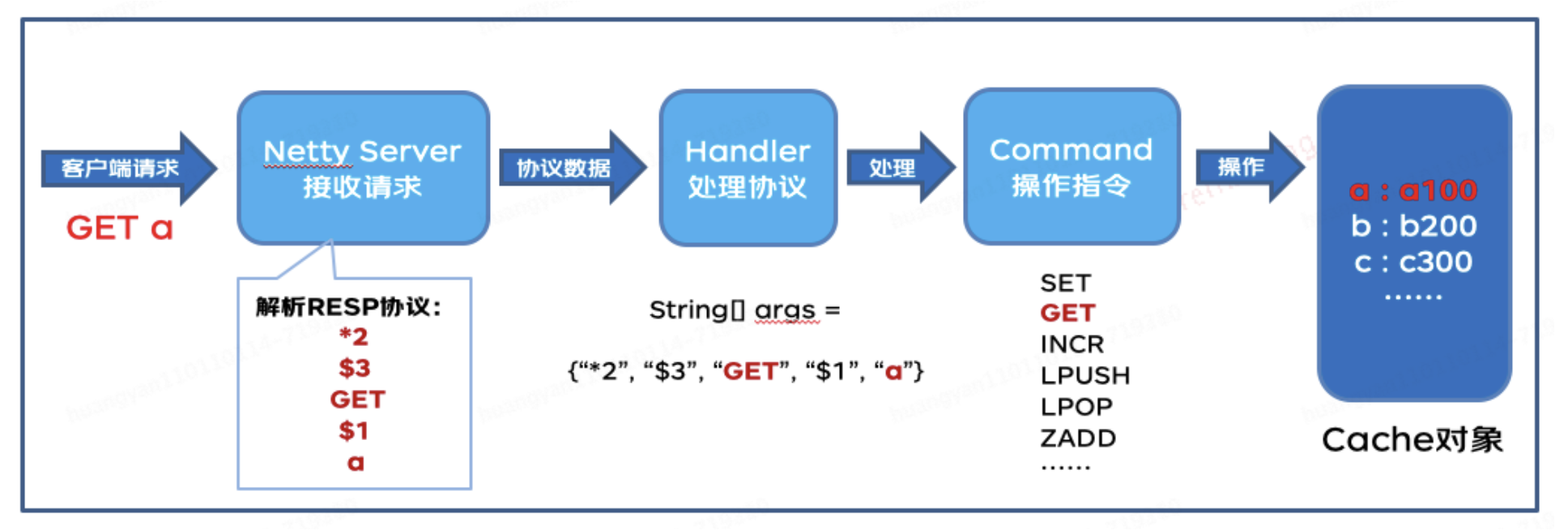
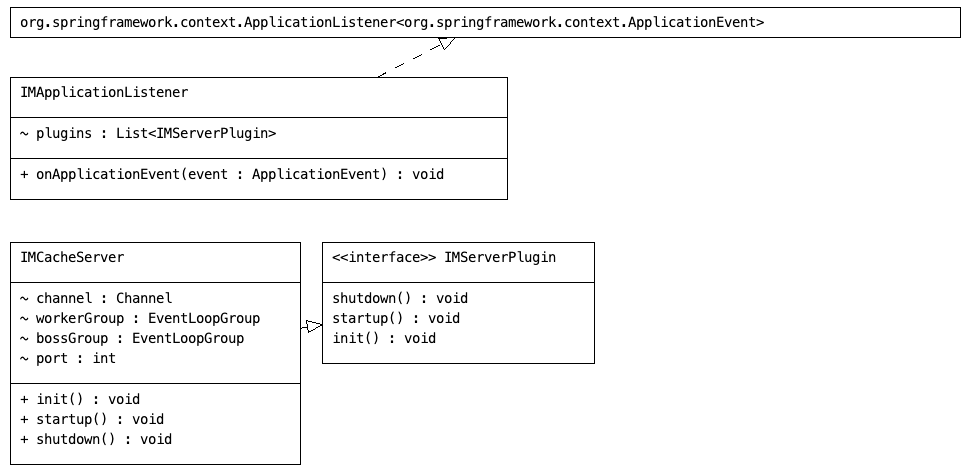
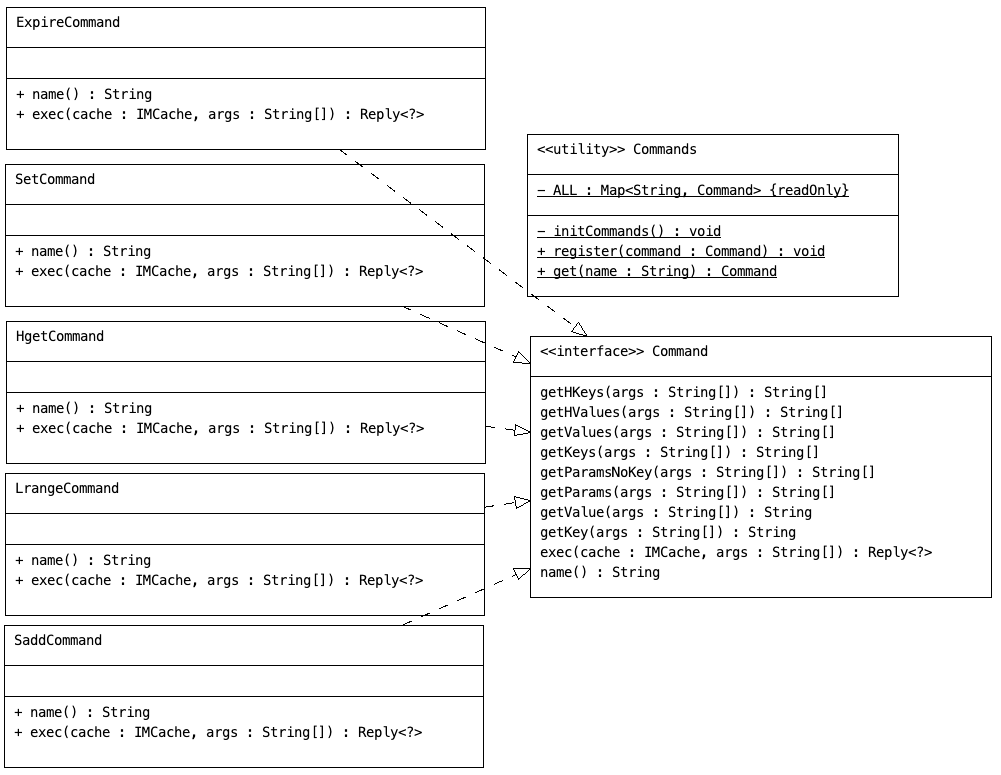
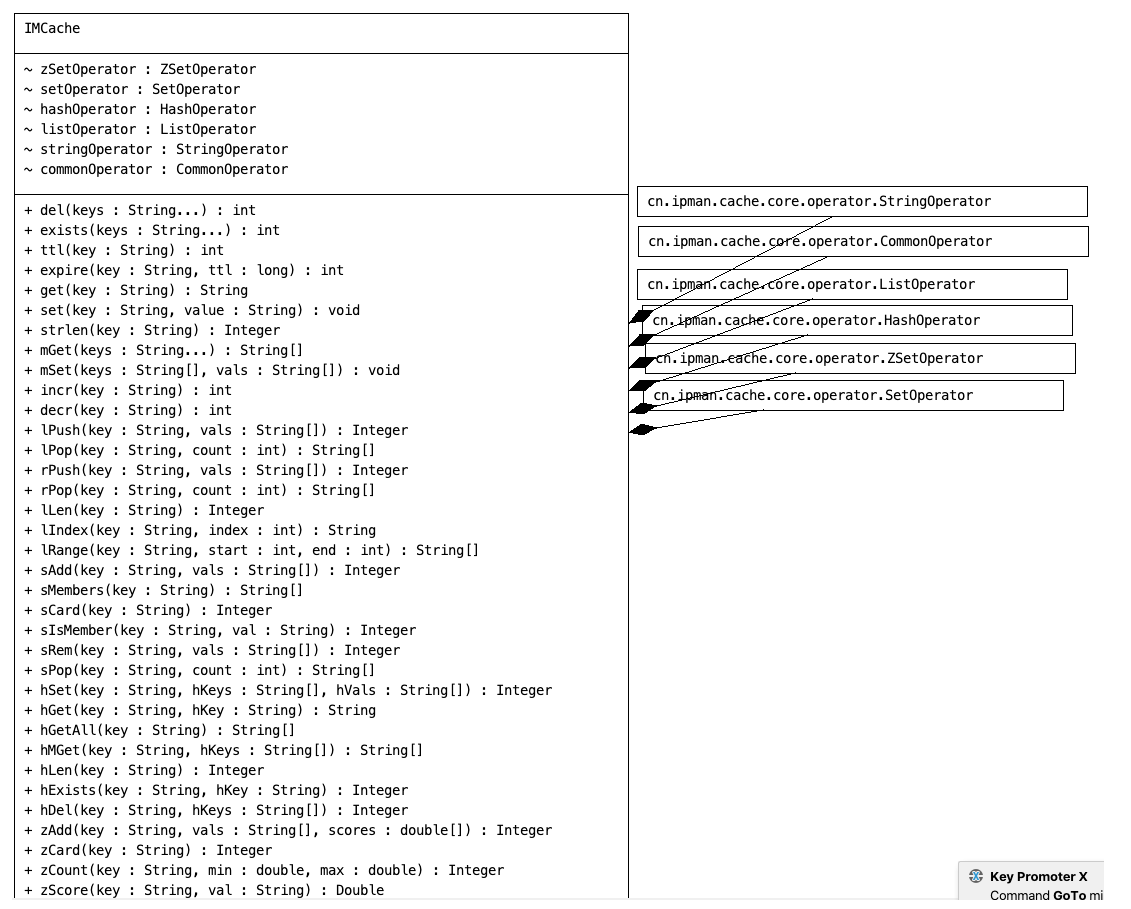
以下只是一个非常简易的Redis版本,通过以下讲述能大致理解Redis执行原理,仅是用来学习和探讨。
在现代软件开发中,缓存系统作为提升应用性能的关键组件,其重要性不言而喻。从零开始构建一个简易的Java版Redis-like缓存框架,不仅能够加深对缓存原理的理解,而且能灵活应用于实际项目中,提高数据访问速度和系统响应效率。本框架设计结合了高性能网络编程库Netty与Redis协议,以实现轻量级、高效的数据缓存解决方案。
- 网络通信层:基于Netty实现异步非阻塞的网络通信,处理客户端的连接、请求解析与响应发送。
- 协议解析层:实现RESP协议解析器,负责将接收到的网络数据包解析为可执行命令及参数。
- 命令处理器:设计一系列命令处理器,对应Redis的五种基本数据结构(字符串、列表、集合、散列、有序集合)的操作。
- 数据存储层:采用内存存储机制,实现高效的数据读写操作。未来可扩展至磁盘或分布式存储。
- Lua脚本支持:集成Lua脚本引擎,允许用户提交Lua脚本进行复杂逻辑处理,进一步提升执行效率和灵活性。
- 高性能:利用Netty的事件驱动模型,确保高并发下的低延迟。
- 兼容性:遵循Redis的RESP协议,易于对接现有Redis客户端。
- 灵活性:支持基础数据类型及Lua脚本,满足多样化缓存需求。
- 启动服务:配置Netty服务器,监听指定端口,接受客户端连接。
- 请求响应:实现ChannelInboundHandler,处理网络事件,包括解码请求、执行命令、编码响应。
- 协议解析:开发自定义Decoder和Encoder,实现RESP协议的解析与封装。
- 字符串(String):实现SET/GET/DEL等命令。
- 列表(List):实现LPUSH/RPUSH/LPOP/RPOP等命令。
- 集合(Set):实现SADD/SMEMBERS/SREM等命令。
- 散列(Hash):实现HSET/HGET/HDEL等命令。
- 有序集合(Sorted Set):实现ZADD/ZRANGE/ZREM等命令。
- 通用指令:实现EXPIRE/TTL/EXISTS等命令
- 脚本加载与执行:提供接口接收Lua脚本,通过Lua引擎执行并返回结果。
- Spring Boot:用于管理 Cache 框架的生命周期,通过
ApplicationListener初始化或优雅地关闭CacheServer。 - Netty 4:作为
CacheServer,监听 6379 端口以模拟 Redis 服务,负责 Redis RESP 协议的编解码。 - luaj-jse:作为 Lua 解释器,仅用于模拟执行
EVAL命令,通过 Lua 脚本操作CacheServer的具体指令。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.104.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.luaj</groupId>
<artifactId>luaj-jse</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
IMApplicationListener:插件入口点类,负责在Spring应用启动和关闭时管理插件的生命周期
IMServerPlugin:插件接口的用途,即定义Netty服务器的生命周期
IMCacheServer:实现了IMServerPlugin接口,用来实现初始化、启动、关闭Netty
首先,定义一个IMServerPlugin接口作为服务器插件
// IMServerPlugin:插件接口的用途,即定义Netty服务器的生命周期
public interface IMServerPlugin {
void init(); // 初始化netty
void startup(); // 启动netty
void shutdown(); // 关停netty
}
将实现Server接口的类注入到 Spring 容器中,使用 Netty 模拟 Redis 启动一个 TCP 服务,监听端口为 6379(编解码和处理器的细节将在后续讲解)。
/**
* 实现了IMServerPlugin接口,用来实现初始化、启动、关闭Netty
