` para definir o idioma da build posteriormente.
+- `availableLangs`: adiciona a nova propriedade do enum `Languages` aos dois arrays, `client` e `curriculum`.
+- `i18nextCodes`: esses são os códigos ISO de cada linguagem. Você vai precisar do código ISO apropriado para o idioma que você está habilitando. Eles precisam ser únicos para cada idioma.
+- `LangNames`: esses são os nomes dos idiomas que aparecerão para a seleção no menu de navegação.
+- `LangCodes`: esses são os códigos de idiomas usados para formatar datas e números. Esses deverão ser códigos Unicode CLDR ao invés de códigos ISO.
+- `hiddenLangs`: Esses idiomas não serão exibidos no menu de navegação. Isto é usado para idiomas que ainda não estão prontos para liberação. Inclua seu idioma nesse array no primeiro PR e peça à equipe para preparar a instância de VM para o seu idioma. Quando a VM estiver pronta, faça outro PR para removê-lo do array.
+- `rtlLangs`: estes são os idiomas que leem da direita para a esquerda.
+
+Como um exemplo, se você tivesse que habilitar o idioma Dothraki como seu idioma, os objetos `i18n.ts` devem ficar assim:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Quando um idioma for configurado no pipeline de implantação E tiver uma instância pública de `/learn` ativa, ele pode ser removido da matriz `hiddenLangs` e ser disponibilizado ao público.
+
+### Configuração dos superblocos traduzidos
+
+No arquivo [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts), adicione o novo idioma ao objeto `notAuditedSuperBlocks`. Isso lista todos os superblocos que não estão totalmente traduzidos. Adicione um array de superblocos que não foram totalmente traduzidos a ele. Por exemplo:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Certifique-se de adicionar apenas os superblocos que **não** estão totalmente traduzidos e aprovados. Os superblocos traduzidos serão calculados a partir desse objeto. Quando um novo superbloco estiver totalmente traduzido, remova-o do array para esse idioma.
+
+Veja o enum `SuperBlocks` no início do mesmo arquivo para ver a lista completa de superblocos.
+
+### Configurar a busca
+
+Agora, abra o arquivo [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts). Esse dado é usado para a barra de busca que carrega os artigos `/news`. Embora seja improvável que você venha a testar essa funcionalidade, não ter os dados para o seu idioma pode levar a erros quando tentar criar a base de código localmente.
+
+Adicione um objeto para seu idioma no objeto `algoliaIndices`. Você deve usar os mesmos valores do objeto `english` para o teste local, substituindo a chave `english` pelo valor de `availableLangs` do seu idioma.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se nós já implantamos uma instância do editorial em sua língua-alvo, você pode atualizar os valores para refletir a instância que já está implantada. Do contrário, use os valores em inglês.
+
+Se você fosse adicionar Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // Se já tivermos /news no idioma de destino, é possível atualizar os valores assim:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Interface do client
+
+Você precisará dar um passo adicional para lidar com as traduções da interface do client.
+
+Os fluxos de trabalho do Crowdin serão automaticamente puxados _algumas_ das traduções da UI, mas há alguns arquivos que precisam ser movidos manualmente.
+
+Você vai querer copiar os seguintes arquivos de [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>` e aplicar as traduções conforme necessário:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+Você não precisa ter tudo nestes 3 arquivos traduzidos no começo. É possível traduzir somente as partes relevantes e fazer ajustes mais tarde.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+Você pode substituir qualquer URL que tenha páginas correspondentes prontas no seu idioma.
+
+Por exemplo, se você tiver uma publicação no seu idioma, você pode substituir o URL para `"news"`. Se quiser traduzir artigos listados nos links de rodapé, consulte [Como traduzir artigos nos links de rodapé](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+Este arquivo contém metadados para a página da web de `/learn` no seu idioma. Você pode traduzir os valores para `"title"`, `"description"` e `"social-description"`. O valor de `"youre-unsubscribed"` é usado quando alguém cancela sua inscrição no e-mail semanal do Quincy.
+
+Além disso, você pode traduzir ou adicionar palavras-chave relevantes em seu idioma para o array `"keywords"`.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+Este arquivo contém os elogios que serão exibidos para os campers quando completarem um desafio, bem como as citações motivacionais que são exibidas na parte superior da página do `/learn`.
+
+Você pode traduzi-los, ou até mesmo substituí-los por elogios/citações relevantes de sua escolha no seu idioma.
+
+### Ativar os vídeos localizados
+
+Esta seção só se aplica se você tiver vídeos localizados nos desafios. Caso contrário, você pode pular esta seção.
+
+Para os desafios em vídeo, você precisa fazer algumas alterações. Primeiro, adicione o novo idioma (locale) à consulta do GraphQL no arquivo [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx). Por exemplo, para adicionar Dothraki à consulta:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Em seguida, adicione um id para o novo idioma para qualquer desafio em vídeo em um bloco auditado. Por exemplo, se `auditedCerts` em `i18n.ts` inclui `scientific-computing-with-python` para `dothraki`, você deve adicionar uma entrada em `dothraki` em `videoLocaleIds`. O frontmatter dever ter essa aparência:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+nomeComTracos: introducao-por-que-programa
+---
+```
+
+Atualize a interface de `VideoLocaleIds` em `client/src/redux/prop-types` para que ela inclua o novo idioma.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+Por fim, atualize o schema de desafios em `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testar traduções localmente
+
+Se quiser testar as traduções localmente, antes de adicioná-las ao nosso repositório principal - pule as alterações de fluxo de trabalho do Crowdin. Siga as etapas para habilitar um idioma e, em seguida, baixe as traduções do Crowdin e as carregue em seu código local.
+
+Como o idioma ainda não foi aprovado para produção, nossos scripts ainda não estão baixando automaticamente as traduções. Somente membros da equipe têm acesso para baixar as traduções diretamente – entre em contato conosco quando quiser em nossa [sala de chat dos contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) ou traduza os arquivos de markdown em inglês localmente para fins de teste.
+
+Quando tiver os arquivos em mãos, você precisará colocá-los no diretório correto. Para os desafios do currículo, você deve colocar as pastas de certificação (por exemplo, `01-responsive-web-design`) no diretório `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Para nossas traduções em Dothraki, esse diretório seria `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. Os arquivos `.json` de tradução do client vão no diretório `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Atualize seu arquivo `.env` para usar seu novo idioma para `CLIENT_LOCALE` e `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Quando estes arquivos estiverem no local certo, você deve poder usar `pnpm run develop` para ver sua versão traduzida do freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+Se você fizer a build do client em um idioma e quiser fazer a build em um idioma diferente, precisará usar o comando `pnpm run clean-and-develop` depois de alterar o arquivo `.env`, pois o Gatsby armazenará em cache o primeiro idioma.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+Embora você possa realizar as traduções localmente para fins de teste, lembramos a todos que as traduções _não_ devem ser enviadas pelo GitHub e devem ser feitas somente pelo Crowdin. Certifique-se de reiniciar sua base de código local após realizar os testes.
+:::
+
+## Mostrar o idioma no menu de navegação
+
+Quando seu PR anterior for mesclado e sua VM para seu idioma estiver pronta, faça outro PR para mostrar seu idioma no menu de navegação.
+
+No arquivo [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts), você incluiu seu idioma no array `hiddenLangs` no PR anterior. Retire-o do array agora.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove seu idioma do array
+```
+
+Quando esse PR é mesclado e implantado, o currículo em seu idioma estará disponível na página.
+
+# Implantar novos idiomas em `/news`
+
+Para implantar novos idiomas em News, você precisa criar dois PRs. Um PR será para o [repositório do CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), enquanto o outro será para o [repositório News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Preparar o repositório do CDN para o novo idioma
+
+News busca os links de tendências e títulos de artigos do nosso CDN durante a build e adiciona-os ao rodapé. News também busca os arquivos Day.js do CDN durante a build para fazer a localização das datas e horários para cada idioma.
+
+### Adicionar um arquivo YAML para os artigos populares
+
+Faça a clonagem do repositório [CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) e crie um branch.
+
+No diretório [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending), crie um arquivo e dê a ele o nome de `language.yaml` (onde "language" é o idioma que você deseja inserir). Por exemplo, se você estiver lançando News em dothraki, nomeie o arquivo `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Em seguida, copie o conteúdo do arquivo trending de [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) e cole-o no novo arquivo YAML que você acaba de criar.
+
+O conteúdo será parecido com isto:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Adicionar um arquivo de localização Day.js para o novo idioma
+
+Por padrão, Day.js só inclui inglês como local. Para habilitá-lo para funcionar com outros idiomas, você precisa adicionar um novo arquivo de locale Day.js ao CDN.
+
+No diretório [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale), crie um arquivo e dê a ele o nome de `isocode.min.js` (onde "isocode" é o c[odigo iso do idioma que você deseja inserir). Por exemplo, se você estiver lançando News em dothraki, nomeie o arquivo `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] O número da versão mudará já que as dependências são atualizadas.
+
+Em seguida, visite [esta página no cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) com todos os arquivos Day.js disponíveis para a versão que estamos usando, encontre o link de `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` para o novo idioma, e abra-o em uma nova aba.
+
+> [!NOTE] Você só precisa adicionar o arquivo de locale .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js. Você não precisa adicionar mais nenhum arquivo Day.js.
+
+Copie o código de local de Day.js da nova aba para o novo arquivo que você criou. Por exemplo, aqui está uma versão não minificada do código de localidade do inglês para Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Em seguida, abra um PR para o repositório do CDN para adicionar os arquivos YAML e Day.js para revisão.
+
+## Preparar o repositório do editorial para o novo idioma
+
+O [repositório de News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) puxa dados de uma instância do Ghost, os arquivos que você adicionou ao CDN, faz a build de News e o implementa.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests para o repositório News _precisam_ vir do mesmo repositório. Você não deve trabalhar a partir de um fork nesse passo.
+
+### Modificar o arquivo de configuração principal
+
+Clonar o repositório News e criar uma branch.
+
+Abra o arquivo `config/index.js` para adicionar o novo idioma e configurar os valores necessários. Há alguns objetos e arrays que precisam ser modificados:
+
+- `locales`: esse array contém os idiomas de News ativos e futuros. Esses são os valores usados no arquivo `.env` para escolher a instância e a interface do usuário do Ghost a serem usados em cada build. Adicione o nome textual do novo idioma em minúsculas a esse array.
+- `localeCodes`: esse objeto é um mapa de códigos ISO para cada idioma. Ele é usado para configurar o i18next antes da build da interface de usuário. Para adicionar um novo idioma, use o nome do idioma em minúsculas como _key_ (chave) e o código do idioma ISO 639-1 como o _value_ (valor).
+- `algoliaIndices`: esse objeto é um mapa dos índices do Algolia para cada idioma. Para adicionar um novo idioma, use o nome do idioma em minúsculas como _key_ (chave) e `news-`, seguido do código do idioma ISO 639-1 como o _value_ (valor).
+
+> [!NOTE] Se você não tem certeza sobre a string a ser usada durante a configuração de `algoliaIndices`, envie uma mensagem para o Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo) ou para outra pessoa com acesso ao Algolia, pedindo para que confira para você.
+
+Por exemplo, se você estiver lançando News em dothraki, aqui está o modo como os objetos/arrays acima devem parecer:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Adicionar os arquivos em JSON do i18next para o novo idioma
+
+Em seguida, vá para o diretório `shared/config/i18n/locales`, crie uma pasta e informe o nome do novo idioma que você está adicionando. Por exemplo, se você estiver lançando News em dothraki, crie uma pasta chamada `dothraki`.
+
+Em seguida, copie os arquivos JSON do diretório `english` para a sua nova pasta.
+
+Na sua nova pasta, abra o arquivo `redirects.json` e substitua seu conteúdo por um array vazio:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Em seguida, faça o commit e o push de sua branch diretamente para o repositório News.
+
+> [!NOTE] Você precisa estar em uma das equipes com acesso ao repositório de News para enviar branches diretamente para esse repositório. Atualmente, apenas as equipes de desenvolvimento, i18n e staff podem fazer isso.
+
+Por fim, abra um PR para análise.
+
+Uma vez que os PRs para o repositório do CDN e de News tenham sido aprovados, eles podem ser mesclados.
+
+> [!NOTE] A implantação será realizada posteriormente pelos membros da equipe. Aqui temos uma amostra de PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485). Nela, vemos como a equipe faz isso. Mais detalhes estão disponíveis na [Wiki da equipe](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2a947ad5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: Como ajudar com os desafios em vídeo
+---
+
+Os desafios em vídeo são um novo tipo de desafio no currículo freeCodeCamp.
+
+Um desafio em vídeo é uma seção de um curso completo sobre um determinado tópico. Uma página de desafio em vídeo incorpora um vídeo do YouTube. Cada página de desafio tem uma única pergunta de múltipla escolha relacionada ao vídeo. O usuário deve responder a pergunta corretamente antes de avançar para o próximo desafio em vídeo.
+
+As páginas de desafio em vídeo são criadas por membros da equipe freeCodeCamp. Vídeos do YouTube também são enviados por membros da equipe freeCodeCamp. Muitos dos desafios em vídeo ainda não possuem perguntas associadas a eles.
+
+Você pode ajudar criando questões de múltipla escolha e adicionando-as aos arquivos 'markdown' para os desafios em vídeo.
+
+## Modelo de desafio
+
+Abaixo está um modelo de arquivo markdown do desafio.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Identificador exclusivo (alfanumérico, MongoDB_id)
+title: Título do desafio
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'videoId do desafio por vídeo no YouTube'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --descrição--
+
+Texto de descrição do desafio, em markdown
+
+```html
+<div>código de exemplo</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+Esses espaços são normalmente utilizados para questões de múltipla escolha dos desafios de Python.
+
+## --text--
+
+O texto da questão vêm aqui.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Resposta 1
+
+---
+
+Resposta 2
+
+---
+
+Mais respostas
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+O número da resposta correta fica aqui.
+
+```
+
+## Criando perguntas para desafios em video
+
+### Acessar os arquivos markdown do desafio em vídeo
+
+Os arquivos markdown dos desafios estão localizadas no currículo em:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Escolha um arquivo dentre as opções acima.
+
+### Explore o vídeo associado ao desafio e crie uma questão de múltipla escolha
+
+Primeiro, localize o `videoId`.
+
+Por exemplo, no código a seguir a partir do cabeçalho de um arquivo markdown de desafio de vídeo, o `videoId` é "nVAaxZ34khk". No GitHub, a informação deve estar contida em formato tabular.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Em seguida, acesse o vídeo no YouTube correspondente com aquele `videoId`. A URL do vídeo será:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (troque `videoId` na URL pelo ID do vídeo - sem colchetes)
+
+No exemplo acima, a URL seria https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Assista ao vídeo no YouTube daquele `videoId` e pense em uma questão de múltipla escolha baseada em seu conteúdo.
+
+### Adicione a pergunta ao arquivo markdown
+
+Você pode adicionar a pergunta localmente ou utilizando a interface do Github. Para adicionar a pergunta localmente, você precisa [configurar o freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Você também pode encontrar o arquivo no GitHub e clicar no botão editar para adicionar a pergunta diretamente em seu navegador.
+
+Se uma pergunta não tiver sido adicionada a um desafio de vídeo ainda, ela terá a seguinte forma padrão:
+
+```md
+# --question-
+
+## --text--
+
+Texto da questão
+
+## --answers--
+
+Resposta 1
+
+---
+
+Resposta 2
+
+---
+
+Mais respostas
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Adicione/atualize o texto da pergunta sob a parte que diz:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Adicione/Atualize (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, e assim por diante) sob `## --answers--`. Confirme se o número sob `## --video-solution--` seja o número da resposta correta. Você pode adicionar mais respostas possíveis usando o mesmo formato. Tanto as perguntas quanto as respostas podem estar entre aspas.
+
+### Exemplos de perguntas
+
+````md
+# --pergunta--
+
+## --texto--
+
+O que esse código JavaScript mostra no console?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --pergunta--
+
+## --texto--
+
+O que aparecerá após executar esse código:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+Para mais exemplos, você pode ver os arquivos markdown para o seguinte curso em vídeo. Todos os desafios já possuem perguntas: [Python for Everybody Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Abrir um pull request
+
+Depois de criar uma ou mais perguntas, você pode confirmar as mudanças em uma nova branch e [abrir um pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a8d9b78e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: Como abrir um Pull Request (PR)
+---
+
+Um pull request (PR) permite que você envie alterações do seu fork do GitHub para o repositório principal do freeCodeCamp.org. Depois de terminar de fazer alterações no código, você pode seguir essas diretrizes para abrir um PR.
+
+Esperamos que nossos colaboradores estejam cientes do processo específico deste projeto. Seguindo as orientações cuidadosamente, você terá o respeito de outros mantenedores e poupará o tempo de todos.
+
+Alguns exemplos disso são:
+
+1. Não edite arquivos diretamente no GitHub – enquanto você puder, não é uma boa ideia.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Certifique-se de seguir a lista de verificação de PR e não apenas desmarcar as coisas; caso contrário, não levaremos você a sério.
+4. Utilize a maneira correta de ligar issues na descrição do PR, atualizando o `XXXXXX`. Não adicione apenas números de issues em todo e qualquer lugar e que quiser.
+5. Não faça menções com @ nem solicite as revisões de outra pessoa diversas vezes.
+
+ Entendemos que você está animado para contribuir. Por mais que os mantenedores adorem a ideia de responder você, lembre-se de que eles são pessoas ocupadas que cuidam de centenas de solicitações como as suas. Seja paciente, alguém responderá você mais cedo ou mais tarde.
+
+6. Não trabalhe diretamente na branch `main` - crie uma outra branch para as alterações em que está trabalhando.
+
+> [!NOTE] Seu PR deve se destinar apenas a alterações no currículo em inglês. Veja [este guia](index#translations) para contribuir com traduções.
+
+## Prepare um bom título para o PR
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. A convenção tem o seguinte formato:
+
+> `<type>([escopo(s) opcional(is)]): <description>`
+>
+> Por exemplo:
+>
+> `fix(learn): testes para o desafio de ciclo do...while`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Tipo:**
+
+| Tipo | Quando selecionar |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| fix | Funcionalidade mudada ou atualizada/melhorada, testes, a explicação de uma lição etc. |
+| feat | Somente se você estiver adicionando novas funcionalidades, testes, etc. |
+| chore | Mudanças não relacionadas ao código, testes ou explicação de uma lição. |
+| docs | Mudanças no diretório `/docs` ou nas diretrizes de contribuição, etc. |
+
+**Escopo:**
+
+Você pode selecionar um escopo a partir [desta lista de etiquetas](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Descrição:**
+
+Escreva pouco (menos de 30 caracteres) e de modo simples. Você pode adicionar mais informações na caixa de descrição do PR e nos comentários.
+
+Alguns exemplos de bons títulos de PRs seriam:
+
+- `fix(a11y): contraste melhorado da barra de pesquisa`
+- `feat: adicionar mais testes aos desafios de HTML e CSS`
+- `fix(api,cliente): prevenir erros CORS no envio do formulário`
+- `docs(i18n): correção dos links para relativos em vez de absolutos`
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request
+
+1. Uma vez que as edições tenham sido realizadas, será solicitado que você crie um pull request na página do GitHub do seu fork.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Ver captura de tela</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. Por padrão, todos os pull requests devem ser feitos no repositório principal do freeCodeCamp, branch `main`.
+
+ Certifique-se de que seu Base Fork está definido como freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp ao criar um Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Ver captura de tela</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Envie o pull request do seu branch para o branch `main` do freeCodeCamp.
+
+4. Inclua um resumo mais detalhado das alterações feitas e como suas alterações são úteis no corpo do PR.
+
+ - Será apresentado um modelo de pull request. É uma checklist que você deve seguir antes de abrir o pull request.
+
+ - Preencha os detalhes como quiser. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - Se o PR tem como objetivo resolver uma issue GitHub existente, então, no final do corpo da descrição de seu PR, use a palavra-chave _Closes_ com o número da issue para [automaticamente fechá-la, se o PR for aceito e dado merge](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Exemplo: `Closes #123` fechará a issue 123
+
+5. Indique se você testou em uma cópia local do site ou não.
+
+ - Isso é muito importante quando se está fazendo mudanças que não são apenas edições no conteúdo do texto como a documentação ou descrição de um desafio. Exemplos de mudanças que precisam ser testadas localmente incluem JavaScript, CSS ou HTML que podem mudar a funcionalidade ou aparência de uma página.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Comentários nos pull requests
+
+> :tada: Parabéns por fazer um PR e muito obrigado(a) por contribuir.
+
+Nossos moderadores vão dar uma olhada e deixar um comentário para você. Seja paciente com os outros moderadores e respeite o tempo deles. Todos os pull requests são revisados no tempo devido.
+
+E como sempre, fique à vontade em perguntar na [categoria 'Contributors' (colaboradores) do fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [na sala de chat de colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+Se você vai contribuir com mais pull requests, recomendamos ler as diretrizes sobre [fazer mudanças e sincronizá-las](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) para evitar o apagamento de seu fork.
+:::
+
+## Conflitos em um pull request
+
+Conflitos podem surgir porque muitos colaboradores trabalham no repositório, e as alterações podem afetar o seu PR, que está aguardando uma revisão e mesclagem.
+
+Como fazemos o squash de todos os commits, você pode não precisar fazer o rebase. Porém, se um rebase for solicitado, verifique nossos guias [Para os consertos de bugs e recursos comuns](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) ou [Para o currículo futuro e recursos](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) para saber como fazer esse processo para seu PR correspondente.
+
+### Para funcionalidades e correções de erros comuns
+
+Quando se está trabalhando em erros normais e funcionalidades no seu branch `main` de desenvolvimento, você pode fazer um simples ajuste:
+
+1. Faça um rebase na sua cópia local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Resolva quaisquer conflitos e adicione / edite commits
+
+ ```bash
+ # isso
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflitos"
+
+ # ou
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Faça um push das suas alterações para o PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### Para o próximo currículo e próximas funcionalidades
+
+Quando você estiver trabalhando em funcionalidades para nossos próximos branches `next-*` de currículo, você tem que fazer um `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Certifique-se de que seu upstream esteja sincronizado com seu local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Faça um backup
+
+ a. Exclua seu branch local depois de ter feito um backup (se você ainda o tem localmente):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-nome>
+
+ # exemplo:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-nome>
+
+ # exemplo:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-nome>
+ ```
+
+ b. Ou apenas faça um backup do seu branch de PR (se você não o tem localmente):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-nome> origin/<pr-branch-nome>
+
+ # exemplo:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Comece do zero:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-nome> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolva os conflitos, faça a limpeza, instale as dependências e execute os testes
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # exemplo:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. Se tudo estiver correto, faça um push ao PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-nome>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0418b376
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Como revisar as traduções
+---
+
+Nossa equipe de revisão é responsável por garantir que as traduções reflitam com exatidão o texto original. Confiamos em nossos revisores para que tenhamos traduções de alta qualidade.
+
+Todas as nossas traduções são feitas a mão, por humanos reais. A revisão mantém um tom consistente em todos os recursos traduzidos, como o currículo.
+
+Para iniciar a revisão, visite [nossa plataforma de tradução](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) e faça o login. Selecione "Go to console" na barra de navegação superior para mudar da visualização pública para a visualização do espaço de trabalho.
+
+## Selecione um arquivo
+
+Você deve ver a lista de projetos aos quais foi concedido acesso. Selecione o projeto que você gostaria de revisar e, em seguida, selecione o idioma.
+
+
+
+Agora você deve ver a lista de arquivos disponíveis. Escolha seu arquivo selecionando o botão `Proofread` à direita do arquivo, depois escolha `Proofreading` no menu que aparece.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se você estiver nesta visão de espaço de trabalho, mas quiser [traduzir um arquivo](how-to-translate-files) em vez de revisar, você pode selecionar `Crowdsourcing` no menu suspenso.
+
+## Traduções revisadas
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Aqui você verá a lista de strings do arquivo selecionado, com suas respectivas traduções. A tradução que é exibida aqui é a tradução que recebeu a maior pontuação (entre votos positivos e negativos) da comunidade de tradução.
+
+Enquanto você pode ver _todas_ as traduções propostas para uma determinada string, a pontuação da comunidade (determinada pelos votos positivos e negativos) deve ser levada em consideração na escolha da tradução a ser aprovada. A comunidade pode revisar as traduções propostas e recomendar qual delas é a mais precisa e clara.
+
+1. Esta é a string original (em inglês).
+2. Esta é a string de tradução correspondente. A proposta de tradução mais popular, baseada em votos a favor e contra, será exibida aqui.
+3. Clicando neste botão de verificação, a tradução será aprovada.
+4. Crowdin exibirá o estado de cada string. `Done` significa que uma tradução foi aprovada e será baixada em nosso próximo Crowdin pull. `Todo` significa que a string não foi revisada. `Hidden` significa que a string está bloqueada e _não deve ser traduzida_. `Comment` significa que a string tem um comentário relacionado.
+5. As traduções podem ser selecionadas com as caixas de seleção e aprovadas aqui com uma única ação.
+6. Você pode ver as traduções propostas pela comunidade, suas pontuações de popularidade, e traduções sugeridas pela Crowdin aqui.
+7. Este botão mostra/esconde o painel do lado direito, onde você pode ver traduções, comentários, memória de tradução e termos do glossário.
+8. Crowdin exibe aqui mensagens de erro a partir das verificações de garantia de qualidade. Em outras palavras, se algo não parecer correto na tradução, o Crowdin notificará você. Estas traduções devem ser aprovadas com cuidado.
+
+Nenhuma ação adicional é necessária quando o arquivo terminou de ser revisado.
+
+> [!NOTE] A aprovação de uma string na visualização de revisão a marcará como completa e será baixada em nosso próximo pull da Crowdin para o GitHub.
+
+## Tornando-se um revisor
+
+Se você tiver qualquer dúvida, ou estiver interessado em se tornar um revisor, sinta-se a vontade em nos enviar uma mensagem no nosso [ chat de contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Vamos te dar acesso se você já estiver contribuindo para freeCodeCamp por um tempo.
+
+Nosso time de desenvolvedores e times de moderadores da comunidade está sempre procurando por voluntários gentis como você, que nos ajuda a deixar traduções de alta qualidade disponíveis para o mundo.
+
+> [!NOTE] O Crowdin permitirá que você aprove suas traduções. Em geral, é melhor permitir que outro revisor reveja suas traduções propostas como segurança extra para garantir que não haja erros.
+
+## Criando um canal no chat para um idioma
+
+Para a maior parte das mensagens, encorajamos você a usar o [chat de contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) para todas as interações. Entretanto, se o time de voluntários crescer para um idioma específico, nós consideramos criar um canal adicional para o idioma.
+
+Se você já é um revisor e está interessado em ter um canal dedicado a um idioma específico, [preencha nosso formulário](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..598cf995
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Siga estas orientações para criar um ambiente de desenvolvimento para o freeCodeCamp. Isso é altamente recomendado se você quer contribuir regularmente.
+
+## Escolha entre o Gitpod ou seu próprio computador (configuração local)
+
+:::danger
+
+- o freeCodeCamp não faz a build nem é executado nativamente no Windows. É [preciso usar o WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) para ter um ambiente similar ao do Linux no Windows. - Você não pode usar o prompt de comando do Windows, o Git Bash nem PowerShell para fazer a build e executar o código. - Observe que, se estiver usando o Windows, os requisitos de hardware precisam ser mais do que [aquele que mencionamos](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) para acomodar a configuração baseada em WSL.
+ :::
+
+Se você deseja fazer uma contribuição única, use o Gitpod para fazer alterações. A configuração do Gitpod abre um ambiente pronto para código em poucos minutos no seu navegador. Para contribuir a longo prazo, recomendamos que você instale o freeCodeCamp em seu computador.
+
+Aqui estão alguns prós e contras que devem ajudá-lo a decidir qual opção é a melhor para você:
+
+| Gitpod | Sua própria máquina (configuração local) |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| Sem requisitos mínimos de hardware | Requisitos específicos e mínimos |
+| Não é necessário instalar nenhum software | Software adicional necessário |
+| Sempre atualize a cópia do repositório | É necessário manter uma cópia local do repositório |
+| Mais lento e pode levar alguns minutos para abrir | Mais rápido e pode ser iniciado em segundos |
+| Precisa de uma conexão com a internet para funcionar | Conexão com a internet mínima necessária (uma vez configurada) |
+| Algumas tarefas, como a compilação e testes, podem demorar mais para serem concluídas | Completa as tarefas mais rapidamente (dependendo das capacidades da sua máquina) |
+
+### Como preparar um espaço de trabalho no GitPod
+
+Nós automatizamos o processo de instalação de todas as dependências e ferramentas de que você precisará. Com o Gitpod, você terá um ambiente gratuito e pronto para o código em alguns minutos. Isso é útil caso você não tenha acesso a um computador ou queira fazer alterações únicas.
+
+Existem várias maneiras de se abrir um espaço de trabalho no Gitpod:
+
+1. **(Mais rápida)** Anexe `gitpod.io/#` na frente de qualquer URL do GitHub.
+
+ Por exemplo, se você for visitar o seu fork em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, adicione `gitpod.io/#` na frente do URL na barra de endereços e clique em enter.
+
+ Isso significa que você pode navegar para `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` e você verá uma área de trabalho criada para você. Isso funciona para qualquer repositório ou pull request no GitHub.
+
+2. Como alternativa, instale uma das extensões abaixo para o seu navegador.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - trabalha com navegadores baseados no Chromium, como o Google Chrome, o Brave, o Edge etc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Uma vez instalado, você verá um botão 'Gitpod' em cada repositório, pull request etc. Ele será um atalho útil para abrir um espaço de trabalho a partir de lá. Veja a página da extensão para detalhes, capturas de tela etc.
+
+É isso. Agora, você pode pular para a seção 'sincronizando a partir do pai' depois de ter iniciado um espaço de trabalho no Gitpod. A maior parte deste guia se aplica a espaços de trabalho no Gitpod, mas preste atenção em [como funcionam os URLs e as portas em um espaço de trabalho do Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports).
+
+**Observação: solucionando problemas de portas no Gitpod**
+
+Às vezes, o serviço na porta `8000` não vai subir. Isso é comum quando você está reiniciando um espaço de trabalho inativo.
+
+Se o serviço não estiver funcionando na porta `8000`, você pode resolver problemas usando estas etapas:
+
+- **Inicie o servidor**: execute `pnpm run develop:server` em uma janela de terminal do diretório do projeto raiz (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) para iniciar o servidor.
+
+- **Inicie o client**: em outra janela do terminal, execute `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` do diretório do client (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) para iniciá-lo.
+
+Isso deve tornar a porta `8000` disponível.
+
+### Como preparar sua máquina local
+
+Aqui está um requisito mínimo de sistema para executar o freeCodeCamp localmente:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- CPU relativamente rápida (4 núcleos ou mais)
+- Windows 10 ou 11 (com WSL), macOS ou Linux
+
+Comece instalando o software pré-requisito para seu sistema operacional.
+
+Apoiamos principalmente o desenvolvimento em sistemas Linux e Unix, como o Ubuntu e o MacOS. Você pode desenvolver no Windows 10 ou 11 somente com WSL2. Você pode seguir [este guia](how-to-setup-wsl) para configurar o WSL2. Você não pode usar o prompt de comando, o Git Bash ou o PowerShell para executar freeCodeCamp nativamente no Windows.
+
+#### Pré-requisitos:
+
+| Pré-requisito | Versão | Observações |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | Usamos a versão "Active LTS". Consulte [Agenda LTS](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [Servidor da Comunidade MongoDB](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+Se você tem uma versão diferente, instale a versão recomendada. Só podemos suportar problemas de instalação para versões recomendadas. Veja [a seção de solução de problemas](troubleshooting-development-issues) para detalhes.
+:::
+
+Se o Node.js já estiver instalado em sua máquina, execute os seguintes comandos para validar as versões:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+É altamente recomendável atualizar para o mais atual lançamento estável do software listado acima, também conhecido como Lançamentos de Suporte de Longo Prazo (LTS).
+:::
+
+Depois de ter os pré-requisitos instalados, você precisa preparar seu ambiente de desenvolvimento. Isto é comum para muitos fluxos de trabalho de desenvolvimento. Você só precisará fazer isso uma vez.
+
+##### Siga estas etapas para deixar seu ambiente de desenvolvimento pronto:
+
+1. Instale o [Git](https://git-scm.com/) ou seu cliente Git favorito, se você ainda não fez isso. Atualize para a versão mais recente. A versão que veio com seu SO pode estar desatualizada.
+
+2. (Opcional, mas recomendado) [Configure uma chave SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) para o GitHub.
+
+3. Instale um editor de código de sua escolha. Se você não tem certeza sobre qual editor usar, recomendamos o [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — é gratuito e de código aberto.
+
+4. Configure um linting no seu editor de código.
+
+ Você deve ter o [ESLint executando no seu editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), e ele vai destacar qualquer coisa que não esteja em conformidade com o [Guia de estilo JavaScript do freeCodeCamp](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ :::tip
+ Não ignore nenhum erro de linting. Eles têm como objetivo **ajudar** você e garantir uma base de código simples e limpa.
+ :::
+
+## Faça o fork do repositório no GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) é uma etapa onde você obtém sua própria cópia do repositório principal do freeCodeCamp (vulgo _repo_) no GitHub.
+
+Isso é essencial, pois permite que você trabalhe em sua própria cópia do freeCodeCamp no GitHub, ou que faça download (clone) do repositório para trabalhar localmente. Mais tarde, você poderá solicitar que alterações serem enviadas para o repositório principal através de um pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+O repositório principal em `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` é frequentemente chamado de repositório `upstream`.
+Seu fork em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` frequentemente é referenciado como o repositório de `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub.
+:::
+
+**Siga estes passos para criar um fork do repositório `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`:**
+
+1. Vá até o repositório freeCodeCamp no GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Clique no botão "Fork" no canto superior direito da interface ([Mais detalhes aqui](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Depois que o repositório recebeu um fork, você será redirecionado a cópia do repositório freeCodeCamp em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`(`YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Como criar um fork do freeCodeCamp no GitHub (imagem)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="Como criar um fork do freeCodeCamp no GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Clonar o seu fork no GitHub
+
+[Clonar](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) é a ação de **baixar** uma cópia de um repositório de um local `remote` que pertence a você ou a outra pessoa. No seu caso, este local remoto é o seu `fork` do repositório freeCodeCamp que deve estar disponível em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub.)
+
+> [!WARNING] Se você está usando uma distribuição WSL2 Linux, você talvez tenha problemas relacionados a performance e estabilidade ao executar esse projeto em uma pasta compartilhada entre Windows e WSL2 (ex. `/mnt/c/Users/`). Recomendarmos clonar esse repositório em uma pasta que é principalmente usada pela sua distribuição WSL2 Linux e não diretamente compartilhada com Windows (ex. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> Veja [essa issue no GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) para mais informações sobre esse problema.
+
+Execute estes comandos em sua máquina local:
+
+1. Abra um Terminal/Prompt de Comando/Shell no diretório de seus projetos
+
+ _ex.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone seu fork do freeCodeCamp, substituindo `YOUR_USER_NAME` pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+Isto vai baixar todo o repositório do freeCodeCamp para seu diretório de projetos.
+
+Observação: `--depth=1` cria um clone raso do seu fork, apenas com o histórico mais recente.
+
+## Configurar sincronização a partir do pai
+
+Agora que você baixou uma cópia do seu fork, será necessário configurar um remote `upstream` para o repositório pai.
+
+[Como mencionado anteriormente](#fork-the-repository-on-github), o repositório principal é referenciado como repositório `upstream`. Seu fork é referenciado como repositório `origin`.
+
+É necessária uma referência do seu clone local para o repositório `upstream` além do repositório `origin`. Isso é para que você possa sincronizar alterações do repositório principal sem a exigência de fazer fork e clone várias vezes.
+
+1. Mude o diretório para o novo diretório freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Adicione uma referência remota ao repositório principal freeCodeCampo:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Certifique-se de que a configuração esteja correta:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ O resultado deve ser algo parecido com o mostrado abaixo (substituindo `YOUR_USER_NAME` com seu nome de usuário do GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Executando freeCodeCamp localmente
+
+Agora que você tem uma cópia local do freeCodeCamp, você pode seguir estas instruções para executá-lo localmente. Isso permitirá que você:
+
+- Pré-visualize edições das páginas como aparecerão na plataforma de aprendizagem.
+- Trabalhe em issues relacionadas à interface do usuário e melhoramentos.
+- Faça a depuração e corrija problemas com servidores de aplicação e aplicações de client.
+
+Se você encontrar problemas, primeiro faça uma busca na web e procurar por respostas. Se encontrar uma solução, procure em nossa página de [issues do GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) para encontrar uma solução e reporte o problema se ainda não foi reportado.
+
+Como sempre, fique à vontade para perguntar na [categoria 'Contributors' (colaboradores) do fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [no servidor de chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configurar dependências
+
+#### Passo 1: Configure o arquivo de variável de ambiente
+
+As chaves de API padrão e variáveis de ambiente são armazenadas no arquivo `sample.env`. Esse arquivo precisa ser copiado para um novo arquivo chamado `.env` que é acessado dinamicamente durante a etapa de instalação.
+
+```bash
+# Crie uma cópia da "sample.env" e a nomeie como ".env".
+# Preencha-o com as chaves e segredos de API necessários
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+As chaves no arquivo `.env` _não_ precisam ser alteradas para executar o aplicativo localmente. Você pode deixar os valores padrão copiados de `sample.env` como estão.
+
+:::tip
+Lembre-se: se quiser usar serviços como Auth0 ou Algolia, você terá que adquirir suas próprias chaves da API para estes serviços e editar as entradas no arquivo `.env`.
+:::
+
+#### Passo 2: Instale as dependências
+
+Esta etapa vai instalar as dependências necessárias para a execução da aplicação:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Passo 3: Inicie o MongoDB e crie o banco de dados
+
+Antes de executar a aplicação localmente, você precisará iniciar o serviço MongoDB.
+
+> [!NOTE] A menos que você tenha o MongoDB executando em uma configuração diferente da padrão, a URL armazenada como valor para `MONGOHQ_URL` no arquivo `.env` funcionará. Se você está usando uma configuração diferente, modifique este valor caso necessário.
+>
+> Se você seguiu as instruções de [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), será capaz de pular este passo se o servidor do MongoDB daquele guia já estiver em execução. Você pode confirmar isso verificando se pode acessar `http://localhost:27017` em seu computador local.
+
+Inicie o servidor do MongoDB em um terminal separado:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+Você pode evitar ter que executar o MongoDB toda vez instalando-o como um serviço em segundo plano. Você pode [aprender mais sobre isso na documentação para seu OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Em seguida, vamos criar o banco de dados. Nesta etapa, executamos o comando abaixo que preenche o servidor MongoDB com alguns conjuntos de dados iniciais que são requeridos pelos serviços. Dentre outras coisas, incluem alguns esquemas.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+Por padrão, você será conectado como um novo usuário sem nenhuma certificação concluída. Execute o seguinte comando se precisar desenvolver com certificados concluídos ou escrever testes do Playwright:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Executar `pnpm run seed:certified-user` desconectará você. Você precisará limpar os cookies do seu navegador e fazer login novamente.
+
+#### Passo 4: Inicie o aplicativo de client do freeCodeCamp e o servidor de API
+
+Agora você pode iniciar o servidor de API e os aplicativos do client.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+Este único comando vai disparar todos os serviços, incluindo o servidor API e os aplicativos do cliente disponíveis para você trabalhar.
+
+Uma vez pronto, abra um navegador e acesse <http://localhost:8000>. Se o aplicativo carregar, faça o login. Parabéns – está tudo pronto! Agora você tem uma cópia da plataforma do freeCodeCamp de aprendizagem inteira rodando em sua máquina local.
+
+O servidor de API serve os endpoints em `http://localhost:3000`. O aplicativo Gatsby atende a aplicação de client em `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+Quando estiver conectado, se você visitar <http://localhost:3000/explorer> poderá ver as APIs disponíveis.
+
+> [!WARNING] Limpar seus cookies ou executar `pnpm run seed:certified-user` desconectará você e será preciso fazer o login novamente.
+
+Se você tiver problemas durante a instalação, confira a [seção de solução de problemas](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Referência de comandos rápidos
+
+Uma rápida referência aos comandos que você precisará ao trabalhar localmente.
+
+| comando | descrição |
+| ------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Instala/reinstala todas as dependências e inicializa os diferentes serviços. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Cria usuários de testes autorizados e os insere no MongoDB. Também executa `seed:exams` e `seed:surveys` abaixo. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Cria usuários de testes autorizados com certificações totalmente completas e os insere no MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Cria exames e os insere no MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Cria pesquisas para usuários padrão e as insere no MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Inicia o servidor de API do freeCodeCamp e aplicações de client. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Desinstala todas as dependências e limpa os caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cab77cfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp Mobile App locally
+---
+
+Siga este guia para configurar a aplicação para dispositivos móveis do freeCodeCamp localmente no seu sistema. Isso é altamente recomendado se você quer contribuir regularmente.
+
+Alguns dos fluxos de trabalho de contribuição — como a correção de erros na base de código — necessitam que você execute a aplicação do freeCodeCamp localmente.
+
+## Como preparar sua máquina local
+
+Comece instalando o software pré-requisito para seu sistema operacional.
+
+### Pré-requisitos
+
+| Pré-requisito | Versão | Observações |
+| ------------------------------- | ------ | -------------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (vem junto com o Flutter) | `3.x` | Utilizamos a versão integrada com o Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+Se você tem uma versão diferente, instale a versão recomendada. Só podemos dar suporte a problemas de instalação para versões recomendadas.
+:::
+
+Se o Flutter já estiver instalado em sua máquina, execute os seguintes comandos para validar as versões:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+É altamente recomendável atualizar para as versões estáveis mais recentes do software listado acima.
+:::
+
+Depois de ter os pré-requisitos instalados, você precisa preparar seu ambiente de desenvolvimento. Isto é comum para muitos fluxos de trabalho de desenvolvimento, e você só precisará fazer isso uma vez.
+
+#### Siga estas etapas para deixar seu ambiente de desenvolvimento pronto:
+
+1. Instale o [Git](https://git-scm.com/) ou seu cliente Git favorito, se você ainda não fez isso. Atualize para a versão mais recente. A versão que veio com seu SO pode estar desatualizada.
+
+2. Configure o [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) e os [emuladores do Android](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) com a versão mais recente do Android. Recomendamos usar a Pixel 3a XL e a Nexus One (para emulação de telas menores).
+
+3. (Opcional para MacOS) Configuração do Xcode e do iOS Simulator com a versão mais recente do iOS lançada.
+
+4. (Opcional, mas recomendado) [Configure uma chave SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) para o GitHub.
+
+5. Instale um editor de código de sua escolha.
+
+ Nós recomendamos muito usar o [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) ou o Android Studio. Também recomendamos instalar as [extensões](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode) oficiais.
+
+## Como fazer o fork do repositório no GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) é uma etapa onde você obtém sua própria cópia do repositório (vulgo _repo_) no GitHub.
+
+Isso é essencial, pois permite que você trabalhe em sua própria cópia da aplicação para dispositivos móveis do freeCodeCamp no GitHub, ou fazer download (clone) do repositório para trabalhar localmente. Mais tarde, você poderá solicitar alterações para serem enviadas para o repositório principal através de um pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+O repositório principal em `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` é frequentemente chamado de repositório `upstream`.
+Seu fork em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` frequentemente é referenciado como o repositório `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub.
+:::
+
+**Siga estes passos para criar um fork do repositório `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile`:**
+
+1. Vá até o repositório da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis no GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Clique no botão "Fork" no canto superior direito da interface ([Mais detalhes aqui](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Depois que o repositório recebeu um fork, você será redirecionado para a cópia do repositório em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub).
+
+## Como clonar o seu fork no GitHub
+
+[Clonar](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) é onde ** você faz o download de uma cópia** de um repositório de um local `remoto` que pertence a você ou a outra pessoa. No seu caso, este local remoto é o seu `fork` do repositório freeCodeCamp que deve estar disponível em `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` será substituído pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub.)
+
+Execute esses comandos em sua máquina local:
+
+1. Abra um Terminal/Prompt de Comando/Shell no diretório de seus projetos
+
+ _ex.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone seu fork do freeCodeCamp, substituindo `YOUR_USER_NAME` pelo seu nome de usuário do GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+Isto vai baixar todo o repositório da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis para seu diretório de projetos.
+
+Nota: `--depth=1` cria um clone raso do seu fork, com apenas o histórico mais recente.
+
+## Como configurar a sincronização a partir do repositório pai
+
+Agora que você baixou uma cópia do seu fork, será necessário configurar um remote `upstream` para o repositório pai.
+
+[Como mencionado anteriormente](#fork-the-repository-on-github), o repositório principal é referenciado como repositório `upstream`. Seu fork é referenciado como repositório `origin`.
+
+É necessária uma referência do seu clone local para o repositório `upstream` além do repositório `origin`. Isso é para que você possa sincronizar alterações do repositório principal sem a exigência de fazer fork e clone várias vezes.
+
+1. Mude o diretório para o novo diretório `mobile`:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Adicione uma referência remota ao repositório principal mobile do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Certifique-se de que a configuração esteja correta:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ O resultado deve ser algo parecido com o mostrado abaixo (substituindo `YOUR_USER_NAME` com seu nome de usuário do GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Como executar a aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis localmente
+
+Agora que você tem uma cópia local da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis, você pode seguir estas instruções para executá-la localmente.
+
+Se você encontrar problemas, primeiro faça uma busca na web e procurar por respostas. Se não for encontrada uma solução, por favor, procure em nossa página de [issues do GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) para encontrar uma solução e reporte o problema se ainda não foi reportado.
+
+E como sempre, fique à vontade em perguntar na [categoria 'Contributors' (colaboradores) do fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [no servidor de chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] O diretório `mobile` contém duas pastas, `mobile-api` e `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contém o código da API usada para servir os podcasts. `mobile-app` contém a aplicação em Flutter, que é onde você deve estar quando seguir os passos abaixo.
+
+### Configurar dependências
+
+#### Passo 1: Configure o arquivo de variável de ambiente
+
+As chaves de API padrão e variáveis de ambiente são armazenadas no arquivo `sample.env`. Esse arquivo precisa ser copiado para um novo arquivo chamado `.env` que é acessado dinamicamente durante a etapa de instalação. Lembre-se de mudar o diretório para `mobile-app` antes de executar os comandos a seguir.
+
+```bash
+# Crie uma cópia da "sample.env" e a nomeie como ".env".
+# Preencha-o com as chaves e segredos de API necessários:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+As chaves no arquivo `.env` _ não _ precisam ser alteradas para executar o aplicativo localmente. Você pode deixar os valores padrão copiados de `sample.env` como estão.
+
+#### Passo 2: Instalar as dependências
+
+Esta etapa vai instalar as dependências necessárias para a execução do aplicativo:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Passo 3: Iniciar a aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis
+
+Inicie o emulador de sua escolha (Android ou iOS) e aguarde a conclusão do processo de inicialização.
+
+Agora, você pode iniciar o aplicativo executando o seguinte comando:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+Se estiver usando o VSCode ou o Android Studio, poderá iniciar a aplicação facilmente sem ter de executar os comandos no terminal. Mais informações [aqui](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Como fazer alterações localmente
+
+Agora você pode fazer alterações nos arquivos e fazer commit das suas alterações no clone local do seu fork.
+
+Siga estes passos:
+
+1. Certifique-se que está no branch `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Você deve ver um resultado como este:
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch main
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'origin/main'.
+
+ nada para enviar no commit, diretório de trabalho limpo
+ ```
+
+ Se você não está no main ou seu diretório de trabalho não está limpo, resolva quaisquer arquivos/commits e saia do `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sincronize as últimas mudanças da branch `main` upstream para sua branch main local:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Se você possui qualquer pull request feito a partir da branch `main`, você os perderá ao fim desta etapa.
+ >
+ > Certifique-se de que foi feito um merge no seu pull request por um moderador antes de executar este passo. Para evitar essa situação, você **sempre** deve trabalhar em uma brach que não seja a `main`.
+
+ Este passo **irá sincronizar as últimas alterações** do repositório principal da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis. É importante fazer um rebase em sua branch usando `upstream/main` frequentemente para evitar conflitos depois.
+
+ Atualize sua cópia local do repositório upstream da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Faça um hard reset na sua branch main com a main da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Faça um push da sua branch main para a origin para obter um histórico claro em seu fork do GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ Você pode validar se sua main atual combina com upstream/main fazendo um diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ O resultado deve mostrar vazio.
+
+3. Crie uma branch novinha em folha:
+
+ Trabalhar em uma branch separada para cada issue ajuda a manter sua cópia de trabalho local limpa. Você nunca deve trabalhar na `main`. Isso vai sujar sua cópia da aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis e você pode ter que começar de novo com um clone ou fork.
+
+ Veja se você está na `main` como explicado antes e crie uma branch a partir dela:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Seu nome de branch deve começar com `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Evite usar números de issues em branches. Mantenha-os curtos, significativos e únicos.
+
+ Alguns exemplos de bons nomes para branches são:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edite páginas e trabalhe no código em seu editor de texto favorito.
+
+5. Quando estiver satisfeito com as alterações, você deve opcionalmente executar a aplicação do freeCodeCamp para dispositivos móveis localmente para visualizar as alterações.
+
+6. Certifique-se de corrigir quaisquer erros e verificar a formatação de suas alterações.
+
+7. Verifique e confirme os arquivos que você está atualizando:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Isso deve mostrar uma lista dos arquivos `unstaged` que você editou.
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch feat/documentation
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ As mudanças não estão organizadas para commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." para atualizar o que será enviado)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." para descartar as alterações no diretório de trabalho)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Organize as alterações e faça um commit:
+
+ Nesta etapa, você só deve marcar arquivos que você editou ou adicionou. Você pode executar um reset e resolver arquivos que você não pretendeu mudar se necessário.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add caminho/para/meu/arquivo/alterado.ext
+ ```
+
+ Ou você pode adicionar todos os arquivos `unstaged` para a área de preparação:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Apenas os arquivos que foram movidos para a área de staging serão adicionados quando você fizer um commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Resultado:
+
+ ```bash
+ Na branch feat/documentation
+ Sua branch está atualizada com 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Alterações a serem enviadas:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." para retirar do staging)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Agora, você pode fazer o commit das alterações com uma pequena mensagem assim:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Alguns exemplos:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Opcional:
+
+ É altamente recomendável fazer uma mensagem convencional de commit. Esta é uma boa prática que você verá em alguns dos repositórios de código aberto populares. Como um desenvolvedor, isso incentiva você a seguir os padrões.
+
+ Alguns exemplos de mensagens convencionais de commit são:
+
+ ```md
+ correção: atualizar artigo do guia HTML
+ fix: atualizar scripts de compilação para Travis-CI
+ fear: adicionar artigo para a documentação de hoisting em JavaScript
+ docs: atualizar diretrizes de contribuição
+ ```
+
+ Escreva pouco, não mais do que 50 caracteres. Você sempre pode adicionar informações extras na descrição da mensagem de commit.
+
+ Isso não leva mais tempo do que uma mensagem não convencional como 'atualizar arquivo' ou 'adicionar index.md'
+
+ Você pode aprender mais sobre o motivo de usar commits convencionais [aqui](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Se você se deu conta que precisa editar um arquivo ou atualizar a mensagem de commit você pode fazer isso assim:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Isso abrirá um editor de texto padrão, como `nano` ou `vi` onde você pode editar o título da mensagem de commit e adicionar/editar a descrição.
+
+10. Em seguida, você pode fazer push das suas alterações no seu fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/nome-aqui
+ ```
+
+## Executando testes do currículo para dispositivos móveis
+
+> [!NOTE] Você somente precisa seguir esta seção se estiver modificando o executador de testes de desafio na aplicação para dispositivos móveis. Caso contrário, vá para a próxima seção sobre [como abrir um pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Faça a clonagem do [repositório do freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) localmente e fora da cópia local do repositório para dispositivos móveis do freeCodeCamp. A estrutura de pastas deve ficar assim:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Mude o diretório para o novo diretório do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Faça uma cópia do arquivo `.env`:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Instale as dependências para o repositório do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Gere o arquivo JSON dos dados de desafio:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copie o arquivo JSON gerado para a aplicação para dispositivos móveis:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Mude o diretório para o diretório da aplicação para dispositivos móveis:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Instale as dependências para a aplicação para dispositivos móveis:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Atualize o arquivo de testes para que use o arquivo JSON de dados do desafio:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Gere os arquivos do desafio:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Inicie um servidor local para servir os arquivos de desafio com a ajuda do pacote `serve`:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. Em um terminal diferente, volte ao repositório do freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Execute os testes do Cypress:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Solução de problemas
+
+### Problemas com a instalação dos pré-requisitos recomendados
+
+Regularmente desenvolvemos nos sistemas mais populares como macOS 10.15, Ubuntu 18.04 e Windows 10 (com WSL2).
+
+É recomendado pesquisar seu issue específico em recursos como Google, Stack Overflow e Stack Exchange. É possível que alguém já tenha enfrentado o mesmo problema que o seu e já possui uma solução.
+
+Se você está em um sistema operacional diferente e/ou ainda está com problemas, veja [obtendo ajuda](#getting-help).
+
+### Problemas com a Interface do Usuário, fontes, errors de build, etc.
+
+Se você enfrenta problemas com a interface do usuário ou erros de build, uma limpeza pode ser útil:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Problemas ao instalar dependências
+
+Se você receber erros durante a instalação das dependências, certifique-se de que você não está em uma rede restrita ou suas configurações de firewall não impedem você de acessar os recursos.
+
+Seja paciente, pois a primeira configuração pode demorar um pouco, dependendo da largura de banda da sua rede.
+
+## Obtendo ajuda
+
+Se você está com dificuldades e precisa de ajuda, fique à vontade em perguntar na categoria ['Contributors' (colaboradores) em nosso fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [na sala de bate-papo dos colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Pode haver um erro no console do seu navegador ou no Bash/Terminal/Linha de Comando que ajudará a identificar o problema. Forneça esta mensagem de erro na descrição do seu problema para que outros possam identificá-lo mais facilmente e ajudá-lo a encontrar uma solução.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0189221a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Configure o freeCodeCamp no subsistema Windows para Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Antes de seguir estas instruções, verifique se o sistema atende aos requisitos.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Versão 2004, Build 19041 ou superior) - disponível para todas as distribuições, incluindo o Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop para Windows**: Veja os respectivos requisitos para [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) e [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+Este guia abrange algumas etapas comuns sobre a instalação do WSL2. Uma vez resolvidos alguns dos problemas comuns com o WSL2, você deve seguir o nosso [guia de instalação local](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) para trabalhar com o freeCodeCamp no Windows executando uma distro WSL como o Ubuntu.
+
+## Ative o WSL
+
+Siga as instruções na [documentação oficial](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) para instalar o WSL2.
+
+## Instale o Ubuntu
+
+1. Recomendamos usar Ubuntu-18.04 ou superior com WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > Embora você possa usar outras distribuições não baseadas em Debian, todas vêm com seus próprios empecilhos, que estão além do escopo deste guia.
+
+ A partir de novembro de 2023, Ubuntu e Debian serão as únicas distribuições de Linux [oficialmente suportadas pelo Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), a biblioteca de testes de ponta a ponta usada pelo freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Atualize as dependências para o sistema operacional
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Configure o Git
+
+O Git vem pré-instalado com Ubuntu 18.04, verifique sua versão do Git com `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Opcional, mas recomendado) Agora você pode prosseguir para [configurar suas chaves ssh](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) com o GitHub.
+
+## Instalando um Editor de Código
+
+É altamente recomendável instalar o [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) no Windows 10. Tem um ótimo suporte para WSL e instala automaticamente todas as extensões necessárias na distribuição WSL.
+
+Essencialmente, você irá editar e armazenar seu código no Ubuntu-18.04 com o VS Code instalado no Windows.
+
+Se você usa o [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), talvez precise atualizar seu interpretador do Node e seu gerenciador de pacotes npm pelo que estiver instalado em sua distro WSL.
+
+Você pode checar essas configurações indo em Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Instalando o Docker Desktop
+
+**O Docker Desktop para Windows** permite instalar e executar banco de dados e serviços como MongoDB, NGINX, etc. Isso é útil para evitar problemas comuns com a instalação do MongoDB ou outros serviços diretamente no Windows ou WSL2.
+
+Siga as instruções da [documentação oficial](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) e instale o Docker Desktop para a sua distribuição no Windows.
+
+Existem alguns requisitos mínimos de hardware para melhor experiência.
+
+## Configure o Docker Desktop para WSL
+
+Quando o Docker Desktop estiver instalado, [siga estas instruções](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) e configure-o para usar a instalação do Ubuntu-18.04 como backend.
+
+Isso faz com que os contêineres sejam executados no lado do WSL em vez de serem executados no Windows. Você será capaz de acessar os serviços através do `http://localhost` tanto no Windows quanto no Ubuntu.
+
+## Instale MongoDB usando Docker Hub
+
+Depois de ter configurado o Docker Desktop para trabalhar com o WSL2, siga essas etapas para iniciar um serviço no MongoDB:
+
+1. Inicie um novo terminal do Ubuntu
+
+2. Faça o pull do MongoDB a partir do Docker Hub. Consulte a tabela de [Pré-requisitos](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) para ver a versão atual do MongoDB usada pelo freeCodeCamp. Por exemplo, se o número da versão for `5.0.x`, substitua `<x.y>` por `5.0` nos dois trechos de código a seguir.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Inicie o serviço MongoDB na porta `27017` e configure-o para ser executado automaticamente ao reiniciar o sistema
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Agora você pode acessar o serviço no Windows ou Ubuntu em `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Instalando o Node.js e o pnpm
+
+Recomendamos que você instale a versão LTS para Node.js com um gerenciador de versões do node - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Uma vez instalado, use este comando para instalar e usar a versão do Node.js LTS mais recente:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+Para ver instruções de instalação e de uso de uma versão diferente do Node.js, consulte a [documentação do nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+O Node.js vem com o `npm`, que você pode usar para instalar o `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Configure o freeCodeCamp localmente
+
+Agora que você instalou os pré-requisitos, siga [nosso guia de instalação local](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) para clonar, instalar e configurar o freeCodeCamp em sua máquina.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Por favor note que, neste momento, a configuração para testes do Cypress (e necessidades relacionadas à GUI) é um trabalho em andamento. Você ainda deve ser capaz de trabalhar na maior parte do código.
+
+## Otimizar o Windows e o WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> As dicas a seguir foram coletadas de toda a web e não passaram por diversos testes. A quilometragem pode variar.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+Isso pode reduzir os incidentes dos contêineres do Docker causando um crash devido à falta de recursos.
+
+Abra o painel de controle das Propriedades do Sistema pressionando <kbd>Win + R</kbd> e digitando `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Digite <code>sysdm.cpl</code> na caixa de diálogo Executar (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Digite `sysdm.cpl` na caixa de diálogo Executar" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Vá para Avançado -> Desempenho -> Configurações…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Botão de Configurações na parte de Desempenho na guia Avançado das Propriedades do Sistema (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Botão Configurações na parte de Desempenho na guia Avançado em Propriedades do Sistema" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Em Avançado -> Agendamento do processador, escolha "Serviços em segundo plano". Não feche a janela. Continue para a próxima dica.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Botão de seleção dos Serviços em segundo plano na aba Avançado em Opções de Desempenho (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Botão de opção dos Serviços em segundo plano na guia Avançado em Opções de Desempenho" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Aumente o tamanho do arquivo de paginação do Windows para a unidade do sistema
+
+Em Avançado -> Memória virtual, clique em "Alterar…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Botão para alterar a memória virtual na aba Avançado em Opções de Desempenho (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Botão de alterar a memória virtual na guia Avançado em Opções de Desempenho" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Escolha "Tamanho personalizado". Defina o tamanho inicial para 1.5x e o tamanho máximo para 3x da sua memória física. Em seguida, clique em "Definir".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Botão Definir o tamanho personalizado na janela de Memória Virtual (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Botão Definir o tamanho personalizado na janela de Memória Virtual" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Aumentar o tamanho da memória alocada para o WSL
+
+Crie um arquivo [`.wslconfig`](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) no diretório [`%UserProfile%`](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (tipicamente `C:\Users\<NomeDoUsuário>\.wslconfig`). Leia a documentação do [WSL](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) cuidadosamente e substitua `x` por valores que correspondam às suas próprias necessidades:
+
+```ini
+# As configurações se aplicam a todas as distribuições do Linux que rodam no WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# Quanta memória atribuir à VM do WSL 2. O valor padrão pode não ser suficiente
+memory=xGB
+
+# Quanto de espaço de swap para adicionar à VM do WSL 2. O padrão é 25% da RAM disponível
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Aumentar o tamanho do espaço antigo máximo do Node.js
+
+Isso corrige o erro ["JavaScript heap out of memory"](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) com o ESLint. Adicione o seguinte à sua `~/.bashrc` ou `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Evite `pnpm run test`
+
+Ao invés disso, use o script [apropriado ao seu PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.): `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum` ou `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Links úteis
+
+- [Configuração de desenvolvimento do WSL2 com Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code e Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - um artigo de Mrugesh Mohapatra (desenvolvedor da equipe do freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Perguntas frequentes sobre:
+ - [Subsistema Windows para Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop para Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e1ffcabf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: Como testar traduções localmente
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Esse processo não é obrigatório, mas documentado caso você queira visualizar como suas traduções ficarão.
+
+Se você gostaria de testar suas traduções em uma instância local do site FreeCodeCamp `/learn`, primeiro certifique-se de que você [configurou a base de código](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Habilitando um idioma
+
+Existem algumas etapas a serem seguidas para permitir que a base de código seja compilada no idioma desejado.
+
+Primeiro, visite o arquivo `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` para adicionar o idioma à lista de idiomas disponíveis e configurar os valores. Existem quatro objetos aqui.
+
+- `availableLangs`: tanto para o array `client` quanto para o array `curriculum`, adicione o nome do idioma. Esse valor é o que será usado no arquivo `.env` depois.
+- `auditedCerts`: adicione o nome do texto do idioma como a _chave_ e adicione um array de variáveis `SuperBlocks.{cert}` como o _valor_. Isto informa ao cliente quais certificações estão totalmente traduzidas.
+- `i18nextCodes`: esses são os códigos ISO de cada linguagem. Você vai precisar do código ISO apropriado para o idioma que você está habilitando. Eles precisam ser únicos para cada idioma.
+- `LangNames`: esses são os nomes dos idiomas que aparecerão para a seleção no menu de navegação.
+- `LangCodes`: esses são os códigos de idiomas usados para formatar datas e números. Esses deverão ser códigos Unicode CLDR ao invés de códigos ISO.
+
+Como um exemplo, se você tivesse que habilitar o idioma Dothraki como seu idioma, os objetos `all-langs.js` devem ficar assim:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Agora, abra o arquivo `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`. Esse dado é usado para a barra de busca que carrega os artigos `/news`. Embora seja improvável que você venha a testar essa funcionalidade, não ter os dados para o seu idioma pode levar a erros quando tentar criar a base de código localmente.
+
+Adicione um objeto para seu idioma no objeto `algoliaIndices`. Você deve usar os mesmos valores do objeto `english` para o teste local, substituindo a chave `english` pelo valor de `availableLangs` do seu idioma.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se nós já implantamos uma instância do editorial em sua língua-alvo, você pode atualizar os valores para refletir a instância que já está implantada. Do contrário, use os valores em inglês.
+
+Se você fosse adicionar Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Por fim, em seu arquivo `.env`, definimos `CLIENT_LOCALE` e `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` com o valor de seu novo idioma (use o valor de `availableLangs`.)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Liberar um superbloco
+
+Após um superbloco ter sido totalmente traduzido para um idioma, há duas etapas necessárias para seu lançamento. Primeiro, adicione o enum do superblock ao array `auditedCerts` do idioma. Assim, se você quiser liberar o novo superbloco de Design Responsivo para a Web para o dothraki, o array deverá ter essa aparência:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // outros idiomas
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // o superbloco recém-traduzido
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Por fim, o array `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` deve ser atualizado para incluir o novo idioma, assim:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+Isso moverá o novo superbloco para o lugar correto no mapa do currículo em `/learn`.
+
+## Ativando vídeos localizados
+
+Para os desafios em vídeo, você precisa fazer algumas alterações. Primeiro, adicione o novo idioma (locale) à consilta do GraphQL no arquivo `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`. Por exemplo, para adicionar Dothraki à consulta:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Em seguida, adicione um id para o novo idioma para qualquer desafio em vídeo em um bloco auditado. Por exemplo, se `auditedCerts` em `all-langs.ts` inclui `scientific-computing-with-python` para `dothraki`, você deve adicionar uma entrada em `dothraki` em `videoLocaleIds`. O frontmatter dever ter essa aparência:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+nomeComTracos: introducao-por-que-programa
+---
+```
+
+Atualize a interface de `VideoLocaleIds` em `client/src/redux/prop-types` para que ela inclua o novo idioma.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+Por fim, atualize o schema de desafios em `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Carregando traduções
+
+Como o idioma ainda não foi aprovado para produção, nossos scripts ainda não estão baixando automaticamente as traduções. Somente membros da equipe têm acesso para baixar as traduções diretamente – entre em contato conosco quando quiser em nossa [sala de chat dos contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) ou traduza os arquivos de markdown em inglês localmente para fins de teste.
+
+Quando tiver os arquivos em mãos, você precisará colocá-los no diretório correto. Para os desafios do currículo, você deve colocar as pastas de certificação (por exemplo, `01-responsive-web-design`) no diretório `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Para nossas traduções em Dothraki, esse diretório seria `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. Os arquivos `.json` de tradução do client vão no diretório `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Quando estes arquivos estiverem no local certo, você deve poder usar `npm run develop` para ver sua versão traduzida do freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+Embora você possa realizar as traduções localmente para fins de teste, lembramos a todos que as traduções _não_ devem ser enviadas pelo GitHub e devem ser feitas somente pelo Crowdin. Certifique-se de reiniciar sua base de código local após realizar os testes.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f04359a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: Como traduzir arquivos do freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+## Prepare-se para as contribuições
+
+> O roadmap de localização do freeCodeCamp - não há limites de velocidade
+
+:::tip
+Você pode começar lendo [este anúncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-ajudar-a-traduzir-o-freecodecamp-para-seu-idioma/). Recomendamos que entre [em nosso fórum da comunidade](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) e [no servidor de chat do Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+Você pode traduzir o quanto você quiser e quando você puder. O que realmente importa é o quanto de tempo e energia você estará disposto a investir como um voluntário de tradução.
+
+Pedimos apenas que entenda os seguintes pontos:
+
+1. **As traduções são um esforço em equipe.**
+
+ A tradução dos recursos do freeCodeCamp é uma das mais divertidas e gratificantes como um contribuidor. Ela fica ainda melhor quando envolve amigos e colegas que falam o mesmo idioma que você.
+
+ Você pode começar lendo [este anúncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-ajudar-a-traduzir-o-freecodecamp-para-seu-idioma/). Recomendamos que entre [em nosso fórum da comunidade](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) e no [servidor de chat do Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) com seus amigos e mostre seu interesse antes de começar a traduzir. O Crowdin, assim como outras ferramentas, facilita a contribuição com traduções, mas ainda há bastante trabalho.
+
+ Nós esperamos que você goste de contribuir e não venha a se sentir esgotado ou perder o interesse.
+
+ Um grupo pequeno de 4 à 5 indivíduos é um bom tamanho para iniciar o nicho para o seu idioma. Você pode, então, recrutar cada vez mais amigos para se juntarem ao time.
+
+2. **Custa muito aos servidores rodar cada linguagem.**
+
+ Na superfície, os componentes técnicos não parecem ser tão complicados, mas, para que os componentes continuem rodando, há um alto custo. Nisto está incluso o provisionamento adicional de servidores e uma equipe dedicada poder cuidar deles.
+
+ O freeCodeCamp.org comprometeu-se em providenciar de forma gratuita como sempre. No entanto, precisamos priorizar os recursos para os que mais necessitam deles. A última coisa que queremos é desligar os servidores para uma linguagem se a atividade de tradução encerrar e se tornar desatualizada.
+
+ Para traduzir o currículo, quando cada idioma alcançar pelo menos algumas certificações no currículo, podemos começar a implantar o idioma no [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn) enquanto você continua a traduzir o restante das certificações.
+
+ Por exemplo, gostaríamos de implantar pelo menos todo o conjunto de certificações de front-end quando entregarmos uma nova linguagem pela primeira vez.
+
+3. **E quanto às linguagens que não estão listadas na plataforma de tradução?**
+
+ Nós buscamos em nossa base de usuários e adicionamos os mais de 30 idiomas mais falados para a lista de idiomas habilitados na plataforma de traduções. Alguns idiomas, como o chinês e o espanhol já estão implantados no **/learn** neste momento.
+
+ Infelizmente, a lista não inclui as centenas de idiomas existentes. Nós recebemos dezenas de requisições de contribuidores como você, todos os dias. Eles também gostariam de ajudar na tradução do site no idioma que falam.
+
+ Nós estamos definitivamente torcendo para adicionar mais idiomas na lista, mas, como você já sabe, só seria viável se conseguíssemos um impulso suficiente em torno de um idioma.
+
+ Se você gostaria que nós incluíssemos um novo idioma, recomendamos que você deixe seus amigos animados com isso.
+
+ Quando você tiver um pequeno grupo de pessoas (pelo menos 4-5) interessadas e comprometidas, nós poderemos entrar em contato. Explicaremos todos os detalhes e orientaremos você em algumas das ferramentas e processos.
+
+## Visão geral do Crowdin
+
+É nosso sonho fornecer recursos para você aprender, não importando qual idioma fala. Para nos ajudar com isso, integramos nossa base de código open-source e nosso currículo com o [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/), uma ferramenta que nos ajuda a traduzir nosso código.
+
+> [!NOTE] Usamos uma ferramenta e um fluxo de trabalho diferentes para traduzir os [artigos do editorial](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). Se você estiver interessado em traduzir artigos, leia [este anúncio](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-ajudar-a-traduzir-o-freecodecamp-para-seu-idioma/) e entre em contato com o líder das traduções para o seu idioma.
+
+O fluxo de tradução é dividido em duas atividades principais:
+
+- **Traduzir** arquivos do currículo, documentação e elementos da interface como botões, rótulos e etc.:
+
+ Como um tradutor, você pode se cadastrar em [nossa plataforma de tradução](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) e contribuir com traduções em mais de 30 idiomas disponíveis.
+
+- **Revisar** as traduções de todo conteúdo.
+
+ Os revisores verificam se as traduções da comunidade têm um tom uniforme e não contêm problemas como erros de digitação, entre outros. Resumidamente, eles garantem a alta qualidade das traduções. Note que nós não usamos tradução automática por um motivo.
+
+> [!WARNING] Não usamos mais o GitHub para traduzir arquivos diretamente. Se você está voltando a contribuir, vá para nossa [plataforma de tradução](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+## Primeiros passos
+
+Primeiro, não se esqueça de vir dar um "Oi" no nosso [servidor do Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Nós postamos atualizações regulares sobre recursos de tradução e respondemos a muitas de suas dúvidas lá.
+
+Depois, vá para a nossa [plataforma de tradução](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) e faça o login (se você não contribuiu com traduções anteriormente, você precisará criar uma conta).
+
+Finalmente, faça o nosso passo a passo abaixo para entender as ferramentas de tradução e fluxos de trabalho à sua disposição.
+
+Boa tradução.
+
+## Selecione um projeto e um arquivo
+
+Quando você visita a plataforma de tradução, você deve ver vários "projetos" disponíveis para tradução:
+
+1. Projeto de [Contribuição de documentação](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs), que contém os arquivos para a documentação deste site.
+2. Projeto do [Currículo de programação](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum), que contém nossos arquivos de desafios para nosso currículo.
+3. Projeto de [Interface de aprendizagem do usuário](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui), que contém as "strings" para elementos de UI como botões, "labels", etc. para nossa plataforma de aprendizagem.
+
+Selecione qualquer projeto no qual que deseje contribuir e você verá uma lista de idiomas disponíveis para tradução.
+
+
+
+Selecione o idioma que deseja trabalhar e você verá a estrutura completa do arquivo.
+
+
+
+Cada arquivo e pasta aparecerá na barra de progresso. A porção **azul** da barra de progresso indica a porcentagem de tradução do arquivo, enquanto a porção **verde** da barra indica a porcentagem aprovada pelo time de revisão.
+
+Selecione um arquivo para traduzir e o Crowdin vai abrir o editor.
+
+> [!NOTE] Quando o editor abrir, você precisará clicar no ícone de configurações (mostrado como uma engrenagem) e mudar a configuração 'HTML tags displaying' para 'SHOW'. Isso garantirá que você verá tags como `<code></code>` ao invés de `<0></0>`.
+
+## Traduzir o currículo
+
+
+
+O Crowdin separa o documento em "strings" traduzíveis, geralmente frases. Cada string é traduzida individualmente. Referente à imagem acima:
+
+1. Uma string marcada em verde já tem uma proposta de tradução.
+2. Uma string em vermelho ainda _não_ possui uma proposta de tradução.
+3. Uma string com texto acinzentado não é traduzível. Esse é o caso para blocos de código e outros conteúdos que não devem ser traduzidos. Você não poderá selecionar essas strings no editor.
+4. Se um contribuidor propôs uma tradução para uma string, o Crowdin vai mostrar a proposta aqui. Você não pode salvar uma tradução idêntica - ao invés disso, se a tradução estiver precisa, você deve clicar no ícone `+` para "aprová-la". Uma tradução imprecisa pode ser "desaprovada" com o ícone `-`.
+5. O Crowdin vai recomendar traduções baseadas na TM (Translation Memory) ou na MT (Machine Translation). Translation Memory se refere a strings similares ou idênticas que já foram traduzidas/aprovadas em outros arquivos. Machine Translation refere-se a traduções recomendadas por bibliotecas integradas.
+6. Esse é o painel do editor, onde você pode propor traduções para a string selecionada.
+7. A string selecionada no editor estará marcada em amarelo.
+8. Aqui você verá tags indicando o estado da string. `Done` significa que a string possui pelo menos uma proposta de tradução. `Todo` significa que a string não possui nenhuma proposta de tradução.
+9. Aqui você pode ver a janela de comentários. Se você tem perguntas ou preocupações acerca de uma string em particular, você pode comentar aqui para que outros tradutores vejam.
+10. Esses dois "botões de painel" esconderão o documento à esquerda e os comentários à direita.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se você encontrar uma string escondida que inclui traduções, notifique-a no [servidor do Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) para que possamos remover a tradução da memória.
+
+Quando tiver terminado de traduzir uma string, clique em `Save` para salvar sua tradução no Crowdin. Outros contribuintes poderão votar em sua tradução e os revisores poderão aprová-la.
+
+Fique à vontade para traduzir quantas strings quiser - não há nenhuma etapa adicional requerida quando você completar um arquivo inteiro ou propor uma nova tradução. Clicar em `Save` é tudo de que você precisa para salvar sua tradução.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se você ver algo no arquivo fonte em Inglês que esteja impreciso ou incorreto, por favor não conserte-o pelo mecanismo de tradução. No lugar, deixe um comentário na string para nos notificar de uma discrepância ou crie uma "GitHub issue".
+
+## Traduzir a interface de aprendizagem
+
+Nossa interface `/learn` depende de arquivos JSON carregados em um plugin i18n para gerar o texto traduzido. Esse esforço de tradução está dividido entre o Crowdin e o GitHub.
+
+### No GitHub
+
+Os arquivos `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json` e `trending.json` contêm informações que precisam ser atualizadas para refletirem em seu idioma. No entanto, não podemos carregá-los no Crowdin, já que seu conteúdo não seria uma tradução direta.
+
+Esses arquivos provavelmente serão atualizados pelo líder do seu idioma, mas fique à vontade para [ler sobre como os traduzimos](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### No Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Não edite o seguintes arquivos por meio de um PR no GitHub.
+:::
+
+Os arquivos `intro.json` e `translations.json` são traduzidos no Crowdin, no projeto Learn User Interface (Learn UI). A tradução dessas traduções pode ser um pouco complicada, já que cada valor JSON individual tem sua própria sequência de caracteres e, às vezes, o contexto não é suficiente.
+
+Porém, as informações de `Context` fornecidas no Crowdin podem ajudar a entender onde a string se encaixa em uma estrutura maior.
+
+
+
+Se tiver perguntas sobre onde uma string se encaixa em seu contexto, fale conosco no [chat dos colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Traduzir a documentação
+
+Traduzir nossa documentação de contribuição é similar a traduzir nossos arquivos de currículo.
+
+> [!NOTE] Nossa documentação de contribuição utiliza`docsify`, e nós temos uma análise especial para caixas de mensagem como essa. Caso veja strings iniciadas com `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]`, ou `[!TIP]`, essas palavras NÃO devem ser traduzidas.
+
+### Como traduzir a documentação com links internos
+
+Quando você trabalha na tradução da documentação de contribuição, fique atento aos links internos direcionados a uma seção diferente da documentação.
+
+Certifique-se de substituir o id da seção de destino (a parte depois de `#`) pelo id do documento traduzido. Por exemplo, essa será a aparência em português:
+
+Antes da tradução
+
+```
+// em HTML
+<a href="nome-do-arquivo-de-destino.md#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino">Link text</a>
+<a href="#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino">Link text</a>
+
+// em Markdown
+[Link text]($1#$2)
+[Link text](#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino)
+```
+
+Após a tradução
+
+```
+// em HTML
+<a href="nome-do-arquivo-de-destino.md#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino">Texto do link</a>
+<a href="#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino">Texto do link</a>
+
+// em Markdown
+[Texto do link]($1#$2)
+[Texto do link](#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino)
+```
+
+Os arquivos na documentação são escritos em markdown, mas eles aparecerão como tags HTML no Crowdin.
+
+Você pode descobrir como o `docsify` converte uma string em seu idioma em um ID, analisando as páginas traduzidas. Se a tradução ainda não tiver sido implementada, você pode pré-visualizá-la [executando o site da documentação localmente](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#serving-the-documentation-site-locally).
+
+Você pode aprender mais sobre [links internos em nossa documentação aqui](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#how-to-create-an-internal-link).
+
+## Traduzir o RPG LearnToCode
+
+O RPG LearnToCode é executado no Ren'Py, que usa uma sintaxe especial para strings traduzidas: (Consulte a [documentação sobre textos do Ren'Py](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- As frases a serem traduzidas estarão sempre entre `""`. Elas são diálogos ou strings da UI. As palavras-chave que vêm antes ou depois do diálogo são palavras-chave de controle do mecanismo do jogo e serão explicadas em detalhes nas regras subsequentes. Observe que esta primeira regra rege todas as regras subsequentes listadas.
+- No caso de `new "..."`, não traduza a palavra-chave `new`.
+- Prefixos como `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (ou variantes como `player happy`, `player @ happy`) não devem ser traduzidos. Eles são palavras-chave de controle para exibir corretamente a imagem do personagem no jogo.
+- Textos após as aspas do diálogo, como `nointeract`, não devem ser traduzidos.
+- Não traduza o que estiver entre `[]` e `{}`. Estas são interpolações de variáveis e tags de texto. Estes parênteses devem permanecer com metade da largura `[]` e `{}` em vez de seus equivalentes de largura total `【】` e `「」`
+- Não traduza a palavra-chave `nointeract` ao final da frase.
+- Se tentarmos usar parênteses de largura total `()`, receberemos um aviso de controle de qualidade (QA). Para evitar o aviso de QA, use parênteses com metade da largura `()`
+
+### Exemplos
+
+---
+
+#### Antes da tradução
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- esta é a linha que precisa ser traduzida. veja a tradução abaixo
+```
+
+#### Após a tradução
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?Que coincidência! Nosso membro VIP da equipe, {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} ficará honrado ao saber disso."
+```
+
+Observação: as tags `[]` e `{}` devem permanecer intactas.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes da tradução
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- traduza essa linha, ver abaixo
+```
+
+#### Após a tradução
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Avançar"
+```
+
+Observação: novamente, o prefixo `new` e a tag `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` devem ser mantidos intactos.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes da tradução
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### Após a tradução
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Ha ha, [player_name], é divertido falar com você. Tenho certeza de que você vai gostar de trabalhar em desenvolvimento."
+```
+
+Observação: `layla @ neutral` e `[player_name]` permanecem inalterados.
+
+---
+
+#### Antes da tradução
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### Após a tradução
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Será que isso tudo é um sonho?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Uma observação sobre o modo como o Crowdin segmenta uma frase
+
+Preste atenção na maneira como o Crowdin segmenta uma linha de diálogo envolvida por aspas de abertura e fechamento `""`. Quando traduzirmos o diálogo, temos de manter as aspas de abertura e fechamento, mesmo que as aspas apareçam em diferentes segmentos.
+
+Esta é a linha que precisa ser traduzida:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+O Crowdin segmenta a string em três partes, como vemos abaixo:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# traduzido, mantendo as aspas de abertura `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+What is that?
+# tradução, sem aspas dos dois lados
+O que é isso?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# traduzido, mantendo as aspas de fechamento `"`
+É melhor eu anotar para saber mais a respeito."
+```
+
+## Avaliar Traduções
+
+Crowdin permite que você avalie propostas de tradução existentes. Se você tentar salvar uma tradução, você pode ver uma mensagem indicando que você não pode salvar a duplicata de uma tradução - isso significa que outro contribuinte já propôs uma tradução idêntica. Se você concorda com aquela tradução, clique em `+` para "aprová-la".
+
+Se você ver uma tradução que não possui a mesma clareza da string original, clique em `-` para "desaprová-la".
+
+Crowdin usa esses votos para pontuar cada proposta de tradução de cada string, o que ajuda o time de revisão a determinar qual tradução é a melhor para cada string.
+
+## Verificações de qualidade
+
+Nós disponibilizamos algumas verificações de qualidade para assegurar que as traduções estejam precisas - isso ajuda nossos revisores a analisarem as traduções propostas.
+
+Quando você tenta salvar uma tradução, talvez veja uma mensagem de aviso aparecer a respeito da sua tradução proposta.
+
+
+
+Essa mensagem aparece quando o sistema QA (Verificação de Qualidade) do Crowdin identificou algum erro em potencial na tradução proposta. Nesse exemplo, nós modificamos o texto da tag `<code>` e o sistema viu isto.
+
+> [!WARNING] Você tem a opção de salvar uma tradução apesar dos erros. Se fizer isso, clicando em "Save Anyway", você também deve marcar um revisor ou gerenciador do projeto e explicar o motivo do aviso ter sido ignorado nesse caso.
+
+## Boas práticas na tradução
+
+Siga essas diretrizes para se certificar de que nossas traduções estão o mais precisas possível:
+
+- Não traduza o conteúdo dentro de tags `<code>`. Essas tags indicam que o texto está formatado para o código e deve ser deixado em inglês.
+- Não adicione conteúdo extra. Se você acha que um desafio necessita de mudanças no texto e conteúdo adicional, você deve propor as mudanças através de uma issue no GitHub ou um pull request que modifique o arquivo em inglês.
+- Não mude a ordem do conteúdo.
+
+Se você tiver alguma dúvida, sinta-se à vontade para entrar em contato conosco através do [servidor do Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) e nós ficaremos felizes em ajudar você.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3d1751a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Como usar o Docker no Windows Home
+---
+
+Há alguns contratempos a serem evitados ao configurar o Docker no Windows Home. Primeiramente, você deve usar o [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) como Administrador. Infelizmente, o Windows Home não suporta o Docker para Windows Desktop, então o Toolbox deve ser usado. Ele tem que ser executado como Administrador, já que a instalação utiliza links simbólicos, que não podem ser criados caso contrário.
+
+Uma vez que você instalou o Toolbox, execute o Terminal Docker como Administrador. Isso criará uma maquina virtual `default` se ainda não houver uma. Quando isso acontecer, feche o terminal e abra o VirtualBox (também como Administrador). Você deve ser capaz de ver a máquina `default`. O site consome bastante recurso, então pare a máquina virtual e aumente as configurações o máximo que puder - da memória em particular. Foi confirmado que usa 4 GB de RAM.
+
+Uma vez que você esteja feliz que o Docker está funcionando, clone o repositório freeCodeCamp para um diretório dentro de `C:\Users`. Estes diretórios são compartilhados, dando acesso ao Docker aos diretórios locais, que ele precisa durante a instalação.
+
+Se você ver mensagens como
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+quando você usar `pnpm run docker:init`, esse é provavelmente o culpado.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..86fb94be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,740 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar em desafios de programação
+---
+
+Nosso objetivo é desenvolver uma experiência de aprendizado divertida e interativa.
+
+Projetar desafios interativos de programação é difícil. Seria muito mais fácil escrever uma explicação longa ou criar um tutorial em vídeo. Mas no nosso currículo principal, estamos buscando o que funciona melhor para a maioria das pessoas - uma experiência de jogo totalmente interativa e parecida com vídeo.
+
+Queremos que os usuários freeCodeCamp atinjam um estado ativo no aprendizado. Queremos que eles sejam impulsionados a percorrer o nosso currículo com o mínimo possível de empecilhos. Nós queremos que eles iniciem os projetos com confiança e adquiram uma ampla exposição aos conceitos de programação.
+
+Note que para a versão 7.0 do currículo do freeCodeCamp, nós estamos migrando para [um modelo inteiramente focado em projetos e com muito mais repetições](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+A criação destes desafios exige imensa criatividade e atenção aos pormenores. Há muita ajuda disponível. Você terá o apoio de toda uma equipe de colaboradores para quem você pode buscar ideias e provar seus desafios.
+
+E como sempre, fique à vontade em perguntar na [categoria 'Contribuidores' do fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [no chat dos contribuidores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Com sua ajuda, nós podemos projetar um currículo de programação interativo que ajudará milhões de pessoas a aprender a programar nos próximos anos.
+
+O conteúdo para cada desafio é guardado em um arquivo markdown. Este arquivo markdown é posteriormente convertido em HTML usando nossas ferramentas para criar páginas web interativas.
+
+Você pode encontrar todo o conteúdo curricular do freeCodeCamp.org no diretório [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges).
+
+## Configure as ferramentas para o currículo
+
+Antes de trabalhar no currículo, você precisará configurar algumas ferramentas para ajudá-lo a testar suas alterações. Você pode usar qualquer opção abaixo:
+
+- Você pode [configurar freeCodeCamp localmente](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Isto é **altamente recomendado** para contribuições regulares/repetidas. Esta configuração permite que você trabalhe e teste suas alterações.
+- Use o Gitpod, um ambiente gratuito de desenvolvimento on-line. Clicar no botão abaixo irá iniciar um ambiente de desenvolvimento pronto para programar para freeCodeCamp em seu navegador. Leva só alguns minutos.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### Trabalhe em projetos práticos
+
+Os projetos práticos tem algumas ferramentas adicionais para criar novos projetos e passos. Para saber mais, veja [esses documentos](how-to-work-on-practice-projects)
+
+## Modelo de desafio
+
+````md
+---
+id: Identificador exclusivo (alfanumérico, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Título do desafio'
+challengeType: Inteiro, definido em `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url de explicação do vídeo'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --descrição--
+
+Texto descritivo do desafio, em markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Texto com instruções para o desafio, em markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+Testes para executar o código do usuário, em par com o markdown e bloco de código de teste.
+
+```js
+Código para o teste um
+```
+
+Se você quer um resultado dinâmico baseada no código do usuário, --fcc-expected-- e --fcc-actual-- serão substituídos pelos valores esperados e reais da verificação do teste. Tome cuidado se você tiver várias afirmações já que a primeira afirmação em que houver uma falha determinará os valores de --fcc-expected-- e --fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'isso substituirá --fcc-actual--',
+ 'isso substituirá --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Informações extras para um desafio, em markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Código avaliado antes do código do usuário.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Código avaliado após o código do usuário, e pouco antes dos testes
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Código Boilerplate para renderizar para o editor. Esta seção deve somente conter código dentro de crases, como o seguinte exemplo:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Olá mundo!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Soluções são usadas para os testes CI a fim de garantir que mudanças nas dicas ainda passem conforme o esperado
+
+```js
+// primeira solução - a(s) linguagem(ns) deve(m) ser a mesma do código fornecido.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// segunda solução - então se o código fornecido está em HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// terceira solução etc. - Suas soluções devem estar em HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+Isto mostrará uma caixa de seleção que os campers precisam verificar antes de completar um desafio
+
+---
+
+Isto mostrará outra caixa de seleção que os campers precisam verificar antes de completar um desafio
+
+# --question--
+
+Esses espaços são utilizados geralmente para questões de múltipla escolha dos desafios de Python.
+
+## --text--
+
+O texto da questão vem aqui.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Resposta 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Isto será exibido como feedback quando os campers adivinharem essa resposta
+
+---
+
+Resposta 2
+
+---
+
+Mais respostas
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+O número da resposta correta fica aqui.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+Estes são os desafios do currículos de inglês.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Frase a ser mostrada com espaços em branco que os campers têm de preencher. Exemplo:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+Os dois sublinhados aparecerão como lacunas para preencher. A frase deve ser cercada por backticks (sinais de crase).
+
+## --blanks--
+
+A solução para a primeira lacuna na frase acima. Exemplo:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback mostrado quando campers inserem a solução errada para esta lacuna.
+
+---
+
+Solução para a segunda lacuna. Exemplo:
+
+`right`
+
+Se não houver feedback aqui, será exibida uma mensagem genérica de "resposta errada".
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. Nas seções acima, exemplos de `lang` são:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Numeração dos desafios
+
+Todo desafio precisa de um `id`. Se você não especifica um, então o MongoDB criará um aleatório quando os dados forem salvos. Porém, não queremos que ele faça isso. Queremos que os ids dos desafios sejam consistentes em diferentes ambientes (staging, produção, vários desenvolvedores diferentes, etc.).
+
+Para gerar um novo no shell (assumindo que o MongoDB está executando separadamente):
+
+1. Execute o comando `mongo`.
+2. Execute o comando `ObjectId()`.
+
+Por exemplo:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+O resultado é um novo id, por exemplo `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` acima.
+
+Quando tiver seu id, coloque-o no arquivo markdown como campo `id` no topo, ex.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Título do desafio
+```
+
+## Nomeando desafios
+
+Nomear coisas é difícil. Nós facilitamos com algumas restrições.
+
+Todos os títulos dos desafios devem estar explícitos e devem seguir este padrão:
+
+\[verbo\]\[frase objetiva\]
+
+Aqui estão alguns exemplos de nomes para desafios:
+
+- Usar a notação de sentido horário para especificar o preenchimento (padding) de um elemento
+- Condensar arrays com .reduce
+- Usar notação de colchetes para encontrar o primeiro caractere em uma string
+
+## Descrições/instruções do desafio
+
+As frases devem ser claras e resumidas com o mínimo de termos técnicos. Se usado, o termo técnico deve ser imediatamente definido em inglês simples.
+
+Mantenha os parágrafos curtos (em torno de 1-4 frases). É mais provável que as pessoas leiam vários parágrafos curtos do que um parágrafo enorme.
+
+Use inglês americano. Por exemplo, use `labeled` em vez de `labelled`.
+
+O desafio de texto deve usar a segunda pessoa ("você") para ajudar a dar um tom coloquial. Dessa forma, o texto e as instruções parecem falar diretamente ao usuário freeCodeCamp que está resolvendo o desafio. Tente evitar usar a primeira pessoa ("eu", "nós", "vamos").
+
+Não use links externos. Eles interrompem o fluxo. Os usuários do freeCodeCamp nunca devem precisar pesquisar nada no Google durante esses desafios. Se há recursos que você acha que os usuários aproveitarão, adicione-os no artigo relacionado ao guia do desafio.
+
+Você pode adicionar diagramas se necessário.
+
+Não use emojis ou emoticons em desafios. O freeCodeCamp possui uma comunidade global, e o significado cultural de um emoji ou emoticon pode ser diferente ao redor do mundo. Além disso, emojis podem ser mostrados de maneiras diferentes em diferentes sistemas.
+
+Substantivos próprios devem começar com letra maiúscula quando possível. Abaixo está uma lista de palavras e como devem aparecem nos desafios.
+
+- JavaScript (letras maiúsculas em "J" e "S" e sem abreviações)
+- Node.js
+- Embora às vezes imprecisas, as formas não hifenizadas de 'back end' e 'front end' devem ser usadas, pois são mais amplamente utilizadas.
+
+### A regra dos 2 minutos
+
+Cada desafio deve ser resolvido em 120 segundos por um nativo da língua inglesa que tenha concluído os desafios anteriores. Isso inclui a quantidade de tempo que leva para ler as instruções, entender o código fornecido, escrever o código e passar nos testes.
+
+Se levar mais do que dois minutos para completar um desafio, você tem duas opções:
+
+- Simplifique o desafio, ou
+- Divida o desafio em dois desafios.
+
+A regra dos 2 minutos força quem criou o desafio a deixar as instruções resumidas, o código fornecido limpo e seus testes diretos.
+
+Acompanhamos o tempo que leva para os usuários resolverem os desafios e usamos essa informação para identificar desafios que precisem ser simplificados ou divididos.
+
+### Modularidade
+
+Cada desafio deve ensinar exatamente um conceito, e esse conceito deve estar aparente a partir do nome do desafio.
+
+Podemos reforçar conceitos citados anteriormente através de repetição e variações - por exemplo, introduzir elementos h1 em um desafio, então elementos h3 depois.
+
+Nossa meta é ter vários desafios de 2 minutos. Eles podem se completar e relembrar conceitos anteriormente citados.
+
+### Formatando o texto do desafio
+
+Aqui estão diretrizes de formatação específicas para o texto do desafio e exemplos:
+
+- Palavras chaves da linguagem ficam entre `` \` `` crases. Por exemplo, nomes de tags HTML ou nomes de propriedade CSS.
+- Referências a códigos (ex. função, método ou nomes de variáveis) devem estar entre `` \` ``. Veja o exemplo abaixo:
+
+```md
+Use `parseInt` para converter a variável `realNumber` em um número inteiro.
+```
+
+- Referências a nomes de arquivos e caminhos (ex. `package.json`, `src/components`) devem estar entre `` \` ``.
+- Blocos de código com várias linhas **devem ser precedidos por uma linha vazia**. A próxima linha deve começar com três crases seguidas imediatamente por uma das [linguagens suportadas](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). Para completar o bloco de código, você deve começar uma nova linha que apenas possui três crases e **outra linha vazia**. Veja o exemplo abaixo:
+- Os espaços importam no Markdown. Então, recomendamos que os mantenham visíveis no seu editor.
+
+**Observação:** se você for usar um exemplo de código em YAML, use `yaml` ao invés de `yml` para a linguagem à direita das crases.
+
+Exemplo de código:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[SEU CÓDIGO]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Informações extras, como observações, devem estar entre linhas em branco e formatadas:
+`**Observação:** Texto da observação...`
+- Se muitas observações são necessárias, liste todas elas em frases separadas usando o formato:
+`**Observações:** Texto da primeira observação.
+ Texto da segunda observação.`
+- Use aspas simples quando necessário
+
+**Observação:** O _Markdown_ equivalente deve ser usado ao invés de tags _HTML_.
+
+## Escrevendo testes
+
+Desafios devem ter um número mínimo de testes necessários para verificar que um usuário freeCodeCamp entendeu o conceito.
+
+Nossa meta é comunicar o ponto que o desafio está tentando ensinar e testar se eles entenderam esse ponto.
+
+Os testes do desafio podem usar bibliotecas Node.js e Chai.js. Se necessário, o código gerado pro usuário pode ser acessado na variável `code` também. Além disso, os objetos `__helpers` expõem várias funções que simplificam o processo de escrita dos testes. As funções disponíveis estão definidas no repositório [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts).
+
+## Formatação do código seed
+
+Aqui vemos diretrizes de formatação específicas para o código seed do desafio:
+
+- Use dois espaços para indentação
+- Declarações em JavaScript terminam em ponto-e-vírgula
+- Use aspas duplas onde for aplicável
+
+### Comentários do código seed
+
+Temos um [dicionário de comentários](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) que contém os únicos comentários que podem ser usados no código seed. O espaçamento e as letras maiúsculas e minúsculas do dicionário de comentário devem ser usadas exatamente como são. O dicionário de comentário não deve ser expandido sem uma discussão prévia com o time de desenvolvimento (dev-team).
+
+Os comentários usados devem ter um espaço entre os caracteres do comentário e o comentário em si. Geralmente, os comentários devem ser usados com moderação. Sempre considere reescrever a descrição de um desafio ou instrução se for possível evitar usar um comentário de código fornecido.
+
+Exemplo de um comentário de uma linha em JavaScript:
+
+```js
+// Mude somente abaixo dessa linha
+````
+
+Exemplo de um comentário válido em CSS:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+Se um desafio tem apenas um lugar onde as mudanças de código são necessárias, use os comentários seguindo o exemplo a seguir para instruir o usuário sobre o local onde as mudanças devem ser feitas.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+Se um desafio tem múltiplos lugares onde se espera que o usuário faça mudanças no código (ex. os desafios de React)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Altere o código abaixo desta linha
+
+ // Altere o código acima desta linha
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Altere o código abaixo desta linha */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Altere o código acima desta linha */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Tradução de comentários de código seed
+
+Existem dicionários de comentários separados para cada linguagem. A [versão em inglês do dicionário de comentários](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) é a base para as traduções encontradas nas versões correspondentes dos arquivos em outros idiomas. A versão do dicionário de comentários em chinês (não a versão em inglês) pode ser encontrada em `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Cada dicionário consiste em um array de objetos com uma propriedade de `id` única e uma propriedade de `text`. Somente a propriedade `text` deve ser modificada para englobar a tradução do comentário correspondente em inglês.
+
+Alguns comentários podem conter uma palavra/frase que não deve ser traduzida. Por exemplo, nomes de variáveis, ou nomes próprios de bibliotecas como "React" não devem ser traduzidas. Veja o comentário abaixo como um exemplo. A palavra `myGlobal` não deve ser traduzida.
+
+```text
+Declare a variável myGlobal abaixo desta linha
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Estamos trabalhando em uma integração para ser possível trabalhar no i18n para o dicionário de comentário.
+
+## Dicas e soluções
+
+Cada desafio tem um botão `Get a Hint`, assim, o usuário pode acessar qualquer dica/solução que foi criada para aquele desafio. Os tópicos de dicas/soluções são encontrados no [nosso fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide), abaixo da categoria `Guide`.
+
+Se você encontrar um problema nas dicas/tópicos de solução de um desafio existente, você pode fazer sugestões na [categoria de contribuidores](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) no fórum. Os moderadores e usuários com o nível de confiança 3 vão revisar os comentários e decidir quais incluir as mudanças nos tópicos correspondentes de dicas/soluções.
+
+### Adicionando um novo tópico de dicas/soluções em um desafio
+
+Faça o passo-a-passo a seguir quando for adicionar novos tópicos de dicas/soluções relacionadas a um desafio.
+
+1. Comece seguindo os mesmos passos para criar um novo tópico, mas revise o seguinte para criar o título.
+2. O título do tópico deve começar com `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` concatenado com o título atual do desafio de currículo. Por exemplo, se o desafio é chamado "`Chunky Monkey`", o título do tópico seria "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. O `camperbot` deve ser o proprietário destes tópicos/postagens. Então, você precisará solicitar um administrador para alterar a propriedade da postagem principal para `camperbot`.
+4. Depois que o novo tópico for criado, será criado um id para o tópico do fórum. Está localizado no final da URL do tópico do fórum. Este id deve ser adicionado ao arquivo de desafio do currículo através do processo normal de pull request para o botão `Get a Hint` para vincular ao tópico.
+
+### Diretrizes para o conteúdo dos tópicos de dicas e soluções
+
+Ao propor uma solução para um tópico do guia relacionado a um desafio de currículo, o código completo deve ser adicionado. Isso inclui todo o código seed original, assim como as alterações necessárias para passar em todos os testes do desafio. O modelo a seguir deve ser usado ao criar um novo tópico de dicas/soluções:
+
+````md
+# O nome do desafio fica aqui
+
+---
+
+## Explicação do problema
+
+Resume o que precisa ser feito sem copiar a descrição do desafio e/ou instruções. Essa é uma seção opcional
+
+#### Links relevantes
+
+- [Texto do link](url_do_link_fica_aqui)
+- [Texto do link](url_do_link_fica_aqui)
+
+---
+
+## Dicas
+
+### Dica 1
+
+A dica fica aqui
+
+### Dica 2
+
+A dica fica aqui
+
+---
+
+## Soluções
+
+<details><summary>Solução 1 (Clique para mostrar/ocultar)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Explicação de Código
+
+- A explicação do código fica aqui
+- A explicação do código fica aqui
+
+#### Links relevantes
+
+- [Texto do link](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Texto do link](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Testando desafios
+
+Antes de [criar um pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) para suas modificações, você precisa validar que as mudanças feitas não causam problemas no desafio.
+
+1. Para testar todos os desafios, execute o comando abaixo a partir do diretório raiz
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. Para testar um único desafio, você pode usar o id do desafio com o seguinte comando
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. Você também pode testar um bloco ou superbloco de desafios com esses comandos
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+Você também pode testar desafios por título utilizando as seguintes etapas:
+
+1. Mude para o diretório `curriculum`:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Execute o comando a seguir para cada arquivo de desafio no qual você fez alteraçõess (substituindo `challenge-title-goes-here` com o título completo do desafio):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g titulo-do-desafio-aqui
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> Você pode definir a váriavel de ambiente `LOCALE` no arquivo `.env` para o idioma do(s) desafio(s) que você precisa testar.
+>
+> Os valores aceitos de momento são `english` e `chinese`, com `english` sendo o valor padrão.
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Depois de fazer o commit de suas alterações, confira aqui [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Links úteis
+
+Criação e edição de desafios:
+
+1. [Tipos de desafio](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - o que significam os valores do tipo de desafio numérico (enum).
+
+2. [Contribuindo para o FreeCodeCamp - Escrevendo testes para desafios de ES6](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - um vídeo que acompanha [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) durante sua contribuição para a versão antiga do currículo.
+
+## Scripts auxiliares
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> Se estiver trabalhando com os desafios baseados em passos, consulte a seção [Trabalho com projetos práticos](how-to-work-on-practice-projects).
+
+Existem alguns scripts auxiliares que podem ser usados para gerenciar os desafios em um bloco. Observe que todos esses comandos devem ser executados no diretório do bloco. Por exemplo:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Adicionar um novo desafio
+
+Para adicionar um novo desafio no final de um bloco, chame o script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+Ele solicitará a informação do desafio e criará o arquivo de desafio, atualizando o arquivo `meta.json` com as novas informações de desafio.
