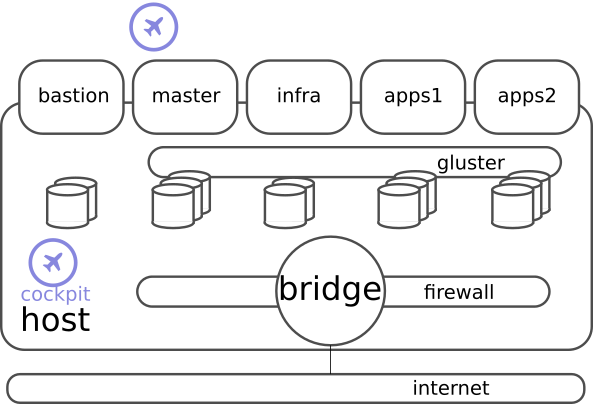
This is ansible automation for creating RHEL virtual machines on libvirt host.
Personally I use this to setup demoes for OpenShift. I use this ansible to create OpenShift cluster virtual machines on top of generic libvirt host (RHEL7/CentOS7).
I have run this on CentOS7, which is set up with LVM. There is plenty of free space on logical volume group (VG), where I create logical volumes of RHEL KVM image filesystem. This way I can easily manage virtual disks as LVs. All virtual machines get cloud-init CD created and attached before boot. This way some basic settings can be applied for guests, like ssh -key. All that is automated here by ansible.
- Do git clone this repo.
- Download RHEL KVM image and save it to:
roles/virt-host/files/rhel-7-kvm.qcow2. You get it here for free: https://access.redhat.com/downloads/content/69/ver=/rhel---7/latest/x86_64/product-software - Create a settings file into:
vars/main.yml. There is example file available:vars/example-main.yml - Some of the secrets are in
vars/vault.ymlfile, see example invars/example-vault.yml. An example with vault:ansible-playbook --vault-password-file .vault-password -i hosts <playbook> - you can add and remove hosts by adding entries into virtual_machines table in the above settings file
- run ansible to setup the host with necessary tools:
ansible-playbook -i hosts do-host.yml - run ansible to setup the guests (see note about rerun):
ansible-playbook -i hosts do-guests.yml - you can cleanup all guest stuff:
ansible-playbook -i hosts nuke-guests.yml
Note about re-running do-guests.yml: It will always rewrite the guest disks with plain RHEL7 image. In case you want to rerun it without overwriting guest disks, do: ansible-playbook -i hosts do-guests.yml --skip-tags qemu_root_disks
BR, ikke