*/
@Component
public class IMCacheServer implements IMServerPlugin {
// 服务器端口号
int port = 6379;
// boss 线程组,用于接受客户端连接
EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
// worker 线程组,用于处理客户端IO操作
EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
// 服务器通道
Channel channel;
@Override
public void init() {
// 初始化 boss 线程组,指定线程工厂
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new DefaultThreadFactory("redis-boss"));
// 初始化 worker 线程组,指定线程工厂
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16, new DefaultThreadFactory("redis-work"));
}
@Override
public void startup() {
try {
// 创建 ServerBootstrap 对象,用于配置服务器
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 连接队列大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // 关闭Nagle,即时传输
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 支持长连接
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true) // 共享端口
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 32 * 1024) // 操作缓冲区的大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32 * 1024) // 发送缓冲区的大小
.childOption(EpollChannelOption.SO_REUSEPORT, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
// 配置 ServerBootstrap
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
// 添加解码器和处理器到管道
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IMCacheDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IMCacheHandler());
}
});
channel = b.bind(port).sync().channel();
System.out.println("开启netty redis服务器,端口为 " + port);
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// clonse server
@Override
public void shutdown() {
if (this.channel != null) {
this.channel.close();
this.channel = null;
}
if (this.bossGroup != null) {
this.bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
this.bossGroup = null;
}
if (this.workerGroup != null) {
this.workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
this.workerGroup = null;
}
}
}
通过Spring事件机制 注入所有IMServerPlugin实现,并监听应用的启动和停止事件。在应用启动后,初始化并启动Netty服务
/**
* 插件入口点类,负责在Spring应用启动和关闭时管理插件的生命周期