+
+### Excluir um desafio
+
+Para excluir um desafio, chame o script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+Ele solicitará que você selecione qual desafio deve ser excluído. Em seguida, excluirá o arquivo e atualizará o arquivo `meta.json` para remover o desafio da ordem.
+
+### Inserir um desafio
+
+Para inserir um desafio antes de um desafio existente, chame o script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+Ele solicitará a informação do desafio e, em seguida, o desafio será inserido antes do desafio informado. Por exemplo, se suas escolhas forem:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+Se você escolher `b`, a nova ordem será:
+
+```bash
+a
+novo desafio
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Atualizar a ordem dos desafios
+
+Se você precisar reordenar manualmente os desafios, chame o script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+Ele vai orientá-lo através de um processo interativo para selecionar a ordem dos desafios.
+
+## Solução de problemas
+
+### Loop infinito detectado
+
+Se você ver o seguinte erro no console ao pré-visualizar um desafio:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+Isso significa que o plug-in de proteção de loops encontrou um loop de longa duração ou uma função recursiva. Se o desafio precisar fazer isso (por exemplo, contém um loop de eventos que deve ser executado indefinidamente), então você pode impedir que o plug-in seja usado na visualização. Para fazer isso, adicione `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` ao arquivo `meta.json` do bloco.
+
+Se os testes demandam muitos cálculos, você poderá ver esse erro quando eles forem executados. Se isso acontecer, adicione `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` ao arquivo `meta.json` do bloco.
+
+Normalmente, não é necessário ter os dois definidos como true, Defina-os, apenas, conforme necessário.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..97333e98
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar na aplicação de client da web traduzida
+---
+
+A nossa aplicação de client da web com base em React alimenta nossa plataforma de aprendizado e foi criada usando o Gatsby. Ela é traduzida em vários idiomas do mundo todo usando [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) e [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+Você pode aprender mais sobre configurar o client localmente para desenvolvimento seguindo [nosso guia de configuração aqui](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Por padrão, a aplicação está disponível somente em inglês.
+
+Assim que você tiver o projeto configurado localmente, você poderá seguir essa documentação para rodar o client no idioma de sua escolha a partir de uma lista de idiomas disponíveis.
+
+Isso pode ser de grande ajuda quando você estiver trabalhando em uma nova feature que envolva tradução, em especial, e que necessite que você valide, por exemplo, uma label de botão em um idioma diferente.
+
+:::tip
+Você não precisa seguir esse documento para traduzir o currículo do freeCodeCamp ou contribuir com a documentação. Em vez disso, leia [esse guia aqui](how-to-translate-files).
+:::
+
+Vamos entender como o framework i18n e suas ferramentas funcionam.
+
+## Estrutura de arquivos
+
+A maioria dos arquivos para tradução da plataforma ficam localizados na pasta [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n). Cada idioma tem uma pasta contendo arquivos JSON com as traduções.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Alguns desses arquivos estão traduzidos na nossa plataforma de tradução (Crowdin), outros são traduzidos ou criados por meio de PRs no GitHub.
+
+**Arquivos traduzidos na nossa plataforma de tradução:**
+
+- O arquivo `translations.json` contém a maioria do texto que aparece nos elementos de interface de usuário. As chaves são usadas na base de código para obter o texto correto para qualquer idioma definido. Este arquivo precisa ter as mesmas chaves em todos os idiomas.
+
+- O arquivo `intro.json` contém os pares chave-valor para o texto de introdução nas páginas de certificação.
+
+ Se você deseja adicionar/atualizar traduções para as chaves, [leia este guia aqui](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Arquivos NÃO traduzidos na nossa plataforma de tradução:**
+
+- Os arquivos `motivation.json` não precisam ter as mesmas citações, elogios ou comprimento de array. Apenas a mesma estrutura do JSON.
+
+- O arquivo `meta-tags.json` contém as informações para a tag meta do nosso site.
+
+ Mudanças nesses arquivos são tipicamente feitas pelo time da staff. Se você vir algo fora do ordinário, nós recomendamos que você nos contate na [sala de chat dos colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Teste da aplicação do client em um idioma mundial
+
+Você pode testar a aplicação do client em qualquer idioma disponível na [lista de idiomas disponíveis, `availableLangs`, aqui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+Se você estiver testando um idioma novo, crie uma pasta com o nome do idioma como título próximo dos outros idiomas e copie os arquivos JSON de outro idioma para a sua pasta.
+
+Adicione o novo idioma ao enum `Languages` e ao array `client` no topo do arquivo [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+A seguir, siga as instruções nos comentários dentro do mesmo arquivo para adicionar/atualizar o rest das variáveis se necessário.
+
+Por fim, defina a variável `CLIENT_LOCALE` no seu arquivo `.env` arquivo para a string do idioma cujo build você deseja fazer a partir do enum `Languages` no arquivo acima.
+
+## Como estruturar os componentes
+
+Se você estiver trabalhando em uma feature ou em um bug para o client da web (por exemplo, adicionando novos itens de IU na pagina de configuração), você deve seguir as diretrizes abaixo. Elas vão ajudar você a preparar os componentes para tradução em todos os idiomas mundiais suportados.
+
+### Componente funcional
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// in the render method:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // more details below
+```
+
+### Componente de classe
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation adds the "t" function to props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // more details below
+
+// export without redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// or with redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Traduza usando a função "t"
+
+### Tradução básica
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### Com dados dinâmicos
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+O exemplo acima passa um objeto para a função `t` com uma variável `username`. A variável será usada no valor JSON onde `{{username}}` está.
+
+## Traduza com o componente `Trans`
+
+A regra geral é usar a função "t" quando puder. Mas existe o componente `Trans` para quando isso não for o suficiente, geralmente quando você tem elementos embutidos no texto. Você pode usar o componente `Trans` com qualquer tipo de componente React.
+
+### Elementos básicos aninhados
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+Você pode colocar a chave dentro das tags do componente como no exemplo acima se o texto contém tags "simples" sem atributos. `br`, `strong`, `i` e `p` são padrões, mas essa lista pode ser expandida na configuração do i18n.
+
+### Elementos complexos aninhados
+
+Em outras situações, você vai querer ter um texto específico dentro de outro elemento, uma tag "a" é um bom exemplo:
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+No exemplo acima, a chave é definida nos atributos do componente `Trans`. O `<0>` e `</0>` no JSON representam o primeiro filho do componente, neste caso, o elemento âncora. Se há mais filhos, eles apenas vão se somar ali usando a mesma sintaxe. Você pode encontrar os filhos de um componente na ferramenta de desenvolvedor React fazendo uma inspeção. `placeholder` está ali pois o linter estava reclamando sobre um elemento `<a>` vazio.
+
+### Com uma variável
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+No exemplo acima, a chave e a variável estão configuradas nos atributos do componente `Trans`. `{{ email }}` precisa estar em algum lugar no componente `Trans` também, não importa aonde.
+
+## Mudando texto
+
+Para mudar o texto no lado do client, vá para o arquivo `.json`, ache a chave usada no componente React, e mude o valor para o novo texto que você deseja. Você deve pesquisar na base do código por aquela chave para ter certeza de que não está sendo usada em outro lugar. Ou, se está, se as mudanças fazem sentido em todos os lugares.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Adicionando texto
+
+Se o texto que você deseja adicionar ao client existe no arquivo `.json`, use a chave existente. Caso contrário, crie uma nova chave.
+
+O arquivo em inglês é a "fonte da verdade" para todos os arquivos `.json` que compartilham o mesmo nome. Se você precisa adicionar uma nova chave, a adicione lá. Então, adicione a chave em **todos** os arquivos `translations.json`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Use texto em inglês para todos os idiomas se o arquivo está sendo traduzido via Crowdin. Os testes vão falhar se você não fizer isso.
+
+Seria bom manter as chaves na mesma ordem entre todos os arquivos também. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] O underscore (`_`) é um caractere reservado para chaves dos arquivos que ficam do lado do client. Veja [a documentação](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) para saber como são usados.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Documentação útil
+
+- [documentação react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [documentação i18next](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..04a62a60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar em projetos práticos
+---
+
+Nossos projetos práticos usam uma abordagem baseada em passos para ensinar conceitos aos campers. Um projeto será composto por vários arquivos, aos quais nos referimos como **"passos"**. Esses arquivos são nomeados pelo ID de desafio para evitar problemas com o fluxo de tradução. Infelizmente, isso torna difícil encontrar o arquivo associado a um passo específico.
+
+Criamos uma ferramenta de edição de desafios que ajuda a remediar isso. Essa ferramenta permite navegar pelos projetos disponíveis e pelas etapas para cada projeto (em ordem). Há também um editor de código embutido que você pode usar para trabalhar nos arquivos diretamente.
+
+## Usando o editor de desafios
+
+Essas instruções informarão como usar a nossa ferramenta de edição de desafios para trabalhar nos projetos práticos.
+
+### Iniciando o editor
+
+Para iniciar o editor, certifique-se de estar no diretório raiz do freecodecamp. Em seguida, execute `pnpm run challenge-editor` para iniciar tanto o client quanto a API que alimenta o editor.
+
+O client será executado na porta `3300`, então você pode acessá-la em `http://localhost:3300`. A API é executada na porta `3200`, para evitar conflitos com o client de aprendizagem e com o servidor. Isso permitirá que você execute o aplicativo do freeCodeCamp ao mesmo tempo que o editor, para poder testar as alterações localmente.
+
+### Navegando pelo editor
+
+A exibição padrão listará os `superblocks` disponíveis - eles são as certificações. Clique no link de certificação em que você deseja trabalhar.
+
+Isso levará você à lista de blocos. Esses são os projetos práticos. Clique no link do projeto em que você deseja trabalhar.
+
+Isso levará você a uma lista de passos para o projeto. Se você estiver trabalhando em um passo existente, clique no link do passo para abrir o editor. Se você estiver adicionando ou removendo etapas, clique no link `Use the step tools` para alternar para as ferramentas de passos para esse desafio.
+
+### Edição dos passos
+
+Ao clicar em um passo, você será levado ao editor. Esse é um editor de texto básico, mas que oferece destaque de sintaxe.
+
+Após realizar as alterações, clique no botão `Save Changes` para salvar as alterações. Você receberá um alerta do navegador informando que as alterações estão prontas para o commit. Observe que você precisará usar o `git` manualmente para colocar as alterações em staging e para fazer o commit dos arquivos - essa ferramenta não fará isso por você.
+
+### Ferramentas de passo
+
+Ao clicar no link `Use the step tools`, você será levado à página step tools (Ferramentas de passo). Isso permitirá que você adicione ou remova passos do projeto.
+
+#### Criar o próximo passo (Create Next Step)
+
+Clicar neste botão adicionará um novo passo ao final do projeto. Esse passo usará o código do passo anterior como seed (ou referência).
+
+#### Criar passos vazios (Create Empty Steps)
+
+Insira o número de passos que você deseja adicionar na entrada. Depois, ao clicar no botão, você criará as diversas etapas vazias ao final do projeto.
+
+#### Inserir passo (Insert Step)
+
+Insira o número do passo que deseja adicionar. Em seguida, clique no botão `Insert Step` para adicionar o passo. Os passos posteriores serão reordenados.
+
+#### Excluir passo (Delete Step)
+
+Insira o número do passo que deseja excluir. Em seguida, clique no botão `Delete Step` para excluir o passo. Isto atualizará automaticamente os números dos passos posteriores.
+
+#### Atualizar os títulos dos passos (Update Step Titles)
+
+Você não deve precisar usar essa ferramenta a menos que tenha excluído ou adicionado passos manualmente. Esta ferramenta reordenará os números dos passos.
+
+## Usando os scripts manualmente
+
+Se quiser trabalhar nos passos manualmente, em seu IDE local, você pode executar os scripts de gerenciamento de passos diretamente.
+
+A pasta `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` contém ferramentas para ajudar a facilitar a criação e a manutenção dos projetos baseados no currículo do freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Criando um projeto
+
+Mude o diretório para `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` e execute `pnpm run create-project`. Esse comando abrirá uma interface de linha de comando que vai guiar você através do processo. Uma vez que tiver terminado, deverá aparecer um novo desafio no currículo em inglês que você pode usar para começar o projeto. Por exemplo, se você tiver criado um projeto chamado `test-project` na certificação de Design responsivo para a web, ele estará em `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+Se você quer criar outros passos, as ferramentas a seguir vão simplificar o processo.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+Um script único que adicionará automaticamente o próximo passo com base no último passo do projeto. O código seed do desafio usará o código do desafio do passo anterior.
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+Um script único que adiciona automaticamente um número específico de passos. O código seed de todos os passos criados estarão vazios.
+
+**Observação:** esse script também executa [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X #, onde X é o número de etapas a serem criadas.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+Um script único que adiciona automaticamente um novo passo em uma posição especificada, incrementando todos os passos subsequentes (seus títulos e em seu meta.json). O código inicial de desafio usará o código inicial de desafio do passo anterior com os marcadores de região editáveis (ERMs) removidos.
+
+**Observação:** esse script também executa [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X #, onde X é a posição para inserir a nova etapa.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+Um script único que exclui um passo existente e decrementa todos os passos posteriores (seus títulos e em seu meta.json)
+
+**Observação:** esse script também executa [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X #, onde X é o número do passo a ser excluído.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+Um script único que atualiza automaticamente a frontmatter nos arquivos markdown de um projeto para que eles sejam consistentes com o meta.json do projeto. Garante que o título de cada passo (e seu dashedName) corresponda ao `challengeOrder` do arquivo meta.
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+Um script único para analisar os nomes dos passos do projeto e atualizar a ordem de meta.json para refletir esses passos. Útil se você perdeu acidentalmente as alterações para o arquivo meta.json ao adicionar/remover passos.
+
+#### Como executar o script
+
+1. Mude para o diretório do projeto.
+2. Execute o comando a seguir:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5de25007
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar na biblioteca de componentes
+---
+
+Bem-vindo à biblioteca `ui-components` do freeCodeCamp. Os componentes são construídos, em grande parte, do zero, com elementos HTML básicos e [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> O freeCodeCamp tem usado componentes do Bootstrap na interface do usuário. No entanto, estamos nos afastando disso e construindo nossa própria biblioteca de componentes, o que ajuda a padronizar nossos padrões de UX/UI e melhorar a acessibilidade. O projeto é acompanhado [nesta issue do GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+São recomendados os seguintes passos ao trabalhar em um novo componente:
+
+- Pesquisar e planejar
+- Implementar o componente
+- Exibir os casos de uso no Storybook
+- Escrever testes unitários
+
+## Pesquisar e planejar
+
+Antes de construir um componente, você precisa pesquisar e documentar como a versão existente se comporta e qual é sua aparência, para garantir que o novo tenha estilos correspondentes e suporte todos os usos atuais. Para atender aos requisitos de acessibilidade da web, você também deve prestar atenção ao aspecto de acessibilidade do componente, ver quais elementos HTML e atributos ARIA são usados por baixo dos panos.
+
+Depois de coletar informações suficientes sobre o componente, você pode começar a pensar na interface de propriedades. Idealmente, a interface deveria ser o mais semelhante possível à versão atual, a fim de facilitar a adoção mais tarde. Como estamos usando componentes do Bootstrap, a abordagem mais simples é imitar a [implementação deles](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+Preferimos pull requests menores do que grandes, porque eles aceleram o tempo de revisão e reduzem a sobrecarga cognitiva para os revisores. Por essa razão, pense em como dividiria a implementação e apresentaria um plano de entrega.
+
+Recomendamos abrir uma issue separada no GitHub para cada componente e incluir todas as observações na descrição da issue. Ela pode ser usada como um lugar para hospedar todas as suas notas de trabalho, assim como uma maneira de comunicar a abordagem aos revisores. Utilizaremos o tópico da issue para continuar a discussão, se necessário. [A issue sobre o componente Button](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) pode ser usada como uma referência.
+
+## Implementar o componente
+
+Um novo componente pode ser criado usando o seguinte comando a partir do diretório raiz:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+O comando gerará uma nova pasta dentro do diretório `ui-components`, com os seguintes arquivos:
+
+| Nome do arquivo | Finalidade |
+| -------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | É utilizado para exportar os componentes e os seus tipos. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | É utilizado para fazer a demonstração do componente no Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | É um arquivo de teste. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | É onde implementamos o componente. |
+| `types.ts` | É onde localizamos a interface e os tipos do componente. |
+
+Cada componente é diferente, mas, em geral, os componentes devem:
+
+- Dar suporte à ref de encaminhamento
+- Ser estilizados para temas claros e escuros
+- Ser estilizados internamente com base em suas propriedades (os consumidores não devem precisar reestilizar o componente com a propriedade `className`)
+- Usar o sistema de estilo integrado do Tailwind ao invés de ter estilos personalizados
+
+### Uso de cores
+
+Existem duas "camadas" de cores na biblioteca de componentes:
+
+- A camada de base, onde os nomes das cores descrevem o que são as cores, por exemplo, `gray00`, `blue50`
+- A camada semântica, onde os nomes das cores descrevem para que servem as cores, por exemplo, `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Geralmente, ao usar cores em um componente, você deve preferir as variáveis semânticas às de base. No entanto, há exceções, especificamente quando você está estilizando os estados do componente como hover, active, disabled etc. Nestes casos, recomendamos o uso das variáveis de base diretamente em vez de criar variáveis semânticas, já que cada componente pode ter estilos diferentes para seus estados.
+
+> [!NOTE] A definição de cor pode ser encontrada no arquivo [`colors.css`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). Uma cor só estará disponível para uso se for adicionada ao arquivo [`tailwind.config.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) abaixo da propriedade `colors`.
+
+### Links úteis
+
+- [Configuração do Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [Documentação do React Bootstrap v0.33](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Folha de estilos do Bootstrap 3.3.7](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [Implementação atual do React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [Testes atuais do React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Exibir os casos de uso no Storybook
+
+Os casos de uso do componente devem ser adicionados ao arquivo Storybook (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+Para iniciar o Storybook, execute o seguinte comando a partir do diretório raiz:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+A página do Storybook está disponível em [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Escrever testes unitários
+
+Usamos a [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) (biblioteca de testes do React) para escrever testes unitários. Os testes devem investigar se os componentes se comportam como esperados e se estão acessíveis.
+
+Para executar testes contra a biblioteca de componentes, execute o seguinte comando a partir do diretório raiz:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adicionando pacotes à biblioteca de componentes da UI
+
+Restringimos a adição de novos pacotes aos componentes da UI para ajudar com a manutenção do projeto. Na hipótese de você achar que uma dependência é necessária, consulte os gestores primeiro e use o seguinte comando para adicionar um pacote:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Links úteis
+
+- [Testes de acessibilidade](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Ordem de prioridade das consultas da biblioteca de testes do React](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Erros comuns com a biblioteca de testes do React](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..568a89d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar na documentação
+---
+
+## Trabalhar no conteúdo da documentação
+
+Para trabalhar nas diretrizes de contribuição, você pode editar ou adicionar arquivos no diretório `docs` [disponível aqui](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). Ao fazermos o merge de suas alterações, elas são disponibilizadas automaticamente no site da documentação.
+
+Ao adicionar um novo arquivo ao diretório `docs`, você deve avaliar se o arquivo também deve ser adicionado à navegação na barra lateral. Normalmente, criamos um link no arquivo [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) para guias novos e independentes. Como alternativa, você pode seguir as instruções abaixo para criar um link interno para os guias de suporte.
+
+### Como criar um link interno
+
+Se você quiser criar um link direcionando a uma outra seção das diretrizes de contribuição, siga este formato:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// Se a seção de destino estiver dentro da mesma página, você pode omitir o nome do arquivo
+[texto do link](#id-do-cabeçalho-da-seção-de-destino)
+```
+
+Certifique-se de incluir a extensão de arquivo (`.md`). Não especifique o URL completo nem acrescente `/` antes do nome do arquivo.
+
+Isso é necessário para que esses links funcionem para a versão traduzida do documento. Caso contrário, eles redirecionarão para a versão em inglês da página, independentemente do idioma.
+
+#### Traduzindo a documentação com links internos
+
+Ao trabalhar na tradução da documentação no Crowdin, certifique-se de substituir o `#target-section-heading-id` (id do cabeçalho da seção de destino) pelo id no documento traduzido. [Saiba mais sobre como traduzir a documentação aqui](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Trabalhar no tema da documentação
+
+> [!NOTE] Um lembrete rápido de que você não precisa configurar nada para ajudar no conteúdo da documentação do site.
+>
+> Para trabalhar nas diretrizes de contribuição, consulte a seção [trabalho no conteúdo de documentação](#work-on-the-docs-content).
+
+### Estrutura do site da documentação
+
+O site é gerado usando [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) e veiculado usando GitHub Pages.
+
+Normalmente, você não precisaria alterar nenhuma configuração ou compilar o site localmente. Caso esteja interessado, funciona assim:
+
+- A fonte da página inicial para este site está disponível em [`docs/index.html`](index.html).
+- Veiculamos este arquivo como uma SPA usando `docsify` e GitHub Pages.
+- O script do `docsify` gera o conteúdo dos arquivos em `markdown` no diretório `docs` sob demanda.
+- A página inicial é gerada a partir do [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage).
+- A navegação da barra lateral é gerada a partir de [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Veiculando localmente o site da documentação
+
+Instale o freeCodeCamp localmente ([veja o guia de instalação local](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)). Nós empacotamos a CLI com as ferramentas de desenvolvimento para que você possa executar o comando abaixo, conforme necessário, a partir da raiz do repositório:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> O site da documentação deve estar disponível em <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Propondo um Pull Request (PR)
+
+Após ter feito as alterações, veja [como abrir um Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1a75349a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: Como trabalhar no tema de notícias de desenvolvedor do freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+As notícias de desenvolvimento, também conhecidas como o site de [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news), são fornecidas por [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). Usamos um tema personalizado para a aparência do site. O código fonte do tema está disponível aqui: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## O tema
+
+Ghost usa uma linguagem simples de template chamada [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) para seus temas. O tema usado em `/news` é baseado no [tema casper](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper) padrão.
+
+O tema padrão é bastante comentado então deve ser razoavelmente fácil resolver o que for preciso apenas lendo o código e os comentários. Quando você se sentir confortável com a forma como tudo lá funciona, Ghost também tem uma [documentação da API de tema](https://themes.ghost.org) completa que explica cada helper e template do Handlebars possível.
+
+**Os arquivos principais são:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - O arquivo de template principal
+- `index.hbs` - Usado para a página inicial
+- `post.hbs` - Usado para postagens individuais
+- `page.hbs` - Usado para páginas individuais
+- `tag.hbs` - Usado para arquivos de tags
+- `author.hbs` - Usado para arquivamentos de autor
+
+Um truque muito legal é que você também pode criar modelos personalizados únicos, apenas adicionando o slug de uma página a um arquivo de modelo. Por exemplo:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Modelo personalizado para a página `/about/`
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Modelo personalizado para o arquivo `/tag/news/`
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Modelo personalizado para o arquivo `/author/ali/`
+
+## Desenvolvimento
+
+1. Instale o Ghost localmente.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Observação: atualmente, o freeCodeCamp usa a versão `2.9.0` do Ghost. Então, certifique-se de estar usando uma versão maior que essa.
+
+ Certifique-se de executar comandos `ghost` do diretório `ghost-local-site`. Siga instruções adicionais na [documentação oficial do Ghost](https://docs.ghost.org) se não estiver familiarizado com a interface.
+
+2. Faça fork e clone o repositório no seu diretório tema (substituindo `YOUR_USERNAME` com seu nome de usuário do GitHub):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Certifique-se de que você tem todos os pré-requisitos.
+
+ Os estilos do tema são compilados utilizando Gulp/PostCSS para poliencher as especificações CSS futuras. Você precisará do [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Certifique-se de que sua versão do Node.js é compatível com o `ghost`.
+
+4. Instale as dependências e desenvolva o tema
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Agora você pode editar os arquivos `/assets/css/`, que serão compilados automaticamente para `/assets/built/`.
+
+6. Acessar o site de desenvolvimento.
+
+ a. Digite `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` na sua barra de pesquisa. Continue com a configuração solicitada na página (se estiver executando ghost pela primeira vez).
+
+ b. _(Apenas uma vez, durante a configuração)_ Reinicie o Ghost, em um terminal separado para garantir que o tema esteja disponível.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(Apenas uma vez, durante a configuração)_ Uma vez que você tenha feito isso, vá até `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` e role para baixo. Certifique-se de clicar em ativar no `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Faça um zip do código final e faça um pull-request
+
+ O `zip` do Gulp task empacota os arquivos de tema em `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, que podemos carregar no site de produção.
+
+ Quando você criar uma PR, por favor certifique-se de ter executado o script abaixo antes de confirmar o código e enviar uma PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Outras Referências e recursos
+
+### Características do PostCSS utilizadas
+
+- Autoprefixer - Não se preocupe em escrever os prefixos do navegador de qualquer tipo, tudo é feito automaticamente com suporte para as 2 versões principais mais recentes de cada navegador.
+- Variáveis - Variáveis CSS simples
+- [Função de Cor](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### Ícones SVG
+
+O tema usa ícones SVG embutidos, incluídos via partial Handlebars. Você pode encontrar todos os ícones dentro de `/partials/icons`. Para usar um ícone, inclua o nome do arquivo relevante, por exemplo. Para incluir o ícone SVG em `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - use `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+Você pode adicionar seus próprios ícones SVG da mesma maneira.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4748e4e6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+Esta página descreve como contribuir para os tutoriais e projetos do freeCodeCamp que são concluídos usando a extensão CodeRoad do VS Code.
+
+## Como funcionam os tutoriais
+
+Cada um dos tutoriais do freeCodeCamp que usa o CodeRoad tem seu próprio repositório na organização do GitHub do freeCodeCamp. Todos eles começam com `learn-`. Por exemplo, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Cada repositório de tutorial tem um branch `main` e um branch de "versão", como `v1.0.0`, por exemplo.
+
+Os dois arquivos principais do branch `main` são `TUTORIAL.md` e `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contém todas as instruções, dicas, títulos e outros detalhes do tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contém as instruções para o CodeRoad, como os comandos a serem executados e quando fazê-lo, que arquivos devem ser observados para ver se há mudanças e qual branch de versão deve ser usado para as etapas.
+
+O branch de "versão" contém os commits que serão carregados em cada etapa do tutorial. As mensagens de commit desse branch precisam ser específicas. O primeiro commit precisa de `INIT` em sua mensagem e contém todos os arquivos a serem carregados antes da primeira lição.
+
+Mensagens de commits posteriores devem corresponder ao número da etapa em `TUTORIAL.md` do branch `main`. Por exemplo, o commit com a mensagem `10.1` será carregado quando um usuário passar para a etapa `10.1`.
+
+Para fazer mudanças nos commits de um branch de versão, você precisa fazer o rebase e editar os commits que deseja alterar. Isso reescreverá o histórico do Git, por isso não podemos aceitar PRs (pull requests) para esses tipos de branch. Assim que um branch de versão vai para o repositório do freeCodeCamp, ele jamais deve ser alterado.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Nunca faça ou envie mudanças para um branch de versão que estiver em um dos repositórios do freeCodeCamp. Sempre crie um novo.
+
+## Como contribuir
+
+### Pré-requisitos
+
+Instale as [ferramentas da CLI do CodeRoad](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) com `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+Houve alguns problemas com a última versão. Se `coderoad --version` não funcionar após a instalação, faça um downgrade para a versão `0.7.0` com `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Trabalhando no branch `main`
+
+Este conjunto de instruções é para PRs (pull requests) que façam apenas pequenas mudanças no branch `main` para **lições já existentes**. Isso consiste basicamente em erros de digitação, gramática, dicas e mudanças ou reparos nas instruções do arquivo `TUTORIAL.md`.
+
+Para todo o resto, incluindo adicionar e excluir lições, siga as [instruções de Trabalhando em um branch de versão](#working-on-version-branch). Você não precisará criar um novo branch de versão para isso. Pode criar um PR seguindo as instruções abaixo.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Essas mudanças usarão o branch de versão existente. Se elas forem substanciais, aproveite para adicioná-las ao `CHANGELOG.md`. Na maioria das vezes, uma boa mensagem de commit deverá ser o suficiente.
+
+Você nunca precisará modificar o arquivo `tutorial.json` diretamente. Ele será criado pelas ferramentas da CLI.
+
+Se estiver fazendo somente mudanças pequenas, como corrigir um erro de digitação ou gramatical, não é necessário testar suas mudanças.
+
+Siga essas instruções para fazer um PR, tendo em conta que as instruções geralmente usam as lições ao redor delas para obter contexto:
+
+- Crie uma cópia do branch de versão mais recente com `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`. Não é necessário fazer check out nesse branch. Ele só precisa existir.
+- Crie um novo branch a partir do `main` e faça check out nele.
+- Faça e **dê um commit** em suas mudanças. Lembrete: você não precisa fazer alterações no arquivo `tutorial.json`. Provavelmente, você só precisará modificar o `TUTORIAL.md`.
+- Execute `coderoad build` para recriar o arquivo `tutorial.json`.
+- Faça o commit das mudanças, com `update json` como mensagem.
+- Faça um pull request.
+
+### Testando as mudanças na branch `main`
+
+Se você quer testar suas alterações na `main` depois de usar as instruções acima, siga essas:
+
+- Siga as instruções no [repositório rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para rodar um contêiner
+- Comece o tutorial usando o arquivo `tutorial.json` no novo branch
+
+### Revisando PRs para `main`
+
+Se estiver revisando um PR que tem apenas mudanças no `main` relacionadas à problemas de instrução ou gramaticais como descrito acima, as mudanças em `TUTORIAL.md` devem corresponder às mudanças em `tutorial.json`.
+
+O arquivo `tutorial.json` não deverá conter alterações para fazer o commit de hashes ou ids de passos/níveis. Comandos de inicialização ou de nível, ou prováveis observadores de arquivo não devem ser alterados. Há exceções caso exista algum problema com um passo, mas eles devem ser tratados com mais atenção.
+
+Também tenha em mente que instruções geralmente usam as lições ao seu redor para contextualizar, então garanta que elas façam sentido.
+
+### Trabalhando na branch de versão
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Lembrete: Nunca faça ou envie mudanças para um branch de versão que esteja em um dos repositórios do freeCodeCamp. Sempre crie um novo
+
+Não existe um jeito fácil de ver exatamente o que mudou entre branches de versão, pois o histórico do Git será reescrito. Aceitar novos branches de versão para usar precisará ser feito com uma consideração cautelosa e testando.
+
+Essas instruções são para mudar qualquer coisa em um branch de versão, como testes, texto de teste, resetar arquivos, adicionar a remover passos, etc.
+
+Siga as próximas instruções para criar uma nova versão:
+
+- Vá para o **último** branch de versão com `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Crie um novo branch fora daquele, aumentando a versão, com `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Efetue suas alterações para o branch de versão. Confira mais informações na [Documentação CodeRoad](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) para saber como trabralhar com tutoriais
+- Envie o novo branch para seu fork com `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Vá para o branch `main`
+- Crie um novo branch fora do `main`. por exemplo, `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Mude a `uri` em `coderoad.yaml` para o seu fork do repositório. Assim, você e revisadores podem testá-lo antes de enviá-lo para o repositório do freeCodeCamp. Mude a versão para o novo branch em dois lugares naquele arquivo. Adicione suas mudanças para a nova versão no arquivo `CHANGELOG.md`. Faça qualquer outras alterações que você precise.
+- Commit suas alterações com a mensagem `feat: release version X.X.Y - <descrição opcional>`
+- Rode `coderoad build` para criar um novo arquivo `tutorial.json`
+- Adicione e faça o commit do arquivo
+- Envie as mudanças para o seu fork
+- Teste suas alterações as [instruções para teste abaixo](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Faça qualquer mudança adicional e faça commit delas como você fez anteriormente, ou, se você estiver satisfeito(a), siga o resto das instruções
+- Faça um PR para a `main` usando seu novo branch `feat/version-X.X.Y`. Dê o título de `version X.X.Y ready for review`. Não acontecerá o merge disso, é apenas para quem for revisar saiba que existe uma nova versão pronta
+- Após isso, suas mudanças serão revisadas
+
+### Testando alterações em uma branch de versão
+
+- Siga as instruções no [repositório rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para rodar um contêiner
+- Comece o tutorial usando o arquivo `tutorial.json` em qualquer fork onde as alterações estejam presentes. Tenha certeza de usar o arquivo no `feat: version-X.X.Y` branch e não no `main` branch
+
+### Enviando uma nova versão
+
+Antes de enviar uma nova versão, veja o novo branch `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (acontecerá o merge para a `main`) no fork do usuário. Tenha certeza que há adições no arquivo `CHANGELOG.md` que incluem as novas alterações, e a versão em dois lugares do arquivo `coderoad.yaml` correspondem com o novo branch de versão.
+
+Se você tiver acesso de escrita no repositório do freeCodeCamp, verificou os arquivos `CHANGELOG` e `coderoad.yaml`, testou as mudanças usando as instruções acima, e quer enviar uma nova versão de um tutorial:
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Lembrete: Nunca faça ou envie mudanças para um branch de versão que estiver em um dos repositórios do freeCodeCamp. Sempre crie um novo
+
+- Se você não tiver um branch remoto onde existem novas alterações, crie um para o fork do usuário com `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Exclua qualquer branches **locais** que tenham o mesmo nome do novo branch. Parecidos com nomes como `vX.X.Y` ou `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Vá para o novo branch de versão com `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
+- Envie o novo branch de versão para o repositório do freeCodeCamp com `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. Você precisa enviar o novo branch antes de atualizar a `main` com o novo arquivo `tutorial.json`
+- Vá para os branches dos usuários em que ocorrerá o merge na `main` com `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Mude a `uri` em `coderoad.yaml` para o seu fork do repositório
+- Adicione e faça o commit do arquivo com as mudanças
+- Rode `coderoad build` para criar um novo arquivo `tutorial.json`
+- Adicione e faça o commit do arquivo
+- Envie o novo branch para seu fork com `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Faça um PR para o `main` no repositório do freeCodeCamp
+- Se você estiver satisfeito(a), faça o merge ou deixe-o e peça que alguém revise
+- Depois que for dado o merge do PR, abra o tutorial seguindo as instruções no [repositório rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) para ter certeza que está carregando corretamente e que você pode passar por alguns passos
+- Por fim, se existem PRs para esta versão, feche-os
+
+### Como reverter para a versão anterior
+
+- Crie um novo branch fora do último `main` com `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Reverta todos os commits desse branch a partir do commit da versão depois da que você quer reverter. Por exemplo, você deve ter commits que parecem com isso:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+Se você quiser reverter para a v1.0.0, reverta todos os commits a partir de `release: version 1.0.1`
+
+- Crie um PR. Dê o título de `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/intro.md b/src/content/docs/pt/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..86fa31c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+A comunidade do [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) é possível graças a milhares de voluntários como você. Se você quer contribuir com o seu tempo e com suas habilidades, ficamos felizes em recebê-lo(a).
+
+:::intro
+Antes de continuar, reserve 2 minutinhos para ler o nosso [Código de Conduta](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct). Nós o aplicamos rigorosamente em toda a nossa comunidade para que contribuir com o freeCodeCamp.org seja uma experiência segura e inclusiva para todos.
+:::
+
+Fique à vontade para criar, atualizar e corrigir bugs em nosso [currículo](#curriculum), ajude-nos a corrigir bugs na [plataforma de aprendizagem](#learning-platform) do freeCodeCamp ou [ajude-nos a traduzir](#translations) o freeCodeCamp.org para idiomas do mundo inteiro.
+
+Respondemos às perguntas mais comuns sobre como contribuir [no nosso FAQ do colaborador](FAQ).
+
+Boas contribuições.
+
+---
+
+## Currículo
+
+Nosso currículo é sustentado pela comunidade global do freeCodeCamp. Desta forma, podemos incorporar conhecimentos especializados de voluntários como você.
+
+Você pode ajudar a expandir e melhorar o currículo. Você também pode atualizar as histórias de usuário do projeto para explicar melhor os conceitos. E você pode melhorar nossos testes automatizados para que possamos testar com mais precisão o código das pessoas.
+
+**Se você está interessado em melhorar nosso currículo, aqui está [como contribuir para o currículo](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges).**
+
+## Traduções
+
+Estamos traduzindo o freeCodeCamp.org para os principais idiomas do mundo.
+
+As certificações já estão disponíveis em alguns dos principais idiomas mundiais, como vemos abaixo:
+
+- [Chinês (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Espanhol (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italiano](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Português](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ucraniano (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japonês (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [Alemão (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+Recomendamos a leitura do [anúncio aqui](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-ajudar-a-traduzir-o-freecodecamp-para-seu-idioma/) e o compartilhamento com seus amigos.
+
+**Se você está interessado em traduzir, veja como traduzir os recursos do [freeCodeCamp](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## Plataforma de aprendizagem
+
+Nossa plataforma de aprendizado é executada em uma stack moderna do JavaScript. Ela possui vários componentes, ferramentas e bibliotecas. Estes incluem Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack e mais.
+
+De modo geral, temos um servidor de API baseado em Node.js, um conjunto de aplicativos de client baseados em React, testes de scripts para avaliar projetos de currículo apresentados pelos campers e muito mais. Se você deseja contribuir produtivamente para nossa plataforma de aprendizagem, recomendamos alguma familiaridade com estas ferramentas.
+
+**Se quiser nos ajudar a melhorar nossa base de código, aqui está [como configurar o freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/pt/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed8c0810
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: O manual oficial para os líderes de cada idioma do freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Este manual o ajudará a configurar e utilizar as ferramentas para seus esforços de localização.
+
+## Como convidar novos colaboradores para o Ghost
+
+O Ghost permite que você defina colaboradores com diferentes níveis de autorização.
+
+A maioria de seus convites será para o nível "Contributor" (Colaborador). Esse nível permite que o usuário crie rascunhos. Selecione esta função ao convidar um novo tradutor.
+
+O nível "Author" (Autor) permite ao usuário criar rascunhos e publicá-los.
+
+O nível "Editor" permite ao usuário acessar todos os rascunhos e publicá-los. Selecione esta função ao convidar um novo revisor.
+
+O nível "Administrator" (Administrador) é reservado para funcionários e líderes de idiomas do freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Como são feitos os artigos
+
+Usamos uma abordagem baseada em [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack) para criar e implementar os artigos. Esta estratégia faz com que um site estático seja armazenado em cache e servido a partir de uma CDN rapidamente.
+
+O [Ghost](https://ghost.org) atua como nossa plataforma de gerenciamento de conteúdo. O [11ty](https://11ty.dev) compila os artigos na forma de recursos estáticos – HTML, JavaScript e CSS. Apenas esses recursos estáticos são implantados em nossos servidores.
+
+Esse processo é automatizado e executado periodicamente. Se você publicar algo agora, estará disponível no site de notícias dentro de algumas horas.
+
+Você pode encontrar as agendas de compilação e o status atualizado aqui: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## Como mencionar o autor original de um artigo traduzido
+
+O autor original e o artigo original são vinculados automaticamente, adicionando este código à seção de cabeçalho Code Injection -> em Draft Setiings (Configurações de rascunho) no Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+Sendo `link` o link do artigo original.
+
+## Como atualizar os artigos em destaque
+
+:::tip
+Alterar os artigos no rodapé pelo menos uma vez por mês significa dar um impulso aos artigos vinculados nos resultados do Google.
+:::
+
+Para atualizar os artigos de tendência no rodapé, você precisa atualizar o [arquivo yaml no repositório CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) para o seu idioma. Tanto o currículo como o editorial fazem referência a esse arquivo.
+
+Por exemplo, aqui está o conteúdo do arquivo para os primeiros 6 artigos:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: 'Nova aba em HTML'
+article0link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-usar-o-html-para-abrir-um-link-em-uma-nova-aba/'
+article1
+title: 'Máscaras de sub-rede'
+article1link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/ficha-informativa-de-sub-redes-mascara-de-sub-rede-24-30-26-27-29/'
+article2
+title: '40 projetos em JavaScript'
+article2link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/40-projetos-em-javascript-para-iniciantes-ideias-simples-para-comecar-a-programar-em-js/'
+article3
+title: 'Tutorial de button onClick'
+article3link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/tutorial-sobre-button-onclick-em-html-e-evento-de-clique-em-javascript/'
+article4
+title: 'Bot do Discord'
+article4link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/tutorial-de-criacao-de-bot-para-o-discord-em-python/'
+article5
+title: 'Centralizar em CSS'
+article5link: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/news/como-centralizar-tudo-com-css/'
+```
+
+Cada número representa um dos 30 artigos do rodapé. Veriifique se a correspondência entre o título e o link está correta.
+
+Para cada artigo, você precisará criar um título menor para usar no rodapé. Cada título deve permanecer em uma única linha e não deve ir para uma nova linha.
+
+Você vai querer [fazer a build do client traduzido localmente](how-to-enable-new-languages) para ver se os títulos têm o comprimento correto. Você pode visualizar as alterações editando o arquivo `trending.json` em seu ambiente local:
+
+1. Atualize o arquivo `.env` para usar seu idioma em `CLIENT_LOCALE` e `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Execute `pnpm run create:shared`. Isso gerará automaticamente o arquivo `trending.json` para o seu idioma no diretório `/client/i18n/locales/`.
+
+3. Inicie o servidor executando `pnpm run develop:server` em uma janela do terminal.
+
+4. Edite o arquivo `trending.json` para que contenha os títulos que você deseja visualizar. Você pode querer converter o seu arquivo `.yaml` em formato JSON com uma ferramenta automática.
+
+5. Em outra janela do terminal, execute `pnpm run clean:client` e, em seguida, `pnpm run develop: client`
+
+## Como traduzir os artigos dos links de rodapé
+
+Existem alguns links listados no final do rodapé (Sobre, Rede de ex-alunos, Código aberto etc.) e alguns deles podem ser traduzidos para seu idioma do mesmo modo que os outros artigos.
+
+Artigos que podem ser traduzidos:
+
+- Sobre
+- Suporte
+- Honestidade acadêmica
+- Código de conduta
+
+Os seguintes artigos **não** devem ser traduzidos:
+
+- Loja
+- Patrocinadores
+- Política de privacidade
+- Termos de serviço
+- Política de direitos autorais
+
+Os links a seguir estão apontando para sites externos e não podem ser traduzidos:
+
+- Rede de ex-alunos
+- Código aberto
+
+### Alterações nos links de rodapé do editorial
+
+Depois de ter traduzido e publicado os artigos listados como "podem ser traduzidos" acima, você poderá atualizar os links no rodapé de `/news` editando o arquivo `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` no repositório [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+> [!NOTE] As solicitações de pull request para este repositório estão atualmente limitadas apenas à equipe. Se quiser atualizar este arquivo, peça ajuda a alguém da equipe.
+
+Atualize a seguinte parte do arquivo:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Alterações nos links de rodapé do curr[iculo
+
+Depois de ter traduzido e publicado os artigos listados como "podem ser traduzidos" acima e quando o curr[iculo em seu idioma estiver pronto para o lançamento, você poderá atualizar os links no rodapé de `/learn` editando o arquivo `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` no repositório [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!WARNING] Apenas "Sobre", "Suporte", "Honestidade acadêmica" e "Código de conduta" podem ser traduzidos. Deixar os outros URLs inalterados.
+
+Atualize a seguinte parte do arquivo:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## Como traduzir os cabeçalhos das caixas informativas na documentação
+
+Você pode encontrar essas caixas por toda a documentação:
+
+> [!NOTE] Eu sou uma caixa de notificação
+
+:::tip
+Eu sou uma caixa de dica
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] Eu sou uma caixa de advertência
+
+:::danger
+Eu sou uma caixa de atenção
+:::
+
+Por padrão, os cabeçalhos deles aparecem em inglês, mesmo na documentação traduzida.
+
+É possível traduzir os cabeçalhos para a documentação para o seu idioma alterando o arquivo `docs/index.html`, desta forma:
+
+Dentro do elemento `script` existe um objeto. Nele, você encontra a propriedade `flexibleAlerts`, que tem esta forma:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Dentro do objeto da propriedade label, antes da propriedade `'/'`, você adiciona uma nova propriedade para o seu idioma, assim: `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+Por exemplo, ao adicionar as traduções para o português, você terá algo assim:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## Como traduzir as citações motivacionais
+
+As citações motivacionais podem ser encontradas no [repositório de currículos](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/), no arquivo `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json`.
+
+Esse arquivo tem a seguinte estrutura geral:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+Os elogios são as frases curtas que aparecem na conclusão de um desafio.
+
+Você não precisa traduzir diretamente as frases usadas em inglês. Você pode escrever um conjunto de frases curtas que sejam apropriadas para mostrar na conclusão de um desafio.
+
+O array `compliments` é um array de strings. Então, por exemplo, você escreveria:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["Top de linha!", "Agora não para mais!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Você deve começar com pelo menos uma dúzia de elogios para ter alguma variedade quando os usuários completarem os desafios.
+:::
+
+As citações motivacionais são as citações que aparecem em https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+O array `motivationalQuotes` é um array de objetos. Esses objetos devem incluir uma propriedade `quote` e uma propriedade`author`. assim:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Seja lá o que você fizer, seja bom nisso.",
+ "author": "Abraham Lincoln"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "Uma mudança de perspectiva já faz subir 80 pontos de QI.",
+ "author": "Alan Kay"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Você deve começar com pelo menos uma dúzia de citações para ter alguma variedade. Uma nova citação é mostrada toda vez que o usuário recarrega a página.
+:::
+
+## Como atualizar os links comuns
+
+Mantemos um arquivo de links comuns usados por todo o nosso [site do currículo](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) no arquivo `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json`.
+
+Alguns desses links não mudarão - mas você deve atualizar os links dos artigos `/news` para que apontem para a versão traduzida do seu idioma quando ele é publicado.
+
+Você também deve atualizar as categorias de `help` para que apontem para o sub-fórum do seu idioma (geralmente `language/category`, como, por exemplo, `portuguese/HTML-CSS`). Isto permitirá que os campers criem "posts de ajuda" no local correto do fórum.
+
+## Como atualizar os metadados do site
+
+Os metadados do site estão no arquivo `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json`. Este arquivo tem cinco chaves: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords` e `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+O valor de `youre-unsubscribed` deve ser traduzido diretamente. Os outros valores precisarão ser traduzidos o mais próximo possível, considerando também termos e frases de busca comuns usados em seu idioma.
+
+Se você precisar de ajuda com isso, entre em contato conosco no [chat dos colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Fluxo de trabalho de pré-tradução no Crowdin
+
+O fluxo de trabalho de pré-tradução pode ser usado para aplicar traduções da memória de tradução às frases.
+
+:::tip
+É bastante útil restaurar muitas traduções da memória de tradução ao mesmo tempo quando muitos arquivos foram atualizados.
+:::
+
+Você pode encontrar o fluxo de trabalho de pré-tradução no topo da página no console de um projeto. Se você ver "Go to console", no canto superior direito, clique lá primeiro.
+
+
+
+
+
+Você pode escolher "From Machine Translation" (da tradução de máquina) ou "From Translation Memory" (da memória de tradução). Selecione "Translation Memory" para recuperar as traduções da memória.
+
+Depois, há três etapas a concluir:
+
+1. Arquivos. Escolha quais arquivos traduzir. Você pode fazer todos os projetos ou pastas e arquivos específicos.
+2. Idiomas. Defina o seu idioma aqui.
+3. Traduções existentes. A melhor combinação aqui é "100% match" (100% correspondente) e "Apply to untranslated strings only" (aplicar apenas a frases não traduzidas). Não aprove automaticamente, já que é sempre melhor que um olho humano revise tudo.
+
+
+
+Quando você tiver terminado de fazer essa configuração, pressione o botão Pre-Translate e aguarde. Ele alertará você quando terminar. O tempo que leva depende de quantas frases não traduzidas existem nos arquivos escolhidos.
+
+## Como atualizar o glossário do Crowdin
+
+:::tip
+Um glossário atualizado ajuda a ter uma tradução dos termos técnicos mais homogênea.
+:::
+
+O glossário do Crowdin é mantido no repositório [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries).
+
+Na pasta `glossaries` há vários arquivos `*.csv` (valores separados por vírgulas, um para cada um dos projetos no Crowdin que têm um glossário que pode ser atualizado a partir deste fluxo de trabalho.
+
+O arquivo `client.csv` é para o projeto "Learn User Interface" (Interface de aprendizagem do usuário), `curriculum.csv` é para o projeto "Coding Curriculum" (Currículo de programação) e o arquivo `docs.csv` é para o projeto "Contributing Documentation" (Documentação colaborativa).
+
+Para atualizar os glossários do Crowdin você precisa clonar este repositório localmente. Abra o arquivo `.csv` com um programa apropriado - por exemplo, o Microsoft Excel.
+
+No arquivo `.csv`, que você verá que a língua inglesa ocupa as primeiras três colunas, `Term:English` é a coluna para o termo em inglês, `Description:English` é a coluna para a descrição em inglês e `Part:English` é para a classe gramatical (por exemplo, substantivo, verbo etc.) do termo.
+
+Depois delas, cada idioma-alvo tem duas colunas. Se você traduzir para o Dothraki, estará interessado nas colunas `Term:Dothraki` e `Description:Dothraki`. A coluna `Term:Dothraki` é para a tradução do termo em Dothraki, enquanto a coluna `Description:Dothraki` é para uma descrição do termo em Dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+Em programas como o Microsoft Excel, você pode ocultar as colunas dos outros idiomas para liberar espaço em tela e ver as colunas em inglês e as colunas do idioma de destino ao lado umas das outras.
+:::
+
+Após ter feito as alterações e salvo o arquivo, você precisará fazer um PR com as alterações propostas. Depois de o PR ter sido aceito, você precisará executar o fluxo de trabalho do GitHub Action para atualizar o glossário do Crowdin. Suas alterações no glossário não terão efeitos imediatos, mas aparecerão em breve.
+
+## Como promover um colaborador a revisor
+
+Se você considerar que um colaborador pode se tornar um revisor de Crowdin, você pode dar a ele a função de revisor deste modo:
+
+No Crowdin, você individualiza `User management` (gerenciamento do usuário) no menu do lado esquerdo.
+
+Isto abrirá as ferramentas de gerenciamento de usuário, você será capaz de ver a lista de todos os usuários.
+
+Procure pelo usuário que se tornará um revisor. Use o menu de três pontos na linha do usuário para abrir um menu e selecione "Add to team" (Adicionar à equipe). As equipes de revisão têm o nome padrão de `Proof Readers (<language>)`. Você pode pesquisar a equipe usando o nome do idioma. Depois de selecionar a equipe, use o botão "ADD" na parte inferior da página para finalizar.
+
+O usuário agora é um revisor.
+
+:::tip
+O revisor recém-promovido pode se beneficiar de ler a documentação em [How to Proofread Files](how-to-proofread-files).
+:::
+
+## Como adicionar ou atualizar um idioma
+
+Confira a documentação sobre [como ativar um novo idioma](how-to-enable-new-languages). Se você estiver atualizando um idioma, a seção sobre a [configuração dos superblocos traduzidos](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) deve ser útil.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c62e227f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+---
+title: O manual oficial para os moderadores do freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Esse manual vai ajudá-lo a moderar lugares diferentes em nossa comunidade. Ele cobre conversas e interações nos tópicos de "pull request" e "issues" do GitHub, no fórum da comunidade, nas salas de conversa e em outras comunidades oficiais fomentadas por nós.
+
+> [!NOTE] Todos os moderadores do freeCodeCamp são moderadores de toda a comunidade. Isso significa que confiamos em você para supervisionar qualquer um destes lugares.
+
+Você pode atuar como moderador em qualquer uma das plataformas de seu interesse. Alguns moderadores ajudam apenas no GitHub, enquanto outros ajudam apenas no fórum. Outros moderadores estão ativos em todos os lugares.
+
+O mais importante é que queremos que você goste de ser um moderador, investindo seu tempo escasso em lugares que sejam de interesse para você.
+
+> "Com grandes poderes vêm grandes responsabilidades." - Tio Ben
+
+Como moderador, seu temperamento é mais importante do que habilidade técnica.
+
+Escute. Seja útil. Não abuse do seu poder.
+
+O freeCodeCamp é uma comunidade inclusiva e temos de mantê-la assim.
+
+Temos um único [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), que rege toda a nossa comunidade. Quanto menos regras, mais fáceis elas são de lembrar. Você pode ler essas regras e guardá-las na memória [aqui](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+> [!NOTE] Como moderador, nós adicionaríamos você a um ou mais times no GitHub, nos nossos fóruns comunitários e nos servidores de chat. Caso você não tenha acesso a uma plataforma que queira moderar, [entre em contato com um membro da equipe](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## Moderando no GitHub
+
+Moderadores têm duas responsabilidades primárias em relação ao GitHub:
+
+1. Avaliar e responder "issues".
+2. Revisar e dar "merge" nos "pull requests" (também conhecido como controle de qualidade).
+
+### Moderando issues do GitHub
+
+Nós usamos nosso repositório principal [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) como a central de rastreamento de "issues" para todos os nossos repositórios. Todos os dias recebemos novas issues. Todas elas precisam ser testadas e identificadas. Esse é também um ótimo lugar para começar a ajudar repositórios de código aberto com suas contribuições.
+
+#### Triagem de issues
+
+[Triagem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) é um processo de priorizar atenção a cada nova issue. Nós temos uma lista extensa de etiquetas que usamos para marcar a prioridade, categoria, situação e escopo de cada issue.
+
+Você pode nos ajudar a organizar e moderar issues usando etiquetas [dessa lista](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels). Normalmente, uma descrição é disponibilizada juntamente com a etiqueta, explicando o seu significado.
+
+Preste atenção especial às etiquetas `"help wanted"` e `"first timers only"`. Elas devem ser adicionadas aos tópicos que você considere que possam ser abertos aos potenciais contribuidores para realizar um "pull request".
+
+Para a triagem de uma issue trivial como uma correção de ortografia, é recomendado aplicar uma etiqueta "first timers only" juntamente com informações adicionais. Você pode usar o [modelo de resposta](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) fornecido para esta finalidade.
+
+#### Fechando issues e pull requests parados, desatualizados ou inativos
+
+- Issues ou PRs parados são aqueles que não tiveram nenhuma interação do criador por 21 dias (3 semanas desde a última interação), mas apenas depois que um moderador pediu mais informações/mudanças.
+
+- Atividade é definida como: comentários solicitando uma atualização no PR e triagens como a etiqueta `status: update needed`, entre outras.
+
+- Se o criador do PR pedir assistência adicional ou mais tempo, as regras acima podem ser revistas após uma resposta. Em todo caso, os moderadores devem usar o melhor julgamento para resolverem o estado do PR.
+
+:::tip
+Recomendamos usar essa lista de [modelos de resposta](reply-templates) padrão enquanto estiver monitorando issues.
+:::
+
+### Moderando pull requests
+
+Pull Requests (PRs) são como os colaboradores enviam alterações para o repositório do freeCodeCamp. Nós temos que garantir a qualidade dos pull requests antes de decidirmos fazer merge, pedir mudanças ou fechá-los.
+
+#### Tipos de pull requests
+
+1. **Edições das instruções de desafios**
+
+ Essas são mudanças no texto dos desafios - no texto da descrição, da instrução ou do teste.
+
+ Você também pode revisar isso diretamente no GitHub e decidir fazer merge ou não. Precisamos ter um pouco mais de cuidado com relação a isso, pois milhões de pessoas encontrarão este texto enquanto usam o currículo do freeCodeCamp. O pull request deixa o texto mais claro sem deixá-lo muito mais longo? As edições são relevantes e não são excessivamente pedantes? Lembre-se que nosso objetivo é que os desafios sejam mais claros e curtos dentro do possível. Não são o lugar para detalhes obscuros. Os contribuidores talvez tentem adicionar links para recursos dos desafios.
+
+ Você pode fechar pull requests inválidos e respondê-los com esses [modelos de resposta](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Se as mudanças parecem boas, por favor aprove-as comentando "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me - me parece bom, em inglês). Uma vez que um pull request tiver pelo menos duas aprovações (incluindo a sua) dos moderadores ou equipe de desenvolvedores, você pode fazer o merge.
+
+2. **Edições de código de desafio**
+
+ São mudanças feitas no código do desafio - o objetivo do desafio, a solução do desafio e o texto.
+
+ Esses pull requests precisam ser baixados do GitHub e testados no seu computador ou GitPod para garantir que os testes do desafio ainda passam com a solução atual e para garantir que o novo código não introduz nenhum erro.
+
+ Alguns contribuidores podem tentar adicionar mais testes para cobrir casos confusos pedantes. Precisamos ter cuidado para não deixarmos o desafio muito complicado. Esses desafios e seus testes devem ser simples e intuitivos na medida do possível. Além dos desafios de algoritmo e a seção de preparação para entrevistas, os estudantes devem ser capazes de resolver cada desafio em aproximadamente 2 minutos.
+
+ Você pode fechar pull requests inválidos e respondê-los com esses [modelos de resposta](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Se as mudanças parecem boas, por favor aprove-as comentando "LGTM". Uma vez que um pull request tiver pelo menos duas aprovações (incluindo a sua) dos moderadores ou equipe de desenvolvedores, você pode fazer o merge.
+
+3. **Mudanças na plataforma**
+
+ Essas edições de código mudam a funcionalidade da plataforma freeCodeCamp em si.
+
+ Às vezes os contribuidores tentam fazer mudanças sem muita explicação, mas para mudanças no código, precisamos garantir que há uma necessidade genuína para a mudança. Esses pull requests devem referenciar uma issue existente no GitHub onde os motivos para a mudança são discutidos. Então você pode abrir o pull request no seu computador e testá-lo localmente.
+
+ Depois de pronto, se as mudanças estão boas, não faça o merge ainda. Você pode comentar "LGTM" no pull request e mencionar **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** para eles darem uma olhada.
+
+4. **Pull Requests automáticos (Dependabot)**
+
+ Alguns PRs são atualizações de dependência automáticos feitos a partir de uma integração. Você não deve dar merge ou aprovar esses PRs. Um dos membros do time de desenvolvimento cuidará da revisão e irá dar merge em PRs automáticos.
+
+#### Como revisar, fazer o merge ou fechar pull requests
+
+##### Seja responsável por um pull request:
+
+Em primeiro lugar, quando você escolhe um pull request para revisar, você deve atribuí-lo a si mesmo. Você pode fazer isso clicando no link "assign yourself" abaixo da parte "assignees" na coluna da direita da interface do GitHub.
+
+Dependendo do tipo de pull request, siga as regras correspondentes listadas anteriormente.
+
+##### Certifique-se de que as verificações de CI passaram:
+
+Antes de dar merge em qualquer pull request, certifique-se de que haja um aviso dizendo que todos os testes passaram (todos marcados em verde) no pull request. Se alguma das verificações falhou, investigue e tente descobrir qual é a causa raíz. A mudança proposta está quebrando nossos testes? O site vai compilar corretamente se darmos merge no PR? Essas verificações são importantes para a estabilidade da plataforma.
+
+> [!WARNING] Fazer merge em um PR que falhou nas verificações CI/CD pode causar dificuldades para todas as partes interessadas, incluindo o time de desenvolvimento e contribuidores.
+
+##### Lidando com conflitos de merge:
+
+Às vezes haverá um conflito de merges.
+
+Isso quer dizer que outro pull request fez mudanças na mesma parte de um arquivo. O GitHub tem uma ferramenta para resolver esses conflitos de merges diretamente no GitHub. Você pode tentar resolver esses conflitos. Use seu melhor julgamento.
+
+As mudanças do pull request estarão no topo e as mudanças da branch principal (main) estarão embaixo. Às vezes, haverá informação redundante que pode ser apagada. Antes de terminar, certifique-se de excluir o `<<<<<<`, `======` e o `>>>>>>` que o Git adiciona para indicar áreas de conflito.
+
+Se não tem certeza, peça ajuda para algum moderador ou para o time de desenvolvimento.
+
+##### Fazendo merge em um pull request válido:
+
+Se o pull request parece pronto para merge (e não requer aprovações adicionais - lembre-se, precisamos de pelo menos duas), você pode ir em frente e fazer o merge. Certifique-se de usar a opção padrão **"Squash and Merge"**. Isto vai comprimir todos os commits de pull requests em um único commit, o que deixará o histórico do Git muito mais fácil de ler.
+
+> Em seguida, você deve comentar no pull request, agradecendo ao colaborador usando sua própria maneira pessoal!
+
+Se o autor do pull request estiver contribuindo pela primeira vez, você também deve parabenizá-lo(a) pelo seu primeiro merge no repositório. Pode-se olhar para o canto superior direito do corpo do PR para saber se é a primeira contribuição da pessoa. Mostrará `First-time contributor` assim:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Identificação de First-time contributor nos pull requests (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="Identificação de First-time contributor nos pull requests" />
+</details>
+
+Se o pull request não parece pronto para fazer o merge, você pode responder educadamente dizendo ao autor o que ele deve fazer para prepará-lo. Com sorte, ele responderá e deixará o pull request mais próximo de ficar pronto.
+
+Se você precisar de uma segunda opinião em um pull request, vá em frente e deixe seus comentários nele, em seguida, adicione o rótulo "discussing".
+
+##### Fechando um pull request inválido:
+
+Muitas vezes, um pull request será obviamente de baixo esforço. Muitas vezes, você perceberá isso imediatamente quando o colaborador não se importar em verificar os checkboxes do template de requisição de pull request ou quando ele utilizar um título de pull request genérico como "Alterações feitas" ou "Atualizar índice.md".
+
+Há também situações em que o colaborador está tentando adicionar um link para o seu próprio site, incluir uma biblioteca que criou, ou tem uma edição frívola que não serve para ajudar ninguém, exceto a si mesmo.
+
+Você pode fechar pull requests inválidos e respondê-los com esses [modelos de resposta](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtrando pull requests
+
+Para ordenar Pull Requests para Garantia de Qualidade para acesso rápido a PRs que estão prontos para revisão, não tenham conflitos de merge, não estejam bloqueadas e tenham todas as verificações de status em verde, use o seguinte link para aplicar os filtros:
+
+[Link direto com filtro aplicado](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Outras diretrizes para moderadores no GitHub
+
+Embora você tenha acesso de escrita ao repositório do freeCodeCamp, **você nunca deve enviar o código diretamente para repositórios do freeCodeCamp**. Todos os códigos devem entrar na base de código do freeCodeCamp em forma de pull request a partir de um fork do repositório.
+
+Além disso, você nunca deve aceitar seus próprios PRs. Outro moderador deve revisá-los, assim como qualquer outro PR.
+
+Se você notar que alguém quebrou o [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) em issues do GitHub, ou abriu pull requests com conteúdo ou código malicioso, mande um e-mail para `support[at]freecodecamp.org` com o link do pull request e podemos considerar bani-los da organização do freeCodeCamp no GitHub.
+
+## Moderando o Fórum
+
+Como moderador, você ajuda a manter nossa comunidade um lugar agradável para qualquer pessoa aprender e buscar ajuda. Você lidará com postagens sinalizadas e tratará spam, mensagens fora do assunto e outras conversas inapropriadas.
+
+Note que, ao se tornar um moderador no fórum, você vai começar a ver dicas azuis sobre os membros do fórum, como "esta é a primeira vez que [person] postou - vamos dar as boas-vindas à comunidade!" ou "[person] não postou há muito tempo - vamos recebê-lo de volta."
+
+![Uma mensagem de texto azul dizendo "Esta é a primeira vez que [person] postou - vamos dar as boas-vindas à comunidade!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+São oportunidades para você recebê-lo(a) e fazê-lo(a) sentir-se mais especial. Nunca se sabe quais pessoas que estão pouco envolvidas e que podem ser nossos próximos superajudantes, ajudando muitas outras pessoas na sua jornada de programação. Mesmo a menor bondade pode desencadear várias boas ações.
+
+### Excluindo publicações do fórum
+
+Moderadores do fórum podem apagar as postagens dos usuários. Você só deve fazer isso para as seguintes instâncias:
+
+1. Alguém postou uma imagem pornográfica ou graficamente violenta.
+2. Alguém postou um link ou código de natureza maliciosa que pode prejudicar os(as) outros(as) usuários(as) freeCodeCamp que clicarem nele.
+3. Alguém lotou um tópico com muitas mensagens de spam.
+4. Uma conta foi criada, sem qualquer sombra de dúvida, com o intuito de fazer spam.
+
+### Lidando com spam
+
+Para o primeiro post de spam de um usuário legítimo (ou seja, cuja intenção não é fazer spam no fórum, mas sim de aprender/contribuir), envie uma mensagem explicando o problema e remova o link ou post apropriadamente. Deixe uma observação no perfil do usuário explicando a ação que você tomou. Se o problema persistir, então bloqueie silenciosamente o usuário de postar (usando a opção de silêncio no painel de Administração de Usuário). Envie ao usuário um aviso com o [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Marque a opção na mensagem privada que indica que a sua mensagem é um "aviso formal."
+
+Como moderador, você pode fazer perguntas e relatar incidentes na [seção do fórum da equipe de moderadores](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Lidando com conversas fora do assunto
+
+Postagens ou tópicos que parecem estar no lugar errado podem ser renomeados para o que for apropriado.
+
+Em circunstâncias excepcionais, pode ser apropriado que um moderador faça o fork de uma discussão em vários assuntos.
+
+Novamente, se você tiver algum problema ou dúvida, faça uma postagem com suas ações na categoria `"Staff"`, e marque outro moderador se você quiser que eles revisem suas ações de moderação.
+
+### Lidando com soluções publicadas
+
+Se um usuário responder em uma thread de ajuda para o currículo do freeCodeCamp com uma solução, remova-a e use a resposta pronta **Solution Instead of Help** (ou uma resposta semelhante em suas próprias palavras).
+
+Se o OP (pessoa que publicou o pedido de ajuda original) responder em sua própria thread de ajuda para o currículo do freeCodeCamp com sua solução final, desfoque-a e use a resposta pronta **Blurred Spoiler Solution**.
+
+Se um usuário criar uma thread pedindo feedback de uma solução, mova o tópico para o subfórum de feedback e desfoque a solução, conforme necessário. Se o usuário estiver apenas publicando a solução para se exibir, reitre o tópico das listas e use a resposta pronta **Solutions Thread**.
+
+### Usuários menores de idade
+
+Nossos [termos de serviço](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) requerem que os usuários do freeCodeCamp tenham, pelo menos, 13 anos de idade. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+ASSUNTO: Usuários com menos de 13 anos não têm permissão para usar o fórum de acordo com os nossos Termos de Serviço.
+
+Chegou à nossa atenção o fato de que você tem menos de 13 anos de idade. Segundo os [Termos de Serviço do freeCodeCamp](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), você deve ter pelo menos 13 anos de idade para usar o site ou fórum. Apagaremos suas contas do fórum e do site freeCodeCamp. Essa restrição nos deixa em acordo com as leis dos Estados Unidos.
+
+Por favor, compareça quando estiver com pelo menos 13 anos de idade.
+
+Obrigado(a) pela compreensão.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderando via celular
+
+É possível moderar o fórum por um celular, mas você pode encontrar algumas peculiaridades. Esta não é uma lista exaustiva.
+
+- Ao tentar incluir uma "Resposta pronta" em uma resposta, se o menu não abrir (após clicar na engrenagem), clique na área de texto primeiro e tente novamente.
+- A 'ferramenta de chave' do moderador está na parte inferior da janela de visualização, mas, se você clicar nela e não puder ver o botão "Select Posts" (Selecionar Posts) pelo fato de ele estar fora de visualização, você pode precisar rolar até ele, embora, às vezes, isso não funcione. Neste caso, pode ser necessário passar para um monitor desktop/laptop.
+- Às vezes, clicar no menu de três pontos abaixo de uma postagem pode ocultar o ícone de resposta. Recarregue a página para recuperá-la.
+
+## Moderando no Facebook
+
+Se você ver algo que pareça quebrar nosso [código de conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), exclua imediatamente.
+
+Às vezes, as pessoas publicarão coisas que acham engraçadas. Elas não percebem que o que disseram ou compartilharam pode ser interpretado como ofensivo. Você deve excluir essas publicações, mas não necessariamente banir a pessoa. Espera-se que o usuário entenda que aquilo que postou foi inapropriado, pois a postagem foi apagada.
+
+Mas se é um delito flagrante, isso não pode razoavelmente ser atribuído a uma diferença cultural ou a um mal-entendido da língua inglesa. Nesse caso, você deve considerar fortemente bloquear o membro do grupo do Facebook.
+
+## Moderando o Discord
+
+É assim que os moderadores lidam com violações do nosso [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) em nosso servidor de bate-papo:
+
+> [!NOTE] O Camperbot serve como nosso bot de moderação, e todos os comandos usam a interface de comando nativa do Discord. Você pode ver uma lista de todos os comandos digitando `/` em qualquer canal.
+
+1. **Certifique-se de que o usuário tentou violar o [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Nem todas as violações do [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) têm esse propósito. Um novo usuário do freeCodeCamp pode postar uma grande quantidade de códigos para ajudar, sem notar que isso pode ser disruptivo para a conversa. Nesses casos, você pode simplesmente pedir para que eles coloquem seus códigos em serviços como Codepen ou Pastebin.
+
+2. **Se o camper violar clara e intencionalmente o [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), o moderador procederá da seguinte forma:**
+
+ Para delitos menores, um aviso pode ser emitido com o comando `/warn`. Para mais erros flagrantes, você pode remover o membro do servidor temporariamente com o comando `/kick` ou permanentemente com o comando `/ban`. Em alguns casos, um membro pode precisar de algum tempo para resfriar e coletar seus pensamentos - o comando `/mute` permite que você evite que ele se envolva com a nossa comunidade por um determinado período de tempo. Um membro silenciado pode ver a conversa, mas não pode postar mensagens ou adicionar reações.
+
+ Todos os comandos de moderação levarão um parâmetro `reason`, que deve ser uma breve explicação do motivo da ação ter sido tomada. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. Como tal, devemos evitar o uso das ferramentas de moderação embutidas no Discord, pois elas não serão registradas.
+
+ > [!WARNING] A razão fornecida para um comando de moderação também será incluída na notificação de DM ao camper. Por favor, lembre-se de ser profissional aqui.
+
+3. **Criando uma discussão privada**
+
+ Há várias situações onde você deve abordar um problema com um usuário freeCodeCamp em privado. Isso não deve ser feito por DMs, já que isso pode levar a situações onde você diz uma coisa e o usuário freeCodeCamp diz outra. Em vez disso, use a funcionalidade do bot para criar uma discussão privada:
+
+ - Utilize o comando `/private`, onde `target` é o usuário com o qual você deseja abrir um canal privado.
+ - O bot vai criar um canal e adicionar o usuário do freeCodeCamp mencionado e todos os moderadores com a função `Your Friendly Moderator`. Enquanto todos os moderadores são adicionados ao canal por uma questão de transparência, o moderador que selecionar esse comando deve ser o único a interagir com o usuário do freeCodeCamp, a não ser que eles peçam assistência.
+ - Quando a conversa estiver completa, clique no botão `❌ Close` _na primeira mensagem no canal privado_ para que o bot feche e exclua o canal.
+
+4. **Apagando mensagens**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. Se uma mensagem não estiver de acordo com o nosso Código de Conduta, ou não é apropriado para a nossa comunidade, geralmente você pode excluí-la.
+
+ Note que se a mensagem contiver conteúdo que viole os termos de serviço do Discord, você deverá denunciá-la em https://dis.gd/report **antes de** excluí-la.
+
+5. **Não tenha medo de tomar uma ação**
+
+ Se um usuário do freeCodeCamp violar o [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), não ameace realizar ações de moderação e nunca os avise em público. Em vez disso, fale com eles usando o comando `/private` do bot ou use os comandos de moderação do bot.
+
+ Se uma violação foi claramente sem intenção e não justifica uma ação de moderação ou conversa privada, deixe o(a) ofensor(a) ciente de sua ação sem que isso soe como uma advertência.
+
+ Por exemplo:
+
+ - O usuário do freeCodeCamp posta um longo bloco de código para pedir ajuda:
+
+ Moderador: **@username** Por favor, use o Codepen ou Pastebin ao postar uma grande quantidade de linhas de código.
+
+ - Ou se você realmente tiver que explicar o motivo:
+
+ Moderador: **@username** Por favor, use Codepen ou Pastebin ao postar uma grande quantidade de linhas de código, pois isso atrapalha o chat e pode ser considerado spam segundo o nosso [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - Para violações leves e não intencionais do [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderador: este é um lembrete amigável para que todos sigam o [código de conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Não se gabe por ser um moderador**
+
+ Não se veja como superior dentro da comunidade. **Vocês são a comunidade.** E a comunidade lhe tem confiado para ajudar a proteger algo raro que todos nós compartilhamos - um lugar _acolhedor_ para novos desenvolvedores.
+
+ Se você se gabar por ser um moderador, as pessoas podem se sentir desconfortáveis perto de você, do mesmo modo que as pessoas podem se sentir desconfortáveis perto de um policial, mesmo que elas não estejam fazendo nada de errado. É apenas a natureza humana.
+
+7. **Não contrarie outros moderadores **
+
+ Se você não concorda com a ação de um moderador, fale com ele em privado ou no canal #mod-chat. Nunca passe por cima da ação de um moderador, e nunca contradiga outros moderadores publicamente. Ao invés disso, tenha uma conversa tranquila no `#mod-chat` e convença o moderador de que ele deveria reverter o banimento e mudar seu ponto de vista.
+
+ _Lembre-se: estamos todos no mesmo time. Queremos dignificar o papel dos moderadores e apresentar uma frente unida._
+
+8. **Fale com outros moderadores**
+
+ Temos uma sala chamada `#mod-chat` somente para moderadores. Use-a! Se você se sentir desconfortável em como lidar com certa situação, peça ajuda a outros moderadores. Se você achar que algo deve ser discutido, faça-o. Você é parte do time e nós damos valor a cada opinião de cada membro do time! Mesmo se você discordar totalmente de algo nestas diretrizes ou do [Código de Conduta](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporariamente inativo**
+
+ Se você não for ficar ativo como Moderador por um tempo devido a motivo de viagem, doença ou qualquer outra razão, certifique-se de avisar aos outros no canal `#mod-chat`. Isso para sabermos se podemos contar contigo para ser regularmente ativo no servidor ou não.
+
+## Como se tornar um moderador
+
+Suponha que você esteja ajudando pessoas da comunidade de modo consistente ao longo do tempo. Nesse caso, nosso time de moderadores vai notar você e um deles vai mencionar você como um possível moderador da [nossa equipe](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). Não existem atalhos para se tornar um moderador.
+
+Se for aprovado, nós adicionaremos você ao nosso time de moderadores no [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+> [!NOTE] GitHub: Depois que foi aceito como moderador, você receberá um convite de repositório do GitHub. Você precisará visitar [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) para poder aceitar o convite.
+>
+> Isso é necessário para nós podermos dar a você acesso de escrita em alguns de nossos repositórios.
+
+## Como funciona nossa sala de Colaboradores
+
+Todos são bem-vindos no [chat de colaboradores do nosso servidor](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Esse é o chat destinado aos moderadores e outros usuários do freeCodeCamp que estão contribuindo para nossa comunidade de diversas formas, incluindo através de grupos de estudo.
+
+Assumimos que os colaboradores lerão qualquer coisa neste chat que os mencione diretamente com um **@username**. Tudo o mais é opcional, mas fique à vontade para ler e interagir com qualquer coisa que alguém poste lá dentro.
+
+## Lidando com solicitantes
+
+Você pode ser abordado por organizações que queiram formar uma parceria com o freeCodeCamp de alguma maneira. Quando você perceber que essa é a intenção deles, **pedimos que pare de conversar com eles** e diga-lhes para enviar um e-mail para `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+Recebemos propostas como essa com frequência. A equipe está em melhor posição para julgar se tal relação valerá a pena para nossa comunidade (e raramente vale).
+
+## Lidando com consultas sobre saúde (mental)
+
+Você pode encontrar situações onde os usuários procuram aconselhamento médico ou estão lidando com questões de saúde mental e buscando apoio.
+
+Como parte de nossa política, você deve evitar falar em privado sobre essas questões. Se a situação em algum ponto refletir de volta para o freeCodeCamp, queremos que as conversas fiquem registradas. Deixe claro que não somos profissionais da medicina e que você encoraja o usuário a procurar ajuda profissional.
+
+Apesar de ser difícil às vezes, evite dar quaisquer dicas ou conselhos que não sejam indicar ao usuário buscar ajuda profissional!
+
+Se isso ocorrer no nosso servidor de chat: crie um canal privado para o usuário e o time de moderadores. Isso pode ser feito com o comando `private` do bot.
+
+- O usuário tem a privacidade garantida.
+- O chat público não será mais perturbado.
+- Outros membros do time podem contribuir caso você se sinta desconfortável ao lidar com a situação sozinho.
+
+Links úteis:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## Uma nota sobre liberdade de expressão
+
+Às vezes, as pessoas vão defender algo ofensivo ou instigante que elas disseram como sendo "liberdade de expressão."
+
+Essa tirinha da XKDC resume perfeitamente o pensamento da maioria das comunidades sobre liberdade de expressão.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Obrigado por ler isto, e obrigado por ajudar a comunidade de desenvolvedores!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..dcaee605
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: O manual oficial de integração de moderadores do freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Este guia ajudará novos moderadores a implementarem os processos e procedimentos seguidos por moderadores experientes no fórum da comunidade do freeCodeCamp e em outras comunidades oficiais que abrigamos.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se você ainda não leu [O Manual do Moderador](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook), comece lendo esse manual primeiro.
+
+## O fórum
+
+### Primeiros passos
+
+A primeira coisa que você pode notar após receber o status de moderador no fórum é que sua interface ficará um pouco diferente, com novas ferramentas de administrador para explorar e acesso ao subfórum Mod-Team.
+
+Algumas das novas ferramentas aparecerão dentro de um novo item de menu que se parece com uma chave inglesa. Outras aparecerão como novas guias, botões ou, até mesmo, novas opções ativadas nos menus do fórum.
+
+Para se familiarizar com as novas ferramentas e poderes, você pode combinar um ou mais dos seguintes métodos durante sua primeira semana com essa função elevado:
+
+:::tip
+Os dois primeiros são os mais importantes.
+:::
+
+### Familiarize-se com as ferramentas administrativas do Discourse
+
+O fórum do freeCodeCamp é um fórum do Discourse e segue muitas das mesmas orientações de outros fóruns criados na plataforma. Para começar a se familiarizar com o Discourse e o papel de moderação, primeiro leia o [novo guia do usuário](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) e o [novo guia do moderador](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116) do Discourse.
+
+### Acompanhe de perto um moderador
+
+Todas as ações dos moderadores podem ser seguidas analisando os [logs de ação](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). As ações tomadas por ferramentas automatizadas como o `Akismet` ou o `system` podem ser, em grande parte, ignoradas até que resultem em uma postagem que precisa ser analisada. Publicações a serem revisadas aparecerão na área do fórum chamada [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review).
+
+Na primeira semana, aproximadamente, você vai querer prestar atenção ao que está sendo sinalizado e ao que está sendo analisado. Compare isso com as ações que estão sendo tomadas sobre os posts sinalizados. Você pode ver a conta do sistema sinalizar uma publicação porque o usuário a criou muito rapidamente. Em muitos casos, os moderadores desmarcarão a publicação clicando no botão "Approve post" ou a marcarão como "Not Spam" (dependendo do tipo de sinalização).
+
+Comumente, sinalizações de spam também podem ser levantadas por membros ou moderadores. Comportamento comum e dúbio envolve a abertura de uma conta, criar uma publicação que parece inofensiva, editando essa postagem mais tarde para adicionar um link para um site externo com o objetivo de fazer publicidade. Nesse caso, geralmente, a conta do membro é bastante nova e só fez essa única publicação até agora, o que indica que a conta foi aberta com o único propósito de fazer spam à comunidade. A decisão a ser tomada deverá ser excluir a conta depois do primeiro delito, nesse caso. O mesmo se aplica às contas cuja primeira publicação é considerada spam.
+
+Você pode notar que os moderadores executam um procedimento chamado 'dividir o tópico' (split topic). Esse pode ser um caso em que um moderador dividiu uma publicação que foi erroneamente feita em um tópico existente em um novo tópico, ou um moderador mesclou tópicos duplicados que um único usuário criou para a mesma pergunta. Acompanhar esse procedimento destacará as diferentes ações e suas causas.
+
+Outro recurso útil que é ativado para todos os moderadores é a habilidade de publicar uma "resposta automatizada" (canned reply), que é uma resposta pré-escrita desenvolvida pela equipe de moderadores para responder rapidamente a alguns cenários conhecidos e repetitivos. Elas incluem:
+
+- Dar as boas-vindas a um novo membro do fórum que postou código sem uma pergunta -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Lembrar aos membros de que não devem publicar soluções de código, mas fornecer dicas e sugestões -> "Solutions instead of help"
+- Responder a uma situação em que o código de alguém funciona para você mas não para eles -> "Browser Issues"
+- Incentivar membros a abrir issues no GitHub quando um possível erro for encontrado -> "Bug Report"
+
+Há mais respostas do tipo, as quais podem ser lidas para ajudar a se familiarizar com as respectivas utilizações. Você também pode encontrar discussões sobre os templates no subfórum Mod-Team. Fique à vontade para fazer perguntas se não tiver certeza de como um template deve ser usado.
+
+### Ler as publicações do sub-fórum Mod-Team
+
+O subfórum Mod-Team contém várias publicações de moderadores passados e atuais discutindo as diferentes exigências e/ou desafios de moderação do fórum.
+
+Ler essas publicações pode ajudar a descobrir algumas das metas e processos subjacentes, que dizem respeito aos moderadores do fórum. Alguns dos tópicos também podem lançar alguma luz sobre o tratamento de spam e conteúdo impróprio no fórum.
+
+## Onde pedir ajuda
+
+Para obter ajuda para lidar com uma situação com a qual você está desconfortável ou incerto sobre como lidar, discuta com seus colegas moderadores no [sub-fórum Mod-Team](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) ou no [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) no Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/pt/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c3f305a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Modelos de resposta
+---
+
+Esses são alguns dos modelos de resposta que você talvez use enquanto estiver revisando issues/pull requests.
+
+> Você pode fazer seu próprio modelo com a funcionalidade embutida do GitHub chamada [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) ou usar as citadas abaixo.
+
+## Obrigado
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Obrigado e parabéns
+
+> Para agradecer e encorajar colaboradores de primeira viagem.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Erro de compilação
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Sincronização de forks
+
+> Quando um PR não está atualizado com a branch `main`.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Conflitos ao fazer o merge
+
+> Quando um PR tem conflitos de merge isso precisa ser resolvido.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ Se é a primeira vez de um colaborador e se ele tem um conflito de merge, os mantenedores resolverão o conflito para ele.
+
+## Duplicado
+
+> Quando um PR é duplo ou repetitivo.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Fechando pull requests inválidos
+
+> Quando um PR é inválido.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Quando o PR adiciona links para recursos externos.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adicionando comentário sobre erros de iniciante
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> Quando um PR é aberto para uma issue que não passou por triagem e marcada como pronta para contribuição.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Fechando issues inválidas
+
+> Quando uma issue se refere ao código do usuário do freeCodeCamp.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Quando uma issue é a mesma que uma issue anterior.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Quando uma issue foi resolvida na fase de preparo.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Issues de `first timer only`
+
+> Quando uma issue é considerada eligível pela primeira vez como contribuição ao código.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Solicitações de atribuição
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/pt/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..45492807
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Divulgação responsável - Lista dos famosos
+---
+
+Apreciamos qualquer divulgação responsável de vulnerabilidades que possam impactar a integridade de nossas plataformas e usuários. Se você está interessado em contribuir para a segurança de nossa plataforma, leia nossa [política de segurança descrita aqui](security).
+
+Embora não possamos oferecer nenhuma recompensa ou troca no momento, agradecemos a essas pessoas incríveis por nos ajudar a manter a plataforma segura para todos:
+
+- Mehul Mohan, da [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Fix de vulnerabilidade](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) trabalhando com IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Agradecemos por suas contribuições :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/security.md b/src/content/docs/pt/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e13e2dec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Política de segurança do freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Este documento descreve a nossa política de segurança para as bases de código, para as plataformas que operamos, além de mostrar como relatar vulnerabilidades.
+
+## Relatando uma vulnerabilidade
+
+> [!NOTE] Se achar que encontrou uma vulnerabilidade, **reporte-a de modo responsável**. Não crie issues no GitHub para problemas de segurança. Em vez disso, siga este guia.
+
+### Diretrizes
+
+Apreciamos a divulgação responsável de vulnerabilidades que possa impactar a integridade de nossas plataformas e usuários. No interesse de poupar o tempo de todos, recomendamos que você relate as vulnerabilidades com isso em mente:
+
+1. Certifique-se de estar usando as versões **mais recentes**, **estáveis** e **atualizadas** do sistema operacional e do navegador da web disponível para você em sua máquina.
+2. Consideramos o uso de ferramentas e utilitários on-line para relatar issues com SPF e configurações DKIM, testes de servidor SSL e outros na categoria de ["recompensas por migalhas"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) e não responderemos a estes relatórios.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Relatórios
+
+Depois de confirmar as diretrizes acima, fique à vontade para enviar um e-mail para `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. Você também pode nos enviar uma mensagem criptografada com PGP para `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Ao reportar uma vulnerabilidade, vamos analisá-la e garantir que ela não é um falso positivo. Se precisarmos esclarecer alguns pormenores, entraremos em contato com você. Você pode enviar relatórios separados para cada issue que encontrar. Lembre-se de que não poderemos responder a issues que entendermos que se encontram fora das diretrizes.
+
+## Plataformas e bases de código
+
+Aqui está uma lista das plataformas e bases de código para as quais estamos aceitando relatórios:
+
+### Plataforma de aprendizagem
+
+| Versão | Branch | Suportado | Site da web ativo |
+| --------------- | -------------- | --------- | ------------------------ |
+| produção | `prod-current` | Sim | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| staging | `prod-staging` | Sim | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| desenvolvimento | `main` | Não | |
+
+### Plataforma de publicação
+
+| Versão | Suportado | Site da web ativo |
+| ---------- | --------- | -------------------------------- |
+| produção | Sim | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localizado | Sim | `freecodecamp.org/<idioma>/news` |
+
+### Aplicativo móvel
+
+| Versão | Suportado | Site da web ativo |
+| -------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| produção | Sim | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Outras plataformas
+
+Além dos itens acima, também aceitamos relatórios para repositórios hospedados no GitHub, da organização do freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Outras aplicações auto-hospedadas
+
+Hospedamos algumas de nossas próprias plataformas usando softwares de código aberto, como o Ghost e o Discourse. Se você está relatando uma vulnerabilidade, certifique-se de que não é um erro no software do upstream.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/pt/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1d2b9119
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+Se estiver com problemas, há grandes probabilidades de a resolução constar desta documentação.
+
+## Problemas com a instalação dos pré-requisitos recomendados
+
+Desenvolvemos regularmente nos sistemas mais recentes e populares, como o macOS 10.15, o Ubuntu 18.04 e o Windows 10 (com WSL2).
+
+É recomendado pesquisar seu issue específico em recursos como Google, Stack Overflow e Stack Exchange. É possível que alguém já tenha enfrentado o mesmo problema que o seu e já possua uma solução.
+
+Se você está em um sistema operacional diferente ou se ainda está encontrando problemas, veja [obtendo ajuda](#getting-help).
+
+:::caution
+Evite criar issues no GitHub para problemas com as tecnologias que são requisitadas de antemão. Estão fora do escopo deste projeto.
+:::
+
+## Problemas de ausência da interface do usuário, fontes, strings de idioma ou erro de build
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. Se um deles não estiver em cache, execute o seguinte:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+OU
+
+Use o atalho
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+Se você continua enfrentando problemas com a compilação, é recomendável limpar o espaço de trabalho.
+
+Use `git clean` no modo interativo:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Como limpar arquivos não rastreados do git (captura de tela)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="Como limpar arquivos git não rastreados" />
+</details>
+
+## Problemas com API, login, envio de desafios, etc.
+
+Se você não conseguir fazer o login e se vir um banner com uma mensagem de erro dizendo que o erro será reportado ao freeCodeCamp, verifique novamente se a porta local `3000` não está em uso por um programa diferente.
+
+#### **A partir do Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Problemas de logout ao navegar
+
+Enquanto estiver em desenvolvimento, sua sessão é armazenada como cookies. Limpar os cookies os retirará de sua conta de desenvolvimento.
+
+Executar `pnpm run seed:certified-user` também deslogará você. Isso sobrescreverá o usuário de desenvolvimento em seu banco de dados local.
+
+## Problema de obter 404 ao navegar na página de perfil
+
+Ao tentar navegar para http://localhost:8000/developmentuser para ver a página de perfil, o Gatsby assume o controle do serviço das páginas do lado do client e, portanto, você obterá uma página 404 para o perfil do usuário quando estiver trabalhando.
+
+Há um botão de "Pré-visualização personalizada da página de 404". Clique nele para ver o perfil.
+
+## Problemas ao instalar dependências
+
+Se você receber erros durante a instalação das dependências, certifique-se de que você não está em uma rede restrita ou suas configurações de firewall não impedem você de acessar os recursos.
+
+A primeira configuração pode demorar um pouco, dependendo da largura de banda da sua rede. Tenha paciência. Se você ainda tiver problemas, recomendamos usar o GitPod invés de uma configuração off-line.
+
+> [!NOTE] Se estiver usando dispositivos da Apple com o chip M1 para executar a aplicação localmente, sugerimos usar o Node v14.7 ou uma versão mais recente. Do contrário, você poderá ter problemas com dependências como o Sharp.
+
+## Como trabalhar com outros idiomas
+
+Para ver como o client é renderizado em outro idioma, acesse [teste da aplicação do client em um idioma mundial.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Obter ajuda
+
+Se você está com dificuldades e precisa de ajuda, fique à vontade em perguntar na categoria ['Contributors' (colaboradores) em nosso fórum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) ou [na sala de bate-papo dos colaboradores](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Pode haver um erro no console do seu navegador ou no Bash/Terminal/Linha de Comando que ajudará a identificar o problema. Forneça esta mensagem de erro na descrição do seu problema para que outros possam identificá-lo mais facilmente e ajudá-lo a encontrar uma solução.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/pt/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/pt/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2f51c310
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/pt/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Como funciona o fluxo de trabalho do token do usuário
+---
+
+Os tokens de usuário são usados para identificar os usuários para terceiros. Assim, os desafios concluídos usando esses serviços podem ser salvos na conta de um usuário.
+
+## Como eles são criados
+
+No momento, os tokens são usados apenas para enviar os desafios de Bancos de dados relacionais. Um token é criado quando um usuário conectado clica em "Clique aqui para iniciar o curso" ou "Clique aqui para iniciar o projeto" para iniciar um dos cursos ou projetos de Banco de dados relacionais.
+
+## Quando eles são excluídos
+
+Um token de usuário será excluído quando um usuário sai do freeCodeCamp, redefine seu progresso, exclui a conta ou exclui manualmente o token usando o widget na página de configurações.
+
+## Como eles funcionam
+
+Os tokens são armazenados em uma coleção chamada `UserToken` no banco de dados. Cada registro tem um `_id` único, que é o token, e um `user_id` que se vincula à conta do usuário da coleção `user`. O token é codificado utilizando JWT e enviado para o cliente quando ele é criado. Esse token codificado é então enviado aos serviços de terceiros que precisam dele e para a nossa API por eles quando um desafio é concluído. Quando nossa API o receber, ele é decodificado para que possamos identificar o usuário que está enviando um desafio e salvar o desafio completo em seus `completedChallenges`.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/uk/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f30b9fdf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Керівництво з аналітики
+---
+
+Якщо ви є автором публікацій та маєте доступ до Google Analytics (News), ви можете використати це керівництво для перегляду статистики публікацій та пошуку публікацій за мовою.
+
+## Пошук за мовою
+
+Перегляд статистики певної мови:
+
+
+
+1. Оберіть `News` із верхнього випадного меню.
+1. Натисніть `Reports` на бічній панелі.
+1. У другорядній бічній панелі оберіть `Engagement`.
+1. Натисніть `Pages and Screens`.
+1. У рядку пошуку введіть підшлях потрібної мови.
+1. Оберіть `Page path and screen class` у випадному меню під рядком пошуку.
+
+## Статистика автора
+
+Після отримання вищезгаданої статистики `Pages and Screens` використайте наступні кроки, щоб переглянути статистику певного автора.
+
+
+
+1. Натисніть на кнопку `Add filter`.
+1. Оберіть `Author` на бічній навігації.
+1. Виберіть ім’я автора із випадного меню `Dimensions values`.
+1. Натисніть на кнопку `Apply`, щоб застосувати зміни.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/uk/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d2b05ec8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: Рекомендації щодо кодової бази
+---
+
+## Стилізація компоненту
+
+Ми рекомендуємо стилізувати компоненти, використовуючи наш [посібник зі стилю](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+Кольори визначені у [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css), а шрифти визначені у [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+Ми категоричні щодо додавання нових змінних/токенів до кольорів. Після ретельного аналізу ми обрали кольори, які відповідають ідентичності бренду freeCodeCamp, досвіду розробників і доступності.
+
+Ключове слово `!important` може бути використане для заміни значень у деяких випадках (наприклад, проблеми доступності). Ви повинні додати коментар з описом проблеми, щоб її не видалили у майбутньому рефакторингу.
+
+### Підтримка RTL
+
+Ми прагнемо підтримувати макети справа наліво (RTL) у кодовій базі для мов, які використовують письмо в такому напрямку. Для цього потрібно бути уважними щодо стилізації компонентів. Ось деякі правила, яких потрібно дотримуватись:
+
+- Не використовуйте властивості `float`
+ - Натомість використовуйте макети Flexbox та Grid, оскільки вони мають вбудовану підтримку RTL, і їх буде простіше підтримувати та переглядати.
+- Не визначайте напрямок, використовуючи `margin` та `padding`: використання `padding-right` та `margin-left` може здаватись безобідним, але ці напрямки не відображаються, коли макет змінюється на RTL, а додавання протилежних значень ускладнює утримання кодової бази.
+ - Використовуйте логічні властивості: ви можете додати однаковий інтервал, використовуючи `padding-inline-end` та `margin-inline-start`, і вам не доведеться переживати про макет RTL, оскільки вони відповідають тому, де починається та закінчується рядок. Крім того, вам не доведеться турбуватися про додавання додаткових значень до файлів RTL, і, відповідно, не доведеться пам’ятати про зміну однакових значень у двох файлах.
+- Не використовуйте `!important` у `font-family`: для макетів RTL та LTR використовуються різні шрифти; додавання `!important` до властивості `font-family` також впливає на макет RTL.
+
+## Загальний JavaScript
+
+У більшості випадків наш [лінтер](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) попереджатиме про будь-яке форматування, яке суперечить вподобанням нашої кодової бази.
+
+Рекомендовано використовувати функціональні компоненти, а не класові.
+
+## Особливий TypeScript
+
+### Перенесення файлу JavaScript до TypeScript
+
+#### Збереження історії файлів Git
+
+Іноді зміна файлу з `<filename>.js` на `<filename>.ts` (або `.tsx`) призводить до видалення вихідного файлу та створення нового, а в іншому випадку просто змінюється назва файлу, згідно з Git. В ідеалі ми хочемо, щоб історія файлів була збережена.
+
+Для цього потрібно:
+
+1. Перейменувати файл
+2. Позначити прапорцем `--no-verify`, щоб Хаскі не скаржився на помилки лінтера
+3. Провести рефакторинг для перенесення у TypeScript в окремому коміті
+
+> [!NOTE] Редактори типу VSCode однаково показуватимуть, що файл видалено та створено новий. Якщо ви використаєте CLI для `git add .`, то VSCode показуватиме файл як перейменований
+
+### Конвенції про іменування
+
+#### Інтерфейси та типи
+
+У більшості випадків рекомендовано використовувати оголошення інтерфейсу, а не оголошення типу.
+
+Пропси компоненту React — суфікс `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+Stateful-компоненти React — суфікс `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+За замовчуванням — ім’я об’єкта ВерблюдячимРегістром
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Визначення дій
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### Як використовувати reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### Як використовувати dispatch
+
+Імпортуйте необхідні дії та селектори всередині компонента.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Тестування
+
+Тести `api/` розділені на дві частини:
+
+1. Модульні тести
+2. Інтеграційні тести
+
+#### Модульні тести
+
+Модульні тести виокремлюють певну функцію чи компонент. Тестам не потрібне мокування, але вони вимагають фікстури.
+
+Модульні тести розміщені у новому файлі поруч з експортованим файлом, який тестується:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Інтеграційні тести
+
+Інтеграційні тести тестують API загалом. Тести вимагатимуть імітації та не повинні вимагати виправлень, окрім даних заповнення бази даних і методу автентифікації.
+
+Зазвичай кожен файл інтеграційного тесту пов’язаний з маршрутом. Інтеграційні тести розміщені у каталозі `api/tests/`:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Додаткова література
+
+- [Документація TypeScript](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [Шпаргалка для TypeScript із React](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/uk/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c5ab0f1f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Розширення VSCode Courses
+---
+
+Тут детально описано інструкції з обслуговування репозиторію [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension), який містить вихідний код для розширення [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses).
+
+## Публікування розширення
+
+GitHub Action автоматично публікує розширення для Visual Studio Marketplace після випуску нового GitHub Release.
+
+1. Запакуйте нову версію розширення:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Де `<tag_type>` є одним із: `major`, `minor`, `patch`.
+
+2. Надішліть нову версію до `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+За бажанням, ви можете надіслати її одразу до `upstream/main`, але ми рекомендуємо створити новий PR для перевірки працездатності.
+
+3. Створіть новий GitHub Release, використовуючи GitHub UI:
+
+- Правильно збільште номер версії під час створення нового тегу.
+- Завантажте файл `.vsix` із випуском.
+- Опублікуйте випуск та підтвердьте успішність дії.
+
+> [!NOTE] Для створення випуску потрібен письмовий доступ до репозиторію `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension`.
+
+## Публікування розширення вручну
+
+Завантаження до Visual Studio Marketplace можна здійснити вручну, дотримуючись таких дій:
+
+1. Відвідайте https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ та увійдіть
+2. Перейдіть на [сторінку freeCodeCamp Publisher](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Виберіть відповідне розширення та оберіть `Update`
+4. Завантажте файл зі своїх локальних файлів
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5f78ebf4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Структура навчальної програми
+---
+
+Наш основний навчальний вміст знаходиться у каталозі під назвою `curriculum`. На цій сторінці буде детально описано, як ці файли організовані.
+
+## Термінологія
+
+При обговоренні навчальної програми важливо знати декілька термінів.
+
+- `certification` : коли йдеться про сертифікацію, мається на увазі сертифікати, які отримують користувачі. Це не те саме, що й superBlock.
+- `superBlock` : збірка найскладніших завдань. Кожен суперблок відповідає сертифікації в навчальній програмі (наприклад, «Адаптивний вебдизайн»).
+- `block` : розділ у межах суперблоку. Блок відповідає групі завдань у даній сертифікації (наприклад, «Основи HTML та HTML5»)
+- `challenge` : це окремий урок у навчальній програмі (наприклад, «Ознайомлення з елементами HTML»)
+
+## Дерево файлів
+
+Ось як буде виглядати структура файлів з цими термінами:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## Каталог `_meta`
+
+Каталог `_meta` — це особливий каталог, який містить файли `.json`. Ці файли відповідають кожному окремому блоку в навчальній програмі та використовуються, щоб визначити до якого суперблоку належить блок та порядок завдань у цьому блоці.
+
+## Перейменування файлів
+
+Інколи вам потрібно перейменувати сертифікат, суперблок, блок чи завдання. У цьому розділі будуть описані важливі кроки, які допоможуть вам уникнути помилок збірки.
+
+:::danger
+Перейменування файлів у структурі навчальної програми часто змінює шлях (або URL-адресу) вмісту на головній вебсторінці. Робити це варто з обережністю, оскільки перенаправлення потрібно налаштовувати для кожної внесеної зміни.
+:::
+
+### Перейменування сертифікації
+
+Під час перейменування сертифікації вам, ймовірно, доведеться перейменувати пов’язаний суперблок. Виконайте наступні дії, щоб перейменувати лише сертифікацію:
+
+1. Оберіть нову назву для папки `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate`.
+1. У файлі `meta.json` тієї папки змініть значення у `name`, `dashedName` та `challengeOrder` на нову назву сертифікації.
+1. Перейменуйте папку `{superBlock}-certificate` та файл YAML у `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`.
+1. Змініть `title` у файлі YAML на нову назву.
+1. Перейменуйте файл та папку з третього кроку для решти мов навчальної програми.
+1. Оновіть `client/src/redux/index.ts` для роботи з правильним `title`.
+1. За бажанням оновіть і `certSlug` для суперблока у цьому ж файлі. **Зауважте**, що перейменування `certSlug` змінить URL-адресу для сертифікацій, тому це варто робити обережно.
+1. Оновіть `title` у `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` на нові значення. **Зверніть увагу**, що ця зміна `title` **зруйнує** сторінку superBlock для відповідної сертифікації. Це пов’язано із тим, що назва суперблоку повинна відповідати назві сертифікації. Бажано одночасно змінити й назву суперблоку.
+1. Якщо ви перейменували `certSlug` у сьомому кроці, змініть його для сертифікації та усіх вкладених значень `projects`.
+1. Оновіть значення `certTypeTitleMap` в `shared/config/certification-settings.js` на нову назву.
+1. Якщо ви перейменували `certSlug` у сьомому кроці, оновіть ключ `certSlugTypeMap` у цьому ж файлі.
+1. В разі потреби оновіть назву сертифікації у масиві `legacyCerts` у `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx`.
+1. Змініть основний файл `README.md` на нову назву.
+
+### Перейменування суперблоку
+
+> [!NOTE] Під час перейменування суперблоку нова назва папки використовується як шлях і її варто вважати «правильною» назвою. Усі інші значення потрібно оновити, щоб показати цю зміну.
+
+Коли ви перейменовуєте суперблок, потрібно перейменувати сертифікацію та блок `{superBlock}-projects`, оскільки вони мають спільну назву. Виконайте наступні кроки, щоб перейменувати лише суперблок:
+
+1. Перейменуйте папку superBlock у каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Перейменуйте папку superBlock у _всіх_ інших каталогах `curriculum/challenges/{language}`.
+1. Для кожного блоку у цьому суперблоці оновіть значення `superBlock` у файлі `meta.json` на його dashedName. Наразі вам не потрібно перейменовувати папки. Зробіть це при перейменуванні блоку.
+1. Перейменуйте папку суперблоку в `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Оновіть файл `index.md` у вищевказаній папці, змінивши значення `title` та `superBlock` на нову назву.
+1. Для кожної вищезазначеної папки у блоці оновіть `index.md` для роботи з правильним значенням `superBlock`.
+1. Оновіть шлях сертифікації зверху файлу `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`, а також оновіть значення `title` цього суперблоку. **Зверніть увагу**, що змінивши `title` **зникне** можливість переглядати сертифікацію цього суперблоку. Це пов’язано з тим, що назва суперблоку повинна відповідати назві сертифікації. Бажано одночасно змінити й назву сертифікації.
+1. Оновіть ключ `superBlockCertTypeMap` в `shared/config/certification-settings.js` на нову назву суперблоку.
+1. Оновіть значення шляху в `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. Оновіть файл `intro.json` для кожної мови в `client/i18n/locales` для роботи з новим суперблоком `dashedName`. В англійському файлі також оновіть `title`.
+1. Перевірте файл `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js`, щоб дізнатись чи суперблок активний у збірках i18n. Оновіть усі значення, де він використовується.
+1. Оновіть назву головного файлу `README.md`.
+
+### Перейменування блоку
+
+Для перейменування блоку навчальної програми виконайте наступне:
+
+1. Змініть назву папки блоку в каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}`.
+1. Змініть назву тієї самої папки блоку в _усіх_ іншомовних каталогах, щоб вони збігалися. Вони повинні збігатися з англійською структурою, інакше виникне помилка збірки.
+1. Змініть назву папки блоку в каталозі `_meta`.
+1. Оновіть властивості `name` та `dashedName` для файлу `meta.json` цього блоку.
+1. Оновіть папку блоку в `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. Оновіть значення `block` у передмові файлу `index.md` папки вище.
+1. Оновіть назву блоку на нову назву для всіх мов у файлах `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json`. Також оновіть `title` в англійському файлі `intro.json`.
+1. Оновіть основний файл `README.md` на нову назву.
+
+### Перейменування завдання
+
+Для перейменування окремого файлу завдання виконайте наступне:
+
+1. Змініть назву файлу завдання в каталозі `curriculum/challenges/english`.
+1. Змініть назву `title` та `dashedName` у цьому файлі.
+1. Змініть назву файлу та `dashedName` у цих файлах для _всіх_ каталогів мов так, щоб вони збігалися.
+1. Оновіть назву завдання у відповідному файлі `meta.json`. Ці назви завдань не використовуються у збірці, але забезпечують зручний спосіб ідентифікації порядку завдань.
+1. Якщо завданням є сертифікаційний проєкт, оновіть файл YAML у `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` на нову назву.
+1. Якщо завданням є сертифікаційний проєкт, оновіть `title` та `link` у `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. Якщо завданням є сертифікаційний проєкт, оновіть основний файл `README.md` на нову назву.
+
+## Властивість `dashedName`
+
+Властивість `dashedName` використовується для створення шляху URL-адреси для суперблока, блока або завдання. Загалом вони повинні відповідати тому, що помічник `/utils/slugs.js` виведе для імені файлу.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8a64ba8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Помічники з навчальної програми
+---
+
+Тестувальник має доступ до декількох помічників, які можуть допомогти з тестуванням коду кемпера.
+
+## Помічник CSS
+
+Щоб створити екземпляр помічника в межах тестового блоку, використайте:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+У цьому прикладі змінна `document` посилається на об’єкт-документ вбудованого фрейму тестувальника.
+
+### Методи
+
+Існує декілька доступних методів для парсингу та тестування CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+Метод `.getStyle()` приймає селектор CSS та повертає об’єкт оголошення стилю CSS.
+
+Наприклад, якщо кемпер написав такий CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+Ви отримаєте такий об’єкт:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+Цей метод дозволяє перевірити, що були встановлені конкретні властивості:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+Помічник прикріплює метод `.getPropVal()` до об’єкта оголошення стилю, що дозволяє отримати значення конкретної властивості:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+Метод `.getCSSRules()` приймає в-правило з `media | fontface | import | keyframes` та повертає масив правил CSS, що відповідають цьому в-правилу.
+
+Наприклад, якщо кемпер написав такий код:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Поверненим значенням `helper.getCSSRules('media')` буде цей масив:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+Потім ви можете перевірити, чи кемпер написав правильний медіазапит:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+Метод `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` приймає медіатекст (наприклад, `("max-width: 200")`) та повертає правила CSS в межах цього медіазапиту.
+
+Повернений результат дорівнює властивості медіаправила `cssRules` з поверненого значення `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Менш поширені методи
+
+Ці методи не настільки поширені, але доступні за необхідності.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+Метод `.getStyleDeclarations()` приймає селектор CSS та повертає масив об’єктів оголошення стилю CSS (з методу `.getStyle()`).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+Метод `.isPropertyUsed()` приймає **властивість** CSS та перевіряє, чи її встановлено/використано в CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+Метод `.getStyleRule()` приймає селектор CSS та повертає оголошення стилю CSS, схоже до `.getStyle()`. Однак оголошення, повернене з цього методу, містить додатковий метод `.isDeclaredAfter()`, який приймає селектор та повертає інформацію, чи це правило оголошене після передачі селектора.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+Метод `.getStyleSheet()` повертає CSS кемпера, проаналізований в об’єкт таблиці стилів CSS.
+
+## Вилучення змісту
+
+До об’єкта `__helpers` можна застосувати декілька методів, щоб вилучити вміст з коду кемпера.
+
+Для них НЕ потрібно створювати екземпляри, оскільки це статичні методи.
+
+### Видалення коментарів
+
+Методи `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()` та `__helpers.removeJSComments()` дозволяють передати код кемпера (через змінну `code`), щоб вилучити коментарі, які відповідають синтаксису коментарів мови.
+
+### Видалення пробілів
+
+Метод `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` дозволяє передати код кемпера (через змінну `code`), щоб видалити всі пробіли.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/devops.md b/src/content/docs/uk/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4072e96d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: Довідник DevOps
+---
+
+Цей посібник допоможе вам зрозуміти наш стек інфраструктури і те, як ми підтримуємо наші платформи. Хоча цей посібник не містить повних деталей всіх операцій, його можна використовувати як довідник для розуміння систем.
+
+Зв’яжіться з нами, якщо у вас виникнуть запитання, і ми з радістю роз’яснимо всі деталі.
+
+## Керівництво з розгортання коду
+
+Цей репозиторій постійно будується, тестується та розробляється на **окремих наборах інфраструктури (серверах, базах даних, CDN тощо)**.
+
+Це передбачає три кроки, які потрібно виконувати послідовно:
+
+1. Нові зміни (виправлення та функціональності) об’єднуються до нашої основної гілки (`main`) через запити на злиття.
+2. Ці зміни проходять через ряд автоматизованих тестів.
+3. Після проходження тестів ми випускаємо зміни (або оновлюємо їх, якщо потрібно) для розгортання у нашій інфраструктурі.
+
+### Побудова бази коду: відображення гілок Git для розгортання
+
+[`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (гілка розробки за замовчуванням) зазвичай об’єднується до гілки [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) раз на день та випускається в ізольовану інфраструктуру.
+
+Це проміжний випуск для наших розробників і волонтерів. Він також відомий як «staging» або «beta».
+
+Він ідентичний нашому робочому середовищу на `freeCodeCamp.org`, але використовує окремі набори баз даних, сервери, вебпроксі тощо. Ця ізоляція дозволяє нам протестувати поточну розробку та функції у «виробничому» сценарії, не впливаючи на звичайних користувачів основних платформ freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+Як тільки команда [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) задоволена змінами на проміжній платформі, ці зміни переносяться кожні декілька днів до гілки [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current).
+
+Це кінцевий випуск, який переносить зміни до наших виробничих платформ на freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Тестування змін: інтеграція та приймальне користувацьке тестування
+
+Ми використовуємо різні рівні інтеграції та приймального тестування, щоб перевірити якість коду. Всі наші тести виконуються за допомогою такого програмного забезпечення, як [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) та [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+Ми маємо модульні тести для тестування розв’язків завдань, API серверів та інтерфейсів користувача. Це допомагає протестувати інтеграцію різних компонентів.
+
+> [!NOTE] Ми також в процесі написання тестів кінцевого користувача, що допоможе відтворити реальні сценарії, як-от оновлення електронної пошти або дзвінок до API чи сторонніх служб.
+
+Ці тести допомагають запобігти повторенню проблем і гарантують, що ми не вводимо нову помилку під час роботи над іншою помилкою або функцією.
+
+### Розгортання змін: надсилання змін до серверів
+
+Ми налаштували безперервне програмне забезпечення доставки для надсилання змін до наших серверів розробки та виробництва.
+
+Як тільки зміни відправлені в захищені гілки випуску, для гілки автоматично запускається конвеєр збірки. Конвеєри збірки відповідають за створення артефактів та їх зберігання в холодному сховищі для подальшого використання.
+
+Конвеєр збірки працює для запуску відповідного конвеєра випуску, якщо він завершить успішний запуск. Конвеєри випуску відповідають за збір артефактів збірки, їх переміщення на сервери та запуск в експлуатацію.
+
+Статуси збірок та випуски [доступні тут](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Запуск збірки, тесту та розгортання
+
+Наразі лише команда розробників може надсилати зміни до виробничих гілок. Зміни до гілок `production-*` можна внести лише через швидке об’єднання до [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!NOTE] Найближчими днями ми вдосконалимо цей потік для кращого керування доступом і прозорості, щоб він здійснювався за допомогою запитів на злиття.
+
+### Надсилання змін до проміжних застосунків
+
+1. Налаштуйте віддалені гілки правильно.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Результат:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Переконайтеся, що гілка `main` чиста та синхронізована з головною гілкою.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Переконайтеся, що GitHub CI передає гілку `main` до головної гілки.
+
+ Тести [безперервної інтеграції](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) повинні бути зеленими та проходити УСПІШНО для гілки `main`. Натисніть зелений прапорець біля хешу затвердження при перегляді коду гілки `main`.
+
+ <details> <summary> Перевірка статусу на GitHub Actions (знімок екрана) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ Якщо у вас виникають проблеми, вам потрібно зупинитись і дослідити помилки.
+
+4. Підтвердьте, що ви можете побудувати репозиторій локально.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Перенесіть зміни з `main` до `prod-staging` через швидке об’єднання
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] Ви не зможете примусово надсилати зміни і якщо ви переписали історію, ці команди призведуть до помилки.
+ >
+ > В такому випадку ви, можливо, зробили щось неправильно та повинні просто почати спочатку.
+
+Попередні кроки автоматично запустять конвеєр збірки для гілки `prod-staging`. Як тільки збірка завершиться, артефакти будуть збережені як файли `.zip` в холодному сховищі для використання пізніше.
+
+Конвеєр випуску запускається автоматично, коли новий артефакт доступний з підключеного конвеєра збірки. Для проміжних платформ цей процес не передбачає затвердження вручну, а артефакти надсилаються до клієнтських CDN та серверів API.
+
+### Надсилання змін до виробничих застосунків
+
+Процес здебільшого такий самий, як і для проміжних платформ, але містить декілька додаткових пунктів. Це потрібно, щоб переконатися, що ми нічого не порушуємо на freeCodeCamp.org, що можуть побачити сотні користувачів, які використовують його.
+
+| НЕ виконуйте ці команди, якщо не переконались, що все працює на проміжній платформі. Не пропускайте жодних тестів, перш ніж продовжити процес. |
+| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Переконайтеся, що гілка `prod-staging` чиста та синхронізована з головною гілкою.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Перенесіть зміни з `prod-staging` до `prod-current` через швидке об’єднання
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] Ви не зможете примусово надсилати зміни і якщо ви переписали історію, ці команди призведуть до помилки.
+ >
+ > В такому випадку ви, можливо, зробили щось неправильно та повинні просто почати спочатку.
+
+Попередні кроки автоматично запустять конвеєр збірки для гілки `prod-current`. Як тільки артефакт збірки готовий, він запустить конвеєр випуску.
+
+**Додаткові кроки для персоналу**
+
+Як тільки запуск випуску ініційовано, команда розробників отримає автоматизований лист про ручне втручання. Вони можуть _затвердити_ або _відхилити_ запуск випуску.
+
+Якщо зміни працюють і вони протестовані на проміжній платформі, їх можна затвердити. Підтвердження потрібно надати протягом 4 годин після активації релізу перед автоматичним відхиленням. Персонал може повторно запустити відхилені запуски або чекати наступного циклу.
+
+Для персоналу:
+
+| Перевірте свою електронну пошту для прямого посилання або [перейдіть до панелі випусків](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) після того, як завершиться збірка. |
+| :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Як тільки хтось з персоналу затвердить випуск, конвеєр відправить зміни до виробничої CDN та серверів API freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+## Збірка, тест та статус розгортання
+
+Ось поточний тест, збірка та статус розгортання кодової бази.
+
+| Гілка | Модульні тести | Інтеграційні тести | Збірки та розгортання |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (експериментальне, майбутнє) | - | - | - |
+
+## Ранній доступ та бета-тестування
+
+Ми вітаємо вас протестувати ці випуски в режимі **публічного бета-тестування** та отримати ранній доступ до майбутніх функціональностей платформи. Іноді ці функціональності/зміни також називають **наступними, бета, проміжними** тощо.
+
+Ваші внески у вигляді зворотного зв’язку та повідомлень про проблеми допоможуть нам зробити платформу `freeCodeCamp.org` більш **стійкою**, **послідовною** та **стабільною** для кожного.
+
+Ми вдячні за повідомлення про помилки, з якими ви стикаєтесь. Це допомагає покращити freeCodeCamp.org. Ви круті!
+
+### Ідентифікація майбутньої версії платформ
+
+Наразі публічне бета-тестування доступне на:
+
+| Програма | Мова | URL |
+| :------- | :--------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Навчання | Англійська | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Іспанська | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Китайська | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| Новини | Англійська | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Форум | Англійська | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Китайська | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] Назва домену відрізняється від **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. Це є навмисним, щоб відвернути індексацію пошукової системи і запобігти непорозумінь для користувачів платформи.
+>
+> Наведений вище список не є повним списком усіх програм, які ми забезпечуємо. Також не всі мовні варіанти розгорнуті у проміжній версії, щоб зберегти ресурси.
+
+### Ідентифікація поточної версії платформ
+
+**Поточна версія платформи завжди доступна на [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+Команда розробників об’єднує зміни з гілки `prod-staging` до `prod-current`, коли вони випускають зміни. Верхнім затвердженням має бути те, що ви побачите на сайті.
+
+Ви можете ідентифікувати точну розгорнуту версію, відвідавши збірку та журнали розгортання, доступні в розділі статусу. Або ж ви можете написати нам у [чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) для підтвердження.
+
+### Відомі обмеження
+
+Існують деякі відомі обмеження і компроміси при використанні бета-версії платформи.
+
+- **Всі дані та особистий прогрес на бета-платформі НЕ будуть збережені чи перенесені до робочої версії**
+
+ **Користувачі бета-версії матимуть окремий обліковий запис.** Бета-версія використовує іншу фізичну базу даних. Це дає можливість запобігти випадковій втраті даних чи змін. В разі потреби команда розробників може очистити базу даних цієї бета-версії.
+
+- **Бета-платформи не надають жодних гарантій щодо працездатності та надійності**
+
+ Очікується, що розгортання відбуватиметься часто та у швидких ітераціях, іноді декілька разів на день. В результаті іноді в бета-версії будуть неочікувані простої чи неробочі функціональності.
+
+- **Щоб забезпечити ефективність виправлення, радимо не надсилати регулярних користувачів на цей вебсайт з метою перевірки.**
+
+ Метою бета-сайту завжди було вдосконалити локальну розробку та тестування, нічого іншого. Це не майбутня версія платформи, а звичайний перегляд того, над чим ми працюємо.
+
+- **Сторінка входу може відрізнятись від робочої версії**
+
+ Ми використовуємо тестовий клієнт для freeCodeCamp.dev на Auth0, тому не можемо встановити власний домен. Це дозволяє зробити так, що всі зворотні виклики й сторінки авторизації з’являтимуться на домені за замовчуванням: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. Це не впливає на функціональність та є максимально приближеним до робочої версії.
+
+## Повідомлення про проблеми та зворотний зв’язок
+
+Будь ласка, створюйте нові завдання для обговорення чи повідомлення про помилки.
+
+Ви можете надіслати електронний лист на `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` у разі виникнення будь-яких запитів. Про вразливість безпеки потрібно повідомляти на `security[at]freecodecamp.org`, а не публічному журналі чи форумі.
+
+## Керівництво з обслуговування сервера
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. Це керівництво стосується **лише персоналу freeCodeCamp**.
+> 2. У цих інструкціях вказано не всю інформацію, тому будьте обережними.
+
+Можливо, як персоналу вам надано доступ до наших хмарних провайдерів (Azure, Digital Ocean тощо).
+
+Ось кілька зручних команд, які можна використовувати для роботи на віртуальних машинах (VM), наприклад, для оновлення технічного обслуговування або для загального ведення.
+
+## Отримайте список віртуальних машин
+
+> [!NOTE] Ви можете мати SSH-доступ до віртуальних машин, однак його недостатньо для отримання списку віртуальних машин. Вам також потрібен доступ до хмарних порталів.
+
+### Azure
+
+Встановіть Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(Одноразово) Встановіть на macOS за допомогою [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(Одноразовий) Вхід:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Отримайте список назв віртуальних машин та IP-адрес:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Встановіть Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(Одноразово) Встановіть на macOS за допомогою [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(Одноразовий) Вхід:**
+
+Автентифікація та зміна контексту: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Отримайте список назв віртуальних машин та IP-адрес:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Створюйте нові ресурси
+
+Ми працюємо над створенням налаштування IaC. Поки це відбувається, ви можете використовувати портал Azure або Azure CLI, щоб створити нову віртуальну машину та інші ресурси.
+
+:::tip
+Незалежно від того, що ви використовуєте для створення нових ресурсів, у нас є декілька [корисних файлів конфігурації хмарної ініціалізації](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init), які допоможуть зробити базову ініціалізацію, як-от встановлення Docker або додавання SSH-ключів тощо.
+:::
+
+## Зберігайте віртуальні машини в актуальному стані
+
+Ви повинні встановлювати на віртуальну машину останні оновлення. Це гарантує, що віртуальна машина залатана найновішими виправленнями безпеки.
+
+> [!WARNING] Перед запуском цих команд:
+>
+> - Переконайтеся, що віртуальну машину повністю підготовлено та не виконується жодних кроків після встановлення.
+> - Якщо ви оновлюєте пакети на віртуальній машині, яка вже обслуговує програму, переконайтеся, що програма зупинена/збережена. Оновлення пакетів спричинить стрибки у навантаженні мережі, памʼяті та/або центрального процесора, що призведе до відключення запущених програм.
+
+Оновіть інформацію пакетів
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Оновіть встановлені пакети
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Очистьте невикористані пакети
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Працюйте над вебсерверами (проксі)
+
+Ми запускаємо збалансовані екземпляри (Azure Load Balancer) для наших вебсерверів. На цих серверах працює NGINX, який перенаправляє весь трафік до freeCodeCamp.org із різних застосунків, що працюють на власних інфраструктурах.
+
+Конфігурація NGINX доступна у [цьому репозиторію](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### Перше завантаження
+
+Підготовка віртуальних машин за допомогою коду
+
+1. Завантажте і налаштуйте NGINX з репозиторію.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Встановіть сертифікати Cloudflare і конфігурацію головної програми.
+
+ Отримайте оригінальні сертифікати зі сховища безпеки та встановіть їх в потрібних місцях.
+
+ **АБО**
+
+ Перемістіть наявні сертифікати:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Оновіть головні конфігурації:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Додайте/оновіть вихідні IP-адреси програми.
+
+3. Налаштуйте мережу та брандмауери.
+
+ Налаштуйте брандмауери Azure та `ufw` відповідно до доступу до вихідних адрес.
+
+4. Додайте віртуальну машину до балансувальника навантаження.
+
+ За потреби налаштуйте та додайте правила до балансувальника навантаження. Можливо, також знадобиться додати віртуальну машину до пулу балансувальника навантаження.
+
+### Журналювання та моніторинг
+
+1. Перевірте стан служби NGINX за допомогою наступної команди:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Журналювання та моніторинг служб доступні на:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com') — наша поточна базова панель моніторингу. Ми працюємо над детальнішими показниками для кращого спостереження
+
+### Оновлення екземплярів (обслуговування)
+
+Налаштуйте зміни в екземплярах NGINX, які зберігаються на GitHub. Їх потрібно розгорнути в кожному екземплярі:
+
+1. SSH в екземпляр і введіть sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Отримайте останній код конфігурації.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Протестуйте та повторно завантажте конфігурації [з Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Робота на екземплярах API
+
+1. Встановіть інструменти збірки для бінарних файлів node (`node-gyp`) тощо.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Перше завантаження
+
+Підготовка віртуальних машин за допомогою коду
+
+1. Встановіть Node LTS.
+
+2. Встановіть pnpm глобально.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Встановіть pm2 глобально.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Клонуйте freeCodeCamp, налаштуйте середовище та ключі.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Створіть `.env` із безпечного сховища облікових даних.
+
+6. Встановіть залежності
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Налаштуйте pm2 `logrotate` та запустіть під час завантаження
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Побудуйте сервер
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Запустіть екземпляри
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Журналювання та моніторинг
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Оновлення екземплярів (обслуговування)
+
+Зміни коду потрібно час від часу вносити в екземпляри API. Це може бути постійним оновленням або оновленням вручну. Останнє є обов’язковим при зміні залежностей або додаванні змінних середовища.
+
+:::danger
+Наразі автоматизовані конвеєри не обробляють оновлення залежностей. Перед запуском будь-якого конвеєра розгортання нам потрібно виконати оновлення вручну.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Оновлення вручну: використовується для оновлення залежностей, змінних середовища.
+
+1. Зупиніть всі екземпляри
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Встановіть залежності
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Побудуйте сервер
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Запустіть екземпляри
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Постійне оновлення: використовується для логічних змін коду.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Ми обробляємо постійні оновлення коду та логіки через конвеєри. Вам не потрібно запускати ці команди. Вони тут для документації.
+
+#### 3. Оновлення Node
+
+1. Встановіть нову версію Node
+
+2. Оновіть pm2 для використання нової версії
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Робота над екземплярами клієнта
+
+1. Встановіть інструменти збірки для бінарних файлів node (`node-gyp`) тощо.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### Перше завантаження
+
+Підготовка віртуальних машин за допомогою коду
+
+1. Встановіть Node LTS.
+
+2. Оновіть `npm`, встановіть PM2, налаштуйте `logrotate` та запустіть під час завантаження
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Клонуйте конфігурацію клієнта, налаштування середовища та ключі.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Запустіть екземпляри заповнювачів для вебклієнта, вони будуть оновлені артефактами з конвеєра Azure.
+
+ > Завдання: це налаштування потрібно перемістити в сховище S3 або Azure Blob
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Журналювання та моніторинг
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Оновлення екземплярів (обслуговування)
+
+Зміни коду потрібно час від часу вносити в екземпляри API. Це може бути постійним оновленням або оновленням вручну. Останнє є обов’язковим при зміні залежностей або додаванні змінних середовища.
+
+:::danger
+Наразі автоматизовані конвеєри не обробляють оновлення залежностей. Перед запуском будь-якого конвеєра розгортання нам потрібно виконати оновлення вручну.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Оновлення вручну: використовується для оновлення залежностей, змінних середовища.
+
+1. Зупиніть всі екземпляри
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Встановіть чи оновіть залежності
+
+3. Запустіть екземпляри
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Постійне оновлення: використовується для логічних змін коду.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Ми обробляємо постійні оновлення коду та логіки через конвеєри. Вам не потрібно запускати ці команди. Вони тут для документації.
+
+## Робота над чат-серверами
+
+Наші чат-сервери доступні з конфігурацією високої доступності, [рекомендованою в документації Rocket.Chat](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). Файл `docker-compose` можна знайти [тут](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+Ми пропонуємо надлишкові екземпляри NGINX, які самі збалансовують навантаження (Azure Load Balancer) перед кластером Rocket.Chat. Файл конфігурації NGINX [доступний тут](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### Перше завантаження
+
+Підготовка віртуальних машин за допомогою коду
+
+**Кластер NGINX:**
+
+1. Завантажте і налаштуйте NGINX з репозиторію.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Встановіть сертифікати Cloudflare і конфігурацію головної програми.
+
+ Отримайте оригінальні сертифікати зі сховища безпеки та встановіть їх в потрібних місцях.
+
+ **АБО**
+
+ Перемістіть наявні сертифікати:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Локально
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Віддалено
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Оновіть головні конфігурації:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Додайте/оновіть вихідні IP-адреси програми.
+
+3. Налаштуйте мережу та брандмауери.
+
+ Налаштуйте брандмауери Azure та `ufw` відповідно до доступу до вихідних адрес.
+
+4. Додайте віртуальну машину до балансувальника навантаження.
+
+ За потреби налаштуйте та додайте правила до балансувальника навантаження. Можливо, також знадобиться додати віртуальну машину до пулу балансувальника навантаження.
+
+**Кластер Docker:**
+
+1. Завантажте і налаштуйте Docker з репозиторію
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Налаштуйте необхідні змінні середовища та IP-адреси екземплярів.
+
+3. Запустіть сервер rocket-chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Журналювання та моніторинг
+
+1. Перевірте стан служби NGINX за допомогою наступної команди:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Перевірте стан запущених екземплярів docker за допомогою:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Оновлення екземплярів (обслуговування)
+
+**Кластер NGINX:**
+
+Налаштуйте зміни в екземплярах NGINX, які зберігаються на GitHub. Їх потрібно розгорнути в кожному екземплярі:
+
+1. SSH в екземпляр і введіть sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Отримайте останній код конфігурації.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Протестуйте та повторно завантажте конфігурації [з Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Кластер Docker:**
+
+1. SSH в екземпляр та перейдіть до шляху налаштування чату
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Отримайте останній код конфігурації.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Отримайте останній образ docker для Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Оновіть запущені екземпляри
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Переконайтесь, що екземпляри запущені
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Вилучіть зайві ресурси
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Вивід:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Виберіть «так» (y), щоб видалити все, що не використовується. Це видалить всі зупинені контейнери, мережі та томи, які не використовуються принаймні одним контейнером, а також завислі образи та кеш збірки.
+
+## Робота над інструментами помічника
+
+### Розгорніть оновлення
+
+ssh у віртуальну машину (розміщену на Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Оновлення версій Node.js на віртуальних машинах
+
+Отримайте список наразі встановлених версій node та npm
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Встановіть останню версію Node.js LTS і перевстановіть всі глобальні пакети
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Перевірте встановлені пакети
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Зробіть псевдонім версії Node.js `default` для поточної LTS (закріплена до останньої основної версії)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Необов’язково) Видаліть старі версії
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+Сценарій оболонки для клієнтських програм не можна відновити між версіями Node.js за допомогою `pm2 resurrect`. Замість цього розгорніть процеси з нуля. Цей процес стане простішим, коли ми перейдемо до налаштування на основі docker.
+:::
+
+> Якщо для процесів використовується PM2, вам також потрібно буде запустити програми та зберегти список процесів для автоматичного відновлення під час перезапуску.
+
+Отримайте інструкції/команди видалення за допомогою команди `unstartup` та використайте вивід, щоб видалити служби systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Отримайте інструкції/команди встановлення за допомогою команди `startup` та використайте вивід, щоб додати служби systemctl
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Швидкі команди для PM2 для перерахування, відновлення збережених процесів і т. д.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Встановлення та оновлення агентів Azure Pipeline
+
+Див. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops та дотримуйтесь інструкцій, щоб зупинити, видалити та перевстановити агентів. Загалом ви можете дотримуватись кроків, наведених нижче.
+
+Вам знадобиться PAT, який можна взяти тут: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Встановлення агентів на цілях розгортання
+
+Перейдіть до [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) та зареєструйте агента з нуля у необхідних [групах розгортання](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+> [!NOTE] Вам потрібно запустити сценарії в основному каталозі та переконатись, що не існує іншого каталогу `azagent`.
+
+### Оновлення агентів
+
+Наразі оновлення агентів вимагає їхнього видалення та переналаштування. Це необхідно для того, щоб вони правильно підбирали значення `PATH` та інші змінні оточення системи. Нам потрібно зробити це, щоб оновити Node.js на цільових віртуальних машинах розгортання.
+
+1. Перейдіть та перевірте статус служби
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Зупиніть службу
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Видаліть службу
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Видаліть агента з пулу конвеєра
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Видаліть файли конфігурації
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Як тільки ви виконали вищевказані кроки, ви можете повторити ті самі кроки, що й при встановленні агента.
+
+## Керівництво з розсилки листів
+
+Ми використовуємо [інструмент CLI](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) для наших тижневих листів. Щоб підготувати та почати цей процес потрібно:
+
+1. Увійдіть до DigitalOcean та почніть використовувати нові краплі в межах проєкту `Sendgrid`. Використайте знімок Ubuntu Sendgrid з найновішою датою. Він попередньо завантажений з інструментом CLI та сценарієм для отримання електронних пошт з бази даних. Зважаючи на поточний обсяг, трьох крапель достатньо для своєчасного надсилання листів.
+
+2. Налаштуйте сценарій, щоб отримати віддалений доступ до списку електронних пошт.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ Вам потрібно буде замінити значення заповнювачів у файлі `.env` на свої облікові дані.
+
+3. Запустіть сценарій.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ Це збереже список електронних пошт у файлі `emails.csv`.
+
+4. Розділіть електронні пошти на декілька файлів, залежно від кількості потрібних крапель. Це найлегше зробити за допомогою `scp`, щоб локально отримати список електронних пошт та, використовуючи свій улюблений текстовий редактор, розділити їх на декілька файлів. Кожен файл потребує заголовку `email,unsubscribeId`.
+
+5. Перейдіть до каталогу CLI за допомогою `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` та налаштуйте інструмент [згідно документації](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Запустіть інструмент, щоб надіслати листи, дотримуючись [документації з користування](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. Як тільки розсилка листів завершиться, переконайтеся, що усі повідомлення доставлено успішно, перш ніж знищити краплі.
+
+## Керівництво з додавання екземплярів новин нових мов
+
+### Зміни теми
+
+Ми використовуємо власну [тему](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) для публікацій новин. Виконавши наступні зміни теми, можна додати нову мову.
+
+1. Врахуйте інструкцію `else if` до [коду ISO нової мови](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) у [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Створіть початкову папку конфігурації, створивши копію папки [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) та змінивши її назву на код нової мови. (`en` —> `es` для іспанської)
+3. Всередині папки нової мови змініть назви змінних у `main.js` та `footer.js` на відповідні скорочені коди мови (`enMain` —> `esMain` для іспанської)
+4. Створіть копію [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) та змініть її назву на код нової мови.
+5. Додайте сценарії для щойно створених файлів конфігурації до [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs).
+6. Додайте сценарій відповідної мови `day.js` з [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) до [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Зміни інформаційної панелі Ghost
+
+Оновіть активи публікацій, перейшовши на Ghost Dashboard > Settings > General та завантаживши [піктограму](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [логотип](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png) та [зображення](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/faq.md b/src/content/docs/uk/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0de3e6d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Поширені питання
+---
+
+Відповіді на часті питання.
+
+## Я лише починаю ознайомлення з GitHub та відкритим вихідним кодом. З чого мені варто почати?
+
+Прочитайте [«Як зробити внесок до відкритого вихідного коду»](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). Там є вичерпні вказівки для тих, хто вперше стикається з такими проєктами. Там також є багато порад для роботи з відкритим вихідним кодом.
+
+## Що мені потрібно знати, щоб зробити внесок до кодової бази?
+
+freeCodeCamp працює на сучасному стеку JavaScript. Якщо ви хочете зробити внесок до нашої кодової бази, ви повинні бути ознайомленими із JavaScript та іншими технологіями, якими ми користуємось: Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby та Webpack.
+
+## Чи можу я перекладати ресурси freeCodeCamp?
+
+Так! Ви можете почати перекладати на будь-яку з 30+ мов, які доступні на нашій локалізаційній платформі.
+
+Деякі з перекладів вже доступні на сайті. Ми хочемо локалізувати freeCodeCamp на популярні мови. Деталі можна дізнатися [тут](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/news/yak-dopomohty-z-perekladom-freecodecamp-na-ridnu-movu/).
+
+Якщо ви хочете зробити внесок до перекладу, будь ласка, спочатку [прочитайте цей довідник](how-to-translate-files).
+
+## Чи можу я писати публікації або знімати відео для freeCodeCamp?
+
+Так! Ви можете зробити внесок до новин та каналу на YouTube.
+
+Якщо ви зацікавлені в написанні публікацій, відвідайте цей [посібник з публікацій](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). А ще прочитайте нашу [інструкцію зі стилістичного оформлення](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/); вона допомагає в написанні кращих публікацій.
+
+Щоб допомогти у створенні навчальних відео, слідуйте [посібнику з каналу на YouTube](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## Як повідомити про нову помилку?
+
+Якщо ви вважаєте, що знайшли помилку, то спершу прочитайте публікацію [«Як повідомити про помилку»](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) та виконайте її вказівки.
+
+Якщо ви впевнені, що це нова помилка, то, будь ласка, створіть нове завдання на GitHub. Надайте якомога більше інформації для того, щоб ми могли відтворити помилку. У нас є заздалегідь заготовлений шаблон, який може вам допомогти.
+
+Будь ласка, зверніть увагу на те, що завдання на GitHub стосуються лише проблем щодо кодової бази та не мають ніякого відношення до допомоги з програмування. Якщо у вас є сумніви, то варто [звернутися за допомогою на форум](https://forum.freecodecamp.org), а вже потім створювати завдання на GitHub.
+
+## Як повідомити про проблему з безпекою?
+
+Будь ласка, не створюйте завдань на GitHub щодо питань безпеки. Натомість [слідуйте нашій політиці безпеки](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## Я здобуваю освіту. Чи може робота на платформі зараховуватися мені в залікові кредити?
+
+Так. Але зверніть, будь ласка, увагу, що ми не можемо надати жодних графіків чи документів, які вимагатиме ваш коледж або університет. Ми отримуємо багато запитів на злиття та внесків до коду від розробників-волонтерів і ми поважаємо їхні час та зусилля. Ми поважаємо усіх наших користувачів, а тому не надаємо жодним запитам особливого пріоритету лише через те, що вони пов’язані з навчанням у закладах освіти.
+
+Ми просимо вас враховувати це та відповідно планувати свій час заздалегідь під час роботи над кодом.
+
+## Чому на завданнях бувають різні позначки?
+
+Техпідтримка, що відповідає за код, [сортує](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) завдання та запити на злиття залежно від пріоритету, складності та інших факторів. [Тут ви можете ознайомитися з усіма їхніми значеннями](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Звідки почати, якщо я хочу працювати над завданням?
+
+Вам варто переглянути [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) або [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22), щоб швидко ознайомитись з доступними завданнями.
+
+:::tip
+Завдання в **`help wanted`** загальнодоступні, тож вам не треба отримувати дозволи на роботу з ними. А ось завдання з позначкою **`first timers only`** — це спеціальні завдання для людей, які ще не робили внесок до кодової бази freeCodeCamp.
+:::
+
+## Знайшлась друкарська помилка. Чи потрібно повідомляти про цю проблему, перш ніж зробити запит на злиття?
+
+Для друкарських та орфографічних помилок можна відразу відкрити запит на злиття без створення завдання. Не забудьте вказати деталі в описі запиту на злиття, щоб допомогти нам переглянути ваш внесок (навіть якщо там незначна зміна).
+
+Створюйте завдання, якщо ви хочете обговорити глобальніші аспекти кодової бази або навчальної програми.
+
+## Яким чином можна отримати доручене завдання?
+
+Зазвичай ми доручаємо завдання лише тим користувачам, які вже давно нам допомагають. Натомість ми дотримуємось такої політики, щоб бути справедливими до кожного:
+
+1. Скоріш за все ми приймемо перший запит на злиття, який описує завдання.
+2. Якщо декілька користувачів одночасно відкривають запит на злиття для одного завдання, ми надаємо пріоритет тому, який найкраще її описує. На що ми звертаємо увагу:
+ - Чи враховано тести?
+ - Чи враховано всі випадки використання?
+ - Чи ви переконалися, що всі тести виконуються і працюють локально?
+3. Також ми даємо пріоритет тим запитам на злиття, які дотримуються наших рекомендацій.
+ - Чи дотримано списку запитів на злиття?
+ - Чи змістовна назва у вашого запиту на злиття?
+
+## Я хочу бути модератором freeCodeCamp. З чого мені варто почати?
+
+Модератори нашої спільноти — наші герої. Їхні добровільні внески роблять freeCodeCamp безпечною та гостинною спільнотою.
+
+Перш за все, ви повинні бути активним учасником нашої спільноти та дотримуватись нашого [Кодексу поведінки](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (а не просто обіцяти його виконання).
+
+Декілька рекомендацій стосовно наших платформ:
+
+- Щоб бути модератором **дискорду/чату**, будьте активними у нашому чаті та взаємодійте з іншими, навчаючись та практикуючи вирішення потенційних конфліктів.
+- Щоб бути модератором **форуму**, будьте активними та взаємодійте з іншими людьми на форумі, підтримуйте їх та надавайте зворотний зв’язок за потреби. Див. [посібник керівника підфоруму](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) для додаткової інформації.
+- Щоб бути модератором **GitHub**, допомагайте з обробкою завдань GitHub, перевіряючи, чи вони дійсні та (в ідеалі) пропонуйте їх вирішення (власне чи чуже).
+
+Коротко: поважайте інших. Ми — люди з усього світу. Зважаючи на це, будь ласка, слідкуйте за своїм спілкуванням із людьми інших культур.
+
+Якщо ви практикували вищезгадане **деякий час** та хтось із модераторів рекомендує вас, з вами зв’яжеться співробітник та залучить до команди модераторів. Робота над відкритим кодом є волонтерською, і наш час обмежений. Ми розуміємо, що у вашому випадку це правда. Тому ми наголошуємо на тому, щоб бути **послідовними**, а не взаємодіяти у спільноті 24/7.
+
+Див. наш [довідник модератора](moderator-handbook) для детальнішого списку обов’язків модератора та наших очікувань від них.
+
+## Моя проблема не висвітлена у цій документації.
+
+**Не соромтеся звертатися за допомогою до:**
+
+- Категорії `Contributors` на [форумі нашої спільноти](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- Каналу `#Contributors` на [нашому чат-сервері](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Ми раді допомогти вам зробити внесок до будь-якої цікавої для вас теми. Якщо ви поставите нам запитання у відповідній до нього темі, ми з радістю надамо вам роз’яснення. Перш ніж публікувати своє запитання, пошукайте чи не було його вирішено раніше.
+
+Заздалегідь дякуємо за ваші ввічливість та терпіння. Пам'ятайте, що ця спільнота здебільшого складається з волонтерів.
+
+## Додаткова допомога
+
+Якщо у вас є запитання щодо стека, архітектури коду, перекладів чи будь-чого іншого, зв’яжіться з нашою командою [на форумі](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**Ви можете написати на електронну пошту нашим розробникам: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3ae18514
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: Як додати тести Cypress
+---
+
+При внесенні змін до JavaScript, CSS або HTML, які можуть змінити функціональність або макет сторінки, важливо додати відповідні інтеграційні тести [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io).
+
+Щоб дізнатися, як писати тести Cypress, або «специфікації», будь ласка, зверніться до офіційної [документації Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html).
+
+## Куди додати тест
+
+- Тести Cypress знаходяться в каталозі `./cypress`.
+
+- Тести Cypress для модуля навчальної програми знаходяться у відповідному каталозі навчальної програми, тобто `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## Як проводити тести
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви використовуєте Gitpod, див. [налаштування Cypress-Gitpod](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Переконайтеся, що MongoDB і клієнтські програми запущені
+
+- [Запустіть MongoDB і заповнiть базу даних](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Запустіть клієнтський застосунок freeCodeCamp і сервер API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Запустіть тести Cypress
+
+Щоб запустити тести кінцевої збірки, замініть `dev` на `prd` нижче.
+
+- Щоб запустити всі тести в каталозі `./cypress`:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- Щоб запустити один тест:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ Наприклад:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- Щоб створити збірку розробки, запустіть сервер розробки і виконайте всі наявні тести cypress:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Налаштування Cypress-Gitpod
+
+### 1. Переконайтеся, що середовище розробки запущене
+
+Якщо запуск середовища Gitpod не розробив середовище автоматично:
+
+- Дотримуйтесь [посібнику з налаштування MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Створіть конфігураційний файл.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Заповніть базу даних
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Розробіть сервер та клієнта
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Встановіть інструменти збірки Cypress
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- Якщо керований в терміналі, виберіть розкладку клавіатури за мовою/регіоном
+
+Тепер [Cypress можна запустити](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Розв’язання проблем розробки
+
+### Не вдалося під’єднатися до порту 8000
+
+Якщо Cypress видає наступну помилку:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+Як розв’язати цю проблему:
+
+- Перейдіть до кореневого файлу `package.json` та додайте `--host 0.0.0.0` до команди `develop:client`:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Потім знову виконайте `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f6045bee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: Як додати тести Playwright
+---
+
+## Встановлення
+
+Щоб встановити Playwright:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Або ж ви можете дотримуватись офіційної документації:
+
+Щоб встановити та налаштувати Playwright на своїй машині, див. [документацію](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+Щоб дізнатися, як писати тести Playwright, або «специфікації», зверніться до офіційної [документації Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Куди додати тест
+
+- Тести Playwright знаходяться в каталозі `./e2e`.
+
+- Файли тестів Playwright завжди мають розширення `.spec.ts`.
+
+## Найкращі практики для написання тестів E2E
+
+Цей розділ детально пояснить найкращі практики написання та документування тестів E2E на основі документації Playwright та кодового стилю нашої спільноти.
+
+### - Імпорт
+
+Завжди починайте необхідні імпорти на початку файлу.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Визначення елемента DOM
+
+Playwright поставляється з [декількома вбудованими локаторами](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), але ми рекомендуємо взяти до уваги наступні:
+
+- `getByRole` для запиту семантичних елементів, роль яких важлива та дозволяє технічним засобам реабілітації правильно сприймати сторінку.
+- `getByText` для запитів не семантичних елементів, таких як `div`, `span` чи `p`.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+У крайніх випадках, коли запит елементів не можна здійснити за допомогою локаторів вище, використайте атрибут `data-playwright-test-label`. Цей атрибут використовують, щоб ідентифікувати елементи в DOM лише для тестування Playwright. Його не використовують для стилізації або будь-чого іншого.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+У файлі тестів можна використати метод `getByTestId`, щоб ідентифікувати елемент.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Константи
+
+Визначте будь-які константні елементи, набори даних чи конфігурації, використані в тестах, для спрощеного посилання.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Спільний контекст
+
+Якщо тести залежать від спільного контексту (наприклад, завантаженої сторінки), використайте хуки beforeAll та afterAll, щоб налаштувати та розбити контекст.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Описові назви тестів
+
+Кожен тестовий блок повинен мати чітку і лаконічну назву, описуючи саме те, що перевіряє.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Людиносприйнятні твердження
+
+Кожне твердження має бути максимально розбірливим для людини. Таким чином простіше зрозуміти, що робить тест та чого очікувати.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Дотримуйтесь принципу DRY
+
+Переконайтеся, що тести не повторюють однаковий код знову і знову. Якщо однаковий код повторюється, реорганізуйте його як цикл або функцію.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Тести для мобільних екранів
+
+Використайте аргумент `isMobile`, щоб запустити тести, які містять логіку, що змінюється для мобільних екранів.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Групові тести
+
+Згрупуйте пов’язані тести, використовуючи описові блоки. Таким чином простіше зрозуміти, що роблять тести та чого очікувати.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## Як проводити тести
+
+### 1. Переконайтеся, що MongoDB і клієнтські програми запущені
+
+- [Запустіть MongoDB та додайте базу даних](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). Щоб тести Playwright працювали, переконайтесь, що використали команду `pnpm run seed:certified-user`.
+
+- [Запустіть клієнтський застосунок freeCodeCamp і сервер API](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Запустіть тести Playwright
+
+Щоб запустити тести Playwright, зверніть увагу на інформацію нижче
+
+- Переконайтесь, що перейшли до репозиторію e2e:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- Щоб запустити тести в режимі помічника UI:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- Щоб запустити один тест:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ Наприклад:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Щоб запустити набір файлів тестів у відповідних папках:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ Наприклад:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Щоб запустити тест із заголовком:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ Наприклад:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Налагодження тестів
+
+Оскільки Playwright працює в Node.js, його можна налагодити за допомогою власного налагоджувача. Наприклад, використавши console.log або в IDE
+
+- Налагодження всіх тестів:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Налагодження одного файлу тесту:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Формування звіту про тести
+
+HTML Reporter надає повний звіт про ваші тести, що дає змогу фільтрувати звіт за браузерами, пройденими тестами, проваленими тестами, пропущеними тестами та ненадійними тестами.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Розв’язання проблем розробки
+
+Playwright, як правило, є інструментом з дуже малим шансом на помилку. Помічник вже налаштував тести для виконання на машинах з усіма операційними системами, включно з найважливішими дистрибутивами Windows, MacOS і Linux.
+
+- (MacOs та Linux) Якщо запуск Playwright призводить до помилки через залежності ядра, запустіть цю команду:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- Поширена помилка в Playwright виглядає так:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ Цю помилку можна виправити за допомогою таких кроків:
+
+ 1. **Перевірте URL:** переконайтесь, що URL, на який ви намагаєтесь перейти, правильний та відформатований. Переконайтесь, що в посиланні немає помилок.
+
+ 2. **Стан сервера:** перевірте, чи сервер працює та доступний. Ви можете зіткнутися з цією помилкою, якщо сервер не працює або недоступний.
+
+ 3. **Доступність порту:** переконайтесь, що порт, згаданий в URL (у цьому випадку 8000) правильний та доступний для використання. Переконайтеся, що жоден інший процес не використовує цей порт.
+
+ 4. **Брандмауер та безпечне програмне забезпечення:** брандмауери та безпечне програмне забезпечення іноді можуть блокувати підключення до певних портів. Перевірте налаштування брандмауера, щоб переконатися, що порт дозволений.
+
+ 5. **Підключення до мережі:** переконайтесь, що ваша система з’єднана з мережею та може отримати доступ до зовнішніх ресурсів.
+
+- Ще одна поширена помилка в Playwright виглядає так:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. Мережевий запит було зроблено за допомогою методу, який не містить тіла відповіді (наприклад, HEAD або CONNECT).
+ 2. Мережевий запит було зроблено через безпечне з’єднання (HTTPS), а тіло відповіді недоступне з міркувань безпеки.
+ 3. Мережевий запит зроблено стороннім ресурсом (наприклад, рекламою чи пікселем відстеження), який не контролюється сценарієм.
+ 4. Мережевий запит було зроблено сценарієм, який було призупинено або зупинено до отримання відповіді.
+
+**Для отримання додаткової інформації відвідайте офіційну документацію.**
+
+## Налаштування Playwright-Gitpod
+
+### 1. Переконайтеся, що середовище розробки запущене
+
+Якщо запуск середовища Gitpod не розробив середовище автоматично:
+
+- Дотримуйтесь [посібнику з налаштування MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Створіть .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Створіть конфігураційний файл.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Заповніть базу даних
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Розробіть сервер та клієнта
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Встановіть інструменти збірки Playwright
+
+Щоб встановити необхідні залежності для запуску Playwright, виконайте цю команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Запустіть тести Playwright на Gitpod
+
+Щоб запустити всі тести Playwright, виконайте цю команду:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..849cb9cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **Примітка:** це **необов’язковий** крок, необхідний лише при роботі з електронною поштою
+
+- [Вступ](#introduction)
+- [Встановлення MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Використання MailHog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Корисні посилання](#useful-links)
+
+## Вступ
+
+Деякі робочі процеси (наприклад, зміна електронної пошти користувача) вимагають сервер API, який надсилатиме вихідні листи. MailHog — це альтернатива провайдерам електронної пошти для надсилання листів. Це інструмент для тестування електронної пошти, на який приходитимуть усі листи, відправлені екземпляром freeCodeCamp.
+
+## Встановлення MailHog
+
+MailHog можна встановити на macOS, Windows та Linux або використовувати через Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Встановлення MailHog за допомогою Docker</summary>
+
+Якщо у вас встановлений Docker, ви можете використати
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+для запуску MailHog у фоновому режимі та
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+для його зупинки.
+
+Коли встановлення завершено, ви можете почати [використовувати MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Встановлення MailHog на macOS</summary>
+
+Встановіть MailHog на macOS за допомогою [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+Наведені вище команди запустять службу MailHog у фоновому режимі.
+
+Коли встановлення завершено, ви можете почати [використовувати MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Встановлення MailHog на Windows</summary>
+
+Завантажте останню версію MailHog з [офіційного репозиторію MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Знайдіть та натисніть посилання для вашої версії Windows (32 або 64), і файл `.exe` буде завантажений на ваш комп’ютер.
+
+Коли завантаження завершиться, натисніть на файл, щоб відкрити його. Може з’явитись сповіщення про заблоковані з’єднання із запитом на дозвіл для MailHog. Після надання доступу відкриється стандартний командний рядок Windows, де виконуватиметься MailHog.
+
+Закрийте MailHog, закривши вікно командного рядка. Щоб знову запустити MailHog, натисніть на виконуваний файл MailHog (`.exe`), який був завантажений раніше — необов’язково завантажувати новий файл MailHog.
+
+Почніть [використовувати MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Встановлення MailHog на Linux</summary>
+
+Спочатку встановіть [Go](https://golang.org).
+
+Виконайте наступні команди, щоб встановити GO на системах з основою Debian (наприклад, Ubuntu та Linux Mint).
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+Виконайте наступні команди, щоб встановити GO на системах з основою RPM (наприклад, CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat Linux тощо).
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+Або запустіть наступні команди, щоб встановити GO.
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+Тепер налаштуйте шлях для GO, використовуючи наступні команди.
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+Останнім кроком буде введення команди нижче, щоб встановити та запустити MailHog.
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+Почніть [використовувати MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+## Використання MailHog
+
+Відкрийте нову вкладку/вікно браузера та перейдіть до [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025), щоб відкрити вхідні повідомлення на MailHog, коли налаштування MailHog буде завершене та MailHog запуститься.
+
+## Корисні посилання
+
+- Див. репозиторій [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) для детальнішої інформації, яка стосується MailHog. Додаткова інформація щодо конфігурацій MailHog також доступна.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..045910ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Дотримуйтесь цих вказівок, щоб зробити внесок до кодової бази. Особливо рекомендовано, якщо ви хочете робити внесок регулярно.
+
+Ігнорування цих кроків може призвести до того, що ви ускладните свій внесок, обслуговування та перегляд.
+
+## Внесок до кодової бази
+
+Тепер ви можете робити зміни у файлах та затверджувати їх у розгалуженнях, прочитавши [як налаштувати freeCodeCamp локально](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Дотримуйтеся цих вказівок:
+
+1. Переконайтесь, що знаходитесь на гілці `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Ви повинні отримати такий вивід:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ Якщо ви отримали інше повідомлення, значить ви не перебуваєте на головній гілці (main) або ваш робочий каталог не чистий. Розв’яжіть будь-які невиконані файли/затвердження та перевірте `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Синхронізуйте останні зміни віддаленої гілки `main` зі своєю розгалуженою гілкою `main`:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Якщо у вас є невиконані запити на злиття, зроблені з гілки `main` свого розгалуження, ви втратите їх під кінець цього кроку.
+ >
+ > Перед виконанням цього кроку потрібно переконатись, що ваш запит на злиття об’єднав модератор. Щоб уникнути цього, **ніколи** не працюйте на гілці `main`.
+
+ Цей крок **синхронізує останні зміни** з головного репозиторію freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Оновіть свою копію віддаленого репозиторію freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Скиньте свою головну гілку з головною гілкою freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Перемістіть свою головну гілку до джерела, щоб мати чисту історію розгалуження на GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ Ви можете переконатись, що ваша поточна головна гілка відповідає upstream/main, виконавши diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Отриманий вивід має бути порожнім. Важливо якомога частіше перебазовувати свою гілку на останню версію `upstream/main`, щоб уникнути конфліктів пізніше.
+
+3. Створіть нову гілку:
+
+ Ваша робоча копія буде чистою, якщо ви працюватимете на окремій гілці для кожного завдання. Ніколи не працюйте на `main`. Це забруднить вашу копію freeCodeCamp, через що, можливо, доведеться починати з нового клону чи розгалуження.
+
+ Переконайтесь, що знаходитесь на `main` та починайте розгалуження звідси:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Назва вашої гілки повинна починатись з `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/` тощо. Не використовуйте номери завдань у гілках. Вони мають бути короткими, змістовними та унікальними.
+
+ Декілька прикладів хороших назв гілок:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Відредагуйте сторінки та працюйте над кодом у своєму улюбленому текстовому редакторі.
+
+5. Як тільки ви задоволені змінами, за бажанням запустіть freeCodeCamp для перегляду змін.
+
+6. Переконайтеся, що виправили помилки та перевірте форматування своїх змін.
+
+7. Перевірте та підтвердьте файли, які оновлюєте:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Має з’явитись список файлів `unstaged`, які ви відредагували.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Проіндексуйте зміни та зробіть затвердження:
+
+ У цьому кроці потрібно позначити лише ті файли, які редагували чи додавали самостійно. Якщо необхідно, ви можете виконати скидання та виправити файли, які не збираєтеся змінювати.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Або ви можете додати всі файли `unstaged` до області тимчасового зберігання:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Лише ті файли, які було переміщено до області тимчасового зберігання, будуть додані під час затвердження.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Вивід:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Тепер ви можете затвердити свої зміни, використовуючи коротке повідомлення:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Декілька прикладів:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Створюйте загальноприйняті повідомлення затверджень. Це хороша практика, яка спонукає дотримуватись стандартів.
+
+ Декілька прикладів хороших повідомлень затверджень:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Пишіть їх короткими, не більше 50 символів. Додаткову інформацію можна додати в описі затвердження.
+
+ Це не займе більше часу ніж нестандартне повідомлення (наприклад, «update file» чи «add index.md»)
+
+ Ви можете дізнатись більше, чому потрібно використовувати загальноприйнятні затвердження, [тут](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Якщо ви усвідомили, що вам потрібно відредагувати файл або оновити повідомлення затвердження після того, як зробили затвердження, ви можете зробити так після редагування файлів:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Це відкриє текстовий редактор за замовчуванням (наприклад, `nano` або `vi`), де можна редагувати заголовок повідомлення та додавати/редагувати опис.
+
+10. Тепер надішліть свої зміни до розгалуження:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Коротко про команди
+
+Короткий довідник команд, які знадобляться при роботі.
+
+| команда | опис |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| `pnpm test` | Запускає всі тести JS у системі, включно з клієнтом, сервером, лінтером і тестами завдань. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Запускає набір тестів клієнта. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Запускає набір тестів клієнта, оновлюючи несинхронізовані знімки Jest. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Запускає набір тестів навчальної програми. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Тестує конкретний блок. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Тестує конкретний суперблок. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Запускає набір тестів навчальної програми без збоїв після першої помилки |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Запускає набір тестів сервера. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Запускає наскрізне тестування Cypress. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Видаляє всі залежності й очищає кеш. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Запускає Storybook для розробки бібліотеки компонентів. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d1d3fd35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Додавання нових мов для `/learn`
+---
+
+Виконайте такі кроки, щоб додати нову мову на `/learn` (навчальна програма):
+
+- Перекладіть та відредагуйте перші три сертифікації на Crowdin. (Новий адаптивний вебдизайн, Алгоритми JavaScript та структури даних, Бібліотеки Front End)
+- Перекладіть та відредагуйте всі рядки проєкту «Learn UI» на Crowdin.
+- Оновіть налаштування Crowdin, додавши власний код нової мови.
+- Відкрийте перший PR, щоб налаштувати GitHub Actions. Потрібно оновити 2 файли:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Відрийте другий PR, щоб додати інші налаштування. Потрібно оновити/додати такі файли:
+ - Оновіть `i18n.ts`
+ - Оновіть `superblocks.ts`
+ - Оновіть `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Додайте `links.json`
+ - Додайте `meta-tags.json`
+ - Додайте `motivation.json`
+- Попросіть команду інфраструктури налаштувати та запустити віртуальну машину для нової мови.
+- Як тільки віртуальна машина готова, відрийте третій PR, щоб додати нову мову до навігаційного меню.
+
+Ми пояснимо кожен крок у наступних розділах.
+
+## Оновлення налаштувань Crowdin
+
+Перш ніж випустити нову мову, потрібно дозволити завантаження мов з Crowdin. Для цього потрібно додати власний код нової мови.
+
+Оберіть `Settings` > `Languages` на бічній панелі проєктів `Curriculum` та `Learn UI` на Crowdin. Прокрутіть вниз до `Language Mapping`, де ви побачите опцію додавання нового коду мови. Додайте нову мову, обравши значення `language` для `Placeholder` та ввівши назву мови у нижньому регістрі для `Custom code`. Якщо ви не впевнені, що використовувати або у вас немає ролі адміністратора і ви не бачите налаштувань, напишіть у чаті та ми вам допоможемо.
+
+## Оновлення робочих процесів для GitHub Actions
+
+Потім потрібно налаштувати синхронізацію між Crowdin та GitHub.
+
+Вам потрібно додати крок до [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) та [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). Він буде однаковим. Наприклад, якщо ви хочете завантажувати дотракійську мову:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Зауважте, що ключ `download_language` потрібно встановити на код мови, вказаний на Crowdin.
+
+## Додавання мови
+
+> [!NOTE] Перед тим як продовжити, потрібно виконати вищеподаний розділ оновлення потоку робіт. Їх потрібно виконати окремо, інакше збірка не виконуватиметься.
+
+Щоб дозволити кодовій базі функціонувати на обраній вами мові, потрібно зробити декілька кроків.
+
+Спочатку відвідайте файл [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts), щоб додати мову до списку доступних мов та налаштувати значення. У ньому розміщено декілька об’єктів.
+
+- `Languages`: додайте нову мову до запису `Languages`, схоже до інших. Значення рядка пізніше буде використане у файлі `.env`, щоб налаштувати збірку мови.
+- `availableLangs`: додайте нову властивість із запису `Languages` до масивів `client` та `curriculum`.
+- `i18nextCodes`: мовні коди ISO для кожної мови. Вам потрібно додати відповідний код ISO для мови, з якою працюєте. Вони повинні бути унікальними для кожної мови.
+- `LangNames`: назви мов для перемикача мови у навігаційному меню.
+- `LangCodes`: мовні коди, які використовуються для форматування дат і чисел. Ними повинні бути коди Unicode CLDR замість кодів ISO.
+- `hiddenLangs`: мови, які не показано у навігаційному меню. Використовують для мов, які не готові до випуску. Додайте мову до цього масиву в першому PR та попросіть персонал підготувати екземпляр VM для вашої мови. Коли VM буде готова, створіть інший PR, щоб видалити її з масиву.
+- `rtlLangs`: мови, які читаються справа наліво.
+
+Наприклад, якщо ви хочете використовувати дотракійську мову, об’єкти `i18n.ts` повинні виглядати так:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] Коли мова буде налаштована у послідовності розгортання ТА матиме публічний активний екземпляр `/learn`, її можна видалити з масиву `hiddenLangs` та зробити доступною.
+
+### Налаштуйте перекладені суперблоки
+
+Додайте нову мову до об’єкта `notAuditedSuperBlocks` у файлі [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts). Це виведе список усіх суперблоків, які не повністю перекладені. Додайте сюди масив суперблоків, які не повністю перекладені. Наприклад:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Переконайтесь, що додали лише ті суперблоки, які **не** повністю перекладені та затверджені. Перекладені суперблоки будуть вирахувані з цього об’єкта. Коли новий суперблок буде повністю перекладений, вилучіть його з масиву цієї мови.
+
+Див. запис `SuperBlocks` на початку того ж файлу для повного списку суперблоків.
+
+### Налаштування пошуку
+
+Потім відкрийте файл [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts). Ці дані використовуються для рядка пошуку, який завантажує статті `/news`. Хоча й малоймовірно, що ви будете тестувати цю функціональність, відсутність даних мови може призвести до помилок при спробі створити кодову базу локально.
+
+Додайте об’єкт своєї мови до об’єкта `algoliaIndices`. Використовуйте значення об’єкта `english` для локального тестування, замінивши ключ `english` на значення своєї мови `availableLangs`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви вже розгорнули екземпляр новин потрібною мовою, ви можете оновити значення, щоб зобразити активний екземпляр. В іншому випадку використовуйте значення англійської мови.
+
+Якби ви додали дотракійську:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Інтерфейс клієнта
+
+Вам потрібно здійснити додатковий крок для роботи з перекладами інтерфейсу клієнта.
+
+Робочі процеси на Crowdin автоматично завантажують _деякі_ переклади інтерфейсу, однак певні файли потрібно перемістити вручну.
+
+Вам потрібно скопіювати такі файли з [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) до `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>` та застосувати переклади там, де потрібно:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+Спершу необов’язково мати всі значення цих трьох файлів. Ви можете перекласти лише потрібні частини та відредагувати все інше пізніше.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+Ви можете замінити URL, які мають відповідні сторінки вашою мовою.
+
+Наприклад, якщо публікації доступні вашою мовою, можна замінити посилання на `"news"`. Якщо ви хочете перекласти статті з нижнього колонтитула, див. [як перекладати статті в нижньому колонтитулі](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+Цей файл містить метадані для вебсторінки `/learn` вашою мовою. Ви можете перекласти значення `"title"`, `"description"` та `"social-description"`. Значення `"youre-unsubscribed"` використовується, якщо хтось відписався від щотижневого повідомлення Квінсі.
+
+Ви також можете перекласти та додати відповідні ключові слова до масиву `"keywords"`.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+Цей файл містить похвали, які з’являються після виконаного завдання та мотиваційні цитати, які з’являються зверху сторінки `/learn`.
+
+Ви можете перекласти їх або замінити відповідними фразами вашою мовою.
+
+### Додавання локалізованих відео
+
+Цей розділ корисний, якщо у вас є локалізовані відео до завдань. В іншому випадку ви можете пропустити його.
+
+Вам потрібно дещо змінити стосовно відеозавдань. Спочатку додайте нову локаль до запиту GraphQL у файлі [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx). Ось так додається дотракійська мова:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Потім додайте ідентифікатор нової мови до будь-якого відеозавдання в перевіреному блоці. Наприклад, якщо `auditedCerts` у `i18n.ts` містить `scientific-computing-with-python` для `dothraki`, тоді ви повинні додати запис `dothraki` в `videoLocaleIds`. Тоді вступна частина має виглядати так:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Оновіть інтерфейс `VideoLocaleIds` у `client/src/redux/prop-types`, додавши нову мову.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+Вкінці оновіть схему завдань у `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Тестування перекладів локально
+
+Якщо ви хочете перевірити переклади локально, перш ніж додати їх до нашого основного репозиторію, то пропустіть зміни робочого процесу на Crowdin. Виконайте кроки для додавання мови, а потім завантажте переклади з Crowdin і додайте їх до свого локального коду.
+
+Оскільки мова не затверджена для випуску, наші скрипти поки не завантажуватимуть переклади автоматично. Лише робочий персонал має доступ до завантаження перекладів. Ви можете звернутися до нас у [чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) або можете локально перекласти файли розмітки з метою тестування.
+
+Як тільки ви отримаєте файли, їх потрібно розмістити у правильному каталозі. Щодо завдань навчальної програми: вам потрібно розмістити папки сертифікацій (наприклад, `01-responsive-web-design`) в межах каталогу `curriculum/challenges/{lang}`. Для перекладів дотракійською це був би `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. Файли `.json` з перекладом клієнта будуть розміщені в каталозі `client/i18n/locales/{lang}`.
+
+Оновіть файл `.env` так, щоб він використовував нову мову для `CLIENT_LOCALE` та `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Як тільки все на місці, ви зможете запустити `pnpm run develop`, щоб переглянути перекладену версію freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+Якщо ви побудували клієнта однією мовою та потім хочете побудувати його іншою мовою, вам потрібно використати команду `pnpm run clean-and-develop` після зміни файлу `.env`, оскільки Gatsby кешуватиме першу мову.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+Ви можете працювати з перекладами локально, щоб провести тестування. Ми нагадуємо, що переклади _не_ потрібно надсилати через GitHub, а лише через Crowdin. Не забудьте скинути локальну кодову базу після закінчення тестування.
+:::
+
+## Додавання нової мови до навігаційного меню
+
+Як тільки попередній PR буде об’єднаний, а VM для вашої мови буде готовою, створіть ще один PR, щоб додати нову мову до навігаційного меню.
+
+У файлі [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) ви додали мову до масиву `hiddenLangs` у попередньому PR. Тепер видаліть її з масиву.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // видаліть свою мову з масиву
+```
+
+Коли PR буде об’єднаний та розроблений, навчальна програма стане доступною вашою мовою.
+
+# Додавання нових мов для `/news`
+
+Щоб започаткувати новини новою мовою, потрібно створити два PR. Один PR буде для [репозиторію CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), а інший — для [репозиторію News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Приготуйте репозиторій CDN для нової мови
+
+News отримує популярні посилання й назви статей із нашого CDN під час збірки та додає їх у нижній колонтитул. News також отримує файли Day.js із CDN під час збірки, щоб локалізувати дати та час кожної мови.
+
+### Додайте файл YAML для популярних статей
+
+Клонуйте [репозиторій CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) та створіть нову гілку.
+
+Створіть новий файл у каталозі [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) та назвіть його `language.yaml`. Наприклад, якщо ви запускаєте новини дотракійською мовою, назвіть файл `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Потім скопіюйте вміст файлу [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) до нового файлу YAML, який ви щойно створили.
+
+Вміст виглядатиме приблизно так:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Додайте файл локалі Day.js для нової мови
+
+Day.js містить лише англійську локаль за замовчуванням. Щоб дозволити роботу з іншими мовами, потрібно додати новий файл локалі Day.js до CDN.
+
+Створіть новий файл у каталозі [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) та назвіть його `isocode.min.js`. Наприклад, якщо ви запускаєте новини дотракійською мовою, назвіть файл `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Номер версії буде змінено, оскільки залежності оновлюються.
+
+Потім відвідайте [цю сторінку на cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) з усіма доступними файлами Day.js для вашої версії, знайдіть посилання `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` для нової мови та відкрийте його у новій вкладці.
+
+> [!NOTE] Вам потрібно додати лише файл локалі .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js. Не додавайте інших файлів Day.js.
+
+Скопіюйте код локалі Day.js з нової вкладки до файлу, який ви створили. Наприклад, ось мінімізована версія коду англійської локалі для Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Потім відкрийте PR до репозиторію CDN, щоб додати файли YAML та Day.js для перегляду.
+
+## Приготуйте репозиторій News для нової мови
+
+[Репозиторій News](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) отримує дані з екземпляра Ghost, файли, додані до CDN, будує News та розробляє їх.
+
+> [!WARN] PR для репозиторію News _повинні_ надходити з одного репозиторію. Не працюйте над цим кроком з розгалуження.
+
+### Змініть головний файл конфігурації
+
+Клонуйте репозиторій News та створіть нову гілку.
+
+Відкрийте файл `config/index.js`, щоб додати нову мову та налаштувати потрібні значення. Потрібно змінити декілька об’єктів та масивів:
+
+- `locales`: масив, який містить активні та майбутні мови для новин. Це значення, які використовуються у файлі `.env`, щоб обрати екземпляр та інтерфейс Ghost для кожної збірки. Додайте назву нової мови в нижньому регістрі до цього масиву.
+- `localeCodes`: цей об’єкт є картою кодів ISO для кожної мови, який використовують, щоб налаштувати i18next перед побудовою інтерфейсу. Щоб додати нову мову, використайте назву мови в нижньому регістрі як _ключ_ та код мови ISO 639-1 як _значення_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: цей об’єкт є картою індексів Algolia для кожної мови. Щоб додати нову мову, використайте назву мови в нижньому регістрі як _ключ_ та `news-` із кодом мови ISO 639-1 у нижньому регістрі як _значення_.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви невпевнені, який рядок потрібно використовувати при налаштуванні `algoliaIndices`, напишіть Крісу (@scissorsneedfoodtoo) або комусь іншому з доступом до Algolia.
+
+Наприклад, якщо ви запускаєте новини дотракійською мовою, об’єкти/масиви повинні виглядати ось так:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Додайте файли JSON i18next для нової мови
+
+Перейдіть до каталогу `shared/config/i18n/locales`, створіть нову папку та надайте їй назву мови, яку додаєте. Наприклад, якщо ви додаєте новини дотракійською мовою, створіть папку під назвою `dothraki`.
+
+Потім скопіюйте файли JSON з каталогу `english` до нової папки.
+
+Відкрийте файл `redirects.json` у новій папці та замініть його вміст на порожній масив:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Потім зафіксуйте та відправте гілку до репозиторію News.
+
+> [!NOTE] Ви повинні знаходитись в одній з команд з доступом до репозиторію News, щоб відправити гілки одразу до News. Наразі такий доступ мають лише dev, i18n та staff.
+
+Вкінці відкрийте PR для розгляду.
+
+Як тільки ваші PR для CDN та News затверджені, їх можна об’єднати.
+
+> [!NOTE] Розгортання оброблятиме робочий персонал. Ось зразок PR [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) з прикладом. Для детальнішої інформації див. [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b23b8004
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: Як допомогти з відеозавданнями
+---
+
+Відеозавдання — це новий вид завдань у навчальній програмі freeCodeCamp.
+
+Відеозавдання — це маленька частина повноформатного відеокурсу на певну тему. Сторінка з відеозавданням містить відео на ютубі. Кожна сторінка має одне запитання з декількома варіантами відповідей, що стосуються відео. Користувач повинен правильно відповісти на запитання перед тим, як перейти до наступного відеозавдання курсу.
+
+Сторінки з відеозавданнями створюються учасниками команди freeCodeCamp. Відео на ютуб також завантажуються учасниками команди freeCodeCamp. Багато відеозавдань ще не мають запитань, пов’язаних з ними.
+
+Ви можете допомогти, створивши запитання з декількома варіантами відповіді, повʼязаних з розділами відео, та додавши ці запитання до markdown-файлів для відеозавдань.
+
+## Зразок завдання
+
+Нижче наведено зразок того, як виглядають markdown-файли завдання.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Опис завдання, у markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+Наразі ці поля використовуються у завданнях з декількома варіантами відповідей на тему Python.
+
+## --text--
+
+Запитання повинне бути тут.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Відповідь 1
+
+---
+
+Відповідь 2
+
+---
+
+Інші відповіді
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+Номер правильної відповіді повинен бути тут.
+
+```
+
+## Створення запитань для відеозавдань
+
+### Отримання доступу до markdown-файлів відеозавдань
+
+Markdow-файли до відеозавдань можна знайти у наступних локаціях навчальної програми:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Оберіть markdown-файл завдання із поданих нижче.
+
+### Ознайомтеся із відео, пов’язаним із завданням, та створіть запитання із декількома варіантами відповіді
+
+Спершу знайдіть `videoId`.
+
+Наприклад, у наступному коді із заголовка markdown-файлу завдання, `videoId` є «nVAaxZ34khk». На GitHub інформація повинна бути поданою у форматі таблиці.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Потім отримайте доступ до відео на ютубі за допомогою `videoId`. Посиланням на відео буде:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (замініть `videoId` у посиланні на ID відео, без квадратних дужок)
+
+У прикладі вище посиланням є https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Перегляньте відео із цим `videoId` та на його основі придумайте запитання із декількома варіантами відповіді.
+
+### Додайте запитання до markdown-файлу
+
+Ви можете додати запитання локально або скориставшись інтерфейсом GitHub. Щоб додати запитання локально, вам потрібно [налаштувати freeCodeCamp локально](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Ви також можете знайти файл на GitHub та клацнути кнопку редагування, щоб додати запитання прямо у своєму браузері.
+
+Якщо запитання ще не додано до певного відеозавдання, воно матиме наступне запитання за замовчуванням:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Запитання
+
+## --answers--
+
+Відповідь 1
+
+---
+
+Відповідь 2
+
+---
+
+Інші відповіді
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Додайте/оновіть текст запитання під частиною, яка зображає:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Додайте/оновіть відповіді (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2` і так далі) під `## --answers--`. Переконайтеся, що оновили номер правильної відповіді під `## --video-solution--`. Ви можете додати більше можливих відповідей, використовуючи такий самий формат. Запитання та відповіді можуть бути в лапках.
+
+### Приклади запитань
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Що виведе на консоль даний код JavaScript?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Що виведеться на екран після цього коду:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+Більше прикладів ви можете побачити в markdown-файлах даного відеокурсу. Всі завдання вже мають запитання: [Python for Everybody Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Відкрийте PR
+
+Після створення одного чи більше запитань, ви можете затвердити зміни в новій гілці та [відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f6dcc73
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: Як відкрити запит на злиття (PR)
+---
+
+Запит на злиття (PR) дозволяє надсилати зміни зі свого форку на GitHub до головного репозиторію freeCodeCamp.org. Як тільки ви закінчите вносити зміни до коду, дотримуйтесь цих рекомендацій, щоб відкрити PR.
+
+Ми очікуємо, що наші помічники обізнані щодо процесу проєкту. Ви заощадите час та отримаєте повагу тих, хто відповідає за технічне обслуговування, дотримуючись цих вказівок.
+
+Деякі приклади:
+
+1. Не редагуйте файли напряму через GitHub, це не дуже хороша ідея.
+2. Переконайтесь, що заголовок для PR відповідає [нашій конвенції](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Переконайтесь, що дотримуєтесь контрольного списку PR, а не просто ставите галочки. В такому випадку ми не сприйматимемо вас серйозно.
+4. Використовуйте правильний спосіб пов’язати завдання в описі PR, оновивши `XXXXXX`. Не додавайте номери завдань будь-де.
+5. Не «@згадуйте» чи запитуйте відгук кілька разів.
+
+ Ми розуміємо, що ви раді зробити свій внесок. Модераторам подобається відповідати кожному, однак пам’ятайте: вони зайняті люди, які розглядають сотні запитів. Рано чи пізно, хтось дійде і до вашого запиту.
+
+6. Не працюйте напряму зі своєї гілки `main`. Створіть нову гілку для змін, над якими ви працюєте.
+
+> [!NOTE] Ваш PR повинен націлюватись лише на зміни навчальної програми англійською мовою. Див. [цей довідник](index#translations), щоб зробити внесок до перекладу.
+
+## Підготуйте хороший заголовок для PR
+
+Ми використовуємо [загальноприйнятні заголовки та повідомлення](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) для затверджень і запитів на злиття. Конвенція вимагає наступного формату:
+
+> `<тип>([область (необов’язково)]): <опис>`
+>
+> Наприклад:
+>
+> `fix(learn): тести для завдання з циклу do...while`
+
+Щоразу, коли ви відкриваєте запит на злиття (PR), використовуйте нижчеподану інформацію, щоб визначити тип, область та опис.
+
+**Тип:**
+
+| Тип | Коли обирати |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| fix | Змінені або оновлені/вдосконалені функції, тести, формулювання уроку тощо. |
+| feat | Лише при додаванні нової функції, тестів тощо. |
+| chore | Зміни, які не повʼязані з кодом, тестами або формулюванням уроку. |
+| docs | Зміни до каталогу `/docs` чи настанов щодо внесків тощо. |
+
+**Область:**
+
+Область можна обрати із [цього списку міток](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Опис:**
+
+Опис повинен бути коротким (не більше 30 символів) та простим; більше інформації можна додати в полі опису PR та коментарях.
+
+Декілька прикладів хороших заголовків:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## Запропонуйте PR
+
+1. Як тільки зміни будуть збережені, вам буде запропоновано створити PR на сторінці вашого розгалуження GitHub.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Переглянути знімок екрану</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. Усі PR потрібно надсилати до головного репозиторію freeCodeCamp — гілки `main`.
+
+ Переконайтеся, що значення base fork встановлено на freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp під час створення PR.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>Переглянути знімок екрану</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Надішліть PR зі своєї гілки до гілки freeCodeCamp `main`.
+
+4. У тілі свого PR вкажіть детальну інформацію про внесені зміни та чим вони корисні.
+
+ - Вам буде надано шаблон PR. Це список, якого потрібно дотримуватись перед відкриттям PR.
+
+ - Заповніть деталі, які ви вважаєте за потрібне. Переконайтеся, що надали рецензентам достатньо контексту для перегляду змін. Якщо PR вносить зміни до інтерфейсу, обов’язково використайте знімки екрана зі змінами. Ця інформація буде розглянута, а рецензенти вирішать, чи ваш PR буде прийнятий.
+
+ - Якщо PR призначений для вирішення наявного завдання на GitHub, то використайте ключове слово _Closes_ та номер завдання в кінці опису, щоб [автоматично закрити цю проблему, якщо PR прийнятий та об’єднаний](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Наприклад: `Closes#123` закриватиме завдання 123
+
+5. Вкажіть, чи ви проводили тести на локальній копії сайту.
+
+ - Це надзвичайно важливо при внесенні змін, які не стосуються зміни тексту (наприклад, документації чи опису завдань). До змін, яким потрібне локальне тестування, входять JavaScript, CSS або HTML (тобто ті, які можуть змінити функціональність чи макет сторінки).
+
+ - Якщо ваш PR впливає на поведінку сторінки, він повинен супроводжуватися відповідними [інтеграційними тестами Playwright](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Зворотний зв’язок по PR
+
+> :tada: Вітаємо зі створенням PR та дуже дякуємо, що знайшли час зробити свій внесок.
+
+Наші модератори все переглянуть та залишать свій відгук. Будь ласка, наберіться терпіння та поважайте їхній час. Усі запити на злиття розглядаються за усталеним порядком.
+
+І як завжди, не соромтесь ставити запитання [на форумі у категорії «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+Якщо ви хочете внести ще більше PR, ми рекомендуємо прочитати про [внесення змін та синхронізацію](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally), щоб уникнути видалення вашого розгалуження.
+:::
+
+## Конфлікти PR
+
+Конфлікти можуть виникнути, якщо над репозиторієм працює багато помічників. Зміни можуть вплинути на PR, який очікує на перегляд та злиття.
+
+Оскільки ми об’єднуємо всі затвердження, можливо, вам не знадобиться перебазовування. Якщо перебазовування обов’язкове, див. розділи [«Звичайні помилки та функціональності»](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) або [«Майбутня навчальна програма та функціональності»](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features), щоб дізнатись процес для відповідного PR.
+
+### Звичайні помилки та функціональності
+
+Коли ви працюєте над звичайними помилками та функціональностями на нашій гілці розробки `main`, ви можете виконати просте перебазовування:
+
+1. Перебазуйте свою локальну копію:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Вирішіть будь-які конфлікти та додайте/редагуйте затвердження
+
+ ```bash
+ # Або
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Або
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Відправте зміни до PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### Майбутня навчальна програма та функціональності
+
+Коли ви працюєте над функціональностями для майбутньої навчальної програми на гілках `next-*`, потрібно виконати команду `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Переконайтесь, що upstream синхронізовано з локальною гілкою:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Зробіть резервну копію
+
+ a. Або видаліть локальну гілку після створення резервної копії (якщо вона досі існує локально):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # приклад:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # приклад:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Або зробіть резервну копію гілки PR (якщо вона не існує локально):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # приклад:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Розпочніть з нуля:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Розв’яжіть будь-які конфлікти, поприбирайте, встановіть залежності та запустіть тести
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # приклад:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. Якщо все виглядає добре, передайте до PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..02f01794
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Як редагувати переклади
+---
+
+Наша команда з редагування відповідає за забезпечення точних перекладів оригінального тексту. Редактори гарантують високу якість перекладів наших матеріалів.
+
+Всі наші переклади зроблені від руки, живими людьми. Редагування гарантує, що всі матеріали, як-от наша навчальна програма, перекладені систематично та коректно.
+
+Щоб почати редагувати, перейдіть на [нашу перекладацьку платформу](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) та зареєструйтеся. Виберіть «Go to console» зверху на навігаційній панелі, щоб перемикнутися з публічного типу сторінки на робочий.
+
+## Оберіть файл
+
+Там ви побачите список проєктів, до яких вам надається доступ. Оберіть проєкт, який би ви хотіли редагувати, та мову.
+
+
+
+Тепер ви повинні побачити список доступних файлів. Виберіть файл, натиснувши клавішу `Proofread` справа від файлу, тоді виберіть `Proofreading` з меню, що з’явилось.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви перейшли на робочий тип сторінки, але хочете [перекладати](how-to-translate-files), а не редагувати, натомість виберіть `Crowdsourcing` у запропонованому меню.
+
+## Редагуйте переклади
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Тут ви побачите список рядків у вибраному файлі разом з їхніми перекладами. Тут показано переклад, який отримав найвищий бал (між голосами «за» та «проти») від спільноти перекладачів.
+
+Поки ви можете переглядати _всі_ запропоновані переклади для цього рядка, оцінки спільноти (між голосами «за» та «проти») повинні бути взяті до уваги під час вибору перекладу для затвердження. Спільнота може розглядати запропоновані переклади та рекомендувати, який саме найбільш точний і зрозумілий.
+
+1. Це оригінальний рядок (англійською мовою).
+2. Це відповідний перекладений рядок. Найпопулярніший переклад, базований на голосах «за» та «проти», буде тут.
+3. Якщо натиснути на цю галочку, переклад буде затверджений.
+4. Crowdin показує статус кожного рядка. `Done` означає, що переклад затверджений і він буде завантажений в нашому наступному пулі Crowdin. `Todo` означає, що рядок ще не редагували. `Hidden` означає, що рядок заблокований і _його не потрібно перекладати_. `Comment` означає, що рядок має коментарі.
+5. Переклади можна виділяти та затверджувати однією дією.
+6. Ви можете переглядати переклади, запропоновані спільнотою, їхню оцінку та переклади, запропоновані Crowdin, тут.
+7. Ця кнопка показує/приховує праву панель вікна, де ви можете переглядати переклади, коментарі, збережені переклади та терміни з глосарію.
+8. Crowdin показує повідомлення про помилки з системи перевірки якості тут. Іншими словами, якщо щось видається неправильним у перекладі, Crowdin повідомить вас. Ці переклади мають затверджуватися з обережністю.
+
+Як тільки файл буде відредагований, він не підлягає ніяким додатковим діям.
+
+> [!NOTE] Затвердження рядку в робочому типі позначить його як завершений та його буде завантажено в наступному пулі від Crowdin на GitHub.
+
+## Як стати редактором
+
+Якщо у вас є запитання, або ви хочете стати редактором, напишіть у [чаті помічників](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Як правило, ми надамо вам доступ до редагування, якщо ви вже деякий час мали справу з freeCodeCamp.
+
+Наша команда завжди шукає охочих волонтерів, які допоможуть зробити високоякісні переклади, доступні для світової спільноти.
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin дозволить вам затверджувати свої переклади. Загалом, краще дозволити іншому редактору переглянути запропоновані вами переклади, щоб переконатися у відсутності помилок.
+
+## Створення в чаті каналу для світової мови
+
+В основному, ми рекомендуємо використовувати [чат помічників](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) для комунікації. Проте, якщо команда волонтерів-перекладачів для однієї мови зростатиме, ми можемо розглянути питання про створення окремого каналу.
+
+Якщо ви вже є редактором та зацікавлені в окремому каналі нашого чату, створеному для конкретної мови, [заповніть цю форму](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d2687426
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Дотримуйтесь цих рекомендацій, щоб налаштувати середовище розробки freeCodeCamp. Особливо рекомендовано, якщо ви хочете робити внески регулярно.
+
+## Оберіть між Gitpod чи власною машиною (локальне налаштування)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp не збирається та не запускається на Windows, тому вам [потрібно використати WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) для налаштування типу Linux на Windows. - Ви не можете використовувати командний рядок Windows, Git Bash або PowerShell, щоб створити та запустити кодову базу. - Зверніть увагу, що вимоги до комп’ютерного устаткування при використанні Windows відрізнятимуться [від вказаних](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine), щоб відповідати налаштуванню на основі WSL.
+ :::
+
+Якщо ви бажаєте зробити одноразовий внесок, використовуйте Gitpod. Налаштування Gitpod надає готове середовище у вашому браузері за декілька хвилин. Для тривалих внесків ми рекомендуємо налаштувати freeCodeCamp на локальній машині.
+
+Ось деякі плюси та мінуси, які допоможуть із вибором:
+
+| Gitpod | Власна машина (локальне налаштування) |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| Відсутність мінімальних вимог обладнання | Специфічні та мінімальні вимоги |
+| Не потрібно встановлювати програмне забезпечення | Потрібно додаткове програмне забезпечення |
+| Копія репозиторію завжди актуальна | Потрібно підтримувати локальну копію репозиторію |
+| Повільніший та може займати декілька хвилин для запуску | Швидший та займає декілька секунд для запуску |
+| Потрібне інтернет-з’єднання | Мінімальне інтернет-з’єднання (після налаштування) |
+| Деякі завдання (наприклад, компіляція та тестування) можуть тривати довше | Швидше виконання завдань (залежно від можливостей вашої машини) |
+
+### Як підготувати робоче середовище Gitpod
+
+Ми автоматизували процес встановлення усіх необхідних залежностей та інструментів. Завдяки Gitpod ви отримаєте готове середовище за декілька хвилин, яке буде корисним, якщо ви не маєте доступу до комп’ютера чи хочете зробити одноразові зміни.
+
+Існує декілька способів запустити робоче середовище Gitpod:
+
+1. **(Найшвидший спосіб)** Додайте `gitpod.io/#` на початку будь-якого URL з GitHub.
+
+ Наприклад, якщо ви відвідуєте розгалуження на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, додайте `gitpod.io/#` на початку URL-адреси та натисніть клавішу enter.
+
+ Ви перейдете на `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` та побачите робоче середовище, створене для вас. Це працює для будь-якого репозиторію чи PR на GitHub.
+
+2. В іншому випадку встановіть одне з нижчеподаних розширень браузера.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) — працює з браузерами на основі Chromium (Google Chrome, Brave, Edge тощо)
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) — Firefox
+
+ Як тільки розширення встановлено, ви побачите кнопку «Gitpod» на кожному репозиторії, PR тощо, що дозволить запустити робоче середовище. Перегляньте сторінку розширень для детальнішої інформації, знімків екрану тощо.
+
+Ви можете пропустити розділ «Налаштуйте синхронізацію з батьківського елемента», як тільки запустите робоче середовище Gitpod. Більша частина цього посібника стосується робочих середовищ Gitpod, однак потрібно пам’ятати [як працюють URL-адреси та порти в межах робочого середовища Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports).
+
+**Примітка: розв’язок проблем з портом на Gitpod**
+
+Служба на порті `8000` іноді не працює. Це типово, якщо ви перезапускаєте неактивне робоче середовище.
+
+Якщо служба не з’являється на порті `8000`, розв’яжіть проблему за допомогою наступних кроків:
+
+- **Запустіть сервер**: виконайте `pnpm run develop:server` у вікні терміналу з кореневого каталогу проєкту (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`), щоб запустити сервер.
+
+- **Запустіть клієнта**: в іншому вікні терміналу виконайте `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` з каталогу клієнта (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`), щоб запустити клієнта.
+
+Це має зробити порт `8000` доступним.
+
+### Як підготувати локальну машину
+
+Мінімальні вимоги для локального запуску freeCodeCamp:
+
+- 8 ГБ оперативної пам’яті
+- Відносно швидкий процесор (4+ ядер)
+- Windows 10 чи 11 (з WSL), macOS або Linux
+
+Для початку встановіть передумовне програмне забезпечення для своєї операційної системи.
+
+Здебільшого ми підтримуємо розробку на системах, які базуються на Linux та Unix (наприклад, Ubuntu та macOS). На Windows 10 чи 11 можна працювати лише з WSL2. Використовуйте [цей посібник](how-to-setup-wsl), щоб налаштувати WSL2. Ви не можете використовувати командний рядок, Git Bash або PowerShell для запуску freeCodeCamp на Windows.
+
+#### Передумови:
+
+| Передумова | Версія | Примітки |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | Ми використовуємо версію «Active LTS», див. [розклад LTS](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [Сервер спільноти MongoDB](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+Якщо у вас інша версія, встановіть рекомендовану версію. Ми можемо вирішити проблеми зі встановленням лише для рекомендованих версій. Для детальнішої інформації див. [розділ з розв’язання проблем розробки](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+:::
+
+Якщо на вашій машині вже встановлено Node.js, запустіть наступні команди для перевірки версій:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+Ми наполегливо рекомендуємо оновити вищевказані програмні забезпечення до останнього стабільного випуску, також відомого як довгострокова підтримка (LTS).
+:::
+
+Як тільки ви встановили передумови, потрібно підготувати середовище розробки. Це характерно для багатьох робочих процесів розробки, і це потрібно зробити лише один раз.
+
+##### Виконайте наступні дії, щоб підготувати середовище розробки:
+
+1. Встановіть [Git](https://git-scm.com/) або інший клієнт Git, якщо ви досі цього не зробили. Оновіть його до останньої версії; версія, яка пов’язана з вашою ОС, може бути застарілою.
+
+2. (Необов’язково, але рекомендовано) [Налаштуйте ключ SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) для GitHub.
+
+3. Встановіть редактор коду на свій вибір. Якщо ви вагаєтесь, ми рекомендуємо [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — він безоплатний та має відкритий код.
+
+4. Налаштуйте лінтинг для редактора коду.
+
+ Ви повинні [запустити ESLint у своєму редакторі](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), оскільки він виділятиме все, що не відповідає [нашій інструкції з оформлення JavaScript](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+ :::tip
+ Будь ласка, не ігноруйте помилки лінтингу. Вони **допомагають** забезпечувати чисту й просту базу коду.
+ :::
+
+## Розгалужте репозиторій на GitHub
+
+[Розгалуження](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) — це етап, на якому ви отримаєте власну копію головного репозиторію freeCodeCamp на GitHub.
+
+Це дуже важливо, оскільки ви зможете працювати над власною копією freeCodeCamp на GitHub або завантажити (клонувати) репозиторій для локальної роботи. Пізніше ви зможете запропонувати внести зміни до головного репозиторію зі свого розгалуження за допомогою запиту на злиття (PR).
+
+:::tip
+Головний репозиторій на `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` часто називають репозиторієм `upstream`.
+Ваше розгалуження на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` часто називають репозиторієм `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.
+:::
+
+**Виконайте наступні кроки, щоб розгалужити репозиторій `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`:**
+
+1. Перейдіть до репозиторію freeCodeCamp на GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Натисніть кнопку «Fork» у верхньому правому куті інтерфейсу ([детальніша інформація тут](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Як тільки репозиторій розгалужено, вас буде переміщено до копії репозиторію freeCodeCamp на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Як розгалужити freeCodeCamp на GitHub (знімок екрана)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="Як розгалужити freeCodeCamp на GitHub" />
+</details>
+
+## Клонуйте розгалуження з GitHub
+
+[Клонування](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) — це **завантаження** копії репозиторію з `віддаленого` розташування, що належить вам або комусь іншому. У цьому випадку віддаленим розташуванням є ваш `fork` репозиторію freeCodeCamp, який доступний на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.)
+
+> [!WARNING] Якщо ви використовуєте дистрибутив WSL2 Linux, у вас можуть виникнути проблеми, пов’язані з продуктивністю та стабільністю під час запуску цього проєкту в папці, спільній між Windows і WSL2 (наприклад, `/mnt/c/Users/`). Ми рекомендуємо клонувати цей репозиторій до папки, яка в основному використовується дистрибутивом WSL2 Linux і не має прямого доступу до Windows (наприклад, `~/PROJECTS/`).
+>
+> Див. [завдання на GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) для детальнішої інформації щодо цієї проблеми.
+
+Запустіть ці команди на своїй локальній машині:
+
+1. Відкрийте термінал / командний рядок / оболонку в каталозі проєктів
+
+ _тобто `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Клонуйте своє розгалуження freeCodeCamp, замінивши `YOUR_USER_NAME` на ім’я користувача GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+Це завантажить весь репозиторій freeCodeCamp у ваш каталог проєктів.
+
+Зверніть увагу: `--depth=1` створює поверхневий клон вашого розгалуження, використовуючи лише останню історію/затвердження.
+
+## Налаштуйте синхронізацію з батьківського репозиторію
+
+Ви завантажили копію розгалуження, а отже вам потрібно налаштувати `upstream` віддалено від батьківського репозиторію.
+
+[Як згадувалось раніше](#fork-the-repository-on-github), головний репозиторій має назву `upstream`. Розгалуження називають репозиторієм `origin`.
+
+Вам потрібне посилання від локального клону на репозиторій `upstream` на додаток до репозиторію `origin`. Це необхідно для того, щоб ви могли синхронізувати зміни з головного репозиторію без багаторазового розгалуження і клонування.
+
+1. Змініть каталог на новий каталог freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Додайте віддалене посилання на основний репозиторій freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Переконайтеся, що конфігурація правильна:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ Вивід повинен бути схожим на нижчеподаний приклад (замініть `YOUR_USER_NAME` на своє ім’я користувача GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Локальний запуск freeCodeCamp
+
+Тепер у вас є локальна копія freeCodeCamp, тому дотримуйтесь цих інструкцій для локального запуску. Це дозволить вам:
+
+- Переглядати як виглядатиме навчальна платформа з внесеними змінами.
+- Працювати над завданнями та покращеннями UI.
+- Виправляти помилки серверів застосунків та клієнтських застосунків.
+
+Якщо у вас виникли проблеми, спочатку спробуйте знайти розв’язок в інтернеті. Якщо розв’язку немає, пошукайте його на нашій сторінці [завдань GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) та повідомте про проблему, якщо про неї ще не повідомляли.
+
+І як завжди, не соромтесь ставити запитання [на форумі у категорії «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Налаштування залежностей
+
+#### Крок 1: налаштуйте файл змінних середовища
+
+Ключі API та змінні середовища за замовчуванням зберігаються у файлі `sample.env`. Цей файл потрібно скопіювати в новий файл під назвою `.env`, доступ до якого відкривається динамічно на кроці встановлення.
+
+```bash
+# Створіть копію «sample.env» та назвіть її «.env».
+# Заповніть її необхідними ключами та секретами API
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+Для локального запуску застосунку _необов’язково_ змінювати ключі у файлі `.env`. Ви можете залишити значення за замовчуванням, скопійовані з `sample.env`.
+
+:::tip
+Майте на увазі, якщо ви використовуватимете Auth0 або Algolia, вам потрібно отримати власні ключі API для цих служб та відредагувати введені дані у файлі `.env`.
+:::
+
+#### Крок 2: встановіть залежності
+
+У цьому кроці буде встановлено залежності, необхідні для запуску застосунку:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Крок 3: запустіть MongoDB та додайте базу даних
+
+Перш ніж локально запустити застосунок, потрібно запустити службу MongoDB.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо MongoDB працює за замовчуванням, то URL-адреса, збережена як значення `MONGOHQ_URL` у файлі `.env`, має працювати. Якщо ви використовуєте власне налаштування, змініть значення за потреби.
+>
+> Якщо ви дотримувались [посібника з налаштування Windows 10 з WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl), ви можете пропустити цей крок за умови, що сервер MongoDB вже працює. Це можна перевірити, зв’язавшись із `http://localhost:27017` на локальній машині.
+
+Запустіть сервер MongoDB в окремому терміналі:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+Ви можете не запускати MongoDB кожного разу, встановивши його як фонову службу. Для детальнішої інформації див. [документацію MongoDB для вашої ОС](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Тепер додамо базу даних. На цьому кроці ми запускаємо нижченаведену команду, яка заповнює сервер MongoDB деякими початковими наборами даних, потрібних службам. До них належать деякі схеми та інше.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+Ви увійдете як новий користувач без будь-яких завершених сертифікацій за замовчуванням. Запустіть цю команду, якщо потрібно використати виконані сертифікації або написати тести Playwright:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+> [!WARNING] Якщо запустити `pnpm run seed:certified-user`, ви вийдете з облікового запису. Вам доведеться очистити cookies свого браузера та увійти знову.
+
+#### Крок 4: запустіть клієнтську програму freeCodeCamp та сервер API
+
+Тепер ви можете запустити сервер API та клієнтську програму.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+Ця команда запустить всі служби, включно з сервером API та клієнтською програмою, з якими ви можете працювати.
+
+Після цього відкрийте веббраузер та відвідайте <http://localhost:8000>. Якщо застосунок завантажується, увійдіть в систему. Вітання — все готово! Тепер ви маєте копію повної навчальної платформи freeCodeCamp на своїй локальній машині.
+
+Сервер API обслуговує кінцеві точки на `http://localhost:3000`. Gatsby обслуговує клієнтську програму на `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+Якщо ви увійшли в систему, відвідайте <http://localhost:3000/explorer> і побачите доступні API.
+
+> [!WARNING] Якщо очистити cookies чи запустити `pnpm run seed:certified-user`, ви вийдете з системи та вам доведеться увійти знову.
+
+Якщо у вас виникли проблеми, див. розділ з [розв’язання проблем розробки](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Коротко про команди
+
+Короткий довідник команд, які знадобляться при локальній роботі.
+
+| команда | опис |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| `pnpm install` | Встановлює/перевстановлює всі залежності та запускає різні служби. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Створює авторизованих тестових користувачів і розміщує їх в MongoDB. Також виконує `seed:exams` та `seed:surveys` нижче. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Створює автоматизованих тестових користувачів, які завершили сертифікації, і розміщує їх у MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Створює екзамени та вставляє їх в MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Створює опитування для користувачів за замовчуванням та розміщує їх в MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Запускає сервер API та клієнтські програми freeCodeCamp. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Видаляє всі залежності й очищає кеш. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..810ec39a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp Mobile App locally
+---
+
+Дотримуйтесь цього посібника, щоб локально налаштувати мобільний застосунок freeCodeCamp на своїй системі. Особливо рекомендовано, якщо ви хочете робити внески регулярно.
+
+Деякі з робочих процесів (наприклад, виправлення помилок у кодовій базі) вимагають локального запуску freeCodeCamp.
+
+## Як підготувати локальну машину
+
+Для початку встановіть передумовне програмне забезпечення для своєї операційної системи.
+
+### Передумови
+
+| Передумова | Версія | Примітки |
+| ------------------------------- | ------ | --------------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (разом із Flutter) | `3.x` | Ми використовуємо версію, з’єднану з Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+Якщо у вас інша версія, встановіть рекомендовану версію. Ми можемо розв’язати проблеми зі встановленням лише для рекомендованих версій.
+:::
+
+Якщо на вашій машині вже встановлено Flutter, запустіть наступні команди для перевірки версій:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+Ми наполегливо рекомендуємо оновити вищевказані програмні забезпечення до останнього стабільного випуску.
+:::
+
+Як тільки ви встановили передумови, потрібно підготувати середовище розробки. Це характерно для багатьох робочих процесів розробки, і це потрібно зробити лише один раз.
+
+#### Виконайте наступні дії, щоб підготувати середовище розробки:
+
+1. Встановіть [Git](https://git-scm.com/) або інший клієнт Git, якщо ви досі цього не зробили. Оновіть його до останньої версії; версія, яка пов’язана з вашою ОС, може бути застарілою.
+
+2. Встановіть [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) та [емулятори Android](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) з останньою випущеною версією Android. Ми рекомендуємо використовувати Pixel 3a XL та Nexus One (для емуляції менших екранів).
+
+3. (Додатково для MacOS) Встановіть Xcode та симулятор iOS з останньою випущеною версією iOS.
+
+4. (Необов’язково, але рекомендовано) [Налаштуйте ключ SSH](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) для GitHub.
+
+5. Встановіть редактор коду на свій вибір.
+
+ Ми наполегливо рекомендуємо використовувати [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) або Android Studio. Ми також рекомендуємо встановити офіційні [розширення](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Розгалужте репозиторій на GitHub
+
+[Розгалуження](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) — це етап, на якому ви отримаєте власну копію репозиторію на GitHub.
+
+Це дуже важливо, оскільки ви зможете працювати над власною копією мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp на GitHub або завантажити (клонувати) репозиторій для локальної роботи. Пізніше ви зможете запропонувати внести зміни до головного репозиторію зі свого розгалуження за допомогою запиту на злиття (PR).
+
+:::tip
+Головний репозиторій на `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` часто називають репозиторієм `upstream`.
+Ваше розгалуження на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` часто називають репозиторієм `origin`. `YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.
+:::
+
+**Виконайте наступні кроки, щоб розгалужити репозиторій `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile`:**
+
+1. Перейдіть до мобільного репозиторію freeCodeCamp на GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Натисніть кнопку «Fork» у верхньому правому куті інтерфейсу ([детальніша інформація тут](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. Як тільки репозиторій розгалужено, вас буде переміщено до копії репозиторію на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.)
+
+## Клонуйте розгалуження з GitHub
+
+[Клонування](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) — це **завантаження** копії репозиторію з `віддаленого` розташування, що належить вам або комусь іншому. У цьому випадку віддаленим розташуванням є ваш `fork` репозиторію freeCodeCamp, який доступний на `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` буде змінено на ваше ім’я користувача GitHub.)
+
+Запустіть ці команди на своїй локальній машині:
+
+1. Відкрийте термінал / командний рядок / оболонку в каталозі проєктів
+
+ _тобто `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Клонуйте своє розгалуження freeCodeCamp, замінивши `YOUR_USER_NAME` на ім’я користувача GitHub
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+Це завантажить весь мобільний репозиторій freeCodeCamp у ваш каталог проєктів.
+
+Зверніть увагу: `--depth=1` створює поверхневий клон вашого розгалуження, використовуючи лише останню історію/затвердження.
+
+## Налаштуйте синхронізацію з батьківського репозиторію
+
+Ви завантажили копію розгалуження, а отже вам потрібно налаштувати `upstream` віддалено від батьківського репозиторію.
+
+[Як згадувалось раніше](#fork-the-repository-on-github), головний репозиторій має назву `upstream`. Розгалуження називають репозиторієм `origin`.
+
+Вам потрібне посилання від локального клону на репозиторій `upstream` на додаток до репозиторію `origin`. Це необхідно для того, щоб ви могли синхронізувати зміни з головного репозиторію без багаторазового розгалуження і клонування.