*/
@Component
public class IMApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
// 自动注入所有实现了 IMServerPlugin 接口的插件
@Autowired
List<IMServerPlugin> plugins;
/**
* 处理应用程序事件的方法。
*
* @param event 应用程序事件
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(@NonNull ApplicationEvent event) {
// 如果事件是 ApplicationReadyEvent(应用启动完成事件)
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent) {
// 遍历所有插件,依次初始化并启动
for (IMServerPlugin plugin : plugins) {
plugin.init(); // 初始化插件
plugin.startup(); // 启动插件
}
// 如果事件是 ContextClosedEvent(应用上下文关闭事件)
} else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
// 遍历所有插件,依次关闭
for (IMServerPlugin plugin : plugins) {
plugin.shutdown(); // 关闭插件
}
}
}
}
下面测试下Server启动后, 用 redis-cli 或 telnet 127.0.0.1 6379 去连接测试
redis-cli
由于 Netty 服务器本质上处理的是字节数据(Byte),为了便于后续程序处理,需要自定义解码器将字节数据转换为字符串。虽然 Netty 本身提供了对 Redis 的默认编解码实现(如 RedisDecoder、RedisEncoder),但编写自定义解码器有助于更好地理解和控制数据处理过程。
IMCacheDecoder:将 Netty 接收到的二进制流(ByteBuf in)解码为字符串,并输出到管道(Listout)中。
/**
* 缓存解码器,用于将字节流解码为可识别的消息对象。
* 此解码器负责从ByteBuf中读取数据,并将其转换为字符串形式添加到输出列表中。
*/
public class IMCacheDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
/**
* 解码方法,Netty框架调用此方法进行实际的解码操作。
*
* @param channelHandlerContext Netty的通道处理上下文,用于通道的管理和操作。
* @param in 输入的ByteBuf,包含待解码的数据。
* @param out 输出列表,解码后的消息对象将被添加到此列表中。
* @throws Exception 如果解码过程中发生错误。
*/
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("IMCacheDecoder decodeCount:" + counter.incrementAndGet());
// 获取当前可读字节的长度和读取索引
if (in.readableBytes() <= 0) return;
int count = in.readableBytes();
int index = in.readerIndex();
System.out.println("IMCacheDecoder count:" + count + ", index:" + index);
// 根据可读字节长度创建字节数组,并从ByteBuf中读取字节到字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
in.readBytes(bytes);
// 将字节数组转换为字符串
String ret = new String(bytes);
System.out.println("IMCacheDecoder ret:" + ret);
// 将解码后的字符串添加到输出列表中
out.add(ret);
}
}
在通过IMCacheDecoder解码器处理后,字节流已经被转换为字符串。对于 Redis 客户端来说,这个字符串是遵循 Redis RESP 协议的。