+
+1. Змініть каталог на новий каталог `mobile`:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Додайте віддалене посилання на головний репозиторій мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Переконайтеся, що конфігурація правильна:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ Вивід повинен бути схожим на нижчеподаний приклад (замініть `YOUR_USER_NAME` на своє ім’я користувача GitHub):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Локальний запуск мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp
+
+Тепер у вас є локальна копія мобільного застосунку, тому дотримуйтесь цих інструкцій для локального запуску.
+
+Якщо у вас виникли проблеми, спочатку спробуйте знайти розв’язок в інтернеті. Якщо розв’язку немає, пошукайте його на нашій сторінці [завдань GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) та повідомте про проблему, якщо про неї ще не повідомляли.
+
+І як завжди, не соромтесь ставити запитання [на форумі у категорії «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] Каталог `mobile` містить дві папки, тобто `mobile-api` та `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` містить код API, який використовується для обслуговування подкастів. `mobile-app` містить застосунок Flutter, у якому ви повинні знаходитись під час виконання нижчеподаних кроків.
+
+### Налаштування залежностей
+
+#### Крок 1: налаштуйте файл змінних середовища
+
+Ключі API та змінні середовища за замовчуванням зберігаються у файлі `sample.env`. Цей файл потрібно скопіювати в новий файл під назвою `.env`, доступ до якого відкривається динамічно на кроці встановлення. Не забудьте змінити каталог на `mobile-app` перед виконанням наступних команд.
+
+```bash
+# Створіть копію «sample.env» та назвіть її «.env».
+# Заповніть її необхідними ключами та секретами API:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+Для локального запуску застосунку _необов’язково_ змінювати ключі у файлі `.env`. Ви можете залишити значення за замовчуванням, скопійовані з `sample.env`.
+
+#### Крок 2: встановіть залежності
+
+У цьому кроці буде встановлено залежності, необхідні для запуску застосунку:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Крок 3: запустіть мобільний застосунок freeCodeCamp
+
+Запустіть емулятор (Android або iOS) та зачекайте, поки не завершиться завантаження.
+
+Тепер ви можете запустити застосунок, виконавши наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+Якщо ви використовуєте VSCode або Android Studio, ви можете запустити застосунок, не виконуючи жодних термінальних команд. Більше інформації [тут](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Введення змін локально
+
+Тепер ви можете вносити зміни до файлів та затверджувати їх у локальному клоні розгалуження.
+
+Дотримуйтеся цих вказівок:
+
+1. Переконайтесь, що знаходитесь на гілці `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Ви повинні отримати такий вивід:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ Якщо ви не перебуваєте на головній гілці (main) або ваш робочий каталог не чистий, розв’яжіть будь-які невиконані файли/затвердження та перевірте `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Синхронізуйте останні зміни віддаленої гілки `main` зі своєю локальною гілкою main:
+
+ > [!WARNING] Якщо у вас є невиконані запити на злиття, зроблені з гілки `main` свого розгалуження, ви втратите їх під кінець цього кроку.
+ >
+ > Перед виконанням цього кроку потрібно переконатись, що ваш запит на злиття об’єднав модератор. Щоб уникнути цього, **ніколи** не працюйте на гілці `main`.
+
+ Цей крок **синхронізує останні зміни** з головного репозиторію мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp. Важливо якомога частіше перебазовувати свою гілку на останню версію `upstream/main`, щоб уникнути конфліктів пізніше.
+
+ Оновіть свою локальну копію віддаленого репозиторію мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Скиньте свою головну гілку з головною гілкою мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Перемістіть свою головну гілку до джерела, щоб мати чисту історію розгалуження на GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ Ви можете переконатись, що ваша поточна головна гілка відповідає upstream/main, виконавши diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Отриманий вивід має бути порожнім.
+
+3. Створіть нову гілку:
+
+ Ваша локальна робоча копія буде чистою, якщо ви працюватимете на окремій гілці для кожного завдання. Ніколи не працюйте на `main`. Це забруднить вашу копію мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp, через що, можливо, доведеться починати з нового клону чи розгалуження.
+
+ Переконайтесь, що знаходитесь на `main` та починайте розгалуження звідси:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Назва вашої гілки повинна починатись з `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/` тощо. Не використовуйте номери завдань у гілках. Вони мають бути короткими, змістовними та унікальними.
+
+ Декілька прикладів хороших назв гілок:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Відредагуйте сторінки та працюйте над кодом у своєму улюбленому текстовому редакторі.
+
+5. Як тільки ви задоволені змінами, за бажанням запустіть мобільний додаток локально для перегляду змін.
+
+6. Переконайтеся, що виправили помилки та перевірте форматування своїх змін.
+
+7. Перевірте та підтвердьте файли, які оновлюєте:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Має з’явитись список файлів `unstaged`, які ви відредагували.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Проіндексуйте зміни та зробіть затвердження:
+
+ У цьому кроці потрібно позначити лише ті файли, які редагували чи додавали самостійно. Якщо необхідно, ви можете виконати скидання та виправити файли, які не збираєтеся змінювати.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Або ви можете додати всі файли `unstaged` до області тимчасового зберігання:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Лише ті файли, які було переміщено до області тимчасового зберігання, будуть додані під час затвердження.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Вивід:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Тепер ви можете затвердити свої зміни, використовуючи коротке повідомлення:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Декілька прикладів:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Додатково:
+
+ Ми наполегливо рекомендуємо створювати загальноприйняті повідомлення затверджень. Це хороша практика, яку можна помітити на деяких популярних репозиторіях з відкритим кодом. Це спонукає дотримуватись стандартних практик.
+
+ Декілька прикладів хороших повідомлень затверджень:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Пишіть їх короткими, не більше 50 символів. Додаткову інформацію можна додати в описі затвердження.
+
+ Це не займе більше часу ніж нестандартне повідомлення (наприклад, «update file» чи «add index.md»)
+
+ Ви можете дізнатись більше, чому потрібно використовувати загальноприйнятні затвердження, [тут](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. Якщо вам потрібно відредагувати файл або оновити повідомлення після створення затвердження, це можна зробити після редагування файлів за допомогою:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ Це відкриє текстовий редактор за замовчуванням (наприклад, `nano` або `vi`), де можна редагувати заголовок повідомлення та додавати/редагувати опис.
+
+10. Тепер надішліть свої зміни до розгалуження:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Запуск тестів навчальної програми мобільного застосунку
+
+> [!NOTE] Дотримуйтесь цього розділу, якщо змінюєте тестер завдань у мобільному застосунку. В іншому випадку перейдіть до наступного розділу [як відкрити запит на злиття](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Клонуйте копію [репозиторію freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) локально зі своєї локальної копії репозиторію мобільного застосунку freeCodeCamp. Структура файлів має виглядати так:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Змініть каталог на репозиторій freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Зробіть копію файлу `.env`:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Встановіть залежності для репозиторію freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Створіть файл JSON з даними завдань:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Скопіюйте створений файл JSON до мобільного застосунку:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Змініть каталог на мобільний застосунок:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Встановіть залежності для мобільного застосунку:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Оновіть файл тестів, щоб використовувати файл JSON з даними завдань:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Створіть файли завдань:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Запустіть локальний сервер для обслуговування файлів завдань за допомогою пакету `serve`:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. В іншому терміналі поверніться до репозиторію freeCodeCamp:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Запустіть тести cypress:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Розв’язання проблем розробки
+
+### Проблеми з встановленням рекомендованих попередніх умов
+
+Ми регулярно використовуємо найновіші та найпопулярніші операційні системи, як-от macOS 10.15 і вище, Ubuntu 18.04 і вище та Windows 10 (із WSL2).
+
+Рекомендовано шукати розв’язок певної проблеми у Google, Stack Overflow та Stack Exchange. Ймовірно, хтось вже стикався із тією ж проблемою і на ваш запит вже є відповідь.
+
+Якщо ви використовуєте іншу ОС та/або досі стикаєтесь із проблемами, див. [отримання допомоги](#getting-help).
+
+### Проблеми з UI, помилки збірки тощо
+
+Якщо у вас виникли проблеми з інтерфейсом чи збіркою, може допомогти очищення:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Проблеми при встановленні залежностей
+
+Якщо при встановленні залежностей виникають помилки, переконайтеся, що ви не перебуваєте в мережі з обмеженнями або налаштування мережевого екрана не перешкоджають доступу до ресурсів.
+
+Перше налаштування може зайняти деякий час (залежно від пропускної здатності вашої мережі).
+
+## Отримання допомоги
+
+Якщо вам потрібна допомога, не соромтесь ставити питання [на нашому форумі у розділі «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+У консолі вашого браузера або в Bash / терміналі / командному рядку може з’явитися помилка, яка допоможе визначити проблему. Поділіться цим повідомленням про помилку в описі проблеми, щоб іншим було легше визначити проблему і знайти рішення.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e529b2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Налаштування freeCodeCamp на Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Перш ніж виконувати ці інструкції, переконайтеся, що ваша система відповідає вимогам.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 чи вище) — доступно для всіх дистрибутивів, включно з Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop для Windows**: див. відповідні вимоги для [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) та [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+Цей посібник охоплює деякі загальні кроки з налаштуванням WSL2. Як тільки загальні питання з WSL2 вирішено, ви зможете використовувати [цей посібник з локального налаштування](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally), щоб працювати з freeCodeCamp на Windows, запускаючи дистрибутив WSL як Ubuntu.
+
+## Активуйте WSL
+
+Дотримуйтесь інструкцій з [офіційної документації](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10), щоб встановити WSL2.
+
+## Встановіть Ubuntu
+
+1. Рекомендуємо використовувати Ubuntu-18.04 або вище з WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > Ви можете використовувати інші дистрибутиви, основою яких не є Debian, але у них наявні певні недоліки та вони виходять за рамки цього посібника.
+
+ Станом на листопад 2023 року, Ubuntu та Debian є єдиними дистрибутивами Linux, [офіційно підтримуваними Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements) — наскрізною тестовою бібліотекою, яку використовує freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Оновіть залежності ОС
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Налаштуйте Git
+
+Git попередньо встановлений в Ubuntu 18.04. Перевірте версію Git за допомогою команди `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Необов’язково, але рекомендовано) Тепер ви можете перейти до [налаштування ключів ssh](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) на GitHub.
+
+## Встановлення редактора коду
+
+Ми наполегливо рекомендуємо встановити [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) на Windows 10. Цей редактор підтримує WSL та автоматично встановлює всі необхідні розширення на вашому дистрибутиві WSL.
+
+По суті, ви змінюватимете та зберігатимете свій код на Ubuntu-18.04 із VS Code, встановленим на Windows.
+
+Якщо ви використовуєте [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), можливо, вам знадобиться оновити інтерпретатор Node та керування пакунками npm до версії, налаштованої у вашому дистрибутиві WSL.
+
+Ви можете перевірити ці налаштування в розділі Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Встановлення Docker Desktop
+
+**Docker Desktop на Windows** дозволяє встановити й запускати бази даних (наприклад, MongoDB) та інші служби (наприклад, NGINX), а також багато іншого. Це важливо для того, щоб уникнути помилок при налаштуванні MongoDB чи інших служб одразу на Windows або WSL2.
+
+Дотримуйтесь інструкцій з [офіційної документації](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) та встановіть Docker Desktop на свій дистрибутив Windows.
+
+Для кращого досвіду існують деякі мінімальні вимоги до апаратного забезпечення.
+
+## Налаштуйте Docker Desktop на WSL
+
+Як тільки Docker Desktop встановлено, [дотримуйтесь цих інструкцій](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) та налаштуйте його для роботи з Ubuntu-18.04 як бекенду.
+
+Завдяки цьому контейнери працюють на стороні WSL, а не Windows. Ви можете отримати доступ до служб на `http://localhost` (як на Windows, так і на Ubuntu).
+
+## Встановіть MongoDB із Docker Hub
+
+Як тільки ви налаштували Docker Desktop для роботи з WSL2, дотримуйтесь цих кроків, щоб запустити службу MongoDB:
+
+1. Запустіть новий термінал Ubuntu
+
+2. Витягніть MongoDB із Docker Hub. Будь ласка, зверніться до таблиці з [передумовами](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) поточної версії MongoDB, яку використовує freeCodeCamp. Наприклад, якщо номером версії є `5.0.x`, замініть `<x.y>` на `5.0` у двох наступних фрагментах коду.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Запустіть службу MongoDB на порті `27017` та налаштуйте її на автоматичний запуск після перезавантаження системи
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. Тепер ви можете отримати доступ до служби з Windows чи Ubuntu на `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Встановлення Node.js та pnpm
+
+Ми рекомендуємо встановити випуск LTS для Node.js за допомогою Node Version Manager ([nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating)).
+
+Як тільки його буде встановлено, використайте цю команду, щоб встановити та використовувати найновішу версію LTS Node.js:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+Для інструкцій з встановлення та використання іншої версії Node.js, будь ласка, зверніться до [документації nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js надходить разом з `npm`, який можна використати для встановлення `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Налаштуйте freeCodeCamp локально
+
+Ви встановили передумови, тому дотримуйтесь [нашого посібника з локального налаштування](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally), щоб клонувати, встановити та налаштувати freeCodeCamp локально на своїй машині.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Зауважте, що наразі налаштування тестів Cypress (та пов’язаних потреб GUI) знаходяться в стадії розробки. Ви повинні вміти працювати над більшою частиною кодової бази.
+
+## Оптимізуйте Windows та WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Наступні поради були зібрані з різних джерел і не пройшли високоякісне тестування. Ваш результат може відрізнятися.
+
+### Налаштування розкладу процесора для фонових служб
+
+Це може знизити випадки збоїв контейнерів Docker через брак ресурсів.
+
+Відкрийте панель керування системними налаштуваннями, натиснувши <kbd>Win + R</kbd> та ввівши `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Введіть <code>sysdm.cpl</code> у вікні діалогу (знімок екрану)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Введіть `sysdm.cpl` у вікні діалогу" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Перейдіть до Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Кнопка Performance Settings розташована під вкладкою Advanced в System Properties (знімок екрану)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Кнопка Performance Settings розташована під вкладкою Advanced в System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Під Advanced -> Processor scheduling, виберіть Background services. Не закривайте вікно. Перейдіть до наступної поради.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Радіокнопка Background services розташована під вкладкою Advanced в Performance Options (знімок екрана)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Радіокнопка Background services розташована під вкладкою Advanced в Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Збільшення розміру файлу сторінки Windows для системного диска
+
+Під Advanced -> Virtual memory, натисніть Change…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Кнопка Change virtual memory розташована під вкладкою Advanced в Performance Options (знімок екрану)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Кнопка Change virtual memory розташована під вкладкою Advanced в Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Виберіть Custom size. Встановіть початковий розмір на 1.5x та максимальний розмір на 3x від фізичної пам’яті. Потім натисніть Set.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Налаштування кнопки розміру у вікні Virtual Memory (знімок екрану)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Налаштування кнопки розміру у вікні Virtual Memory" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Збільшення обсягу пам’яті, виділеної для WSL
+
+Створіть файл [`.wslconfig`](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) у своєму каталозі [`%UserProfile%`](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (зазвичай `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Будь ласка, уважно прочитайте [документацію WSL](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) та замініть `x` на потрібні значення:
+
+```ini
+# Налаштування застосовуються до всіх дистрибутивів Linux, які працюють на WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# Кількість пам’яті, що призначається для віртуальної машини WSL 2. Значення за замовчуванням може бути недостатньо
+memory=xGB
+
+# На скільки збільшити swap-простір в WSL 2 VM; за замовчуванням це 25% від доступної оперативної пам’яті
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Збільшення максимального розміру старого простору Node.js
+
+Це виправляє помилку [«JavaScript heap out of memory»](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) з ESLint. Додайте наступне до `~/.bashrc` або `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Уникайте `pnpm run test`
+
+Натомість використайте скрипт, [який відповідає вашому PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.): `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum` або `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Корисні посилання
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) — стаття Мругеша Мохапатри (штатний розробник freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Часті питання:
+ - [Підсистема Windows для Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop для Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..56373755
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: How to Test Translations Locally
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] This process is not required, but documented in case you would like to preview what your translations will look like.
+
+If you would like to test your translations on a local instance of the freeCodeCamp `/learn` site, first ensure you have [set up the codebase](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` file to add the language to the available languages list and configure the values. There are four objects here.
+
+- `availableLangs`: For both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays, add the text name of the language. This is the value that will be used in the `.env` file later.
+- `auditedCerts`: Add the text name of the language as the _key_, and add an array of `SuperBlocks.{cert}` variables as the _value_. This tells the client which certifications are fully translated.
+- `i18nextCodes`: These are the ISO language codes for each language. You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `all-langs.js` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Next, open the `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts` file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Finally, in your `.env` file, set `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` to your new language (use the `availableLangs` value.)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## Enabling Localized Videos
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Loading Translations
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68c90a5b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: Як перекладати ресурси freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+## Приготуйтеся до своєї участі
+
+> Детальний план локалізації freeCodeCamp: жодних обмежень швидкості
+
+:::tip
+Ви можете почати з цього [оголошення](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). Ми рекомендуємо приєднатися до [форуму](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) та [чат-серверу Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+Ви можете перекладати скільки завгодно і коли завгодно. Єдине, що має значення — це скільки часу та сил ви готові приділити перекладу у ролі волонтера-перекладача.
+
+Будь ласка, ознайомтеся з наступним:
+
+1. **Переклад — це командна робота.**
+
+ Переклад ресурсів freeCodeCamp — один із найцікавіших та найцінніших досвідів. Ще краще, якщо ви залучаєте своїх друзів та колег, які говорять тією самою мовою, що і ви.
+
+ Ви можете почати з цього [оголошення](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). Але перш ніж розпочати перекладати, ми рекомендуємо приєднатися до [форуму](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) та [чат-серверу Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Завдяки Crowdin та іншим інструментам перекладати легко, але це однаково передбачає багато роботи.
+
+ Ми хочемо, щоб ви насолоджувалися внеском, який робите, але не вигорали та не втрачали інтерес.
+
+ Невелика група з 4-5 осіб — це хороші умови для початку. Згодом ви зможете залучити до команди ще більше друзів.
+
+2. **Функціонування мовних серверів коштує досить багато.**
+
+ На перший погляд не видно наскільки складним є технічний стек, але підтримувати роботу — досить дорого. Сюди входить надання додаткових серверів та виділення персоналу для догляду за ними.
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org прагне забезпечити їх безоплатно, однак нам потрібно надати пріоритет тим, хто найбільше їх потребує. Ми не хочемо закривати мовні сервери, якщо діяльність перекладу припиниться і зникне попит на певну мову.
+
+ Щодо перекладу навчальної програми: як тільки буде перекладено принаймні декілька сертифікацій, їх буде опубліковано на [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), а ви продовжуватимете перекладати інші сертифікації.
+
+ Наприклад, перш ніж представити нову мову, ми б хотіли мати перекладеними принаймні сертифікації front-end.
+
+3. **Але як щодо мов, яких немає на перекладацькій платформі?**
+
+ Ми переглянули нашу базу користувачів і додали 30+ найпоширеніших мов до списку дозволених мов на перекладацькій платформі. Деякі мови, такі як китайська та іспанська, вже опубліковані на **/learn**.
+
+ На жаль, наш список не містить сотень мов. Щодня ми отримуємо десятки запитів від учасників, які хочуть допомогти перекласти сайт своєю мовою.
+
+ Ми, безумовно, з нетерпінням чекаємо додавання до цього списку нових мов. Але, як ви вже здогадуєтесь, це здійсниться лише в тому випадку, якщо ми отримаємо достатній потенціал стосовно тієї мови.
+
+ Якщо ви хочете, щоб ми зарахували нову мову, радимо залучити до цього своїх друзів.
+
+ Якщо у вас є невелика група людей (принаймні 4-5), зацікавлених і відданих справі, ми можемо зв’язатись через дзвінок. Ми пояснимо всі деталі та ознайомимо з деякими інструментами й процесами.
+
+## Загальне про Crowdin
+
+Наша мрія — це надати навчальні матеріали незалежно від того, якою мовою ви розмовляєте. Аби впоратися із цією непростою задачею, ми інтегрували нашу відкриту базу коду та навчальної програми на інструмент для локалізації [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE] У нас інший інструмент та робочий процес для перекладу [публікацій](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). Якщо ви зацікавлені у перекладі публікацій, прочитайте [це оголошення](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) та зверніться до свого мовного керівника.
+
+Перекладацький процес поділяється на два основних:
+
+- **Переклад** файлів навчальної програми, документації та елементів інтерфейсу (кнопки, мітки тощо):
+
+ Перекладачі можуть долучитися до [нашої перекладацької платформи](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) та зробити свій внесок, перекладаючи 30+ доступними мовами.
+
+- **Редагування** перекладених текстів.
+
+ Редактори підтверджують, що переклади, запропоновані спільнотою, написані в одному стилі та не містять помилок. Тобто вони забезпечують високу якість перекладу. Зверніть увагу, що ми не використовуємо машинний переклад.
+
+> [!WARNING] Ми більше не використовуємо GitHub для перекладу файлів. Якщо ви вже перекладали раніше, перейдіть на нашу [перекладацьку платформу](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+## Початок роботи
+
+По-перше, привітайтесь у нашому [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Саме тут ми регулярно публікуємо оновлення щодо перекладу та відповідаємо на багато ваших запитань.
+
+Потім перейдіть на нашу [перекладацьку платформу](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) та увійдіть (якщо ви раніше не перекладали на цій платформі, потрібно створити новий обліковий запис).
+
+Ознайомтеся з детальним описом нижче, щоб розібратись з інструментами та робочим процесом.
+
+Щасливого перекладу!
+
+## Оберіть проєкт та файл
+
+На платформі ви побачите декілька «проєктів», доступних для перекладу:
+
+1. [Contributing documentation](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs), що містить файли з документацією сайту.
+2. [Coding Curriculum](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum), що містить файли із завданнями навчальної програми.
+3. [Learn User Interface](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui), що містить елементи інтерфейсу, як-от кнопки, мітки тощо.
+
+Виберіть будь-який проєкт, до якого ви хочете долучитися. Ви побачите список доступних мов для перекладу.
+
+
+
+Оберіть мову, над якою хочете працювати, і тоді побачите повне дерево файлів.
+
+
+
+Кожен файл і папка мають індикатор виконання. **Синя** частина індикатору показує відсоток файлу, який вже перекладено, а **зелена** — відсоток, який вже затверджено.
+
+Виберіть файл, після чого Crowdin відкриє редактор.
+
+> [!NOTE] Коли відкриється редактор, вам необхідно натиснути на значок налаштувань (зубчасте колесо) і встановити «HTML tags displaying» на «SHOW». Це допоможе бачити `<code></code>` замість `<0></0>`.
+
+## Перекладайте навчальну програму
+
+
+
+Crowdin розділяє документ на «рядки», зазвичай на речення. Кожен такий рядок перекладається окремо. Посилаючись на зображення вище:
+
+1. Рядок, виділений зеленим, вже має запропонований переклад.
+2. Рядок, виділений червоним, _не_ має запропонованого перекладу.
+3. Рядок з сірим текстом не перекладається. Цей стосується коду та іншого контенту, який не потрібно перекладати. Ви не зможете обрати ці рядки у редакторі.
+4. Якщо хтось вже запропонував переклад рядка, Crowdin зобразить всі варіанти тут. Ви не зможете зберегти ідентичний переклад. Проте, якщо ви бачите, що переклад точний, натисніть `+`, щоб проголосувати за нього. Якщо переклад неточний — можна проголосувати проти нього, натиснувши `-`.
+5. Crowdin пропонуватиме переклади на основі пам’яті перекладів (TM) або машинного перекладу (MT). Пам’ять перекладів посилається на схожі або ідентичні рядки, які вже перекладено/затверджено в інших файлах. Машинний переклад посилається на переклади, рекомендовані інтегрованою бібліотекою.
+6. Це вікно редактора, де ви можете писати переклад вибраного рядка.
+7. Поточний вибраний рядок в редакторі буде виділено жовтим кольором.
+8. Тут ви побачите теги, які вказують на статус рядка. `Done` означає, що рядок має принаймні один запропонований переклад. `Todo` означає, що рядок не має жодних запропонованих перекладів.
+9. Це вікно для коментарів. Якщо ви маєте запитання або зауваження щодо конкретного рядка, то можете залишити коментарі тут, щоб інші перекладачі могли їх бачити.
+10. Ці дві кнопки приховують ліве (документ) і праве (коментарі) вікна.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви бачите прихований рядок, який містить переклад, будь ласка, повідомте нам в [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), щоб ми видалили переклад з памʼяті.
+
+Коли ви завершили переклад рядка, натисніть `Save`, щоб зберегти переклад у Crowdin. Інші помічники зможуть проголосувати за ваш переклад, а редактори зможуть його затвердити.
+
+Ви можете перекласти стільки рядків, скільки вам завгодно: інші кроки від вас не вимагаються. Щоб зберегти переклад, потрібно тільки натиснути `Save`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви бачите якісь неточності в оригінальному файлі англійською мовою, будь ласка, не виправляйте їх у процесі перекладу. Натомість залиште коментар або створіть завдання на GitHub.
+
+## Перекладайте навчальний інтерфейс
+
+Наш інтерфейс `/learn` покладається на файли JSON, завантажені в плагін i18n, що створений для перекладеного тексту. Цей переклад розподілений між Crowdin та GitHub.
+
+### На GitHub
+
+Файли `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json` та `trending.json` містять інформацію, яку потрібно оновити на вашу мову. Однак ми не можемо завантажити їх у Crowdin, оскільки вони не є прямим перекладом.
+
+Ймовірно, за цими файлами слідкує мовний керівник. Але ви можете [прочитати, як їх перекладати](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### На Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Не редагуйте наведені нижче файли через GitHub PR.
+:::
+
+Обидва файли `intro.json` та `translations.json` перекладають у проєкті «Learn User Interface» на Crowdin. Перекласти їх може бути дещо складно, оскільки кожне значення JSON зображається як окремий рядок, а контекст іноді відсутній.
+
+Однак Crowdin може надати більше `контексту` про те, де вписується рядок.
+
+
+
+Якщо у вас є запитання щодо розташування рядка, напишіть нам у [чаті помічників](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Перекладайте документацію
+
+Переклад нашої документації схожий до перекладу файлів навчальної програми.
+
+> [!NOTE] Наша документація підтримує `docsify` та у нас є спеціальний аналіз для таких повідомлень. Якщо ви бачите рядки, які починаються з `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]` або `[!TIP]` — ці слова НЕ перекладаються.
+
+### Як перекладати документацію з внутрішніми посиланнями
+
+Коли ви працюєте над документацією, стежте за внутрішніми посиланнями, які спрямовані на інший розділ документації.
+
+Обов’язково замініть ідентифікатор цільового розділу (частина після `#`) на ідентифікатор перекладеного документа. Японською це буде виглядати так:
+
+До перекладу
+
+```
+// в HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// в Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Після перекладу
+
+```
+// в HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// в Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト]($1#$2)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+Файли в документації написані в Markdown, але на Crowdin вони будуть зображатися як теги HTML.
+
+Ви можете дізнатися, як `docsify` перетворює рядок вашою мовою на ідентифікатор, переглянувши перекладені сторінки. Якщо переклад ще не виконано, ви можете переглянути його, [запустивши сайт документації локально](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#serving-the-documentation-site-locally).
+
+Ви можете дізнатися більше про [внутрішні посилання в наших документах тут](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#how-to-create-an-internal-link).
+
+## Перекладайте рольову гру LearnToCode
+
+Рольова гра LearnToCode RPG працює на Ren'Py, який використовує спеціальний синтаксис для перекладених рядків (див. [Текстову документацію Ren'Py](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- Речення для перекладу завжди знаходиться між `""`. Це рядки діалогу або інтерфейсу користувача. Ключові слова, які йдуть до або після діалогу, є ключовими словами ігрового рушія та будуть детально пояснені в наступних правилах. Зауважте, що від першого правила відштовхуються всі інші.
+- У випадку `new "..."` не перекладайте ключове слово `new`.
+- Не потрібно перекладати префікси, як-от `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (або варіації `player happy`, `player @ happy`). Це контрольні ключові слова для правильного зображення спрайту персонажа в грі.
+- Не потрібно перекладати постфікси, як-от `nointeract`.
+- Не перекладайте текст між `[]` та `{}`. Це інтерполяції змінних та текстові теги. Вони мають залишатися дужками напівширини `[]` та `{}`, замість відповідників повної ширини `【】` та `「」`
+- Не перекладайте ключове слово `nointeract` у кінці речення.
+- Якщо ми спробуємо використати дужки повної ширини `()`, з’явиться попередження QA. Щоб уникнути попередження QA, використовуйте дужки напівширини `()`
+
+### Приклади
+
+---
+
+#### До перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- це рядок, який потрібно перекласти. дивіться переклад нижче
+```
+
+#### Після перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我们的VIP队友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}会很高兴的。"
+```
+
+Примітка: теги `[]` та `{}` повинні бути без змін.
+
+---
+
+#### До перекладу
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- перекладіть цей рядок, дивіться нижче
+```
+
+#### Після перекладу
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳过"
+```
+
+Примітка: префікс `new` та тег `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` повинні бути без змін.
+
+---
+
+#### До перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### Після перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定会喜欢你的开发者工作的。"
+```
+
+Примітка: `layla @ neutral` та `[player_name]` повинні бути без змін.
+
+---
+
+#### До перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### Після перекладу
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也许这都是一场梦?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### Примітка про те, як Crowdin ділить речення
+
+Зверніть увагу на те, як Crowdin ділить рядок діалогу в лапках `""`. При перекладі діалогу нам потрібно переконатися, що лапки збережені, навіть якщо вони з’являються в різних частинах.
+
+Цей рядок потрібно перекласти:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin ділить його на три частини, як показано нижче:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Знімок екрана 2022-01-23 о 10.36.43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# оригінал
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# перекладено, зберігаючи початкові лапки `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Знімок екрана 2022-01-23 о 10.36.49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# оригінал
+What is that?
+# перекладено, без лапок з обох сторін
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Знімок екрана 2022-01-23 о 10.36.54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# оригінал
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# перекладено, зберігаючи кінцеві лапки `"`
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## Оцінюйте переклади
+
+Crowdin дозволяє вам оцінювати вже запропоновані переклади. Якщо ви спробуєте зберегти переклад, ви можете побачити повідомлення, що його неможливо зберегти — це означає, що інший помічник запропонував ідентичний переклад. Якщо ви згідні з перекладом, натисніть `+`, щоб проголосувати «за» переклад.
+
+Якщо ви бачите переклад, який неточний або не передає суті рядка, натисніть `-`, щоб проголосувати «проти».
+
+Crowdin використовує ці голоси, щоб дати оцінку кожному запропонованому перекладу. Це допомагає команді редакторів визначити, який переклад найкраще підходить для кожного рядка.
+
+## Перевірка якості
+
+Ми дозволили деякі кроки щодо забезпечення якості, які підтверджують, що переклад є максимально точним — це допомагає нашим редакторам перевіряти запропоновані переклади.
+
+Якщо ви спробуєте зберегти переклад, ви можете побачити попереджувальне повідомлення щодо свого перекладу.
+
+
+
+Це повідомлення зʼявиться, коли система перевірки на якість виявить потенційну помилку в запропонованому перекладі. У прикладі ми змінили текст тегу `<code>` і Crowdin помітив помилку.
+
+> [!WARNING] Ви можете зберегти переклад, незважаючи на помилки. Якщо ви це зробите, клацнувши «Save Anyway», вам потрібно буде позначити редактора або менеджера, і пояснити чому у цьому випадку потрібно проігнорувати повідомлення.
+
+## Найкращі практики перекладу
+
+Дотримуйтеся цих правил, щоб впевнитись, що переклад якомога точніший:
+
+- Не перекладайте вміст тегів `<code>`. Ці теги позначають текст, який знаходиться в коді та повинен бути англійською мовою.
+- Не додавайте додаткового вмісту. Якщо вам здається, що завдання потребує змін в тексті або додаткової інформації, запропонуйте це через GitHub, що змінить англійський файл.
+- Не змінюйте порядок вмісту.
+
+Якщо ви маєте запитання, пишіть нам у [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) і ми будемо раді допомогти.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..41106b92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Як використовувати Docker на Windows Home
+---
+
+Є декілька підводних каменів, яких треба уникнути, коли налаштовуєте Docker на Windows Home. По-перше, ви маєте використовувати [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) як адміністратор. На жаль, Windows Home не підтримує Docker для робочого столу Windows, тому замість нього необхідно використовувати панель інструментів. Використайте роль адміністратора, оскільки при встановленні використовуються символічні посилання, які інакше створити неможливо.
+
+Після встановлення панелі інструментів запустіть термінал Docker Quickstart від імені адміністратора. Це створить віртуальну машину `default`, якщо вона ще не створена. Одразу після цього закрийте термінал та відкрийте VirtualBox (знову як адміністратор). Ви можете побачити машину `default`. Цей сайт є доволі ресурсомістким, тому зупиніть віртуальну машину і підвищте налаштування наскільки зможете — зокрема, пам’ять. Було підтверджено, що він працює з 4 ГБ оперативної пам’яті.
+
+Після того, як ви будете переконані, що Docker працює, скопіюйте репозиторій freeCodeCamp до `C:\Users`. Ці каталоги є загальними, надаючи Docker доступ до локальних каталогів, які йому необхідні під час встановлення.
+
+Якщо ви бачите такі повідомлення
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+коли використовуєте `pnpm run docker:init`, то це, ймовірно, є причиною помилки.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a81d8f4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: Як працювати над завданнями з кодом
+---
+
+Наша мета — розробити веселе та зрозуміле інтерактивне навчання.
+
+Розробити інтерактивні завдання для програмування — важко. Було б набагато простіше написати довге пояснення чи створити відеоурок. Але для нашої основної навчальної програми ми використовуємо те, що найкраще працює для більшості людей — інтерактив, схожий на відеогру.
+
+Ми хочемо, щоб кемпери досягли стану потоку. Ми хочемо, щоб вони наростили темп та пройшли навчальну програму з мінімальною кількістю помилок. Ми хочемо, щоб вони впевнено виконували проєкти та ознайомились з багатьма поняттями програмування.
+
+Зауважте, що для версії 7.0 навчальної програми freeCodeCamp ми переходимо до [проєктноорієнтованої моделі з багатьма повтореннями](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+Ці завдання вимагають креативності та уваги до деталей. Ви не залишитесь без допомоги. Вас підтримуватиме ціла команда помічників, з якими можна поділитись власними ідеями та завданнями.
+
+І як завжди, не соромтесь ставити запитання [на форумі у категорії «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+Завдяки вашій допомозі ми створюємо інтерактивну навчальну програму для програмування, що допоможе мільйонам людей навчитися писати код.
+
+Вміст кожного завдання зберігається у відповідному файлі markdown. Потім, щоб створити інтерактивну вебсторінку, цей файл конвертується у HTML за допомогою наших інструментів.
+
+Ви можете знайти весь навчальний матеріал freeCodeCamp.org у каталозі [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges).
+
+## Налаштування інструментів для навчальної програми
+
+Перш ніж працювати над навчальною програмою, потрібно налаштувати деякі інструменти, які допоможуть перевіряти ваші зміни. Ви можете використовувати будь-який варіант нижче:
+
+- Ви можете [налаштувати freeCodeCamp локально](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Це **рекомендовано** для регулярних/повторних внесків. Це налаштування дозволяє працювати над змінами та перевіряти їх.
+- Використовуйте безоплатне онлайн середовище Gitpod. Натисніть на кнопку нижче, щоб запустити готове середовище розробки для freeCodeCamp у своєму браузері. Це займе лише кілька хвилин.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### Як працювати над практичними проєктами
+
+Практичні проєкти мають деякі додаткові інструменти, які допомагають створити нові проєкти та кроки. Щоб дізнатися більше, див. [документацію](how-to-work-on-practice-projects).
+
+## Шаблон завдання
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Challenge Title'
+challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Текст інструкції тестів у markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+Тести для запуску коду користувача в поєднанні з текстом markdown та тестовим блоком коду.
+
+```js
+Код для першого тесту
+```
+
+Якщо вам потрібен динамічний вивід на основі коду користувача, --fcc-expected-- та --fcc-actual-- будуть змінені на очікувані та фактичні значення тестового припущення. Будьте обережними, якщо у вас є декілька припущень, оскільки перше невдале припущення визначить значення --fcc-expected-- та --fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Додаткова інформація щодо завдання у markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Код, перевірений перед кодом користувача.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Код, перевірений після коду користувача і перед тестами.
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Шаблонний код для відображення у редакторі. Цей розділ повинен містити код лише у зворотних лапках:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Розв’язки використовуються для тестів CI, щоб переконатись, що зміни до підказок працюватимуть як потрібно
+
+```js
+// перший розв’язок - мова має відповідати джерелу.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// другий розв’язок - тобто, якщо джерело написане на HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// третій розв’язок і т. д. - ваш розв’язок має бути на HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+Це покаже прапорець, де кемпери мають поставити галочку перед тим, як завершити завдання
+
+---
+
+Це покаже інший прапорець, де кемпери мають поставити галочку перед тим, як завершити завдання
+
+# --question--
+
+Наразі ці поля використовуються для завдань з Python з декількома варіантами відповіді.
+
+## --text--
+
+Запитання повинне бути тут.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Відповідь 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Тут буде зворотний зв’язок після того, як кемпери вгадають відповідь
+
+---
+
+Відповідь 2
+
+---
+
+Інші відповіді
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+Номер правильної відповіді знаходиться тут.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+Це стосується завдань для навчальної програми з вивчення англійської мови.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Тут написане речення з пропусками, які повинен заповнити користувач. Наприклад:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+Два знаки підкреслення відтворюватимуться як пропуски. Речення має знаходитись у зворотних лапках.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+Розв’язок для першого пропуску в реченні вище. Наприклад:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Зворотний зв’язок з’являється, якщо користувач ввів неправильну відповідь.
+
+---
+
+Розв’язок для другого пропуску. Наприклад:
+
+`right`
+
+Якщо зворотного зв’язку немає, з’явиться повідомлення «wrong answer».
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- може складатись лише з одного об’єкту json
+{
+ // Налаштуйте дію. Властивості, не позначені як додаткові, є обов’язковими.
+ "setup": {
+ // Файл фону, щоб запустити дію. Список всіх файлів можна знайти тут: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Масив всіх персонажів, які з’являться на місці дії
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Ім’я персонажа. Список доступних персонажів знаходиться в scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Де з’являється персонаж. Марія з’явиться на екрані ліворуч
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Том з’явиться на 70% ліворуч та буде в 1,5 рази більший за звичайний розмір.
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Необов’язково, за замовчуванням 1. Спочатку Том буде невидимим
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Секунди після початку дії до початку програвання аудіо
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Необов’язково. Часова мітка аудіофайлу, з якого він починає відтворюватися.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Необов’язково. Часова мітка аудіофайлу, з якого він перестає відтворюватися. Якщо ці мітки не використати, аудіофайл відтвориться повністю.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Необов’язково, за замовчуванням false. Використовуйте для довгих діалогів. Це призводить до того, що іконка доступності не відображається, що дає користувачам змогу показувати або приховувати текст діалогу
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Масив команд, з яких складається дія
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Персонаж, який виконує цю команду
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Необов’язково, за замовчуванням попереднє значення. Марія переміститься на 25% ліворуч від екрана. Переміщення триває 0,5 секунди
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // Коли розпочнеться команда. Нуль секунд після того, як користувач натисне програвання
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Необов’язково, за замовчуванням попереднє значення. Том з’явиться, розчиняючись. Перехід триває 0,5 секунди. Переміщення та непрозорість займають 0,5 секунди
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Том з’явиться на екрані через 0,5 секунди (одразу після того, як Марія завершить переміщення)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Коли розпочнеться команда, Марія почне вимовляти цей рядок через 1,3 секунди після початку. Зверніть увагу, що час той самий, що й для audio.startTime вище. Вони необов’язково збігатимуться (можливо, на початку аудіо є пауза чи щось інше)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Персонаж перестане рухати ротом на finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Текст, який з’явиться, якщо діалог видимий
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Вирівнювання тексту діалогу. Може бути 'left', 'center' або 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // фон зміниться на інший через 5,4 секунд від початку дії
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Текст Тома буде вирівняний за правим краєм, оскільки він розташований праворуч
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Том розчиниться
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // За бажанням можна переміщувати персонажів за межі екрану або розчинити їх через 0,5 секунди після останнього говоріння
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Марія переміститься ліворуч
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // Анімація припинить відтворення через 0,5 секунди після 'finishTime' останньої команди, або через 0,5 секунди після 'startTime', якщо 'finishTime' немає.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. Прикладами `lang` у прикладах вище є:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Нумерація завдань
+
+Кожне завдання вимагає `id`. Якщо ви не вкажете його, то MongoDB створить випадкове id, коли зберігатиме дані. Нам цього непотрібно, оскільки id завдань повинні бути послідовними у всіх середовищах (проміжному, робочому, розробницькому тощо).
+
+Щоб згенерувати id в оболонці (припускаючи, що MongoDB запущене окремо):
+
+1. Запустіть команду `mongo`.
+2. Запустіть команду `ObjectId()`.
+
+Наприклад:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+Результатом є новий id (наприклад, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` вище).
+
+Як тільки ви отримали id, розмістіть його у файлі markdown як поле `id` зверху, тобто
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Challenge Title
+```
+
+## Найменування завдань
+
+Давати назву — важко. Проте ми полегшили цей процес, впровадивши деякі обмеження.
+
+Усі назви завдань повинні бути чіткими та дотримуватись цього шаблону:
+
+\[дієслово\]\[підрядна частина\]
+
+Нижче подано декілька прикладів назв завдань:
+
+- Використайте запис за годинниковою стрілкою, щоб визначити відступ елемента
+- Стисніть масиви за допомогою .reduce
+- Використайте дужкову нотацію, щоб знайти перший символ у рядку
+
+## Опис/інструкції завдань
+
+Речення повинні бути зрозумілими і стислими, з мінімальною кількістю жаргону. Якщо жаргон все-таки був використаний, то його потрібно пояснити звичайною мовою.
+
+Надавайте перевагу коротким абзацам (1-4 речення). Найімовірніше, люди прочитають декілька коротких абзаців, а не суцільний текст.
+
+Використовуйте американську англійську. Наприклад, `labeled` замість `labelled`.
+
+У тексті завдання потрібно використовувати 2-гу особу множини («ви»). У такий спосіб текст та інструкції будуть звернені напряму до учня, який виконує завдання. Намагайтеся уникати звертань у 1-й особі, як-от «я», «ми», «нам».
+
+Не використовуйте зовнішні посилання. Вони переривають робочий процес. Учні не повинні використовувати гугл під час виконання завдань. Якщо є ресурси, які, на вашу думку, допоможуть учням, додайте їх до статті, пов’язаної з керівництвом до завдання.
+
+В разі потреби можна додати діаграми.
+
+Не використовуйте емоджі в завданнях. freeCodeCamp — глобальна спільнота, а значення емоджі може відрізнятись в різних частинах світу. Крім цього, емоджі можуть по-різному зображатися у різних системах.
+
+Власні іменники потрібно писати з великої літери, коли це можливо. Нижче поданий список, у якому показано, як повинні писатись слова в завданнях.
+
+- JavaScript (великі літери «J» і «S», без скорочень)
+- Node.js
+- Іноді потрібно вживати деякі неточні форми, як-от «back end» і «front end» без дефіса, оскільки таке вживання більш поширене.
+
+### Правило двох хвилин
+
+Кожне завдання повинне бути вирішене протягом 120 секунд носієм англійської мови, який виконав попередні завдання. У цей час входять прочитання вказівок/інструкцій для розуміння початкового коду, написання власного коду і проходження всіх тестів.
+
+Якщо виконання завдання займає більше двох хвилин, у вас є два шляхи:
+
+- Спростіть завдання, або
+- Розділіть завдання на два кроки.
+
+Завдяки правилу двох хвилин ви зробите лаконічні вказівки, зрозумілий початковий код та прості тести.
+
+Ми відстежуємо скільки часу займає розв’язок завдань та використовуємо цю інформацію, щоб виявити завдання, які потрібно спростити чи розділити.
+
+### Модульність
+
+Кожне завдання повинне навчати лише одному поняттю, і це поняття повинне бути очевидним з назви завдання.
+
+Ми можемо закріпити раніше вивчені поняття за допомогою повторення та варіацій. Наприклад, ознайомити користувача з елементами h1 в одному завданні, а пізніше з елементами h3.
+
+Наша мета — розробити тисячі двохвилинних завдань. Вони можуть йти нарівні, а також нагадувати про раніше вивчені поняття.
+
+### Форматування тексту завдання
+
+Тут подано конкретні рекомендації щодо форматування тексту завдання та приклади:
+
+- Ключові слова мови знаходяться у зворотних лапках `` \` ``. Наприклад, назви тегів HTML чи назви властивостей CSS.
+- Посилання на частини коду (тобто назви функцій, методів чи змінних) потрібно брати у зворотні лапки `` \ ```. Розгляньте приклад нижче:
+
+```md
+Використовуйте `parseInt`, щоб перетворити змінну `realNumber` в ціле число.
+```
+
+- Посилання на назви файлів чи шляхи директорій (тобто `package.json`, `src/components`) потрібно брати у зворотні лапки `` \` ``.
+- Перед блоками багаторядкового коду **має бути порожній рядок**. Наступний рядок повинен починатись з трьох зворотних лапок, після яких йде одна з [підтримуваних мов](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). Щоб закінчити блок коду, потрібно почати новий рядок, який має лише три зворотні лапки та **ще один порожній рядок**. Розгляньте приклад нижче:
+- Пробіл має значення у markdown, тому ми рекомендуємо зробити його видимим у редакторі.
+
+**Примітка:** якщо ви збираєтесь використовувати код прикладу в YAML, використовуйте `yaml` замість `yml` для мови справа від зворотних лапок.
+
+Нижче поданий приклад коду:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[ТУТ МІСЦЕ ДЛЯ ВАШОГО КОДУ]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Додаткова інформація у нотатках повинна бути оточена порожніми рядками та відформатована: `**Примітка:** Решта тексту примітки...`
+- Якщо потрібно написати декілька приміток, перерахуйте всі примітки в окремих реченнях, використовуючи такий формат: `**Примітки:** Текст першої примітки. Текст другої примітки.`
+- Використовуйте одинарні лапки там, де потрібно
+
+**Примітка:** Еквівалент _Markdown_ потрібно використовувати на місці тегів _HTML_.
+
+## Написання тестів
+
+Завдання повинні мати мінімальну кількість тестів, необхідних для підтвердження знань кемпера щодо певного поняття.
+
+Наша мета — пояснити поняття, описане в завданні, та перевірити, що його зрозуміли.
+
+Тести завдань можуть використовувати бібліотеки Node.js та Chai.js. Якщо необхідно, у змінній `code` можна отримати доступ до коду, створеного користувачами. Крім того, об’єкт `__helpers` надає декілька функцій, які полегшують процес написання тестів. Доступні функції визначені в [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts).
+
+## Форматування вихідного коду
+
+Ось вказівки для форматування вихідного коду завдань:
+
+- Використовуйте два пробіли для відступу
+- Інструкції JavaScript закінчуються крапкою з комою
+- Використовуйте подвійні лапки там, де потрібно
+
+### Коментарі вихідного коду
+
+У нас є [словник з коментарями](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json), який містить лише ті коментарі, які можна використовувати у вихідному коді. Використовуйте той самий регістр та інтервал, що в словнику коментарів. Не доповнюйте словник коментарів, не обговоривши з командою розробників.
+
+Використані коментарі повинні мати пробіл між символами коментаря та самим коментарем. Коментарі потрібно використовувати в міру. Намагайтесь писати опис чи інструкції завдання так, щоб уникнути використання коментаря у вихідному коді.
+
+Приклад дійсного однорядкового коментаря JavaScript:
+
+```js
+// Змініть код під цим рядком
+````
+
+Приклад дійсного коментаря CSS:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+Якщо завдання має лише одне місце, де потрібно змінити код, будь ласка, використайте коментарі з наступного прикладу, щоб проінформувати користувача, де потрібно внести зміни.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+Якщо завдання має декілька місць, де користувач повинен змінити код (наприклад, завдання з React)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Змініть код під цим рядком
+
+ // Змініть код над цим рядком
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Змініть код під цим рядком */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* змініть код над цим рядком */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Переклад коментарів початкового коду
+
+Існують окремі словники з коментарями для кожної мови. [Англійська версія словника з коментарями](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) є основою для перекладів іншомовних версій файлів. Китайська версія словника з коментарями буде розташована на `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Кожен словник складається з масиву об’єктів з унікальною властивістю `id` та властивістю `text`. Щоб охопити переклад англійського коментаря, потрібно змінювати лише `text`.
+
+Деякі коментарі можуть містити слова чи фрази, які не потрібно перекладати. Наприклад, назви змінних або власні назви бібліотек (як-от «React») не потрібно перекладати. Розгляньте приклад нижче. Слово `myGlobal` не потрібно перекладати.
+
+```text
+Оголосіть змінну myGlobal під цим рядком
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Ми працюємо над інтеграцією, щоб дозволити працювати над словником коментарів для i18n.
+
+## Підказки та розв’язки
+
+Кожне завдання має кнопку `Get a Hint` для того, щоб користувач отримав доступ до будь-яких підказок/розв’язків, які були створені для цього завдання. Підказки та розв’язки навчальної програми розташовані на [нашому форумі](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) у категорії `Guide`.
+
+Якщо ви виявили помилку в наявних підказках чи розв’язках, повідомте про це на форумі [у розділі «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors). Модератори й користувачі з 3-м рівнем довіри розглянуть коментарі та приймуть рішення щодо наданих вами змін.
+
+### Додавання нових тем для підказок чи розв’язків завдань
+
+Виконайте наступні кроки, щоб додати нову тему для підказок чи розв’язків завдань.
+
+1. Розпочніть з тих самих кроків для створення нової теми, але зверніть увагу на наступні щодо заголовка.
+2. Заголовок теми повинен починатись з `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:`, з’єднаного з назвою завдання навчальної програми. Наприклад, якщо завдання має назву `Chunky Monkey`, заголовком теми буде `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`.
+3. `camperbot` повинен бути власником цих тем/дописів, тому попросіть адміністратора змінити власника головного допису на `camperbot`.
+4. Після створення нової теми створюється id теми форуму. Він розташований в кінці URL-адреси теми форуму. Цей id потрібно додати до передмови файлу завдання за допомогою звичайного запиту на злиття, щоб кнопка `Get a Hint` посилалась на тему.
+
+### Вказівки щодо змісту тем підказок і розв’язків
+
+Пропонуючи розв’язок до теми завдання навчальної програми, потрібно додати повний код. Сюди входить весь вихідний код та будь-які зміни, необхідні для проходження тестів. Використовуйте цей шаблон для створення нових тем підказок/розв’язків:
+
+````md
+# Тут назва завдання
+
+---
+
+## Пояснення проблеми
+
+Тут узагальнюється те, що потрібно зробити (без повторення опису та/або інструкцій). Це додатковий розділ
+
+#### Релевантні посилання
+
+- [Текст посилання](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Текст посилання](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## Підказки
+
+### Підказка 1
+
+Тут підказка
+
+### Підказка 2
+
+Тут підказка
+
+---
+
+## Розв’язок
+
+<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Пояснення коду
+
+- Тут пояснення коду
+- Тут пояснення коду
+
+#### Релевантні посилання
+
+- [Текст посилання](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Текст посилання](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Тестування завдань
+
+Перш ніж [створити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request) для своїх змін, вам потрібно переконатись, що зроблені зміни не призводять до проблем у завданні.
+
+1. Запустіть нижчеподану команду з кореневого каталогу для того, щоб перевірити всі завдання
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. Щоб перевірити окреме завдання, використайте його id з цією командою
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. Ви можете перевірити блок або суперблок завдань за допомогою цих команд
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+Ви також можете перевірити завдання за заголовками, виконавши такі кроки:
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу `curriculum`:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Виконайте цю команду для кожного файлу завдання, до якого ви внесли зміни (замінивши `challenge-title-goes-here` на повну назву завдання):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> Ви можете встановити змінну середовища `LOCALE` у `.env` на мову завдань, які потрібно протестувати.
+>
+> Наразі прийнятними значеннями є `english` та `chinese` (`english` за замовчуванням).
+
+## Відкриття запиту на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Корисні посилання
+
+Створення та редагування завдань:
+
+1. [Види завдань](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) — що означають числові значення завдань (перелік).
+
+2. [Внесок до FreeCodeCamp: написання тестів до завдань ES6](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) — відео [Ітана Арровуда](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) про його внесок до старої версії навчальної програми.
+
+## Допоміжні скрипти
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> Якщо ви працюєте над покроковими завданнями, див. розділ щодо [роботи над практичними проєктами](how-to-work-on-practice-projects).
+
+Існує декілька допоміжних скриптів, які можна використовувати для завдань у блоці. Зверніть увагу, що ці команди потрібно виконувати у каталозі блоків. Наприклад:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Додати нове завдання
+
+Щоб додати нове завдання в кінці блоку, викличте скрипт:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+Це допоможе отримати інформацію про завдання та створити файл з завданням, оновивши файл `meta.json` новою інформацією про завдання.
+
+### Видалити завдання
+
+Щоб видалити завдання, викличте скрипт:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+Це допоможе обрати потрібне завдання, видалити файл та оновити файл `meta.json`, щоб видалити завдання з порядку.
+
+### Вставити завдання
+
+Щоб вставити завдання перед наявним завданням, викличте скрипт:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+Це допоможе отримати інформацію про нове завдання, а також про наявне завдання. Наприклад, якщо варіанти такі:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+Якщо оберете `b`, то новим порядком буде:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Оновити порядок завдань
+
+Якщо вам потрібно змінити порядок завдань вручну, викличте скрипт:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+Він проведе вас через інтерактивний процес, який допоможе впорядкувати завдання.
+
+## Розв’язання проблем розробки
+
+### Виявлено нескінченний цикл
+
+Якщо ви бачите цю помилку в консолі під час попереднього перегляду завдання:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+Це означає, що плагін для захисту циклу знайшов довгий цикл або рекурсивну функцію. Якщо ваше завдання передбачає їх (тобто містить нескінченний цикл), ви можете запобігти використанню плагіну в попередньому перегляді. Для цього додайте `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` до файлу блоку `meta.json`.
+
+Якщо ваші тести інтенсивно обчислюються, ви можете побачити цю помилку під час запуску. Якщо це відбувається, додайте `disableLoopProtectTests: true` до файлу блоку `meta.json`.
+
+Значенням обох необов’язково має бути true, тому налаштовуйте їх лише за потреби.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6fb446e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: Як працювати над локалізованим клієнтським вебзастосунком
+---
+
+Клієнтський вебзастосунок на основі React, який забезпечує роботу нашої навчальної платформи, побудований за допомогою Gatsby. Він перекладений різними мовами світу, використовуючи [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) та [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+Ви можете дізнатись більше про локальне налаштування клієнтського застосунку, дотримуючись [цього посібника](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). Застосунок доступний лише англійською за замовчуванням.
+
+Як тільки ви налаштували проєкт локально, дотримуйтесь цієї документації, щоб запустити клієнта потрібною мовою зі списку доступних мов.
+
+Це може бути корисно, якщо ви працюєте над функціональністю, яка конкретно націлена на щось, що передбачає локалізацію та вимагає, наприклад, підтвердження кнопки з надписом іншою мовою.
+
+:::tip
+Вам не потрібно дотримуватись цього документу для перекладу навчальної програми чи документації freeCodeCamp. Натомість див. [цей посібник](how-to-translate-files).
+:::
+
+З’ясуємо, як працюють фреймворки та інструменти i18n.
+
+## Структура файлів
+
+Більшість файлів для перекладу платформи розташовані у папці [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n). Для кожної мови є каталог, що містить файли JSON з перекладами.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Деякі з цих файлів перекладаються на нашій перекладацькій платформі (Crowdin), а інші перекладені чи створені через PR на GitHub.
+
+**Файли, перекладені на нашій перекладацькій платформі:**
+
+- Файл `translations.json` містить більшу частину тексту, який з’являється на елементах інтерфейсу користувача. Для отримання потрібного тексту встановленої мови у кодовій базі використовуються ключі. Цей файл повинен містити одинакові ключі в усіх мовах.
+
+- Файл `intro.json` містить пари ключ-значення для вступного тексту на сторінках сертифікації.
+
+ Якщо ви хочете додати/оновити переклад для ключів, див. [цей посібник](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Файли, НЕ перекладені на нашій перекладацькій платформі:**
+
+- У файлах `motivation.json` не обов’язково повинні бути однакові цитати, вербальне оцінювання чи довжина масивів. Лише однакова структура JSON.
+
+- Файл `meta-tags.json` містить інформацію про наш вебсайт для метатегів.
+
+ Зазвичай ці файли змінює персонал. Якщо ви помітили щось незвичне, ми радимо зв’язатися з нами у [чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Тестування клієнтського застосунку світовою мовою
+
+Ви можете протестувати клієнтський застосунок будь-якою мовою [зі списку `availableLangs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+Якщо ви тестуєте нову мову, створіть папку під назвою мови поряд з іншими мовами та скопіюйте файли JSON з іншої мови до нової папки.
+
+Додайте нову мову до запису `Languages` та масиву `client` зверху файлу [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+Потім дотримуйтесь інструкцій з коментарів того ж файлу, щоб при потребі додати/оновити решту змінних.
+
+Вкінці налаштуйте змінну `CLIENT_LOCALE` у файлі `.env` на рядок потрібної локалі із запису `Languages` у файлі вище.
+
+## Як структурувати компоненти
+
+Дотримуйтесь нижчеподаних вказівок, якщо працюєте над функціональністю чи помилкою клієнтського вебзастосунку (наприклад, додаєте елементи інтерфейсу користувача на сторінці налаштувань). Вони допоможуть підготувати компоненти для локалізації усіма підтримуваними мовами світу.
+
+### Функціональний компонент
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// у методі render:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// виклик функції «t» з ключем із файлу JSON:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // детальніше нижче
+```
+
+### Класовий компонент
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation додає функцію «t» до пропсів:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// виклик функції «t» з ключем із файлу JSON:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // детальніше нижче
+
+// експорт без redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// або з redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Переклад із використанням функції «t»
+
+### Звичайний переклад
+
+```js
+// у компоненті:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// у файлі JSON:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// вивід:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### З динамічними даними
+
+```js
+// у компоненті:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// у файлі JSON:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// вивід:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+Приклад вище передає об’єкт до функції `t` зі змінною `username`. Змінна буде використана у значенні JSON, де є `{{username}}`.
+
+## Переклад із компонентом `Trans`
+
+Загальне правило: використовуйте функцію «t», коли можете. Якщо того недостатньо, існує компонент `Trans` (зазвичай потрібен тоді, коли у тексті наявні вбудовані елементи). Ви можете використовувати компонент `Trans` з будь-яким типом компонента react.
+
+### Звичайні вкладені елементи
+
+```js
+// у компоненті:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// у файлі JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// вивід:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+Ви можете розміщувати ключі всередині тегів компоненту, як у прикладі вище, якщо текст містить «прості» теги без атрибутів. До тегів за замовчуванням належать `br`, `strong`, `i` та `p`, але цей список може бути більшим у конфігурації і18n.
+
+### Складні вкладені елементи
+
+В інших випадках ви захочете розмістити певний текст всередині іншого елемента. Тег посилання є хорошим прикладом:
+
+```js
+// у компоненті:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// у файлі JSON:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// вивід:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+У прикладі вище ключ розміщений в атрибутах компонента `Trans`. `<0>` та `</0>` у JSON представляють перший дочірній елемент компонента (у цьому разі елемент посилання). Якщо існує більше дочірніх елементів, то вони просто перераховуються, використовуючи такий самий синтаксис. Ви можете знайти дочірні елементи компонента в інструментах розробки react. `placeholder` наявний лише через те, що лінтер жалівся щодо порожніх елементів `<a>`.
+
+### Зі змінною
+
+```js
+// у компоненті:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// у файлі JSON:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// вивід:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+У прикладі вище ключ та змінна розміщені в атрибутах компонента `Trans`. `{{ email }}` також повинен знаходитись у компоненті `Trans`, незалежно де саме.
+
+## Зміна тексту
+
+Щоб змінити текст клієнтської частини, перейдіть до відповідного файлу `.json`, знайдіть ключ, який використовується у компоненті React, та змініть його значення на новий текст. Шукайте цей ключ у кодовій базі, щоб переконатися, що він не використовується в іншому місці. Якщо використовується, переконайтесь, чи є сенс застосовувати зміни.
+
+Запустіть `pnpm run clean-and-develop`, щоб застосувати зміни.
+
+## Додавання тексту
+
+Якщо текст, який ви хочете додати до клієнта, існує у відповідному файлі `.json`, використовуйте наявний ключ. В іншому випадку створіть новий ключ.
+
+Файл англійською мовою є «джерелом правди» для всіх файлів `.json` з однаковою назвою. Якщо вам потрібно додати новий ключ, додайте його там. Потім додайте цей ключ до **усіх** файлів `translations.json`.
+
+> [!NOTE] Використовуйте англомовний текст для усіх мов, якщо файл перекладається на Crowdin. Якщо ви цього не зробите, тести не пройдуть.
+
+Також було б добре тримати усі ключі в одному порядку для усіх файлів. Спробуйте розставити всю пунктуацію, інтервали, лапки тощо у файлах JSON, а не у файлах компонента чи сервера.
+
+> [!NOTE] Підкреслення (`_`) є зарезервованим знаком для ключів у файлах клієнтської частини. Див. [документацію](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) про те, як вони використовуються.
+
+Запустіть `pnpm run clean-and-develop`, щоб застосувати зміни.
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Корисна документація
+
+- [Документація react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [Документація i18next](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c39f1f75
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: Робота над практичними проєктами
+---
+
+Для практичних проєктів ми використовуємо покроковий підхід, щоб кемпери вивчили основи. Проєкт складається з декількох файлів, які ми називаємо **кроками**. Ці файли називаються ідентифікаторами завдання, щоб уникнути проблем із перекладом. На жаль, через це важко знайти файл, пов’язаний з певним кроком.
+
+Ми створили редактор завдань, який допомагає розв’язати цю проблему. Цей інструмент дозволяє орієнтуватись на доступні проєкти та кроки (за порядком). Існує також вбудований редактор коду, який можна використовувати для безпосередньої роботи з файлами.
+
+## Використання редактора завдань
+
+У цих інструкціях ви дізнаєтесь, як працювати над практичними проєктами за допомогою нашого редактора завдань.
+
+### Запуск редактора
+
+Щоб запустити редактор, переконайтесь, що знаходитесь у кореневому каталозі freeCodeCamp. Потім запустіть `pnpm run challenge-editor`, щоб запустити клієнта та API, який підтримує редактор.
+
+Клієнт запуститься через порт `3300`, тому доступ можна отримати на `http://localhost:3300`. API запуститься через порт `3200`, щоб уникнути конфліктів з навчальним клієнтом та сервером. Це дозволить запустити програму freeCodeCamp одночасно з редактором, щоб ви могли перевірити свої зміни локально.
+
+### Навігація по редактору
+
+За замовчуванням ви побачите доступні `superblocks` — це сертифікації. Натисніть посилання сертифікації, над якою хочете працювати.
+
+Ви перейдете до списку блоків. Це практичні проєкти. Натисніть посилання проєкту, над яким хочете працювати.
+
+Ви перейдете до списку кроків проєкту. Якщо ви працюєте над наявним кроком, можна натиснути посилання кроку, щоб відкрити редактор. Якщо ви додаєте чи вилучаєте кроки, натисніть посилання `Use the step tools`, щоб перейти до інструментів для цього завдання.
+
+### Редагування кроків
+
+Якщо натиснути на крок, ви перейдете до редактора. Це базовий текстовий редактор, який пропонує підсвічування синтаксису.
+
+Після того, як ви застосували зміни, натисніть кнопку `Save Changes`, щоб зберегти зміни. Ви отримаєте сповіщення браузера про те, що ваші зміни готові до внесення. Зауважте, що вам потрібно буде вручну використати `git` для зміни та внесення файлів — інструмент не зробить цього.
+
+### Інструменти для кроків
+
+Якщо натиснути посилання `Use the step tools`, ви перейдете до сторінки з інструментами кроку. Це дозволить додавати чи вилучати кроки проєкту.
+
+#### Створення наступного кроку
+
+Натисніть цю кнопку, щоб додати новий крок в кінці проєкту. У цьому кроці використовуватиметься код попереднього кроку як зразок.
+
+#### Створення порожнього кроку
+
+Введіть кількість кроків, які хочете додати. Потім натисніть кнопку, що створить задану кількість кроків в кінці проєкту.
+
+#### Додавання кроку
+
+Введіть номер кроку, який хочете додати. Потім натисніть кнопку `Insert Step`, щоб додати крок. Порядок наступних кроків буде змінено.
+
+#### Видалення кроку
+
+Введіть номер кроку, який хочете видалити. Потім натисніть кнопку `Delete Step`, щоб видалити крок. Номери наступних кроків автоматично оновляться.
+
+#### Оновлення заголовків кроку
+
+Використовуйте цей інструмент лише тоді, коли додали чи вилучили крок вручну. Цей інструмент змінить порядок номерів кроків.
+
+## Використання скриптів вручну
+
+Якщо ви хочете працювати над кроками вручну у локальному IDE, ви можете запустити скрипти керування кроками.
+
+Папка `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` містить інструменти, які допоможуть зі створенням та обслуговуванням проєктноорієнтованої навчальної програми freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Створіть новий проєкт
+
+Змініть каталог на `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` та запустіть `pnpm run create-project`. Ця команда відкриє інтерфейс командного рядка, який допомагатиме. Після цього в англомовній навчальній програмі має з’явитися нове завдання, яке можна використовувати як перший крок проєкту. Наприклад, якщо ви створили проєкт під назвою `test-project` у сертифікації з адаптивного вебдизайну, завдання з’явиться у `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+Якщо ви хочете створити нові кроки, наступні інструменти допоможуть.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+Це разовий скрипт, який автоматично додасть наступний крок на основі останнього кроку проєкту. Початковий код завдання використовуватиме початковий код попереднього кроку.
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+Це разовий скрипт, який автоматично додасть вказану кількість кроків. Початковий код буде порожнім для всіх створених кроків.
+
+**Примітка:** цей скрипт також запускає [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # де X є кількістю кроків, які потрібно створити.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+Це разовий скрипт, який автоматично додає новий крок у визначеному місці, збільшуючи наступні кроки (їхні заголовки та meta.json). Початковий код завдання використовуватиме початковий код попереднього кроку, вилучивши маркери редагованих регіонів (ERM).
+
+**Примітка:** цей скрипт також запускає [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # де X є місцем, куди потрібно вставити новий крок.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+Це разовий скрипт, який видаляє наявний крок, зменшуючи наступні кроки (їхні заголовки та meta.json)
+
+**Примітка:** цей скрипт також запускає [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # де X є номером кроку, який потрібно видалити.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+Це разовий скрипт, який автоматично оновлює початковий матеріал у файлах розмітки проєкту, щоб вони відповідали meta.json. Він гарантує, що заголовки кроків (та dashedName) відповідають `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+Разовий скрипт, щоб проаналізувати назви кроків проєкту та оновити порядок meta.json, щоб відповідати цим крокам. Корисно, якщо ви випадково втратили зміни файлу meta.json, коли додавали чи видаляли кроки.
+
+#### Як запустити скрипт
+
+1. Перейдіть до каталогу проєкту.
+2. Виконайте наступну команду:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5ee19f99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Як працювати над компонентною бібліотекою
+---
+
+Ласкаво просимо до бібліотеки freeCodeCamp `ui-components`. Переважно компоненти побудовані з нуля завдяки базовим елементам HTML та [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp використовує компоненти Bootstrap в UI. Однак ми віддаляємось від цього та будуємо власну компонентну бібліотеку, яка допоможе стандартизувати наші шаблони UX/UI та покращити доступність. Проєкт відстежується у [цьому завданні на GitHub](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+Для роботи над новим компонентом рекомендовані наступні кроки:
+
+- Дослідження та планування
+- Реалізація компонента
+- Показ сценаріїв використання на Storybook
+- Написання модульних тестів
+
+## Дослідження та планування
+
+Перед побудовою компонента вам потрібно дослідити та задокументувати поведінку й вигляд поточної версії, щоб переконатись, що нова версія відповідатиме стилю та підтримуватиме усі поточні використання. Щоб відповідати вимогам доступності мережі, також звертайте увагу на аспекти доступності компонента, перегляньте, які елементи HTML та атрибути ARIA використовуються під капотом.
+
+Як тільки ви зібрали достатньо інформації про компонент, можна почати думати про інтерфейс властивостей. В ідеалі інтерфейс повинен бути максимально схожим до поточної версії, щоб полегшити майбутнє впровадження. Оскільки ми використовуємо компоненти Bootstrap, найпростіший спосіб — імітувати [їхню реалізацію](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+Ми надаємо перевагу коротким запитам на злиття, оскільки вони пришвидшують час на перегляд та зменшують когнітивне навантаження на рецензентів. З цієї причини подумайте, як би ви розбили реалізацію та розробили план доставки.
+
+Ми рекомендуємо відкривати окреме завдання на GitHub для кожного компонента та додавати всі нотатки в опис завдання. Його можна використовувати як місце для розміщення всіх робочих нотаток, а також як спосіб донести свій підхід до рецензентів. За потреби ми використаємо тред завдання для подальшого обговорення. [Завдання для компонента Button](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) можна використати як зразок.
+
+## Реалізація компонента
+
+Новий компонент можна створити за допомогою наступної команди з кореневого каталогу:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+Всередині каталогу `ui-components` команда згенерує папку з наступними файлами:
+
+| Назва файлу | Призначення |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | Використовується для експорту компонента та його типів. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | Використовується для демонстрації компонента на Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | Тестовий файл. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | Місце реалізації компонента. |
+| `types.ts` | Місце розташування інтерфейсу та типів компонента. |
+
+Кожен компонент відрізняється, але загалом він повинен:
+
+- Підтримувати перенаправлення ref
+- Бути стилізованим для світлої та темної тем
+- Бути внутрішньо стилізованим на основі своїх властивостей (споживачам не знадобиться ще раз стилізувати компонент за допомогою властивості `className`)
+- Використовувати вбудовану систему стилізації з Tailwind замість власних стилів
+
+### Використання кольорів
+
+У компонентній бібліотеці є два «шари» кольорів:
+
+- Базовий шар, де назви кольорів описують колір, тобто `gray00`, `blue50`
+- Семантичний шар, де назви кольорів описують для чого використані кольори, тобто `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Під час використання кольору в компоненті варто надавати перевагу семантичним змінним. Однак бувають винятки, особливо коли ви стилізуєте стани компонента (hover, active, disabled тощо). У таких випадках ми рекомендуємо використовувати базові змінні, а не створювати семантичні змінні, оскільки кожен компонент може мати різні стилі для своїх станів.
+
+> [!NOTE] Визначення кольору можна знайти у файлі [`colors.css`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). Колір доступний для використання лише якщо його додано до [ файлу `tailwind.config.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) під властивістю `colors`.
+
+### Корисні посилання
+
+- [Конфігурація CSS Tailwind](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [Документація React Bootstrap v0.33](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Таблиця стилів Bootstrap 3.3.7](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [Поточне впровадження React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [Поточні тести React Bootstrap](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Показ сценаріїв використання на Storybook
+
+Сценарії використання компонентів потрібно додати до файлу Storybook (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+Щоб запустити Storybook, виконайте наступну команду з кореневого каталогу:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+Сторінка Storybook доступна на [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Написання модульних тестів
+
+Ми використовуємо [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) для написання модульних тестів. Тести повинні підтверджувати, що компоненти поводяться як потрібно та є доступними.
+
+Щоб запустити тести компонентної бібліотеки, виконайте наступну команду з кореневого каталогу:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Додавання пакетів до компонентної бібліотеки UI
+
+Ми обмежуємо додавання нових пакетів до компонентів UI, щоб допомогти з обслуговуванням проєкту. За рідкісних випадків, якщо на вашу думку потрібна залежність, будь ласка, обговоріть це зі спеціалістом з обслуговування та використайте наступну команду, щоб додати пакет:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Корисні посилання
+
+- [Тестування доступності](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Черговість запитів React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Часті помилки при роботі з React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..410d2bb8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: Як працювати над документацією
+---
+
+## Робота над вмістом документації
+
+Щоб працювати над рекомендаціями щодо внеску, ви можете редагувати або додавати файли в каталозі `docs`, [доступному тут](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). Коли ваші зміни об’єднані, вони будуть автоматично доступними на документаційному сайті.
+
+Подумайте, чи потрібно додавати файл до бічної панелі навігації, коли додаєте новий файл до каталогу `docs`. Зазвичай ми створюємо посилання у файлі [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) для нових та незалежних посібників. Крім того, ви можете дотримуватись наведених нижче інструкцій для створення внутрішнього посилання для допоміжних посібників.
+
+### Як створити внутрішнє посилання
+
+Якщо ви хочете створити внутрішнє посилання, націлене на інший розділ рекомендацій щодо внеску, використовуйте цей формат:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// Якщо цільовий розділ знаходиться на тій же сторінці, ви можете опустити назву файлу
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Не забудьте додати розширення файлу (`.md`). Не вказуйте повну URL-адресу та не додавайте `/` перед назвою файлу.
+
+Це важливо для того, щоб посилання працювали для перекладеної версії документа. В іншому випадку вони перенаправлятимуть на англійську версію сторінки, незалежно від мови.
+
+#### Переклад документації з внутрішніми посиланнями
+
+Коли ви працюєте над перекладом документації на Crowdin, не забудьте змінити `#target-section-heading-id` на ідентифікацію в перекладеному документі. [Дізнатись більше про переклад документації](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Робота над темою документації
+
+> [!NOTE] Коротке нагадування, що вам не потрібно нічого налаштовувати для роботи над вмістом документації.
+>
+> Щоб працювати над рекомендаціями щодо внеску, див. [робота над вмістом документації](#work-on-the-docs-content).
+
+### Структура вебсайту документації
+
+Сайт створений з використанням [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) та обслуговується завдяки GitHub Pages.
+
+Зазвичай вам не потрібно буде змінювати конфігурації або створювати сайт локально. Якщо ви зацікавлені, це працює ось так:
+
+- Джерело домашньої сторінки для цього сайту доступне в [`docs/index.html`](index.html).
+- Ми обслуговуємо цей файл як SPA, використовуючи `docsify` та GitHub Pages.
+- Скрипт `docsify` генерує вміст файлів `markdown` в каталозі `docs` за запитом.
+- Домашня сторінка генерується з [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage).
+- Бічна панель навігації генерується з [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Обслуговування документаційного сайту локально
+
+Налаштуйте freeCodeCamp локально ([див. посібник з локального налаштування](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)). Ми зібрали CLI з інструментами веброзробки, щоб ви могли запустити будь-яку з наведених нижче команд з кореня репозиторію:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> Сайт документації повинен бути доступним на <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Запропонуйте запит на злиття (PR)
+
+Як тільки ви затвердили свої зміни, див. [як відкрити запит на злиття](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9a8ad624
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: How to work on freeCodeCamp.org's developer news theme
+---
+
+The developer news also known as [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) site is powered by [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). We use a custom theme for the look and feel of the site. The source code of the theme is available here: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## The Theme
+
+Ghost uses a simple templating language called [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) for its themes. The theme used on `/news` is based off of the default [casper theme](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
+
+The default theme is commented pretty heavily so that it should be fairly easy to work out what's going on just by reading the code and the comments. Once you feel comfortable with how everything works, Ghost also has a full [theme API documentation](https://themes.ghost.org) which explains every possible Handlebars helper and template.
+
+**The main files are:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - The main template file
+- `index.hbs` - Used for the home page
+- `post.hbs` - Used for individual posts
+- `page.hbs` - Used for individual pages
+- `tag.hbs` - Used for tag archives
+- `author.hbs` - Used for author archives
+
+One really neat trick is that you can also create custom one-off templates just by adding the slug of a page to a template file. For example:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Custom template for the `/about/` page
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Custom template for `/tag/news/` archive
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Custom template for `/author/ali/` archive
+
+## Development
+
+1. Get Ghost installed locally.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Note: Currently freeCodeCamp uses Ghost version `2.9.0`, so make sure you are using a version higher than that.
+
+ Be sure to run `ghost` commands from the `ghost-local-site` directory. Follow additional instructions on [Ghost's official documentation](https://docs.ghost.org) if are not familiar with its interface.
+
+2. Fork and clone the repository in your theme directory (replacing `YOUR_USERNAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Make sure you have all the pre-requisites.
+
+ The theme styles are compiled using Gulp/PostCSS to polyfill future CSS spec. You'll need [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Make sure that your Node.js version is compatible with `ghost`.
+
+4. Install dependencies and develop the theme
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Now you can edit `/assets/css/` files, which will be compiled to `/assets/built/` automatically.
+
+6. Access the development site.
+
+ a. Enter `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` into your address bar. Continue with the setup prompted on the page (if running ghost for the first time).
+
+ b. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Restart Ghost, on a separate terminal once to ensure the theme is available.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Once you've done this, go to `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` and scroll to the bottom. Make sure you click activate on the `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Zip the final code and make a pull-request
+
+ The `zip` Gulp task packages the theme files into `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, which we can then upload to the production site.
+
+ When you make a PR, please make sure you have run the below script prior to commiting the code and sending a PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Other Reference and resources
+
+### PostCSS Features Used
+
+- Autoprefixer - Don't worry about writing browser prefixes of any kind, it's all done automatically with support for the latest 2 major versions of every browser.
+- Variables - Simple pure CSS variables
+- [Color Function](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### SVG Icons
+
+The theme uses inline SVG icons, included via Handlebars partials. You can find all icons inside `/partials/icons`. To use an icon just include the name of the relevant file, eg. To include the SVG icon in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - use `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+You can add your own SVG icons in the same manner.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..df7c3b42
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+На цій сторінці описано, як зробити внесок до матеріалів та проєктів freeCodeCamp, які використовують розширення CodeRoad VS Code.
+
+## Як працюють матеріали
+
+Кожен матеріал freeCodeCamp, який використовує CodeRoad, має власний репозиторій в рамках організації freeCodeCamp GitHub. Всі вони починаються з `learn-`. Наприклад, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Кожен репозиторій матеріалу має гілку `main` та гілку «версії», тобто `v1.0.0`.
+
+Двома основними файлами на гілці `main` є `TUTORIAL.md` та `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` містить усі інструкції, підказки, заголовки і т. д. для даного матеріалу. `coderoad.yaml` містить інструкції для CodeRoad, наприклад, які команди виконувати й коли, у яких файлах відстежувати зміни, і яку гілку версії використовувати для кроків.
+
+Гілка «версії» містить затвердження, які будуть завантажені на кожному кроці матеріалу. Повідомлення затверджень у цій гілці повинні бути особливими. Перше затвердження має складатися з текстового повідомлення `INIT` та містити всі файли, які необхідно завантажити перед першим уроком.
+
+Послідовні повідомлення затверджень мають відповідати номеру кроку в `TUTORIAL.md` з гілки `main`. Наприклад, затвердження з повідомленням `10.1` буде завантажено тоді, коли користувач перейде до кроку `10.1`.
+
+Щоб внести зміни до затверджень на гілці версії, потрібно перебазувати та відредагувати ті затвердження, які хочете змінити. Це перепише історію Git, тому ми не можемо приймати PR до гілок цього типу. Гілку версії не можна змінювати, як тільки вона з’явиться на репозиторії freeCodeCamp.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Ніколи не вносьте чи затверджуйте зміни до гілки версії, яка розташована на одному з репозиторіїв freeCodeCamp. Завжди створюйте нову
+
+## Як зробити внесок
+
+### Передумови
+
+Встановіть [інструменти CodeRoad CLI](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) за допомогою `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+З останньою версією виникали деякі проблеми. Якщо `coderoad --version` не працює після налаштування, перейдіть на версію `0.7.0` за допомогою `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Робота на `main`
+
+Ці інструкції призначені для PR, які вносять незначні зміни на `main` до **наявних уроків**. Зазвичай це друкарські й граматичні помилки, підказки, інструкції та виправлення у файлі `TUTORIAL.md`.
+
+Для всього іншого, включно з додаванням чи видаленням уроків, див. [інструкцію з роботи над гілкою версії](#working-on-version-branch). Вам не потрібно створювати нову гілку версії — просто створіть PR, дотримуючись інструкцій нижче.
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> Ці зміни використовуватимуть наявну гілку версії. Якщо це значні зміни, їх можна додати до `CHANGELOG.md`. У більшості випадків достатньо хорошого повідомлення затвердження
+
+Ніколи не змінюйте файл `tutorial.json` напряму. Це виконується за допомогою інструментів CLI.
+
+Якщо ви вносите незначні зміни (наприклад, виправляєте друкарську чи граматичну помилку), їх необов’язково перевіряти.
+
+Дотримуйтесь цих інструкцій, щоб створити PR (пам’ятайте, що зазвичай інструкції використовують уроки навколо себе для контексту):
+
+- Створіть копію останньої гілки версії за допомогою `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`. Цю гілку не потрібно перевіряти, вона має існувати.
+- Створіть та перевірте нову гілку від `main`
+- Внесіть **та затвердьте** зміни. Нагадування: нічого не змінюйте у файлі `tutorial.json`. Найімовірніше, вам потрібно внести зміни лише до `TUTORIAL.md`
+- Запустіть `coderoad build`, щоб повторно створити файл `tutorial.json`
+- Затвердьте зміни з `update json` як повідомленням
+- Створіть PR
+
+### Тестування змін на `main`
+
+Якщо після інструкцій вище ви хочете перевірити зміни, внесені до `main`, дотримуйтесь цього:
+
+- Виконайте інструкції з [репозиторію rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha), щоб запустити контейнер
+- Запустіть матеріал, використовуючи файл `tutorial.json` на новій гілці
+
+### Перевірка PR до `main`
+
+Якщо ви переглядаєте PR, який містить граматичні чи інструкційні зміни до `main`, як описано вище, зміни у `TUTORIAL.md` мають відповідати змінам у `tutorial.json`.
+
+Файл `tutorial.json` не повинен містити змін хешів затвердження чи ідентифікаторів кроків/рівнів. Також не варто змінювати команди запуску/рівня або наглядачів за файлами. Бувають винятки, якщо наявні проблеми з кроком, але до них потрібно ставитись обережно.
+
+Також майте на увазі, що інструкції часто використовують уроки навколо себе для контексту, тому переконайтеся, що вони зрозумілі.
+
+### Робота над гілкою версії
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Нагадування: ніколи не вносьте чи затверджуйте зміни до гілки версії, яка розташована на одному з репозиторіїв freeCodeCamp. Завжди створюйте нову
+
+Ви не зможете побачити зміни між гілками версій, оскільки історія Git буде переписана. Ретельно розглядайте та тестуйте нові гілки версій перед їх прийняттям для використання.
+
+Ці інструкції призначені для змін на гілці версії, тобто тестів, тексту тестів, скидання файлів, додавання та видалення кроків тощо.
+
+Дотримуйтесь цих інструкцій, щоб створити нову версію:
+
+- Перевірте **останню** гілку версії за допомогою `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Створіть нову гілку від тієї, збільшивши версію за допомогою `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Внесіть зміни до гілки версії. Для детальнішої інформації щодо роботи з матеріалами див. [документацію CodeRoad](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial)
+- Надішліть нову гілку до розгалуження за допомогою `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Перевірте гілку `main`
+- Створіть нову гілку від `main`. Наприклад, `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Змініть `uri` у `coderoad.yaml` на своє розгалуження репозиторію. Таким чином ви та рецензент зможете провести тестування перед тим, як надіслати зміни до репозиторію freeCodeCamp. Змініть версію на нову гілку у двох місцях цього файлу. Додайте зміни нової версії до `CHANGELOG.md`. Внесіть будь-які інші потрібні зміни.
+- Затвердьте зміни за допомогою повідомлення `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>`
+- Запустіть `coderoad build`, щоб створити новий файл `tutorial.json`
+- Додайте та затвердьте файл
+- Надішліть зміни до розгалуження
+- Протестуйте зміни, дотримуючись [інструкцій нижче](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Внесіть нові зміни та затвердьте їх так само, або, якщо ви задоволені, дотримуйтесь решти інструкцій
+- Створіть PR до `main`, використовуючи нову гілку `feat/version-X.X.Y`. Назвіть його `version X.X.Y ready for review`. Його не буде об’єднано, але таким чином рецензенти знатимуть про готову нову версію
+- Залиште решту для рецензентів
+
+### Тестування змін на гілці версії
+
+- Виконайте інструкції з [репозиторію rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha), щоб запустити контейнер
+- Запустіть матеріал, використовуючи файл `tutorial.json` на розгалуженні зі змінами. Переконайтесь, що використовуєте файл на гілці `feat: version-X.X.Y`, а не `main`
+
+### Надсилання нової версії
+
+Перед надсиланням нової версії перегляньте нову гілку `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (буде об’єднана до `main`) на розгалуженні користувача. Переконайтесь, що у файлі `CHANGELOG.md` є додатки, які містять нові зміни, та версія у двох місцях `coderoad.yaml` відповідає новій гілці версії.
+
+Якщо ви маєте письмовий доступ до репозиторію freeCodeCamp, підтвердили файли `CHANGELOG` та `coderoad.yaml`, протестували зміни, використовуючи інструкції вище, та хочете надіслати нову версію матеріалу:
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Нагадування: ніколи не вносьте чи затверджуйте зміни до гілки версії, яка розташована на одному з репозиторіїв freeCodeCamp. Завжди створюйте нову
+
+- Якщо у вас немає віддаленого доступу до місця, де наявні нові зміни, створіть віддалений доступ до розгалуження користувача за допомогою `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Видаліть будь-які **локальні** гілки, назва яких збігається з новими гілками. Скоріш за все `vX.X.Y` або `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Перевірте гілку нової версії за допомогою `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
+- Надішліть гілку нової версії до репозиторію freeCodeCamp за допомогою `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. Вам потрібно надіслати нову гілку перед тим, як оновити `main` з новим файлом `tutorial.json`
+- Перевірте гілку користувача, яка буде об’єднана до `main`, за допомогою `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Змініть `uri` у `coderoad.yaml` на репозиторій freeCodeCamp
+- Додайте та затвердьте зміни
+- Запустіть `coderoad build`, щоб створити новий файл `tutorial.json`
+- Додайте та затвердьте файл
+- Надішліть зміни до розгалуження за допомогою `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Створіть PR до `main` на репозиторії freeCodeCamp
+- Якщо ви задоволені, об’єднайте його або залиште й попросіть когось іншого перевірити
+- Як тільки PR об’єднано, відкрийте матеріал, дотримуючись інструкцій з [репозиторію rdb-alpha](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha), щоб переконатись, що все завантажується правильно та ви можете пройти декілька кроків
+- Якщо будь-який PR для цієї версії існує, закрийте його
+
+### Як повернутися до попередньої версії
+
+- Створіть нову гілку від останньої `main` за допомогою `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Скасуйте всі затвердження гілки до потрібної вам версії. Наприклад, у вас є такі затвердження:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+Якщо ви хочете повернутись до v1.0.0, скасуйте всі затвердження від `release: version 1.0.1` та пізніше
+
+- Створіть PR. Назвіть його `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/intro.md b/src/content/docs/uk/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..07b099de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+Спільнота [freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) існує завдяки тисячам волонтерам. Якщо ви хочете поділитися своїм часом та досвідом, ми з радістю приймемо вас до себе.
+
+:::note
+Перш ніж продовжити, прочитайте, будь ласка, наш [Кодекс поведінки](https://www.freecodecamp.org/code-of-conduct). У нашій спільноті ми чітко керуємося цими правилами, щоб кожен міг вільно та безпечно долучитися до freeCodeCamp.org.
+:::
+
+Ви можете створювати, оновлювати та виправляти помилки в нашій [навчальній програмі](#curriculum), допомагати нам виправляти помилки на [навчальній платформі](#learning-platform) freeCodeCamp.org або [перекладати](#translations) freeCodeCamp.org на інші мови.
+
+Ми відповідаємо на поширені питання [в нашому FAQ](FAQ).
+
+Щасливої співпраці.
+
+---
+
+## Навчальна програма
+
+Нашу навчальну програму курує міжнародна спільнота freeCodeCamp. Завдяки цьому ми можемо постійно враховувати та додавати думки волонтерів.
+
+Ви можете допомогти нам збагатити та покращити навчальну програму. Ви також можете оновлювати історії користувачів з проєктів, щоб доповнити поняття тих чи інших концепцій. Ви також можете покращити наші автоматизовані тести, щоб ми могли максимально точно перевіряти код людей.
+
+**Якщо ви хочете покращити нашу навчальну програму, то перегляньте [як зробити внесок до навчальної програми](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges).**
+
+## Переклади
+
+Ми локалізуємо freeCodeCamp.org найпоширенішими мовами світу.
+
+Сертифікації вже доступні деякими поширеними мовами світу:
+
+- [Китайська (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Іспанська (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Італійська (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Португальська (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Українська](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Японська (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [Німецька (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+Радимо вам прочитати [це оголошення](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) та поділитися ним зі своїми друзями, аби зацікавити ще і їх.
+
+**Якщо ви хочете перекладати, див. [як перекладати ресурси freeCodeCamp](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## Навчальна платформа
+
+Наша навчальна платформа працює на сучасному стеку JavaScript. Він містить різноманітні компоненти, інструменти та бібліотеки. Сюди входять Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack та багато інших.
+
+В цілому ми маємо сервер API на основі Node.js, набір клієнтських застосунків на основі React, тестові скрипти для оцінки проєктів кемперів та багато іншого. Якщо ви хочете здійснити внесок до навчальної платформи, ми радимо ознайомитися із цими інструментами.
+
+**Якщо ви хочете допомогти нам покращити нашу кодову базу, див. [як налаштувати freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/uk/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..23b12604
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: Офіційний довідник мовного керівника freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Цей посібник допоможе вам налаштувати та використовувати інструменти для локалізації.
+
+## Як запросити нових помічників до Ghost
+
+Ghost дозволяє налаштувати декілька рівнів користувачів.
+
+Більшість запрошень матимуть рівень «Contributor». Цей рівень дозволяє користувачеві створювати чернетки. Обирайте цю роль, коли запрошуєте нового перекладача.
+
+Рівень «Author» дозволяє користувачу створювати чернетки та публікувати їх.
+
+Рівень «Editor» дозволяє користувачу переглядати всі чернетки та публікувати їх. Обирайте цю роль, коли запрошуєте нового редактора.
+
+Рівень «Administrator» використовується для персоналу freeCodeCamp та мовних керівників.
+
+### Як побудовані статті
+
+Ми використовуємо підхід на основі [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack), щоб імплементувати статті. Ця стратегія призводить до того, що статичний вебсайт швидко кешується та обслуговується з CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) діє як наша платформа керування вмістом, а [11ty](https://11ty.dev) надає статтям статичних ресурсів (HTML, JavaScript та CSS). На наших серверах розгортаються тільки ці статичні ресурси.
+
+Цей процес автоматичний та запускається періодично. Якщо ви опублікуєте щось зараз, на сайті новин воно з’явиться через пару годин.
+
+Ви можете знайти розклад збірки та статус тут: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## Як вказати автора перекладеної статті
+
+Автор та оригінал статті прив’язуються автоматично, якщо цей код додано до Code Injection -> головної секції в налаштуваннях чернеток на Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+Де `link` — посилання на оригінал статті.
+
+## Як оновити популярні статті
+
+:::tip
+Змінювати статті у нижньому колонтитулі принаймні раз на місяць дозволяє покращити результати пошуку в гуглі.
+:::
+
+Щоб оновити статті у нижньому колонтитулі, вам потрібно оновити [файл yaml у репозиторії CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) для своєї мови. Це стосується і навчальної програми, і новин.
+
+Наприклад, ось вміст файлу для перших шести статей:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Кожне число представляє одну із 30 статей у колонтитулі. Переконайтесь, що заголовок та посилання відповідають один одному.
+
+Для кожної статті потрібно створювати коротший заголовок, який використовуватиметься у нижньому колонтитулі. Кожен заголовок повинен залишатися в одному рядку та не переходити в інший.
+
+Вам доведеться [побудувати перекладеного клієнта локально](how-to-enable-new-languages), щоб переконатись, що довжина заголовків правильна. Ви можете переглянути зміни, відредагувавши файл `trending.json` у своєму локальному середовищі:
+
+1. Оновіть файл `.env` так, щоб він використовував вашу мову для `CLIENT_LOCALE` та `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Запустіть `pnpm run create:shared`. Це автоматично згенерує файл `trending.json` для вашої мови у каталозі `/client/i18n/locales/`.
+
+3. Запустіть сервер, виконавши `pnpm run develop:server` у вікні терміналу.
+
+4. Відредагуйте файл `trending.json`, щоб він містив потрібні заголовки. Можливо, знадобиться конвертувати файл `.yaml` у формат JSON.
+
+5. В іншому вікні терміналу запустіть `pnpm run clean:client`, а потім `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## Як перекладати статті в нижньому колонтитулі
+
+У нижньому колонтитулі наявні певні посилання (про нас, спільнота випускників, відкритий вихідний код тощо), деякі з яких можна перекласти так само, як і статті.
+
+Статті, які можна перекладати:
+
+- Про нас
+- Допомога
+- Академічна доброчесність
+- Кодекс поведінки
+
+Статті, які **не** потрібно перекладати:
+
+- Магазин
+- Спонсори
+- Політика конфіденційності
+- Умови надання послуг
+- Політика захисту авторських прав
+
+Наступні посилання вказують на зовнішні сайти і не можуть бути перекладені:
+
+- Спільнота випускників
+- Відкритий вихідний код
+
+### Як змінити посилання у нижньому колонтитулі новин
+
+Як тільки ви переклали та опублікували статті, позначені вище як «можна перекладати», ви можете оновити посилання у нижньому колонтитулі для `/news`, відредагувавши файл `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` у репозиторії [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+> [!NOTE] Наразі PR цього репозиторію доступні лише робочому персоналу. Якщо ви хочете оновити цей файл, попросіть персонал про допомогу.
+
+Оновіть наступну частину файлу:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Як змінити посилання у нижньому колонтитулі навчальної програми
+
+Як тільки ви переклали та опублікували статті, позначені вище як «можна перекладати», ви можете оновити посилання у нижньому колонтитулі для`/learn`, відредагувавши файл `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` у репозиторії [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!WARNING] Можна перекладати лише «Про нас», «Допомога», «Академічна доброчесність» та «Кодекс поведінки». Не змінюйте інших URL.
+
+Оновіть цю частину файлу:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## Як перекладати інформаційні коробочки документації
+
+Ви можете знайти безліч таких коробочок у документації:
+
+> [!NOTE] Я ділюсь нотатками
+
+:::tip
+Я ділюсь порадами
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] Я ділюсь попередженнями
+
+:::danger
+Я ділюсь важливою інформацією
+:::
+
+Заголовки за замовчуванням з’являються англійською мовою навіть у перекладених файлах.
+
+Ви можете перекласти заголовки своєю мовою, змінивши файл `docs/index.html` таким чином:
+
+Всередині елементу `script` є об’єкт, знайдіть властивість `flexibleAlerts` з такою формою:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Всередині об’єкта властивості label, перед властивістю `'/'`, додайте нову властивість для своєї мови, схоже до `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+Наприклад, це виглядатиме так, якщо додати переклади португальською:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## Як перекладати мотиваційні цитати
+
+Мотиваційні цитати можна знайти в [репозиторії навчальної програми](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) у файлі `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json`.
+
+Цей файл має загальну структуру:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+Компліменти — це короткі фрази, які з’являються після виконання завдання.
+
+Не потрібно перекладати речення з англійської буквально. Можна написати пару коротких речень, які доречні для завершення завдання.
+
+Масив `compliments` є масивом рядків. Тому ви б писали:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Для різноманіття вам потрібно почати з принаймні десяти компліментів.
+:::
+
+Мотиваційні цитати — це цитати, які з’являються на https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+Масив `motivationalQuotes` — це масив об’єктів, які повинні містити властивість `quote` та властивість `author`. Ось так:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+Для різноманіття вам потрібно почати принаймні з десяти цитат. Нова цитата відображається кожного разу, коли користувач перезавантажує сторінку.
+:::
+
+## Як оновити загальні посилання
+
+Ми підтримуємо файл загальних посилань, які використовуються на нашому [сайті навчальної програми](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) у файлі `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json`.
+
+Деякі з цих посилань не змінюються. Але вам потрібно оновлювати посилання статей `/news`, які вказуватимуть на перекладену версію цієї статті.
+
+Вам також потрібно оновлювати категорії `help`, щоб вказувати на підфорум вашої мови (зазвичай `language/category`, як-от `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). Це допоможе кемперам створити «допис допомоги» у правильному місці.
+
+## Як оновити метадані сайту
+
+Метадані сайту знаходяться у файлі `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json`. Цей файл має п’ять ключів: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords` та `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+Значення `youre-unsubscribed` повинне бути перекладене дослівно. Інші значення потрібно перекладати якомога ближче, зважаючи на поширені пошукові запити вашої мови.
+
+Якщо вам потрібна допомога, зв’яжіться з нами у [чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Попередній переклад на Crowdin
+
+Попередній переклад можна використовувати, щоб застосувати переклади з пам’яті перекладів.
+
+:::tip
+Особливо корисно відновлювати переклади з пам’яті перекладів, якщо оновлена велика кількість файлів.
+:::
+
+Ви можете знайти попередній переклад у верхній частині сторінки на консолі проєкту. Якщо ви бачите кнопку «Go to console» у верхньому правому куті, натисніть на неї.
+
+
+
+
+
+Ви можете обрати «From Machine Translation» або «From Translation Memory». Оберіть «Translation Memory», щоб відновити переклади з пам’яті.
+
+Залишається виконати три кроки:
+
+1. Files. Виберіть файли, які потрібно перекласти (ви можете обрати цілий проєкт або певну папку чи файл).
+2. Languages. Вкажіть свою мову.
+3. Existing Translations. Найкращою комбінацією є «100% match» та «Apply to untranslated strings only». Не затверджуйте їх автоматично, оскільки завжди краще перевіряти вручну.
+
+
+
+Коли ви закінчите, натисніть кнопку «Pre-Translate» та зачекайте. Вас попередять, коли робота закінчиться. Час залежить від кількості неперекладених рядків у вибраних файлах.
+
+## Як оновити глосарій Crowdin
+
+:::tip
+Оновлений глосарій дозволяє дотримуватись однорідного перекладу технічних термінів.
+:::
+
+Глосарій Crowdin зберігається у репозиторії [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries).
+
+У папці `glossaries` розміщено декілька файлів `*.csv` (значення, розділені комою), по одному для кожного проєкту на Crowdin, що мають глосарій.
+
+Файл `client.csv` використовується для інтерфейсу користувача, файл `curriculum.csv` — для навчальної програми, а файл `docs.csv` — для документації.
+
+Щоб оновити глосарії Crowdin, вам потрібно клонувати репозиторій локально. Відкрийте файл `.csv` за допомогою відповідної програми (наприклад, Microsoft Excel).
+
+У файлі `.csv` ви побачите, що перші три стовпчики написані англійською мовою: `Term:English` для терміна англійською мовою, `Description:English` для опису англійською мовою та `Part:English` для частини мови (іменник, дієслово тощо).
+
+Кожна цільова мова має два стовпчики. Якщо ви перекладаєте на дотракійську мову, вам потрібні стовпчики `Term:Dothraki` та `Description:Dothraki`. Стовпчик `Term:Dothraki` використовується для перекладу терміну на дотракійську мову, а `Description:Dothraki` — для опису терміну дотракійською мовою.
+
+:::tip
+У деяких програмах (наприклад, Microsoft Excel) можна приховати стовпчики з іншими мовами, щоб звільнити місце на екрані та бачити англомовні стовпчики поруч із потрібною мовою.
+:::
+
+Після того, як ви внесли зміни та зберегли файл, потрібно створити PR із запропонованими змінами. Як тільки PR буде прийнятий, вам потрібно запустити GitHub Action, щоб оновити глосарій Crowdin. Внесені зміни до глосарію не набудуть чинності одразу, а з’являться пізніше.
+
+## Як підвищити помічника до редактора
+
+Якщо ви вважаєте, що помічника можна підвищити до редактора на Crowdin, ви можете надати йому цю посаду наступним чином:
+
+Перейдіть до `User management` в меню зліва на Crowdin.
+
+Це відкриє панель керування, де ви побачите список всіх користувачів.
+
+Знайдіть користувача, який стане редактором. Натисніть на три крапки та оберіть «Add to team». Команди редакторів мають стандартну назву `Proof Readers (<language>)`, тому ви можете знайти команду, використавши назву мови. Як тільки ви обрали команду, використайте кнопку «ADD», щоб завершити.
+
+Тепер користувач є редактором.
+
+:::tip
+Новий редактор може багато чого дізнатись, прочитавши [як редагувати файли](how-to-proofread-files).
+:::
+
+## Як додати чи оновити мову
+
+Перейдіть до документації з [додавання нової мови](how-to-enable-new-languages). Якщо ви оновлюєте мову, див. розділ з [налаштування перекладених суперблоків](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4bd2b3e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+---
+title: Офіційний довідник модератора freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Цей довідник допоможе із модерацією у нашій спільноті. Сюди входять розмови та взаємодії у завданнях та запитах на злиття на GitHub, форумі, чатах та інших офіційних спільнотах, які ми підтримуємо.
+
+> [!NOTE] Модератори freeCodeCamp мають доступ до всіх частин спільноти. Це означає, що ми довіряємо вам наглядати за будь-якою з них.
+
+Ви можете стати модератором будь-якої цікавої вам платформи. Деякі модератори допомагають тільки на GitHub, а інші залучені на форумі. Деякі модератори активні всюди.
+
+Для нас важливо, щоб ви насолоджувались роллю модератора та проводили свій час там, де вам цікаво.
+
+> «З великою владою приходить велика відповідальність.» - Дядько Бен
+
+Темперамент модератора важливіший за технічні навички.
+
+Слухайте. Допомагайте. Не зловживайте владою.
+
+Спільнота freeCodeCamp вітає кожного і ми хочемо, щоб так було надалі.
+
+У нас є [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), який керує нашою спільнотою. Чим менше правил, тим легше їх запам’ятати. Ви можете прочитати ці правила та закріпити їх у пам’яті [тут](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+> [!NOTE] Ми додамо вас до однієї або більше команд на GitHub, форумі нашої спільноти та чат-серверах. Якщо у вас немає дозволу до платформи, яку хочете модерувати, [зверніться до персоналу](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## Mодерація GitHub
+
+Модератори мають два головних обов’язки на GitHub:
+
+1. Сортувати завдання та відповідати на них.
+2. Переглядати та сортувати запити на злиття (тобто QA).
+
+### Модерація завдань на GitHub
+
+Ми використовуємо головний репозиторій [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues), щоб відстежувати завдання всіх репозиторіїв. Щодня ми отримуємо завдання, які потрібно відсортувати, позначити та вирішити. Це також чудове місце, щоб почати робити внески до відкритої кодової бази.
+
+#### Сортування завдань
+
+[Сортування](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage) — це процес визначення пріоритету кожного нового завдання. У нас є список позначок, які ми використовуємо для визначення пріоритету, категорії, статусу та масштабу завдання.
+
+Ви можете допомогти нам організовувати та сортувати завдання, використовуючи позначки з [цього списку](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels). Зазвичай поруч біля кожної позначки описано її значення.
+
+Зверніть увагу на позначки `"help wanted"` та `"first timers only"`. Їх потрібно додавати до тредів, які підійдуть потенційним помічникам для створення запиту на злиття.
+
+Для розв’язання незначної проблеми, як-от друкарської помилки, рекомендовано застосувати позначку «first timers only» разом із додатковою інформацією. Для цього ви можете використати [шаблони відповідей](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues).
+
+#### Закриті, застарілі, неактивні завдання та запити на злиття
+
+- Старими завданнями або PR називають ті, на яких не було жодної активності від автора протягом 21 дня (3 тижні від останньої активності), але лише після того, як модератор запросив більше інформації/змін.
+
+- Ми визначаємо активність як коментарі із запитом оновлення PR та сортування типу `status: update needed` тощо.
+
+- Якщо помічнику потрібні допомога або час, ми повернемося до нього після отримання відповіді. У будь-якому випадку, модератори повинні розсудливо вирішувати спірні статуси запитів.
+
+:::tip
+Рекомендуємо використовувати список стандартних [шаблонів відповідей](reply-templates) під час сортування завдань.
+:::
+
+### Модерація запитів на злиття
+
+Помічники вносять зміни до репозиторію freeCodeCamp завдяки запитам на злиття (PR). Нам потрібно перевірити запит на злиття на забезпечення якості (QA) перед тим, як об’єднати чи закрити його.
+
+#### Види запитів на злиття
+
+1. **Редагування інструкції завдань**
+
+ Ці зміни стосуються тексту завдань (опису, інструкції або тесту).
+
+ Це можна зробити одразу на GitHub та вирішити, чи потрібно їх об’єднувати. Нам потрібно подбати про мільйони людей, які працюють з цим текстом під час навчання на freeCodeCamp. Чи дійсно текст буде зрозумілішим, але не стане більшим? Чи доречні ці зміни? Пам’ятайте, що наша ціль — зробити завдання зрозумілими та короткими. Зайві деталі лише відволікають. Можна додати посилання на ресурс, який стосується теми завдання.
+
+ Ви можете закрити недійсний PR та відповісти на нього за допомогою [шаблона](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Якщо зміни позитивні, залиште коментар «LGTM» (Looks Good To Me). Як тільки запит отримає принаймні два схвалення від модераторів чи розробників (включно з вашим), ви можете об’єднати його.
+
+2. **Редагування коду завдань**
+
+ Це зміни коду завдання: початок виконання, розв’язок завдання та тестові рядки.
+
+ Такі PR необхідно обрати зі списку GitHub і перевірити на локальному комп’ютері або Gitpod, щоб переконатися, що тести завдань працюватимуть з поточним розв’язком та новий код не призводить до помилок.
+
+ Деякі помічники можуть спробувати додати додаткові тести, щоб покрити всі можливі випадки. Важливо, аби завдання не виявилось занадто складним. Завдання та їх тести повинні бути максимально простими для розуміння. Окрім алгоритмічних завдань та розділу з інтерв’ю, учні повинні вирішити кожне завдання протягом двох хвилин.
+
+ Ви можете закрити недійсний PR та відповісти на нього за допомогою [шаблона](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ Якщо зміни позитивні, залиште коментар «LGTM». Як тільки запит отримає принаймні два схвалення від модераторів чи розробників (включно з вашим), ви можете об’єднати його.
+
+3. **Зміни до платформи**
+
+ Ці зміни коду змінюють функціональність платформи freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Часом розробники вносять зміни без пояснень, але нам потрібно знати причину для зміни коду. Такі PR мають містити посилання на наявне завдання на GitHub, де обговорюються причини внесення змін. Тоді ви зможете відкрити PR на своєму комп’ютері та протестувати їх локально.
+
+ Якщо ви бачите позитивні зміни, не об’єднуйте їх одразу. Напишіть коментар «LGTM» та згадайте **@freeCodeCamp/dev-team**, щоб вони остаточно затвердили зміни.
+
+4. **Автоматизовані PR (Dependabot)**
+
+ Деякі PR є автоматизованими оновленнями залежностей, які відбуваються через інтеграцію. Вам не потрібно об’єднувати чи схвалювати такі запити. Хтось із команди розробників займеться переглядом і об’єднанням цих автоматизованих PR.
+
+#### Як переглядати, об’єднувати та закривати PR
+
+##### Призначте собі запит на злиття:
+
+Перш за все, якщо ви обираєте запит для перегляду, його потрібно призначити собі. Для цього потрібно натиснути на посилання «assign yourself» під «assignees» у правій частині інтерфейсу GitHub.
+
+Дотримуйтесь вищевказаних правил залежно від виду запиту на злиття.
+
+##### Переконайтеся, що пройшла перевірка CI:
+
+Перед об’єднанням будь-якого запиту потрібно переконатись, що GitHub звітує проходження перевірки (повинні стояти зелені прапорці). Якщо бракує якогось з прапорців, виявіть причину. Внесена зміна заважає тестам? Якщо об’єднати запит, чи функціонуватиме сайт? Такі перевірки важливі для стійкості платформи.
+
+> [!WARNING] Об’єднання запитів, які не пройшли перевірку CI/CD, може спричинити труднощі зацікавленим сторонам, включно з розробниками та помічниками.
+
+##### Як діяти при конфлікті об’єднання:
+
+Інколи виникають конфлікти об’єднання.
+
+Це означає, що зроблено інший запит, який вносить зміни до тієї самої частини файлу. GitHub має інструмент для боротьби з конфліктами об’єднання. Ви можете спробувати розв’язати ці конфлікти. Будьте розсудливими.
+
+Зміни запиту знаходяться зверху, а головної гілки — знизу. Інколи там буде багато непотрібної інформації, яку можна видалити. Як закінчите, не забудьте видалити `<<<<<<`, `======` та `>>>>>>`, які Git додає для визначення місць конфлікту.
+
+Якщо ви невпевнені, попросіть допомоги в когось з модераторів чи розробників.
+
+##### Об’єднання дійсного запиту на злиття:
+
+Якщо запит вже готовий і він не вимагає додаткових схвалень (пам’ятайте, що потрібно принаймні два), його потрібно об’єднати. Використайте опцію за замовчуванням **"Squash and Merge"**. Це збере всі запити на злиття в одне затвердження, що зробить історію Git легкою для читання.
+
+> Після цього потрібно залишити коментар на запиті та особисто подякувати помічнику!
+
+Якщо автором є «first-time contributor», привітайте його з першим успішним запитом, об’єднаним з репозиторієм. Статус автора можна побачити у правому верхньому куті запиту. Ви побачите `First-time contributor`:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Значок нового помічника на запиті (знімок екрана)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="Значок нового помічника на запиті" />
+</details>
+
+Якщо запит не готовий до об’єднання, надайте автору ввічливу відповідь щодо подальших дій. Сподіваємося, вони нададуть відповідь та внесуть зміни до свого запиту.
+
+Якщо вам потрібна чиясь думка щодо запиту, залиште коментар та додайте позначку «discussing».
+
+##### Закриття недійсного запиту на злиття:
+
+Запитам часто приділяють мало уваги та зусиль. Це помітно з того, що помічник не відмітив прапорці або використав загальні назви, схожі до «Made changes» чи «Update index.md».
+
+Бувають і ситуації, коли помічник додає посилання на свій вебсайт, включно зі створеною ним бібліотекою, або вносить поверхневі зміни, які на користь лише йому.
+
+Ви можете закрити недійсні PR та відповісти на них за допомогою [шаблона](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Фільтрування запитів на злиття
+
+Щоб відсортувати запити на злиття для QA для швидкого доступу до запитів, які готові до перегляду, не містять конфліктів, не заблоковані та всі прапорці яких є зеленими, використайте це посилання, щоб застосувати фільтри:
+
+[Пряме посилання із застосованим фільтром](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Інші вказівки для модераторів на GitHub
+
+Ви матимете доступ до репозиторію freeCodeCamp, але **не оновлюйте код одразу в репозиторіях freeCodeCamp**. Весь код повинен надходити до кодової бази freeCodeCamp у вигляді запиту з розгалуження репозиторію.
+
+Ніколи не приймайте власні запити. Їх повинен розглянути інший модератор.
+
+Якщо ви помітили, що хтось порушує [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) на завданнях GitHub або відкриває запит з підозрілим вмістом, напишіть на `support[at]freecodecamp.org` із посиланням на цей запит. Ми розглянемо можливість залокувати автора для нашого GitHub назавжди.
+
+## Модерація форуму
+
+Як модератор, ви допомагаєте нашій спільноті бути приємним місцем для всіх, хто бажає навчатися чи отримати допомогу. Ви матимете справу із позначеними дописами та оброблятимете спам, повідомлення поза темою та інші недоречні розмови.
+
+Зверніть увагу на те, що як тільки ви станете модератором на форумі, то почнете бачити сині підказки щодо користувачів форуму. Наприклад, «[person] вперше публікує повідомлення. Привітайте нового користувача у нашій спільноті!» або «[person] публікує повідомлення за довгий час. Привітайте користувача з поверненням у спільноту!»
+
+![Блакитне повідомлення «[person] вперше публікує повідомлення. Привітайте нового користувача у нашій спільноті!»](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+Це надасть шанс привітати користувачів та змусити їх почуватись особливими. Можливо, хтось з нових учасників стане майбутнім помічником, який допомагатиме безлічі людей вивчати програмування. Навіть найменший вияв доброти може спонукати до низки добрих справ.
+
+### Видалення повідомлень на форумі
+
+Модератори форуму можуть видаляти дописи користувачів. Це потрібно робити лише в таких випадках:
+
+1. Користувач опублікував зображення порнографічного характеру або насильницького змісту.
+2. Користувач розмістив посилання або код зловмисного характеру, що може завдати шкоди іншим користувачам, які натискають на них.
+3. Користувач заповнив тред величезною кількістю спаму.
+4. Обліковий запис був створений, без сумніву, для спаму.
+
+### Що робити зі спамом
+
+Якщо допис зі спамом опублікував легітимний користувач (тобто він хотів не спамити, а навчатись/зробити внесок), надішліть йому повідомлення щодо проблеми та видаліть посилання чи допис, якщо потрібно. Залиште примітку у профілі користувача, де пояснюєте причини вжитих заходів. Якщо проблема не зникає, то заблокуйте можливість користувача публікувати дописи (для цього використайте опцію тиші на панелі адміністратора). Надішліть користувачу попередження із [Кодексом поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). У приватному повідомленні встановіть прапорець, який вказує на те, що ваше повідомлення є «офіційним попередженням».
+
+Як модератор, ви можете ставити запитання і звітувати про порушення на [форумі у розділі mod-team](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Що робити із розмовами поза темою
+
+Дописи або теми, які розміщені в неправильному місці, можна перемістити або перейменувати так, щоб це було доречним.
+
+За виняткових обставин модератор може поділити дискусію на декілька тредів.
+
+Знову ж таки, якщо у вас виникають проблеми чи запитання, напишіть у категорії `«Staff»` та позначте іншого модератора, аби він переглянув ваші дії.
+
+### Що робити з опублікованим розв’язком
+
+Якщо у своїй відповіді користувач надсилає розв’язок до навчальної програми freeCodeCamp, видаліть її та використайте відповідь **Solution Instead of Help** (або іншу своїми словами).
+
+Якщо у своїй відповіді користувач надсилає кінцевий розв’язок до навчальної програми freeCodeCamp, розмийте її та використайте відповідь **Blurred Spoiler Solution**.
+
+Якщо користувач просить відгук щодо розв’язку, перемістіть тред до підфоруму зворотного зв’язку та розмийте розв’язок за потреби. Якщо користувач публікує розв’язок для того, щоб похвастатися, вилучіть тред зі списку та використайте відповідь **Solutions Thread**.
+
+### Користувачі, які не досягнули відповідного віку
+
+Наші [Умови користування](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) вимагають, щоб користувачі freeCodeCamp досягли 13-річного віку. Якщо користувач зізнався, що не досягнув 13-річного віку, надішліть йому повідомлення (нижче) та призупиніть обліковий запис. Потім напишіть на `support[at]freecodecamp.org` (із посиланням на обліковий запис на форумі), щоб видалити облікові записи на /learn та форумі.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per our Terms of Service.
+
+It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
+
+Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
+
+Thank you for understanding.
+```
+
+### Запити на видалення облікового запису
+
+Якщо користувач надсилає запит на видалення свого облікового запису, надішліть наступне:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+Якщо користувач наполягає на видаленні свого облікового запису, попросіть його написати лист на `support[at]freecodecamp.org` з посиланням на обліковий запис на форумі.
+
+### Модерація через мобільний телефон
+
+Форум можливо модерувати через мобільний телефон, але ви можете зіткнутися з певними проблемами. У списку перелічено не всі проблеми.
+
+- Якщо при спробі «заготовленої відповіді» не відкривається меню (після натискання на зубчасте колесо), натисніть на текстове поле та спробуйте ще раз.
+- Модераторський «гайковий ключ» знаходиться в нижній частині вікна попереднього перегляду, але якщо ви натиснете на нього, і не бачите кнопку «Select Posts», тому що вона поза полем зору, вам доведеться прокрутити екран, хоча іноді це не працює. У такому випадку вам потрібно перейти на монітор комп’ютера/ноутбука.
+- Іноді значок відповіді може приховатись, якщо натиснути на меню з трьома крапками під публікацією. Перезавантажте сторінку, щоб повернути його.
+
+## Модерація Facebook
+
+Якщо ви помітили будь-що, що порушує наш [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), вам необхідно негайно це видалити.
+
+Іноді люди публікують те, що вважають смішним. Вони не усвідомлюють, що те, що вони сказали чи поширили, може трактуватися як образа. Такі дописи потрібно видаляти, але немає потреби кидати користувача в бан. Ми надіємося, що користувач зрозуміє, що його допис був неприйнятним та, відповідно, видаленим.
+
+Іноді допис є кричущим порушенням норм і не може бути розумно обґрунтованим з позиції культурних відмінностей чи нерозуміння англійської мови. У такому випадку вам потрібно серйозно розглянути можливість заблокувати користувача у групі на Facebook.
+
+## Модерація Discord
+
+Модератори вирішують порушення нашого [Кодексу поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) у чаті наступним чином:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot служить нашим ботом та всі команди використовують дискордовий інтерфейс команд. Ви можете переглянути список всіх команд, ввівши `/` у будь-якому каналі.
+
+1. **Переконайтеся, що користувач навмисно порушив [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Не всі порушення [Кодексу поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) є навмисними. Нові користувачі можуть публікувати велику кількість коду для допомоги, не знаючи, що це може заважати розмові. У таких випадках ви можете просто попросити їх скористатися такими службами, як CodePen чи Pastebin.
+
+2. **Якщо користувач безсумнівно та навмисно порушує [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), модератор робить наступне:**
+
+ Через незначне порушення можна видати попередження за допомогою команди `/warn`. Через грубші порушення користувача можна видалити із сервера тимчасово (за допомогою команди `/kick`) або назавжди (за допомогою команди `/ban`). У деяких випадках користувачу просто потрібен час, щоб охолонути та зібрати свої думки: команда `/mute` дозволяє запобігти взаємодії користувача зі спільнотою на встановлений час. Заглушений користувач бачить розмову, але не може публікувати повідомлення чи додавати реакції.
+
+ Усі модераційні команди приймають параметр `reason`, що вимагає короткого пояснення вжитих дій. Модераційні дії, виконані із допомогою бота, будуть записані до `#mod-actions`, що дозволяє нам залишатись на одній хвилі. Вбудовані інструменти дискорду не записуються, тому їх потрібно уникати.
+
+ > [!WARNING] Причина модераційної команди буде додана до особистого повідомлення користувачу. Не забудьте бути професіоналом.
+
+3. **Створення приватного обговорення**
+
+ Можуть виникнути ситуації, коли до користувача варто звернутися особисто. Цього не варто робити в особистих повідомленнях, бо це може призвести до ситуацій, коли ви заявляєте одне, а кемпер — інше. Замість цього використайте функціональність бота та створіть приватне обговорення:
+
+ - Викличте команду `/private`, де `target` — користувач, з яким ви бажаєте відкрити особисте обговорення.
+ - Бот створить новий канал та додасть згаданого користувача, а також всіх модераторів із роллю `Your Friendly Moderator`. До каналу додані усі модератори для прозорості, але лише модератор, який викликав команду може взаємодіяти з учасником. Виняток: модератор просить допомоги.
+ - Коли обговорення закінчено, натисніть кнопку `❌ Close` _на першому повідомленні у приватному каналі_, щоб бот закрив та видалив канал.
+
+4. **Видалення повідомлень**
+
+ Наш бот автоматично вносить видалені повідомлення до каналу `#mod-actions`. Якщо повідомлення не відповідає нашому Кодексу поведінки або є неприпустимим для нашої спільноти, його можна видалити.
+
+ Зауважте: якщо повідомлення порушує умови використання дискорду, про це потрібно повідомити через https://dis.gd/report **перед** видаленням.
+
+5. **Не погрожуйте вжити заходів**
+
+ Якщо користувач порушує [Кодекс поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), ніколи не погрожуйте вжити заходів та не попереджайте їх публічно. Натомість поговоріть приватно, використовуючи команду `/private` або модераційні команди бота.
+
+ Якщо порушення очевидно ненавмисне і не потребує модерації чи приватної бесіди, повідомте користувача-правопорушника про його дії.
+
+ Наприклад:
+
+ - Користувач публікує великий код та просить допомоги:
+
+ Модератор: **@username**, будь ласка, використовуйте CodePen або Pastebin, коли публікуєте довгий код.
+
+ - Або вам потрібно пояснити причину:
+
+ Модератор: **@username**, будь ласка, використовуйте CodePen або Pastebin, коли публікуєте довгий код, оскільки це порушує чат та може вважатися спамом згідно із нашим [Кодексом поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - Дрібні та ненавмисні порушення [Кодексу поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Модератор: дружнє нагадування дотримуватись [Кодексу поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Не хвастайтесь тим, що ви модератор**
+
+ Не ставте себе вище спільноти. **Ви — спільнота.** І спільнота довірила вам захищати щось особливе, що ми всі розділяємо: _привітне_ місце для нових розробників.
+
+ Якщо ви вихваляєтесь своєю посадою модератора, люди можуть почуватися некомфортно поруч з вами так само, як почуваються некомфортно поруч із поліцією, попри те, що не порушували закон. Це лише людська природа.
+
+7. **Не суперечте іншим модераторам**
+
+ Якщо ви не погоджуєтесь із діями іншого модератора, обговоріть це особисто з ним або у каналі #mod-chat. Ніколи не відхиляйте дії модератора і ніколи не суперечте іншим модераторам привселюдно. Натомість спокійно все обговоріть у `#mod-chat` та переконайте модератора, що він сам повинен скасувати бан або змінити свою думку.
+
+ _Пам’ятайте: ми всі в одній команді. Ми хочемо гідно представляти роль модераторів і діяти у взаємній згоді._
+
+8. **Бесіда з іншими модераторами**
+
+ У нас є кімната `#mod-chat` лише для модераторів. Скористайтеся нею! Якщо ви сумніваєтесь в тій чи іншій ситуації, зверніться за допомогою до інших модераторів. Якщо ви вважаєте, що якісь питання потрібно обговорити — зробіть це. Ви — частина команди, а ми цінуємо вклад кожного! Навіть якщо ви не погоджуєтесь із цими рекомендаціями або [Кодексом поведінки](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Тимчасова неактивність**
+
+ Якщо протягом певного часу ви не можете бути активним модератором у зв’язку із відпусткою, хворобою чи іншою причиною, переконайтесь, що ви попередили інших у каналі `#mod-chat`. Це для того, щоб ми розуміли, чи зможемо розраховувати на вашу регулярну активність на сервері чи ні.
+
+## Як стати модератором
+
+Припустимо, ви допомагаєте іншим у спільноті протягом певного часу. У такому випадку наша команда модераторів зверне на вас увагу та запропонує вас як потенційного модератора [нашому персоналу](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). Легшого та коротшого шляху немає.
+
+Якщо вас затвердили, ми додамо вас до команд модераторів на [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [форумі](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), чаті тощо.
+
+> [!NOTE] Для GitHub: після того, як вас затвердять модератором, ви отримаєте запрошення до репозиторію Github. Вам потрібно перейти за посиланням [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation), щоб отримати запрошення.
+>
+> Це необхідно для того, щоб ми могли надати вам дозвіл робити записи у наших репозиторіях.
+
+## Як працює кімната помічників
+
+Ми вітаємо кожного у [кімнаті помічників на нашому чат-сервері](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). Ми створили її для модераторів та інших кемперів, які роблять внесок до нашої спільноти будь-яким чином, включно з навчальними групами.
+
+Ми прискаємо, що помічники читають всі повідомлення, у яких вони згадуються через **@username**. Все інше за бажанням, однак не соромтесь читати інші дописи та взаємодіяти з ними.
+
+## Комунікація із посередниками
+
+До вас можуть звернутися організації, які хочуть стати партнерами або співвласниками бренду freeCodeCamp. Як тільки ви зрозумієте їхні наміри, **закінчуйте діалог** та направте їх на пошту `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+Нам часто надходять такі пропозиції, тому вигоду співпраці для нашої спільноти краще вирішувати персоналу (зазвичай воно того не варте).
+
+## Як діяти при зверненнях щодо (психічного) здоров’я
+
+Іноді трапляються ситуації, коли користувачам потрібна медична допомога, або у них наявні ментальні порушення та вони шукають підтримки.
+
+Згідно з нашою політикою вам варто уникати приватних розмов на такі теми. Якщо ситуація напряму стосується freeCodeCamp, потрібно мати запис розмови. Наголосіть, що ми не медичні працівники та заохотьте користувача звернутись по медичну допомогу.
+
+Попри те, що іноді це важко, уникайте порад, а радше направте користувача на пошук професійної допомоги!
+
+Якщо таке трапилося у чаті, створіть приватний канал для користувача та команди модераторів. Це можна зробити за допомогою команди `private`.
+
+- Користувачу гарантована конфіденційність.
+- У публічному чаті більше немає порушень.
+- Інші учасники команди можуть втрутитися, якщо вам некомфортно справлятися із ситуацією самостійно.
+
+Корисні посилання:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## Примітка щодо свободи слова
+
+Інколи люди захищатимуть щось образливе або провокативне, обґрунтовуючи це «свободою слова».
+
+Цей вебкомікс від XKCD ідеально підсумовує думки більшості спільнот стосовно свободи слова.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Дякуємо за увагу та допомогу спільноті розробників!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..10568748
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: Офіційний посібник з адаптації модератора freeCodeCamp
+---
+
+Цей посібник допоможе новим модераторам розібратись з підходами, яких дотримуються досвідчені модератори форуму freeCodeCamp та інших офіційних спільнот, за якими ми доглядаємо.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви не прочитали [Довідник модератора](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook), почніть з нього.
+
+## Форум
+
+### Перші кроки
+
+Після надання статусу модератора ви помітите, що інтерфейс виглядає по-іншому, оскільки з’являться нові інструменти та доступ до підфоруму команди модераторів.
+
+Деякі з нових інструментів будуть відображатися в новому меню, яке виглядає як гайковий ключ. Деякі будуть представлені новими вкладками та кнопками, або навіть опціями у меню форуму.
+
+Щоб ознайомитись з новими інструментами та можливостями, дотримуйтесь наведених методів протягом першого тижня:
+
+:::tip
+Перші два є найважливішими.
+:::
+
+### Ознайомтесь з інструментами адміністратора на Discourse
+
+Форум freeCodeCamp є форумом Discourse, тому ми дотримуємось правил інших форумів, створених на Discourse. Щоб ознайомитись з Discourse та модераторством, прочитайте [довідник нового користувача Discourse](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) та [довідник нового модератора Discourse](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116).
+
+### Стежте за іншими модераторами
+
+Усі дії модераторів можна переглянути у [журналі дій](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). Дії автоматичних інструментів (наприклад, `Akismet` чи `system`) можна ігнорувати, якщо вони не стосуються допису, який потрібно переглянути. Дописи, які потрібно переглянути, розміщені на форумі у розділі [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review).
+
+Протягом першого тижня звертайте увагу на те, які дописи позначаються прапорцем та розглядаються, а також на застосовані до них дії. Ви можете побачити, що системний обліковий запис позначає публікацію, оскільки користувач створив її надто швидко. У багатьох випадках модератори заберуть прапорець, натиснувши кнопку «Approve Post» або позначивши допис як «Not Spam» (залежно від типу прапорця).
+
+Прапорці спаму можуть використовувати користувачі та модератори. Досить часто створюють обліковий запис, пишуть допис, а потім редагують його, додаючи посилання на зовнішній сайт з метою реклами. Такий обліковий запис відносно новий та створив лише один допис, що вказує на те, що обліковий запис створили для спаму. У такому разі доцільно прийняти рішення про видалення облікового запису після першого порушення. Це також стосується облікових записів, перше повідомлення яких вважається спамом.
+
+Ви можете помітити, що модератори виконують дію під назвою «розділення теми» (split topic). Це може бути випадок, коли модератор перемістив допис, який було створено у наявному дописі, у новий допис, або модератор об’єднав повторювані дописи, створені одним користувачем для того самого запитання. Подивившись на цю процедуру, можна виділити різні дії та причини.
+
+Іншою корисною функцією є заготовлені відповіді (canned reply), тобто попередньо написані відповіді, які створила команда модераторів для того, щоб швидко відповідати на повторювані дописи. До них належать:
+
+- Привітання нового користувача форуму, який опублікував код без запитання -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Нагадування користувачам не публікувати розв’язок коду, а ділитись підказками та порадами -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Відповідь на випадок, якщо код працює для вас, але не для інших -> "Browser Issues"
+- Заохочення користувачів відкрити проблеми на GitHub, якщо знайдено можливу помилку -> "Bug Report"
+
+Існує й багато інших функцій, які потрібно прочитати для ознайомлення. Ви також можете знайти обговорення шаблонів у підфорумі mod-team, і можете ставити запитання, якщо не знаєте, як використовувати шаблон.
+
+### Прочитайте дописи на підфорумі Mod-Team
+
+Підфорум Mod-Team містить деякі дописи від старих та нових модераторів, де обговорюються різні вимоги та/або проблеми модерації форуму.
+
+Ці дописи допоможуть зрозуміти приховані цілі та процеси, які стосуються модераторів форуму. Деякі треди пояснять, що робити зі спамом та неприпустимим вмістом.
+
+## Де просити про допомогу
+
+Щоб отримати допомогу щодо незручної чи незрозумілої ситуації, порадьтесь з іншими модераторами на [підфорумі Mod-Team](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) або в [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) на дискорді.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/uk/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..235deba9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Шаблони відповідей
+---
+
+Це шаблони відповідей, які можна використовувати під час розгляду PR/завдань та їх сортування.
+
+> Ви можете створити власний список збережених відповідей за допомогою вбудованої функції [збережених відповідей](https://github.com/settings/replies/) на GitHub або використовувати подані нижче.
+
+## Подяка
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Подяка та вітання
+
+> Подяка та заохочення помічників-початківців.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Помилка збірки
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Синхронізація розгалуження
+
+> Якщо PR не відповідає даті гілки `main`.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Конфлікти об’єднання
+
+> Якщо запит має конфлікти об’єднання, які потрібно вирішити.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ Якщо у новачка виникає конфлікт злиття, то спеціалісти розв’яжуть цю проблему замість нього.
+
+## Дублікат
+
+> Якщо PR повторюється або є дублікатом.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Закриття недійсних запитів на злиття
+
+> Якщо PR недійсний.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Якщо PR містить посилання на зовнішні джерела.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Додавання коментарів про помилки новачків
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR відкрито, а завдання невідсортоване
+
+> Якщо PR відкрито для завдання, яке не відсортоване та не позначене як готове для внеску.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Закриття недійсних завдань
+
+> Якщо завдання стосується коду користувача.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Якщо завдання повторює вже наявне.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> Якщо завдання вирішено на проміжній версії.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Завдання `first timer only`
+
+> Якщо завдання вважається прийнятним для тих, хто робить внесок до коду вперше.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Запити на призначення
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Запити на призначення невідсортованих завдань
+
+> Якщо помічник запитує призначення, але завдання не було відсортоване або позначене як готове до внеску.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/uk/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d8eff282
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Відповідальне розкриття інформації. Зала слави
+---
+
+Ми цінуємо будь-яке відповідальне розкриття інформації, що може вплинути на цілісність наших платформ та користувачів. Якщо ви зацікавлені в тому, щоб зробити свій внесок до безпеки нашої платформи, ознайомтесь з нашою [політикою безпеки](security).
+
+Наразі ми не пропонуємо жодних щедрот, але ми вдячні цим неймовірним людям, які допомагають нам зберегти платформу безпечною для всіх:
+
+- Мехул Мохан з [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) — [Виправлення вразливості](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Пітер Самір https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Лоуренс Теннант ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) працює з IncludeSecurity.com — [GHSA-c3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Міхал Бесяда ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) — [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Дякуємо за ваш вклад :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/security.md b/src/content/docs/uk/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..78dca81f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: Політика безпеки freeCodeCamp.org
+---
+
+Цей документ визначає нашу політику безпеки для бази кодів, платформ, які ми використовуємо, та як повідомити про вразливість.
+
+## Повідомлення про вразливість
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви вважаєте, що знайшли вразливість, **будь ласка, повідомте про це**. Не створюйте завдань на GitHub щодо питань безпеки. Натомість дотримуйтесь цієї інструкції.
+
+### Настанови
+
+Ми цінуємо відповідальне розкриття інформації, що може вплинути на цілісність наших платформ та користувачів. В інтересах збереження часу ми просимо вас повідомити про вразливість, враховуючи наступне:
+
+1. Переконайтесь, що використовуєте **найновіші**, **стабільні** та **оновлені** версії операційної системи та веббраузера, доступних на вашій машині.
+2. Ми відносимо звіти, для яких використовувались інструменти та утиліти про повідомлення проблеми із конфігурацією SPF та DKIM, тестами SSL тощо, до категорії [«випрошування щедрот»](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) та не відповідаємо на них.
+3. Наразі ми не пропонуємо жодних винагород, але будемо раді розмістити ваше ім’я у нашому списку [Зали слави](security-hall-of-fame), при умові, що звіти забрали чимало зусиль.
+
+### Звітність
+
+Після підтвердження вищезгаданих настанов, будь ласка, напишіть на `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. Також ви можете надіслати PGP-зашифроване повідомлення на `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Як тільки ви повідомите про вразливість, ми розглянемо та впевнимось, що вона не хибно позитивна. Якщо нам необхідно прояснити будь-яку інформацію, то ми зв’яжемося з вами. Ви можете надіслати окремі звіти для кожної знайденої вами проблеми. Зверніть увагу, що ми не можемо відповісти на проблеми, які, на нашу думку, не входять до настанов.
+
+## Платформи та кодові бази
+
+Ось перелік платформ та кодових баз, на які ми приймаємо звіти:
+
+### Платформа для навчання
+
+| Версія | Гілка | Підтримується | Актив вебсайту |
+| --------------- | -------------- | ------------- | ------------------------ |
+| кінцева версія | `prod-current` | Так | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| проміжна версія | `prod-staging` | Так | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| розробка | `main` | Ні | |
+
+### Платформа для публікацій
+
+| Версія | Підтримується | Актив вебсайту |
+| ------------------- | ------------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| кінцева версія | Так | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| локалізована версія | Так | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Мобільний застосунок
+
+| Версія | Підтримується | Актив вебсайту |
+| -------------- | ------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| кінцева версія | Так | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Інші платформи
+
+Крім вищезазначеного, ми також приймаємо звіти для репозиторіїв, розміщених на GitHub під організацією freeCodeCamp.
+
+### Інші програми із самостійним розміщенням
+
+Ми самостійно розміщуємо деякі з наших платформ, використовуючи програмне забезпечення із відкритим кодом, наприклад Ghost та Discourse. Перш ніж повідомити про вразливість, будь ласка, переконайтеся, що помилка не належить до програмного забезпечення.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/uk/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f1335b08
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+Якщо ви зіткнулися з проблемою, найімовірніше, у цій документації написано її вирішення.
+
+## Проблеми з встановленням рекомендованих попередніх умов
+
+Ми регулярно використовуємо найновіші та найпопулярніші операційні системи, як-от macOS 10.15 і вище, Ubuntu 18.04 і вище та Windows 10 (із WSL2).
+
+Рекомендовано шукати розв’язок певної проблеми у Google, Stack Overflow та Stack Exchange. Ймовірно, хтось вже стикався із тією ж проблемою і на ваш запит вже є відповідь.
+
+Якщо ви використовуєте іншу ОС або досі стикаєтесь із проблемами, див. [отримання допомоги](#getting-help).
+
+:::caution
+Будь ласка, уникайте створення проблем на GitHub щодо попередніх умов. Вони не входять у межі проєкту.
+:::
+
+## Проблеми відсутніх UI, шрифтів, мовних рядків чи помилки збірки
+
+Коли ви будуєте клієнта, Gatsby кешує шрифти, мовні рядки та UI. Якщо щось з переліченого не кешоване, виконайте наступне:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+АБО
+
+Скористайтеся скороченням
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+Якщо ви надалі стикаєтесь з помилками збірки, рекомендовано очистити робоче середовище.
+
+Використайте `git clean` в інтерактивному режимі:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Як очистити файли git, які не відстежуються (знімок екрану)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="Як очистити файли git, які не відстежуються" />
+</details>
+
+## Проблеми з API, входом, здачею завдань тощо
+
+Якщо ви не можете увійти, а замість цього бачите банер з повідомленням про помилку, яка буде відправлена до freeCodeCamp, будь ласка, перевірте, чи не використовується ваш локальний порт `3000` іншою програмою.
+
+#### **З термінала:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Проблеми з виходом під час перегляду
+
+Ваш сеанс зберігається як файли cookies під час розробки. Якщо їх видалити, ви вийдете з облікового запису розробки.
+
+Якщо запустити `pnpm run seed:certified-user`, ви також вийдете з облікового запису. Це замінить користувача розробки у вашій локальній базі даних.
+
+## Проблема отримання 404 під час перегляду облікового запису
+
+Коли ви намагаєтесь перейти до http://localhost:8000/developmentuser, щоб переглянути обліковий запис, Gatsby піклується про обслуговування сторінок на стороні клієнта, тому під час роботи ви отримаєте сторінку з помилкою 404.
+
+Натисніть на кнопку «Preview Custom 404 Page», щоб переглянути обліковий запис.
+
+## Проблеми при встановленні залежностей
+
+Якщо при встановленні залежностей виникають помилки, переконайтеся, що ви не перебуваєте в мережі з обмеженнями або налаштування мережевого екрана не перешкоджають доступу до ресурсів.
+
+Перше налаштування може зайняти деякий час (залежно від пропускної здатності вашої мережі). Будьте терплячими. Якщо ви досі не знайшли рішення, ми рекомендуємо використати Gitpod замість автономної роботи.
+
+> [!NOTE] Якщо ви використовуєте пристрої Apple із чипом M1 для локального запуску застосунку, рекомендовано використовувати Node v14.7 і вище. В іншому випадку ви можете натрапити на проблеми із залежностями, як-от Sharp.
+
+## Робота з іншими мовами
+
+Щоб переглянути роботу клієнта іншою мовою, перейдіть до [тестування клієнтського застосунку за мовою.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Отримання допомоги
+
+Якщо вам потрібна допомога, не соромтесь ставити питання [на нашому форумі у розділі «Contributors»](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) або [у чаті](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+У консолі вашого браузера або в Bash / терміналі / командному рядку може з’явитися помилка, яка допоможе визначити проблему. Поділіться цим повідомленням про помилку в описі проблеми, щоб іншим було легше визначити проблему і знайти рішення.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/uk/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/uk/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d3c10fe7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/uk/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: Про робочий процес токенів користувача
+---
+
+Токени користувачів використовуються для ідентифікації користувачів сторонніми службами, щоб завдання, виконані з їх використанням, були збережені в обліковому записі користувача.
+
+## Як їх створюють
+
+Зараз токени використовуються лише для надсилання завдань над реляційною базою даних. Токен створюється, коли зареєстрований користувач натискає «Натисніть тут, щоб розпочати курс» або «Натисніть тут, щоб розпочати проєкт», щоб розпочати один із курсів чи проєктів реляційної бази даних.
+
+## Коли їх видаляють
+
+Токен користувача видаляється, якщо користувач вийде із freeCodeCamp, скине свій прогрес, видалить свій обліковий запис або самостійно видалить токен за допомогою віджета у налаштуваннях.
+
+## Як вони працюють
+
+Токени зберігаються у колекції `UserToken` у базі даних. Кожен запис має унікальний `_id`, який є токеном та `user_id`, який посилає на обліковий запис користувача із колекції `user`. Токен закодовано за допомогою JWT та відправлено клієнту під час його створення. Потім цей закодований токен надають стороннім службам, які потребують його, а коли завдання виконане — відправляють його на наш API. Коли наш API отримує токен, він буде розкодованим, щоб ми могли ідентифікувати користувача та зберегти виконане завдання до його `completedChallenges`.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a33bb9ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Authors Analytics Manual
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Search by Language
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+
+
+1. From the top dropdown menu, select `News`.
+1. From the sidebar, click on `Reports`.
+1. From the secondary sidebar, select `Engagement`.
+1. Click on `Pages and Screens`.
+1. In the search bar, type the subpath for the desired language.
+1. From the dropdown under the search bar, choose `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filter Reports by Author
+
+After arriving at the `Pages and Screens` reports mentioned above, use the following steps to filter the results by specific authors.
+
+
+
+1. Click on the `Add filter` button.
+1. From the side navigation include `Author`.
+1. From the `Dimensions values` dropdown, choose an author's name.
+1. Click on the `Apply` button to apply changes.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ece2406a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: Codebase Best Practices
+---
+
+## Styling a component
+
+We recommend styling components using our [design style guide](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+The colors are defined in [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css), and the fonts are in [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+We are strongly opinionated about adding new variables/tokens to the colors. After careful research, the colors have been chosen to respect the freeCodeCamp brand identity, developer experience, and accessibility.
+
+The `!important` keyword may be used to override values in some cases (e.g. accessibility concerns). You should add a comment describing the issue, so it doesn't get removed in future refactoring.
+
+### RTL support
+
+We are striving to support right-to-left (RTL) layout in the codebase for languages that are read in this direction. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Here are some quick rules of thumb to follow:
+
+- Don't use `float` properties
+ - Use Flexbox and Grid layouts instead, as they have RTL support already built-in, and those will be easier to maintain and review.
+- Don't define the direction while using `margin` and `padding`: it may seem harmless to use `padding-right` and `margin-left`, but these directions aren't mirrored when the layout changes to RTL, and adding counter values for them in the RTL file makes maintaining the codebase harder.
+ - Use logical properties for them: You can add the same spacing by using `padding-inline-end` and `margin-inline-start`, and you won't need to worry about RTL layout, as they follow where the line starts and ends, and you won't need to add any extra values in the RTL files, so people won't need to remember to change the same values in two files.
+- Don't use `!important` in `font-family`: RTL layout uses different fonts compared to the LTR layout, when you add `!important` in the `font-family` property it affects the RTL layout too.
+
+## General JavaScript
+
+In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
+
+It is encouraged to use functional components over class-based components.
+
+## Specific TypeScript
+
+### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
+
+#### Retaining Git File History
+
+Sometimes changing the file from `<filename>.js` to `<filename>.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
+
+The best bet at achieving this is to:
+
+1. Rename the file
+2. Commit with the flag `--no-verify` to prevent Husky from complaining about the lint errors
+3. Refactor to TypeScript for migration, in a separate commit
+
+> [!NOTE] Editors like VSCode are still likely to show you the file has been deleted and a new one created. If you use the CLI to `git add .`, then VSCode will show the file as renamed in stage
+
+### Naming Conventions
+
+#### Interfaces and Types
+
+For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
+
+React Component Props - suffix with `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+React Stateful Components - suffix with `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Default - object name in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Action Definitions
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### How to Reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### How to Dispatch
+
+Within a component, import the actions and selectors needed.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [TypeScript Docs](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [TypeScript with React CheatSheet](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a4c86ccb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Courses VSCode Extension
+---
+
+This details the maintenance guidelines for the [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) repository which contains the source code for the [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses) extension.
+
+## Publishing the Extension
+
+A GitHub Action automagically publishes the extension to the Visual Studio Marketplace, on the release of a new GitHub Release.
+
+1. Package a new version of the extension:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Where `<tag_type>` is one of: `major`, `minor`, `patch`.
+
+2. Push the new version to `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Optionally, you can push directly to `upstream/main`, but opening a new PR is recommended for a sanity check.
+
+3. Create a new GitHub Release using the GitHub UI:
+
+- Correctly increment the version number, when creating a new tag.
+- Upload the `.vsix` file with the release.
+- Publish the release, and confirm the action succeeded.
+
+> [!NOTE] Creating a release requires write access to the `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension` repository.
+
+## Manually Publishing the Extension
+
+A manual upload to the Visual Studio Marketplace can be achieved, by following these steps:
+
+1. Visit https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ and sign in
+2. Navigate to the [freeCodeCamp Publisher page](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Select the relevant extension, and select `Update`
+4. Upload the file from your local files
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..16942845
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Curriculum File Structure
+---
+
+Our core instructional content is located within the conveniently named `curriculum` directory. This page will break down how these files are organized.
+
+## Terminology
+
+There are a few terms we use when discussing our curriculum content.
+
+- `certification` : When referring to a certification in this instance, it is talking about the actual certificate that users claim. Which is separate from the name of the superBlock.
+- `superBlock` : A superblock is the top level collection of challenges. Each superblock corresponds to a certification in the curriculum (e.g. Responsive Web Design).
+- `block` : A block is a section within a superblock. A block corresponds to a group of challenges in a given certification (e.g. Basic HTML and HTML5)
+- `challenge` : A challenge is a single lesson within the curriculum (e.g. Say Hello to HTML Elements)
+
+## File Tree
+
+Using those terms, here is how the file structure would be defined:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## The `_meta` Directory
+
+The `_meta` directory is a special directory which contains `.json` files. These files correspond to each block in the curriculum, and are used to determine which superBlock a block belongs to, and the order of the challenges within that block.
+
+## Renaming Files
+
+There may be times when you need to rename a certificate, superblock, block, or challenge. This section will outline the steps needed to avoid build errors when doing so.
+
+:::danger
+Renaming files within the curriculum structure will often change the path (or URL) of the content on the main webpage. Doing so should be done with care, as redirects have to be set up for each change that is made.
+:::
+
+### Renaming a Certification
+
+When renaming a certification, you will likely want to rename the associated superblock along with it. Do the following to rename only the certificate:
+
+1. Rename the `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` folder to the new name.
+1. In the `meta.json` file of that folder, rename the values in `name`, `dashedName`, and `challengeOrder` to the new cert name.
+1. In `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, rename the `{superBlock}-certificate` folder, and the YAML file within it, to the new name.
+1. In the YAML file, change the `title` to the new name.
+1. Rename the file and folder from step 3 for the rest of the curriculum languages.
+1. Update `client/src/redux/index.ts` to use the correct `title`.
+1. Optionally, update the `certSlug` for the superblock in the same file. **Note** that renaming a `certSlug` will change the URL for certifications and should only be done with careful consideration.
+1. Update the `title` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` to the new value. **Note** that changing the `title` here **will break** the superBlock page for the associated certification. It relies on the superBlock title to match the certification title. You will likely want to rename the superBlock at the same time.
+1. If you renamed the `certSlug` in step 7, change it here for the cert and all the nested `projects` values.
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. If you renamed the `certSlug` in step 7, update the key of `certSlugTypeMap` in the same file.
+1. Update the certificate name in the `legacyCerts` array of the `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx` if needed.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Superblock
+
+> [!NOTE] When you rename a superBlock, the new folder name is used as the path and should be considered the "correct" name. All other values should be updated to reflect that change.
+
+Also, you will likely want to rename the certificate and the `{superBlock}-projects` block when you rename a superBlock since they all share a name. To rename only a superBlock you need to:
+
+1. Rename the superBlock folder in the `curriculum/challenges/english` directory.
+1. Rename the superBlock folder in _all_ other `curriculum/challenges/{language}` directories.
+1. For each block within that superBlock, update the `superBlock` value in the `meta.json` file to its dashedName. You don't need to rename any folders here. Do that when renaming a block.
+1. Rename the superblock folder in `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Update the `index.md` file in the above folder, changing the `title` and `superBlock` values to the new name.
+1. For each block folder within the above, update the `index.md` to use the correct `superBlock` value.
+1. In the `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` file, update the path for the cert at the top of the file, and the `title` value for that superBlock. **Note** that changing the `title` here **will break** the ability to view the actual certification for this superBlock. It relies on the superBlock title to match the certification title. You will likely want to rename the certification at the same time.
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. Update the path value in `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. For each language in `client/i18n/locales`, update the `intro.json` file to use the new superBlock `dashedName`. In the English file, also update the `title`.
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. Update all the values where it is used.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Block
+
+When renaming a curriculum block, you need to:
+
+1. Change the name of the block folder in the `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}` directory.
+1. Change the name of the same block folder in _all_ of the other language directories to match. These must all be the same as the English structure or the build will error out.
+1. Change the name of the block folder in the `_meta` directory.
+1. Update the `name` and `dashedName` property for that block's `meta.json` file.
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Challenge
+
+When renaming a single challenge file, you need to:
+
+1. Change the name of the challenge file in the `curriculum/challenges/english` directory.
+1. Change the name of the `title` and `dashedName` within that file.
+1. Change the name of the file, and the `dashedName` in those files for _all_ of the other language directories to match.
+1. Update the name of the challenge in the relevant `meta.json` file. The challenge names here are not used in the build, but provide a user-friendly way to identify the challenge order.
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the YAML file in `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` to the new name.
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the `title` and `link` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+## The `dashedName` Property
+
+The `dashedName` property is used to generate the URL path for the superblock, block, or challenge. These should generally match what the `/utils/slugs.js` helper would output for the file name.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/devops.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e112a53b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,991 @@
+---
+title: DevOps Handbook
+---
+
+This guide will help you understand our infrastructure stack and how we maintain our platforms. While this guide does not have exhaustive details for all operations, it could be used as a reference for your understanding of the systems.
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+This involves three steps to be followed in sequence:
+
+1. New changes (both fixes and features) are merged into our primary development branch (`main`) via pull requests.
+2. These changes are run through a series of automated tests.
+3. Once the tests pass we release the changes (or update them if needed) to deployments on our infrastructure.
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+Typically, [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (the default development branch) is merged into the [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) branch once a day and is released into an isolated infrastructure.
+
+This is an intermediate release for our developers and volunteer contributors. It is also known as our "staging" or "beta" release.
+
+It is identical to our live production environment at `freeCodeCamp.org`, other than it using a separate set of databases, servers, web-proxies, etc. This isolation lets us test ongoing development and features in a "production" like scenario, without affecting regular users of freeCodeCamp.org's main platforms.
+
+Once the developer team [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) is happy with the changes on the staging platform, these changes are moved every few days to the [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) branch.
+
+This is the final release that moves changes to our production platforms on freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+We employ various levels of integration and acceptance testing to check on the quality of the code. All our tests are done through software like [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) and [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. These help us test the integration between different components.
+
+:::note
+We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+:::
+
+Together these tests help in preventing issues from repeating themselves and ensure we do not introduce a bug while working on another bug or a feature.
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+We have configured continuous delivery software to push changes to our development and production servers.
+
+Once the changes are pushed to the protected release branches, a build pipeline is automatically triggered for the branch. The build pipelines are responsible for building artifacts and keeping them in a cold storage for later use.
+
+The build pipeline goes on to trigger a corresponding release pipeline if it completes a successful run. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. The changes to the `production-*` branches can land only via fast-forward merge to the [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. Configure your remotes correctly.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Results:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Make sure your `main` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Check that the GitHub CI is passing on the `main` branch for upstream.
+
+ The [continuous integration](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) tests should be green and PASSING for the `main` branch. Click the green check mark next to the commit hash when viewing the `main` branch code.
+
+ <details> <summary> Checking status on GitHub Actions (screenshot) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ If this is failing you should stop and investigate the errors.
+
+4. Confirm that you are able to build the repository locally.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Move changes from `main` to `prod-staging` via a fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
+
+The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-staging` branch. Once the build is complete, the artifacts are saved as `.zip` files in a cold storage to be retrieved and used later.
+
+The release pipeline is triggered automatically when a fresh artifact is available from the connected build pipeline. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+The process is mostly the same as the staging platforms, with a few extra checks in place. This is just to make sure, we do not break anything on freeCodeCamp.org which can see hundreds of users using it at any moment.
+
+| Do NOT execute these commands unless you have verified that everything is working on the staging platform. You should not bypass or skip any testing on staging before proceeding further. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Make sure your `prod-staging` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Move changes from `prod-staging` to `prod-current` via a fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
+
+The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-current` branch. Once a build artifact is ready, it will trigger a run on the release pipeline.
+
+**Additional Steps for Staff Action**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. They can either _approve_ or _reject_ the release run.
+
+If the changes are working nicely and have been tested on the staging platform, then it can be approved. The approval must be given within 4 hours of the release being triggered before getting rejected automatically. A staff can re-trigger the release run manually for rejected runs, or wait for the next cycle of release.
+
+For staff use:
+
+| Check your email for a direct link or [go to the release dashboard](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) after the build run is complete. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Once one of the staff members approves a release, the pipeline will push the changes live to freeCodeCamp.org's production CDN and API servers.
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+Here is the current test, build and deployment status of the codebase.
+
+| Branch | Unit Tests | Integration Tests | Builds & Deployments |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (experimental, upcoming) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+We welcome you to test these releases in a **"public beta testing"** mode and get early access to upcoming features to the platforms. Sometimes these features/changes are referred to as **next, beta, staging,** etc. interchangeably.
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+We thank you for reporting bugs that you encounter and help in making freeCodeCamp.org better. You rock!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| Application | Language | URL |
+| :---------- | :------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Learn | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Espanol | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Chinese | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| News | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Forum | English | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Chinese | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] The domain name is different than **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. This is intentional to prevent search engine indexing and avoid confusion for regular users of the platform.
+>
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**The current version of the platform is always available at [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+The dev-team merges changes from the `prod-staging` branch to `prod-current` when they release changes. The top commit should be what you see live on the site.
+
+You can identify the exact version deployed by visiting the build and deployment logs available in the status section. Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+There are some known limitations and tradeoffs when using the beta version of the platform.
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **Users on the beta version will have a separate account from the production.** The beta version uses a physically separate database from production. This gives us the ability to prevent any accidental loss of data or modifications. The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ Deployment is expected to be frequent and in rapid iterations, sometimes multiple times a day. As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ The beta site is and always has been to augment local development and testing, nothing else. It's not a promise of what’s coming, but a glimpse of what is being worked upon.
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ We use a test tenant for freeCodeCamp.dev on Auth0, and hence do not have the ability to set a custom domain. This makes it so that all the redirect callbacks and the login page appear at a default domain like: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. This does not affect the functionality and is as close to production as we can get.
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+Please open fresh issues for discussions and reporting bugs.
+
+You may send an email to `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` if you have any queries. As always all security vulnerabilities should be reported to `security[at]freecodecamp.org` instead of the public tracker and forum.
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. The guide applies to the **freeCodeCamp Staff members only**.
+> 2. These instructions should not be considered exhaustive, please use caution.
+
+As a member of the staff, you may have been given access to our cloud service providers like Azure, Digital Ocean, etc.
+
+Here are some handy commands that you can use to work on the Virtual Machines (VM), for instance performing maintenance updates or doing general housekeeping.
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+
+### Azure
+
+Install Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(One-time) Login:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Get the list of VM names and IP addresses:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Install Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(One-time) Login:**
+
+Authentication and context switching: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Get the list of VM names and IP addresses:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+We are working on creating our IaC setup, and while that is in works you can use the Azure portal or the Azure CLI to spin new virtual machines and other resources.
+
+:::tip
+No matter your choice of spinning resources, we have a few [handy cloud-init config files](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) to help you do some of the basic provisioning like installing docker or adding SSH keys, etc.
+:::
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+You should keep the VMs up to date by performing updates and upgrades. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Before you run these commands:
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - If you are updating packages on a VM that is already serving an application, make sure the app has been stopped / saved. Package updates will cause network bandwidth, memory and/or CPU usage spikes leading to outages on running applications.
+
+Update package information
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Upgrade installed packages
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Cleanup unused packages
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+We are running load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) instances for our web servers. These servers are running NGINX which reverse proxy all of the traffic to freeCodeCamp.org from various applications running on their own infrastructures.
+
+The NGINX config is available on [this repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Logging and monitoring for the servers are available at:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), our current basic monitoring dashboard. We are working on more granular metrics for better observability
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The later is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code, logic, via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+Our chat servers are available with a HA configuration [recommended in Rocket.Chat docs](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). The `docker-compose` file for this is [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+We provision redundant NGINX instances which are themselves load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) in front of the Rocket.Chat cluster. The NGINX configuration file are [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+ssh into the VM (hosted on Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+List currently installed node & npm versions
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Install the latest Node.js LTS, and reinstall any global packages
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Verify installed packages
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Optional) Uninstall old versions
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+For client applications, the shell script can't be resurrected between Node.js versions with `pm2 resurrect`. Deploy processes from scratch instead. This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> If using PM2 for processes you would also need to bring up the applications and save the process list for automatic recovery on restarts.
+
+Get the uninstall instructions/commands with the `unstartup` command and use the output to remove the systemctl services
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Get the install instructions/commands with the `startup` command and use the output to add the systemctl services
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Quick commands for PM2 to list, resurrect saved processes, etc.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. Broadly you can follow the steps listed here.
+
+You would need a PAT, that you can grab from here: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+Navigate to [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) and register the agent from scratch in the requisite [deployment groups](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+> [!NOTE] 你應該在主目錄運行腳本,並確保沒有其他 `azagent` 目錄存在。
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+Currently updating agents requires them to be removed and reconfigured. This is required for them to correctly pick up `PATH` values and other system environment variables. 例如,我們需要在部署目標虛擬機上更新 Node.js 時這樣做。
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Once You have completed the steps above, you can repeat the same steps as installing the agent.
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+We use [a CLI tool](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) to send out the weekly newsletter. To spin this up and begin the process:
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+We use a custom [theme](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) for our news publication. Adding the following changes to the theme enables the addition of new languages.
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Update the publication assets by going to the Ghost dashboard > settings > general and uploading the publications's [icon](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png), and [cover](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/faq.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..848a293a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+:::tip
+**`help wanted`** issues are up for grabs, and you do not need to seek permission before working on them. 然而,具有 **`first timers only`** 標籤的 issue 是特別爲以前沒有爲 freeCodeCodeCamp 代碼庫貢獻的人設計的任務。
+:::
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. We are most likely to merge the first pull request that addresses the issue.
+2. In the case of multiple contributors opening a pull request for the same issue at around the same time, we will give priority to the pull request that best addresses the issue. Some of the things we consider:
+ - Did you include tests?
+ - 你是否考慮了所有用例?
+ - 你是否確保通過所有測試,並確認所有東西在本地正常運行?
+3. Finally, we give priority to pull requests which follow our recommended guidelines.
+ - Did you follow the pull request checklist?
+ - Did you give your pull request a meaningful title?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- To be a **Discord/Chat** moderator, have an active presence in our chat and have positive engagements with others, while also learning and practicing how to deal with potential conflicts that may arise.
+- To be a **Forum** moderator, similar to a chat moderator, have an active presence and engage with other forum posters, supporting others in their learning journey, and even giving feedback when asked. Take a look at [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) for more information.
+- To be a **GitHub** moderator, help process GitHub issues that are brought up to see if they are valid and (ideally) try to propose solutions for these issues to be picked up by others (or yourself).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- The `Contributors` category of [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- The `#Contributors` channel on [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..851061ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: How to add Cypress tests
+---
+
+When making changes to JavaScript, CSS, or HTML which could change the functionality or layout of a page, it's important to add corresponding [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io) integration tests.
+
+To learn how to write Cypress tests, or 'specs', please see Cypress' official [documentation](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Cypress tests are in the `./cypress` directory.
+
+- Cypress tests for a curriculum module are in the corresponding curriculum directory, i.e. `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+> [!NOTE] If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+To run tests against production builds, replace `dev` with `prd` below.
+
+- To run all tests in the `./cypress` directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- To create a development build, start the development server, and run all existing cypress end-to-end tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Install Cypress Build Tools
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- When prompted in the terminal, select your keyboard layout by language/area
+
+Now, [Cypress can be run](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..adb2adc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **注意:** 這是一個 **可選的** 步驟,並且僅在處理電子郵件工作流時需要
+
+- [Introduction](#introduction)
+- [Installing MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Using MailHog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Useful Links](#useful-links)
+
+## Introduction
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog is an alternative to using an email service provider to send actual email messages. It is a developer tool for email testing that will catch the email messages sent by your freeCodeCamp instance.
+
+## Installing MailHog
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog with Docker</summary>
+
+If you have Docker installed then you can use
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+to start MailHog in the background and
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+to stop it.
+
+When the installation completes, you can start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on macOS</summary>
+
+使用 [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) 在 macOS 上安裝 MailHog:
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+安裝完成後,你可以開始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Windows</summary>
+
+Download the latest version of MailHog from [MailHog's official repository](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a `.exe` file will be downloaded to your computer.
+
+下載完成後,單擊以打開文件。 可能會出現 Windows 防火牆通知,爲 MailHog 請求訪問權限。 一旦授予防火牆訪問權限,將打開一個標準的 Windows 命令行提示符,MailHog 將在其中運行。
+
+通過關閉命令提示符窗口來關閉 MailHog。 To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (`.exe`) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
+
+開始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Linux</summary>
+
+首先,安裝 [Go](https://golang.org)。
+
+在基於 Debian 的系統(如 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint)上,運行以下命令安裝 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+在基於 RPM 的系統(如 CentOS、Fedora、Red Hat Linux 等)上,運行以下命令安裝 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+或者,運行以下命令來安裝 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+現在使用以下命令設置 Go 的路徑。
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+最後,輸入以下命令來安裝和運行 MailHog。
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+開始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+## Using MailHog
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- Check out the [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) repository for further information related to MailHog. Additional information is also available regarding custom MailHog configurations.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a18642b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines to contribute to the codebase. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+Ignoring these steps may soil your copy which makes the contributing, maintaining, and reviewing processes difficult.
+
+## Contributing to the Codebase
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the freeCodeCamp upstream `main` branch to your `main` fork branch:
+
+:::warning
+If you have any outstanding pull requests that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+
+You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+:::
+
+This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp.
+
+Update your copy of the freeCodeCamp upstream repository:
+
+```bash
+git fetch upstream
+```
+
+Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp main:
+
+```bash
+git reset --hard upstream/main
+```
+
+Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+```bash
+git push origin main --force
+```
+
+You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+```bash
+git diff upstream/main
+```
+
+The resulting output should be empty. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run freeCodeCamp to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Make a conventional commit message. This is a good practice as a developer, and you will be following standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any more time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Quick commands reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working.
+
+| command | description |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Run all JS tests in the system, including client, server, lint and challenge tests. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Run the client test suite. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Run the curriculum test suite. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific Block. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific SuperBlock. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Run the curriculum test suite, without bailing after the first error |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Run the server test suite. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Run the Cypress end to end tests. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Starts Storybook for component library development. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1f1c0bcf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Deploying New Languages on `/learn`
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Updating Crowdin Settings
+
+Before you can release a new language, you will need to allow the languages to download from Crowdin. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Then scroll down to `Language Mapping`, where you will see an option to add custom language codes. Add a new entry for the language you are releasing, selecting `language` as the `Placeholder` value, and entering a URL-friendly lower-case spelling of your language's name for the `Custom code`. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). The step for these will be the same. For example, if you want to enable Dothraki downloads:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Note that the `download_language` key needs to be set to the language code displayed on Crowdin.
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+> [!NOTE] The above section with updating the workflows should be completed before proceeding - these need to be done in separate steps or the builds will fail.
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. There are several objects here.
+
+- `Languages`: Add the new language to `Languages` enum, similar to the others. The string value here will be used in the `.env` file to set a build language later.
+- `availableLangs`: Add the new property from the `Languages` enum to both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays.
+- `i18nextCodes`:這些是每種語言的 ISO 語言代碼。 You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+- `hiddenLangs`: These languages will not be displayed in the navigation menu. This is used for languages that are not yet ready for release. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: These are languages that read from right to left.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `i18n.ts` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(簡體字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configure Search
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+You will need to take an additional step to handle the client UI translations.
+
+The Crowdin workflows will automatically pull down _some_ of the UI translations, but there are a couple of files that need to be moved manually.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+If you would like to test translations locally, before adding them to our main repository - skip the Crowdin workflow changes. Follow the steps for enabling a language, then download the translations from Crowdin and load them into your local code.
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Update your `.env` file to use your new language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `pnpm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+If you build the client in one language and then want to build it in a different language, you will need to use the command `pnpm run clean-and-develop` after changing the `.env` file, as Gatsby will cache the first language.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Deploying New Languages on `/news`
+
+To deploy News for a new language, you'll need to create two PRs. One PR will be to the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), and the other will be to the [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News sources trending links and article titles from our CDN during the build and adds them to the footer. News also fetches Day.js files from the CDN during the build to localize dates and times for each language.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Clone the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) and create a new branch.
+
+In the [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) directory, create a new file and name it `language.yaml`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Then copy the contents of the [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) trending file and paste it into the new YAML file you just created.
+
+The contents will look something like this:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+By default, Day.js only includes English as a locale. To enable it to work with other languages, you need to add a new Day.js locale file to the CDN.
+
+In the [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) directory, create a new file and name it `isocode.min.js`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] The version number will change as the dependencies are updated.
+
+Then, visit [this page on cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) with all available Day.js files for the version we're using, find the `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` link for the new language, and open it in a new tab.
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to add the .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js locale file. You do not need to add any other Day.js files.
+
+Copy the Day.js locale code from the new tab into the new file you created. For example, here is an un-minified version of the English locale code for Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Then open a PR to the CDN repo to add both the YAML and Day.js files for review.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+The [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) pulls data from a Ghost instance, the files you added to the CDN, builds News, and deploys it.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. You should not work off of a fork for this step.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Clone the News repo and create a new branch.
+
+Open the `config/index.js` file to add the new language and configure the necessary values. There are a few objects and arrays to modify:
+
+- `locales`: This array contains the active and upcoming News languages. These are the values that are used in the `.env` file to choose the Ghost instance and UI to use for each build. Add the text name of the new language in lowercase to this array.
+- `localeCodes`: This object is a map of ISO codes for each language, and is used to configure i18next before building the UI. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_ and the ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: This object is a map of Algolia indices for each language. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_, and `news-` followed by the lowercase ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are unsure about the string to use while setting `algoliaIndices`, send a message to Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo), or someone else with access to Algolia, and ask them to check.
+
+For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, here are what the objects / arrays above should look like:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. For example, if you're launching Dothraki News, create a new folder named `dothraki`.
+
+Then copy the JSON files from the `english` directory to your new folder.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Then commit and push your branch directly to the News repo.
+
+> [!NOTE] You need to be on one of the teams with access to the News repo to push branches directly to News. Currently, only the dev, i18n, and staff teams are allowed to do this.
+
+Finally, open a PR for review.
+
+Once both your PRs to the CDN and News repo have been approved, they can be merged.
+
+> [!NOTE] Deployment will be handled subsequently by the staff. Here is a sample PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) of how they do it and more details are available in the [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5f2b3462
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+Video challenges are a new type of challenge in the freeCodeCamp curriculum.
+
+A video challenge is a small section of a full-length video course on a particular topic. A video challenge page embeds a YouTube video. Each challenge page has a single multiple-choice question related to the video. A user must answer the question correctly before moving on to the next video challenge in the course.
+
+The video challenge pages are created by members of the freeCodeCamp team. YouTube videos are also uploaded by members of the freeCodeCamp team. Many of the video challenges do not yet have questions associated with them.
+
+You can help by creating multiple-choice questions related to video sections and adding the questions to the markdown files for the video challenges.
+
+## Challenge Template
+
+Below is a template of what the challenge markdown files look like.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Skim through the video associated with the challenge and create a multiple-choice question
+
+First, find the `videoId`.
+
+For example, in the following code from the header of a video challenge markdown file, the `videoId` is "nVAaxZ34khk". On GitHub, the information should be laid out in a table format.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Next, access the YouTube video with that `videoId`. The URL for the video will be:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (replace `videoId` in the URL with the video's ID - without square brackets)
+
+In the example above, the URL is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Skim the YouTube video with that `videoId` and think of a multiple-choice question based on the content of the video.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. To add the question locally, you need to [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). You can also find the file on GitHub and click the edit button to add the question right in your browser.
+
+If a question has not yet been added to a particular video challenge, it will have the following default question:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Question text
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Add/Update the question text under the part that shows:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Add/Update answers (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, and so on) under `## --answers--`. Make sure to update the number under `## --video-solution--` with the correct answer number. You can add more possible answers using the same format. The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### Question examples
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+What does this JavaScript code log to the console?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+What will print out after running this code:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+For more examples, you can look at the markdown files for the following video course. All the challenges already have questions: [Python for Everybody Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+After creating one or more questions, you can commit the changes to a new branch and [open a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c37cb789
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: How to open a Pull Request (PR)
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Once you are done making changes to the code, you can follow these guidelines to open a PR.
+
+We expect our contributors to be aware of the process specific to this project. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Some examples of this are:
+
+1. Do not edit files directly through GitHub – while you can, it's not a good idea.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Make sure you follow the PR checklist and not just tick things off; otherwise, we won't take you seriously.
+4. Use the correct way to link issues in the description of the PR by updating the `XXXXXX`. Do not just add issue numbers everywhere and anywhere you feel like.
+5. Do not "@mention" or request someone for reviews too many times.
+
+ We understand you are excited about contributing. As much as a maintainer will love to get back to you, they are busy people looking after hundreds of requests just like yours. Be patient, someone will get to you sooner or later.
+
+6. Do not work directly off your `main` branch - create a new branch for the changes you are working on.
+
+> [!NOTE] Your PR should be targeting changes to the English curriculum only. Read [this guide](index#translations) instead for contributing to translations.
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. The convention has the following format:
+
+> `<type>([optional scope(s)]): <description>`
+>
+> For example:
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Type:**
+
+| Type | When to select |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | Only if you are adding new functionality, tests, etc. |
+| chore | Changes that are not related to code, tests, or verbiage of a lesson. |
+| docs | Changes to `/docs` directory or the contributing guidelines, etc. |
+
+**Scope:**
+
+You can select a scope from [this list of labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Description:**
+
+Keep it short (less than 30 characters) and simple; you can add more information in the PR description box and comments.
+
+Some examples of good PR titles would be:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request
+
+1. Once the edits have been committed, you will be prompted to create a pull request on your fork's GitHub Page.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. By default, all pull requests should be against the freeCodeCamp main repo, `main` branch.
+
+ Make sure that your Base Fork is set to freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp when raising a Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Submit the pull request from your branch to freeCodeCamp's `main` branch.
+
+4. Include a more detailed summary of the changes you made and how your changes are helpful in the body of your PR.
+
+ - You will be presented with a pull request template. This is a checklist that you should have followed before opening the pull request.
+
+ - Fill in the details as you see fit. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - If the PR is meant to address an existing GitHub Issue then, at the end of your PR's description body, use the keyword _Closes_ with the issue number to [automatically close that issue if the PR is accepted and merged](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Example: `Closes #123` will close issue 123
+
+5. Indicate if you have tested on a local copy of the site or not.
+
+ - This is very important when making changes that are not just edits to text content like documentation or a challenge description. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: Congratulations on making a PR and thanks a lot for taking the time to contribute.
+
+Our moderators will now take a look and leave you feedback. Please be patient with the fellow moderators and respect their time. All pull requests are reviewed in due course.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+If you are to be contributing more pull requests, we recommend you read the [making changes and syncing](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) guidelines to avoid having to delete your fork.
+:::
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+Conflicts can arise because many contributors work on the repository, and changes can break your PR which is pending a review and merge.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+When you are working on regular bugs and features on our development branch `main`, you are able to do a simple rebase:
+
+1. Rebase your local copy:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Resolve any conflicts and add / edit commits
+
+ ```bash
+ # Either
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Or
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Push back your changes to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Make sure your upstream comes in sync with your local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Either delete your local branch after taking a backup (if you still have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Start off with a clean slate:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # example:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..aa5d9c7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: 如何校對譯文
+---
+
+Our proofreading team is responsible for ensuring that translations accurately reflect the source text. We trust our proofreaders to ensure that we have very high quality translations.
+
+All our translations are done by hand, by real humans. Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+To begin proofreading, visit [our translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) and login. Select "Go to console" in the top navigation bar to switch from the public view to the workspace view.
+
+## 選擇文件
+
+You should see the list of projects you have been granted access to. Select the project that you would like to proofread, then select the language.
+
+
+
+You should now see the list of available files. Choose your file by selecting the `Proofread` button on the right of that file, then choosing `Proofreading` from the drop-down menu that appears.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are in this workspace view, but want to work on [translating a file](how-to-translate-files) instead of proofreading, you may select `Crowdsourcing` from the dropdown menu instead.
+
+## 校對譯文
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Here you will see the list of strings in the selected file, with their related translations. The translation that is displayed here is the translation that has received the highest score (between upvotes and downvotes) from the translation community.
+
+While you can view _all_ proposed translations for a given string, the community scores (determined by the upvotes and downvotes) should be taken into consideration when choosing which translation to approve. The community can review proposed translations and recommend which one is most accurate and clear.
+
+1. 這是源文件的字符串(英文)。
+2. 這是相匹配的翻譯的字符串。 此處將顯示基於贊同和反對票數的最受歡迎的譯文建議。
+3. 點擊這個選擇標記按鈕確認該譯文。
+4. Crowdin 將顯示每個字符串的狀態。 `Done` 的意思是已經確認了譯文,我們將在下次從 Crowdin 拉取內容的時候下載已確認的譯文。 `Todo` 的意思是字符串的譯文還未被校對確認。 `Hidden` means the string is locked and _should not be translated_. `Comment` 的意思是對此字符串有評論消息。
+5. 可以使用復框選擇多條譯文,並在此處一次性批量確認。
+6. 你可以在此處查看社區建議的譯文,社區對其的評分,以及 Crowdin 建議的譯文。
+7. 這個按鈕顯示/隱藏右側的顯示窗口,你可以在其中查看翻譯、評論、翻譯記憶和詞彙表術語。
+8. Crowdin 在此處顯示來自質量保證檢查的報錯消息。 也就是說,如果譯文中有不正確的地方,Crowdin 會通知你。 請仔細校對確認出現報錯消息的譯文。
+
+No additional actions are required once a file has been proofread.
+
+> [!NOTE] Approving a string in the proofreading view will mark it as complete and it will be downloaded in our next pull from Crowdin to GitHub.
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+If you have any questions, or are interested in becoming a proofreader, feel free to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). We will typically grant you proofreading access if you have been contributing to freeCodeCamp for a while.
+
+Our staff team and community moderators teams are always looking for kind volunteers like you who help us make high quality translations available to the world.
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin 會允許你校對你自己的譯文。 一般來說,最好是讓另一位校對者審覈你的譯文,以確保最終內容的準確性。
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+If you are already a proofreader and are interested in having a dedicated channel on our chat servers for a specific language, [fill out this form](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4bc73267
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,318 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCamp. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows.
+- You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase.
+- Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+
+:::
+
+If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Here are some pros and cons which should help you decide which option is best for you:
+
+| Gitpod | Your own machine (local setup) |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| No minimum hardware requirements | Specific and minimum requirements |
+| No need to install any software | Additional software required |
+| Always up to date copy of repository | Need to maintain a local copy of the repository |
+| Slower and can take a few minutes to launch | Faster and can be launched in seconds |
+| Need an internet connection to work | Minimal internet connection required (once setup) |
+| Some tasks like compilation and tests can take longer to complete | Faster completion of tasks (depending on your machine's capabilities) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+We have automated the process of installing all the dependencies & tools you will need. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Fastest)** Prepend `gitpod.io/#` in front of any URL from GitHub.
+
+ For example, if you visit your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, add `gitpod.io/#` in the front of the URL in the address bar and hit enter.
+
+ That is you can navigate to `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` and you should see a workspace created for you. This works for any repository or pull-request on GitHub.
+
+2. Alternatively install one of the below extensions for your browser.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - works with Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. See the extension page for details, screenshots, etc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### Prerequisites:
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+:::tip
+Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+:::
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+
+:::
+
+> Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub">
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+:::caution
+If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`).
+
+Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+
+See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further information about this problem.
+:::
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+:::tip
+Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
+:::
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+:::note
+Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
+
+If you followed along with the [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), then you should be able to skip this step if the MongoDB server from that guide is already running. You can confirm this by checking that you can reach `http://localhost:27017` on your local machine.
+:::
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+:::caution
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+:::
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+:::caution
+Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+:::
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8b0bb9de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow this guide for setting up the freeCodeCamp mobile app locally on your system. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (comes bundled with Flutter) | `3.x` | We use the version bundled with Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions.
+:::
+
+If Flutter is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. We recommend using the Pixel 3a XL and Nexus One(for emulating smaller screens).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+5. Install a code editor of your choice.
+
+ We highly recommend using [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) or Android Studio. We also recommend installing the official [extensions](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of the repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp mobile repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp mobile repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change directory to the new `mobile` directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp mobile repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of the mobile app, you can follow these instructions to run it locally.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] The `mobile` directory contains two folders ie. `mobile-api` and `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contains the API code used for serving the podcasts. `mobile-app` contains the Flutter app which is where you should be when you follow the below steps.
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Remember to change the directory to `mobile-app` before running the following commands.
+
+```bash
+# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+#### Step 2: Install dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start the freeCodeCamp mobile app
+
+Start the emulator of your choice(Android or iOS) and wait for the bootup process to complete.
+
+You can now start the app by running the following command:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+If you're using VSCode or Android Studio then you can easily start the app without having to execute any terminal commands. More information [here](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you are not on main or your working directory is not clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the upstream `main` branch to your local main branch:
+
+ > [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull request that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+ >
+ > You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+ This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp mobile. It is important that you rebase your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+ Update your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile upstream repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp mobile main:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ The resulting output should be empty.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your local work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp mobile and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run the mobile app locally to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Optional:
+
+ We highly recommend making a conventional commit message. This is a good practice that you will see on some of the popular Open Source repositories. As a developer, this encourages you to follow standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any additional time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Issues with installing the recommended prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS and/or are still running into issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+### Issues with the UI, build errors, etc.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9660adb4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 or higher) - available for all distributions including Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop for Windows**: See respective requirements for [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) and [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+This guide covers some common steps with the setup of WSL2. Once some of the common issues with WSL2 are addressed, you should be able to follow [this local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to work with freeCodeCamp on Windows running a WSL distro like Ubuntu.
+
+## Enable WSL
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Install Ubuntu
+
+1. We recommended using Ubuntu-18.04 or above with WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Update the dependencies for the OS
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Set up Git
+
+Git comes pre-installed with Ubuntu 18.04, verify your Git version with `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Optional but recommended) You can now proceed to [setting up your ssh keys](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) with GitHub.
+
+## Installing a Code Editor
+
+We highly recommend installing [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) on Windows 10. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+Essentially, you will edit and store your code on Ubuntu-18.04 with VS Code installed on Windows.
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Installing Docker Desktop
+
+**Docker Desktop for Windows** allows you to install and run databases like MongoDB and other services like NGINX and more. This is useful to avoid common pitfalls with installing MongoDB or other services directly on Windows or WSL2.
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
+
+There are some minimum hardware requirements for the best experience.
+
+## Configure Docker Desktop for WSL
+
+Once Docker Desktop is installed, [follow these instructions](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) and configure it to use the Ubuntu-18.04 installation as a backend.
+
+This makes it so that the containers run on the WSL side instead of running on Windows. You will be able to access the services over `http://localhost` on both Windows and Ubuntu.
+
+## Install MongoDB from Docker Hub
+
+Once you have configured Docker Desktop to work with WSL2, follow these steps to start a MongoDB service:
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Start the MongoDB service at port `27017`, and configure it to run automatically on system restarts
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. You can now access the service from both Windows or Ubuntu at `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Installing Node.js and pnpm
+
+We recommend you install the LTS release for Node.js with a node version manager - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. You should still be able to work on most of the codebase.
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Frequently asked questions on:
+ - [Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop for Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c3f3021b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: How to Test Translations Locally
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] This process is not required, but documented in case you would like to preview what your translations will look like.
+
+If you would like to test your translations on a local instance of the freeCodeCamp `/learn` site, first ensure you have [set up the codebase](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` file to add the language to the available languages list and configure the values. There are four objects here.
+
+- `availableLangs`: For both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays, add the text name of the language. This is the value that will be used in the `.env` file later.
+- `auditedCerts`: Add the text name of the language as the _key_, and add an array of `SuperBlocks.{cert}` variables as the _value_. This tells the client which certifications are fully translated.
+- `i18nextCodes`: These are the ISO language codes for each language. You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `all-langs.js` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(簡體字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Next, open the `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts` file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Finally, in your `.env` file, set `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` to your new language (use the `availableLangs` value.)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## Enabling Localized Videos
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Loading Translations
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..621125bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: 如何翻譯 freeCodeCamp 的資源
+---
+
+## Prepare yourself for Contributions
+
+> The freeCodeCamp Localization Roadmap – There Are No Speed Limits
+
+:::tip
+You can start by reading [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). We recommend joining [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) and [Discord chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+You can translate as much as you want, when you want. It's only a matter of how much time and energy you are willing to invest as a volunteer translator.
+
+We just ask that you understand the following:
+
+1. **翻譯是一件團隊協作的事情。**
+
+ 翻譯 freeCodeCamp 的資源是對貢獻者來說最有趣和最有意義的經歷之一。如果你邀請與你使用同一種語言的朋友和同事參與,那麼效果最好。
+
+ You can start by reading [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). We recommend joining [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) and [Discord chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) with your friends and showing your interest before starting off with translations. Crowdin and other tools make it easy to contribute translations, but it's still a lot of work.
+
+ 我們希望你在貢獻過程感到快樂,而不是感到疲憊,然後失去興趣。
+
+ 如果你們有一個四到五人的小組,就可以開始翻譯一種新的語言了。 你可以再招募更多的朋友來加入這個隊伍。
+
+2. **爲每種語言版本提供服務器,需要較高的成本。**
+
+ 表面上來看,技術棧可能看起來沒那麼複雜,但是實際上消耗了很多資源來讓引擎跑起來。 這包括提供額外的服務器和專職人員來管理它們。
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org is committed to providing these for free as always, however we need to prioritize resources for those who need them the most. 我們非常不想看到某種語言的翻譯活動結束了,並且內容過時了,然後我們不得不關閉相應的服務器。
+
+ For translating the curriculum, once a language reaches at least a few certifications we can begin deploying the language live on [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), while you continue to translate the remaining certifications.
+
+ 舉個例子, 當我們正式上線一個新的語言版本的時候,我們希望至少上線整個前端認證的內容。
+
+3. **但是,如果一種語言沒有在翻譯平臺上列出來,怎麼辦呢?**
+
+ 我們已經查看了我們的用戶羣,並且在翻譯平臺的可用語言列表上添加了三十多種的常用語言。 有一些語言,例如中文和西班牙語,已經在 **"/learn"** 上線了。
+
+ 然而遺憾的是,這個語言列表並沒有涵蓋所有的世界語言。 我們每天都能收到許多像你一樣的貢獻者的需求, 希望將我們的資源翻譯成他們的語言。
+
+ 我們當然希望在這個列表上增加更多的語言種類, 但是你可能已經猜到了, 假如我們有足夠的人來翻譯某一語言才能讓這件事變得實際。
+
+ 假如你希望我們增加某一種新的語言, 我們建議你鼓動你的朋友一起來參與貢獻。
+
+ 如果你們有一個組的人(至少四到五人)對某一種語言感興趣,並且承諾翻譯這種語言, 那麼我們可以在翻譯平臺上增加這種語言。 我們會解釋一切的細節,並且幫助你掌握這些翻譯工具和理解這些翻譯的過程。
+
+## Overview of Crowdin
+
+It's our dream to provide you with the resources to learn, no matter the world language you speak. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source codebase & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
+
+> [!NOTE] We use a different tool and workflow for translating [news articles](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). If you are interested in translating articles, read [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) and reach out to your Language Lead.
+
+The translation workflow is split into two main activities:
+
+- **翻譯**課程文件、文檔和 UI 元素(如按鈕、標籤):
+
+ 譯者可以在[我們的翻譯平臺](https://translate.freecodecamp.org)註冊,然後從 30+ 種語言版本中選擇要參與貢獻的版本,進行翻譯。
+
+- **校對**上述翻譯。
+
+ 校對者確認社區成員貢獻的譯文語調一致,沒有錯別字等常見問題。 簡而言之,校對者需要確保譯文是高質量的。 注意,我們不使用任何機器翻譯。
+
+> [!WARNING] We are no longer using GitHub to translate files directly, if you are a returning contributor head to our [translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) instead.
+
+## Getting Started
+
+First, make sure you come say "Hi" in our [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). 我們會在聊天室定期更新翻譯的資源和回答很多問題。
+
+其次,去我們的[翻譯平臺](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/)並且登陸(假如你以前沒有貢獻翻譯過,你需要創建一個新賬戶)。
+
+最後,瀏覽下面提供的細節圖來理解怎麼使用翻譯工具和流程。
+
+祝你在翻譯過程中感到快樂哦!
+
+## Select a Project and File
+
+當你訪問翻譯平臺,你應該可以看到很多不同的等待翻譯的項目:
+
+1. [貢獻文檔](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs)項目,其中包含此文檔站點的文件。
+2. [編程課程](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum)項目,其中包含我們課程的挑戰文件。
+3. [學習用戶界面](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui)項目,其中包含我們學習平臺的按鈕、標籤等 UI 元素的字符串。
+
+選擇你想參與的任何項目,你將看到可供翻譯的語言列表。
+
+
+
+選擇你要使用的語言,你將看到完整的文件樹。
+
+
+
+每個文件和文件夾都會顯示一個進度條。 進度條的**藍色**部分表示多少百分比的文件已經被翻譯了,而**綠色**部分表示多少百分比的文件已經被校對團隊審覈確認。
+
+選擇你想翻譯的文件,然後 Crowdin 會打開編輯界面。
+
+> [!NOTE] When the editor view opens, you will need to click the settings icon (shown as a gear) and switch the 'HTML tags displaying' setting to 'SHOW'. This will ensure you can see tags such as `<code></code>` instead of `<0></0>`.
+
+## Translate Curriculum
+
+
+
+Crowdin 將文檔分成可翻譯的“字符串”,通常是句子。 每個字符串都被單獨翻譯。 參考上圖:
+
+1. 以綠色標示的字符串已經有了一個建議的翻譯。
+2. 以紅色標示的字符串*沒有*建議的翻譯。
+3. 帶有灰色文本的字符串不可翻譯。 對於代碼塊和其他必須不被翻譯的內容,就是這種情況。 你將無法在編輯器中選擇這些字符串。
+4. 如果某位貢獻者對某個字符串有建議的譯文,那麼 Crowdin 將在此處顯示所有的建議。 你無法保存相同的譯文。如果某個譯文是正確的,那麼你可以點擊 `+` 圖標,給它投票表示贊同。 如果你覺得某個譯文不正確,那麼你可以點擊 `-` 圖標,投反對票。
+5. Crowdin 將基於翻譯記憶(TM)或機器翻譯(MT)推薦譯文。 翻譯記憶是指我們已在其他文件中翻譯過/批准過的相似的或相同的字符串。 機器翻譯是指由 Crowdin 系統推薦的翻譯。
+6. 這是編輯器窗口,你可以在其中輸入你對於所選字符串建議的譯文。
+7. 編輯窗口當前選中的字符串將被標註爲黃色。
+8. 這裏的標籤是表示字符串的狀態。 `Done` 標籤表示字符串有至少一個建議的譯文。 `Todo` 標籤表示字符串還沒有建議的譯文。
+9. 這裏是評論窗口。 如果你對某個字符串有疑問或疑慮,可以在此處對字符串發表評論,以便其他翻譯人員查看。
+10. 點擊這兩個“窗格”按鈕,可以隱藏左邊的(文件)視圖和右邊的(評論)視圖。
+
+> [!NOTE] If you see a hidden string that includes translations, please notify us in the [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) so we can remove the translation from memory.
+
+當你翻譯完一個字符串,請點擊 `Save` 按鈕,將你的譯文保存在 Crowdin 中。 然後其他貢獻者可以給你的譯文投票,而校對者也將審覈確認你的譯文。
+
+你想翻譯多少字符串,都可以,我們非常歡迎你貢獻!當你翻譯完某個文件或某個字符串之後,你不需要採取其他步驟。 你只需要點擊 `Save` 按鈕,就能保存你的譯文了。
+
+> [!NOTE] If you see something in the English source file that is inaccurate or incorrect, please do not fix it through the translation flow. Instead, leave a comment on the string to notify us that there is a discrepancy, or create a GitHub issue.
+
+## Translate the Learn Interface
+
+Our `/learn` interface relies on JSON files loaded into an i18n plugin to generate translated text. This translation effort is split across both Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+### On GitHub
+
+The `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json`, and `trending.json` files contain information that needs to be updated to reflect your language. However, we cannot load these into Crowdin, as the content isn't something that would be a one-to-one translation.
+
+These files will most likely be maintained by your language lead but you are welcome to [read about how to translate them](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### On Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Do not edit the following files through a GitHub PR.
+:::
+
+The `intro.json` and `translations.json` files are both translated on Crowdin, in the Learn User Interface project. Translating these can be a bit tricky, as each individual JSON value appears as its own string and sometimes the context is missing.
+
+However, the `Context` information provided in Crowdin can help understand where the string fits in to the larger structure.
+
+
+
+If you have any questions about where a string fits in to the prose, reach out to us in our [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Translate Documentation
+
+Translating our contributing documentation is a similar flow to translating our curriculum files.
+
+> [!NOTE] Our contributing documentation is powered by `docsify`, and we have special parsing for message boxes like this one. If you see strings that start with `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]`, or `[!TIP]`, these words should NOT be translated.
+
+### How to Translate Documentation with Internal Links
+
+When you work on translating contributing documentation, watch out for internal links targeting a different section of the documentation.
+
+Make sure to replace the id of the target section (the part after `#`) with the id on the translated document. For example, it will look like this in Japanese:
+
+Before translation
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+After translation
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+The actual files in docs are written in Markdown, but they will appear as HTML tags on Crowdin.
+
+You can find out how `docsify` converts a string in your language into an id by looking into the translated pages. If the translation is not deployed yet, you can preview it by [running the docs site locally](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#serving-the-documentation-site-locally).
+
+You can learn more about [internal links in our docs here](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#how-to-create-an-internal-link).
+
+## Translate the LearnToCode RPG
+
+The LearnToCode RPG runs on Ren'Py, which uses special syntax for translated strings: (See [Ren'Py Text documentation](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- The sentences to be translated are always between `""`. These are dialogues or UI strings. The keywords that come before or after the dialogue are game engine control keywords and will be explained in details in subsequent rules. Please note that this first rule governs all subsequent rules listed.
+- In case of `new "..."` Do not translate the `new` keyword.
+- Prefixes like `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (or variants like `player happy`, `player @ happy`) should not be translated. These are control keywords to correctly display the character sprite in the game.
+- Postfixes like `nointeract` should not be translated.
+- Do not translate things between `[]` and `{}`. These are variable interpolations and text tags. These must remain halfwidth parentheses `[]` and `{}` instead of their fullwidth counterparts `【】` and `「」`
+- Do not translate the `nointeract` keyword at the end of the sentence.
+- If we try to use fullwidth parentheses `()`, a QA warning will show. To avoid the QA warning, use halfwidth parentheses `()`
+
+### Examples
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- this is the line that needs to be translated. see translation below
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我們的VIP隊友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}會很高興的。"
+```
+
+Note: The `[]` and `{}` tags should be left intact.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- translate this line, see below
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳過"
+```
+
+Note: Again, the `new` prefix and the `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` tag should be left intact.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定會喜歡你的開發者工作的。"
+```
+
+Note: `layla @ neutral` and `[player_name]` are left unchanged.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也許這都是一場夢?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### A Note on How Crowdin Segments a Sentence
+
+Pay attention to how Crowdin segments a line of dialogue wrapped between opening and closing quotes `""`. When we are translating the dialogue, we need to make sure to retain the opening and closing quotes, even if the quotes appear in different segments.
+
+This is the line to be translated:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin segments it into three parts like below:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# translated, keeping the opening quotes `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全棧{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+What is that?
+# translated, no quotes on either side
+這是什麼?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# translated, keeping the closing quotes `"`
+我最好做筆記,這樣我可以學習更多東西。"
+```
+
+## Rate Translations
+
+Crowdin allows you to rate the existing proposed translations. If you attempt to save a translation, you may see a message indicating that you cannot save a duplicate translation - this means another contributor has proposed that identical translation. If you agree with that translation, click the `+` button to "upvote" the translation.
+
+If you see a translation that is inaccurate or does not provide the same clarity as the original string, click the `-` button to "downvote" the translation.
+
+Crowdin uses these votes to give a score to each proposed translation for a string, which helps the proofreading team determine which translation is the best fit for each string.
+
+## Quality Assurance Checks
+
+We have enabled some quality assurance steps that will verify a translation is as accurate as possible - this helps our proofreaders review proposed translations.
+
+When you attempt to save a translation, you may see a warning message appear with a notification regarding your proposed translation.
+
+
+
+This message appears when Crowdin's QA system has identified a potential error in the proposed translation. In this example, we have modified the text of a `<code>` tag and Crowdin has caught that.
+
+> [!WARNING] You have the option to save a translation in spite of errors. If you do, by clicking "Save Anyway", you should also tag a proofreader or project manager and explain why the QA message needs to be ignored in this case.
+
+## Translation Best Practices
+
+Follow these guidelines to ensure our translations are as accurate as possible:
+
+- Do not translate the content within `<code>` tags. These tags indicate text that is found in code and should be left in English.
+- Do not add additional content. If you feel a challenge requires changes in the text content or additional information, you should propose the changes through a GitHub issue or a pull request that modifies the English file.
+- Do not change the order of content.
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us in our [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) and we will be happy to assist you.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c092ea3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: How to use Docker on Windows Home
+---
+
+There are a few pitfalls to be avoided when setting up Docker on Windows Home. First of all, you have to use [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) as Administrator. Unfortunately Windows Home does not support Docker for Windows Desktop, so Toolbox must be used instead. It has to be run as Administrator as the installation uses symlinks, which cannot be created otherwise.
+
+Once you've installed the toolbox, run Docker Quickstart Terminal as Administrator. This will create a `default` virtual machine if it does not already exist. Once that has happened, close the terminal and open VirtualBox (again as Administrator). You should be able to see the `default` machine. The site is quite resource-intensive, so stop the virtual machine and raise the settings as much as you can - memory in particular. It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Once you're happy that Docker is working, clone the freeCodeCamp repository to a directory inside `C:\Users`. These directories are shared giving Docker access to the local directories, which it needs during installation.
+
+If you see messages like
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+when you `pnpm run docker:init` this is likely the culprit.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3e394497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: How to work on coding challenges
+---
+
+Our goal is to develop a fun and clear interactive learning experience.
+
+Designing interactive coding challenges is difficult. It would be much easier to write a lengthy explanation or to create a video tutorial. But for our core curriculum, we're sticking with what works best for most people - a fully interactive, video game-like experience.
+
+We want campers to achieve a flow state. We want them to build momentum and blast through our curriculum with as few snags as possible. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+Note that for Version 7.0 of the freeCodeCamp curriculum, we are moving toward [an entirely project-focused model with a lot more repetition](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+Creating these challenges requires immense creativity and attention to detail. There's plenty of help available. You'll have support from a whole team of contributors to whom you can bounce ideas off and demo your challenges.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+With your help, we can design an interactive coding curriculum that will help millions of people learn to code for years to come.
+
+The content for each challenge is stored in its markdown file. This markdown file is later converted to HTML using our tools to create interactive web pages.
+
+You can find all of freeCodeCamp.org's curricular content in the [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges) directory.
+
+## Set up the tooling for the curriculum
+
+Before you work on the curriculum, you would need to set up some tooling to help you test your changes. You can use any option from the below:
+
+- You can [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). This is **highly recommended** for regular/repeat contributions. This setup allows you to work and test your changes.
+- Use Gitpod, a free online dev environment. Clicking the button below will start a ready-to-code dev environment for freeCodeCamp in your browser. It only takes a few minutes.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### How to work on practice projects
+
+The practice projects have some additional tooling to help create new projects and steps. To read more, see [these docs](how-to-work-on-practice-projects)
+
+## Challenge Template
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Challenge Title'
+challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Challenge instruction text, in markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+Tests to run against user code, in pairs of markdown text and code block test code.
+
+```js
+Code for test one
+```
+
+If you want dynamic output based on the user's code, --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual-- will be replaced with the expected and actual values of the test's assertion. Take care if you have multiple assertions since the first failing assertion will determine the values of --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Extra information for a challenge, in markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Code evaluated before the user’s code.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Code evaluated after the user’s code, and just before the tests
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Boilerplate code to render to the editor. This section should only contain code inside backticks, like the following:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Solutions are used for the CI tests to ensure that changes to the hints will still pass as intended
+
+```js
+// first solution - the language(s) should match the seed.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// second solution - so if the seed is written in HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// third solution etc. - Your solutions should be in HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. In the above sections, examples of `lang` are:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Numbering Challenges
+
+Every challenge needs an `id`. If you don't specify one, then MongoDB will create a new random one when it saves the data; however, we don't want it to do that, since we want the challenge ids to be consistent across different environments (staging, production, lots of different developers, etc.).
+
+To generate a new one in a shell (assuming MongoDB is running separately):
+
+1. Run `mongo` command.
+2. Run `ObjectId()` command.
+
+For example:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Challenge Title
+```
+
+## Naming challenges
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Padding of an Element
+- Condense arrays with .reduce
+- Use Bracket Notation to Find the First Character in a String
+
+## Challenge descriptions/instructions
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (capital letters in "J" and "S" and no abbreviations)
+- Node.js
+- Although sometimes inaccurate, non-hyphenated forms of 'back end' and 'front end' should be used, as they are more widely used.
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- Simplify the challenge, or
+- Split the challenge into two challenges.
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- Language keywords go in `` \` `` backticks. For example, HTML tag names or CSS property names.
+- References to code parts (i.e. function, method, or variable names) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks. See example below:
+
+```md
+Use `parseInt` to convert the variable `realNumber` into an integer.
+```
+
+- References to file names and path directories (e.g. `package.json`, `src/components`) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks.
+- Multi-line code blocks **must be preceded by an empty line**. The next line must start with three backticks followed immediately by one of the [supported languages](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. See example below:
+- Whitespace matters in Markdown, so we recommend that you make it visible in your editor.
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[YOUR CODE HERE]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Additional information in the form of a note should be surrounded by blank lines, and formatted: `**Note:** Rest of note text...`
+- If multiple notes are needed, then list all of the notes in separate sentences using the format: `**Notes:** First note text. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## Writing tests
+
+Challenges should have the minimum number of tests necessary to verify that a camper understands a concept.
+
+Our goal is to communicate the single point that the challenge is trying to teach, and test that they have understood that point.
+
+Challenge tests can make use of the Node.js and Chai.js assertion libraries. Also, if needed, user-generated code can be accessed in the `code` variable. In addition, the `__helpers` object exposes several functions that simplify the process of writing tests. The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. The exact case and spacing of the dictionary comment must be used. The comment dictionary should not be expanded without prior discussion with the dev-team.
+
+Comments used should have a space between the comment characters and the comment themselves. In general, comments should be used sparingly. Always consider rewriting a challenge's description or instructions if it could avoid using a seed code comment.
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Change code below this line
+
+ // Change code above this line
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Change code below this line */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Change code above this line */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+Declare the myGlobal variable below this line
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> We are working on an integration to make it possible to work on i18n for the comment dictionary.
+
+## Hints and Solutions
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. Start by following the same steps for creating a new topic but review the next for creating the title.
+2. The title of the topic should start with `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` concatenated with the actual title of the curriculum challenge. For example, if the challenge is named "`Chunky Monkey`", the topic title would be "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. `camperbot` should be the owner of these topics/posts, so you will need to request an admin to change the ownership of the main post to `camperbot`.
+4. Once the new topic is created, a forum topic id is created. It is located at the end of the forum topic URL. This id must be added to the frontmatter of the curriculum challenge file via the normal pull request process for the `Get a Hint` button to link to the topic.
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# Challenge Name Goes Here
+
+---
+
+## Problem Explanation
+
+This summarizes what needs to be done without just restating the challenge description and/or instructions. This is an optional section
+
+#### Relevant Links
+
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## Hints
+
+### Hint 1
+
+Hint goes here
+
+### Hint 2
+
+Hint goes here
+
+---
+
+## Solutions
+
+<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Code Explanation
+
+- Code explanation goes here
+- Code explanation goes here
+
+#### Relevant Links
+
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Testing Challenges
+
+Before you [create a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) for your changes, you need to validate that the changes you have made do not inadvertently cause problems with the challenge.
+
+1. To test all challenges run the below command from the root directory
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e867b31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. It is translated into various world languages using [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) and [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+You can learn more about setting up the client application locally for development by following [our local setup guide here](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+This could be helpful when you are working on a feature that specifically targets something that involves localization, and requires you to validate for instance a button's label in a different language.
+
+:::tip
+You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. Read [this guide here](how-to-translate-files) instead.
+:::
+
+Let's understand how the i18n frameworks and tooling work.
+
+## File Structure
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**Files translated on our translation platform:**
+
+- The `translations.json` file contains the majority of the text that appears on the user interface elements. The keys are used in the codebase to get the correct text for whatever language is set. This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- The `intro.json` file contains the key-value pairs for the introduction text on the certification pages.
+
+ If you want to add/update translations for the keys please [read this guide here](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Files NOT translated on our translations platform:**
+
+- The `motivation.json` files are not required to have the same quotes, compliments, or array length. Just the same JSON structure.
+
+- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
+
+ Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+If you are testing a new language, create a folder with the language name as the title next to the other languages and copy the JSON files from another language into your new folder.
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+Next, follow the instructions in the comments in the same file to add/update the rest of the variables as needed.
+
+Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the string of the locale you want to build from the `Languages` enum in the above file.
+
+## How to Structure Components
+
+If you are working on a feature or a bug for the client web app, say for example adding new UI items on the settings page, you should follow the guidelines below. They will help you prepare the components for localization into all the supported world languages.
+
+### Functional Component
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// in the render method:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // more details below
+```
+
+### Class Component
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation adds the "t" function to props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // more details below
+
+// export without redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// or with redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Translate Using the "t" Function
+
+### Basic Translation
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### With Dynamic Data
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+The above example passes an object to the `t` function with a `username` variable. The variable will be used in the JSON value where `{{username}}` is.
+
+## Translate with the `Trans` Component
+
+The general rule is to use the "t" function when you can. But there's a `Trans` component for when that isn't enough, usually when you have elements embedded in the text. You can use the `Trans` component with any type of react component.
+
+### Basic Elements Nested
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i`, and `p` are the default, but that list can be expanded in the i18n config.
+
+### Complex Elements Nested
+
+Other times, you will want to have certain text inside another element, an anchor tag is a good example:
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+In the above example, the key is set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. The `<0>` and `</0>` in the JSON represent the first child of the component, in this case, the anchor element. If there were more children, they would just count up from there using the same syntax. You can find the children of a component in the react dev tools by inspecting it. `placeholder` is simply there because the linter complains about empty `<a>` elements.
+
+### With a Variable
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+In the above example, the key and a variable are set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. `{{ email }}` needs to be somewhere in the `Trans` component as well, it doesn't matter where.
+
+## Changing Text
+
+To change text on the client side of things, go to the relevant `.json` file, find the key that is being used in the React component, and change the value to the new text you want. You should search the codebase for that key to make sure it isn't being used elsewhere. Or, if it is, that the changes make sense in all places.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Adding Text
+
+If the text you want to add to the client exists in the relevant `.json` file, use the existing key. Otherwise, create a new key.
+
+The English file is the "source of truth" for all of the `.json` files sharing the same name. If you need to add a new key, add it there. Then, add the key to **all** of the `translations.json` files.
+
+> [!NOTE] Use English text for all languages if the file is translated through Crowdin. The tests will fail if you don't.
+
+It would be nice to keep the keys in the same order across all the files as well. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. See [the documentation](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) for how they are used.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [react-i18next docs](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [i18next docs](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8335ddd3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Practice Projects
+---
+
+Our practice projects use a step-based approach to teach concepts to campers. A project will consist of multiple files, which we refer to as **"steps"**. These files are named by the challenge ID, to avoid issues with the translation flow. Unfortunately, this makes it difficult to find the file associated with a specific step.
+
+We've built a challenge editor tool that helps remedy this. This tool allows you to navigate the available projects, and the steps for each project (in order). There's also an embedded code editor you can use to work on the files directly.
+
+## Using the Challenge Editor
+
+These instructions will tell you how to use our challenge editor tool to work on the practice projects.
+
+### Starting the Editor
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Then, run `pnpm run challenge-editor` to start both the client and the API that powers the editor.