Redis 使用一种称为 Redis Serialization Protocol(RESP)的协议来进行客户端和服务器之间的通信。RESP 协议设计简单且高效,支持多种数据类型。以下是 RESP 语法的详细说明:
RESP 支持以下几种数据类型:
- 简单字符串(Simple Strings)
- 错误(Errors)
- 整数(Integers)
- 批量字符串(Bulk Strings)
- 数组(Arrays)
简单字符串以+开头,后跟字符串内容和 CRLF(回车换行符)。
示例:
+OK\r\n
错误信息以-开头,后跟错误消息和 CRLF。
示例:
-Error message\r\n
整数以:开头,后跟整数值和 CRLF。
示例:
:1000\r\n
批量字符串以$开头,后跟字符串的字节长度、CRLF、字符串内容和最终的 CRLF。如果字符串内容为空,长度为-1。
示例:
$6\r\nfoobar\r\n
$0\r\n\r\n
$-1\r\n
数组以*开头,后跟数组中元素的数量、CRLF 和每个元素的 RESP 表示。如果数组为空,数量为0,如果数组为null,数量为-1。
示例:
*2\r\n$3\r\nfoo\r\n$3\r\nbar\r\n
*3\r\n:1\r\n:2\r\n:3\r\n
*0\r\n
*-1\r\n
客户端发送的每个命令都使用 RESP 数组格式,其中数组的每个元素是一个批量字符串,表示命令及其参数。
示例:
*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$3\r\nkey\r\n$5\r\nvalue\r\n
*2\r\n$3\r\nGET\r\n$3\r\nkey\r\n
Redis 服务器根据不同的命令返回不同类型的 RESP 数据。以下是一些常见的响应示例:
- 简单字符串响应:
+OK\r\n
- 错误响应:
-ERR unknown command 'foobar'\r\n
- 整数响应:
:1000\r\n
- 批量字符串响应:
$6\r\nfoobar\r\n
$0\r\n\r\n
$-1\r\n
- 数组响应:
*2\r\n$3\r\nfoo\r\n$3\r\nbar\r\n
*3\r\n:1\r\n:2\r\n:3\r\n
*0\r\n
*-1\r\n
假设客户端发送以下命令:
*3\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$3\r\nkey\r\n$5\r\nvalue\r\n
这表示一个SET命令,包含三个元素:
- 命令名称
SET - 键
key - 值
value
服务器可能返回简单字符串响应:
+OK\r\n
另一个示例,客户端发送GET命令:
*2\r\n$3\r\nGET\r\n$3\r\nkey\r\n
如果键存在,服务器返回批量字符串响应:
$5\r\nvalue\r\n
如果键不存在,服务器返回空批量字符串:
$-1\r\n
通过遵循这些 RESP 语法规则,客户端和服务器可以高效地进行通信
处理程序首先需要解析 RESP 协议,找到相应的命令指令并执行,最终将结果以 RESP 协议格式返回给 Redis 客户端。以下是类图设计:
IMCacheHandler处理程序:负责在解码后的 RESP 语句中识别具体的命令(如:GET、SET、INFO 等)。在指令列表中找到对应的命令并执行,最终将执行结果转换为 RESP 协议格式返回给 Redis 客户端。
/**
* 缓存处理程序,负责处理缓存相关的命令请求。
*/
public class IMCacheHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
// 定义回车换行符、OK响应、INFO响应的静态字符串,用于命令响应的构建
private static final String CRLF = "\r\n";
private static final String OK = "OK";
// 全局缓存实例,用于存储和检索数据。
public static final IMCache CACHE = new IMCache();
/**
* 处理接收到的缓存命令。
*
* @param ctx 通道上下文,用于发送响应。
* @param message 接收到的命令字符串。
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String message) {
String[] args = message.split(CRLF);
System.out.println("IMCacheHandler ==> " + String.join(",", args));
// 根据redis操作指令,获取具体的执行方法
String cmd = args[2].toUpperCase();
Command command = Commands.get(cmd);
if (command != null) {
try {
Reply<?> reply = command.exec(CACHE, args);
System.out.println("CMD[" + cmd + "] => " + reply.getType() + " => " + reply.getValue());
replyContext(ctx, reply);
} catch (Exception e) {
Reply<?> reply = Reply.error("ERR exception with msg: '" + e.getMessage() + "'");
replyContext(ctx, reply);
}
} else {
Reply<?> reply = Reply.error("ERR unsupported command '" + cmd + "'");
replyContext(ctx, reply);
}
}
// 需要支持的5种数据类型,字符串、错误、数组、整数、批量字符串
private void replyContext(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Reply<?> reply) {
switch (reply.getType()) {
case INT -> integer(ctx, (Integer) reply.getValue());
case ERROR -> error(ctx, (String) reply.getValue());
case SIMPLE_STRING -> simpleString(ctx, (String) reply.getValue());
case BULK_STRING -> bulkString(ctx, (String) reply.getValue());
case ARRAY -> array(ctx, (String[]) reply.getValue());
default -> simpleString(ctx, OK);
}
}
// 发送错误响应
private void error(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {
writeByteBuf(ctx, errorEncode(msg));
}
// 发送数组响应
private void array(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String[] array) {
writeByteBuf(ctx, arrayEncode(array));
}
// 发送整数响应
private void integer(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, int i) {
writeByteBuf(ctx, integerEncode(i));
}
// 发送复杂的string响应
private void bulkString(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String content) {
writeByteBuf(ctx, bulkStringEncode(content));
}
// 发送简单的string响应
private void simpleString(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String content) {
writeByteBuf(ctx, simpleStringEncode(content));
}
// 将数组编码为Redis协议格式的字符串
private static String arrayEncode(Object[] array) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (array == null) {
sb.append("*-1").append(CRLF);