+
+The client will run on port `3300`, so you can access it at `http://localhost:3300`. The API runs on port `3200`, to avoid conflicts with the learn client and server. This will allow you to run the freeCodeCamp application at the same time as the editor, so you can test your changes locally.
+
+### Navigating the Editor
+
+The default view will list the available `superblocks` - these are the certifications. Click on the certification link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to the list of blocks. These are the practice projects. Click on the project link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to a list of steps for the project. If you are working on an existing step, you can click on the step link to open the editor. If you are adding or removing steps, click the `Use the step tools` link to switch to the step tools for that challenge.
+
+### Editing Steps
+
+When you click on a step, you'll be taken to the editor. This is a basic text editor that offers syntax highlighting.
+
+After you have made your changes, click the `Save Changes` button to save your changes. You will get a browser alert letting you know that your changes are ready to commit. Note that you'll need to use `git` manually to stage and commit your files - this tool will not do that for you.
+
+### Step Tools
+
+When you click the `Use the step tools` link, you'll be taken to the step tools page. This allows you to add or remove steps from the project.
+
+#### Create Next Step
+
+Clicking this button will add a new step at the end of the project. This step will use the previous step's code as the seed.
+
+#### Create Empty Steps
+
+Enter the number of steps you want to add in the input. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Insert Step
+
+Enter the step number that you want to add. Then, click the `Insert Step` button to add the step. The following steps will be re-ordered.
+
+#### Delete Step
+
+Enter the step number you want to delete. Then click the `Delete Step` button to remove that step. This will automatically update the step numbers for the remaining steps.
+
+#### Update Step Titles
+
+You should not have to use this tool unless you've manually deleted or added steps. This tool will reorder the step numbers.
+
+## Using the Scripts Manually
+
+If you want to work on the steps manually, in your local IDE, you can run the step management scripts directly.
+
+The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step in the project. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # where X is the number of steps to create.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a new step at a specified position, incrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json). The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # where X is the position to insert the new step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+A one-off script that deletes an existing step, decrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json)
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # where X is the step number to be deleted.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+A one-off script that automatically updates the frontmatter in a project's markdown files so that they are consistent with the project's meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed433453
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on the Component Library
+---
+
+Welcome to freeCodeCamp's `ui-components` library. The components are built mostly from scratch with basic HTML elements and [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp has been using Bootstrap components in the UI. However, we are moving away from it and building our own component library, which helps standardize our UX/UI patterns and improve accessibility. The project is tracked in [this GitHub issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+The following steps are recommended when working on a new component:
+
+- Research and planning
+- Implement the component
+- Display the use cases on Storybook
+- Write unit tests
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Before building a component, you need to research and document on how the existing version behaves and looks, to ensure that the new one has matching styles and supports all the current usages. In order to meet the web accessibility requirements, you should also pay attention to the accessibility aspect of the component, see which HTML elements and ARIA attributes are used under the hood.
+
+Once you have gathered enough information about the component, you can start thinking about the props interface. Ideally, the interface should be as similar to the current version as possible, to ease the adoption later on. Since we are using Bootstrap components, the simplest approach is to mimic [their implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+We prefer smaller pull requests rather than a large one, because they speed up the review time and reduce cognitive overload for the reviewers. For that reason, you should think about how you would break down the implementation and come up with a delivery plan.
+
+We recommend opening a separate GitHub issue for each component and include all the notes in the issue description. It can be used as a place to host all of your working notes, as well as a way to communicate the approach with the reviewers. We will use the issue thread for further discussion if needed. [The issue for Button component](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) can be used as a reference.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+A new component can be created using the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+The command will generate a new folder inside the `ui-components` directory, with the following files:
+
+| File name | Purpose |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | It is used for exporting the component and its types. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | It is used for demoing the component on Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | It is a test file. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | It is where we implement the component. |
+| `types.ts` | It is where we locate the component's interface and types. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Support forwarding ref
+- Be styled for both light and dark themes
+- Be styled internally based on their props (the consumers should not need to restyle the component with the `className` prop)
+- Utilize the built-in styling system from Tailwind instead of having custom styles
+
+### Using Colors
+
+There are two color "layers" in the component library:
+
+- The base layer, where the color names describe what the colors are, e.g. `gray00`, `blue50`
+- The semantic layer, where the color names describe what the colors are for, e.g. `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. There are exceptions, however, specifically when you are styling the component's states such as hover, active, disabled, etc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+> [!NOTE] Color definition can be found in the [`colors.css` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). A color is only available for use if it is added to the [`tailwind.config.js` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) under the `colors` property.
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Tailwind CSS Configuration](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [React Bootstrap v0.33 Docs](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Bootstrap 3.3.7 stylesheet](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [React Bootstrap current implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [React Bootstrap current tests](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Use cases of the component should be added to the Storybook file (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+To start Storybook, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+The Storybook page is available on [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+We use [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) to write unit tests. The tests should assert that the components behave as expected and are accessible.
+
+To run tests against the component library, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Testing for Accessibility](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Order of priority of React Testing Library's queries](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Common mistakes with React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1ead2b3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+To work on the contributing guidelines, you can edit or add files in the `docs` directory [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). When your changes are merged, they will be made available automatically at the documentation site.
+
+When adding a new file to the `docs` directory, you should evaluate if the file should also be added to the sidebar navigation. We typically create a link in the [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) file for new and independent guides. Alternatively, You may follow the instructions below on creating an internal link for supporting guides.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+If you want to create a link targeting a different section of the contributing guidelines, follow this format:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// If the target section is within the same page, you can omit the file name
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Make sure you include the file extension (`.md`). Don't specify the full URL or append `/` before the file name.
+
+This is necessary to make these links work for the translated version of the document. Otherwise, they will redirect to the English version of the page regardless of the language.
+
+#### Translating docs with internal links
+
+When you work on translating docs on Crowdin, make sure to replace the `#target-section-heading-id` with the id on the translated document. [Learn more about translating docs here](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+> [!NOTE] A quick reminder that you do not need to set up anything for working on the content for the documentation site.
+>
+> To work on the contributing guidelines, see [work on the docs content](#work-on-the-docs-content) section.
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+The site is generated using [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) and served using GitHub pages.
+
+Typically you would not need to change any configuration or build the site locally. In case you are interested, here is how it works:
+
+- 此站點的主頁源在 [`docs/index.html`](index.html) 中。
+- 我們使用 `docsify` 和 GitHub Pages 將這個文件作爲一個 SPA。
+- The `docsify` script generates the content of `markdown` files in the `docs` directory on demand.
+- 主頁是由 [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage) 生成的。
+- The sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9a8ad624
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: How to work on freeCodeCamp.org's developer news theme
+---
+
+The developer news also known as [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) site is powered by [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). We use a custom theme for the look and feel of the site. The source code of the theme is available here: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## The Theme
+
+Ghost uses a simple templating language called [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) for its themes. The theme used on `/news` is based off of the default [casper theme](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
+
+The default theme is commented pretty heavily so that it should be fairly easy to work out what's going on just by reading the code and the comments. Once you feel comfortable with how everything works, Ghost also has a full [theme API documentation](https://themes.ghost.org) which explains every possible Handlebars helper and template.
+
+**The main files are:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - The main template file
+- `index.hbs` - Used for the home page
+- `post.hbs` - Used for individual posts
+- `page.hbs` - Used for individual pages
+- `tag.hbs` - Used for tag archives
+- `author.hbs` - Used for author archives
+
+One really neat trick is that you can also create custom one-off templates just by adding the slug of a page to a template file. For example:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Custom template for the `/about/` page
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Custom template for `/tag/news/` archive
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Custom template for `/author/ali/` archive
+
+## Development
+
+1. Get Ghost installed locally.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Note: Currently freeCodeCamp uses Ghost version `2.9.0`, so make sure you are using a version higher than that.
+
+ Be sure to run `ghost` commands from the `ghost-local-site` directory. Follow additional instructions on [Ghost's official documentation](https://docs.ghost.org) if are not familiar with its interface.
+
+2. Fork and clone the repository in your theme directory (replacing `YOUR_USERNAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Make sure you have all the pre-requisites.
+
+ The theme styles are compiled using Gulp/PostCSS to polyfill future CSS spec. You'll need [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Make sure that your Node.js version is compatible with `ghost`.
+
+4. Install dependencies and develop the theme
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Now you can edit `/assets/css/` files, which will be compiled to `/assets/built/` automatically.
+
+6. Access the development site.
+
+ a. Enter `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` into your address bar. Continue with the setup prompted on the page (if running ghost for the first time).
+
+ b. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Restart Ghost, on a separate terminal once to ensure the theme is available.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Once you've done this, go to `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` and scroll to the bottom. Make sure you click activate on the `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Zip the final code and make a pull-request
+
+ The `zip` Gulp task packages the theme files into `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, which we can then upload to the production site.
+
+ When you make a PR, please make sure you have run the below script prior to commiting the code and sending a PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Other Reference and resources
+
+### PostCSS Features Used
+
+- Autoprefixer - Don't worry about writing browser prefixes of any kind, it's all done automatically with support for the latest 2 major versions of every browser.
+- Variables - Simple pure CSS variables
+- [Color Function](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### SVG Icons
+
+The theme uses inline SVG icons, included via Handlebars partials. You can find all icons inside `/partials/icons`. To use an icon just include the name of the relevant file, eg. To include the SVG icon in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - use `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+You can add your own SVG icons in the same manner.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68cf2948
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+This page describes how to contribute to the freeCodeCamp tutorials and projects that are completed using the CodeRoad VS Code extension.
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. They all start with `learn-`. For example, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Each tutorial repo has a `main` branch and a "version" branch, e.g. `v1.0.0`.
+
+The two main files on the `main` branch are `TUTORIAL.md` and `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contains all the instructions, hints, titles, and so on, for the tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contains instructions for CodeRoad, such as what commands to run and when, what files to watch for changes, and what version branch to use for the steps.
+
+The "version" branch contains the commits that will be loaded on each step of a tutorial. The commit messages on this branch have to be specific. The first commit needs `INIT` for its message and contains all the files to load before the first lesson.
+
+Subsequent commit messages have to match the step number in `TUTORIAL.md` from the `main` branch. For example, the commit with the message `10.1` will be loaded when a user goes to step `10.1`.
+
+In order to make changes to commits on a version branch, you would need to rebase and edit the commits you want to change. This will rewrite the Git history, so we cannot accept PRs to these types of branches. Once a version branch is on the freeCodeCamp repo, it should never change.
+
+:::warning
+Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+Install the [CodeRoad CLI tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+There have been some issues with the latest version. If `coderoad --version` doesn't work after installing, downgrade to `0.7.0` with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Working on `main`
+
+This set of instructions is for PRs that only make minor changes on `main` to **existing lessons**. That mainly consists of typo, grammar, hint, and instructional changes or fixes in the `TUTORIAL.md` file.
+
+For everything else, including adding or deleting lessons, follow the [working on a version branch instructions](#working-on-version-branch). You will not need to create a new version branch for this - you can create a PR following the instructions below.
+
+:::note
+These changes will use the existing version branch. If they are substantial, feel free to add them to `CHANGELOG.md`. Most of the time, a good commit message should work
+:::
+
+You never need to modify the `tutorial.json` file directly. That will be created with the CLI tools.
+
+If you are only making minor changes like fixing a typo or grammatical error, you don't have to test your changes.
+
+Follow these instructions to make a PR, keeping in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context:
+
+- Create a copy of the latest version branch with `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - you do not need to check this branch out, it just needs to exist.
+- Create and checkout a new branch off of `main`
+- Make **and commit** your changes. Reminder: You don't need to change anything in the `tutorial.json` file. You likely only need to make changes to `TUTORIAL.md`
+- Run `coderoad build` to recreate the `tutorial.json` file
+- Commit the changes with `update json` as the message
+- Make a PR
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+If you want to test your changes to `main` after using the above instructions, follow these instructions:
+
+- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
+- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on the new branch
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+If reviewing a PR that only changes `main` with instructional or grammar issues as described above, the changes in `TUTORIAL.md` should match the changes in `tutorial.json`.
+
+The `tutorial.json` file should not have changes to commit hashes, or step/level ids. Startup or level commands or file watchers likely should not be changed either. There are exceptions if there's an issue with a step, but they should be treated with more caution.
+
+Also, keep in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context, so make sure they make sense.
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+:::warning
+Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+There's no easy way to see exactly what changed between version branches since the Git history will be rewritten. Accepting new version branches to use will need to be done with careful consideration and testing.
+
+These instructions are for changing anything on a "version" branch, such as tests, test text, reset files, adding and deleting steps, among other things.
+
+Follow these instructions to create a new version:
+
+- Checkout the **latest** version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Create a new branch off of that, incrementing the version, with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Make your changes to the version branch. See more info in the [CodeRoad Documentation](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) for how to work with tutorials
+- Push the new branch to your fork with `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Checkout the `main` branch
+- Create a new branch off `main`. e.g. `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` to your fork of the repo. This is so you and reviewers can test it before pushing it to the freeCodeCamp repo. Change the version to the new branch in the two spots of that file. Add your changes for the new version to `CHANGELOG.md`. Make any other changes you need.
+- Commit your changes with the message `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>`
+- Run `coderoad build` to create a new `tutorial.json` file
+- Add and commit the file
+- Push the changes to your fork
+- Test your changes following the [testing instructions below](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Make any additional changes and commit them as you just did, or, if you are satisfied, follow the rest of the instructions
+- Make a PR to `main` using your new `feat/version-X.X.Y` branch. Give it a title of `version X.X.Y ready for review`. This will not be merged, it is just to let reviewers know that there is a new version ready
+- Leave it here for reviewers
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
+- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on whatever fork the changes are on. Make sure to use the file on the `feat: version-X.X.Y` branch and not the `main` branch
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+Before pushing a new version, view the new `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (will be merged to `main`) branch on the user's fork. Make sure there are additions to the `CHANGELOG.md` file that include the new changes, and the version in the two spots of `coderoad.yaml` matches the new version branch.
+
+If you have write access to the freeCodeCamp repo, have verified the `CHANGELOG` and `coderoad.yaml` files, have tested the changes using the instructions above, and want to push a new version of a tutorial:
+
+:::warning
+Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+- If you don't have a remote to where the new changes exist, create a remote to the user's fork with `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Delete any **local** branches that share a name with the new branches. Likely named either `vX.X.Y` or `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Checkout the new version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
+- Push the new version branch to the freeCodeCamp repo with `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. You need to push the new branch before you update `main` with the new `tutorial.json` file
+- Checkout the users branch that will be merged into `main` with `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` back to the freeCodeCamp repo
+- Add and commit the changes
+- Run `coderoad build` to create the new `tutorial.json` file
+- Add and commit the file
+- Push the changes to your fork with `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Make a PR to `main` on the freeCodeCamp repo
+- If you are satisfied, merge it or leave it and ask for a review from someone
+- After the PR is merged, open the tutorial by following the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to make sure it's loading properly, and that you can get through a few steps
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Revert all commits on this branch up to and including the commit of the version after the one you want to revert to. For example, you may have commits that look like this:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+If you want to revert to v1.0.0, revert all the commits from `release: version 1.0.1` and after
+
+- Create a PR. Give it a title of `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/intro.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d8b748ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+因爲有成千上萬像你這樣善良的志願者,[freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) 才成爲了可能。 如果你想利用業餘時間貢獻你的專業知識,我們將很高興地歡迎你加入社區。
+
+> [!NOTE] 在你繼續之前,請花 2 分鐘時間快速地閱讀我們的[行爲守則](https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/)。 我們在社區中嚴格執行行爲規範,爲 freeCodeCamp.org 的所有貢獻者營造安全、包容的氛圍。
+
+You are welcome to create, update and fix bugs in our [curriculum](#curriculum), help us fix bugs in freeCodeCamp.org's [learning platform](#learning-platform), or [help us translate](#translations) freeCodeCamp.org to world languages.
+
+We answer the most common questions about contributing [in our contributor FAQ](FAQ).
+
+Happy contributing.
+
+---
+
+## 課程
+
+我們的課程由 freeCodeCamp 全球社區的貢獻者協作創建。 因此,我們能夠吸收像你這樣的志願者的專業知識。
+
+你可以幫助擴展和改進課程。 你也可以更新項目需求以更好地解釋概念。 你可以改進我們的自動化測試,以便我們能夠更準確地測試人們的代碼。
+
+**如果你對改進我們的課程感興趣,請查看 [如何爲課程做出貢獻](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges)。**
+
+## 翻譯
+
+We are localizing freeCodeCamp.org to major world languages.
+
+Certifications are already live in some major world languages like below:
+
+- [Chinese (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Spanish (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italian (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Portuguese (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ukrainian (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japanese (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [German (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+We encourage you to read the [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) and share it with your friends to get them excited about this.
+
+**If you're interested in translating, here's [how to translate freeCodeCamp's resources](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## 學習平臺
+
+Our learning platform runs on a modern JavaScript stack. It has various components, tools, and libraries. These include Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack, and more.
+
+Broadly, we have a Node.js based API server, a set of React-based client applications, testing scripts to evaluate camper-submitted curriculum projects, and more. If you want to productively contribute to the learning platform, we recommend some familiarity with these tools.
+
+**If you want to help us improve our codebase here's [how to set up freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..92a50b5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Language Lead Handbook
+---
+
+This handbook will help you set up and use the tools for your localization efforts.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+Most of your invites will be for the "Contributor" level. This level allows the user to create drafts. Select this role when inviting a new translator.
+
+The "Author" level allows the user to create Drafts and publish them.
+
+The "Editor" level allows the user to access all Drafts and publish them. Select this role when inviting a new proofreader.
+
+The "Administrator" level is reserved for freeCodeCamp staff and Language Leads.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+We use a [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack)-based approach to build and deploy the articles. This strategy makes for a speedy static site cached and served from a CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) acts as our content management platform, and [11ty](https://11ty.dev) builds the articles into static assets – plain HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. Only these static assets are deployed to our servers.
+
+This process is automated and runs periodically. If you publish something now, it will be available on the news site in a few hours.
+
+You can find the up-to-date build schedules and status here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+With `link` being the link of the original article.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+:::tip
+Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+:::
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Make sure to match the title and the link correctly.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Each title must stay on a single line and not go to a new line.
+
+You will want to [build the translated client locally](how-to-enable-new-languages) to see if the titles have the right length. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articles that can be translated:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+The following articles should **not** be translated:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+The following links are pointing to external sites and cannot be translated:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Once you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, you can update the links in the footer for `/news` by editing the file at `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) repository.
+
+> [!NOTE] Pull requests to this repository are currently limited to staff only. If you want to update this file, ask someone on the staff team for help.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+When you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, as well as when the curriculum in your language is ready for launch, you can update the links in the footer for `/learn` by editing the file at `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) repository.
+
+> [!WARNING] Only "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", and "Code of Conduct" can be translated. Leave other URLs unchanged.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+You can find these boxes all around the documentation:
+
+> [!NOTE] I am a note box
+
+:::tip
+I am a tip box
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] I am a warning box
+
+:::danger
+I am an attention box
+:::
+
+By default, their headers appear in English even in the translated docs.
+
+You can have the headers translated in the docs in your language by changing the file `docs/index.html`, in this way:
+
+Inside the `script` element there is an object, find the `flexibleAlerts` property, which has this shape:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Inside the object of the label property, before the `'/'` property, you would add a new property for your language, like `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+For example, adding the translations for Portuguese would appear like this:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+The motivational quotes can be found in the [curriculum repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json` file.
+
+This file has a general structure of:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+The compliments are the short sentences that appear at the completion of a challenge.
+
+You don't need to directly translate the sentences used in English, you can write a set of short sentences that are appropriate to show at the completion of a challenge.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen compliments to have some variety when users complete challenges.
+:::
+
+The motivational quotes are the quotes that appear at https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+The `motivationalQuotes` array is an array of objects, these objects should include a `quote` property and an `author` property. like this:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen quotes, to have some variety. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+:::
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+We maintain a file of common links used throughout our [curriculum site](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json` file.
+
+Some of these links will not change - but you should update the `/news` article links to point to your language's translated version of that article when it is published.
+
+You should also update the `help` categories to point to your language's subforum (usually `language/category`, like `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). This will allow campers to create "help posts" in the correct forum location.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+The site meta-data is in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json` file. This file has five keys: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords`, and `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+The `youre-unsubscribed` value should be directly translated. The other values will need to be translated as closely as possible, while also considering common search terms and phrases used in your language.
+
+If you need help with this, reach out to us in the [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Pre-Translate Workflow on Crowdin
+
+The Pre-Translate workflow can be used to apply translations from the Translation Memory to strings.
+
+:::tip
+Really useful to restore a lot of translations from the Translation Memory in bulk when a lot of files have been updated.
+:::
+
+You can find the Pre-Translation workflow at the top of the page in the console of a project. If you see "Go to console" in the upper right corner, click there first.
+
+
+
+
+
+You can choose "From Machine Translation" or "From Translation Memory". Choose "Translation Memory" to recover translations from memory.
+
+Then there are three steps to complete:
+
+1. Files. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Languages. Set your language here.
+3. Existing Translations. The best combination here is "100% match" and "Apply to untranslated strings only". Do not approve automatically, as it's always best to have a human eye on things.
+
+
+
+When you have finished setting this, press the Pre-Translate button and wait. It will alert you once it has finished. The time it takes depends on how many untranslated strings are in the chosen files.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+:::tip
+An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+:::
+
+The Crowdin Glossary is kept in the [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries) repository.
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+The `client.csv` file is for the Learn User Interface project, the `curriculum.csv` file is for the Coding Curriculum project, the `docs.csv` file is for the Contributing Documentation project.
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+In the `.csv` file you will find that the English language occupies the first three columns, `Term:English` is the column for the English term, `Description:English` is the column for the English description, and `Part:English` is for the part of speech (e.g., noun, verb etc.) of the term.
+
+Then, each target language has two columns. If you translate to Dothraki, you will be interested in the columns `Term:Dothraki` and `Description:Dothraki`. The column `Term:Dothraki` is for the translation of the term in Dothraki, and the column `Description:Dothraki` is for a description of the term in Dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+:::
+
+After you have made the changes and saved the file, you will need to make a PR with the proposed changes. After the PR is accepted, you will need to run the GitHub Action workflow to update the Crowdin Glossary. Your glossary changes will not have immediate effects, but they will come.
+
+## How to Promote a Contributor to Proofreader
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+This will open the user management tools, you will be able to see the list of all the users.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Use the three dots menu on the user row to open a menu and select "Add to team". The proofreader teams have a standard name of `Proof Readers (<language>)`, you can search the team using the language name. Once you have selected the team, use the "ADD" button at the bottom of the page to finalize the thing.
+
+The user is now a proofreader.
+
+:::tip
+The newly promoted proofreader could benefit from reading the [How to Proofread Files](how-to-proofread-files) documentation.
+:::
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c9a7b855
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,372 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp 官方管理員手冊
+---
+
+該手冊將幫助您管理我們社區中的不同地方。 This covers conversations and interactions in issues and pull request threads on GitHub, the community forum, the chat rooms, and other official communities that we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] 所有 freeCodeCamp 管理員都是全社區管理員。 That means we trust you to oversee any of these places.
+
+你可以在你感興趣的任何平臺上擔任管理員。 一些管理員只在 GitHub 上提供幫助,而其他管理員在論壇上提供幫助。 一些管理員在各個地方都很活躍。
+
+最重要的是,我們希望你享受作爲管理員的樂趣,並將你寶貴的時間投入到你感興趣的地方。
+
+> “擁有權利的同時也被賦予了重大的責任。” - 本叔叔
+
+作爲一名管理員,氣質比技術能力更重要。
+
+聆聽。 Be helpful. 不要濫用你的權力。
+
+freeCodeCamp 是一個包容的社區,我們需要保持這種狀態。
+
+We have a single [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) that governs our entire community. 規則越少,就越容易記住。 你可以在[這裏](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)閱讀這些規則,並把它們記在心裏。
+
+> [!NOTE] As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## 管理 GitHub
+
+管理員在 GitHub 上有兩個主要職責:
+
+1. Triaging and responding to issues.
+2. Reviewing and merging pull requests (aka QA).
+
+### 管理 GitHub Issue
+
+We use our main [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) repository as a common issue tracker for all of our repositories. We get new issues every day, all of which need to be triaged, labeled, and addressed. 這也是一個開始幫助開源代碼庫貢獻的好地方。
+
+#### Issue 分流
+
+[分流](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage)是一個優先關注每個新 issue 報告的過程。 我們有一個廣泛的標籤列表,用於標記每個 issue 的優先級、類別、狀態和範圍。
+
+你可以通過從[這個列表](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels)中使用標籤來幫助我們組織和分類 issue 報告。 通常,標籤旁邊有描述說明其含義。
+
+請特別注意標籤 `"help wanted"`(“需要幫助”)和 `"first timers only"`(“僅限新手使用”)。 這些標籤將添加到你認爲可以向潛在貢獻者開放,以便他們提出拉取請求的主題中。
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### 關閉陳舊的、過時的、不活躍的 issue 和拉取請求
+
+- Stale issues or PRs are those that have not seen any activity from the author for 21 days (3 weeks from the last activity), but only after a moderator has requested more information/changes.
+
+- Activity is defined as: Comments requesting an update on the PR and triages like `status: update needed` label, etc.
+
+- If the contributor asks for additional assistance or even time, the above can be relaxed and revisited after a response is given. In any case, the mods should use their best judgment to resolve the outstanding PR's status.
+
+:::tip
+We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+:::
+
+### 管理拉取請求(Pull Requests)
+
+Pull Requests (PRs) are how contributors submit changes to freeCodeCamp's repository. We must perform Quality Assurance (QA) on pull requests before we decide whether to merge them, request changes, or close them.
+
+#### Types of Pull Requests
+
+1. **Challenge instruction edits**
+
+ These are changes to the text of challenges - the description, instructions, or test text.
+
+ You can also review these right on GitHub and decide whether to merge them. 因爲會有無數的人通過 freeCodeCamp 課程讀到這段文字, 所以我們應該要更加認真對待。 Does the pull request make the text more clear without making it much longer? Are the edits relevant and not overly pedantic? Remember that our goal is for challenges to be as clear and as short as possible. They aren't the place for obscure details. Contributors may try to add links to resources to the challenges.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me) comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
+
+2. **Challenge code edits**
+
+ These are changes to the code in a challenge - the challenge seed, challenge solution, and test strings.
+
+ These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution and to make sure the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
+
+ Some contributors may try to add additional tests to cover pedantic corner-cases. We need to be careful to not make the challenge too complicated. These challenges and their tests should be as simple and intuitive as possible. Aside from the algorithm challenges and interview prep section, learners should be able to solve each challenge within about 2 minutes.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
+
+3. **Platform changes**
+
+ These code edits change the functionality of the freeCodeCamp platform itself.
+
+ Sometimes contributors try to make changes without much explanation, but for code changes, we need to make sure there's a genuine need for the change. These pull requests should reference an existing GitHub issue where the reasons for the change are discussed. Then you can open the pull request on your computer and test them out locally.
+
+ After you've done so, if the changes look good, don't merge them quite yet. You can comment on the pull request saying "LGTM", then mention **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** so they can take a final look.
+
+4. **Automated PRs (Dependabot)**
+
+ Some PRs are automated dependency updates made via an integration. You should not merge or approve these PRs. One of the dev-team members will take care of reviewing and merging such automated PRs.
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+First of all, when you choose a pull request to review, you should assign yourself to it. You can do this by clicking the "assign yourself" link below the "assignees" part on the right-hand column of GitHub's interface.
+
+Depending on the type of pull request it is, follow the corresponding rules listed previously.
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+Before merging any pull request, make sure that GitHub is reporting all checks to be passing (green check marks) on the pull requests. If you see any of the checks failing, please investigate and clarify the root cause. Is the change being made breaking our tests? Will the site build correctly if the PR is merged? These checks are critical for the stability of the platform.
+
+> [!WARNING] Merging a PR that fails CI/CD checks can cause difficulties for all stakeholders, including the dev-team and contributors.
+
+##### Handling Merge Conflicts:
+
+Sometimes there will be a merge conflict.
+
+This means that another pull request has made a change to that same part of that same file. GitHub has a tool for addressing these merge conflicts right on GitHub. You can try to address these conflicts. Use your best judgment.
+
+The pull request's changes will be on top, and the main branch's changes will be on the bottom. Sometimes there will be redundant information in there that can be deleted. Before you finish, be sure to delete the `<<<<<<`, `======`, and `>>>>>>` that Git adds to indicate areas of conflict.
+
+If you are uncertain, please ask one of the fellow moderators or the dev-team for assistance.
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+If the pull request looks ready to merge (and doesn't require additional approvals - remember we require at least two), you can go ahead and merge it. Be sure to use the default **"Squash and Merge"** option. This will squash all the pull requests commits down into a single commit, making the Git history much easier to read.
+
+> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way!
+
+If the pull request author is a "first-time contributor" you should also congratulate them on their first merged pull request to the repository. You can look at the upper right-hand corner of the PR's body to determine a first-time contributor. It will show `First-time contributor` as shown below:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ First-time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="First time contributor badge on pull requests" />
+</details>
+
+If the pull request doesn't look ready to merge, you can politely reply telling the author what they should do to get it ready. Hopefully, they will reply and get their pull request closer to ready.
+
+If you need a second opinion on a pull request, go ahead and leave your comments on the pull request, then add the "discussing" label to the pull request.
+
+##### Closing an Invalid Pull Request:
+
+Often, a pull request will be low effort. You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "Made changes" or "Update index.md".
+
+There are also situations where the contributor is trying to add a link to their website, include a library they created, or have a frivolous edit that doesn't help anyone but themselves.
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## 管理論壇
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Deleting Forum Posts
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. Someone has posted a pornographic or graphically violent image.
+2. Someone has posted a link or code that is malicious in nature and could harm other campers who click on it.
+3. Someone has flooded a thread with a lot of spam messages.
+4. An account has been created, beyond a reasonable doubt, to spam.
+
+### Dealing with Spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Dealing with Off-Topic Conversations
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Dealing with Posted Solutions
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Underage Users
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per our Terms of Service.
+
+It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
+
+Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
+
+Thank you for understanding.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- When trying to include a "Canned reply" in a response, if the menu doesn't open (after clicking on the gear), click on the text area first then try it again.
+- The moderator's 'wrench' is at the bottom of the view-port but if you click it and cannot see the "Select Posts" button because it has scrolled out of view, you may need to try to scroll to it, though sometimes that doesn't work in which case moving to a desktop/laptop monitor may be needed.
+- Sometimes clicking on the three-dot menu below a post can hide the reply icon. Reload the page to get it back.
+
+## 管理 Facebook 小組
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderating Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot serves as our moderation bot, and all of the commands use Discord's native slash command interface. You can see a list of all of the commands by typing `/` in any channel.
+
+1. **Make sure the user intended to violate the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Not all violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. In these cases, you can just ask them to paste their code with services like CodePen or Pastebin.
+
+2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), the moderator will proceed as follows:**
+
+ For minor offences, a warning may be issued with the `/warn` command. For more egregious offences, you can remove the member from the server temporarily with the `/kick` command, or permanently with the `/ban` command. In some cases, a member may just need some time to cool off and collect their thoughts - the `/mute` command allows you to prevent them from engaging with our community for a set period of time. A muted member can see the conversation, but cannot post messages or add reactions.
+
+ All moderation commands will take a `reason` parameter, which should be a short explanation of why the action was taken. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. As such, we should avoid using Discord's built-in moderation tools, as they will not be logged.
+
+ > [!WARNING] The reason provided to a moderation command will also be included in the DM notification to the camper. Please remember to be professional here.
+
+3. **Creating a private discussion**
+
+ There may be situations where you need to address a concern with a camper privately. This should not be done through DMs, which can lead to situations where you claim one thing and the camper claims another. Instead, use the bot's functionality to create a private discussion:
+
+ - Call the `/private` command, where `target` is the camper you want to open a private channel with.
+ - The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
+ - When the conversation is complete, click the `❌ Close` button _on the first message in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
+
+4. **Deleting messages**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. If a message is not in line with our Code of Conduct, or otherwise not appropriate for our community, you are generally safe to delete it.
+
+ Note that if the message contains content that violates Discord's terms of service, you'll want to report it via https://dis.gd/report **prior to** deleting it.
+
+5. **Don’t threaten to take action**
+
+ If a camper breaks the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `/private` command, or use the bot's moderation commands.
+
+ If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant moderation action or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of their actions without making it come across as a warning.
+
+ For example:
+
+ - Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
+
+ - Or if you really have to explain why:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - For mild and unintentional violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Don’t brag about being a moderator**
+
+ Do not see yourself as above the community. **You are the community.** And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
+
+ If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
+
+7. **Don’t contradict other moderators**
+
+ If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their PoV (Point of View).
+
+ _Remember: We’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front._
+
+8. **Talk with other moderators**
+
+ We have a `#mod-chat` room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporarily inactive**
+
+ If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
+
+## How to Become a Moderator
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+:::note
+For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
+
+This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
+:::
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- The user is guaranteed some privacy.
+- Public chat is no longer disrupted.
+- Other team members can pitch in, should you feel uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ddbc367d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Moderator Onboarding Guide
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you haven't read [The Moderator Handbook](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook) yet, you should start there first.
+
+## The Forum
+
+### First Steps
+
+The first thing you may notice after being given moderator status on the forum is that your interface will look somewhat different, with new admin tools to explore and access to the Mod-Team subforum.
+
+Some of the new tools will appear inside a new menu item that looks like a wrench. Some will appear as new tabs or buttons, or even new enabled options within the forum menus.
+
+To get familiar with the new tools and powers, you can combine one or more of the following methods during your first week with this elevated role:
+
+:::tip
+The first two are the most important.
+:::
+
+### Become Familiar with the Discourse Admin Tools
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. To begin to get familiar with Discourse and the moderation role, start by reading Discourse's [new user guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) and Discourse's [new moderator guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116).
+
+### Shadow a Mod
+
+All moderator actions can be followed by reviewing the [action logs](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. Posts to be reviewed will show up in the [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) area of the forum.
+
+For the first week or so you will want to pay attention to what is getting flagged and what is being reviewed, and compare that to the actions being taken upon the flagged posts. You may see the system account flag a post because the user created it too quickly. In many cases, the moderators will unflag the post by clicking on the "Approve Post" button or mark it as "Not Spam" (depending on the flag type).
+
+Commonly, spam flags can also be raised by members or moderators. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+You may notice moderators performing a procedure called 'split topic'. This may be a case where a moderator has split a post that was made erroneously on an existing topic into a new topic, or a moderator merged duplicate topics that a single user has created for the same question. Watching this procedure will highlight different actions and their causes.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. These include:
+
+- Welcoming a new forum member who has posted code without a question -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Reminding members not to post code solutions but to provide hints and tips instead -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Responding to a situation where someone's code works for you but not for them -> "Browser Issues"
+- Encouraging members to open GitHub issues when a possible bug is found -> "Bug Report"
+
+There are more, which you can read through to become familiar with their respective uses. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Read Mod-Team Subforum Posts
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Where to Ask for Help
+
+To get help dealing with a situation that you are either uncomfortable with or unsure of how to handle, discuss with your fellow moderators on either the [Mod-Team Subforum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) or the [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) on Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ffd17b46
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Responsible Disclosure - Hall of Fame
+---
+
+We appreciate any responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. If you are interested in contributing to the security of our platform, please read our [security policy outlined here](security).
+
+While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we are grateful to these awesome people for helping us keep the platform safe for everyone:
+
+- Mehul Mohan from [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Vulnerability Fix](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) working with IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da7cbcdb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp.org's Security Policy
+---
+
+This document outlines our security policy for the codebases, platforms that we operate, and how to report vulnerabilities.
+
+## Reporting a Vulnerability
+
+> [!NOTE] If you think you have found a vulnerability, **please report it responsibly**. Do not create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, follow this guide.
+
+### Guidelines
+
+We appreciate responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. In the interest of saving everyone time, we encourage you to report vulnerabilities with these in mind:
+
+1. Ensure that you are using the **latest**, **stable**, and **updated** versions of the Operating System and Web Browser(s) available to you on your machine.
+2. We consider using tools & online utilities to report issues with SPF & DKIM configs, SSL Server tests, etc., in the category of ["beg bounties"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) and are unable to respond to these reports.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Reporting
+
+After confirming the above guidelines, please feel free to send an email to `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. You can also send us a PGP encrypted message at `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Once you report a vulnerability, we will look into it and ensure that it is not a false positive. If we need to clarify any details, we will get back to you. You can submit separate reports for each issue you find. Please note that we will not be able to respond to any issues that we think are outside the guidelines.
+
+## Platforms and Codebases
+
+Here is a list of the platforms and codebases we are accepting reports for:
+
+### Learn Platform
+
+| Version | Branch | Supported | Website active |
+| ----------- | -------------- | --------- | ------------------------ |
+| production | `prod-current` | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| staging | `prod-staging` | Yes | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| development | `main` | No | |
+
+### Publication Platform
+
+| Version | Supported | Website active |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| production | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localized | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Mobile App
+
+| Version | Supported | Website active |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| production | Yes | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Other Platforms
+
+Apart from the above, we are also accepting reports for repositories hosted on GitHub under the freeCodeCamp organization.
+
+### Other Self-hosted Applications
+
+We self-host some of our platforms using open-source software like Ghost & Discourse. If you are reporting a vulnerability, please ensure that it is not a bug in the upstream software.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2092b229
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS or are still facing issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+:::warning
+Please avoid creating GitHub issues for problems with the prerequisite technologies. They are out of the scope of this project.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. If one of them isn't cached, run the following:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+OR
+
+Use the shortcut
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Use `git clean` in interactive mode:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to clean git untracked files (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="How to clean git untracked files">
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+While in development, your session is stored as cookies. Clearing them will sign you out of your development account.
+
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, too. It will overwrite the development user in your local database.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+When you try to navigate to http://localhost:8000/developmentuser to view the profile page, Gatsby takes over serving the client-side pages and hence you will get a 404 page for the user profile when working.
+
+There is a "Preview Custom 404 Page" button, click it to see the profile.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+The first time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+:::note
+If you are using Apple Devices with M1 Chip to run the application locally, it is suggested to use Node v14.7 or above. You might run into issues with dependencies like Sharp otherwise.
+:::
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions in the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh-TW/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1531334c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh-TW/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: How the User Token Workflow Works
+---
+
+User tokens are used to identify users to third parties so challenges completed using those services can be saved to a user's account.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+At the moment, the tokens are only used to submit the Relational Database challenges. A token gets created when a signed-in user clicks the "Click here to start the course" or "Click here to start the project" buttons to start one of the Relational Database courses or projects.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+A user token will be deleted when a user signs out of freeCodeCamp, resets their progress, deletes their account, or manually deletes the token using the widget on the settings page.
+
+## How they Work
+
+Tokens are stored in a `UserToken` collection in the database. Each record has a unique `_id`, which is the token, and a `user_id` that links to the user's account from the `user` collection. The token is encoded using JWT and sent to the client when it's created. That encoded token is then given to third-party services that need it and sent to our API by them when a challenge is completed. When our API gets it, it is decoded so we can identify the user submitting a challenge and save the completed challenge to their `completedChallenges`.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/authors-analytics-manual.md b/src/content/docs/zh/authors-analytics-manual.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a33bb9ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/authors-analytics-manual.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+---
+title: Authors Analytics Manual
+---
+
+If you are an author with access to the publication's Google Analytics Property (News), you can use this guide to view your article engagement and search for articles by publication language.
+
+## Search by Language
+
+To search for engagement reports in a specific language:
+
+
+
+1. From the top dropdown menu, select `News`.
+1. From the sidebar, click on `Reports`.
+1. From the secondary sidebar, select `Engagement`.
+1. Click on `Pages and Screens`.
+1. In the search bar, type the subpath for the desired language.
+1. From the dropdown under the search bar, choose `Page path and screen class`.
+
+## Filter Reports by Author
+
+After arriving at the `Pages and Screens` reports mentioned above, use the following steps to filter the results by specific authors.
+
+
+
+1. Click on the `Add filter` button.
+1. From the side navigation include `Author`.
+1. From the `Dimensions values` dropdown, choose an author's name.
+1. Click on the `Apply` button to apply changes.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/codebase-best-practices.md b/src/content/docs/zh/codebase-best-practices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ece2406a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/codebase-best-practices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
+---
+title: Codebase Best Practices
+---
+
+## Styling a component
+
+We recommend styling components using our [design style guide](https://design-style-guide.freecodecamp.org/).
+
+The colors are defined in [`variable.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/variables.css), and the fonts are in [`fonts.css`](/client/src/components/layouts/fonts.css).
+
+We are strongly opinionated about adding new variables/tokens to the colors. After careful research, the colors have been chosen to respect the freeCodeCamp brand identity, developer experience, and accessibility.
+
+The `!important` keyword may be used to override values in some cases (e.g. accessibility concerns). You should add a comment describing the issue, so it doesn't get removed in future refactoring.
+
+### RTL support
+
+We are striving to support right-to-left (RTL) layout in the codebase for languages that are read in this direction. For this, you need to be mindful of how to style components. Here are some quick rules of thumb to follow:
+
+- Don't use `float` properties
+ - Use Flexbox and Grid layouts instead, as they have RTL support already built-in, and those will be easier to maintain and review.
+- Don't define the direction while using `margin` and `padding`: it may seem harmless to use `padding-right` and `margin-left`, but these directions aren't mirrored when the layout changes to RTL, and adding counter values for them in the RTL file makes maintaining the codebase harder.
+ - Use logical properties for them: You can add the same spacing by using `padding-inline-end` and `margin-inline-start`, and you won't need to worry about RTL layout, as they follow where the line starts and ends, and you won't need to add any extra values in the RTL files, so people won't need to remember to change the same values in two files.
+- Don't use `!important` in `font-family`: RTL layout uses different fonts compared to the LTR layout, when you add `!important` in the `font-family` property it affects the RTL layout too.
+
+## General JavaScript
+
+In most cases, our [linter](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#follow-these-steps-to-get-your-development-environment-ready) will warn of any formatting which goes against this codebase's preferred practice.
+
+It is encouraged to use functional components over class-based components.
+
+## Specific TypeScript
+
+### Migrating a JavaScript File to TypeScript
+
+#### Retaining Git File History
+
+Sometimes changing the file from `<filename>.js` to `<filename>.ts` (or `.tsx`) causes the original file to be deleted, and a new one created, and other times the filename just changes - in terms of Git. Ideally, we want the file history to be preserved.
+
+The best bet at achieving this is to:
+
+1. Rename the file
+2. Commit with the flag `--no-verify` to prevent Husky from complaining about the lint errors
+3. Refactor to TypeScript for migration, in a separate commit
+
+> [!NOTE] Editors like VSCode are still likely to show you the file has been deleted and a new one created. If you use the CLI to `git add .`, then VSCode will show the file as renamed in stage
+
+### Naming Conventions
+
+#### Interfaces and Types
+
+For the most part, it is encouraged to use interface declarations over type declarations.
+
+React Component Props - suffix with `Props`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentProps {}
+// type MyComponentProps = {};
+const MyComponent = (props: MyComponentProps) => {};
+```
+
+React Stateful Components - suffix with `State`
+
+```typescript
+interface MyComponentState {}
+// type MyComponentState = {};
+class MyComponent extends Component<MyComponentProps, MyComponentState> {}
+```
+
+Default - object name in PascalCase
+
+```typescript
+interface MyObject {}
+// type MyObject = {};
+const myObject: MyObject = {};
+```
+
+<!-- #### Redux Actions -->
+
+<!-- TODO: Once refactored to TS, showcase naming convention for Reducers/Actions and how to type dispatch funcs -->
+
+## Redux
+
+### Action Definitions
+
+```typescript
+enum AppActionTypes = {
+ actionFunction = 'actionFunction'
+}
+
+export const actionFunction = (
+ arg: Arg
+): ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes.actionFunction> => ({
+ type: AppActionTypes.actionFunction,
+ payload: arg
+});
+```
+
+### How to Reduce
+
+```typescript
+// Base reducer action without payload
+type ReducerBase<T> = { type: T };
+// Logic for handling optional payloads
+type ReducerPayload<T extends AppActionTypes> =
+ T extends AppActionTypes.actionFunction
+ ? ReducerBase<T> & {
+ payload: AppState['property'];
+ }
+ : ReducerBase<T>;
+
+// Switch reducer exported to Redux combineReducers
+export const reducer = (
+ state: AppState = initialState,
+ action: ReducerPayload<AppActionTypes>
+): AppState => {
+ switch (action.type) {
+ case AppActionTypes.actionFunction:
+ return { ...state, property: action.payload };
+ default:
+ return state;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+### How to Dispatch
+
+Within a component, import the actions and selectors needed.
+
+```tsx
+// Add type definition
+interface MyComponentProps {
+ actionFunction: typeof actionFunction;
+}
+// Connect to Redux store
+const mapDispatchToProps = {
+ actionFunction
+};
+// Example React Component connected to store
+const MyComponent = ({ actionFunction }: MyComponentProps): JSX.Element => {
+ const handleClick = () => {
+ // Dispatch function
+ actionFunction();
+ };
+ return <button onClick={handleClick}>freeCodeCamp is awesome!</button>;
+};
+
+export default connect(null, mapDispatchToProps)(MyComponent);
+```
+
+<!-- ### Redux Types File -->
+<!-- The types associated with the Redux store state are located in `client/src/redux/types.ts`... -->
+
+## API
+
+### Testing
+
+The `api/` tests are split into two parts:
+
+1. Unit tests
+2. Integration tests
+
+#### Unit Tests
+
+Unit tests isolate a single function or component. The tests do not need mocking, but will require fixtures.
+
+The unit tests are located in a new file adjacent to the file exporting that is being tested:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── src/
+│ ├── utils.ts
+│ ├── utils.test.ts
+```
+
+#### Integration Tests
+
+Integration tests test the API as a whole. The tests will require mocking and should not require fixtures beyond the database seeding data and a method for authentication.
+
+Typically, each integration test file will be directly related to a route. The integration tests are located in the `api/tests/` directory:
+
+```text
+api/
+├── tests/
+│ ├── settings.ts
+```
+
+## Further Literature
+
+- [TypeScript Docs](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/)
+- [TypeScript with React CheatSheet](https://github.com/typescript-cheatsheets/react#readme)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/courses-vscode-extension.md b/src/content/docs/zh/courses-vscode-extension.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a4c86ccb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/courses-vscode-extension.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+---
+title: Courses VSCode Extension
+---
+
+This details the maintenance guidelines for the [freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension) repository which contains the source code for the [freeCodeCamp - Courses](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=freeCodeCamp.freecodecamp-courses) extension.
+
+## Publishing the Extension
+
+A GitHub Action automagically publishes the extension to the Visual Studio Marketplace, on the release of a new GitHub Release.
+
+1. Package a new version of the extension:
+
+```bash
+npm run pack -- <tag_type>
+```
+
+Where `<tag_type>` is one of: `major`, `minor`, `patch`.
+
+2. Push the new version to `main`:
+
+```bash
+git commit -am "<tag_type>(<version>): <description>"
+git push
+```
+
+Optionally, you can push directly to `upstream/main`, but opening a new PR is recommended for a sanity check.
+
+3. Create a new GitHub Release using the GitHub UI:
+
+- Correctly increment the version number, when creating a new tag.
+- Upload the `.vsix` file with the release.
+- Publish the release, and confirm the action succeeded.
+
+> [!NOTE] Creating a release requires write access to the `freeCodeCamp/courses-vscode-extension` repository.
+
+## Manually Publishing the Extension
+
+A manual upload to the Visual Studio Marketplace can be achieved, by following these steps:
+
+1. Visit https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/ and sign in
+2. Navigate to the [freeCodeCamp Publisher page](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/manage/publishers/freecodecamp)
+3. Select the relevant extension, and select `Update`
+4. Upload the file from your local files
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-file-structure.md b/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-file-structure.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..16942845
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-file-structure.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+---
+title: Curriculum File Structure
+---
+
+Our core instructional content is located within the conveniently named `curriculum` directory. This page will break down how these files are organized.
+
+## Terminology
+
+There are a few terms we use when discussing our curriculum content.
+
+- `certification` : When referring to a certification in this instance, it is talking about the actual certificate that users claim. Which is separate from the name of the superBlock.
+- `superBlock` : A superblock is the top level collection of challenges. Each superblock corresponds to a certification in the curriculum (e.g. Responsive Web Design).
+- `block` : A block is a section within a superblock. A block corresponds to a group of challenges in a given certification (e.g. Basic HTML and HTML5)
+- `challenge` : A challenge is a single lesson within the curriculum (e.g. Say Hello to HTML Elements)
+
+## File Tree
+
+Using those terms, here is how the file structure would be defined:
+
+<!-- prettier-ignore -->
+```md
+
+curriculum/
+├─ _meta/
+│ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ ├─ meta.json
+├─ {language}/
+│ ├─ {superBlock}/
+│ │ ├─ {block}/
+│ │ │ ├─ {challenge}.md
+```
+
+## The `_meta` Directory
+
+The `_meta` directory is a special directory which contains `.json` files. These files correspond to each block in the curriculum, and are used to determine which superBlock a block belongs to, and the order of the challenges within that block.
+
+## Renaming Files
+
+There may be times when you need to rename a certificate, superblock, block, or challenge. This section will outline the steps needed to avoid build errors when doing so.
+
+:::danger
+Renaming files within the curriculum structure will often change the path (or URL) of the content on the main webpage. Doing so should be done with care, as redirects have to be set up for each change that is made.
+:::
+
+### Renaming a Certification
+
+When renaming a certification, you will likely want to rename the associated superblock along with it. Do the following to rename only the certificate:
+
+1. Rename the `curriculum/challenges/_meta/{superBlock}-certificate` folder to the new name.
+1. In the `meta.json` file of that folder, rename the values in `name`, `dashedName`, and `challengeOrder` to the new cert name.
+1. In `curriculum/challenges/english/12-certificate`, rename the `{superBlock}-certificate` folder, and the YAML file within it, to the new name.
+1. In the YAML file, change the `title` to the new name.
+1. Rename the file and folder from step 3 for the rest of the curriculum languages.
+1. Update `client/src/redux/index.ts` to use the correct `title`.
+1. Optionally, update the `certSlug` for the superblock in the same file. **Note** that renaming a `certSlug` will change the URL for certifications and should only be done with careful consideration.
+1. Update the `title` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` to the new value. **Note** that changing the `title` here **will break** the superBlock page for the associated certification. It relies on the superBlock title to match the certification title. You will likely want to rename the superBlock at the same time.
+1. If you renamed the `certSlug` in step 7, change it here for the cert and all the nested `projects` values.
+1. In `shared/config/certification-settings.js`, update the value of `certTypeTitleMap` to the new name.
+1. If you renamed the `certSlug` in step 7, update the key of `certSlugTypeMap` in the same file.
+1. Update the certificate name in the `legacyCerts` array of the `client/src/client-only-routes/show-project-links.tsx` if needed.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Superblock
+
+> [!NOTE] When you rename a superBlock, the new folder name is used as the path and should be considered the "correct" name. All other values should be updated to reflect that change.
+
+Also, you will likely want to rename the certificate and the `{superBlock}-projects` block when you rename a superBlock since they all share a name. To rename only a superBlock you need to:
+
+1. Rename the superBlock folder in the `curriculum/challenges/english` directory.
+1. Rename the superBlock folder in _all_ other `curriculum/challenges/{language}` directories.
+1. For each block within that superBlock, update the `superBlock` value in the `meta.json` file to its dashedName. You don't need to rename any folders here. Do that when renaming a block.
+1. Rename the superblock folder in `client/src/pages/learn`.
+1. Update the `index.md` file in the above folder, changing the `title` and `superBlock` values to the new name.
+1. For each block folder within the above, update the `index.md` to use the correct `superBlock` value.
+1. In the `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts` file, update the path for the cert at the top of the file, and the `title` value for that superBlock. **Note** that changing the `title` here **will break** the ability to view the actual certification for this superBlock. It relies on the superBlock title to match the certification title. You will likely want to rename the certification at the same time.
+1. Update the `superBlockCertTypeMap` key in `shared/config/certification-settings.js` to the new superBlock name.
+1. Update the path value in `client/src/assets/icons/index.tsx`.
+1. For each language in `client/i18n/locales`, update the `intro.json` file to use the new superBlock `dashedName`. In the English file, also update the `title`.
+1. Check the `shared/config/i18n/all-langs.js` file to see if the superBlock is enabled in i18n builds. Update all the values where it is used.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Block
+
+When renaming a curriculum block, you need to:
+
+1. Change the name of the block folder in the `curriculum/challenges/english/{superBlock}` directory.
+1. Change the name of the same block folder in _all_ of the other language directories to match. These must all be the same as the English structure or the build will error out.
+1. Change the name of the block folder in the `_meta` directory.
+1. Update the `name` and `dashedName` property for that block's `meta.json` file.
+1. Update the block folder in `client/src/pages/learn/{superBlock}`.
+1. In the `index.md` file of the above folder, update the `block` value in the frontmatter.
+1. In the `client/i18n/locales/{language}/intro.json` files, update the block name to the new name for all the languages. In the English `intro.json` file, update the `title` as well.
+1. Update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+### Renaming a Challenge
+
+When renaming a single challenge file, you need to:
+
+1. Change the name of the challenge file in the `curriculum/challenges/english` directory.
+1. Change the name of the `title` and `dashedName` within that file.
+1. Change the name of the file, and the `dashedName` in those files for _all_ of the other language directories to match.
+1. Update the name of the challenge in the relevant `meta.json` file. The challenge names here are not used in the build, but provide a user-friendly way to identify the challenge order.
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the YAML file in `curriculum/english/12-certificates/<superBlock>` to the new name.
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the `title` and `link` in `client/src/resources/cert-and-project-map.ts`
+1. If the challenge is a certificate project, update the main `README.md` file to the new name.
+
+## The `dashedName` Property
+
+The `dashedName` property is used to generate the URL path for the superblock, block, or challenge. These should generally match what the `/utils/slugs.js` helper would output for the file name.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-help.md b/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..82848d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/curriculum-help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+---
+title: Using the Curriculum Helpers
+---
+
+The test runner has access to a few helpers that can assist with testing campers' code.
+
+## CSS Helper
+
+To instantiate the helper within a test block, use this:
+
+```js
+const helper = new __helpers.CSSHelp(document);
+```
+
+In that example, the `document` variable refers to the document object of the test runner's iframe.
+
+### Methods
+
+There are a few methods available for parsing and testing CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyle()`
+
+The `.getStyle()` method takes a CSS selector and returns a CSS style declaration object.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following CSS:
+
+```css
+body {
+ background: linear-gradient(45deg, rgb(118, 201, 255), rgb(247, 255, 222));
+ margin: 0;
+ padding: 0;
+ width: 100%;
+ height: 100vh;
+ overflow: hidden;
+}
+```
+
+You would get an object that looks like this:
+
+```js
+{
+ 0: "background-image",
+ 1: "background-position-x",
+ 2: "background-position-y",
+ 3: "background-size",
+ 4: "background-repeat-x",
+ 5: "background-repeat-y",
+ 6: "background-attachment",
+ 7: "background-origin",
+ 8: "background-clip",
+ 9: "background-color",
+ 10: "margin-top",
+ 11: "margin-right",
+ 12: "margin-bottom",
+ 13: "margin-left",
+ 14: "padding-top",
+ 15: "padding-right",
+ 16: "padding-bottom",
+ 17: "padding-left",
+ 18: "width",
+ 19: "height",
+ 20: "overflow-x",
+ 21: "overflow-y",
+ "accentColor": "",
+ "additiveSymbols": "",
+ "alignContent": "",
+ "alignItems": "",
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+This method allows you to test that specific properties have been set:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body')?.width, '100%');
+```
+
+The helper attaches a `.getPropVal()` method to the style declaration object that allows you to get the value of a specific property:
+
+```js
+assert.strictEqual(helper.getStyle('body').getPropVal('width'), '100%');
+```
+
+#### `.getCSSRules()`
+
+The `.getCSSRules()` takes an at-rule type from the union `media | fontface | import | keyframes`, and returns an array of CSS rules matching that at-rule.
+
+For example, if the camper has written the following code:
+
+```css
+@media (max-width: 100px) {
+ body {
+ background-color: green;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Then the returned value of `helper.getCSSRules('media')` would be this array:
+
+```js
+[
+ {
+ conditionText: "(max-width: 100px)",
+ cssRules: [
+ selectorText: 'body',
+ style: CSSStyleDeclaration,
+ styleMap: StylePropertyMap,
+ cssRules: CSSRuleList,
+ type: 1,
+ ...
+ ],
+ cssText: "@media (max-width: 100px) {\n body { background-color: green; }\n}",
+ ...
+ }
+]
+```
+
+You can then test that the camper has written the correct media query:
+
+```js
+const hasCorrectHeight = helper
+ .getCSSRules('media')
+ .some(x => x.style.height === '3px');
+assert.isTrue(hasCorrectHeight);
+```
+
+#### `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()`
+
+The `.getRuleListsWithinMedia()` method takes a media text (e.g. `("max-width: 200")`) and returns the CSS rules within that media query.
+
+The return result is the equivalent of that media rule's `cssRules` property from the return value of `.getCSSRules("media")`.
+
+### Less Frequent Methods
+
+These methods are not as commonly used, but are available if needed.
+
+#### `.getStyleDeclarations()`
+
+The `.getStyleDeclarations()` method takes a CSS selector and returns an array of CSS style declaration objects (from the `.getStyle()` method).
+
+#### `.isPropertyUsed()`
+
+The `.isPropertyUsed()` method takes a CSS **property** and checks if it has been set/used anywhere in the camper's CSS.
+
+#### `.getStyleRule()`
+
+The `.getStyleRule()` method takes a CSS selector and returns the CSS Style Declaration, much like `.getStyle()`. However, the declaration returned from this method includes an additional `.isDeclaredAfter()` method which takes a selector and returns whether this rule is declared after the selector passed in.
+
+#### `.getStyleSheet()`
+
+The `.getStyleSheet()` method returns the camper's CSS, parsed into a CSS Style Sheet object.
+
+## Strip Content
+
+There are a few methods on the `__helpers` object to remove content from the camper's code.
+
+These do NOT need to be instantiated they are static methods.
+
+### Removing Comments
+
+Using `__helpers.removeCssComments()`, `__helpers.removeHTMLComments()`, or `__helpers.removeJSComments()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove comments matching the language's comment syntax.
+
+### Removing Whitespace
+
+Using `__helpers.removeWhitespace()` allows you to pass the camper's code (through the `code` variable) to remove all whitespace.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/devops.md b/src/content/docs/zh/devops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c9bc0e7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/devops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,989 @@
+---
+title: DevOps Handbook
+---
+
+This guide will help you understand our infrastructure stack and how we maintain our platforms. While this guide does not have exhaustive details for all operations, it could be used as a reference for your understanding of the systems.
+
+Let us know if you have feedback or queries and we will be happy to clarify.
+
+## Flight Manual - Code Deployments
+
+This repository is continuously built, tested, and deployed to **separate sets of infrastructure (Servers, Databases, CDNs, etc.)**.
+
+This involves three steps to be followed in sequence:
+
+1. New changes (both fixes and features) are merged into our primary development branch (`main`) via pull requests.
+2. These changes are run through a series of automated tests.
+3. Once the tests pass we release the changes (or update them if needed) to deployments on our infrastructure.
+
+### Building the codebase - Mapping Git Branches to Deployments
+
+Typically, [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) (the default development branch) is merged into the [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) branch once a day and is released into an isolated infrastructure.
+
+This is an intermediate release for our developers and volunteer contributors. It is also known as our "staging" or "beta" release.
+
+It is identical to our live production environment at `freeCodeCamp.org`, other than it using a separate set of databases, servers, web-proxies, etc. This isolation lets us test ongoing development and features in a "production" like scenario, without affecting regular users of freeCodeCamp.org's main platforms.
+
+Once the developer team [`@freeCodeCamp/dev-team`](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/dev-team/members) is happy with the changes on the staging platform, these changes are moved every few days to the [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) branch.
+
+This is the final release that moves changes to our production platforms on freeCodeCamp.org.
+
+### Testing changes - Integration and User Acceptance Testing
+
+We employ various levels of integration and acceptance testing to check on the quality of the code. All our tests are done through software like [GitHub Actions CI](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) and [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp).
+
+We have unit tests for testing our challenge solutions, Server APIs, and Client User interfaces. These help us test the integration between different components.
+
+> [!NOTE] We are also in the process of writing end user tests which will help in replicating real-world scenarios like updating an email or making a call to the API or third-party services.
+
+Together these tests help in preventing issues from repeating themselves and ensure we do not introduce a bug while working on another bug or a feature.
+
+### Deploying Changes - Pushing changes to servers
+
+We have configured continuous delivery software to push changes to our development and production servers.
+
+Once the changes are pushed to the protected release branches, a build pipeline is automatically triggered for the branch. The build pipelines are responsible for building artifacts and keeping them in a cold storage for later use.
+
+The build pipeline goes on to trigger a corresponding release pipeline if it completes a successful run. The release pipelines are responsible for collecting the build artifacts, moving them to the servers, and going live.
+
+The statuses of builds and releases are [available here](#build-test-and-deployment-status).
+
+## Trigger a Build, Test, and Deploy
+
+Currently, only members of the developer team can push to the production branches. The changes to the `production-*` branches can land only via fast-forward merge to the [`upstream`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp).
+
+> [!NOTE] In the upcoming days, we would improve this flow to be done via pull requests, for better access management and transparency.
+
+### Pushing changes to Staging Applications
+
+1. Configure your remotes correctly.
+
+ ```sh
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ **Results:**
+
+ ```
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin git@github.com:raisedadead/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream git@github.com:freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+2. Make sure your `main` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+3. Check that the GitHub CI is passing on the `main` branch for upstream.
+
+ The [continuous integration](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions) tests should be green and PASSING for the `main` branch. Click the green check mark next to the commit hash when viewing the `main` branch code.
+
+ <details> <summary> Checking status on GitHub Actions (screenshot) </summary>
+ <br>
+ 
+ </details>
+
+ If this is failing you should stop and investigate the errors.
+
+4. Confirm that you are able to build the repository locally.
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run clean-and-develop
+ ```
+
+5. Move changes from `main` to `prod-staging` via a fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git merge main
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
+
+The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-staging` branch. Once the build is complete, the artifacts are saved as `.zip` files in a cold storage to be retrieved and used later.
+
+The release pipeline is triggered automatically when a fresh artifact is available from the connected build pipeline. For staging platforms, this process does not involve manual approval, and the artifacts are pushed to the Client CDN and API servers.
+
+### Pushing changes to Production Applications
+
+The process is mostly the same as the staging platforms, with a few extra checks in place. This is just to make sure, we do not break anything on freeCodeCamp.org which can see hundreds of users using it at any moment.
+
+| Do NOT execute these commands unless you have verified that everything is working on the staging platform. You should not bypass or skip any testing on staging before proceeding further. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+1. Make sure your `prod-staging` branch is pristine and in sync with the upstream.
+
+ ```sh
+ git checkout prod-staging
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard upstream/prod-staging
+ ```
+
+2. Move changes from `prod-staging` to `prod-current` via a fast-forward merge
+
+ ```
+ git checkout prod-current
+ git merge prod-staging
+ git push upstream
+ ```
+
+ > [!NOTE] You will not be able to force push and if you have re-written the history in any way, these commands will error out.
+ >
+ > If they do, you may have done something incorrectly and you should just start over.
+
+The above steps will automatically trigger a run on the build pipeline for the `prod-current` branch. Once a build artifact is ready, it will trigger a run on the release pipeline.
+
+**Additional Steps for Staff Action**
+
+Once a release run is triggered, members of the developer staff team will receive an automated manual intervention email. They can either _approve_ or _reject_ the release run.
+
+If the changes are working nicely and have been tested on the staging platform, then it can be approved. The approval must be given within 4 hours of the release being triggered before getting rejected automatically. A staff can re-trigger the release run manually for rejected runs, or wait for the next cycle of release.
+
+For staff use:
+
+| Check your email for a direct link or [go to the release dashboard](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_release) after the build run is complete. |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| |
+
+Once one of the staff members approves a release, the pipeline will push the changes live to freeCodeCamp.org's production CDN and API servers.
+
+## Build, Test and Deployment Status
+
+Here is the current test, build and deployment status of the codebase.
+
+| Branch | Unit Tests | Integration Tests | Builds & Deployments |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [`main`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | - |
+| [`prod-staging`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-staging) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-staging) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| [`prod-current`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/prod-current) | [](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Node.js+CI%22+branch%3Aprod-current) | [](https://dashboard.cypress.io/projects/ke77ns/analytics/runs-over-time) | [Azure Pipelines](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_dashboards/dashboard/d59f36b9-434a-482d-8dbd-d006b71713d4) |
+| `prod-next` (experimental, upcoming) | - | - | - |
+
+## Early Access and Beta Testing
+
+We welcome you to test these releases in a **"public beta testing"** mode and get early access to upcoming features to the platforms. Sometimes these features/changes are referred to as **next, beta, staging,** etc. interchangeably.
+
+Your contributions via feedback and issue reports will help us in making the production platforms at `freeCodeCamp.org` more **resilient**, **consistent**, and **stable** for everyone.
+
+We thank you for reporting bugs that you encounter and help in making freeCodeCamp.org better. You rock!
+
+### Identifying the Upcoming Version of the Platforms
+
+Currently, a public beta testing version is available at:
+
+| Application | Language | URL |
+| :---------- | :------- | :--------------------------------------- |
+| Learn | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Espanol | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/espanol> |
+| | Chinese | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/chinese> |
+| News | English | <https://www.freecodecamp.dev/news> |
+| Forum | English | <https://forum.freecodecamp.dev> |
+| | Chinese | <https://freecodecamp.dev/chinese/forum> |
+| API | - | `https://api.freecodecamp.dev` |
+
+> [!NOTE] The domain name is different than **`freeCodeCamp.org`**. This is intentional to prevent search engine indexing and avoid confusion for regular users of the platform.
+>
+> The above list is not exhaustive of all the applications that we provision. Also, not all language variants are deployed in staging to conserve resources.
+
+### Identifying the Current Version of the Platforms
+
+**The current version of the platform is always available at [`freeCodeCamp.org`](https://www.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+The dev-team merges changes from the `prod-staging` branch to `prod-current` when they release changes. The top commit should be what you see live on the site.
+
+You can identify the exact version deployed by visiting the build and deployment logs available in the status section. Alternatively, you can also ping us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) for a confirmation.
+
+### Known Limitations
+
+There are some known limitations and tradeoffs when using the beta version of the platform.
+
+- **All data / personal progress on these beta platforms will NOT be saved or carried over to production**
+
+ **Users on the beta version will have a separate account from the production.** The beta version uses a physically separate database from production. This gives us the ability to prevent any accidental loss of data or modifications. The dev-team may purge the database on this beta version as needed.
+
+- **The beta platforms do not provide any assurances regarding uptime and reliability**
+
+ Deployment is expected to be frequent and in rapid iterations, sometimes multiple times a day. As a result, there will be unexpected downtime at times or broken functionality on the beta version.
+
+- **To ensure the effectiveness of the fix, it is advised not to direct regular users to this site for verification purposes.**
+
+ The beta site is and always has been to augment local development and testing, nothing else. It's not a promise of what’s coming, but a glimpse of what is being worked upon.
+
+- **Sign in page may look different than production**
+
+ We use a test tenant for freeCodeCamp.dev on Auth0, and hence do not have the ability to set a custom domain. This makes it so that all the redirect callbacks and the login page appear at a default domain like: `https://freecodecamp-dev.auth0.com/`. This does not affect the functionality and is as close to production as we can get.
+
+## Reporting issues and leaving feedback
+
+Please open fresh issues for discussions and reporting bugs.
+
+You may send an email to `dev[at]freecodecamp.org` if you have any queries. As always all security vulnerabilities should be reported to `security[at]freecodecamp.org` instead of the public tracker and forum.
+
+## Flight Manual - Server Maintenance
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> 1. The guide applies to the **freeCodeCamp Staff members only**.
+> 2. These instructions should not be considered exhaustive, please use caution.
+
+As a member of the staff, you may have been given access to our cloud service providers like Azure, Digital Ocean, etc.
+
+Here are some handy commands that you can use to work on the Virtual Machines (VM), for instance performing maintenance updates or doing general housekeeping.
+
+## Get a list of the VMs
+
+> [!NOTE] While you may already have SSH access to the VMs, that alone will not let you list VMs unless you have been granted access to the cloud portals as well.
+
+### Azure
+
+Install Azure CLI `az`: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
+
+> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install azure-cli
+```
+
+> **(One-time) Login:**
+
+```
+az login
+```
+
+> **Get the list of VM names and IP addresses:**
+
+```
+az vm list-ip-addresses --output table
+```
+
+### Digital Ocean
+
+Install Digital Ocean CLI `doctl`: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#installing-doctl
+
+> **(One-time) Install on macOS with [`homebrew`](https://brew.sh):**
+
+```
+brew install doctl
+```
+
+> **(One-time) Login:**
+
+Authentication and context switching: https://github.com/digitalocean/doctl#authenticating-with-digitalocean
+
+```
+doctl auth init
+```
+
+> **Get the list of VM names and IP addresses:**
+
+```
+doctl compute droplet list --format "ID,Name,PublicIPv4"
+```
+
+## Spin New Resources
+
+We are working on creating our IaC setup, and while that is in works you can use the Azure portal or the Azure CLI to spin new virtual machines and other resources.
+
+:::tip
+No matter your choice of spinning resources, we have a few [handy cloud-init config files](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/infra/tree/main/cloud-init) to help you do some of the basic provisioning like installing docker or adding SSH keys, etc.
+:::
+
+## Keep VMs Updated
+
+You should keep the VMs up to date by performing updates and upgrades. This will ensure that the virtual machine is patched with the latest security fixes.
+
+> [!WARNING] Before you run these commands:
+>
+> - Make sure that the VM has been provisioned completely and that there are no post-install steps running.
+> - If you are updating packages on a VM that is already serving an application, make sure the app has been stopped / saved. Package updates will cause network bandwidth, memory and/or CPU usage spikes leading to outages on running applications.
+
+Update package information
+
+```bash
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+Upgrade installed packages
+
+```bash
+sudo apt upgrade -y
+```
+
+Cleanup unused packages
+
+```bash
+sudo apt autoremove -y
+```
+
+## Work on Web Servers (Proxy)
+
+We are running load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) instances for our web servers. These servers are running NGINX which reverse proxy all of the traffic to freeCodeCamp.org from various applications running on their own infrastructures.
+
+The NGINX config is available on [this repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Logging and monitoring for the servers are available at:
+
+ NGINX Amplify: [https://amplify.nginx.com]('https://amplify.nginx.com'), our current basic monitoring dashboard. We are working on more granular metrics for better observability
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+```bash
+sudo su
+```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+```bash
+cd /etc/nginx
+git fetch --all --prune
+git reset --hard origin/main
+```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+```bash
+nginx -t
+nginx -s reload
+```
+
+## Work on API Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Install pnpm globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+3. Install pm2 globally.
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pm2
+```
+
+4. Clone freeCodeCamp, set up env, and keys.
+
+```bash
+git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+cd freeCodeCamp
+git checkout prod-current # or any other branch to be deployed
+```
+
+5. Create the `.env` from the secure credentials storage.
+
+6. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+7. Setup pm2 `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+```bash
+pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+8. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+9. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server
+```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The latter is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+```bash
+pm2 stop all
+```
+
+2. Install dependencies
+
+```bash
+pnpm install
+```
+
+3. Build the server
+
+```bash
+pnpm prebuild && pnpm build:curriculum && pnpm build:server
+```
+
+4. Start Instances
+
+```bash
+pnpm start:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pnpm reload:server && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code and logic via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
+
+#### 3. Updating Node
+
+1. Install new Node version
+
+2. Update pm2 to use the new version
+
+```bash
+pm2 update
+```
+
+## Work on Client Instances
+
+1. Install build tools for node binaries (`node-gyp`) etc.
+
+```bash
+sudo apt install build-essential
+```
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+1. Install Node LTS.
+
+2. Update `npm` and install PM2 and setup `logrotate` and startup on boot
+
+ ```bash
+ npm i -g npm@8
+ npm i -g pm2@4
+ npm install -g serve@13
+ pm2 install pm2-logrotate
+ pm2 startup
+ ```
+
+3. Clone client config, setup env and keys.
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/client-config.git client
+ cd client
+ ```
+
+ Start placeholder instances for the web client, these will be updated with artifacts from the Azure pipeline.
+
+ > Todo: This setup needs to move to S3 or Azure Blob storage
+ >
+ > ```bash
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 50505 www" > client-start-primary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-primary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-primary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-primary.sh --name client-primary
+ > echo "serve -c ../serve.json -p 52525 www" > client-start-secondary.sh
+ > chmod +x client-start-secondary.sh
+ > pm2 delete client-secondary
+ > pm2 start ./client-start-secondary.sh --name client-secondary
+ > ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 monit
+```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+Code changes need to be deployed to the API instances from time to time. It can be a rolling update or a manual update. The later is essential when changing dependencies or adding environment variables.
+
+:::danger
+The automated pipelines are not handling dependencies updates at the minute. We need to do a manual update before any deployment pipeline runs.
+:::
+
+#### 1. Manual Updates - Used for updating dependencies, env variables.
+
+1. Stop all instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 stop all
+ ```
+
+2. Install or update dependencies
+
+3. Start Instances
+
+ ```bash
+ pm2 start all --update-env && pm2 logs
+ ```
+
+#### 2. Rolling updates - Used for logical changes to code.
+
+```bash
+pm2 reload all --update-env && pm2 logs
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] We are handling rolling updates to code, logic, via pipelines. You should not need to run these commands. These are here for documentation.
+
+## Work on Chat Servers
+
+Our chat servers are available with a HA configuration [recommended in Rocket.Chat docs](https://docs.rocket.chat/installation/docker-containers/high-availability-install). The `docker-compose` file for this is [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config).
+
+We provision redundant NGINX instances which are themselves load balanced (Azure Load Balancer) in front of the Rocket.Chat cluster. The NGINX configuration file are [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config).
+
+### First Install
+
+Provisioning VMs with the Code
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+1. Install NGINX and configure from repository.
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+
+ cd /var/www/html
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/error-pages
+
+ cd /etc/
+ rm -rf nginx
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-nginx-config nginx
+
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Install Cloudflare origin certificates and upstream application config.
+
+ Get the Cloudflare origin certificates from the secure storage and install at required locations.
+
+ **OR**
+
+ Move over existing certificates:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Local
+ scp -r username@source-server-public-ip:/etc/nginx/ssl ./
+ scp -pr ./ssl username@target-server-public-ip:/tmp/
+
+ # Remote
+ rm -rf ./ssl
+ mv /tmp/ssl ./
+ ```
+
+ Update Upstream Configurations:
+
+ ```bash
+ vi configs/upstreams.conf
+ ```
+
+ Add/update the source/origin application IP addresses.
+
+3. Set up networking and firewalls.
+
+ Configure Azure firewalls and `ufw` as needed for ingress origin addresses.
+
+4. Add the VM to the load balancer backend pool.
+
+ Configure and add rules to load balancer if needed. You may also need to add the VMs to load balancer backend pool if needed.
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. Install Docker and configure from the repository
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/chat-config.git chat
+ cd chat
+ ```
+
+2. Configure the required environment variables and instance IP addresses.
+
+3. Run rocket-chat server
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose config
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+### Logging and Monitoring
+
+1. Check status for NGINX service using the below command:
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo systemctl status nginx
+ ```
+
+2. Check status for running docker instances with:
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+### Updating Instances (Maintenance)
+
+**NGINX Cluster:**
+
+Config changes to our NGINX instances are maintained on GitHub, these should be deployed on each instance like so:
+
+1. SSH into the instance and enter sudo
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo su
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /etc/nginx
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Test and reload the config [with Signals](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/basic-functionality/runtime-control/#controlling-nginx).
+
+ ```bash
+ nginx -t
+ nginx -s reload
+ ```
+
+**Docker Cluster:**
+
+1. SSH into the instance and navigate to the chat config path
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/chat
+ ```
+
+2. Get the latest config code.
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git reset --hard origin/main
+ ```
+
+3. Pull down the latest docker image for Rocket.Chat
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose pull
+ ```
+
+4. Update the running instances
+
+ ```bash
+ docker-compose up -d
+ ```
+
+5. Validate the instances are up
+
+ ```bash
+ docker ps
+ ```
+
+6. Cleanup extraneous resources
+
+ ```bash
+ docker system prune --volumes
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ WARNING! This will remove:
+ - all stopped containers
+ - all networks not used by at least one container
+ - all volumes not used by at least one container
+ - all dangling images
+ - all dangling build cache
+
+ Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
+ ```
+
+ Select yes (y) to remove everything that is not in use. This will remove all stopped containers, all networks and volumes not used by at least one container, and all dangling images and build caches.
+
+## Work on Contributor Tools
+
+### Deploy Updates
+
+ssh into the VM (hosted on Digital Ocean).
+
+```bash
+cd tools
+git pull origin master
+pnpm install
+pnpm run build
+pm2 restart contribute-app
+```
+
+## Updating Node.js Versions on VMs
+
+List currently installed node & npm versions
+
+```bash
+nvm -v
+node -v
+npm -v
+
+nvm ls
+```
+
+Install the latest Node.js LTS, and reinstall any global packages
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts --reinstall-packages-from=default
+```
+
+Verify installed packages
+
+```bash
+npm ls -g --depth=0
+```
+
+Alias the `default` Node.js version to the current LTS (pinned to the latest major version)
+
+```bash
+nvm alias default 16
+```
+
+(Optional) Uninstall old versions
+
+```bash
+nvm uninstall <version>
+```
+
+:::danger
+For client applications, the shell script can't be resurrected between Node.js versions with `pm2 resurrect`. Deploy processes from scratch instead. This should become nicer when we move to a docker-based setup.
+:::
+
+> If using PM2 for processes you would also need to bring up the applications and save the process list for automatic recovery on restarts.
+
+Get the uninstall instructions/commands with the `unstartup` command and use the output to remove the systemctl services
+
+```bash
+pm2 unstartup
+```
+
+Get the install instructions/commands with the `startup` command and use the output to add the systemctl services
+
+```bash
+pm2 startup
+```
+
+Quick commands for PM2 to list, resurrect saved processes, etc.
+
+```bash
+pm2 ls
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 resurrect
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 save
+```
+
+```bash
+pm2 logs
+```
+
+## Installing and Updating Azure Pipeline Agents
+
+See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/v2-linux?view=azure-devops and follow the instructions to stop, remove, and reinstall agents. Broadly you can follow the steps listed here.
+
+You would need a PAT, that you can grab from here: https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/_usersSettings/tokens
+
+### Installing Agents on Deployment targets
+
+Navigate to [Azure Devops](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org) and register the agent from scratch in the requisite [deployment groups](https://dev.azure.com/freeCodeCamp-org/freeCodeCamp/_machinegroup).
+
+> [!NOTE] 你应该在主目录运行脚本,并确保没有其他 `azagent` 目录存在。
+
+### Updating Agents
+
+Currently updating agents requires them to be removed and reconfigured. This is required for them to correctly pick up `PATH` values and other system environment variables. 例如,我们需要在部署目标虚拟机上更新 Node.js 时这样做。
+
+1. Navigate and check status of the service
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~/azagent
+ sudo ./svc.sh status
+ ```
+
+2. Stop the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh stop
+ ```
+
+3. Uninstall the service
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo ./svc.sh uninstall
+ ```
+
+4. Remove the agent from the pipeline pool
+
+ ```bash
+ ./config.sh remove
+ ```
+
+5. Remove the config files
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ~
+ rm -rf ~/azagent
+ ```
+
+Once You have completed the steps above, you can repeat the same steps as installing the agent.
+
+## Flight Manual - Email Blast
+
+We use [a CLI tool](https://github.com/freecodecamp/sendgrid-email-blast) to send out the weekly newsletter. To spin this up and begin the process:
+
+1. Sign in to DigitalOcean, and spin up new droplets under the `Sendgrid` project. Use the Ubuntu Sendgrid snapshot with the most recent date. This comes pre-loaded with the CLI tool and the script to fetch emails from the database. With the current volume, three droplets are sufficient to send the emails in a timely manner.
+
+2. Set up the script to fetch the email list.
+
+ ```bash
+ cd /home/freecodecamp/scripts/emails
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ You will need to replace the placeholder values in the `.env` file with your credentials.
+
+3. Run the script.
+
+ ```bash
+ node get-emails.js emails.csv
+ ```
+
+ This will save the email list in an `emails.csv` file.
+
+4. Break the emails down into multiple files, depending on the number of droplets you need. This is easiest to do by using `scp` to pull the email list locally and using your preferred text editor to split them into multiple files. Each file will need the `email,unsubscribeId` header.
+
+5. Switch to the CLI directory with `cd /home/sendgrid-email-blast` and configure the tool [per the documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/README).
+
+6. Run the tool to send the emails, following the [usage documentation](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/sendgrid-email-blast/blob/main/docs/cli-steps).
+
+7. When the email blast is complete, verify that no emails have failed before destroying the droplets.
+
+## Flight Manual - Adding news instances for new languages
+
+### Theme Changes
+
+We use a custom [theme](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme) for our news publication. Adding the following changes to the theme enables the addition of new languages.
+
+1. Include an `else if` statement for the new [ISO language code](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) in [`setup-locale.js`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/assets/config/setup-locale.js)
+2. Create an initial config folder by duplicating the [`assets/config/en`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/tree/main/assets/config/en) folder and changing its name to the new language code. (`en` —> `es` for Spanish)
+3. Inside the new language folder, change the variable names in `main.js` and `footer.js` to the relevant language short code (`enMain` —> `esMain` for Spanish)
+4. Duplicate the [`locales/en.json`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/locales/en.json) and rename it to the new language code.
+5. In [`partials/i18n.hbs`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme/blob/main/partials/i18n.hbs), add scripts for the newly created config files.
+6. Add the related language `day.js` script from [cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) to the [freeCodeCamp CDN](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale)
+
+### Ghost Dashboard Changes
+
+Update the publication assets by going to the Ghost dashboard > settings > general and uploading the publications's [icon](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc-puck-500-favicon.png), [logo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/downloads/fcc_primary_large.png), and [cover](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/design-style-guide/blob/master/assets/fcc_ghost_publication_cover.png).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/faq.md b/src/content/docs/zh/faq.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9b70b372
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/faq.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: Frequently Asked Questions
+---
+
+Answers to common questions.
+
+## I am new to GitHub and Open Source. Where should I start?
+
+Read our ["How to Contribute to Open Source Guide"](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/how-to-contribute-to-open-source). It's a comprehensive reference for first-timer-friendly projects. And it includes a lot of open-source contribution tips.
+
+## What do I need to know to contribute to the codebase?
+
+freeCodeCamp runs on a modern JavaScript stack. If you're interested in contributing to our codebase, you will need some familiarity with JavaScript and some of the technologies we use like Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, and Webpack.
+
+## Can I translate freeCodeCamp's resources?
+
+Yes - You can contribute to any of the 30+ languages we have enabled on our translation platform.
+
+We have user-contributed translations live in some languages. We intend to localize freeCodeCamp into several major world languages. You can read all about this in our [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/).
+
+If you are interested in contributing to translations please make sure you [read this guide](how-to-translate-files) first.
+
+## Can I contribute articles to freeCodeCamp News or videos to freeCodeCamp's YouTube channel?
+
+Yes - you can contribute to our publication blog and YouTube channel.
+
+If you're interested in writing articles for freeCodeCamp News, please visit this [publication guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-write-for-freecodecamp/). In addition, please read our [style guide](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/developer-news-style-guide/) as this will help you write stronger and more effective articles.
+
+To help us make educational videos for our YouTube channel, you can follow the [YouTube channel guide here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-contribute-to-the-freecodecamp-community-youtube-channel-b86bce4c865/).
+
+## How can I report a new bug?
+
+If you think you've found a bug, first read the ["How to Report a Bug"](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-report-a-bug-to-freecodecamp/) article and follow its instructions.
+
+If you're confident it's a new bug, go ahead and create a new GitHub issue. Be sure to include as much information as possible so that we can reproduce the bug. We have a pre-defined issue template to help you through this.
+
+Please note that these GitHub issues are for codebase-related issues and discussions – not for getting help with learning to code. Whenever in doubt, you should [seek assistance on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org) before creating a GitHub issue.
+
+## How can I report a security issue?
+
+Please don't create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, please [follow our security policy](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/security).
+
+## I am a student. Can I work on a feature for academic credits?
+
+Yes. Please note we are unable to commit to any timelines or paperwork that may be a requirement by your college or university. We receive many pull-requests and code contributions from volunteer developers, and we respect their time and efforts. Out of respect for all of our other contributors, we will not give any PR special priority just because it happens to be school-related.
+
+We request you to plan ahead and work on code contributions with this in mind.
+
+## What do these different labels that are tagged on issues mean?
+
+The code maintainers [triage](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_bug#Bug_management) issues and pull requests based on their priority, severity, and other factors. You can [find a complete glossary of their meanings here](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp/labels).
+
+## Where do I start if I want to work on an issue?
+
+You should go through [**`help wanted`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22help+wanted%22) or [**`first timers only`**](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22first+timers+only%22) issues for a quick overview of what is available for you to work on.
+
+:::tip
+**`help wanted`** issues are up for grabs, and you do not need to seek permission before working on them. 然而,具有 **`first timers only`** 标签的 issue 是特别为以前没有为 freeCodeCodeCamp 代码库贡献的人设计的任务。
+:::
+
+## I found a typo. Should I report an issue before I can make a pull request?
+
+For typos and other wording changes, you can directly open pull requests without creating an issue first. Please be sure to mention details in the pull request description to help us understand and review your contribution – even if it's just a minor change.
+
+Please do create an issue if you want to discuss bigger aspects of the codebase or curriculum.
+
+## How can I get an issue assigned to me?
+
+We typically do not assign issues to anyone other than long-time contributors. Instead, we follow the below policy to be fair to everyone:
+
+1. We are most likely to merge the first pull request that addresses the issue.
+2. In the case of multiple contributors opening a pull request for the same issue at around the same time, we will give priority to the pull request that best addresses the issue. Some of the things we consider:
+ - Did you include tests?
+ - 你是否考虑了所有用例?
+ - 你是否确保通过所有测试,并确认所有东西在本地正常运行?
+3. Finally, we give priority to pull requests which follow our recommended guidelines.
+ - Did you follow the pull request checklist?
+ - Did you give your pull request a meaningful title?
+
+## I am interested in being a moderator at freeCodeCamp. Where should I start?
+
+Our community moderators are our heroes. Their voluntary contributions make freeCodeCamp a safe and welcoming community.
+
+First and foremost, we would need you to be an active participant in the community, and live by our [code of conduct](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/) (not just enforce it).
+
+Here are some recommended paths for some of our platforms:
+
+- To be a **Discord/Chat** moderator, have an active presence in our chat and have positive engagements with others, while also learning and practicing how to deal with potential conflicts that may arise.
+- To be a **Forum** moderator, similar to a chat moderator, have an active presence and engage with other forum posters, supporting others in their learning journey, and even giving feedback when asked. Take a look at [The Subforum Leader Handbook](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/the-subforum-leader-handbook/326326) for more information.
+- To be a **GitHub** moderator, help process GitHub issues that are brought up to see if they are valid and (ideally) try to propose solutions for these issues to be picked up by others (or yourself).
+
+Altogether, be respectful to others. We are humans from all around the world. With that in mind, please also consider using encouraging or supportive language and be mindful of cross-cultural communication.
+
+If you practice the above **consistently for a while** and our fellow moderator members recommend you, a staff member will reach out and onboard you to the moderators' team. Open source work is voluntary work and our time is limited. We acknowledge that this is probably true in your case as well. So we emphasize being **consistent** rather than engaging in the community 24/7.
+
+Take a look at our [Moderator Handbook](moderator-handbook) for a more exhaustive list of other responsibilities and expectations we have of our moderators.
+
+## I am stuck on something that is not included in this documentation.
+
+**Feel free to ask for help in:**
+
+- The `Contributors` category of [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors).
+- The `#Contributors` channel on [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+We are excited to help you contribute to any of the topics that you would like to work on. If you ask us questions on the related issue threads, we will be glad to clarify. Be sure to search for your question before posting a new one.
+
+Thanks in advance for being polite and patient. Remember – this community is run mainly by volunteers.
+
+## Additional Assistance
+
+If you have queries about the stack, architecture of the codebase, translations, or anything else, feel free to reach out to our staff team [on the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/team).
+
+**You can email our developer staff at: `dev[at]freecodecamp.org`**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..851061ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-cypress-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+---
+title: How to add Cypress tests
+---
+
+When making changes to JavaScript, CSS, or HTML which could change the functionality or layout of a page, it's important to add corresponding [Cypress](https://docs.cypress.io) integration tests.
+
+To learn how to write Cypress tests, or 'specs', please see Cypress' official [documentation](https://docs.cypress.io/guides/getting-started/writing-your-first-test.html).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Cypress tests are in the `./cypress` directory.
+
+- Cypress tests for a curriculum module are in the corresponding curriculum directory, i.e. `cypress/integration/learn/responsive-web-design/basic-css/index.js`.
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+> [!NOTE] If using Gitpod, please see [Cypress-Gitpod Setup](how-to-add-cypress-tests#cypress-gitpod-setup)
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database)
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Cypress Tests
+
+To run tests against production builds, replace `dev` with `prd` below.
+
+- To run all tests in the `./cypress` directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress:dev:run
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/<path_to_test_file>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run cypress run --spec=cypress/e2e/default/landing.ts
+ ```
+
+- To create a development build, start the development server, and run all existing cypress end-to-end tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run e2e:dev:run
+ ```
+
+## Cypress-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+- Create a config file.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+### 2. Install Cypress Build Tools
+
+```bash
+pnpm run cypress:install-build-tools
+```
+
+- When prompted in the terminal, select your keyboard layout by language/area
+
+Now, [Cypress can be run](how-to-add-cypress-tests#_2-run-the-cypress-tests)
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Unable to Connect to Port 8000
+
+If Cypress fails to run with the following error:
+
+```
+CypressError: `cy.visit()` failed trying to load:
+
+http://localhost:3000/signin
+
+We attempted to make an http request to this URL but the request failed without a response.
+
+We received this error at the network level:
+
+ > Error: connect ECONNREFUSED 127.0.0.1:8000
+
+Common situations why this would fail:
+ - you don't have internet access
+ - you forgot to run / boot your web server
+ - your web server isn't accessible
+ - you have weird network configuration settings on your computer
+
+This error occurred while creating the session. Because the session setup failed, we failed the test.
+```
+
+You can resolve the issue by:
+
+- Going to the root `package.json` file and adding `--host 0.0.0.0` to the `develop:client` command:
+ ```json
+ "scripts": {
+ "develop:client": "cd ./client && pnpm run develop --host 0.0.0.0"
+ }
+ ```
+- Then, re-running `pnpm run develop`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..38b58b7c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-add-playwright-tests.md
@@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
+---
+title: How to add Playwright tests
+---
+
+## Installation
+
+To install Playwright run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+Alternatively you can follow official documentation referenced below:
+
+To install and configure Playwright on your machine check out this [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#installing-playwright).
+
+To learn how to write Playwright tests, or 'specs', please see Playwright's official [documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/writing-tests).
+
+## Where to Add a Test
+
+- Playwright tests are in the `./e2e` directory.
+
+- Playwright test files are always with a `.spec.ts` extension.
+
+## Best Practices for writing E2E tests
+
+This section will explain in detail about best practices for writing and documenting E2E tests based on Playwright documentation and our community code-style.
+
+### - Imports
+
+Always start with necessary imports at the beginning of the file.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+import { test, expect, type Page } from '@playwright/test';
+```
+
+### - Identifying a DOM element
+
+Playwright comes with [multiple built-in locators](https://playwright.dev/docs/locators#quick-guide), but we recommend prioritizing the following locators:
+
+- `getByRole` for querying semantic elements, whose role is important and allows assistive technology to perceive the page correctly.
+- `getByText` for querying non-semantic elements such as `div`, `span`, or `p`.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByRole('heading', { name: 'Sign up' })).toBeVisible();
+await expect(page.getByText('Hello World')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+In cases where the elements cannot be queried using the above-mentioned locators, you can use the `data-playwright-test-label` attribute as the last resort. This attribute is used to identify elements in the DOM for testing with playwright only. It is not used for styling or any other purpose.
+
+For example:
+
+```html
+<div data-playwright-test-label="landing-page-figure">
+ <img src="..." alt="..." />
+</div>
+```
+
+In the test file, you can use the `getByTestId` method to identify the element.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure')).toBeVisible();
+```
+
+### - Constants
+
+Define any constant elements, data sets, or configurations used throughout your tests for easy reference.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+const landingPageElements = { ... };
+const superBlocks = [ ... ];
+```
+
+### - Shared Context
+
+If tests depend on a shared context (like a loaded web page), use beforeAll and afterAll hooks to set up and tear down that context.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+let page: Page;
+
+beforeAll(async ({ browser }) => {
+ page = await browser.newPage();
+});
+
+afterAll(async () => {
+ await page.close();
+});
+```
+
+### - Descriptive test names
+
+Each test block should have a clear and concise name describing exactly what it's testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The component landing-top renders correctly', async ({ page }) => {
+ // ...
+});
+```
+
+### - Human readable assertions
+
+Each assertion should be as human readable as possible. This makes it easier to understand what the test is doing and what it's expecting.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+await expect(landingHeading1).toHaveText('Learn to code — for free.');
+```
+
+### - Keep it DRY
+
+Make sure that the tests are not repeating the same code over and over again. If you find yourself repeating the same code, consider refactoring it as a loop or a function.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+for (const logo of await logos.all()) {
+ await expect(logo).toBeVisible();
+}
+```
+
+### - Tests for mobile screens
+
+Use the `isMobile` argument to run tests that include logic that varies for mobile screens.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+}) => {
+ const landingPageImage = page.getByTestId('landing-page-figure');
+
+ if (isMobile) {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeHidden();
+ } else {
+ await expect(landingPageImage).toBeVisible();
+ }
+});
+```
+
+### - Group related tests
+
+Group related tests together using describe blocks. This makes it easier to understand what the tests are doing and what they're testing.
+
+For example:
+
+```ts
+describe('The campers landing page', () => {
+ test('The campers landing page figure is visible on desktop and hidden on mobile view', async ({
+ isMobile
+ }) => {
+ // ...
+ });
+
+ test('The campers landing page figure has the correct image', async () => {
+ // ...
+ });
+});
+```
+
+## How to Run Tests
+
+### 1. Ensure that MongoDB and Client Applications are Running
+
+- [Start MongoDB and seed the database](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-3-start-mongodb-and-seed-the-database). In order for Playwright tests to work, be sure that you use the `pnpm run seed:certified-user` command.
+
+- [Start the freeCodeCamp client application and API server](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#step-4-start-the-freecodecamp-client-application-and-api-server)
+
+### 2. Run the Playwright Tests
+
+To run tests with Playwright check the following below
+
+- Make sure you navigate to the e2e repo first
+
+ ```bash
+ cd e2e
+ ```
+
+- To run tests in UI helper mode:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --ui
+ ```
+
+- To run a single test:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <filename>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test landing-page.spec.ts
+ ```
+
+- Run a set of test files in respective folders:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test <pathToFolder1> <pathToFolder2>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test tests/todo-page/ tests/landing-page/
+ ```
+
+- Run the test with the title:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g <title>
+ ```
+
+ For example:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test -g "add a todo item"
+ ```
+
+### 3. Debugging Tests
+
+Since Playwright runs in Node.js, you can debug it with your debugger of choice e.g. using console.log or inside your IDE
+
+- Debugging all tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test --debug
+ ```
+
+- Debugging one test file:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx playwright test example.spec.ts --debug
+ ```
+
+### 4. Generate Test Reports
+
+The HTML Reporter shows you a full report of your tests allowing you to filter the report by browsers, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests and flaky tests.
+
+```bash
+npx playwright show-report
+```
+
+### 5. Troubleshooting
+
+Playwright is generally a solid bullet-proof tool. The contributor has already configured the tests to run on all OS machines, including major distributions of Windows, MacOS and Linux.
+
+- (MacOs and Linux) If running Playwright results in an error due to kernel dependencies, run the following command:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools-linux
+ ```
+
+- A common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Error: page.goto: Could not connect: Connection refused
+ =========================== logs ===========================
+ navigating to "https://127.0.0.1:8000/", waiting until "load"
+ ============================================================
+ ```
+
+ You can fix the above error with the following steps:
+
+ 1. **Check the URL:** Ensure that the URL you're trying to navigate to is correct and properly formatted. Make sure there are no typos in the URL.
+
+ 2. **Server Status:** Check whether the server at the URL is running and accessible. You might encounter this error if the server is not running or is not accessible.
+
+ 3. **Port Availability:** Verify that the port mentioned in the URL (8000 in this case) is the correct port and is available for use. Make sure no other process is already using that port.
+
+ 4. **Firewall or Security Software:** Sometimes, firewall or security software can block connections to specific ports. Check your firewall settings to ensure that the port is allowed.
+
+ 5. **Network Connectivity:** Ensure that your system has a working network connection and can access external resources.
+
+- Another common error seen in playwright is as follows:
+
+ ```bash
+ Protocol error (Network.getResponseBody): Request content was evicted from inspector cache
+ ```
+
+ 1. The network request was made using a method that does not include a response body, such as HEAD or CONNECT.
+ 2. The network request was made over a secure (HTTPS) connection, and the response body is not available for security reasons.
+ 3. The network request was made by a third-party resource (such as an advertisement or a tracking pixel) that is not controlled by the script.
+ 4. The network request was made by a script that has been paused or stopped before the response was received.
+
+**For more insights on issues visit the official documentation.**
+
+## Playwright-Gitpod Setup
+
+### 1. Ensure Development Environment is Running
+
+If starting the Gitpod environment did not automatically develop the environment:
+
+- Follow the [MongoDB installation guide](https://www.mongodb.com/basics/get-started).
+
+- Create the .env
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+- Create a config file.
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+- Seed the database
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run seed:certified-user
+ ```
+
+- Develop the server and client
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run develop
+ ```
+
+### 2. Install Playwright Build Tools
+
+To install necessary dependencies for running Playwright run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run playwright:install-build-tools
+```
+
+### 3. Run the Playwright Tests on Gitpod
+
+To run all Playwright tests, run the following command:
+
+```bash
+cd e2e
+npx playwright test
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..40633cd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+---
+title: Catching emails locally
+---
+
+> **注意:** 这是一个 **可选的** 步骤,并且仅在处理电子邮件工作流时需要
+
+- [Introduction](#introduction)
+- [Installing MailHog](#installing-mailhog)
+- [Using MailHog](#using-mailhog)
+- [Useful Links](#useful-links)
+
+## Introduction
+
+Some email workflows, like updating a user's email, require the back-end API server to send outgoing emails. MailHog is an alternative to using an email service provider to send actual email messages. It is a developer tool for email testing that will catch the email messages sent by your freeCodeCamp instance.
+
+## Installing MailHog
+
+MailHog can be installed on macOS, Windows, and Linux or used via Docker.
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog with Docker</summary>
+
+If you have Docker installed then you can use
+
+```bash
+docker run -d --name mailhog --network host --rm mailhog/mailhog
+```
+
+to start MailHog in the background and
+
+```bash
+docker stop mailhog
+```
+
+to stop it.
+
+When the installation completes, you can start [using MailHog](#using-mailhog).
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on macOS</summary>
+
+使用 [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) 在 macOS 上安装 MailHog:
+
+```bash
+brew install mailhog
+brew services start mailhog
+```
+
+The above commands will start a MailHog service in the background.
+
+安装完成后,你可以开始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Windows</summary>
+
+Download the latest version of MailHog from [MailHog's official repository](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog/releases). Locate and click on the link for your Windows version (32 or 64 bit) and a `.exe` file will be downloaded to your computer.
+
+下载完成后,单击以打开文件。 可能会出现 Windows 防火墙通知,为 MailHog 请求访问权限。 一旦授予防火墙访问权限,将打开一个标准的 Windows 命令行提示符,MailHog 将在其中运行。
+
+通过关闭命令提示符窗口来关闭 MailHog。 To start MailHog again, click on the MailHog executable (`.exe`) file that was downloaded initially - it is not necessary to download a new MailHog installation file.
+
+开始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+<details><summary>Installing MailHog on Linux</summary>
+
+首先,安装 [Go](https://golang.org)。
+
+在基于 Debian 的系统(如 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint)上,运行以下命令安装 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo apt-get install golang
+```
+
+在基于 RPM 的系统(如 CentOS、Fedora、Red Hat Linux 等)上,运行以下命令安装 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo dnf install golang
+```
+
+或者,运行以下命令来安装 GO。
+
+```bash
+sudo yum install golang
+```
+
+现在使用以下命令设置 Go 的路径。
+
+```bash
+echo "export GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.profile
+echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin' >> ~/.profile
+source ~/.profile
+```
+
+最后,输入以下命令来安装和运行 MailHog。
+
+```bash
+go get github.com/mailhog/MailHog
+sudo cp /home/$(whoami)/go/bin/MailHog /usr/local/bin/mailhog
+mailhog
+```
+
+开始[使用 MailHog](#using-mailhog)。
+
+</details>
+
+## Using MailHog
+
+Open a new browser tab or window and navigate to [http://localhost:8025](http://localhost:8025) to open your MailHog inbox when the MailHog installation has been completed and MailHog is running.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- Check out the [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) repository for further information related to MailHog. Additional information is also available regarding custom MailHog configurations.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..713c41ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the Codebase
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines to contribute to the codebase. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+Ignoring these steps may soil your copy which makes the contributing, maintaining, and reviewing processes difficult.
+
+## Contributing to the Codebase
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to your fork, which you can prepare by reading [how to set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you got a different message, then you aren't on main or your working directory isn't clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the freeCodeCamp upstream `main` branch to your `main` fork branch:
+
+ > [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull requests that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+ >
+ > You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+ This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp.
+
+ Update your copy of the freeCodeCamp upstream repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp main:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ The resulting output should be empty. This process is important, because you will be rebasing your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run freeCodeCamp to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: CONTRIBUTING.md
+ modified: docs/README.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
+ modified: docs/how-to-work-on-guide-articles.md
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: add test for JavaScript - for loop step
+ feat: add link for article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Make a conventional commit message. This is a good practice as a developer, and you will be following standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: improve HTML step
+ fix: fix build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add link to JavaScript hoisting article
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any more time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Quick commands reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working.