} else if (array.length == 0) {
sb.append("*0").append(CRLF); // 空数组
} else {
sb.append("*").append(array.length).append(CRLF);
for (Object obj : array) {
if (obj == null) {
sb.append("$-1" + CRLF);
} else {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
sb.append(integerEncode((Integer) obj));
} else if (obj instanceof String) {
sb.append(bulkStringEncode(obj.toString()));
} else if (obj instanceof Object[] objs) {
sb.append(arrayEncode(objs));
}
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
// 将整数编码为Redis协议格式的字符串
private static String integerEncode(int i) {
return ":" + i + CRLF;
}
// 将错误信息编码为Redis协议格式的字符串
private static String errorEncode(String error) {
return "-" + error + CRLF;
}
// 将复杂的string编码为Redis协议格式的字符串
private static String bulkStringEncode(String content) {
String ret;
if (content == null) {
ret = "$-1";
} else if (content.isEmpty()) { // 字符串空
ret = "$0";
} else {
ret = "$" + content.getBytes().length + CRLF + content;
}
return ret + CRLF;
}
// 将简单的string编码为Redis协议格式的字符串
private static String simpleStringEncode(String content) {
String ret;
if (content == null) {
ret = "$-1";
} else if (content.isEmpty()) { // 字符串空
ret = "$0";
} else {
ret = "+" + content;
}
return ret + CRLF;
}
// 将编码后的字符串写入ByteBuf并发送
private void writeByteBuf(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String content) {
System.out.println("wrap byte buffer and reply: " + content);
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer);
}
}
Redis 提供了多种数据类型,每种类型都适用于不同的应用场景。以下常用的5种 Redis 主要的数据类型及其简介:
- 字符串(String):
- 描述:最基本的 Redis 数据类型,二进制安全,可以包含任何数据,比如文本或序列化的对象。
- 应用场景:缓存数据、计数器、会话信息等。
- 常用命令:
SET、GET、INCR、DECR、APPEND、STRLEN。
- 哈希(Hash):
- 描述:用于存储键值对集合,适合存储对象。
- 应用场景:存储用户信息(如用户名、密码、邮箱等)。
- 常用命令:
HSET、HGET、HGETALL、HDEL、HEXISTS、HINCRBY。
- 列表(List):
- 描述:有序的字符串列表,可以从两端插入和移除元素。
- 应用场景:消息队列、任务列表、时间线等。
- 常用命令:
LPUSH、RPUSH、LPOP、RPOP、LRANGE、LINDEX。
- 集合(Set):
- 描述:无序的字符串集合,不允许重复元素。
- 应用场景:标签、唯一性检查、共同好友等。
- 常用命令:
SADD、SREM、SMEMBERS、SISMEMBER、SUNION、SINTER。
- 有序集合(Sorted Set):
- 描述:类似集合,但每个元素都会关联一个分数,用于排序。
- 应用场景:排行榜、带权重的队列等。
- 常用命令:
ZADD、ZREM、ZRANGE、ZRANK、ZINCRBY、ZREVRANGE。
Redis指令大概有250+种,主要分为通用化命令或基于数据类型之上独有的指令。下面设计中定义 Command 指令接口,并默认实现了一些解析key、value的实现方法,由不同命令 负责实现 Command 接口(如Expire、Set、Get)等等
命令的代码示意如下,就是找到不同命令的key、value找到对应的数据类型进行读写操作:
public class CmdCommand implements Command {
@Override
public String name() {
// *2,$7,COMMAND,$4,DOCS
return "COMMAND";
}
@Override
public Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args) {
return Reply.string(OK);
}
}
public class HexistsCommand implements Command {
@Override
public String name() {
// hexists ===> *3,$7,hexists,$2,h1,$2,f3
return "HEXISTS";
}
@Override
public Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args) {
String key = getKey(args);
String hKey = getValue(args);
return Reply.integer(cache.hExists(key, hKey));
}
}
public class LrangeCommand implements Command {
@Override
public String name() {
// lrange ===> *3,$4,rpop,$2,l1,$1,2
return "LRANGE";
}
@Override
public Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args) {
String key = getKey(args);
String[] params = getParamsNoKey(args);
int start = Integer.parseInt(params[0]);
int end = Integer.parseInt(params[1]);
return Reply.array(cache.lRange(key, start, end));
}
}
public class SmembersCommand implements Command {
@Override
public String name() {
// smembers ===> *2,$8,smembers,$2,s1
return "SMEMBERS";
}
@Override
public Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args) {
String key = getKey(args);
return Reply.array(cache.sMembers(key));
}
}
public class MgetCommand implements Command {
@Override
public String name() {
// MGET ===> *4,$4,mget,$1,a,$1,b,$1,c
return "MGET";
}
@Override
public Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args) {
String[] keys = getParams(args);
return Reply.array(cache.mGet(keys));
}
}
.....
不同的指令实现上,除了操作具体的数据类型,如String、List、Hash等,最重要的是做指令解析,要识别出命令中 [哪些是key?,哪些是val?]
如:左边是命令,右边是RESP的中具体的格式
del a b c ===> *4,$3,del,$1,a,$1,b,$1,c