+
+| command | description |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm test` | Run all JS tests in the system, including client, server, lint and challenge tests. |
+| `pnpm run test-client` | Run the client test suite. |
+| `pnpm run test-client -u` | Run the client test suite, updating the Jest snapshots that are out of sync. |
+| `pnpm run test:curriculum` | Run the curriculum test suite. |
+| `FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific Block. |
+| `FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum` | Test a specific SuperBlock. |
+| `pnpm run test-curriculum-full-output` | Run the curriculum test suite, without bailing after the first error |
+| `pnpm run test-server` | Run the server test suite. |
+| `pnpm run e2e` | Run the Cypress end to end tests. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
+| `pnpm run storybook` | Starts Storybook for component library development. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-enable-new-languages.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f6e4003
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-enable-new-languages.md
@@ -0,0 +1,468 @@
+---
+title: Deploying New Languages on `/learn`
+---
+
+To enable a new language on `/learn` (curriculum), you need to complete the following steps:
+
+- Complete translating and approving the first 3 certifications on Crowdin. (New Responsive Web Design, JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures, and Front End Development Libraries)
+- Complete translating and approving all strings in Learn UI project on Crowdin.
+- Update Crowdin settings to add a custom language code for the new language.
+- Open the 1st PR to configure GitHub Actions. You need to update 2 files:
+ - `crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`
+ - `crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`
+- Open the 2nd PR to add other configurations. You need to update/add the following files:
+ - Update `i18n.ts`
+ - Update `superblocks.ts`
+ - Update `algolia-locale-setup.ts`
+ - Add `links.json`
+ - Add `meta-tags.json`
+ - Add `motivation.json`
+- Ask infrastructure team to spin up the VM for the new language.
+- Once the VM is ready, open the 3rd PR to show the new language in the navigation menu.
+
+We will explain each step in the following sections.
+
+## Updating Crowdin Settings
+
+Before you can release a new language, you will need to allow the languages to download from Crowdin. To configure that, you need to add a custom language code for your language.
+
+In the `Curriculum` and `Learn UI` projects on Crowdin, you will need to select `Settings` > `Languages` from the sidebar. Then scroll down to `Language Mapping`, where you will see an option to add custom language codes. Add a new entry for the language you are releasing, selecting `language` as the `Placeholder` value, and entering a URL-friendly lower-case spelling of your language's name for the `Custom code`. If you aren't sure what to use, or you don't have an admin role and can't see the settings, reach out in our contributor chat and we will assist you.
+
+## Updating Workflows for GitHub Actions
+
+Then you need to configure the syncing between Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+You will need to add a step to the [`crowdin-download.client-ui.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.client-ui.yml) and [`crowdin-download.curriculum.yml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/.github/workflows/crowdin-download.curriculum.yml). The step for these will be the same. For example, if you want to enable Dothraki downloads:
+
+```yml
+##### Download Dothraki #####
+- name: Crowdin Download Dothraki Translations
+ uses: crowdin/github-action@master
+ # options: https://github.com/crowdin/github-action/blob/master/action.yml
+ with:
+ # uploads
+ upload_sources: false
+ upload_translations: false
+ auto_approve_imported: false
+ import_eq_suggestions: false
+
+ # downloads
+ download_translations: true
+ download_language: mis
+ skip_untranslated_files: false
+ export_only_approved: true
+
+ push_translations: false
+
+ # pull-request
+ create_pull_request: false
+
+ # global options
+ config: './crowdin-config.yml'
+ base_url: ${{ secrets.CROWDIN_BASE_URL_FCC }}
+
+ # Uncomment below to debug
+ # dryrun_action: true
+```
+
+Note that the `download_language` key needs to be set to the language code displayed on Crowdin.
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+> [!NOTE] The above section with updating the workflows should be completed before proceeding - these need to be done in separate steps or the builds will fail.
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file to add the language to the list of available languages and configure the values. There are several objects here.
+
+- `Languages`: Add the new language to `Languages` enum, similar to the others. The string value here will be used in the `.env` file to set a build language later.
+- `availableLangs`: Add the new property from the `Languages` enum to both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays.
+- `i18nextCodes`:这些是每种语言的 ISO 语言代码。 You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+- `hiddenLangs`: These languages will not be displayed in the navigation menu. This is used for languages that are not yet ready for release. Include your language in this array in the first PR and ask staff team to prepare the VM instance for your language. When the VM is ready, make another PR to remove it from the array.
+- `rtlLangs`: These are languages that read from right to left.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `i18n.ts` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export enum Languages {
+ English = 'english',
+ Espanol = 'espanol',
+ Chinese = 'chinese',
+ ChineseTraditional = 'chinese-traditional',
+ Dothraki = 'dothraki'
+}
+
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ],
+ curriculum: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Dothraki
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'English',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'Español',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: '中文(简体字)',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: '中文(繁體字)',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ [Languages.English]: 'en-US',
+ [Languages.Espanol]: 'es-419',
+ [Languages.Chinese]: 'zh',
+ [Languages.ChineseTraditional]: 'zh-Hant',
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: 'mis'
+};
+
+export const hiddenLangs = ['dothraki'];
+
+export const rtlLangs = [''];
+```
+
+> [!NOTE] When a language has been set up in the deployment pipeline AND has a public `/learn` instance live, it can be removed from the `hiddenLangs` array and be made available to the public.
+
+### Set Translated SuperBlocks
+
+In the [shared/config/superblocks.ts](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/superblocks.ts) file, add the new language to the `notAuditedSuperBlocks` object. This lists all the superblocks which are not fully translated. Add an array of superblocks that have not been fully translated to it. For example:
+
+```js
+export const notAuditedSuperBlocks: NotAuditedSuperBlocks = {
+ ...
+ [Languages.Dothraki]: [
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.RelationalDb,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy,
+ SuperBlocks.CollegeAlgebraPy,
+ SuperBlocks.FoundationalCSharp,
+ SuperBlocks.CodingInterviewPrep,
+ SuperBlocks.ProjectEuler,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStructNew,
+ SuperBlocks.TheOdinProject
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+Be sure to only add the superblocks that are **not** fully translated and approved. The translated superblocks will be calculated from this object. When a new superblock is finished being fully translated, remove it from the array for that language.
+
+See the `SuperBlocks` enum at the beginning of the same file for the full list of superblocks.
+
+### Configure Search
+
+Next, open the [`client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts) file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+
+ // If we already have /news in the target language up and running, you can update the values like this:
+ // dothraki: {
+ // name: 'news-mis',
+ // searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/dothraki/news/search/'
+ // }
+};
+```
+
+### Client UI
+
+You will need to take an additional step to handle the client UI translations.
+
+The Crowdin workflows will automatically pull down _some_ of the UI translations, but there are a couple of files that need to be moved manually.
+
+You will want to copy the following files from [`/client/i18n/locales/english`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n/locales/english) to `/client/i18n/locales/<your-language>`, and apply translations as needed:
+
+- `links.json`
+- `meta-tags.json`
+- `motivation.json`
+
+You don't have to have everything in these 3 files translated at first. It's possible to translate only the relevant parts and make adjustments later.
+
+#### `links.json`
+
+You can replace any URLs that you have corresponding pages ready in your language.
+
+For example, if you have a publication in your language, you can replace the URL for `"news"`. If you want to translate articles listed in the footer links, see [How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links](language-lead-handbook#how-to-translate-articles-in-the-footer-links).
+
+#### `meta-tags.json`
+
+This file contains metadata for the web page of `/learn` in your language. You can translate the values for `"title"`, `"description"`, and `"social-description"`. The value for `"youre-unsubscribed"` is used when someone unsubscribes from Quincy's weekly email.
+
+Also, you can translate or add relevant keywords in your language to the `"keywords"` array.
+
+#### `motivation.json`
+
+This file contains the compliments that will be displayed to campers when they complete a challenge, and motivational quotes that are displayed on the top page of `/learn`.
+
+You can translate them, or even replace them with relevant compliments/quotes of your choice in your language.
+
+### Enabling Localized Videos
+
+This section is applicable only if you have localized videos in the challenges. Otherwise, you can skip this section.
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First, add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the [`client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/src/templates/Challenges/video/show.tsx) file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `i18n.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally, update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Testing Translations Locally
+
+If you would like to test translations locally, before adding them to our main repository - skip the Crowdin workflow changes. Follow the steps for enabling a language, then download the translations from Crowdin and load them into your local code.
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Update your `.env` file to use your new language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `pnpm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::tip
+If you build the client in one language and then want to build it in a different language, you will need to use the command `pnpm run clean-and-develop` after changing the `.env` file, as Gatsby will cache the first language.
+:::
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
+
+## Show the language in the navigation menu
+
+When your prior PR is merged and the VM for your language is ready, make another PR to show your language in the navigation menu.
+
+In [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file, you have included your language in `hiddenLangs` array in the prior PR. Remove it from the array now.
+
+```js
+export const hiddenLangs = []; // Remove your language from the array
+```
+
+When this PR is merged and deployed, the curriculum in your language will be live.
+
+# Deploying New Languages on `/news`
+
+To deploy News for a new language, you'll need to create two PRs. One PR will be to the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn), and the other will be to the [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news).
+
+## Prep the CDN Repo for the New Language
+
+News sources trending links and article titles from our CDN during the build and adds them to the footer. News also fetches Day.js files from the CDN during the build to localize dates and times for each language.
+
+### Add a YAML File for Trending Articles
+
+Clone the [CDN repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn) and create a new branch.
+
+In the [`build/universal/trending`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) directory, create a new file and name it `language.yaml`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `dothraki.yaml`.
+
+Then copy the contents of the [`english.yaml`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/blob/main/build/universal/trending/english.yaml) trending file and paste it into the new YAML file you just created.
+
+The contents will look something like this:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Learn JavaScript"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/learn-javascript-free-js-courses-for-beginners/"
+article1
+title: "Linux ln Example"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/linux-ln-how-to-create-a-symbolic-link-in-linux-example-bash-command"
+article2
+title: "JS document.ready()"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-document-ready-jquery-example/"
+article3
+title: ...
+article3link: ...
+ ...
+```
+
+### Add a Day.js Locale File for the New Language
+
+By default, Day.js only includes English as a locale. To enable it to work with other languages, you need to add a new Day.js locale file to the CDN.
+
+In the [`build/news-assets/dayjs/<version>/locale`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/news-assets/dayjs/1.10.4/locale) directory, create a new file and name it `isocode.min.js`. For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, name the file `mis.min.js`.
+
+> [!NOTE] The version number will change as the dependencies are updated.
+
+Then, visit [this page on cdnjs](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/dayjs/1.10.4) with all available Day.js files for the version we're using, find the `https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/dayjs/<version>/locale/isocode.min.js` link for the new language, and open it in a new tab.
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to add the .../dayjs/\<version\>/_locale_/isocode.min.js locale file. You do not need to add any other Day.js files.
+
+Copy the Day.js locale code from the new tab into the new file you created. For example, here is an un-minified version of the English locale code for Day.js:
+
+```js
+!(function (e, n) {
+ 'object' == typeof exports && 'undefined' != typeof module
+ ? (module.exports = n())
+ : 'function' == typeof define && define.amd
+ ? define(n)
+ : (e.dayjs_locale_en = n());
+})(this, function () {
+ 'use strict';
+ return {
+ name: 'en',
+ weekdays: 'Sunday_Monday_Tuesday_Wednesday_Thursday_Friday_Saturday'.split(
+ '_'
+ ),
+ months:
+ 'January_February_March_April_May_June_July_August_September_October_November_December'.split(
+ '_'
+ )
+ };
+});
+```
+
+Then open a PR to the CDN repo to add both the YAML and Day.js files for review.
+
+## Prep the News Repo for the New Language
+
+The [News repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) pulls data from a Ghost instance, the files you added to the CDN, builds News, and deploys it.
+
+> [!WARN] Pull requests to the News repo _must_ come from the same repo. You should not work off of a fork for this step.
+
+### Modify the Main Config File
+
+Clone the News repo and create a new branch.
+
+Open the `config/index.js` file to add the new language and configure the necessary values. There are a few objects and arrays to modify:
+
+- `locales`: This array contains the active and upcoming News languages. These are the values that are used in the `.env` file to choose the Ghost instance and UI to use for each build. Add the text name of the new language in lowercase to this array.
+- `localeCodes`: This object is a map of ISO codes for each language, and is used to configure i18next before building the UI. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_ and the ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+- `algoliaIndices`: This object is a map of Algolia indices for each language. To add a new language, use the lowercase language name as the _key_, and `news-` followed by the lowercase ISO 639-1 language code as the _value_.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are unsure about the string to use while setting `algoliaIndices`, send a message to Kris (@scissorsneedfoodtoo), or someone else with access to Algolia, and ask them to check.
+
+For example, if you are launching Dothraki News, here are what the objects / arrays above should look like:
+
+```js
+const locales = ['arabic', 'bengali', 'chinese', 'english', 'dothraki'];
+
+const localeCodes = {
+ arabic: 'ar',
+ bengali: 'bn',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ english: 'en',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ arabic: 'news-ar',
+ bengali: 'news-bn',
+ chinese: 'news-zh',
+ english: 'news',
+ dothraki: 'news-mis'
+};
+```
+
+### Add the i18next JSON Files for the New Language
+
+Next, go to the `shared/config/i18n/locales` directory, create a new folder, and give it the name of the new language you're adding. For example, if you're launching Dothraki News, create a new folder named `dothraki`.
+
+Then copy the JSON files from the `english` directory to your new folder.
+
+In your new folder, open the `redirects.json` file and replace its contents with an empty array:
+
+```json
+[]
+```
+
+Then commit and push your branch directly to the News repo.
+
+> [!NOTE] You need to be on one of the teams with access to the News repo to push branches directly to News. Currently, only the dev, i18n, and staff teams are allowed to do this.
+
+Finally, open a PR for review.
+
+Once both your PRs to the CDN and News repo have been approved, they can be merged.
+
+> [!NOTE] Deployment will be handled subsequently by the staff. Here is a sample PR: [freeCodeCamp/news#485](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news/pull/485) of how they do it and more details are available in the [staff-wiki](https://staff-wiki.freecodecamp.org/docs/flight-manuals/news-instances#jamstack---news--assets).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5f2b3462
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-help-with-video-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+---
+title: How to Help with Video Challenges
+---
+
+Video challenges are a new type of challenge in the freeCodeCamp curriculum.
+
+A video challenge is a small section of a full-length video course on a particular topic. A video challenge page embeds a YouTube video. Each challenge page has a single multiple-choice question related to the video. A user must answer the question correctly before moving on to the next video challenge in the course.
+
+The video challenge pages are created by members of the freeCodeCamp team. YouTube videos are also uploaded by members of the freeCodeCamp team. Many of the video challenges do not yet have questions associated with them.
+
+You can help by creating multiple-choice questions related to video sections and adding the questions to the markdown files for the video challenges.
+
+## Challenge Template
+
+Below is a template of what the challenge markdown files look like.
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: Challenge Title
+challengeType: 11
+videoId: 'YouTube videoId for video challenge'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+```
+
+## Creating Questions for Video Challenges
+
+### Access the Video Challenge Markdown Files
+
+You can find the markdown files for video challenges at the following locations in the curriculum:
+
+- [Data Analysis with Python Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/data-analysis-with-python-course)
+- [TensorFlow 2.0 Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/tensorflow)
+- [Numpy Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/08-data-analysis-with-python/numpy)
+- [How Neural Networks Work Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/11-machine-learning-with-python/how-neural-networks-work)
+
+Pick a challenge markdown file from the options above.
+
+### Skim through the video associated with the challenge and create a multiple-choice question
+
+First, find the `videoId`.
+
+For example, in the following code from the header of a video challenge markdown file, the `videoId` is "nVAaxZ34khk". On GitHub, the information should be laid out in a table format.
+
+```
+
+---
+
+id: 5e9a093a74c4063ca6f7c14d
+title: Data Analysis Example A challengeType: 11
+videoId: nVAaxZ34khk
+
+---
+
+````
+
+Next, access the YouTube video with that `videoId`. The URL for the video will be:
+https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=[videoId] (replace `videoId` in the URL with the video's ID - without square brackets)
+
+In the example above, the URL is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nVAaxZ34khk
+
+Skim the YouTube video with that `videoId` and think of a multiple-choice question based on the content of the video.
+
+### Add the Question to the Markdown File
+
+You can add the question locally or using the GitHub interface. To add the question locally, you need to [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). You can also find the file on GitHub and click the edit button to add the question right in your browser.
+
+If a question has not yet been added to a particular video challenge, it will have the following default question:
+
+```md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+Question text
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+1
+````
+
+Add/Update the question text under the part that shows:
+
+```
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+```
+
+Add/Update answers (`Answer 1`, `Answer 2`, and so on) under `## --answers--`. Make sure to update the number under `## --video-solution--` with the correct answer number. You can add more possible answers using the same format. The questions and answers can be surrounded with quotation marks.
+
+### Question examples
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+What does this JavaScript code log to the console?
+
+```js
+console.log('hello world');
+```
+````
+
+## --answers--
+
+hello _world_
+
+---
+
+**hello** world
+
+---
+
+hello world
+
+---
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3
+
+`````
+
+````md
+# --question--
+
+## --text--
+
+What will print out after running this code:
+
+```py
+width = 15
+height = 12.0
+print(height/3)
+`````
+
+## --answers--
+
+39
+
+---
+
+4
+
+---
+
+4.0
+
+---
+
+5.0
+
+---
+
+5
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+3 ````
+
+For more examples, you can look at the markdown files for the following video course. All the challenges already have questions: [Python for Everybody Course](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges/english/07-scientific-computing-with-python/python-for-everybody)
+
+## Open a Pull Request
+
+After creating one or more questions, you can commit the changes to a new branch and [open a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c37cb789
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-open-a-pull-request.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+---
+title: How to open a Pull Request (PR)
+---
+
+A pull request (PR), enables you to send changes from your fork on GitHub to freeCodeCamp.org's main repository. Once you are done making changes to the code, you can follow these guidelines to open a PR.
+
+We expect our contributors to be aware of the process specific to this project. Following the guidelines carefully earns you the respect of fellow maintainers and saves everyone time.
+
+Some examples of this are:
+
+1. Do not edit files directly through GitHub – while you can, it's not a good idea.
+2. Make sure the PR title follows [our convention](#prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+3. Make sure you follow the PR checklist and not just tick things off; otherwise, we won't take you seriously.
+4. Use the correct way to link issues in the description of the PR by updating the `XXXXXX`. Do not just add issue numbers everywhere and anywhere you feel like.
+5. Do not "@mention" or request someone for reviews too many times.
+
+ We understand you are excited about contributing. As much as a maintainer will love to get back to you, they are busy people looking after hundreds of requests just like yours. Be patient, someone will get to you sooner or later.
+
+6. Do not work directly off your `main` branch - create a new branch for the changes you are working on.
+
+> [!NOTE] Your PR should be targeting changes to the English curriculum only. Read [this guide](index#translations) instead for contributing to translations.
+
+## Prepare a Good PR Title
+
+We use [conventional title and messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/) for commits and pull requests. The convention has the following format:
+
+> `<type>([optional scope(s)]): <description>`
+>
+> For example:
+>
+> `fix(learn): tests for the do...while loop challenge`
+
+Whenever you open a Pull Request (PR), you can use the below to determine the type, scope (optional), and description.
+
+**Type:**
+
+| Type | When to select |
+| :---- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| fix | Changed or updated/improved functionality, tests, the wording of a lesson, etc. |
+| feat | Only if you are adding new functionality, tests, etc. |
+| chore | Changes that are not related to code, tests, or verbiage of a lesson. |
+| docs | Changes to `/docs` directory or the contributing guidelines, etc. |
+
+**Scope:**
+
+You can select a scope from [this list of labels](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels?q=scope).
+
+**Description:**
+
+Keep it short (less than 30 characters) and simple; you can add more information in the PR description box and comments.
+
+Some examples of good PR titles would be:
+
+- `fix(a11y): improved search bar contrast`
+- `feat: add more tests to HTML and CSS challenges`
+- `fix(api,client): prevent CORS errors on form submission`
+- `docs(i18n): fix links to be relative instead of absolute`
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request
+
+1. Once the edits have been committed, you will be prompted to create a pull request on your fork's GitHub Page.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+2. By default, all pull requests should be against the freeCodeCamp main repo, `main` branch.
+
+ Make sure that your Base Fork is set to freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp when raising a Pull Request.
+
+ <details>
+ <summary>See screenshot</summary>
+
+ 
+
+ </details>
+
+3. Submit the pull request from your branch to freeCodeCamp's `main` branch.
+
+4. Include a more detailed summary of the changes you made and how your changes are helpful in the body of your PR.
+
+ - You will be presented with a pull request template. This is a checklist that you should have followed before opening the pull request.
+
+ - Fill in the details as you see fit. Ensure that you give the reviewers enough context to review the changes. If the PR makes changes to the UI, be sure to include screenshots of the changes as well. All of this information will be reviewed and the reviewers will decide whether or not your pull request is accepted.
+
+ - If the PR is meant to address an existing GitHub Issue then, at the end of your PR's description body, use the keyword _Closes_ with the issue number to [automatically close that issue if the PR is accepted and merged](https://help.github.com/en/articles/closing-issues-using-keywords).
+
+ > Example: `Closes #123` will close issue 123
+
+5. Indicate if you have tested on a local copy of the site or not.
+
+ - This is very important when making changes that are not just edits to text content like documentation or a challenge description. Examples of changes that need local testing include JavaScript, CSS, or HTML, which could change the functionality or layout of a page.
+
+ - If your PR affects the behavior of a page, it should be accompanied by corresponding [Playwright integration tests](how-to-add-playwright-tests).
+
+## Feedback on Pull Requests
+
+> :tada: Congratulations on making a PR and thanks a lot for taking the time to contribute.
+
+Our moderators will now take a look and leave you feedback. Please be patient with the fellow moderators and respect their time. All pull requests are reviewed in due course.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+:::tip
+If you are to be contributing more pull requests, we recommend you read the [making changes and syncing](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#making-changes-locally) guidelines to avoid having to delete your fork.
+:::
+
+## Conflicts on a Pull Request
+
+Conflicts can arise because many contributors work on the repository, and changes can break your PR which is pending a review and merge.
+
+Since we squash all commits, you may not need to do a rebase. However, if a rebase is requested, check our [For Usual Bug Fixes and Features](#for-usual-bug-fixes-and-features) or [For Upcoming Curriculum and Features](#for-upcoming-curriculum-and-features) guides to learn how to do this process for your corresponding PR.
+
+### For Usual Bug Fixes and Features
+
+When you are working on regular bugs and features on our development branch `main`, you are able to do a simple rebase:
+
+1. Rebase your local copy:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch>
+ git pull --rebase upstream main
+ ```
+
+2. Resolve any conflicts and add / edit commits
+
+ ```bash
+ # Either
+ git add .
+ git commit -m "chore: resolve conflicts"
+
+ # Or
+ git add .
+ git commit --amend --no-edit
+ ```
+
+3. Push back your changes to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch>
+ ```
+
+### For Upcoming Curriculum and Features
+
+When you are working on features for our upcoming curriculum `next-*` branches, you have to do a `cherry-pick`:
+
+1. Make sure your upstream comes in sync with your local:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ git fetch --all --prune
+ git checkout next-python-projects
+ git reset --hard upstream/next-python-projects
+ ```
+
+2. Take a backup
+
+ a. Either delete your local branch after taking a backup (if you still have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout <pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question
+
+ git branch -D <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
+
+ b. Or just a backup of your PR branch (if you do not have it locally):
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <backup-branch-name> origin/<pr-branch-name>
+
+ # example:
+ # git checkout -b backup-feat/add-numpy-video-question origin/feat/add-numpy-video-question
+ ```
+
+3. Start off with a clean slate:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b <pr-branch-name> next-python-projects
+ git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
+ ```
+
+4. Resolve any conflicts, cleanup, and install dependencies and run tests
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run clean
+
+ pnpm install
+ FCC_SUPERBLOCK='<superblock-name>' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ # example:
+
+ # FCC_SUPERBLOCK='python-for-everybody' pnpm run test:curriculum
+
+ ```
+
+5. If everything looks good, push back to the PR
+
+ ```bash
+ git push --force origin <pr-branch-name>
+ ```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-proofread-files.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-proofread-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2c5fe3b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-proofread-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: 如何校对译文
+---
+
+Our proofreading team is responsible for ensuring that translations accurately reflect the source text. We trust our proofreaders to ensure that we have very high quality translations.
+
+All our translations are done by hand, by real humans. Proofreading ensures that there is a consistent tone across all our translated resources like the curriculum.
+
+To begin proofreading, visit [our translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org) and login. Select "Go to console" in the top navigation bar to switch from the public view to the workspace view.
+
+## 选择文件
+
+You should see the list of projects you have been granted access to. Select the project that you would like to proofread, then select the language.
+
+
+
+You should now see the list of available files. Choose your file by selecting the `Proofread` button on the right of that file, then choosing `Proofreading` from the drop-down menu that appears.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you are in this workspace view, but want to work on [translating a file](how-to-translate-files) instead of proofreading, you may select `Crowdsourcing` from the dropdown menu instead.
+
+## 校对译文
+
+
+
+<!--Add proofread/crowdsource button to the image-->
+
+Here you will see the list of strings in the selected file, with their related translations. The translation that is displayed here is the translation that has received the highest score (between upvotes and downvotes) from the translation community.
+
+While you can view _all_ proposed translations for a given string, the community scores (determined by the upvotes and downvotes) should be taken into consideration when choosing which translation to approve. The community can review proposed translations and recommend which one is most accurate and clear.
+
+1. 这是源文件的字符串(英文)。
+2. 这是相匹配的翻译的字符串。 此处将显示基于赞同和反对票数的最受欢迎的译文建议。
+3. 点击这个选择标记按钮确认该译文。
+4. Crowdin 将显示每个字符串的状态。 `Done` 的意思是已经确认了译文,我们将在下次从 Crowdin 拉取内容的时候下载已确认的译文。 `Todo` 的意思是字符串的译文还未被校对确认。 `Hidden` means the string is locked and _should not be translated_. `Comment` 的意思是对此字符串有评论消息。
+5. 可以使用复框选择多条译文,并在此处一次性批量确认。
+6. 你可以在此处查看社区建议的译文,社区对其的评分,以及 Crowdin 建议的译文。
+7. 这个按钮显示/隐藏右侧的显示窗口,你可以在其中查看翻译、评论、翻译记忆和词汇表术语。
+8. Crowdin 在此处显示来自质量保证检查的报错消息。 也就是说,如果译文中有不正确的地方,Crowdin 会通知你。 请仔细校对确认出现报错消息的译文。
+
+No additional actions are required once a file has been proofread.
+
+> [!NOTE] Approving a string in the proofreading view will mark it as complete and it will be downloaded in our next pull from Crowdin to GitHub.
+
+## Becoming a Proofreader
+
+If you have any questions, or are interested in becoming a proofreader, feel free to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). We will typically grant you proofreading access if you have been contributing to freeCodeCamp for a while.
+
+Our staff team and community moderators teams are always looking for kind volunteers like you who help us make high quality translations available to the world.
+
+> [!NOTE] Crowdin 会允许你校对你自己的译文。 一般来说,最好是让另一位校对者审核你的译文,以确保最终内容的准确性。
+
+## Creating a Channel on Chat for a World Language
+
+For the most part, we encourage you to use the [contributors chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) room for all correspondence. However if the team of volunteer translators grows for a certain language, we can consider creating an additional break-out channel for the language.
+
+If you are already a proofreader and are interested in having a dedicated channel on our chat servers for a specific language, [fill out this form](https://forms.gle/XU5CyutrYCgDYaVZA).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..4bc73267
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,318 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow these guidelines for setting up a development environment for freeCodeCamp. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+## Choose between Gitpod or your Own Machine (local setup)
+
+:::danger
+
+- freeCodeCamp does not build and run natively on Windows, you will [need to use WSL2](how-to-setup-wsl) for a Linux-like setup on Windows.
+- You can't use Windows Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to build and run the codebase.
+- Note that if using Windows, the hardware requirements need to be more than [what we mention](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally?id=how-to-prepare-your-local-machine) to accommodate for WSL-based setup.
+
+:::
+
+If you are looking to make a one-off contribution, you should use Gitpod to make changes. The Gitpod setup launches a ready-to-code environment in a few minutes in your web browser. To contribute long-term, we recommend you set up freeCodeCamp on your local machine.
+
+Here are some pros and cons which should help you decide which option is best for you:
+
+| Gitpod | Your own machine (local setup) |
+| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| No minimum hardware requirements | Specific and minimum requirements |
+| No need to install any software | Additional software required |
+| Always up to date copy of repository | Need to maintain a local copy of the repository |
+| Slower and can take a few minutes to launch | Faster and can be launched in seconds |
+| Need an internet connection to work | Minimal internet connection required (once setup) |
+| Some tasks like compilation and tests can take longer to complete | Faster completion of tasks (depending on your machine's capabilities) |
+
+### How to Prepare a Gitpod Workspace
+
+We have automated the process of installing all the dependencies & tools you will need. With Gitpod you get a free ready-to-code environment in a few minutes, and is useful if you do not have access to a computer or want to make one-time changes.
+
+There are various ways to launch a Gitpod workspace:
+
+1. **(Fastest)** Prepend `gitpod.io/#` in front of any URL from GitHub.
+
+ For example, if you visit your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git`, add `gitpod.io/#` in the front of the URL in the address bar and hit enter.
+
+ That is you can navigate to `gitpod.io/#https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git` and you should see a workspace created for you. This works for any repository or pull-request on GitHub.
+
+2. Alternatively install one of the below extensions for your browser.
+
+ - [Chrome Webstore](https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/gitpod-always-ready-to-co/dodmmooeoklaejobgleioelladacbeki) - works with Chromium-based browsers like Google Chrome, Brave, Edge, etc.
+ - [Firefox Add-on](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/gitpod) - Firefox
+
+ Once installed you will see a 'Gitpod' button on every repository, pull-request, etc. as a handy shortcut to launch a workspace from there. See the extension page for details, screenshots, etc.
+
+That's it, you can now skip to the 'syncing up from parent' section after you have launched a Gitpod workspace. Most parts of this guide applies to Gitpod workspaces, but be mindful of [how the URLs & Ports work within a Gitpod](https://www.gitpod.io/docs/configure/workspaces/ports) workspace.
+
+**Note: Troubleshooting port issues on Gitpod**
+
+Sometimes the service on port `8000` doesn't go live. This is common when you are restarting an inactive workspace.
+
+If the service is not coming up on port `8000`, you can troubleshoot using these steps:
+
+- **Start the server**: Run `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window from the root project directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp`) to start the server.
+
+- **Start the client**: In another terminal window, run `pnpm run develop -- -H '0.0.0.0'` from the client directory (`/workspace/freeCodeCamp/client`) to start the client.
+
+This should make port `8000` available.
+
+### How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Here is a minimum system requirement for running freeCodeCamp locally:
+
+- 8 GB RAM
+- Relatively fast CPU (4+ cores)
+- Windows 10 or 11 (with WSL), macOS, or Linux
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+We primarily support development on Linux and Unix-based systems like Ubuntu and macOS. You can develop on Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 only. You can follow [this guide](how-to-setup-wsl) to set up WSL2. You can't use Command Prompt, Git Bash or PowerShell to run freeCodeCamp natively within windows.
+
+#### Prerequisites:
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [Node.js](http://nodejs.org) | `20.x` | We use the "Active LTS" version, See [LTS Schedule](https://nodejs.org/en/about/releases/). |
+| [pnpm](https://pnpm.io/installation) | `8.x` | - |
+| [MongoDB Community Server](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/) | `5.0.x` | - |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions. See [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues) for details.
+:::
+
+If Node.js is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+node -v
+pnpm -v
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above, also known as Long Term Support (LTS) releases.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+##### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+3. Install a code editor of your choice. If you aren't sure which one to use, we recommend [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) — it's free and open source.
+
+4. Set up linting for your code editor.
+
+ You should have [ESLint running in your editor](http://eslint.org/docs/user-guide/integrations.html), and it will highlight anything that doesn't conform to [freeCodeCamp's JavaScript Style Guide](http://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/free-code-camp-javascript-style-guide/19121).
+
+:::tip
+Please do not ignore any linting errors. They are meant to **help** you and to ensure a clean and simple codebase.
+:::
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of freeCodeCamp's main repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of freeCodeCamp on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+
+:::
+
+> Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the freeCodeCamp repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/github/how-to-fork-freeCodeCamp.gif" alt="How to fork freeCodeCamp on GitHub">
+</details>
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository that should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+:::caution
+If you are working on a WSL2 Linux Distro, you might get performance and stability issues by running this project in a folder which is shared between Windows and WSL2 (e.g. `/mnt/c/Users/`).
+
+Therefore we recommend to clone this repo into a folder which is mainly used by your WSL2 Linux Distro and not directly shared with Windows (e.g. `~/PROJECTS/`).
+
+See [this GitHub Issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/40632) for further information about this problem.
+:::
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change the directory to the new freeCodeCamp directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of freeCodeCamp, you can follow these instructions to run it locally. This will allow you to:
+
+- Preview edits to pages as they would appear on the learning platform.
+- Work on UI related issues and enhancements.
+- Debug and fix issues with the application servers and client apps.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` that is accessed dynamically during the installation step.
+
+```bash
+# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets
+```
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+:::tip
+Keep in mind if you want to use services like Auth0 or Algolia, you'll have to acquire your own API keys for those services and edit the entries accordingly in the `.env` file.
+:::
+
+#### Step 2: Install Dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start MongoDB and Seed the Database
+
+Before you can run the application locally, you will need to start the MongoDB service.
+
+:::note
+Unless you have MongoDB running in a setup different than the default, the URL stored as the `MONGOHQ_URL` value in the `.env` file should work fine. If you are using a custom configuration, modify this value as needed.
+
+If you followed along with the [Windows 10 via WSL2 Setup Guide](how-to-setup-wsl), then you should be able to skip this step if the MongoDB server from that guide is already running. You can confirm this by checking that you can reach `http://localhost:27017` on your local machine.
+:::
+Start the MongoDB server in a separate terminal:
+
+```bash
+mongod
+```
+
+:::tip
+You can avoid having to start MongoDB every time by installing it as a background service. You can [learn more about it in their documentation for your OS](https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/administration/install-community/)
+:::
+
+Next, let's seed the database. In this step, we run the below command that fills the MongoDB server with some initial data sets that are required by services. These include a few schemas, among other things.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed
+```
+
+By default, you will be signed in as a new user without any completed certifications. Run the following command if you need to develop with completed certifications or write Playwright tests:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run seed:certified-user
+```
+
+:::caution
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out. You will have to clear your browser cookies and sign in again.
+:::
+
+#### Step 4: Start the freeCodeCamp Client Application and API Server
+
+You can now start up the API server and the client applications.
+
+```bash
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+This single command will fire up all the services, including the API server and the client applications available for you to work on.
+
+Once ready, open a web browser and visit <http://localhost:8000>. If the app loads, sign in. Congratulations – you're all set! You now have a copy of freeCodeCamp's entire learning platform running on your local machine.
+
+The API server serves endpoints at `http://localhost:3000`. The Gatsby app serves the client application at `http://localhost:8000`.
+
+While you are logged in, if you visit <http://localhost:3000/explorer> you should see the available APIs.
+
+:::caution
+Clearing your cookies or running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, and you will have to sign in again.
+:::
+
+If you have issues while installing it, check out the [troubleshooting section](troubleshooting-development-issues).
+
+## Quick Commands Reference
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `pnpm install` | Installs / re-installs all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `pnpm run seed` | Creates authorized test users and inserts them into MongoDB. Also runs `seed:exams` and `seed:surveys` below. |
+| `pnpm run seed:certified-user` | Creates authorized test users with certifications fully completed, and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:exams` | Creates exams and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run seed:surveys` | Creates surveys for defaults users and inserts them into MongoDB. |
+| `pnpm run develop` | Starts the freeCodeCamp API Server and Client Applications. |
+| `pnpm run clean` | Uninstalls all dependencies and cleans up caches. |
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8b0bb9de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,511 @@
+---
+title: Setup freeCodeCamp locally
+---
+
+Follow this guide for setting up the freeCodeCamp mobile app locally on your system. This is highly recommended if you want to contribute regularly.
+
+Some of the contribution workflows – like fixing bugs in the codebase – need you to run the freeCodeCamp app locally.
+
+## How to Prepare your Local Machine
+
+Start by installing the prerequisite software for your operating system.
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+| Prerequisite | Version | Notes |
+| --------------------------------- | ------- | ---------------------------------------- |
+| [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) | `3.x` | - |
+| Dart (comes bundled with Flutter) | `3.x` | We use the version bundled with Flutter. |
+
+:::danger
+If you have a different version, please install the recommended version. We can only support installation issues for recommended versions.
+:::
+
+If Flutter is already installed on your machine, run the following commands to validate the versions:
+
+```bash
+flutter --version
+dart --version
+```
+
+:::tip
+We highly recommend updating to the latest stable releases of the software listed above.
+:::
+
+Once you have the prerequisites installed, you need to prepare your development environment. This is common for many development workflows, and you will only need to do this once.
+
+#### Follow these steps to get your development environment ready:
+
+1. Install [Git](https://git-scm.com/) or your favorite Git client, if you haven't already. Update to the latest version; the version that came bundled with your OS may be outdated.
+
+2. Set up [Android Studio](https://developer.android.com/studio) and [Android Emulators](https://developer.android.com/studio/run/managing-avds) with the latest released Android version. We recommend using the Pixel 3a XL and Nexus One(for emulating smaller screens).
+
+3. (Optional for MacOS) Set up Xcode and iOS Simulator with the latest released iOS version.
+
+4. (Optional but recommended) [Set up an SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key/) for GitHub.
+
+5. Install a code editor of your choice.
+
+ We highly recommend using [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) or Android Studio. We also recommend installing the official [extensions](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/editor?tab=vscode).
+
+## Fork the Repository on GitHub
+
+[Forking](https://help.github.com/articles/about-forks/) is a step where you get your own copy of the repository (a.k.a _repo_) on GitHub.
+
+This is essential, as it allows you to work on your own copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile app on GitHub, or to download (clone) your repository to work on locally. Later, you will be able to request changes to be pulled into the main repository from your fork via a pull request (PR).
+
+:::tip
+The main repository at `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` is often referred to as the `upstream` repository.
+Your fork at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` is often referred to as the `origin` repository. `YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub username.
+:::
+
+**Follow these steps to fork the `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile` repository:**
+
+1. Go to the freeCodeCamp mobile repository on GitHub: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile>
+
+2. Click the "Fork" Button in the upper right-hand corner of the interface ([More Details Here](https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/))
+
+3. After the repository has been forked, you will be taken to your copy of the repository at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile` (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+## Clone your Fork from GitHub
+
+[Cloning](https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/) is where you **download** a copy of a repository from a `remote` location that is either owned by you or by someone else. In your case, this remote location is your `fork` of freeCodeCamp's repository which should be available at `https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile`. (`YOUR_USER_NAME` would be replaced with your GitHub user name.)
+
+Run these commands on your local machine:
+
+1. Open a Terminal / Command Prompt / Shell in your projects directory
+
+ _i.e.: `/yourprojectsdirectory/`_
+
+2. Clone your fork of freeCodeCamp, replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub Username
+
+ ```bash
+ git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+This will download the entire freeCodeCamp mobile repository to your projects directory.
+
+Note: `--depth=1` creates a shallow clone of your fork, with only the most recent history/commit.
+
+## Set up Syncing from Parent
+
+Now that you have downloaded a copy of your fork, you will need to set up an `upstream` remote to the parent repository.
+
+[As mentioned earlier](#fork-the-repository-on-github), the main repository is referred to as the `upstream` repository. Your fork is referred to as the `origin` repository.
+
+You need a reference from your local clone to the `upstream` repository in addition to the `origin` repository. This is so that you can sync changes from the main repository without the requirement of forking and cloning repeatedly.
+
+1. Change directory to the new `mobile` directory:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Add a remote reference to the main freeCodeCamp mobile repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote add upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git
+ ```
+
+3. Ensure the configuration looks correct:
+
+ ```bash
+ git remote -v
+ ```
+
+ The output should look something like below (replacing `YOUR_USER_NAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```bash
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (fetch)
+ origin https://github.com/YOUR_USER_NAME/mobile.git (push)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (fetch)
+ upstream https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile.git (push)
+ ```
+
+## Running freeCodeCamp Mobile App Locally
+
+Now that you have a local copy of the mobile app, you can follow these instructions to run it locally.
+
+If you do run into issues, first perform a web search for your issue and see if it has already been answered. If you cannot find a solution, please search our [GitHub issues](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/mobile/issues) page for a solution and report the issue if it has not yet been reported.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+> [!NOTE] The `mobile` directory contains two folders ie. `mobile-api` and `mobile-app`. `mobile-api` contains the API code used for serving the podcasts. `mobile-app` contains the Flutter app which is where you should be when you follow the below steps.
+
+### Configuring Dependencies
+
+#### Step 1: Set Up the Environment Variable File
+
+The default API keys and environment variables are stored in the file `sample.env`. This file needs to be copied to a new file named `.env` which is accessed dynamically during the installation step. Remember to change the directory to `mobile-app` before running the following commands.
+
+```bash
+# Create a copy of the "sample.env" and name it ".env".
+# Populate it with the necessary API keys and secrets:
+```
+
+#### **macOS/Linux**
+
+```bash
+cp sample.env .env
+```
+
+#### **Windows**
+
+```bash
+copy sample.env .env
+```
+
+The keys in the `.env` file are _not_ required to be changed to run the app locally. You can leave the default values copied over from `sample.env` as-is.
+
+#### Step 2: Install dependencies
+
+This step will install the dependencies required for the application to run:
+
+```bash
+flutter pub get
+```
+
+#### Step 3: Start the freeCodeCamp mobile app
+
+Start the emulator of your choice(Android or iOS) and wait for the bootup process to complete.
+
+You can now start the app by running the following command:
+
+```bash
+flutter run
+```
+
+:::tip
+If you're using VSCode or Android Studio then you can easily start the app without having to execute any terminal commands. More information [here](https://docs.flutter.dev/get-started/test-drive).
+:::
+
+## Making Changes Locally
+
+You can now make changes to files and commit your changes to the local clone of your fork.
+
+Follow these steps:
+
+1. Validate that you are on the `main` branch:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ You should get an output like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch main
+ Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/main'.
+
+ nothing to commit, working directory clean
+ ```
+
+ If you are not on main or your working directory is not clean, resolve any outstanding files/commits and checkout `main`:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout main
+ ```
+
+2. Sync the latest changes from the upstream `main` branch to your local main branch:
+
+ > [!WARNING] If you have any outstanding pull request that you made from the `main` branch of your fork, you will lose them at the end of this step.
+ >
+ > You should ensure your pull request is merged by a moderator before performing this step. To avoid this scenario, you should **always** work on a branch other than the `main`.
+
+ This step **will sync the latest changes** from the main repository of freeCodeCamp mobile. It is important that you rebase your branch on top of the latest `upstream/main` as often as possible to avoid conflicts later.
+
+ Update your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile upstream repository:
+
+ ```bash
+ git fetch upstream
+ ```
+
+ Hard reset your main branch with the freeCodeCamp mobile main:
+
+ ```bash
+ git reset --hard upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ Push your main branch to your origin to have a clean history on your fork on GitHub:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin main --force
+ ```
+
+ You can validate that your current main matches the upstream/main by performing a diff:
+
+ ```bash
+ git diff upstream/main
+ ```
+
+ The resulting output should be empty.
+
+3. Create a fresh new branch:
+
+ Working on a separate branch for each issue helps you keep your local work copy clean. You should never work on the `main`. This will soil your copy of freeCodeCamp mobile and you may have to start over with a fresh clone or fork.
+
+ Check that you are on `main` as explained previously, and branch off from there:
+
+ ```bash
+ git checkout -b fix/update-guide-for-xyz
+ ```
+
+ Your branch name should start with a `fix/`, `feat/`, `docs/`, etc. Avoid using issue numbers in branches. Keep them short, meaningful, and unique.
+
+ Some examples of good branch names are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix/update-challenges-for-react
+ fix/update-guide-for-html-css
+ fix/platform-bug-sign-in-issues
+ feat/add-guide-article-for-javascript
+ translate/add-spanish-basic-html
+ ```
+
+4. Edit pages and work on code in your favorite text editor.
+
+5. Once you are happy with the changes you should optionally run the mobile app locally to preview the changes.
+
+6. Make sure you fix any errors and check the formatting of your changes.
+
+7. Check and confirm the files you are updating:
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ This should show a list of `unstaged` files that you have edited.
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes were not staged for commit:
+ (use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
+ (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in the working directory)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ...
+ ```
+
+8. Stage the changes and make a commit:
+
+ In this step, you should only mark files that you have edited or added yourself. You can perform a reset and resolve files that you did not intend to change if needed.
+
+ ```bash
+ git add path/to/my/changed/file.ext
+ ```
+
+ Or you can add all the `unstaged` files to the staging area:
+
+ ```bash
+ git add .
+ ```
+
+ Only the files that were moved to the staging area will be added when you make a commit.
+
+ ```bash
+ git status
+ ```
+
+ Output:
+
+ ```bash
+ On branch feat/documentation
+ Your branch is up to date with 'upstream/feat/documentation'.
+
+ Changes to be committed:
+ (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
+
+ modified: README.md
+ modified: mobile-app/lib/main.dart
+ ```
+
+ Now, you can commit your changes with a short message like so:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit -m "fix: my short commit message"
+ ```
+
+ Some examples:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update guide article for Java - for loop
+ feat: add guide article for alexa skills
+ ```
+
+ Optional:
+
+ We highly recommend making a conventional commit message. This is a good practice that you will see on some of the popular Open Source repositories. As a developer, this encourages you to follow standard practices.
+
+ Some examples of conventional commit messages are:
+
+ ```md
+ fix: update HTML guide article
+ fix: update build scripts for Travis-CI
+ feat: add article for JavaScript hoisting
+ docs: update contributing guidelines
+ ```
+
+ Keep these short, not more than 50 characters. You can always add additional information in the description of the commit message.
+
+ This does not take any additional time than an unconventional message like 'update file' or 'add index.md'
+
+ You can learn more about why you should use conventional commits [here](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/v1.0.0-beta.2/#why-use-conventional-commits).
+
+9. If you realize that you need to edit a file or update the commit message after making a commit you can do so after editing the files with:
+
+ ```bash
+ git commit --amend
+ ```
+
+ This will open up a default text editor like `nano` or `vi` where you can edit the commit message title and add/edit the description.
+
+10. Next, you can push your changes to your fork:
+
+ ```bash
+ git push origin branch/name-here
+ ```
+
+## Running mobile curriculum tests
+
+> [!NOTE] You only need to follow this section if you're modifying the challenge test runner in the mobile app. Otherwise, you can go to the next section on [how to open a pull request](#proposing-a-pull-request-pr).
+
+1. Clone a copy of the [freeCodeCamp repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) locally outside of your local copy of the freeCodeCamp mobile repo. Your folder structure should look like this:
+
+ ```bash
+ ├── freeCodeCamp
+ ├── mobile
+ ```
+
+2. Change the directory to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+3. Make a copy of the `.env` file:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy sample.env .env
+ ```
+
+4. Install the dependencies for the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm install && pnpm run create:shared
+ ```
+
+5. Generate the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm run build:curriculum
+ ```
+
+6. Copy the generated JSON file to the mobile app:
+
+ #### **macOS/Linux**
+
+ ```bash
+ cp ./shared/config/curriculum.json ../mobile/mobile-app/curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+ #### **Windows**
+
+ ```bash
+ copy .\shared\config\curriculum.json ..\mobile\mobile-app\curriculum.json
+ ```
+
+7. Change directory to the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../mobile/mobile-app
+ ```
+
+8. Install the dependencies for the mobile app:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter pub get
+ ```
+
+9. Update the test file to use the challenge data JSON file:
+
+ ```bash
+ sed -i '' 's/..\/..\/shared\/config\/curriculum.json/.\/curriculum.json/g' test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+10. Generate the challenge files:
+
+ ```bash
+ flutter test test/widget_test.dart
+ ```
+
+11. Start a local server to serve the challenge files with the help of `serve` package:
+
+ ```bash
+ npx serve
+ ```
+
+12. In a different terminal go back to the freeCodeCamp repo:
+
+ ```bash
+ cd ../../freeCodeCamp
+ ```
+
+13. Run the cypress tests:
+
+ ```bash
+ pnpm cypress run --config retries=1,screenshotOnRunFailure=false,video=false,baseUrl=http://localhost:3000/generated-tests/,specPattern=cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -s cypress/e2e/mobile-learn/test-challenges.js -b chrome
+ ```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+<!-- ## Quick commands reference - NEED TO DISCUSS ABOUT THIS
+
+A quick reference to the commands that you will need when working locally.
+
+| command | description |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `npm ci` | Installs / re-install all dependencies and bootstraps the different services. |
+| `npm run seed` | Parses all the challenge markdown files and inserts them into MongoDB. | -->
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Issues with installing the recommended prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS and/or are still running into issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+### Issues with the UI, build errors, etc.
+
+If you face issues with the UI, or build errors a cleanup can be useful:
+
+```bash
+flutter clean
+```
+
+### Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or that your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+Be patient as the first-time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth.
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-wsl.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-wsl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9660adb4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-setup-wsl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
+---
+title: Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] Before you follow these instructions make sure your system meets the requirements.
+>
+> **WSL 2**: Windows 10 64-bit (Version 2004, Build 19041 or higher) - available for all distributions including Windows 10 Home.
+>
+> **Docker Desktop for Windows**: See respective requirements for [Windows 10 Pro](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/#system-requirements) and [Windows 10 Home](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install-windows-home/#system-requirements)
+
+This guide covers some common steps with the setup of WSL2. Once some of the common issues with WSL2 are addressed, you should be able to follow [this local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to work with freeCodeCamp on Windows running a WSL distro like Ubuntu.
+
+## Enable WSL
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10) to install WSL2.
+
+## Install Ubuntu
+
+1. We recommended using Ubuntu-18.04 or above with WSL2.
+
+ > [!NOTE]
+ >
+ > While you may use other non-Debian-based distributions, they all come with their own 'gotchas' that are beyond the scope of this guide.
+
+ As of November 2023, Ubuntu and Debian are the only Linux distributions [officially supported by Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro#system-requirements), the end-to-end testing library used by freeCodeCamp.
+
+2. Update the dependencies for the OS
+
+ ```bash
+ sudo apt update
+ sudo apt upgrade -y
+
+ # cleanup
+ sudo apt autoremove -y
+ ```
+
+## Set up Git
+
+Git comes pre-installed with Ubuntu 18.04, verify your Git version with `git --version`.
+
+```output
+~
+❯ git --version
+git version 2.25.1
+```
+
+(Optional but recommended) You can now proceed to [setting up your ssh keys](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-an-ssh-key) with GitHub.
+
+## Installing a Code Editor
+
+We highly recommend installing [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com) on Windows 10. It has great support for WSL and automatically installs all the necessary extensions on your WSL distribution.
+
+Essentially, you will edit and store your code on Ubuntu-18.04 with VS Code installed on Windows.
+
+If you use [IntelliJ Idea](https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/), you may need to update your Node interpreter and npm package manager to what is installed on your WSL distro.
+
+You can check these settings by going to Settings > Languages & Frameworks > Node.js and npm.
+
+## Installing Docker Desktop
+
+**Docker Desktop for Windows** allows you to install and run databases like MongoDB and other services like NGINX and more. This is useful to avoid common pitfalls with installing MongoDB or other services directly on Windows or WSL2.
+
+Follow the instructions on the [official documentation](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install) and install Docker Desktop for your Windows distribution.
+
+There are some minimum hardware requirements for the best experience.
+
+## Configure Docker Desktop for WSL
+
+Once Docker Desktop is installed, [follow these instructions](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/wsl) and configure it to use the Ubuntu-18.04 installation as a backend.
+
+This makes it so that the containers run on the WSL side instead of running on Windows. You will be able to access the services over `http://localhost` on both Windows and Ubuntu.
+
+## Install MongoDB from Docker Hub
+
+Once you have configured Docker Desktop to work with WSL2, follow these steps to start a MongoDB service:
+
+1. Launch a new Ubuntu terminal
+
+2. Pull MongoDB from Docker Hub. Please refer to the [Prerequisites](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally#Prerequisites) table for the current version of MongoDB used by freeCodeCamp. For example, if the version number is `5.0.x`, replace `<x.y>` with `5.0` in the following two code snippets.
+
+ ```bash
+ docker pull mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+3. Start the MongoDB service at port `27017`, and configure it to run automatically on system restarts
+
+ ```bash
+ docker run -it \
+ -v mongodata:/data/db \
+ -p 27017:27017 \
+ --name mongodb \
+ --restart unless-stopped \
+ -d mongo:<x.y>
+ ```
+
+4. You can now access the service from both Windows or Ubuntu at `mongodb://localhost:27017`.
+
+## Installing Node.js and pnpm
+
+We recommend you install the LTS release for Node.js with a node version manager - [nvm](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating).
+
+Once installed use this command to install and use the latest Node.js LTS version:
+
+```bash
+nvm install --lts
+```
+
+For instructions on installing and using a different version of Node.js, please refer to the [nvm docs](https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#usage).
+
+Node.js comes bundled with `npm`, which you can use to install `pnpm`:
+
+```bash
+npm install -g pnpm
+```
+
+## Set up freeCodeCamp Locally
+
+Now that you have installed the pre-requisites, follow [our local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally) to clone, install and set up freeCodeCamp locally on your machine.
+
+> [!WARNING]
+>
+> Please note, at this time the setup for Cypress tests (and related GUI needs) is a work in progress. You should still be able to work on most of the codebase.
+
+## Optimize Windows and WSL
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> The following tips were collected from across the web and have not gone through vigorous testing. Your mileage may vary.
+
+### Adjust processor scheduling for background services
+
+This may reduce incidents of Docker containers crashing due to lack of resources.
+
+Open the System Properties control panel by pressing <kbd>Win + R</kbd> and entering `sysdm.cpl`
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Enter <code>sysdm.cpl</code> in the Run dialog (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/run-sysdm.png" alt="Enter `sysdm.cpl` in the Run dialog" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Go to Advanced -> Performance -> Settings…
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-performance-settings.png" alt="Performance Settings button under Advanced tab in System Properties" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Under Advanced -> Processor scheduling, choose "Background services". Do not close the window. Continue to the next tip.
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/background-services.png" alt="Background services radio button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of Windows paging file for the system drive
+
+Under Advanced -> Virtual memory, click "Change…"
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/advanced-virtual-memory.png" alt="Change virtual memory button under Advanced tab in Performance Options" />
+
+</details>
+<br>
+
+Choose "Custom size". Set the initial size to 1.5x and the maximum size to 3x of your physical memory. Then click "Set".
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/main/docs/images/wsl/set-custom-size.png" alt="Set custom size button in Virtual Memory window" />
+
+</details>
+
+### Increase the size of memory allocated to WSL
+
+Create a [`.wslconfig` file](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) in your [`%UserProfile%` directory](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#wslconfig) (typically `C:\Users\<UserName>\.wslconfig`). Please read the [WSL documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#configuration-setting-for-wslconfig) carefully and replace `x` with values that suit your own needs:
+
+```ini
+# Settings apply across all Linux distros running on WSL 2
+[wsl2]
+
+# How much memory to assign to the WSL 2 VM. The default value might not be enough
+memory=xGB
+
+# How much swap space to add to the WSL 2 VM, default is 25% of available RAM
+swap=xGB
+```
+
+### Increase Node.js max old space size
+
+This fixes the ["JavaScript heap out of memory" error](https://stackoverflow.com/a/54456814) with ESLint. Add the following to your `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`:
+
+```sh
+export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
+```
+
+### Avoid `pnpm run test`
+
+Instead, use the script [appropriate to your PR](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/t/wsl-performance-issues-while-working-on-the-codebase/644215/2#:~:text=usually%2C%20you%20just%20want%20to%20test%20something%20specific%20to%20either%20the%20curriculum%20or%20the%20client%20or%20the%20api%20-%20almost%20never%20all%203.); either `pnpm run test:api`, `pnpm run test:curriculum`, or `pnpm run test-client`.
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [A WSL2 Dev Setup with Ubuntu 20.04, Node.js, MongoDB, VS Code, and Docker](https://hn.mrugesh.dev/wsl2-dev-setup-with-ubuntu-nodejs-mongodb-and-docker) - an article by Mrugesh Mohapatra (Staff Developer at freeCodeCamp.org)
+- Frequently asked questions on:
+ - [Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/faq)
+ - [Docker Desktop for Windows](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/faqs)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-test-translations-locally.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..56373755
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-test-translations-locally.md
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
+---
+title: How to Test Translations Locally
+---
+
+> [!NOTE] This process is not required, but documented in case you would like to preview what your translations will look like.
+
+If you would like to test your translations on a local instance of the freeCodeCamp `/learn` site, first ensure you have [set up the codebase](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).
+
+## Enabling a Language
+
+There are a few steps to take in order to allow the codebase to build in your desired language.
+
+First, visit the `config/i18n/all-langs.ts` file to add the language to the available languages list and configure the values. There are four objects here.
+
+- `availableLangs`: For both the `client` and `curriculum` arrays, add the text name of the language. This is the value that will be used in the `.env` file later.
+- `auditedCerts`: Add the text name of the language as the _key_, and add an array of `SuperBlocks.{cert}` variables as the _value_. This tells the client which certifications are fully translated.
+- `i18nextCodes`: These are the ISO language codes for each language. You will need to add the appropriate ISO code for the language you are enabling. These do need to be unique for each language.
+- `LangNames`: These are the display names for the language selector in the navigation menu.
+- `LangCodes`: These are the language codes used for formatting dates and numbers. These should be Unicode CLDR codes instead of ISO codes.
+
+As an example, if you wanted to enable Dothraki as a language, your `all-langs.js` objects should look like this:
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: ['english', 'espanol', 'chinese', 'chinese-traditional', 'dothraki'],
+ curriculum: [
+ 'english',
+ 'espanol',
+ 'chinese',
+ 'chinese-traditional',
+ 'dothraki'
+ ]
+};
+
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ espanol: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis
+ ],
+ chinese: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ 'chinese-traditional': [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs,
+ SuperBlocks.DataVis,
+ SuperBlocks.BackEndDevApis,
+ SuperBlocks.QualityAssurance,
+ SuperBlocks.SciCompPy,
+ SuperBlocks.DataAnalysisPy,
+ SuperBlocks.InfoSec,
+ SuperBlocks.MachineLearningPy
+ ],
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+};
+
+export const i18nextCodes = {
+ english: 'en',
+ espanol: 'es',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+
+export enum LangNames = {
+ english: 'English',
+ espanol: 'Español',
+ chinese: '中文(简体字)',
+ 'chinese-traditional': '中文(繁體字)',
+ dothraki: 'Dothraki'
+};
+
+export enum LangCodes = {
+ english: 'en-US',
+ espanol: 'es-419',
+ chinese: 'zh',
+ 'chinese-traditional': 'zh-Hant',
+ dothraki: 'mis'
+};
+```
+
+Next, open the `client/src/utils/algolia-locale-setup.ts` file. This data is used for the search bar that loads `/news` articles. While it is unlikely that you are going to test this functionality, missing the data for your language can lead to errors when attempting to build the codebase locally.
+
+Add an object for your language to the `algoliaIndices` object. You should use the the same values as the `english` object for local testing, replacing the `english` key with your language's `availableLangs` value.
+
+> [!NOTE] If we have already deployed an instance of news in your target language, you can update the values to reflect the live instance. Otherwise, use the English values.
+
+If you were to add Dothraki:
+
+```js
+const algoliaIndices = {
+ english: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ espanol: {
+ name: 'news-es',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/news/search/'
+ },
+ chinese: {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ },
+ 'chinese-traditional': {
+ name: 'news-zh',
+ searchPage: 'https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/search'
+ },
+ dothraki: {
+ name: 'news',
+ searchPage: 'https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/search/'
+ }
+};
+```
+
+Finally, in your `.env` file, set `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE` to your new language (use the `availableLangs` value.)
+
+```txt
+CLIENT_LOCALE=dothraki
+CURRICULUM_LOCALE=dothraki
+```
+
+### Releasing a Superblock
+
+After a superblock has been fully translated into a language, there are two steps to release it. First add the superblock enum to that language's `auditedCerts` array. So, if you want to release the new Responsive Web Design superblock for Dothraki, the array should look like this:
+
+```ts
+export const auditedCerts = {
+ // other languages
+ dothraki: [
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesignNew, // the newly translated superblock
+ SuperBlocks.RespWebDesign,
+ SuperBlocks.JsAlgoDataStruct,
+ SuperBlocks.FrontEndDevLibs
+ ]
+```
+
+Finally, the `languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases` array should be updated to include the new language like this:
+
+```ts
+export const languagesWithAuditedBetaReleases: ['english', 'dothraki'];
+```
+
+This will move the new superblock to the correct place in the curriculum map on `/learn`.
+
+## Enabling Localized Videos
+
+For the video challenges, you need to change a few things. First add the new locale to the GraphQL query in the `client/src/templates/Challenges/video/Show.tsx` file. For example, adding Dothraki to the query:
+
+```tsx
+ query VideoChallenge($slug: String!) {
+ challengeNode(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
+ videoId
+ videoLocaleIds {
+ espanol
+ italian
+ portuguese
+ dothraki
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+Then add an id for the new language to any video challenge in an audited block. For example, if `auditedCerts` in `all-langs.ts` includes `scientific-computing-with-python` for `dothraki`, then you must add a `dothraki` entry in `videoLocaleIds`. The frontmatter should then look like this:
+
+```yml
+videoLocaleIds:
+ espanol: 3muQV-Im3Z0
+ italian: hiRTRAqNlpE
+ portuguese: AelGAcoMXbI
+ dothraki: new-id-here
+dashedName: introduction-why-program
+---
+```
+
+Update the `VideoLocaleIds` interface in `client/src/redux/prop-types` to include the new language.
+
+```ts
+export interface VideoLocaleIds {
+ espanol?: string;
+ italian?: string;
+ portuguese?: string;
+ dothraki?: string;
+}
+```
+
+And finally update the challenge schema in `curriculum/schema/challengeSchema.js`.
+
+```js
+videoLocaleIds: Joi.when('challengeType', {
+ is: challengeTypes.video,
+ then: Joi.object().keys({
+ espanol: Joi.string(),
+ italian: Joi.string(),
+ portuguese: Joi.string(),
+ dothraki: Joi.string()
+ })
+}),
+```
+
+## Loading Translations
+
+Because the language has not been approved for production, our scripts are not automatically downloading the translations yet. Only staff have the access to directly download the translations - you are welcome to reach out to us in our [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay), or you can translate the English markdown files locally for testing purposes.
+
+Once you have the files, you will need to place them in the correct directory. For the curriculum challenges, you should place the certification folders (i.e. `01-responsive-web-design`) within the `curriculum/challenges/{lang}` directory. For our Dothraki translations, this would be `curriculum/challenges/dothraki`. The client translation `.json` files will go in the `client/i18n/locales/{lang}` directory.
+
+Once these are in place, you should be able to run `npm run develop` to view your translated version of freeCodeCamp.
+
+:::danger
+While you may perform translations locally for the purpose of testing, we remind everyone that translations should _not_ be submitted through GitHub and should only be done through Crowdin. Be sure to reset your local codebase after you are done testing.
+:::
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-translate-files.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-translate-files.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8162b54e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-translate-files.md
@@ -0,0 +1,343 @@
+---
+title: 如何翻译 freeCodeCamp 的资源
+---
+
+## Prepare yourself for Contributions
+
+> The freeCodeCamp Localization Roadmap – There Are No Speed Limits
+
+:::tip
+You can start by reading [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). We recommend joining [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) and [Discord chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+:::
+
+You can translate as much as you want, when you want. It's only a matter of how much time and energy you are willing to invest as a volunteer translator.
+
+We just ask that you understand the following:
+
+1. **翻译是一件团队协作的事情。**
+
+ 翻译 freeCodeCamp 的资源是对贡献者来说最有趣和最有意义的经历之一。如果你邀请与你使用同一种语言的朋友和同事参与,那么效果最好。
+
+ You can start by reading [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/). We recommend joining [our community forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) and [Discord chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) with your friends and showing your interest before starting off with translations. Crowdin and other tools make it easy to contribute translations, but it's still a lot of work.
+
+ 我们希望你在贡献过程感到快乐,而不是感到疲惫,然后失去兴趣。
+
+ 如果你们有一个四到五人的小组,就可以开始翻译一种新的语言了。 你可以再招募更多的朋友来加入这个队伍。
+
+2. **为每种语言版本提供服务器,需要较高的成本。**
+
+ 表面上来看,技术栈可能看起来没那么复杂,但是实际上消耗了很多资源来让引擎跑起来。 这包括提供额外的服务器和专职人员来管理它们。
+
+ freeCodeCamp.org is committed to providing these for free as always, however we need to prioritize resources for those who need them the most. 我们非常不想看到某种语言的翻译活动结束了,并且内容过时了,然后我们不得不关闭相应的服务器。
+
+ For translating the curriculum, once a language reaches at least a few certifications we can begin deploying the language live on [`/learn`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/learn), while you continue to translate the remaining certifications.
+
+ 举个例子, 当我们正式上线一个新的语言版本的时候,我们希望至少上线整个前端认证的内容。
+
+3. **但是,如果一种语言没有在翻译平台上列出来,怎么办呢?**
+
+ 我们已经查看了我们的用户群,并且在翻译平台的可用语言列表上添加了三十多种的常用语言。 有一些语言,例如中文和西班牙语,已经在 **"/learn"** 上线了。
+
+ 然而遗憾的是,这个语言列表并没有涵盖所有的世界语言。 我们每天都能收到许多像你一样的贡献者的需求, 希望将我们的资源翻译成他们的语言。
+
+ 我们当然希望在这个列表上增加更多的语言种类, 但是你可能已经猜到了, 假如我们有足够的人来翻译某一语言才能让这件事变得实际。
+
+ 假如你希望我们增加某一种新的语言, 我们建议你鼓动你的朋友一起来参与贡献。
+
+ 如果你们有一个组的人(至少四到五人)对某一种语言感兴趣,并且承诺翻译这种语言, 那么我们可以在翻译平台上增加这种语言。 我们会解释一切的细节,并且帮助你掌握这些翻译工具和理解这些翻译的过程。
+
+## Overview of Crowdin
+
+It's our dream to provide you with the resources to learn, no matter the world language you speak. To help us with this massive effort, we have integrated our open-source codebase & curriculum with [Crowdin](https://crowdin.com/) - A tool to help us localize our code-base.
+
+> [!NOTE] We use a different tool and workflow for translating [news articles](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news). If you are interested in translating articles, read [this announcement](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) and reach out to your Language Lead.
+
+The translation workflow is split into two main activities:
+
+- **翻译**课程文件、文档和 UI 元素(如按钮、标签):
+
+ 译者可以在[我们的翻译平台](https://translate.freecodecamp.org)注册,然后从 30+ 种语言版本中选择要参与贡献的版本,进行翻译。
+
+- **校对**上述翻译。
+
+ 校对者确认社区成员贡献的译文语调一致,没有错别字等常见问题。 简而言之,校对者需要确保译文是高质量的。 注意,我们不使用任何机器翻译。
+
+> [!WARNING] We are no longer using GitHub to translate files directly, if you are a returning contributor head to our [translation platform](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/) instead.
+
+## Getting Started
+
+First, make sure you come say "Hi" in our [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). 我们会在聊天室定期更新翻译的资源和回答很多问题。
+
+其次,去我们的[翻译平台](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/)并且登陆(假如你以前没有贡献翻译过,你需要创建一个新账户)。
+
+最后,浏览下面提供的细节图来理解怎么使用翻译工具和流程。
+
+祝你在翻译过程中感到快乐哦!
+
+## Select a Project and File
+
+当你访问翻译平台,你应该可以看到很多不同的等待翻译的项目:
+
+1. [贡献文档](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/contributing-docs)项目,其中包含此文档站点的文件。
+2. [编程课程](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/curriculum)项目,其中包含我们课程的挑战文件。
+3. [学习用户界面](https://translate.freecodecamp.org/learn-ui)项目,其中包含我们学习平台的按钮、标签等 UI 元素的字符串。
+
+选择你想参与的任何项目,你将看到可供翻译的语言列表。
+
+
+
+选择你要使用的语言,你将看到完整的文件树。
+
+
+
+每个文件和文件夹都会显示一个进度条。 进度条的**蓝色**部分表示多少百分比的文件已经被翻译了,而**绿色**部分表示多少百分比的文件已经被校对团队审核确认。
+
+选择你想翻译的文件,然后 Crowdin 会打开编辑界面。
+
+> [!NOTE] When the editor view opens, you will need to click the settings icon (shown as a gear) and switch the 'HTML tags displaying' setting to 'SHOW'. This will ensure you can see tags such as `<code></code>` instead of `<0></0>`.
+
+## Translate Curriculum
+
+
+
+Crowdin 将文档分成可翻译的“字符串”,通常是句子。 每个字符串都被单独翻译。 参考上图:
+
+1. 以绿色标示的字符串已经有了一个建议的翻译。
+2. 以红色标示的字符串*没有*建议的翻译。
+3. 带有灰色文本的字符串不可翻译。 对于代码块和其他必须不被翻译的内容,就是这种情况。 你将无法在编辑器中选择这些字符串。
+4. 如果某位贡献者对某个字符串有建议的译文,那么 Crowdin 将在此处显示所有的建议。 你无法保存相同的译文。如果某个译文是正确的,那么你可以点击 `+` 图标,给它投票表示赞同。 如果你觉得某个译文不正确,那么你可以点击 `-` 图标,投反对票。
+5. Crowdin 将基于翻译记忆(TM)或机器翻译(MT)推荐译文。 翻译记忆是指我们已在其他文件中翻译过/批准过的相似的或相同的字符串。 机器翻译是指由 Crowdin 系统推荐的翻译。
+6. 这是编辑器窗口,你可以在其中输入你对于所选字符串建议的译文。
+7. 编辑窗口当前选中的字符串将被标注为黄色。
+8. 这里的标签是表示字符串的状态。 `Done` 标签表示字符串有至少一个建议的译文。 `Todo` 标签表示字符串还没有建议的译文。
+9. 这里是评论窗口。 如果你对某个字符串有疑问或疑虑,可以在此处对字符串发表评论,以便其他翻译人员查看。
+10. 点击这两个“窗格”按钮,可以隐藏左边的(文件)视图和右边的(评论)视图。
+
+> [!NOTE] If you see a hidden string that includes translations, please notify us in the [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) so we can remove the translation from memory.
+
+当你翻译完一个字符串,请点击 `Save` 按钮,将你的译文保存在 Crowdin 中。 然后其他贡献者可以给你的译文投票,而校对者也将审核确认你的译文。
+
+你想翻译多少字符串,都可以,我们非常欢迎你贡献!当你翻译完某个文件或某个字符串之后,你不需要采取其他步骤。 你只需要点击 `Save` 按钮,就能保存你的译文了。
+
+> [!NOTE] If you see something in the English source file that is inaccurate or incorrect, please do not fix it through the translation flow. Instead, leave a comment on the string to notify us that there is a discrepancy, or create a GitHub issue.
+
+## Translate the Learn Interface
+
+Our `/learn` interface relies on JSON files loaded into an i18n plugin to generate translated text. This translation effort is split across both Crowdin and GitHub.
+
+### On GitHub
+
+The `links.json`, `meta-tags.json`, `motivation.json`, and `trending.json` files contain information that needs to be updated to reflect your language. However, we cannot load these into Crowdin, as the content isn't something that would be a one-to-one translation.
+
+These files will most likely be maintained by your language lead but you are welcome to [read about how to translate them](language-lead-handbook).
+
+### On Crowdin
+
+:::danger
+Do not edit the following files through a GitHub PR.
+:::
+
+The `intro.json` and `translations.json` files are both translated on Crowdin, in the Learn User Interface project. Translating these can be a bit tricky, as each individual JSON value appears as its own string and sometimes the context is missing.
+
+However, the `Context` information provided in Crowdin can help understand where the string fits in to the larger structure.
+
+
+
+If you have any questions about where a string fits in to the prose, reach out to us in our [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Translate Documentation
+
+Translating our contributing documentation is a similar flow to translating our curriculum files.
+
+> [!NOTE] Our contributing documentation is powered by `docsify`, and we have special parsing for message boxes like this one. If you see strings that start with `[!NOTE]`, `[!WARNING]`, or `[!TIP]`, these words should NOT be translated.
+
+### How to Translate Documentation with Internal Links
+
+When you work on translating contributing documentation, watch out for internal links targeting a different section of the documentation.
+
+Make sure to replace the id of the target section (the part after `#`) with the id on the translated document. For example, it will look like this in Japanese:
+
+Before translation
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+<a href="#target-section-heading-id">Link text</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+After translation
+
+```
+// in HTML
+<a href="target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+<a href="#翻訳後の-id">翻訳後のリンクテキスト</a>
+
+// in Markdown
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](target-file-name.md#翻訳後の-id)
+[翻訳後のリンクテキスト](#翻訳後の-id)
+```
+
+The actual files in docs are written in Markdown, but they will appear as HTML tags on Crowdin.
+
+You can find out how `docsify` converts a string in your language into an id by looking into the translated pages. If the translation is not deployed yet, you can preview it by [running the docs site locally](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#serving-the-documentation-site-locally).
+
+You can learn more about [internal links in our docs here](how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme#how-to-create-an-internal-link).
+
+## Translate the LearnToCode RPG
+
+The LearnToCode RPG runs on Ren'Py, which uses special syntax for translated strings: (See [Ren'Py Text documentation](https://www.renpy.org/doc/html/text.html))
+
+- The sentences to be translated are always between `""`. These are dialogues or UI strings. The keywords that come before or after the dialogue are game engine control keywords and will be explained in details in subsequent rules. Please note that this first rule governs all subsequent rules listed.
+- In case of `new "..."` Do not translate the `new` keyword.
+- Prefixes like `player`, `annika`, `layla`, `marco` (or variants like `player happy`, `player @ happy`) should not be translated. These are control keywords to correctly display the character sprite in the game.
+- Postfixes like `nointeract` should not be translated.
+- Do not translate things between `[]` and `{}`. These are variable interpolations and text tags. These must remain halfwidth parentheses `[]` and `{}` instead of their fullwidth counterparts `【】` and `「」`
+- Do not translate the `nointeract` keyword at the end of the sentence.
+- If we try to use fullwidth parentheses `()`, a QA warning will show. To avoid the QA warning, use halfwidth parentheses `()`
+
+### Examples
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that." <--- this is the line that needs to be translated. see translation below
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# "[player_name]? What a coincidence! Our VIP team member {a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a} will be honored to hear that."
+"[player_name]?好巧,我们的VIP队友{a=[vip_profile_url]}[player_name]{/a}会很高兴的。"
+```
+
+Note: The `[]` and `{}` tags should be left intact.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip" <-- translate this line, see below
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+old "{icon=icon-fast-forward} Skip"
+new "{icon=icon-fast-forward} 跳过"
+```
+
+Note: Again, the `new` prefix and the `{icon=icon-fast-forward}` tag should be left intact.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# layla @ neutral "Hehe, [player_name], you are a fun one. I'm sure you will enjoy your work as a developer."
+layla @ neutral "哈哈,[player_name],你真有趣。我相信你一定会喜欢你的开发者工作的。"
+```
+
+Note: `layla @ neutral` and `[player_name]` are left unchanged.
+
+---
+
+#### Before translation
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+```
+
+#### After translation
+
+```renpy
+# player "Maybe this is all a dream?" nointeract
+player "也许这都是一场梦?" nointeract
+```
+
+---
+
+### A Note on How Crowdin Segments a Sentence
+
+Pay attention to how Crowdin segments a line of dialogue wrapped between opening and closing quotes `""`. When we are translating the dialogue, we need to make sure to retain the opening and closing quotes, even if the quotes appear in different segments.
+
+This is the line to be translated:
+
+```renpy
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}... What is that? I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+```
+
+Crowdin segments it into three parts like below:
+
+<img width="836" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 43" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693962-d3b091e5-2432-44d0-9d24-195ea7d7aeda.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+player @ surprised "{b}Full-stack{/b}
+# translated, keeping the opening quotes `"`
+player @ surprised "{b}全栈{/b}
+```
+
+<img width="750" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 49" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693965-15411504-791a-4db3-8b14-bc9177be6375.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+What is that?
+# translated, no quotes on either side
+这是什么?
+```
+
+<img width="857" alt="Screen Shot 2022-01-23 at 10 36 54" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/35674052/150693969-062e3268-580f-4ad2-97db-cab6240b6095.png" />
+
+```renpy
+# original
+I better take notes so I can learn more about it."
+# translated, keeping the closing quotes `"`
+我最好做笔记,这样我可以学习更多东西。"
+```
+
+## Rate Translations
+
+Crowdin allows you to rate the existing proposed translations. If you attempt to save a translation, you may see a message indicating that you cannot save a duplicate translation - this means another contributor has proposed that identical translation. If you agree with that translation, click the `+` button to "upvote" the translation.
+
+If you see a translation that is inaccurate or does not provide the same clarity as the original string, click the `-` button to "downvote" the translation.
+
+Crowdin uses these votes to give a score to each proposed translation for a string, which helps the proofreading team determine which translation is the best fit for each string.
+
+## Quality Assurance Checks
+
+We have enabled some quality assurance steps that will verify a translation is as accurate as possible - this helps our proofreaders review proposed translations.
+
+When you attempt to save a translation, you may see a warning message appear with a notification regarding your proposed translation.
+
+
+
+This message appears when Crowdin's QA system has identified a potential error in the proposed translation. In this example, we have modified the text of a `<code>` tag and Crowdin has caught that.
+
+> [!WARNING] You have the option to save a translation in spite of errors. If you do, by clicking "Save Anyway", you should also tag a proofreader or project manager and explain why the QA message needs to be ignored in this case.
+
+## Translation Best Practices
+
+Follow these guidelines to ensure our translations are as accurate as possible:
+
+- Do not translate the content within `<code>` tags. These tags indicate text that is found in code and should be left in English.
+- Do not add additional content. If you feel a challenge requires changes in the text content or additional information, you should propose the changes through a GitHub issue or a pull request that modifies the English file.
+- Do not change the order of content.
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us in our [Discord](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) and we will be happy to assist you.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c092ea3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: How to use Docker on Windows Home
+---
+
+There are a few pitfalls to be avoided when setting up Docker on Windows Home. First of all, you have to use [Docker Toolbox](https://docs.docker.com/toolbox/toolbox_install_windows/) as Administrator. Unfortunately Windows Home does not support Docker for Windows Desktop, so Toolbox must be used instead. It has to be run as Administrator as the installation uses symlinks, which cannot be created otherwise.
+
+Once you've installed the toolbox, run Docker Quickstart Terminal as Administrator. This will create a `default` virtual machine if it does not already exist. Once that has happened, close the terminal and open VirtualBox (again as Administrator). You should be able to see the `default` machine. The site is quite resource-intensive, so stop the virtual machine and raise the settings as much as you can - memory in particular. It has been confirmed to work with 4GB of RAM.
+
+Once you're happy that Docker is working, clone the freeCodeCamp repository to a directory inside `C:\Users`. These directories are shared giving Docker access to the local directories, which it needs during installation.
+
+If you see messages like
+
+```shell
+bash: change_volumes_owner.sh: No such file or directory
+```
+
+when you `pnpm run docker:init` this is likely the culprit.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3e394497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md
@@ -0,0 +1,737 @@
+---
+title: How to work on coding challenges
+---
+
+Our goal is to develop a fun and clear interactive learning experience.
+
+Designing interactive coding challenges is difficult. It would be much easier to write a lengthy explanation or to create a video tutorial. But for our core curriculum, we're sticking with what works best for most people - a fully interactive, video game-like experience.
+
+We want campers to achieve a flow state. We want them to build momentum and blast through our curriculum with as few snags as possible. We want them to go into the projects with confidence and gain wide exposure to programming concepts.
+
+Note that for Version 7.0 of the freeCodeCamp curriculum, we are moving toward [an entirely project-focused model with a lot more repetition](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-curriculum-is-live/).
+
+Creating these challenges requires immense creativity and attention to detail. There's plenty of help available. You'll have support from a whole team of contributors to whom you can bounce ideas off and demo your challenges.
+
+And as always, feel free to ask questions on the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+With your help, we can design an interactive coding curriculum that will help millions of people learn to code for years to come.
+
+The content for each challenge is stored in its markdown file. This markdown file is later converted to HTML using our tools to create interactive web pages.
+
+You can find all of freeCodeCamp.org's curricular content in the [`/curriculum/challenges`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/curriculum/challenges) directory.
+
+## Set up the tooling for the curriculum
+
+Before you work on the curriculum, you would need to set up some tooling to help you test your changes. You can use any option from the below:
+
+- You can [set up freeCodeCamp locally](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). This is **highly recommended** for regular/repeat contributions. This setup allows you to work and test your changes.
+- Use Gitpod, a free online dev environment. Clicking the button below will start a ready-to-code dev environment for freeCodeCamp in your browser. It only takes a few minutes.
+
+ [](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp)
+
+### How to work on practice projects
+
+The practice projects have some additional tooling to help create new projects and steps. To read more, see [these docs](how-to-work-on-practice-projects)
+
+## Challenge Template
+
+````md
+---
+id: Unique identifier (alphanumerical, MongoDB_id)
+title: 'Challenge Title'
+challengeType: Integer, defined in `client/utils/challenge-types.js`
+videoUrl: 'url of video explanation'
+forumTopicId: 12345
+---
+
+# --description--
+
+Challenge description text, in markdown
+
+```html
+<div>example code</div>
+```
+````
+
+# --instructions--
+
+Challenge instruction text, in markdown
+
+# --hints--
+
+Tests to run against user code, in pairs of markdown text and code block test code.
+
+```js
+Code for test one
+```
+
+If you want dynamic output based on the user's code, --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual-- will be replaced with the expected and actual values of the test's assertion. Take care if you have multiple assertions since the first failing assertion will determine the values of --fcc-expected-- and --fcc-actual--.
+
+```js
+assert.equal(
+ 'this will replace --fcc-actual--',
+ 'this will replace --fcc-expected--'
+);
+```
+
+# --notes--
+
+Extra information for a challenge, in markdown
+
+# --seed--
+
+## --before-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Code evaluated before the user’s code.
+```
+
+## --after-user-code--
+
+```lang
+Code evaluated after the user’s code, and just before the tests
+```
+
+## --seed-contents--
+
+Boilerplate code to render to the editor. This section should only contain code inside backticks, like the following:
+
+```html
+<body>
+ <p class="main-text">Hello world!</p>
+</body>
+```
+
+```css
+body {
+ margin: 0;
+ background-color: #3a3240;
+}
+
+.main-text {
+ color: #aea8d3;
+}
+```
+
+```js
+console.log('freeCodeCamp is awesome!');
+```
+
+# --solutions--
+
+Solutions are used for the CI tests to ensure that changes to the hints will still pass as intended
+
+```js
+// first solution - the language(s) should match the seed.
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// second solution - so if the seed is written in HTML...
+```
+
+---
+
+```js
+// third solution etc. - Your solutions should be in HTML.
+```
+
+# --assignments--
+
+This will show a checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+---
+
+This will show another checkbox that campers have to check before completing a challenge
+
+# --question--
+
+These fields are currently used for the multiple-choice Python challenges.
+
+## --text--
+
+The question text goes here.
+
+## --answers--
+
+Answer 1
+
+### --feedback--
+
+This will be shown as feedback when campers guess this answer
+
+---
+
+Answer 2
+
+---
+
+More answers
+
+## --video-solution--
+
+The number for the correct answer goes here.
+
+# --fillInTheBlank--
+
+These are for the English curriculum challenges.
+
+## --sentence--
+
+Sentence to be shown with with blanks that campers have to fill in. Example:
+
+`Hello, You _ the new graphic designer, _?`
+
+The two underscores will show up as blanks. The sentence must be surrounded in backticks.
+
+## --blanks--
+
+The solution for the first blank in the sentence above. Example:
+
+`are`
+
+### --feedback--
+
+Feedback shown when campers input the wrong solution for this blank.
+
+---
+
+Solution for the second blank. Example:
+
+`right`
+
+If no feedback is here, a generic "wrong answer" message will be shown.
+
+# --scene--
+
+```json
+// # --scene-- can only consist of a single json object
+{
+ // Setup the scene. Properties not marked optional are required.
+ "setup": {
+ // Background file to start the scene. A list of scene asset filenames can be found here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/pull/233/files
+ "background": "company2-center.png",
+ // Array of all characters that will appear in the scene
+ "characters": [
+ {
+ // Name of character. See list of available characters in scene-assets.tsx
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Where to start the character. Maria will start off screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will start 70% from the left of the screen and 1.5 times regular size
+ "position": { "x": 70, "y": 0, "z": 1.5 },
+ // Optional, defaults to 1. Tom will start invisible
+ "opacity": 0
+ }
+ ],
+ "audio": {
+ // Audio filename
+ "filename": "1.1-1.mp3",
+ // Seconds after the scene starts before the audio starts playing
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where it starts playing from.
+ "startTimestamp": 0,
+ // Optional. Timestamp of the audio file where is stops playing. If these two aren't used, the whole audio file will play.
+ "finishTimestamp": 8.4
+ },
+ // Optional, defaults to false. Use this for the long dialogues. It stops the accessibility icon from showing which gives campers the option to show or hide the dialogue text
+ "alwaysShowDialogue": true
+ },
+ // Array of commands that make up the scene
+ "commands": [
+ {
+ // Character that will have an action for this command
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Maria will move to 25% from the left of the screen. The movement takes 0.5 seconds
+ "position": { "x": 25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // When the command will start. Zero seconds after the camper presses play
+ "startTime": 0
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Optional, defaults to previous value. Tom will fade into view. The transition take 0.5 seconds. Movement and Opacity transitions take 0.5 seconds
+ "opacity": 1,
+ // Tom will fade into view 0.5 seconds into the scene (immediately after Maria finishes moving on screen)
+ "startTime": 0.5
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // When the command starts: Maria will start saying this line 1.3 seconds into the scene. Note that this is the same time as the audio.startTime above. It doesn't have to match that (maybe there's a pause at the beginning of the audio or something)
+ "startTime": 1.3,
+ // The character will stop moving their mouth at the finishTime
+ "finishTime": 4.95,
+ "dialogue": {
+ // Text that will appear if the dialogue is visible
+ "text": "Hello! You're the new graphic designer, right? I'm Maria, the team lead.",
+ // Where the dialogue text will be aligned. Can be 'left', 'center', or 'right'
+ "align": "left"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ // background will change to this at 5.4 seconds into the scene
+ "background": "company2-breakroom.png",
+ "character": "Tom",
+ "startTime": 5.4,
+ "finishTime": 9.4,
+ "dialogue": {
+ "text": "Hi, that's right! I'm Tom McKenzie. It's a pleasure to meet you.",
+ // Tom's text will be aligned to the right since he is on the right side of the screen
+ "align": "right"
+ }
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Tom",
+ // Tom will fade to 0 opacity
+ "opacity": 0,
+ // I like to move characters off screen or fade them 0.5 second after the last talking command
+ "startTime": 9.9
+ },
+ {
+ "character": "Maria",
+ // Maria will slide back off the screen to the left
+ "position": { "x": -25, "y": 0, "z": 1 },
+ // The animation will stop playing 0.5 seconds after the 'finishTime' of the last command - or 0.5 seconds after 'startTime' if 'finishTime' isn't there.
+ "startTime": 10.4
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+````
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> 1. In the above sections, examples of `lang` are:
+>
+> - `html` - HTML/CSS
+> - `js` - JavaScript
+> - `jsx` - JSX
+
+## Numbering Challenges
+
+Every challenge needs an `id`. If you don't specify one, then MongoDB will create a new random one when it saves the data; however, we don't want it to do that, since we want the challenge ids to be consistent across different environments (staging, production, lots of different developers, etc.).
+
+To generate a new one in a shell (assuming MongoDB is running separately):
+
+1. Run `mongo` command.
+2. Run `ObjectId()` command.
+
+For example:
+
+```bash
+$ mongo
+MongoDB shell version v3.6.1
+connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
+MongoDB server version: 3.4.10
+...
+$ ObjectId()
+ObjectId("5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34")
+````
+
+The result is a new id, for example, `5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34` above.
+
+Once you have your id, put it into the markdown file as the `id` field at the top, e.g.
+
+```yml
+---
+id: 5a474d78df58bafeb3535d34
+title: Challenge Title
+```
+
+## Naming challenges
+
+Naming things is hard. We've made it easier by imposing some constraints.
+
+All challenge titles should be explicit and should follow this pattern:
+
+\[verb\]\[object clause\]
+
+Here are some example challenge names:
+
+- Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Padding of an Element
+- Condense arrays with .reduce
+- Use Bracket Notation to Find the First Character in a String
+
+## Challenge descriptions/instructions
+
+Sentences should be clear and concise with minimal jargon. If used, jargon should be immediately defined in plain English.
+
+Keep paragraphs short (around 1-4 sentences). People are more likely to read several short paragraphs than a wall of text.
+
+Use american english, e.g., use `labeled` instead of `labelled`.
+
+Challenge text should use the second person ("you") to help to give it a conversational tone. This way the text and instructions seem to speak directly to the camper working through the challenge. Try to avoid using the first person ("I", "we", "let's", and "us").
+
+Don't use outbound links. These interrupt the flow. Campers should never have to google anything during these challenges. If there are resources you think campers would benefit from, add them to the challenge's Guide-related article.
+
+You can add diagrams if necessary.
+
+Don't use emojis or emoticons in challenges. freeCodeCamp has a global community, and the cultural meaning of an emoji or emoticon may be different around the world. Also, emojis can render differently on different systems.
+
+Proper nouns should use correct capitalization when possible. Below is a list of words as they should appear in the challenges.
+
+- JavaScript (capital letters in "J" and "S" and no abbreviations)
+- Node.js
+- Although sometimes inaccurate, non-hyphenated forms of 'back end' and 'front end' should be used, as they are more widely used.
+
+### The 2-minute rule
+
+Each challenge should be solvable within 120 seconds by a native English speaker who has completed the challenges leading up to it. This includes the amount of time it takes to read the directions/instructions understand the seeded code, write their code and get all the tests to pass.
+
+If it takes longer than two minutes to complete the challenge, you have two options:
+
+- Simplify the challenge, or
+- Split the challenge into two challenges.
+
+The 2-minute rule forces you, the challenge designer, to make your directions concise, your seed code clear, and your tests straightforward.
+
+We track how long it takes for campers to solve challenges and use this information to identify challenges that need to be simplified or split.
+
+### Modularity
+
+Each challenge should teach exactly one concept, and that concept should be apparent from the challenge's name.
+
+We can reinforce previously covered concepts through repetition and variations - for example, introducing h1 elements in one challenge, then h3 elements a few challenges later.
+
+Our goal is to have thousands of 2-minute challenges. These can flow together and reiterate previously-covered concepts.
+
+### Formatting challenge text
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for challenge text and examples:
+
+- Language keywords go in `` \` `` backticks. For example, HTML tag names or CSS property names.
+- References to code parts (i.e. function, method, or variable names) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks. See example below:
+
+```md
+Use `parseInt` to convert the variable `realNumber` into an integer.
+```
+
+- References to file names and path directories (e.g. `package.json`, `src/components`) should be wrapped in `` \` `` backticks.
+- Multi-line code blocks **must be preceded by an empty line**. The next line must start with three backticks followed immediately by one of the [supported languages](https://prismjs.com/#supported-languages). To complete the code block, you must start a new line that only has three backticks and **another empty line**. See example below:
+- Whitespace matters in Markdown, so we recommend that you make it visible in your editor.
+
+**Note:** If you are going to use an example code in YAML, use `yaml` instead of `yml` for the language to the right of the backticks.
+
+The following is an example of code:
+
+````md
+```{language}
+
+[YOUR CODE HERE]
+```
+````
+
+````
+
+- Additional information in the form of a note should be surrounded by blank lines, and formatted: `**Note:** Rest of note text...`
+- If multiple notes are needed, then list all of the notes in separate sentences using the format: `**Notes:** First note text. Second note text.`
+- Use single quotes where applicable
+
+**Note:** The equivalent _Markdown_ should be used in place of _HTML_ tags.
+
+## Writing tests
+
+Challenges should have the minimum number of tests necessary to verify that a camper understands a concept.
+
+Our goal is to communicate the single point that the challenge is trying to teach, and test that they have understood that point.
+
+Challenge tests can make use of the Node.js and Chai.js assertion libraries. Also, if needed, user-generated code can be accessed in the `code` variable. In addition, the `__helpers` object exposes several functions that simplify the process of writing tests. The available functions are defined in the [curriculum-helpers](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/curriculum-helpers/blob/main/lib/index.ts) repo.
+
+## Formatting Seed Code
+
+Here are specific formatting guidelines for the challenge seed code:
+
+- Use two spaces to indent
+- JavaScript statements end with a semicolon
+- Use double quotes where applicable
+
+### Seed Code Comments
+
+We have a [comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) that contains the only comments that can be used within the seed code. The exact case and spacing of the dictionary comment must be used. The comment dictionary should not be expanded without prior discussion with the dev-team.
+
+Comments used should have a space between the comment characters and the comment themselves. In general, comments should be used sparingly. Always consider rewriting a challenge's description or instructions if it could avoid using a seed code comment.
+
+Example of a valid single-line JavaScript comment:
+
+```js
+// Only change code below this line
+````
+
+Example of a valid CSS comment:
+
+```css
+/* Only change code above this line */
+```
+
+If a challenge only has a single place where code changes are needed, please use the comments in the following example to instruct the user where changes should be made.
+
+```js
+var a = 3;
+var b = 17;
+var c = 12;
+
+// Only change code below this line
+a = a + 12;
+b = 9 + b;
+c = c + 7;
+```
+
+If a challenge has multiple places where the user is expected to change code (i.e. the React challenges)
+
+```jsx
+class MyComponent extends React.Component {
+ constructor(props) {
+ super(props);
+ this.state = {
+ text: 'Hello'
+ };
+ // Change code below this line
+
+ // Change code above this line
+ }
+ handleClick() {
+ this.setState({
+ text: 'You clicked!'
+ });
+ }
+ render() {
+ return (
+ <div>
+ {/* Change code below this line */}
+ <button>Click Me</button>
+ {/* Change code above this line */}
+ <h1>{this.state.text}</h1>
+ </div>
+ );
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Translation of Seed Code Comments
+
+There are separate comment dictionaries for each language. The [English version of the comment dictionary](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/curriculum/dictionaries/english/comments.json) is the basis for the translations found in the corresponding non-English versions of the files. The non-English version of the Chinese comment dictionary would be located at `/curriculum/dictionaries/chinese/comments.json`. Each dictionary consists of an array of objects with a unique `id` property and a `text` property. Only the `text` should be modified to encompass the translation of the corresponding English comment.
+
+Some comments may contain a word/phrase that should not be translated. For example, variable names or proper library names like "React" should not be translated. See the comment below as an example. The word `myGlobal` should not be translated.
+
+```text
+Declare the myGlobal variable below this line
+```
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> We are working on an integration to make it possible to work on i18n for the comment dictionary.
+
+## Hints and Solutions
+
+Each challenge has a `Get a Hint` button, so a user can access any hints/solutions which have been created for the challenge. Curriculum hints/solutions topics are located on [our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/guide) under the `Guide` category.
+
+If you find a problem with an existing challenge's hints/solutions topic, you can make suggestions in the [contributors category](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) on the forum. Moderators and users with trust level 3 will review the comments and decide whether or not to include the changes in the corresponding hint/solutions topic.
+
+### Adding new Challenge hints/solutions Topics
+
+Take the following steps when adding a new challenge hints/solutions-related topic.
+
+1. Start by following the same steps for creating a new topic but review the next for creating the title.
+2. The title of the topic should start with `freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide:` concatenated with the actual title of the curriculum challenge. For example, if the challenge is named "`Chunky Monkey`", the topic title would be "`freeCodeCamp Challenge Guide: Chunky Monkey`".
+3. `camperbot` should be the owner of these topics/posts, so you will need to request an admin to change the ownership of the main post to `camperbot`.
+4. Once the new topic is created, a forum topic id is created. It is located at the end of the forum topic URL. This id must be added to the frontmatter of the curriculum challenge file via the normal pull request process for the `Get a Hint` button to link to the topic.
+
+### Guidelines for Content of Hints and Solutions Topics
+
+When proposing a solution for a curriculum challenge-related Guide topic, the full code must be added. This includes all the original seed code plus any changes needed to pass all the challenge tests. The following template should be used when creating new hints/solutions topics:
+
+````md
+# Challenge Name Goes Here
+
+---
+
+## Problem Explanation
+
+This summarizes what needs to be done without just restating the challenge description and/or instructions. This is an optional section
+
+#### Relevant Links
+
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+---
+
+## Hints
+
+### Hint 1
+
+Hint goes here
+
+### Hint 2
+
+Hint goes here
+
+---
+
+## Solutions
+
+<details><summary>Solution 1 (Click to Show/Hide)</summary>
+
+```js
+function myFunc() {
+ console.log('Hello World!');
+}
+```
+````
+
+#### Code Explanation
+
+- Code explanation goes here
+- Code explanation goes here
+
+#### Relevant Links
+
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+- [Link Text](link_url_goes_here)
+
+</details>
+````
+
+## Testing Challenges
+
+Before you [create a pull request](how-to-open-a-pull-request) for your changes, you need to validate that the changes you have made do not inadvertently cause problems with the challenge.
+
+1. To test all challenges run the below command from the root directory
+
+````
+pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+2. To test single challenge, you can use it challenge id with following command
+
+```
+FCC_CHALLENGE_ID=646cf6cbca98e258da65c979 pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+3. You can also test a block or a superblock of challenges with these commands
+
+```
+FCC_BLOCK='Basic HTML and HTML5' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+```
+FCC_SUPERBLOCK='responsive-web-design' pnpm run test:curriculum
+```
+
+You are also able to test challenges by title by performing the following steps:
+
+1. Switch to the `curriculum` directory:
+
+ ```
+ cd curriculum
+ ```
+
+2. Run the following for each challenge file for which you have changed (replacing `challenge-title-goes-here` with the full title of the challenge):
+
+ ```
+ pnpm run test -- -g challenge-title-goes-here
+ ```
+
+> [!TIP]
+> You can set the environment variable `LOCALE` in the `.env` to the language of the challenge(s) you need to test.
+>
+> The currently accepted values are `english` and `chinese`, with `english` being set by default.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Useful Links
+
+Creating and Editing Challenges:
+
+1. [Challenge types](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/client/utils/challenge-types.js#L1-L13) - what the numeric challenge type values mean (enum).
+
+2. [Contributing to FreeCodeCamp - Writing ES6 Challenge Tests](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOdD84OSfAE#t=2h49m55s) - a video following [Ethan Arrowood](https://twitter.com/ArrowoodTech) as he contributes to the old version of the curriculum.
+
+## Helper Scripts
+
+> [!NOTE]
+> If you are working with the step-based challenges, refer to the [Work on Practice Projects](how-to-work-on-practice-projects) section.
+
+There are a few helper scripts that can be used to manage the challenges in a block. Note that these commands should all be run in the block directory. For example:
+
+```bash
+cd curriculum/challenges/english/02-javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures/basic-algorithm-scripting
+```
+
+### Add New Challenge
+
+To add a new challenge at the end of a block, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information and create the challenge file, updating the `meta.json` file with the new challenge information.
+
+### Delete a Challenge
+
+To delete a challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you to select which challenge should be deleted, then delete the file and update the `meta.json` file to remove the challenge from the order.
+
+### Insert a Challenge
+
+To insert a challenge before an existing challenge, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-challenge
+```
+
+This will prompt you for the challenge information, then for the challenge to insert before. For example, if your choices are:
+
+```bash
+a
+b
+c
+```
+
+If you choose `b`, your new order will be:
+
+```bash
+a
+new challenge
+b
+c
+```
+
+### Update Challenge Order
+
+If you need to manually re-order the challenges, call the script:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-challenge-order
+```
+
+This will take you through an interactive process to select the order of the challenges.
+
+## Troubleshooting
+
+### Infinite Loop Detected
+
+If you see the following error in the console while previewing a challenge:
+
+```text
+Potential infinite loop detected on line <number>...
+```
+
+This means that the loop-protect plugin has found a long-running loop or recursive function. If your challenge needs to do that (e.g. it contains an event loop that is supposed to run indefinitely), then you can prevent the plugin from being used in the preview. To do so, add `disableLoopProtectPreview: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+If your tests are computationally intensive, then you may see this error when they run. If this happens then you can add `disableLoopProtectTests: true` to the block's `meta.json` file.
+
+It's not typically necessary to have both set to true, so only set them as needed.
+````
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2e867b31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Localized Client Webapp
+---
+
+The React-based client web app that powers our learning platform is built using Gatsby. It is translated into various world languages using [react-i18next](https://react.i18next.com/) and [i18next](https://www.i18next.com/).
+
+You can learn more about setting up the client application locally for development by following [our local setup guide here](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally). By default, the application is available only in English.
+
+Once you have set up the project locally you should be able to follow this documentation to run the client in the language of your choice from the list of available languages.
+
+This could be helpful when you are working on a feature that specifically targets something that involves localization, and requires you to validate for instance a button's label in a different language.
+
+:::tip
+You do not need to follow this document to translate freeCodeCamp's curriculum or contributing documentation. Read [this guide here](how-to-translate-files) instead.
+:::
+
+Let's understand how the i18n frameworks and tooling work.
+
+## File Structure
+
+Most of the files for translating the platform are located in the [`client/i18n`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/client/i18n) folder. Each language has a directory that contains JSON files with the translations.
+
+```bash
+ config
+ └── i18n.ts
+ ...
+ client/i18n
+ ├── configForTests.js
+ ├── config.js
+ ├── locales
+ │ ├── chinese
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── dothraki
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ ... ...
+ │ ├── english
+ │ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ │ ├── links.json
+ │ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ │ └── translations.json
+ │ └── espanol
+ │ ├── intro.json
+ │ ├── links.json
+ │ ├── meta-tags.json
+ │ ├── motivation.json
+ │ └── translations.json
+ ├── locales.test.js
+ ├── schema-validation.js
+ └── validate-keys.ts
+```
+
+Some of these files are translated on our translation platform (Crowdin) and some are translated or created via PRs on GitHub.
+
+**Files translated on our translation platform:**
+
+- The `translations.json` file contains the majority of the text that appears on the user interface elements. The keys are used in the codebase to get the correct text for whatever language is set. This file needs to have the same keys in all languages.
+
+- The `intro.json` file contains the key-value pairs for the introduction text on the certification pages.
+
+ If you want to add/update translations for the keys please [read this guide here](how-to-translate-files).
+
+**Files NOT translated on our translations platform:**
+
+- The `motivation.json` files are not required to have the same quotes, compliments, or array length. Just the same JSON structure.
+
+- The `meta-tags.json` file contains the information for our website's meta tag information.
+
+ Changes to these files are typically done by the staff team. If you see something out of the ordinary we recommend you reach us in the [contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+## Testing the Client App in a World Language
+
+You can test the client app in any language available in the [list of `availableLangs` here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts).
+
+```js
+export const availableLangs = {
+ client: [
+ Languages.English,
+ Languages.Espanol,
+ Languages.Chinese,
+ Languages.ChineseTraditional,
+ Languages.Italian,
+ Languages.Portuguese,
+ Languages.Ukrainian,
+ Languages.Japanese,
+ Languages.German,
+ Languages.Arabic
+ ],
+ ...
+};
+```
+
+If you are testing a new language, create a folder with the language name as the title next to the other languages and copy the JSON files from another language into your new folder.
+
+Add the new language to the `Languages` enum and the `client` array at the top of the [`shared/config/i18n.ts`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/shared/config/i18n.ts) file.
+
+Next, follow the instructions in the comments in the same file to add/update the rest of the variables as needed.
+
+Finally, set the `CLIENT_LOCALE` variable in your `.env` file to the string of the locale you want to build from the `Languages` enum in the above file.
+
+## How to Structure Components
+
+If you are working on a feature or a bug for the client web app, say for example adding new UI items on the settings page, you should follow the guidelines below. They will help you prepare the components for localization into all the supported world languages.
+
+### Functional Component
+
+```js
+import { useTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// in the render method:
+const { t } = useTranslation();
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<p>{t('key')}</p>; // more details below
+```
+
+### Class Component
+
+```js
+import { withTranslation } from 'react-i18next';
+
+// withTranslation adds the "t" function to props:
+const { t } = this.props;
+
+// call the "t" function with a key from the JSON file:
+<h1>{t('key')}</h1> // more details below
+
+// export without redux:
+export default withTranslation()(Component);
+
+// or with redux:
+export default connect(...)(withTranslation()(Component));
+```
+
+## Translate Using the "t" Function
+
+### Basic Translation
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>{t('p1')}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "p1": "My paragraph"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>My paragraph</p>
+```
+
+### With Dynamic Data
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const username = 'moT';
+
+<p>{t('welcome', { username: username })}</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "welcome": "Welcome {{username}}"
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome moT</p>
+```
+
+The above example passes an object to the `t` function with a `username` variable. The variable will be used in the JSON value where `{{username}}` is.
+
+## Translate with the `Trans` Component
+
+The general rule is to use the "t" function when you can. But there's a `Trans` component for when that isn't enough, usually when you have elements embedded in the text. You can use the `Trans` component with any type of react component.
+
+### Basic Elements Nested
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+import { Trans } from 'react-i18next'
+
+<p>
+ <Trans>fcc.greeting</Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "greeting": "Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Welcome to <strong>freeCodeCamp</strong></p>
+```
+
+You can place the key inside the component tags like in the above example if the text contains "simple" tags with no attributes. `br`, `strong`, `i`, and `p` are the default, but that list can be expanded in the i18n config.
+
+### Complex Elements Nested
+
+Other times, you will want to have certain text inside another element, an anchor tag is a good example:
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+<p>
+ <Trans i18nKey='check-forum'>
+ <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>placeholder</a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "check-forum": "Check out <0>our forum</0>."
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Check out <a href='https://forum.freecodecamp.org/'>our forum</a></p>
+```
+
+In the above example, the key is set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. The `<0>` and `</0>` in the JSON represent the first child of the component, in this case, the anchor element. If there were more children, they would just count up from there using the same syntax. You can find the children of a component in the react dev tools by inspecting it. `placeholder` is simply there because the linter complains about empty `<a>` elements.
+
+### With a Variable
+
+```js
+// in the component:
+const email = 'team@freecodecamp.org';
+
+<p>
+ <Trans email={email} i18nKey='fcc.email'>
+ <a href={`mailto:${email}`}>
+ {{ email }}
+ </a>
+ </Trans>
+</p>
+
+// in the JSON file:
+{
+ "fcc": {
+ "email": "Send us an email at: <0>{{email}}</0>"
+ }
+}
+
+// output:
+<p>Send us an email at: <a href='mailto:team@freecodecamp.org'>team@freecodecamp.org</a><p>
+```
+
+In the above example, the key and a variable are set in the attributes of the `Trans` component. `{{ email }}` needs to be somewhere in the `Trans` component as well, it doesn't matter where.
+
+## Changing Text
+
+To change text on the client side of things, go to the relevant `.json` file, find the key that is being used in the React component, and change the value to the new text you want. You should search the codebase for that key to make sure it isn't being used elsewhere. Or, if it is, that the changes make sense in all places.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Adding Text
+
+If the text you want to add to the client exists in the relevant `.json` file, use the existing key. Otherwise, create a new key.
+
+The English file is the "source of truth" for all of the `.json` files sharing the same name. If you need to add a new key, add it there. Then, add the key to **all** of the `translations.json` files.
+
+> [!NOTE] Use English text for all languages if the file is translated through Crowdin. The tests will fail if you don't.
+
+It would be nice to keep the keys in the same order across all the files as well. Also, try to put all punctuation, spacing, quotes, etc. in the JSON files and not in the components or server files.
+
+> [!NOTE] The underscore (`_`) is a reserved character for keys in the client-side files. See [the documentation](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/plurals) for how they are used.
+
+Run `pnpm run clean-and-develop` to apply the change.
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Helpful Documentation
+
+- [react-i18next docs](https://react.i18next.com/latest/usetranslation-hook)
+- [i18next docs](https://www.i18next.com/translation-function/essentials)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8335ddd3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-practice-projects.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Practice Projects
+---
+
+Our practice projects use a step-based approach to teach concepts to campers. A project will consist of multiple files, which we refer to as **"steps"**. These files are named by the challenge ID, to avoid issues with the translation flow. Unfortunately, this makes it difficult to find the file associated with a specific step.
+
+We've built a challenge editor tool that helps remedy this. This tool allows you to navigate the available projects, and the steps for each project (in order). There's also an embedded code editor you can use to work on the files directly.
+
+## Using the Challenge Editor
+
+These instructions will tell you how to use our challenge editor tool to work on the practice projects.
+
+### Starting the Editor
+
+To start the editor, make sure you are in the root freeCodeCamp directory. Then, run `pnpm run challenge-editor` to start both the client and the API that powers the editor.
+
+The client will run on port `3300`, so you can access it at `http://localhost:3300`. The API runs on port `3200`, to avoid conflicts with the learn client and server. This will allow you to run the freeCodeCamp application at the same time as the editor, so you can test your changes locally.
+
+### Navigating the Editor
+
+The default view will list the available `superblocks` - these are the certifications. Click on the certification link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to the list of blocks. These are the practice projects. Click on the project link you want to work on.
+
+This will take you to a list of steps for the project. If you are working on an existing step, you can click on the step link to open the editor. If you are adding or removing steps, click the `Use the step tools` link to switch to the step tools for that challenge.
+
+### Editing Steps
+
+When you click on a step, you'll be taken to the editor. This is a basic text editor that offers syntax highlighting.
+
+After you have made your changes, click the `Save Changes` button to save your changes. You will get a browser alert letting you know that your changes are ready to commit. Note that you'll need to use `git` manually to stage and commit your files - this tool will not do that for you.
+
+### Step Tools
+
+When you click the `Use the step tools` link, you'll be taken to the step tools page. This allows you to add or remove steps from the project.
+
+#### Create Next Step
+
+Clicking this button will add a new step at the end of the project. This step will use the previous step's code as the seed.
+
+#### Create Empty Steps
+
+Enter the number of steps you want to add in the input. Then, clicking the button will create many empty steps at the end of the project.
+
+#### Insert Step
+
+Enter the step number that you want to add. Then, click the `Insert Step` button to add the step. The following steps will be re-ordered.
+
+#### Delete Step
+
+Enter the step number you want to delete. Then click the `Delete Step` button to remove that step. This will automatically update the step numbers for the remaining steps.
+
+#### Update Step Titles
+
+You should not have to use this tool unless you've manually deleted or added steps. This tool will reorder the step numbers.
+
+## Using the Scripts Manually
+
+If you want to work on the steps manually, in your local IDE, you can run the step management scripts directly.
+
+The `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` folder contains tools to help facilitate the creation and maintenance of the freeCodeCamp project-based curriculum.
+
+### Create a New Project
+
+Change directory to `tools/challenge-helper-scripts` and run `pnpm run create-project`. This opens up a command line UI that guides you through the process. Once that has finished, there should be a new challenge in the English curriculum that you can use for the first step of the project. For example, if you created a project called `test-project` in the Responsive Web Design certification, it would be in `curriculum/challenges/english/01-responsive-web-design/test-project`.
+
+If you want to create new steps, the following tools simplify that process.
+
+### create-next-step
+
+A one-off script that will automatically add the next step based on the last step in the project. The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-next-step
+```
+
+### create-empty-steps
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a specified number of steps. The challenge seed code for all steps created will be empty.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run create-empty-steps X # where X is the number of steps to create.
+```
+
+### insert-step
+
+A one-off script that automatically adds a new step at a specified position, incrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json). The challenge seed code will use the previous step's challenge seed code with the editable region markers (ERMs) removed.
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run insert-step X # where X is the position to insert the new step.
+```
+
+### delete-step
+
+A one-off script that deletes an existing step, decrementing all subsequent steps (both their titles and in their meta.json)
+
+**Note:** This script also runs [update-step-titles](#update-step-titles).
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run delete-step X # where X is the step number to be deleted.
+```
+
+### update-step-titles
+
+A one-off script that automatically updates the frontmatter in a project's markdown files so that they are consistent with the project's meta.json. It ensures that each step's title (and dashedName) matches the meta's `challengeOrder`.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run update-step-titles
+```
+
+### repair-meta
+
+One-off script to parse the step names from the project and update the meta.json order to reflect those steps. Useful if you've accidentally lost the changes to the meta.json file when adding/removing steps.
+
+#### How to Run the Script
+
+1. Change to the directory of the project.
+2. Run the following command:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run repair-meta
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed433453
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-component-library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on the Component Library
+---
+
+Welcome to freeCodeCamp's `ui-components` library. The components are built mostly from scratch with basic HTML elements and [Tailwind CSS](https://tailwindcss.com/).
+
+> [!NOTE]
+>
+> freeCodeCamp has been using Bootstrap components in the UI. However, we are moving away from it and building our own component library, which helps standardize our UX/UI patterns and improve accessibility. The project is tracked in [this GitHub issue](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/44668).
+
+The following steps are recommended when working on a new component:
+
+- Research and planning
+- Implement the component
+- Display the use cases on Storybook
+- Write unit tests
+
+## Researching and Planning
+
+Before building a component, you need to research and document on how the existing version behaves and looks, to ensure that the new one has matching styles and supports all the current usages. In order to meet the web accessibility requirements, you should also pay attention to the accessibility aspect of the component, see which HTML elements and ARIA attributes are used under the hood.
+
+Once you have gathered enough information about the component, you can start thinking about the props interface. Ideally, the interface should be as similar to the current version as possible, to ease the adoption later on. Since we are using Bootstrap components, the simplest approach is to mimic [their implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src).
+
+We prefer smaller pull requests rather than a large one, because they speed up the review time and reduce cognitive overload for the reviewers. For that reason, you should think about how you would break down the implementation and come up with a delivery plan.
+
+We recommend opening a separate GitHub issue for each component and include all the notes in the issue description. It can be used as a place to host all of your working notes, as well as a way to communicate the approach with the reviewers. We will use the issue thread for further discussion if needed. [The issue for Button component](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues/45357) can be used as a reference.
+
+## Implementing the Component
+
+A new component can be created using the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+
+pnpm run gen-component MyComponent
+```
+
+The command will generate a new folder inside the `ui-components` directory, with the following files:
+
+| File name | Purpose |
+| -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
+| `index.ts` | It is used for exporting the component and its types. |
+| `my-component.stories.tsx` | It is used for demoing the component on Storybook. |
+| `my-component.test.tsx` | It is a test file. |
+| `my-component.tsx` | It is where we implement the component. |
+| `types.ts` | It is where we locate the component's interface and types. |
+
+Each component is different, but in general, a component should:
+
+- Support forwarding ref
+- Be styled for both light and dark themes
+- Be styled internally based on their props (the consumers should not need to restyle the component with the `className` prop)
+- Utilize the built-in styling system from Tailwind instead of having custom styles
+
+### Using Colors
+
+There are two color "layers" in the component library:
+
+- The base layer, where the color names describe what the colors are, e.g. `gray00`, `blue50`
+- The semantic layer, where the color names describe what the colors are for, e.g. `foreground-primary`, `background-danger`
+
+Generally, when using colors in a component, you should choose semantic variables over the base ones. There are exceptions, however, specifically when you are styling the component's states such as hover, active, disabled, etc. In these cases, we recommend using the base variables directly instead of creating new semantic variables, since each component can have different styles for its states.
+
+> [!NOTE] Color definition can be found in the [`colors.css` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/src/colors.css). A color is only available for use if it is added to the [`tailwind.config.js` file](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/main/tools/ui-components/tailwind.config.js) under the `colors` property.
+
+### Useful Links
+
+- [Tailwind CSS Configuration](https://tailwindcss.com/docs/configuration)
+- [React Bootstrap v0.33 Docs](https://react-bootstrap-v3.netlify.app)
+- [Bootstrap 3.3.7 stylesheet](https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.css)
+- [React Bootstrap current implementation](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/src)
+- [React Bootstrap current tests](https://github.com/react-bootstrap/react-bootstrap/tree/master/test)
+
+## Displaying the Use Cases on Storybook
+
+Use cases of the component should be added to the Storybook file (`.stories.tsx`).
+
+To start Storybook, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run storybook
+```
+
+The Storybook page is available on [http://localhost:6006](http://localhost:6006).
+
+## Writing Unit Tests
+
+We use [React Testing Library](https://testing-library.com/docs/react-testing-library/intro/) to write unit tests. The tests should assert that the components behave as expected and are accessible.
+
+To run tests against the component library, run the following command from the root directory:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run test-ui-components
+```
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
+
+## Adding Packages to the UI-Component Library
+
+We restrict adding new packages to the UI Components to help with the project's maintainability. In the rare chance that you think a dependency is needed, please check with the maintainers first and then use the following command to add a package:
+
+```bash
+cd tools/ui-components
+pnpm add package_name
+```
+
+## Useful Links
+
+- [Testing for Accessibility](https://testing-library.com/docs/dom-testing-library/api-accessibility)
+- [Order of priority of React Testing Library's queries](https://testing-library.com/docs/queries/about/#priority)
+- [Common mistakes with React Testing Library](https://kentcdodds.com/blog/common-mistakes-with-react-testing-library)
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ef986a67
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+---
+title: How to Work on Documentation
+---
+
+## Work on the Content of the Docs
+
+To work on the contributing guidelines, you can edit or add files in the `docs` directory [available here](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/tree/main/docs). When your changes are merged, they will be made available automatically at the documentation site.
+
+When adding a new file to the `docs` directory, you should evaluate if the file should also be added to the sidebar navigation. We typically create a link in the [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar) file for new and independent guides. Alternatively, You may follow the instructions below on creating an internal link for supporting guides.
+
+### How to Create an Internal Link
+
+If you want to create a link targeting a different section of the contributing guidelines, follow this format:
+
+```md
+[Link text](target-file-name#target-section-heading-id)
+
+// If the target section is within the same page, you can omit the file name
+[Link text](#target-section-heading-id)
+```
+
+Make sure you include the file extension (`.md`). Don't specify the full URL or append `/` before the file name.
+
+This is necessary to make these links work for the translated version of the document. Otherwise, they will redirect to the English version of the page regardless of the language.
+
+#### Translating docs with internal links
+
+When you work on translating docs on Crowdin, make sure to replace the `#target-section-heading-id` with the id on the translated document. [Learn more about translating docs here](how-to-translate-files#translate-documentation).
+
+## Work on the Docs Theme
+
+> [!NOTE] A quick reminder that you do not need to set up anything for working on the content for the documentation site.
+>
+> To work on the contributing guidelines, see [work on the docs content](#work-on-the-docs-content) section.
+
+### Structure of the Docs Website
+
+The site is generated using [`docsify`](https://docsify.js.org) and served using GitHub pages.
+
+Typically you would not need to change any configuration or build the site locally. In case you are interested, here is how it works:
+
+- 此站点的主页源在 [`docs/index.html`](index.html) 中。
+- 我们使用 `docsify` 和 GitHub Pages 将这个文件作为一个 SPA。
+- The `docsify` script generates the content of `markdown` files in the `docs` directory on demand.
+- 主页是由 [`_coverpage.md`](_coverpage) 生成的。
+- The sidebar navigation is generated from [`_sidebar.md`](_sidebar).
+
+### Serving the Documentation Site Locally
+
+Install freeCodeCamp locally ([see the local setup guide](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally)), we bundled the CLI with the development tools so you can run the command below as needed from the root of the repo:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run docs:serve
+```
+
+> The documentation site should be available at <http://localhost:3400>
+
+## Proposing a Pull Request (PR)
+
+After you've committed your changes, check here for [how to open a Pull Request](how-to-open-a-pull-request).
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9a8ad624
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-the-news-theme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+---
+title: How to work on freeCodeCamp.org's developer news theme
+---
+
+The developer news also known as [`/news`](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news) site is powered by [Ghost](https://ghost.org/). We use a custom theme for the look and feel of the site. The source code of the theme is available here: <https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news-theme>.
+
+## The Theme
+
+Ghost uses a simple templating language called [Handlebars](http://handlebarsjs.com/) for its themes. The theme used on `/news` is based off of the default [casper theme](https://github.com/TryGhost/Casper).
+
+The default theme is commented pretty heavily so that it should be fairly easy to work out what's going on just by reading the code and the comments. Once you feel comfortable with how everything works, Ghost also has a full [theme API documentation](https://themes.ghost.org) which explains every possible Handlebars helper and template.
+
+**The main files are:**
+
+- `default.hbs` - The main template file
+- `index.hbs` - Used for the home page
+- `post.hbs` - Used for individual posts
+- `page.hbs` - Used for individual pages
+- `tag.hbs` - Used for tag archives
+- `author.hbs` - Used for author archives
+
+One really neat trick is that you can also create custom one-off templates just by adding the slug of a page to a template file. For example:
+
+- `page-about.hbs` - Custom template for the `/about/` page
+- `tag-news.hbs` - Custom template for `/tag/news/` archive
+- `author-ali.hbs` - Custom template for `/author/ali/` archive
+
+## Development
+
+1. Get Ghost installed locally.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm install -g ghost-cli@latest
+ mkdir ghost-local-site
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ```
+
+ ```sh
+ ghost install local
+ ghost start
+ ```
+
+ > Note: Currently freeCodeCamp uses Ghost version `2.9.0`, so make sure you are using a version higher than that.
+
+ Be sure to run `ghost` commands from the `ghost-local-site` directory. Follow additional instructions on [Ghost's official documentation](https://docs.ghost.org) if are not familiar with its interface.
+
+2. Fork and clone the repository in your theme directory (replacing `YOUR_USERNAME` with your GitHub username):
+
+ ```sh
+ cd content/themes/
+ git clone https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/news-theme.git
+ ```
+
+3. Make sure you have all the pre-requisites.
+
+ The theme styles are compiled using Gulp/PostCSS to polyfill future CSS spec. You'll need [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/). Make sure that your Node.js version is compatible with `ghost`.
+
+4. Install dependencies and develop the theme
+
+ ```sh
+ npm ci
+ npm run develop
+ ```
+
+5. Now you can edit `/assets/css/` files, which will be compiled to `/assets/built/` automatically.
+
+6. Access the development site.
+
+ a. Enter `http://localhost:2368/ghost/` into your address bar. Continue with the setup prompted on the page (if running ghost for the first time).
+
+ b. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Restart Ghost, on a separate terminal once to ensure the theme is available.
+
+ ```sh
+ cd ghost-local-site
+ ghost restart
+ ```
+
+ c. _(One-time only, during setup)_ Once you've done this, go to `http://localhost:2368/ghost/#/settings/design` and scroll to the bottom. Make sure you click activate on the `freecodecamp-news-theme`.
+
+7. Zip the final code and make a pull-request
+
+ The `zip` Gulp task packages the theme files into `dist/<theme-name>.zip`, which we can then upload to the production site.
+
+ When you make a PR, please make sure you have run the below script prior to commiting the code and sending a PR.
+
+ ```sh
+ npm run zip
+ ```
+
+## Other Reference and resources
+
+### PostCSS Features Used
+
+- Autoprefixer - Don't worry about writing browser prefixes of any kind, it's all done automatically with support for the latest 2 major versions of every browser.
+- Variables - Simple pure CSS variables
+- [Color Function](https://github.com/postcss/postcss-color-function)
+
+### SVG Icons
+
+The theme uses inline SVG icons, included via Handlebars partials. You can find all icons inside `/partials/icons`. To use an icon just include the name of the relevant file, eg. To include the SVG icon in `/partials/icons/rss.hbs` - use `{{> "icons/rss"}}`.
+
+You can add your own SVG icons in the same manner.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..68cf2948
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+---
+title: How to work on CodeRoad
+---
+
+This page describes how to contribute to the freeCodeCamp tutorials and projects that are completed using the CodeRoad VS Code extension.
+
+## How the Tutorials Work
+
+Each of the freeCodeCamp tutorials that use CodeRoad has its own repo under the freeCodeCamp GitHub organization. They all start with `learn-`. For example, `https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/learn-bash-by-building-a-boilerplate/`.
+
+Each tutorial repo has a `main` branch and a "version" branch, e.g. `v1.0.0`.
+
+The two main files on the `main` branch are `TUTORIAL.md` and `coderoad.yaml`. `TUTORIAL.md` contains all the instructions, hints, titles, and so on, for the tutorial. `coderoad.yaml` contains instructions for CodeRoad, such as what commands to run and when, what files to watch for changes, and what version branch to use for the steps.
+
+The "version" branch contains the commits that will be loaded on each step of a tutorial. The commit messages on this branch have to be specific. The first commit needs `INIT` for its message and contains all the files to load before the first lesson.
+
+Subsequent commit messages have to match the step number in `TUTORIAL.md` from the `main` branch. For example, the commit with the message `10.1` will be loaded when a user goes to step `10.1`.
+
+In order to make changes to commits on a version branch, you would need to rebase and edit the commits you want to change. This will rewrite the Git history, so we cannot accept PRs to these types of branches. Once a version branch is on the freeCodeCamp repo, it should never change.
+
+:::warning
+Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+## How to Contribute
+
+### Prerequisites
+
+Install the [CodeRoad CLI tools](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@coderoad/cli) with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli`.
+
+There have been some issues with the latest version. If `coderoad --version` doesn't work after installing, downgrade to `0.7.0` with `npm install -g @coderoad/cli@0.7.0`.
+
+### Working on `main`
+
+This set of instructions is for PRs that only make minor changes on `main` to **existing lessons**. That mainly consists of typo, grammar, hint, and instructional changes or fixes in the `TUTORIAL.md` file.
+
+For everything else, including adding or deleting lessons, follow the [working on a version branch instructions](#working-on-version-branch). You will not need to create a new version branch for this - you can create a PR following the instructions below.
+
+:::note
+These changes will use the existing version branch. If they are substantial, feel free to add them to `CHANGELOG.md`. Most of the time, a good commit message should work
+:::
+
+You never need to modify the `tutorial.json` file directly. That will be created with the CLI tools.
+
+If you are only making minor changes like fixing a typo or grammatical error, you don't have to test your changes.
+
+Follow these instructions to make a PR, keeping in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context:
+
+- Create a copy of the latest version branch with `git branch vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X` - you do not need to check this branch out, it just needs to exist.
+- Create and checkout a new branch off of `main`
+- Make **and commit** your changes. Reminder: You don't need to change anything in the `tutorial.json` file. You likely only need to make changes to `TUTORIAL.md`
+- Run `coderoad build` to recreate the `tutorial.json` file
+- Commit the changes with `update json` as the message
+- Make a PR
+
+### Testing Changes on `main`
+
+If you want to test your changes to `main` after using the above instructions, follow these instructions:
+
+- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
+- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on the new branch
+
+### Reviewing PRs to `main`
+
+If reviewing a PR that only changes `main` with instructional or grammar issues as described above, the changes in `TUTORIAL.md` should match the changes in `tutorial.json`.
+
+The `tutorial.json` file should not have changes to commit hashes, or step/level ids. Startup or level commands or file watchers likely should not be changed either. There are exceptions if there's an issue with a step, but they should be treated with more caution.
+
+Also, keep in mind that instructions usually use the lessons around them for context, so make sure they make sense.
+
+### Working on Version Branch
+
+:::warning
+Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+There's no easy way to see exactly what changed between version branches since the Git history will be rewritten. Accepting new version branches to use will need to be done with careful consideration and testing.
+
+These instructions are for changing anything on a "version" branch, such as tests, test text, reset files, adding and deleting steps, among other things.
+
+Follow these instructions to create a new version:
+
+- Checkout the **latest** version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.X upstream/vX.X.X`
+- Create a new branch off of that, incrementing the version, with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y`
+- Make your changes to the version branch. See more info in the [CodeRoad Documentation](https://coderoad.github.io/docs/edit-tutorial) for how to work with tutorials
+- Push the new branch to your fork with `git push -u origin vX.X.Y`
+- Checkout the `main` branch
+- Create a new branch off `main`. e.g. `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` to your fork of the repo. This is so you and reviewers can test it before pushing it to the freeCodeCamp repo. Change the version to the new branch in the two spots of that file. Add your changes for the new version to `CHANGELOG.md`. Make any other changes you need.
+- Commit your changes with the message `feat: release version X.X.Y - <optional description>`
+- Run `coderoad build` to create a new `tutorial.json` file
+- Add and commit the file
+- Push the changes to your fork
+- Test your changes following the [testing instructions below](#testing-changes-to-a-version-branch). Make any additional changes and commit them as you just did, or, if you are satisfied, follow the rest of the instructions
+- Make a PR to `main` using your new `feat/version-X.X.Y` branch. Give it a title of `version X.X.Y ready for review`. This will not be merged, it is just to let reviewers know that there is a new version ready
+- Leave it here for reviewers
+
+### Testing Changes to a Version Branch
+
+- Follow the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to run a container
+- Start the tutorial using the `tutorial.json` file on whatever fork the changes are on. Make sure to use the file on the `feat: version-X.X.Y` branch and not the `main` branch
+
+### Pushing a New Version
+
+Before pushing a new version, view the new `feat/version-vX.X.Y` (will be merged to `main`) branch on the user's fork. Make sure there are additions to the `CHANGELOG.md` file that include the new changes, and the version in the two spots of `coderoad.yaml` matches the new version branch.
+
+If you have write access to the freeCodeCamp repo, have verified the `CHANGELOG` and `coderoad.yaml` files, have tested the changes using the instructions above, and want to push a new version of a tutorial:
+
+:::warning
+Reminder: Never make or push changes to a version branch that is on one of the freeCodeCamp repos. Always create a new one
+:::
+
+- If you don't have a remote to where the new changes exist, create a remote to the user's fork with `git remote add <users_fork>`
+- Delete any **local** branches that share a name with the new branches. Likely named either `vX.X.Y` or `feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Checkout the new version branch with `git checkout -b vX.X.Y <remote>/vX.X.Y`
+- Push the new version branch to the freeCodeCamp repo with `git push -u upstream/vX.X.Y`. You need to push the new branch before you update `main` with the new `tutorial.json` file
+- Checkout the users branch that will be merged into `main` with `git checkout -b feat/version-X.X.Y <remote>/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Change the `uri` in `coderoad.yaml` back to the freeCodeCamp repo
+- Add and commit the changes
+- Run `coderoad build` to create the new `tutorial.json` file
+- Add and commit the file
+- Push the changes to your fork with `git push -u origin/feat/version-X.X.Y`
+- Make a PR to `main` on the freeCodeCamp repo
+- If you are satisfied, merge it or leave it and ask for a review from someone
+- After the PR is merged, open the tutorial by following the instructions on the [rdb-alpha repo](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/rdb-alpha) to make sure it's loading properly, and that you can get through a few steps
+- Finally, if any PRs for this version exist, close them
+
+### How to Revert to a Previous Version
+
+- Create a new branch off of the latest `main` with `git checkout -b revert/to-version-X.X.X`
+- Revert all commits on this branch up to and including the commit of the version after the one you want to revert to. For example, you may have commits that look like this:
+
+```
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.1
+fix: typo
+release: version 1.0.0
+```
+
+If you want to revert to v1.0.0, revert all the commits from `release: version 1.0.1` and after
+
+- Create a PR. Give it a title of `revert: to version X.X.X`
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/intro.md b/src/content/docs/zh/intro.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8809a58d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/intro.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+---
+title: Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community
+---
+
+因为有成千上万像你这样善良的志愿者,[freeCodeCamp.org](https://freecodecamp.org) 才成为了可能。 如果你想利用业余时间贡献你的专业知识,我们将很高兴地欢迎你加入社区。
+
+:::note
+在你继续之前,请花 2 分钟时间快速地阅读我们的[行为守则](https://chinese.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/)。 我们在社区中严格执行行为规范,为 freeCodeCamp.org 的所有贡献者营造安全、包容的氛围。
+:::
+
+You are welcome to create, update and fix bugs in our [curriculum](#curriculum), help us fix bugs in freeCodeCamp.org's [learning platform](#learning-platform), or [help us translate](#translations) freeCodeCamp.org to world languages.
+
+We answer the most common questions about contributing [in our contributor FAQ](FAQ).
+
+Happy contributing.
+
+---
+
+## 课程
+
+我们的课程由 freeCodeCamp 全球社区的贡献者协作创建。 因此,我们能够吸收像你这样的志愿者的专业知识。
+
+你可以帮助扩展和改进课程。 你也可以更新项目需求以更好地解释概念。 你可以改进我们的自动化测试,以便我们能够更准确地测试人们的代码。
+
+**如果你对改进我们的课程感兴趣,请查看 [如何为课程做出贡献](how-to-work-on-coding-challenges)。**
+
+## 翻译
+
+We are localizing freeCodeCamp.org to major world languages.
+
+Certifications are already live in some major world languages like below:
+
+- [Chinese (中文)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/chinese/learn)
+- [Spanish (Español)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/espanol/learn)
+- [Italian (Italiano)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/learn)
+- [Portuguese (Português)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/portuguese/learn)
+- [Ukrainian (Українська)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/ukrainian/learn)
+- [Japanese (日本語)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/japanese/learn)
+- [German (Deutsch)](https://www.freecodecamp.org/german/learn)
+
+We encourage you to read the [announcement here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/help-translate-freecodecamp-language/) and share it with your friends to get them excited about this.
+
+**If you're interested in translating, here's [how to translate freeCodeCamp's resources](how-to-translate-files).**
+
+## 学习平台
+
+Our learning platform runs on a modern JavaScript stack. It has various components, tools, and libraries. These include Node.js, MongoDB, OAuth 2.0, React, Gatsby, Webpack, and more.
+
+Broadly, we have a Node.js based API server, a set of React-based client applications, testing scripts to evaluate camper-submitted curriculum projects, and more. If you want to productively contribute to the learning platform, we recommend some familiarity with these tools.
+
+**If you want to help us improve our codebase here's [how to set up freeCodeCamp](how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally).**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/language-lead-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/zh/language-lead-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..92a50b5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/language-lead-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,376 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Language Lead Handbook
+---
+
+This handbook will help you set up and use the tools for your localization efforts.
+
+## How to Invite New Contributors to Ghost
+
+Ghost allows you to set contributors with different levels of authorization.
+
+Most of your invites will be for the "Contributor" level. This level allows the user to create drafts. Select this role when inviting a new translator.
+
+The "Author" level allows the user to create Drafts and publish them.
+
+The "Editor" level allows the user to access all Drafts and publish them. Select this role when inviting a new proofreader.
+
+The "Administrator" level is reserved for freeCodeCamp staff and Language Leads.
+
+### How are the Articles Built
+
+We use a [JAMStack](https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+jamstack)-based approach to build and deploy the articles. This strategy makes for a speedy static site cached and served from a CDN.
+
+[Ghost](https://ghost.org) acts as our content management platform, and [11ty](https://11ty.dev) builds the articles into static assets – plain HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. Only these static assets are deployed to our servers.
+
+This process is automated and runs periodically. If you publish something now, it will be available on the news site in a few hours.
+
+You can find the up-to-date build schedules and status here: https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news#build
+
+## How to Mention the Original Author of a Translated Article
+
+The original author and the original article are linked automatically adding this code to the Code Injection -> head section in the Draft Settings on Ghost.
+
+```html
+<script>
+ const fccOriginalPost = 'link';
+</script>
+```
+
+With `link` being the link of the original article.
+
+## How to Update Trending Articles
+
+:::tip
+Changing the articles in the footer at least once a month means giving a boost to the linked articles on Google results.
+:::
+
+To update the trending articles in the footer, you need to update the [yaml file in the CDN repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/cdn/tree/main/build/universal/trending) for your language. Both the curriculum and the publication reference this file.
+
+For example, here is the file content for the first 6 articles:
+
+```yaml
+article0
+title: "Unire CSV con Python"
+article0link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-combinare-file-multipli-in-formato-csv-con-8-righe-di-codice/"
+article1
+title: "Il comando Git push"
+article1link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/il-comando-git-push-spiegato/"
+article2
+title: "Centrare immagini in CSS"
+article2link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-centrare-un-immagine-usando/"
+article3
+title: "I codici Alt"
+article3link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/codici-alt/"
+article4
+title: "Tenere a bada il footer"
+article4link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/come-mantenere-il-footer-al-suo-posto/"
+article5
+title: "Cosa è API?"
+article5link: "https://www.freecodecamp.org/italian/news/cose-un-api-in-italiano-per-favore/"
+```
+
+Each number represents one of the 30 articles in the footer. Make sure to match the title and the link correctly.
+
+For each article, you will need to create a shorter title to use in the footer. Each title must stay on a single line and not go to a new line.
+
+You will want to [build the translated client locally](how-to-enable-new-languages) to see if the titles have the right length. You can preview the changes by editing the `trending.json` file in your local environment:
+
+1. Update your `.env` file to use your language for `CLIENT_LOCALE` and `CURRICULUM_LOCALE`.
+
+2. Run `pnpm run create:shared`. This will automatically generate the `trending.json` file for your language under the `/client/i18n/locales/` directory.
+
+3. Start the server by running `pnpm run develop:server` in one terminal window.
+
+4. Edit the `trending.json` to contain the titles you want to preview. You may want to convert your `.yaml` file into JSON format with an automatic tool.
+
+5. In another terminal window, run `pnpm run clean:client`, and then `pnpm run develop:client`
+
+## How to Translate Articles in the Footer Links
+
+There are some links listed at the bottom of the footer (About, Alumni Network, Open Source, etc.) and some of them can be translated into your language in the same way as other articles.
+
+Articles that can be translated:
+
+- About
+- Support
+- Academic Honesty
+- Code of Conduct
+
+The following articles should **not** be translated:
+
+- Shop
+- Sponsors
+- Privacy Policy
+- Terms of Service
+- Copyright Policy
+
+The following links are pointing to external sites and cannot be translated:
+
+- Alumni Network
+- Open Source
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the News
+
+Once you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, you can update the links in the footer for `/news` by editing the file at `news/config/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/news](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/news) repository.
+
+> [!NOTE] Pull requests to this repository are currently limited to staff only. If you want to update this file, ask someone on the staff team for help.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "support": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "honesty": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+### Change the Footer Links in the Curriculum
+
+When you have translated and published the articles listed as "can be translated" above, as well as when the curriculum in your language is ready for launch, you can update the links in the footer for `/learn` by editing the file at `client/i18n/locales/<your language>/links.json` in the [freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp) repository.
+
+> [!WARNING] Only "About", "Support", "Academic Honesty", and "Code of Conduct" can be translated. Leave other URLs unchanged.
+
+Update the following part in the file:
+
+```json
+{
+ ...
+ "footer": {
+ "about-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/about/",
+ "shop-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/shop/",
+ "support-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/support/",
+ "sponsors-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/sponsors/",
+ "honesty-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/academic-honesty-policy/",
+ "coc-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/code-of-conduct/",
+ "privacy-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/privacy-policy/",
+ "tos-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/terms-of-service/",
+ "copyright-url": "https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/copyright-policy/"
+ },
+ ...
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Info Boxes Headers in the Documentation
+
+You can find these boxes all around the documentation:
+
+> [!NOTE] I am a note box
+
+:::tip
+I am a tip box
+:::
+
+> [!WARNING] I am a warning box
+
+:::danger
+I am an attention box
+:::
+
+By default, their headers appear in English even in the translated docs.
+
+You can have the headers translated in the docs in your language by changing the file `docs/index.html`, in this way:
+
+Inside the `script` element there is an object, find the `flexibleAlerts` property, which has this shape:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Inside the object of the label property, before the `'/'` property, you would add a new property for your language, like `/i18n/<language>/`.
+
+For example, adding the translations for Portuguese would appear like this:
+
+```js
+flexibleAlerts: {
+ note: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Observação',
+ '/': 'Note'
+ }
+ },
+ tip: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Dica',
+ '/': 'Tip'
+ }
+ },
+ warning: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Aviso',
+ '/': 'Warning'
+ }
+ },
+ attention: {
+ label: {
+ '/i18n/portuguese/': 'Atenção',
+ '/': 'Attention'
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## How to Translate the Motivational Quotes
+
+The motivational quotes can be found in the [curriculum repository](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/motivation.json` file.
+
+This file has a general structure of:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+The compliments are the short sentences that appear at the completion of a challenge.
+
+You don't need to directly translate the sentences used in English, you can write a set of short sentences that are appropriate to show at the completion of a challenge.
+
+The `compliments` array is an array of strings. So, for example, you would write:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": ["A tutta birra!", "Pikachu, scelgo te!"],
+ "motivationalQuotes": []
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen compliments to have some variety when users complete challenges.
+:::
+
+The motivational quotes are the quotes that appear at https://freecodecamp.org/learn.
+
+The `motivationalQuotes` array is an array of objects, these objects should include a `quote` property and an `author` property. like this:
+
+```json
+{
+ "compliments": [],
+ "motivationalQuotes": [
+ {
+ "quote": "Se i costruttori costruissero come i programmatori programmano, il primo picchio che passa potrebbe distruggere la civiltà.",
+ "author": "Artur Bloch, Seconda legge di Weinberg"
+ },
+ {
+ "quote": "I bravi programmatori sanno cosa scrivere. I migliori sanno cosa riscrivere.",
+ "author": "Eric Steven Raymond"
+ }
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+:::tip
+You should start with at least a dozen quotes, to have some variety. A new quote is shown every time the user reloads the page.
+:::
+
+## How to Update the Common Links
+
+We maintain a file of common links used throughout our [curriculum site](https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp) in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/links.json` file.
+
+Some of these links will not change - but you should update the `/news` article links to point to your language's translated version of that article when it is published.
+
+You should also update the `help` categories to point to your language's subforum (usually `language/category`, like `Italiano/HTML-CSS`). This will allow campers to create "help posts" in the correct forum location.
+
+## How to Update the Site Meta-Data
+
+The site meta-data is in the `/client/i18n/locales/<language>/meta-tags.json` file. This file has five keys: `title`, `description`, `social-description`, `keywords`, and `youre-unsubscribed`.
+
+The `youre-unsubscribed` value should be directly translated. The other values will need to be translated as closely as possible, while also considering common search terms and phrases used in your language.
+
+If you need help with this, reach out to us in the [contributor chat](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay)
+
+## Pre-Translate Workflow on Crowdin
+
+The Pre-Translate workflow can be used to apply translations from the Translation Memory to strings.
+
+:::tip
+Really useful to restore a lot of translations from the Translation Memory in bulk when a lot of files have been updated.
+:::
+
+You can find the Pre-Translation workflow at the top of the page in the console of a project. If you see "Go to console" in the upper right corner, click there first.
+
+
+
+
+
+You can choose "From Machine Translation" or "From Translation Memory". Choose "Translation Memory" to recover translations from memory.
+
+Then there are three steps to complete:
+
+1. Files. Choose which files to translate, you can do all the projects, or specific folders or files.
+2. Languages. Set your language here.
+3. Existing Translations. The best combination here is "100% match" and "Apply to untranslated strings only". Do not approve automatically, as it's always best to have a human eye on things.
+
+
+
+When you have finished setting this, press the Pre-Translate button and wait. It will alert you once it has finished. The time it takes depends on how many untranslated strings are in the chosen files.
+
+## How to Update Crowdin Glossary
+
+:::tip
+An updated glossary helps in having a homogeneous translation of technical terms.
+:::
+
+The Crowdin Glossary is kept in the [crowdin-glossaries](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/crowdin-glossaries) repository.
+
+In the `glossaries` folder, there are various `*.csv` (comma,separated values) files, one for each of the crowdin projects that have a glossary that can be updated from this workflow.
+
+The `client.csv` file is for the Learn User Interface project, the `curriculum.csv` file is for the Coding Curriculum project, the `docs.csv` file is for the Contributing Documentation project.
+
+To update the Crowdin Glossaries, you need to clone this repo locally. Open the `.csv` file with an appropriate program, for example, Microsoft Excel.
+
+In the `.csv` file you will find that the English language occupies the first three columns, `Term:English` is the column for the English term, `Description:English` is the column for the English description, and `Part:English` is for the part of speech (e.g., noun, verb etc.) of the term.
+
+Then, each target language has two columns. If you translate to Dothraki, you will be interested in the columns `Term:Dothraki` and `Description:Dothraki`. The column `Term:Dothraki` is for the translation of the term in Dothraki, and the column `Description:Dothraki` is for a description of the term in Dothraki.
+
+:::tip
+In programs like Microsoft Excel, you can hide the columns of the other languages to free up screen real-estate and see the English columns and the target language columns near each other.
+:::
+
+After you have made the changes and saved the file, you will need to make a PR with the proposed changes. After the PR is accepted, you will need to run the GitHub Action workflow to update the Crowdin Glossary. Your glossary changes will not have immediate effects, but they will come.
+
+## How to Promote a Contributor to Proofreader
+
+If you consider that a contributor could become a Crowdin Proofreader, you can give the proofreader role to them this way:
+
+In Crowdin, individuate the `User management` on the left-hand side menu.
+
+This will open the user management tools, you will be able to see the list of all the users.
+
+Search for the user who will become a proofreader. Use the three dots menu on the user row to open a menu and select "Add to team". The proofreader teams have a standard name of `Proof Readers (<language>)`, you can search the team using the language name. Once you have selected the team, use the "ADD" button at the bottom of the page to finalize the thing.
+
+The user is now a proofreader.
+
+:::tip
+The newly promoted proofreader could benefit from reading the [How to Proofread Files](how-to-proofread-files) documentation.
+:::
+
+## How to Add or Update a Language
+
+Check out the [how to enable new language](how-to-enable-new-languages) docs. If you are updating a language the section on [set translated superblocks](how-to-enable-new-languages#set-translated-superblocks) should be helpful.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-handbook.md b/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-handbook.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7998e333
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-handbook.md
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp 官方管理员手册
+---
+
+该手册将帮助您管理我们社区中的不同地方。 This covers conversations and interactions in issues and pull request threads on GitHub, the community forum, the chat rooms, and other official communities that we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] 所有 freeCodeCamp 管理员都是全社区管理员。 That means we trust you to oversee any of these places.
+
+你可以在你感兴趣的任何平台上担任管理员。 一些管理员只在 GitHub 上提供帮助,而其他管理员在论坛上提供帮助。 一些管理员在各个地方都很活跃。
+
+最重要的是,我们希望你享受作为管理员的乐趣,并将你宝贵的时间投入到你感兴趣的地方。
+
+> “拥有权利的同时也被赋予了重大的责任。” - 本叔叔
+
+作为一名管理员,气质比技术能力更重要。
+
+聆听。 Be helpful. 不要滥用你的权力。
+
+freeCodeCamp 是一个包容的社区,我们需要保持这种状态。
+
+We have a single [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) that governs our entire community. 规则越少,就越容易记住。 你可以在[这里](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)阅读这些规则,并把它们记在心里。
+
+> [!NOTE] As a moderator, we would add you to one or more teams on GitHub, our community forums & chat servers. If you are missing access to a platform that you would like to moderate, please [reach out to a staff member](FAQ#additional-assistance).
+
+## 管理 GitHub
+
+管理员在 GitHub 上有两个主要职责:
+
+1. Triaging and responding to issues.
+2. Reviewing and merging pull requests (aka QA).
+
+### 管理 GitHub Issue
+
+We use our main [`freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp`](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/issues) repository as a common issue tracker for all of our repositories. We get new issues every day, all of which need to be triaged, labeled, and addressed. 这也是一个开始帮助开源代码库贡献的好地方。
+
+#### Issue 分流
+
+[分流](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triage)是一个优先关注每个新 issue 报告的过程。 我们有一个广泛的标签列表,用于标记每个 issue 的优先级、类别、状态和范围。
+
+你可以通过从[这个列表](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/labels)中使用标签来帮助我们组织和分类 issue 报告。 通常,标签旁边有描述说明其含义。
+
+请特别注意标签 `"help wanted"`(“需要帮助”)和 `"first timers only"`(“仅限新手使用”)。 这些标签将添加到你认为可以向潜在贡献者开放,以便他们提出拉取请求的主题中。
+
+For triaging a trivial issue such as a typo fix, it is recommended to apply a "first timers only" label along with additional information. You can utilize the [reply template](reply-templates#first-timer-only-issues) provided for this purpose.
+
+#### 关闭陈旧的、过时的、不活跃的 issue 和拉取请求
+
+- Stale issues or PRs are those that have not seen any activity from the author for 21 days (3 weeks from the last activity), but only after a moderator has requested more information/changes.
+
+- Activity is defined as: Comments requesting an update on the PR and triages like `status: update needed` label, etc.
+
+- If the contributor asks for additional assistance or even time, the above can be relaxed and revisited after a response is given. In any case, the mods should use their best judgment to resolve the outstanding PR's status.
+
+:::tip
+We recommend you use this list of standard [reply templates](reply-templates) while triaging issues.
+:::
+
+### 管理拉取请求(Pull Requests)
+
+Pull Requests (PRs) are how contributors submit changes to freeCodeCamp's repository. We must perform Quality Assurance (QA) on pull requests before we decide whether to merge them, request changes, or close them.
+
+#### Types of Pull Requests
+
+1. **Challenge instruction edits**
+
+ These are changes to the text of challenges - the description, instructions, or test text.
+
+ You can also review these right on GitHub and decide whether to merge them. 因为会有无数的人通过 freeCodeCamp 课程读到这段文字, 所以我们应该要更加认真对待。 Does the pull request make the text more clear without making it much longer? Are the edits relevant and not overly pedantic? Remember that our goal is for challenges to be as clear and as short as possible. They aren't the place for obscure details. Contributors may try to add links to resources to the challenges.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with a "LGTM" (Looks Good To Me) comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
+
+2. **Challenge code edits**
+
+ These are changes to the code in a challenge - the challenge seed, challenge solution, and test strings.
+
+ These pull requests need to be pulled down from GitHub and tested on your local computer or Gitpod to make sure the challenge tests can still be passed with the current solution and to make sure the new code doesn't introduce any errors.
+
+ Some contributors may try to add additional tests to cover pedantic corner-cases. We need to be careful to not make the challenge too complicated. These challenges and their tests should be as simple and intuitive as possible. Aside from the algorithm challenges and interview prep section, learners should be able to solve each challenge within about 2 minutes.
+
+ You can close invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+ If the changes look good, please ensure to leave an approval with an "LGTM" comment. Once a pull request gets at least two approvals (including yours) from the moderators or the dev-team, you can go ahead and merge it.
+
+3. **Platform changes**
+
+ These code edits change the functionality of the freeCodeCamp platform itself.
+
+ Sometimes contributors try to make changes without much explanation, but for code changes, we need to make sure there's a genuine need for the change. These pull requests should reference an existing GitHub issue where the reasons for the change are discussed. Then you can open the pull request on your computer and test them out locally.
+
+ After you've done so, if the changes look good, don't merge them quite yet. You can comment on the pull request saying "LGTM", then mention **"@freeCodeCamp/dev-team"** so they can take a final look.
+
+4. **Automated PRs (Dependabot)**
+
+ Some PRs are automated dependency updates made via an integration. You should not merge or approve these PRs. One of the dev-team members will take care of reviewing and merging such automated PRs.
+
+#### How to Review, Merge, or Close Pull Requests
+
+##### Assign yourself to a Pull Request:
+
+First of all, when you choose a pull request to review, you should assign yourself to it. You can do this by clicking the "assign yourself" link below the "assignees" part on the right-hand column of GitHub's interface.
+
+Depending on the type of pull request it is, follow the corresponding rules listed previously.
+
+##### Ensure the CI Checks are Passing:
+
+Before merging any pull request, make sure that GitHub is reporting all checks to be passing (green check marks) on the pull requests. If you see any of the checks failing, please investigate and clarify the root cause. Is the change being made breaking our tests? Will the site build correctly if the PR is merged? These checks are critical for the stability of the platform.
+
+> [!WARNING] Merging a PR that fails CI/CD checks can cause difficulties for all stakeholders, including the dev-team and contributors.
+
+##### Handling Merge Conflicts:
+
+Sometimes there will be a merge conflict.
+
+This means that another pull request has made a change to that same part of that same file. GitHub has a tool for addressing these merge conflicts right on GitHub. You can try to address these conflicts. Use your best judgment.
+
+The pull request's changes will be on top, and the main branch's changes will be on the bottom. Sometimes there will be redundant information in there that can be deleted. Before you finish, be sure to delete the `<<<<<<`, `======`, and `>>>>>>` that Git adds to indicate areas of conflict.
+
+If you are uncertain, please ask one of the fellow moderators or the dev-team for assistance.
+
+##### Merging a Valid Pull Request:
+
+If the pull request looks ready to merge (and doesn't require additional approvals - remember we require at least two), you can go ahead and merge it. Be sure to use the default **"Squash and Merge"** option. This will squash all the pull requests commits down into a single commit, making the Git history much easier to read.
+
+> You should then comment on the pull request, thanking the contributor in your own personal way!
+
+If the pull request author is a "first-time contributor" you should also congratulate them on their first merged pull request to the repository. You can look at the upper right-hand corner of the PR's body to determine a first-time contributor. It will show `First-time contributor` as shown below:
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ First-time contributor badge on pull requests (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://i.imgur.com/dTQMjGM.png" alt="First time contributor badge on pull requests" />
+</details>
+
+If the pull request doesn't look ready to merge, you can politely reply telling the author what they should do to get it ready. Hopefully, they will reply and get their pull request closer to ready.
+
+If you need a second opinion on a pull request, go ahead and leave your comments on the pull request, then add the "discussing" label to the pull request.
+
+##### Closing an Invalid Pull Request:
+
+Often, a pull request will be low effort. You can usually tell this immediately when the contributor didn't bother checking the checkboxes in the Pull Request Template or used a generic pull request title like "Made changes" or "Update index.md".
+
+There are also situations where the contributor is trying to add a link to their website, include a library they created, or have a frivolous edit that doesn't help anyone but themselves.
+
+You can close these invalid pull requests and reply to them with these [reply templates](reply-templates#closing-invalid-pull-requests).
+
+#### Filtering Pull Requests
+
+To sort Pull Requests for Quality Assurance for quick access to PRs that are ready for review, do not have a merge conflict, are not blocked, and have all status checks in green, use the following link to apply the filters:
+
+[Direct link with filter applied](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/pulls?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Apr+-label%3A%22status%3A+blocked%22+-label%3A%22status%3A+merge+conflict%22+status%3Asuccess+draft%3Afalse)
+
+#### Other Guidelines for Moderators on GitHub
+
+Though you will have write access to freeCodeCamp's repository, **you should never push code directly to freeCodeCamp repositories**. All code should enter freeCodeCamp's codebase in the form of a pull request from a fork of the repository.
+
+Also, you should never accept your own PRs. They must be reviewed by another moderator, just like any other PR.
+
+If you notice anyone breaking the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) on GitHub issues, or opening pull requests with malicious content or code, email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to the offending pull request, and we can consider banning them from freeCodeCamp's GitHub organization entirely.
+
+## 管理论坛
+
+As a moderator, you help keep our community an enjoyable place for anyone to learn and get help. You will deal with flagged posts and handle spam, off-topic, and other inappropriate conversations.
+
+Note that once you are a moderator on the forum, you will start to see blue moderator hints about forum members, like "this is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!" or "[person] hasn't posted in a long time - let's welcome them back."
+
+![A blue text message saying "This is the first time [person] has posted - let's welcome them to the community!](https://i.imgur.com/mPmVgzK.png)
+
+These are opportunities for you to welcome them and make them feel extra special. You never know which person who's marginally involved may become our next super-helper, helping many other people in their coding journey. Even the slightest kindness may trigger a cascade of good deeds.
+
+### Deleting Forum Posts
+
+Forum moderators can delete users' posts. You should only do this for the following instances:
+
+1. Someone has posted a pornographic or graphically violent image.
+2. Someone has posted a link or code that is malicious in nature and could harm other campers who click on it.
+3. Someone has flooded a thread with a lot of spam messages.
+4. An account has been created, beyond a reasonable doubt, to spam.
+
+### Dealing with Spam
+
+For the first spam post of a legitimate user (ie. whose intent isn't to spam the forum but to learn/contribute to the forum), send them a message explaining the problem, and remove the link or post as appropriate. Leave a note on the user's profile explaining the action you have taken. If the problem persists, then quietly block the user from posting (using the silence option on the User Admin panel). Send the user a warning with the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org). Check the box in the private message indicating that your message is a "formal warning."
+
+As a moderator, you can ask questions and report incidents in the [mod-team forum section](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4).
+
+### Dealing with Off-Topic Conversations
+
+Posts or topics that seem to be in the wrong place can be recategorized or renamed to whatever would be appropriate.
+
+In exceptional circumstances, it may be appropriate for a moderator to fork a discussion into multiple threads.
+
+Again, if you have any problems or questions, make a post with your actions in the `"Staff"` category, and tag another moderator if you want them to review your moderating actions.
+
+### Dealing with Posted Solutions
+
+If a user replies in a help thread for the freeCodeCamp curriculum with a solution, remove it and use the **Solution Instead of Help** canned reply (or a similar response in your own words).
+
+If the OP (Original Poster) replies within a freeCodeCamp curriculum help thread with their final solution, blur it, and use the **Blurred Spoiler Solution** canned reply.
+
+If a user creates a thread asking for feedback on a solution, move the thread to the feedback subforum and blur the solution, as necessary. If the user is only posting the solution to show it off, then unlist the thread and use the **Solutions Thread** canned reply.
+
+### Underage Users
+
+Our [Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms) require that freeCodeCamp users be at least 13 years of age. If a user reveals that they are under the age of 13, send them the message below, suspend their account, then email the link of their forum account to `support[at]freecodecamp.org` for their freeCodeCamp /learn and forum accounts removal.
+
+```markdown
+SUBJECT: Users under 13 are not allowed to use the forum per our Terms of Service.
+
+It has come to our attention that you are under 13 years of age. Per the [freeCodeCamp Terms of Service](https://freecodecamp.org/terms), you must be at least 13 years old to use the site or the forum. We will be deleting both your freeCodeCamp account and your forum account. This restriction keeps us in compliance with United States laws.
+
+Please rejoin once you have reached at least 13 years of age.
+
+Thank you for understanding.
+```
+
+### Account Deletion Requests
+
+If a user requests their account to be deleted, send the following:
+
+```markdown
+Deleting an account with many posts disrupts the flow of conversation, and could remove helpful information for other Campers.
+
+We can anonymize your account, which will remove your username along with any other public information associated with your forum account. Your posts will remain, but will be attributed to an anonymous user, and you will be unable to log in to the account, as it will no longer be associated with an email address.
+
+If you would like to proceed with this, please reply to this message with your consent.
+```
+
+If a user insists on having their account deleted, ask them to email `support[at]freecodecamp.org` with a link to their forum account.
+
+### Moderating Via Cell Phone
+
+Moderating the forum is possible via a cell phone but you may encounter some usage quirks. This is not an exhaustive list.
+
+- When trying to include a "Canned reply" in a response, if the menu doesn't open (after clicking on the gear), click on the text area first then try it again.
+- The moderator's 'wrench' is at the bottom of the view-port but if you click it and cannot see the "Select Posts" button because it has scrolled out of view, you may need to try to scroll to it, though sometimes that doesn't work in which case moving to a desktop/laptop monitor may be needed.
+- Sometimes clicking on the three-dot menu below a post can hide the reply icon. Reload the page to get it back.
+
+## 管理 Facebook 小组
+
+If you see anything that seems to break our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/), you should delete it immediately.
+
+Sometimes people will post things that they think are funny. They don't realize that what they said or what they shared could be interpreted as offensive. You should delete such posts, but not necessarily ban the person. Hopefully, the user will come to understand that what they posted was inappropriate because the post was deleted.
+
+But if it is an egregious offense that can't reasonably be attributed to a cultural difference or a misunderstanding of the English language. In that case, you should strongly consider blocking the member from the Facebook group.
+
+## Moderating Discord
+
+Here's how moderators deal with violations of our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/) on our chat server:
+
+> [!NOTE] Camperbot serves as our moderation bot, and all of the commands use Discord's native slash command interface. You can see a list of all of the commands by typing `/` in any channel.
+
+1. **Make sure the user intended to violate the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).**
+
+ Not all violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org) were intended as such. A new camper might post a large amount of code for help, unaware that this can be disruptive to the conversation. In these cases, you can just ask them to paste their code with services like CodePen or Pastebin.
+
+2. **If the camper clearly and intentionally violates the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), the moderator will proceed as follows:**
+
+ For minor offences, a warning may be issued with the `/warn` command. For more egregious offences, you can remove the member from the server temporarily with the `/kick` command, or permanently with the `/ban` command. In some cases, a member may just need some time to cool off and collect their thoughts - the `/mute` command allows you to prevent them from engaging with our community for a set period of time. A muted member can see the conversation, but cannot post messages or add reactions.
+
+ All moderation commands will take a `reason` parameter, which should be a short explanation of why the action was taken. Moderation actions done with the bot will be logged in `#mod-actions`, which allows us all to stay on the same page. As such, we should avoid using Discord's built-in moderation tools, as they will not be logged.
+
+ > [!WARNING] The reason provided to a moderation command will also be included in the DM notification to the camper. Please remember to be professional here.
+
+3. **Creating a private discussion**
+
+ There may be situations where you need to address a concern with a camper privately. This should not be done through DMs, which can lead to situations where you claim one thing and the camper claims another. Instead, use the bot's functionality to create a private discussion:
+
+ - Call the `/private` command, where `target` is the camper you want to open a private channel with.
+ - The bot will create a new channel, and add the mentioned camper and all moderators with the `Your Friendly Moderator` role. While all moderators are added to the channel for transparency, the moderator who calls this command should be the only one to interact with the camper unless they request assistance.
+ - When the conversation is complete, click the `❌ Close` button _on the first message in the private channel_ to have the bot close and delete that channel.
+
+4. **Deleting messages**
+
+ Our moderation bot is configured to log deleted messages automatically in the `#mod-actions` channel. If a message is not in line with our Code of Conduct, or otherwise not appropriate for our community, you are generally safe to delete it.
+
+ Note that if the message contains content that violates Discord's terms of service, you'll want to report it via https://dis.gd/report **prior to** deleting it.
+
+5. **Don’t threaten to take action**
+
+ If a camper breaks the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org), don’t threaten to take moderator action, and never warn them in public. Instead, talk to them privately using the bot's `/private` command, or use the bot's moderation commands.
+
+ If a violation was clearly unintended and doesn't warrant moderation action or private conversation, make the offending camper aware of their actions without making it come across as a warning.
+
+ For example:
+
+ - Camper posts a wall of code to request help:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code.
+
+ - Or if you really have to explain why:
+
+ Moderator: **@username** Please use CodePen or Pastebin when posting large amounts of code, because it disrupts the chat for everyone and could be considered spamming according to our [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org).
+
+ - For mild and unintentional violations of the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org):
+
+ Moderator: This is a friendly reminder for everyone to follow the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org): https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org/
+
+6. **Don’t brag about being a moderator**
+
+ Do not see yourself as above the community. **You are the community.** And the community has trusted you to help protect something rare that we all share - a _welcoming_ place for new developers.
+
+ If you brag about being a moderator, people may feel uneasy around you, in the same way that people may feel uneasy around a police officer, even if they’re doing nothing wrong. This is just human nature.
+
+7. **Don’t contradict other moderators**
+
+ If you disagree with a moderator's action, talk with them in private or bring it up in the #mod-chat channel. Never override a moderator's action, and never contradict the other moderator(s) publicly. Instead, have a cool-headed discussion in `#mod-chat` and convince the moderator that they themselves should reverse their ban or change their PoV (Point of View).
+
+ _Remember: We’re all on the same team. We want to dignify the role of moderators and present a unified front._
+
+8. **Talk with other moderators**
+
+ We have a `#mod-chat` room for moderators only. Use it! If you feel uncomfortable with handling a certain situation, ask other moderators for help. If you think something should be discussed, do it. You're part of the team, and we value every team member's input! Even if you totally disagree with anything in these guidelines or the [Code of Conduct](https://code-of-conduct.freecodecamp.org)!
+
+9. **Temporarily inactive**
+
+ If you're not going to be active as a Moderator for a while due to vacation, illness, or any other reason, make sure to let the others know in the `#mod-chat` channel. This is so we know if we can count on you to be regularly active on the server or not.
+
+## How to Become a Moderator
+
+Suppose you are helping people in the community consistently over time. In that case, our moderator team will eventually take notice, and one of them will mention you as a possible moderator to [our staff](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/Team). There are no shortcuts to becoming a moderator.
+
+If you are approved, we will add you to our moderator teams on [GitHub](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/teams/moderators), [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/g/moderators), chat, etc.
+
+> [!NOTE] For GitHub: After you've been accepted as a moderator, you will receive a Github repository invitation. You'll need to head over towards [freeCodeCamp GitHub Organization Invitation](https://github.com/orgs/freeCodeCamp/invitation) to be able to accept the invitation.
+>
+> This is required for us to be able to give you write access to some of our repositories.
+
+## How Our Contributors Room Works
+
+Anyone is welcome in the [contributors room on our chat server](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay). It is the designated chat room for moderators and other campers who contribute to our community in any number of ways, including through study groups.
+
+We assume contributors will read anything in this room that directly mentions them with an **@username**. Everything else is optional, but feel free to read anything anyone posts in there and interact.
+
+## Dealing with Solicitors
+
+You may be approached by organizations who want to partner or co-brand with freeCodeCamp somehow. Once you realize that this is what they're after, **please stop talking to them** and tell them to email `team[at]freecodecamp.org`.
+
+We get proposals like this all the time, and the staff are in the best position to judge whether such a relationship will be worth it for our community (and it rarely is).
+
+## Dealing with (Mental) Health Inquiries
+
+You may come across situations where users seek medical advice or are dealing with mental health issues and are looking for support.
+
+As a matter of policy, you should avoid talking privately about these matters. Should the situation reflect back to freeCodeCamp, we want to have the conversation(s) on record. Make it clear that we are not medical professionals and that you encourage the user to find professional help.
+
+As difficult as it sometimes can be, avoid giving any tips or advice and rather point the user in the direction of seeking professional help!
+
+If this happens on our chat server: Create a private channel for the user and the moderator team. This can be done with the bot's `private` command.
+
+- The user is guaranteed some privacy.
+- Public chat is no longer disrupted.
+- Other team members can pitch in, should you feel uncomfortable dealing with the situation yourself.
+
+Helpful URLs:
+
+http://suicide.org/international-suicide-hotlines.html
+
+## A Note on Free Speech
+
+Sometimes people will defend something offensive or incendiary that they said as "free speech."
+
+This XKCD comic summarizes perfectly most communities' thoughts on free speech.
+
+<div align="center"><img src='./images/github/xkcd-free-speech.png' width="400" height="400" /></div>
+
+Thanks for reading this, and thanks for helping the developer community!
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-onboarding-guide.md b/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ddbc367d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/moderator-onboarding-guide.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+---
+title: The Official freeCodeCamp Moderator Onboarding Guide
+---
+
+This guide will help new moderators get up and running with the processes and procedures followed by experienced moderators on the freeCodeCamp community forum and other official communities we foster.
+
+> [!NOTE] If you haven't read [The Moderator Handbook](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/moderator-handbook) yet, you should start there first.
+
+## The Forum
+
+### First Steps
+
+The first thing you may notice after being given moderator status on the forum is that your interface will look somewhat different, with new admin tools to explore and access to the Mod-Team subforum.
+
+Some of the new tools will appear inside a new menu item that looks like a wrench. Some will appear as new tabs or buttons, or even new enabled options within the forum menus.
+
+To get familiar with the new tools and powers, you can combine one or more of the following methods during your first week with this elevated role:
+
+:::tip
+The first two are the most important.
+:::
+
+### Become Familiar with the Discourse Admin Tools
+
+The freeCodeCamp forum is a Discourse forum and follows many of the same guidelines of other forums built on Discourse. To begin to get familiar with Discourse and the moderation role, start by reading Discourse's [new user guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-new-user-guide/96331) and Discourse's [new moderator guide](https://meta.discourse.org/t/discourse-moderation-guide/63116).
+
+### Shadow a Mod
+
+All moderator actions can be followed by reviewing the [action logs](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/admin/logs/staff_action_logs). The actions taken by automated tools like `Akismet` or `system` can mostly be ignored until they result in a post that needs to be reviewed. Posts to be reviewed will show up in the [Review](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/review) area of the forum.
+
+For the first week or so you will want to pay attention to what is getting flagged and what is being reviewed, and compare that to the actions being taken upon the flagged posts. You may see the system account flag a post because the user created it too quickly. In many cases, the moderators will unflag the post by clicking on the "Approve Post" button or mark it as "Not Spam" (depending on the flag type).
+
+Commonly, spam flags can also be raised by members or moderators. Common duplicitous behavior would involve opening an account, making a post that seems harmless, then editing that post later on to add a link to an external site to advertise it. In this case, the member account is usually fairly new and has only made this one post thus far, which indicates that the account was opened solely for spamming the community. The decision should be made to delete the account after the first offense in this case. The same applies to accounts whose first post is deemed to be spam.
+
+You may notice moderators performing a procedure called 'split topic'. This may be a case where a moderator has split a post that was made erroneously on an existing topic into a new topic, or a moderator merged duplicate topics that a single user has created for the same question. Watching this procedure will highlight different actions and their causes.
+
+Another useful feature that becomes enabled for all moderators is the ability to post a "Canned Reply" which is a pre-written response that was worked out with the mod team to quickly respond to some well-known and repetitive scenarios. These include:
+
+- Welcoming a new forum member who has posted code without a question -> "Welcome - remind question"
+- Reminding members not to post code solutions but to provide hints and tips instead -> "Solutions Instead of Help"
+- Responding to a situation where someone's code works for you but not for them -> "Browser Issues"
+- Encouraging members to open GitHub issues when a possible bug is found -> "Bug Report"
+
+There are more, which you can read through to become familiar with their respective uses. You can also find discussions around the templates in the mod-team subforum, and you are welcome to ask questions if you aren't sure how a template should be used.
+
+### Read Mod-Team Subforum Posts
+
+The Mod-Team subforum contains several posts from past and current moderators discussing the different requirements and/or challenges of moderating the forum.
+
+Reading back through these posts can help uncover some of the underlying goals and processes that concern forum moderators. Some of the threads may also shed some light on the handling of spam and inappropriate content on the forum.
+
+## Where to Ask for Help
+
+To get help dealing with a situation that you are either uncomfortable with or unsure of how to handle, discuss with your fellow moderators on either the [Mod-Team Subforum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/mod-team/4) or the [#mod-chat](https://discord.com/channels/692816967895220344/693157007418720277) on Discord.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/reply-templates.md b/src/content/docs/zh/reply-templates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..43bbabfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/reply-templates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
+---
+title: Reply Templates
+---
+
+These are some of the standard reply templates that you may use while reviewing pull requests and triaging issues/pull requests.
+
+> You can make your own saved replies with GitHub's built-in [saved replies](https://github.com/settings/replies/) feature or use the ones below.
+
+## Thank You
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 🎉
+```
+
+## Thank you and congrats
+
+> For thanking and encouraging first-time contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Hi @username. Congrats on your first pull request (PR)! 🎉
+
+Thank you for your contribution to the page! 👍
+We are happy to accept these changes and look forward to future contributions. 📝
+```
+
+## Build Error
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes but it looks like there is an error with the CI build. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these issues, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+Feel free to reference the [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-work-on-coding-challenges.md?id=testing-challenges) for instructions on running the CI build locally. ✅
+```
+
+## Syncing Fork
+
+> When PR is not up to date with the `main` branch.
+
+````markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like the branch is not up to date. ⚠️
+
+To resolve this error, you will have to sync the latest changes from the `main` branch of the `freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp` repo.
+
+Using the command line, you can do this in three easy steps:
+
+```bash
+git remote add upstream git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git
+
+git fetch upstream
+
+git pull upstream main
+```
+
+If you're using a GUI, you can simply `Add a new remote...` and use the link `git://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp.git` from above.
+
+Once you sync your fork and pass the build, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---==crwdHRulesLBB_2_BBsuleRHdwrc==
+
+Feel free to reference the ["Syncing a fork"](https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/) article on GitHub for more insight on how to keep your fork up-to-date with the upstream repository. 🔄
+````
+
+## Merge Conflicts
+
+> When PR has merge conflicts that need to be resolved.¹
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+We would love to be able to merge your changes, but it looks like you have some merge conflicts. ⚠️
+
+Once you resolve these conflicts, we will be able to review your PR and merge it. 😊
+
+---
+
+If you're not familiar with the merge conflict process, feel free to look over GitHub's guide on ["Resolving a merge conflict"](https://help.github.com/articles/resolving-a-merge-conflict-on-github/). 🔍️
+
+Also, it's good practice on GitHub to write a brief description of your changes when creating a PR. 📝
+```
+
+¹ If a first-time-contributor has a merge conflict, maintainers will resolve the conflict for them.
+
+## Duplicate
+
+> When PR is repetitive or a duplicate.
+
+```markdown
+Hey @username
+
+This PR seems to make similar changes as the existing PR <#number>. As such, we are going to close this as a duplicate.
+
+If you feel you have additional changes to expand upon this PR, please feel free to push your commits and request this PR be reopened.
+
+Thanks again! 😊
+
+---
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to ask questions on the ["Contributors" category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Pull Requests
+
+> When PR is invalid.
+
+```markdown
+Hey there,
+
+Thank you for opening this pull request.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that we've reviewed your pull request and have decided not to merge it. We would welcome future pull requests from you.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When PR adds links to external resources.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for your pull request.
+
+We are closing this pull request. Please suggest links and other details to add the challenge's corresponding guide post through [a forum topic](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/new-topic?category=Contributors&title=&body=**What%20is%20your%20hint%20or%20solution%20suggestion%3F**%0A%0A%0A%0A%0A**Challenge%3A**%0A%0A%0A**Link%20to%20the%20challenge%3A**) instead.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## Adding Comment About Newbie Mistakes
+
+```markdown
+Hello,
+
+Firstly, thank you for submitting this pull request!
+
+As you navigate through the process, we have a PR checklist to ensure consistency and quality in our contributions. We kindly ask that you genuinely follow through with each point. This not only facilitates the review process but also demonstrates a mutual respect for the community's efforts.
+
+If you're unfamiliar with certain aspects, our [contributing guidelines](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org) are a helpful resource to get you up to speed.
+
+<details>
+<summary>**Friendly Pointers (click to expand)**</summary>
+
+1. **Editing on GitHub:** While it's possible to edit files directly on GitHub, it's typically better not to. This helps avoid inadvertent mistakes like typos that can disrupt tests.
+
+2. **Pull Request
+ title: ** Please ensure the PR title follows [our convention](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/how-to-open-a-pull-request?id=prepare-a-good-pr-title).
+
+3. **Linking Issues:** Please ensure you link issues using the designated method. Simply update the `XXXXXX` in the PR description to include the issue number. This keeps our records organized and clear.
+
+4. **Engaging with the Team:** We know you're eager, but kindly keep mentions and review requests limited. Our maintainers are always on the lookout and will attend to PRs in the order they come in.
+
+5. **Branch Management:** It's a good practice not to work directly off your `main` branch. Creating separate branches for different changes allows you to smoothly update your PR even as the main repository progresses.
+
+</details>
+
+Please note, there's no need to close this PR. If you have questions or need guidance refining your contribution, don't hesitate to ask. Our community is here to assist.
+
+Thank you for your enthusiasm in contributing to our project. We eagerly await more contributions from you!
+
+**Happy Contributing!** 🌟
+```
+
+## PR Opened While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a PR is opened for an issue that hasn't been triaged and marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```markdown
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for creating this pull request.
+
+The linked issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to update this pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Until the issue is open for contribution, we will not be able to review your pull request.
+```
+
+## Closing Invalid Issues
+
+> When an issue relates to the camper's code.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue seems to be a request for help. Instead of asking for help here, please click the **"Get Help"** button on the challenge on freeCodeCamp and choose the **"Ask for help"** option, which will help you create a question in the right part of the forum. Volunteers on the forum usually respond to questions within a few hours and can help determine if there is an issue with your code or the challenge's tests.
+
+If the forum members determine there is nothing wrong with your code, you can request this issue to be reopened.
+
+Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is a duplicate of an earlier issue.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that this issue appears to be very similar to issue #XXXXX, so we are closing it as a duplicate.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+> When an issue is fixed in staging.
+
+```markdown
+Thank you for reporting this issue.
+
+This is a standard message notifying you that the problem you mentioned here is present in production, but that it has already been fixed in staging. This means that the next time we push our staging branch to production, this problem should be fixed. Because of this, we're closing this issue.
+
+If you think we're wrong in closing this issue, please request for it to be reopened and add further clarification. Thank you and happy coding.
+```
+
+## `first timer only` Issues
+
+> When an issue is deemed to be eligible for first-time code contributors.
+
+```markdown
+Thanks for opening this issue.
+
+This looks like something that can be fixed by "first-time" code contributors to this repository. Here are the files that you should be looking at to work on a fix:
+
+List of files:
+
+1. ...
+2. ...
+3. ...
+
+Please make sure you read our [guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/), we prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guides. Join us in our [chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or our [forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing; our moderators will guide you through this.
+
+Sometimes we may get more than one pull request. We typically accept the most quality contribution followed by the one that is made first.
+
+Happy contributing.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment
+
+```md
+We typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+
+Issues labeled with `help wanted` or `first timers only` are open for contributions.
+
+Please make sure you read [our guidelines for contributing](https://contribute.freecodecamp.org/#/). We prioritize contributors following the instructions in our guide. Join us in [our chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay) or [the forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors/3) if you need help contributing - our community will be happy to assist you.
+```
+
+## Requests for Assignment While Issue Is Not Triaged
+
+> When a contributor requests for assignment but the issue hasn't been triaged or marked as ready for contribution.
+
+```md
+Hi there,
+
+Thanks for your interest in contributing.
+
+This issue has not been triaged yet, and a solution has not been agreed upon. Once the issue is open for contribution, you are welcome to create a pull request to reflect the issue consensus. Please also note that we typically do not assign issues. Instead, we accept the first pull request that comprehensively solves the issue.
+```
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/security-hall-of-fame.md b/src/content/docs/zh/security-hall-of-fame.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ffd17b46
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/security-hall-of-fame.md
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+---
+title: Responsible Disclosure - Hall of Fame
+---
+
+We appreciate any responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. If you are interested in contributing to the security of our platform, please read our [security policy outlined here](security).
+
+While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we are grateful to these awesome people for helping us keep the platform safe for everyone:
+
+- Mehul Mohan from [codedamn](https://codedamn.com) ([@mehulmpt](https://twitter.com/mehulmpt)) - [Vulnerability Fix](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/blob/bb5a9e815313f1f7c91338e171bfe5acb8f3e346/client/src/components/Flash/index.js)
+- Peter Samir https://www.linkedin.com/in/peter-samir/
+- Laurence Tennant ([@hyperreality](https://github.com/hyperreality)) working with IncludeSecurity.com - [GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-cc3r-grh4-27gj)
+- Michal Biesiada ([@mbiesiad](https://github.com/mbiesiad)) - [GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4](https://github.com/freeCodeCamp/freeCodeCamp/security/advisories/GHSA-6c37-r62q-7xf4)
+
+> **Thank you for your contributions :pray:**
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/security.md b/src/content/docs/zh/security.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..da7cbcdb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/security.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+---
+title: freeCodeCamp.org's Security Policy
+---
+
+This document outlines our security policy for the codebases, platforms that we operate, and how to report vulnerabilities.
+
+## Reporting a Vulnerability
+
+> [!NOTE] If you think you have found a vulnerability, **please report it responsibly**. Do not create GitHub issues for security issues. Instead, follow this guide.
+
+### Guidelines
+
+We appreciate responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities that might impact the integrity of our platforms and users. In the interest of saving everyone time, we encourage you to report vulnerabilities with these in mind:
+
+1. Ensure that you are using the **latest**, **stable**, and **updated** versions of the Operating System and Web Browser(s) available to you on your machine.
+2. We consider using tools & online utilities to report issues with SPF & DKIM configs, SSL Server tests, etc., in the category of ["beg bounties"](https://www.troyhunt.com/beg-bounties) and are unable to respond to these reports.
+3. While we do not offer any bounties or swags at the moment, we'll be happy to list your name in our [Hall of Fame](security-hall-of-fame) list, provided the reports are not low-effort.
+
+### Reporting
+
+After confirming the above guidelines, please feel free to send an email to `possible-security-issue [at] freecodecamp.org`. You can also send us a PGP encrypted message at `flowcrypt.com/me/freecodecamp`.
+
+Once you report a vulnerability, we will look into it and ensure that it is not a false positive. If we need to clarify any details, we will get back to you. You can submit separate reports for each issue you find. Please note that we will not be able to respond to any issues that we think are outside the guidelines.
+
+## Platforms and Codebases
+
+Here is a list of the platforms and codebases we are accepting reports for:
+
+### Learn Platform
+
+| Version | Branch | Supported | Website active |
+| ----------- | -------------- | --------- | ------------------------ |
+| production | `prod-current` | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/learn` |
+| staging | `prod-staging` | Yes | `freecodecamp.dev/learn` |
+| development | `main` | No | |
+
+### Publication Platform
+
+| Version | Supported | Website active |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------- |
+| production | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/news` |
+| localized | Yes | `freecodecamp.org/<language>/news` |
+
+### Mobile App
+
+| Version | Supported | Website active |
+| ---------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| production | Yes | `https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.freecodecamp` |
+
+### Other Platforms
+
+Apart from the above, we are also accepting reports for repositories hosted on GitHub under the freeCodeCamp organization.
+
+### Other Self-hosted Applications
+
+We self-host some of our platforms using open-source software like Ghost & Discourse. If you are reporting a vulnerability, please ensure that it is not a bug in the upstream software.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/troubleshooting-development-issues.md b/src/content/docs/zh/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2092b229
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/troubleshooting-development-issues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+---
+title: Troubleshooting Development Issues
+---
+
+If you are facing an issue, there is a high chance that the resolution is in this documentation.
+
+## Issues with Installing the Recommended Prerequisites
+
+We regularly develop on the latest or most popular operating systems like macOS 10.15 or later, Ubuntu 18.04 or later, and Windows 10 (with WSL2).
+
+It is recommended to research your specific issue on resources such as Google, Stack Overflow, and Stack Exchange. There is a good chance that someone has faced the same issue and there is already an answer to your specific query.
+
+If you are on a different OS or are still facing issues, see [getting help](#getting-help).
+
+:::warning
+Please avoid creating GitHub issues for problems with the prerequisite technologies. They are out of the scope of this project.
+:::
+
+## Issues with Missing UI, Fonts, Language Strings, or Build Errors
+
+When you build the client, Gatsby will cache the fonts, language strings, and UI. If one of them isn't cached, run the following:
+
+```bash
+pnpm run clean
+pnpm install
+pnpm run seed
+pnpm run develop
+```
+
+OR
+
+Use the shortcut
+
+```
+pnpm run clean-and-develop
+```
+
+If you continue to face issues with the build, cleaning up the workspace is recommended.
+
+Use `git clean` in interactive mode:
+
+```
+git clean -ifdX
+```
+
+<details>
+ <summary>
+ How to clean git untracked files (screenshot)
+ </summary>
+ <br>
+ <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1884376/94270515-ca579400-ff5d-11ea-8ff1-152cade31654.gif" alt="How to clean git untracked files">
+</details>
+
+## Issues with API, login, Challenge Submissions, etc.
+
+If you can't sign in, and instead you see a banner with an error message saying that the error will be reported to freeCodeCamp, please double-check that your local port `3000` is not in use by a different program.
+
+#### **From Terminal:**
+
+```bash
+netstat -a | grep "3000"
+
+tcp4 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 DESKTOP LISTEN
+```
+
+## Issues Signing Out while Navigating
+
+While in development, your session is stored as cookies. Clearing them will sign you out of your development account.
+
+Running `pnpm run seed:certified-user` will log you out, too. It will overwrite the development user in your local database.
+
+## Issue Getting 404 when Navigating Profile Page
+
+When you try to navigate to http://localhost:8000/developmentuser to view the profile page, Gatsby takes over serving the client-side pages and hence you will get a 404 page for the user profile when working.
+
+There is a "Preview Custom 404 Page" button, click it to see the profile.
+
+## Issues Installing Dependencies
+
+If you get errors while installing the dependencies, please make sure that you are not in a restricted network or your firewall settings do not prevent you from accessing resources.
+
+The first time setup can take a while depending on your network bandwidth. Be patient, and if you are still stuck we recommend using Gitpod instead of an offline setup.
+
+:::note
+If you are using Apple Devices with M1 Chip to run the application locally, it is suggested to use Node v14.7 or above. You might run into issues with dependencies like Sharp otherwise.
+:::
+
+## Working With Other Languages
+
+To see how the client renders in another language go to [testing the client app in a world language.](how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp#Testing-the-Client-App-in-a-World-Language)
+
+## Getting Help
+
+If you are stuck and need help, feel free to ask questions in the ['Contributors' category on our forum](https://forum.freecodecamp.org/c/contributors) or [the contributors chat room](https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay).
+
+There might be an error in the console of your browser or in Bash / Terminal / Command Line that will help identify the problem. Provide this error message in your problem description so others can more easily identify the issue and help you find a resolution.
diff --git a/src/content/docs/zh/user-token-workflow.md b/src/content/docs/zh/user-token-workflow.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1531334c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/docs/zh/user-token-workflow.md
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+---
+title: How the User Token Workflow Works
+---
+
+User tokens are used to identify users to third parties so challenges completed using those services can be saved to a user's account.
+
+## How they are Created
+
+At the moment, the tokens are only used to submit the Relational Database challenges. A token gets created when a signed-in user clicks the "Click here to start the course" or "Click here to start the project" buttons to start one of the Relational Database courses or projects.
+
+## When they Get Deleted
+
+A user token will be deleted when a user signs out of freeCodeCamp, resets their progress, deletes their account, or manually deletes the token using the widget on the settings page.
+
+## How they Work
+
+Tokens are stored in a `UserToken` collection in the database. Each record has a unique `_id`, which is the token, and a `user_id` that links to the user's account from the `user` collection. The token is encoded using JWT and sent to the client when it's created. That encoded token is then given to third-party services that need it and sent to our API by them when a challenge is completed. When our API gets it, it is decoded so we can identify the user submitting a challenge and save the completed challenge to their `completedChallenges`.
diff --git a/src/content/i18n/en.json b/src/content/i18n/en.json
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fc1ba69e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/content/i18n/en.json
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+{
+ "pagefind.clear_search": "Clear",
+ "pagefind.load_more": "Load more results",
+ "pagefind.search_label": "Search this site",
+ "pagefind.filters_label": "Filters",
+ "pagefind.zero_results": "No results for [SEARCH_TERM]",
+ "pagefind.many_results": "[COUNT] results for [SEARCH_TERM]",
+ "pagefind.one_result": "[COUNT] result for [SEARCH_TERM]",
+ "pagefind.alt_search": "No results for [SEARCH_TERM]. Showing results for [DIFFERENT_TERM] instead",
+ "pagefind.search_suggestion": "No results for [SEARCH_TERM]. Try one of the following searches:",
+ "pagefind.searching": "Searching for [SEARCH_TERM]...",
+ "expressiveCode.copyButtonCopied": "Copied!",
+ "expressiveCode.copyButtonTooltip": "Copy to clipboard",
+ "expressiveCode.terminalWindowFallbackTitle": "Terminal window",
+ "skipLink.label": "Skip to content",
+ "search.label": "Search",
+ "search.shortcutLabel": "(Press / to Search)",
+ "search.cancelLabel": "Cancel",
+ "search.devWarning": "Search is only available in production builds. \nTry building and previewing the site to test it out locally.",
+ "themeSelect.accessibleLabel": "Select theme",
+ "themeSelect.dark": "Dark",
+ "themeSelect.light": "Light",
+ "themeSelect.auto": "Auto",
+ "languageSelect.accessibleLabel": "Select language",
+ "menuButton.accessibleLabel": "Menu",
+ "sidebarNav.accessibleLabel": "Main",
+ "tableOfContents.onThisPage": "On this page",
+ "tableOfContents.overview": "Overview",
+ "i18n.untranslatedContent": "This content is not available in your language yet.",
+ "page.editLink": "Edit page",
+ "page.lastUpdated": "Last updated:",
+ "page.previousLink": "Previous",
+ "page.nextLink": "Next",
+ "404.text": "Page not found. Check the URL or try using the search bar.",
+ "aside.note": "Note",
+ "aside.tip": "Tip",
+ "aside.caution": "Caution",
+ "aside.danger": "Danger",
+ "fileTree.directory": "Directory"
+}
diff --git a/src/i18n/chinese-traditional.ts b/src/i18n/chinese-traditional.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..12c43bad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/chinese-traditional.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': '准备开始',
+ Introduction: '介绍',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': '常见问题',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Reporting a Vulnerability',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Translation Contribution',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Work on translating resources',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Work on proofreading translations',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Code Contribution',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Set up freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Follow best-practices',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Additional Guides',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Debug outgoing emails locally',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)': '飞行手册',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': '维护人员手册',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': '我们的社区',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Discourse 论坛',
+ 'Chat Server': '聊天室'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/chinese.ts b/src/i18n/chinese.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..12c43bad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/chinese.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': '准备开始',
+ Introduction: '介绍',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': '常见问题',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Reporting a Vulnerability',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Translation Contribution',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Work on translating resources',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Work on proofreading translations',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Code Contribution',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Set up freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Follow best-practices',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Additional Guides',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Debug outgoing emails locally',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)': '飞行手册',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': '维护人员手册',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': '我们的社区',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Discourse 论坛',
+ 'Chat Server': '聊天室'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/german.ts b/src/i18n/german.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f3177f87
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/german.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'Erste Schritte',
+ Introduction: 'Einführung',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'Häufig gestellte Fragen',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Eine Schwachstelle melden',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Mitwirkung an der Übersetzung',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Helfe bei der Übersetzung von Ressourcen',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations':
+ 'Helfe beim Korrekturlesen von Übersetzungen',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Mitwirkung am Code',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Set up freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Follow best-practices',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Zusätzliche Leitfäden',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Curriculum-Dateistruktur verstehen',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Ausgehende E-Mails lokal debuggen',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)':
+ 'Handbücher (für Mitarbeiter & Moderatoren)',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'Moderatorenhandbuch',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': 'Unsere Community',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Diskussions forum',
+ 'Chat Server': 'Chat Server'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/italian.ts b/src/i18n/italian.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7490168e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/italian.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'Per iniziare',
+ Introduction: 'Introduzione',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'Domande frequenti',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Segnalare una vulnerabilità',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Contribuire alla traduzione',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Lavorare a tradurre le risorse',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Lavorare a correggere le risorse',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Contribuire al codice',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Impostare freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Seguire le migliori pratiche',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Guide aggiuntive',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Capire la struttura dei file del curriculum',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally':
+ 'Fare il debug delle email in uscita localmente',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)':
+ 'Manuali di volo (per membri dello staff & moderatori)',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'Manuale del moderatore',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': 'La nostra comunità',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Forum su Discourse',
+ 'Chat Server': 'Server per chattare'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/japanese.ts b/src/i18n/japanese.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..605d05c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/japanese.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'はじめに',
+ Introduction: 'イントロダクション',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'よくある質問',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': '脆弱性の報告',
+ 'Translation Contribution': '翻訳のコントリビューション',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'リソースを翻訳する',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': '翻訳を校正する',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'コードのコントリビューション',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Set up freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Follow best-practices',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'その他のガイド',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Debug outgoing emails locally',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)': 'マニュアル',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'モデレーターハンドブック',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': '私達のコミュニティ',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Discourse フォーラム',
+ 'Chat Server': 'チャットサーバー'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/portuguese.ts b/src/i18n/portuguese.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f96b8f8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/portuguese.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'Primeiros passos',
+ Introduction: 'Introdução',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'Perguntas frequentes',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Relatando uma vulnerabilidade',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Contribuição de tradução',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Ajude na tradução de recursos',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Ajude na revisão de traduções',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Contribuição de código',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Configurar o freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Seguir as melhores práticas',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Trabalhar na base de código',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Trabalhar em desafios de programação',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Usar os auxiliares do currículo',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Trabalhar na biblioteca de componentes',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Trabalhar em projetos práticos',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Trabalhar na aplicação para dispositivos móveis',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Trabalhar nos tutoriais com o CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Trabalhar na aplicação para a web localizada',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Trabalhar nos testes do Playwright',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Trabalhar nos desafios em vídeo',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Trabalhar com a documentação',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Abrir um pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Guias adicionais',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Compreender a estrutura do arquivo do currículo',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Depurar e-mails enviados localmente',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Trabalhar em testes do Cypress',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Configurar freeCodeCamp no Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Usar o Docker no Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'Fluxo de trabalho do token de usuário',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues':
+ 'Solucionar problemas de desenvolvimento',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Manual de análise dos autores',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)':
+ 'Manuais de Voo (para Equipe & Moderadores)',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'Manual do Moderador',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Modelos de resposta',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Manual do líder do idioma',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'Manual do DevOps',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Extensão do VSCode Coursesc',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Habilitar um novo um idioma',
+ 'Our Community': 'Nossa comunidade',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Fórum de discussão',
+ 'Chat Server': 'Servidor do chat'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/spanish.ts b/src/i18n/spanish.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2b3a2891
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/spanish.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'Comenzando',
+ Introduction: 'Introducción',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'Preguntas más frecuentes',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Informar una vulnerabilidad',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Contribución a la Traducción',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Trabajar en la traducción de recursos',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Revisar las traducciones',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Participa en la programación',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Configuración de FreeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Seguir las mejores prácticas de código',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Work on Codebase',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Work on Component Library',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Work on Mobile app',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Work on Documentation',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Open a pull request',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Guías adicionales',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Entender la estructura de los archivos del currículo',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Depurar localmente los emails salientes',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'User Token Workflow',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)':
+ 'Manuales de Vuelo (para el personal & moderadores)',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'Manual del moderador',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Reply Templates',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'DevOps Handbook',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Enable New Language',
+ 'Our Community': 'Nuestra Comunidad',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Foro Discourse',
+ 'Chat Server': 'Servidor de chat'
+};
diff --git a/src/i18n/ukrainian.ts b/src/i18n/ukrainian.ts
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..01e582f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/i18n/ukrainian.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+export const translations = {
+ 'Getting Started': 'Початок роботи',
+ Introduction: 'Вступ',
+ 'Frequently Asked Questions': 'Поширені питання',
+ 'Reporting a Vulnerability': 'Повідомлення про вразливість',
+ 'Translation Contribution': 'Внесок до перекладу',
+ 'Work on translating resources': 'Робота над перекладом ресурсів',
+ 'Work on proofreading translations': 'Робота над редагуванням перекладів',
+ 'Code Contribution': 'Внесок до коду',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp': 'Налаштування freeCodeCamp',
+ 'Follow best-practices': 'Передові практики написання коду',
+ 'Work on Codebase': 'Робота над кодовою базою',
+ 'Work on Coding Challenges': 'Робота над завданнями з кодом',
+ 'Use the Curriculum Helpers': 'Допомога з навчальної програми',
+ 'Work on Component Library': 'Робота над компонентною бібліотекою',
+ 'Work on Practice Projects': 'Робота над практичними проєктами',
+ 'Work on Mobile app': 'Робота над мобільним застосунком',
+ 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad': 'Робота над матеріалами з CodeRoad',
+ 'Work on Localized Web App': 'Робота над локалізованим вебзастосунком',
+ 'Work on Playwright Tests': 'Робота над тестами Playwright',
+ 'Work on Video Challenges': 'Робота над відеозавданнями',
+ 'Work on Documentation': 'Робота над документацією',
+ 'Open a pull request': 'Відкриття запиту на злиття',
+ 'Additional Guides': 'Додаткові інструкції',
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure':
+ 'Структура файлів навчальної програми',
+ 'Debug outgoing emails locally': 'Налагодження вихідних е-листів локально',
+ 'Work on Cypress Tests': 'Робота над тестами Cypress',
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)':
+ 'Налаштування freeCodeCamp на Windows (WSL)',
+ 'Use Docker on Windows Home': 'Використання Docker на Windows Home',
+ 'User Token Workflow': 'Робочий процес токенів користувача',
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues': 'Розв’язання проблем розробки',
+ 'Authors Analytics Manual': 'Керівництво з аналітики',
+ 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)':
+ 'Довідники (для персоналу та модераторів)',
+ 'Moderator Handbook': 'Довідник модератора',
+ 'Reply Templates': 'Шаблони відповідей',
+ 'Language Lead Handbook': 'Довідник мовного керівника',
+ 'DevOps Handbook': 'Довідник DevOps',
+ 'Courses VSCode Extension': 'Розширення VSCode Courses',
+ 'Enable New Language': 'Додавання нової мови',
+ 'Our Community': 'Наша спільнота',
+ GitHub: 'GitHub',
+ 'Discourse Forum': 'Форум',
+ 'Chat Server': 'Чат'
+};
diff --git a/src/sidebar.ts b/src/sidebar.ts
index a694ed0b..0012da37 100644
--- a/src/sidebar.ts
+++ b/src/sidebar.ts
@@ -1,175 +1,621 @@
+import * as chinese from './i18n/chinese';
+import * as chineseTraditional from './i18n/chinese-traditional';
+import * as spanish from './i18n/spanish';
+import * as german from './i18n/german';
+import * as italian from './i18n/italian';
+import * as japanese from './i18n/japanese';
+import * as portuguese from './i18n/portuguese';
+import * as ukrainian from './i18n/ukrainian';
+
export const sidebar = [
{
label: 'Getting Started',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Getting Started'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Getting Started'],
+ it: italian.translations['Getting Started'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Getting Started'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Getting Started'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Getting Started'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Getting Started'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Getting Started']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'Introduction',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Introduction'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Introduction'],
+ it: italian.translations['Introduction'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Introduction'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Introduction'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Introduction'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Introduction'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Introduction']
+ },
link: '/intro',
description: 'Contribute to the freeCodeCamp.org Community'
},
{
label: 'Frequently Asked Questions',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ it: italian.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Frequently Asked Questions'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Frequently Asked Questions']
+ },
link: '/faq'
},
{
label: 'Reporting a Vulnerability',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ it: italian.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Reporting a Vulnerability']
+ },
link: 'security'
}
]
},
{
label: 'Translation Contribution',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ it: italian.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Translation Contribution'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Translation Contribution']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'Work on translating resources',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on translating resources'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations['Work on translating resources']
+ },
link: 'how-to-translate-files'
},
{
label: 'Work on proofreading translations',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on proofreading translations'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations['Work on proofreading translations']
+ },
link: 'how-to-proofread-files'
}
]
},
{
label: 'Code Contribution',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ it: italian.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Code Contribution'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Code Contribution']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'Set up freeCodeCamp',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ it: italian.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp']
+ },
link: 'how-to-setup-freecodecamp-locally'
},
{
label: 'Follow best-practices',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ it: italian.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Follow best-practices'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Follow best-practices']
+ },
link: 'codebase-best-practices'
},
{
label: 'Work on Codebase',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Codebase'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Codebase']
+ },
link: 'how-to-contribute-to-the-codebase'
},
{
label: 'Work on Coding Challenges',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Coding Challenges'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Coding Challenges']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-coding-challenges'
},
{
label: 'Use the Curriculum Helpers',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ it: italian.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Use the Curriculum Helpers']
+ },
link: 'curriculum-help'
},
{
label: 'Work on Component Library',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Component Library'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Component Library']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-the-component-library'
},
{
label: 'Work on Practice Projects',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Practice Projects'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Practice Projects']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-practice-projects'
},
{
label: 'Work on Mobile app',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Mobile app'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Mobile app']
+ },
link: 'how-to-setup-freecodecamp-mobile-app-locally'
},
{
label: 'Work on tutorials with CodeRoad',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations['Work on tutorials with CodeRoad']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-tutorials-that-use-coderoad'
},
{
label: 'Work on Localized Web App',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Localized Web App'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Localized Web App']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-localized-client-webapp'
},
{
label: 'Work on Playwright Tests',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Playwright Tests'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Playwright Tests']
+ },
link: 'how-to-add-playwright-tests'
},
{
label: 'Work on Video Challenges',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Video Challenges'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Video Challenges']
+ },
link: 'how-to-help-with-video-challenges'
},
{
label: 'Work on Documentation',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Documentation'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Documentation']
+ },
link: 'how-to-work-on-the-docs-theme'
},
{
label: 'Open a pull request',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ it: italian.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Open a pull request'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Open a pull request']
+ },
link: 'how-to-open-a-pull-request'
}
]
},
{
label: 'Additional Guides',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ it: italian.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Additional Guides'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Additional Guides']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'Understand the curriculum file structure',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Understand the curriculum file structure'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Understand the curriculum file structure'],
+ it: italian.translations['Understand the curriculum file structure'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Understand the curriculum file structure'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations[
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure'
+ ],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations[
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure'
+ ],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Understand the curriculum file structure'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations[
+ 'Understand the curriculum file structure'
+ ]
+ },
link: 'curriculum-file-structure'
},
{
label: 'Debug outgoing emails locally',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ it: italian.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations['Debug outgoing emails locally']
+ },
link: 'how-to-catch-outgoing-emails-locally'
},
{
label: 'Work on Cypress Tests',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ it: italian.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Work on Cypress Tests'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Work on Cypress Tests']
+ },
link: 'how-to-add-cypress-tests'
},
{
label: 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ it: italian.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations[
+ 'Set up freeCodeCamp on Windows (WSL)'
+ ]
+ },
link: 'how-to-setup-wsl'
},
{
label: 'Use Docker on Windows Home',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ it: italian.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Use Docker on Windows Home']
+ },
link: 'how-to-use-docker-on-windows-home'
},
{
label: 'User Token Workflow',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ es: spanish.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ it: italian.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['User Token Workflow'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['User Token Workflow']
+ },
link: 'user-token-workflow'
},
{
label: 'Troubleshooting Development Issues',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ it: italian.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Troubleshooting Development Issues'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations[
+ 'Troubleshooting Development Issues'
+ ]
+ },
link: 'troubleshooting-development-issues'
},
{
label: 'Authors Analytics Manual',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ it: italian.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Authors Analytics Manual'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Authors Analytics Manual']
+ },
link: 'authors-analytics-manual'
}
]
},
{
label: 'Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ it: italian.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)'],
+ 'zh-Tw':
+ chineseTraditional.translations['Flight Manuals (for Staff & Mods)']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'Moderator Handbook',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ it: italian.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Moderator Handbook'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Moderator Handbook']
+ },
link: 'moderator-handbook'
},
{
label: 'Reply Templates',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ it: italian.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Reply Templates'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Reply Templates']
+ },
link: 'reply-templates'
},
{
label: 'Language Lead Handbook',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ it: italian.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Language Lead Handbook'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Language Lead Handbook']
+ },
link: 'language-lead-handbook'
},
{
label: 'DevOps Handbook',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ es: spanish.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ it: italian.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['DevOps Handbook'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['DevOps Handbook']
+ },
link: 'devops'
},
{
label: 'Courses VSCode Extension',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ it: italian.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Courses VSCode Extension'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Courses VSCode Extension']
+ },
link: 'courses-vscode-extension'
},
{
label: 'Enable New Language',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ it: italian.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Enable New Language'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Enable New Language']
+ },
link: 'how-to-enable-new-languages'
}
]
},
{
label: 'Our Community',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Our Community'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Our Community'],
+ it: italian.translations['Our Community'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Our Community'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Our Community'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Our Community'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Our Community'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Our Community']
+ },
items: [
{
label: 'GitHub',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['GitHub'],
+ es: spanish.translations['GitHub'],
+ it: italian.translations['GitHub'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['GitHub'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['GitHub'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['GitHub'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['GitHub']
+ },
link: 'https://github.com/freecodecamp/freecodecamp'
},
{
label: 'Discourse Forum',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ it: italian.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Discourse Forum'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Discourse Forum']
+ },
link: 'https://freecodecamp.org/forum/c/contributors'
},
{
label: 'Chat Server',
+ translations: {
+ de: german.translations['Chat Server'],
+ es: spanish.translations['Chat Server'],
+ it: italian.translations['Chat Server'],
+ jp: japanese.translations['Chat Server'],
+ pt: portuguese.translations['Chat Server'],
+ uk: ukrainian.translations['Chat Server'],
+ zh: chinese.translations['Chat Server'],
+ 'zh-Tw': chineseTraditional.translations['Chat Server']
+ },
link: 'https://discord.gg/PRyKn3Vbay'
}
]