hmget h1 f1 f2 f3 ===> *5,$5,hmget,$2,h1,$2,f1,$2,f2,$2,f3
rpsuh a 2 3 ===> *4,$5,rpush,$1,a,$1,2,$1,3
sismember s1 2 ===> *3,$9,sismember,$2,s1,$1,2
incr a 1 ===> *3,$4,incr,$1,a,$1,1具体代码实现如下:
public interface Command {
// 行结束符常量
String CRLF = "\r\n";
// 表示成功的常量
String OK = "OK";
// 获取命令名称
String name();
// 执行命令
Reply<?> exec(IMCache cache, String[] args);
// 获取默认的键参数
default String getKey(String[] args) {
return args[4];
}
// 获取默认的值参数
default String getValue(String[] args) {
return args[6];
}
// 获取参数数组,不包括键
default String[] getParams(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 3) / 2;
String[] keys = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
keys[i] = args[4 + i * 2];
}
return keys;
}
// 获取参数数组,不包括键和第一个参数
default String[] getParamsNoKey(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 5) / 2;
String[] keys = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
keys[i] = args[6 + i * 2];
}
return keys;
}
// 获取键数组
default String[] getKeys(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 3) / 4;
String[] keys = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
keys[i] = args[4 + i * 4];
}
return keys;
}
// 获取值数组
default String[] getValues(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 3) / 4;
String[] vals = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
vals[i] = args[6 + i * 4];
}
return vals;
}
// 获取哈希值数组
default String[] getHValues(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 5) / 4;
String[] vals = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
vals[i] = args[8 + i * 4];
}
return vals;
}
// 获取哈希键数组
default String[] getHKeys(String[] args) {
int len = (args.length - 5) / 4;
String[] keys = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
keys[i] = args[6 + i * 4];
}
return keys;
}
}
通过IMCache类,内部集成了一些通用操作和五种数据类型的操作器。在Command实现类中,可以调用IMCache中相应数据类型的方法来实现数据的读写操作。
相对简单,代码就不具体展开了...
通过IMCacheHandler处理器解析 RESP 协议,可以获取具体的 Redis 操作指令(如:GET、SET、INFO 等)。接下来,我们需要基于这些指令,实现对五种常用数据类型的读写操作。以下是类图设计:
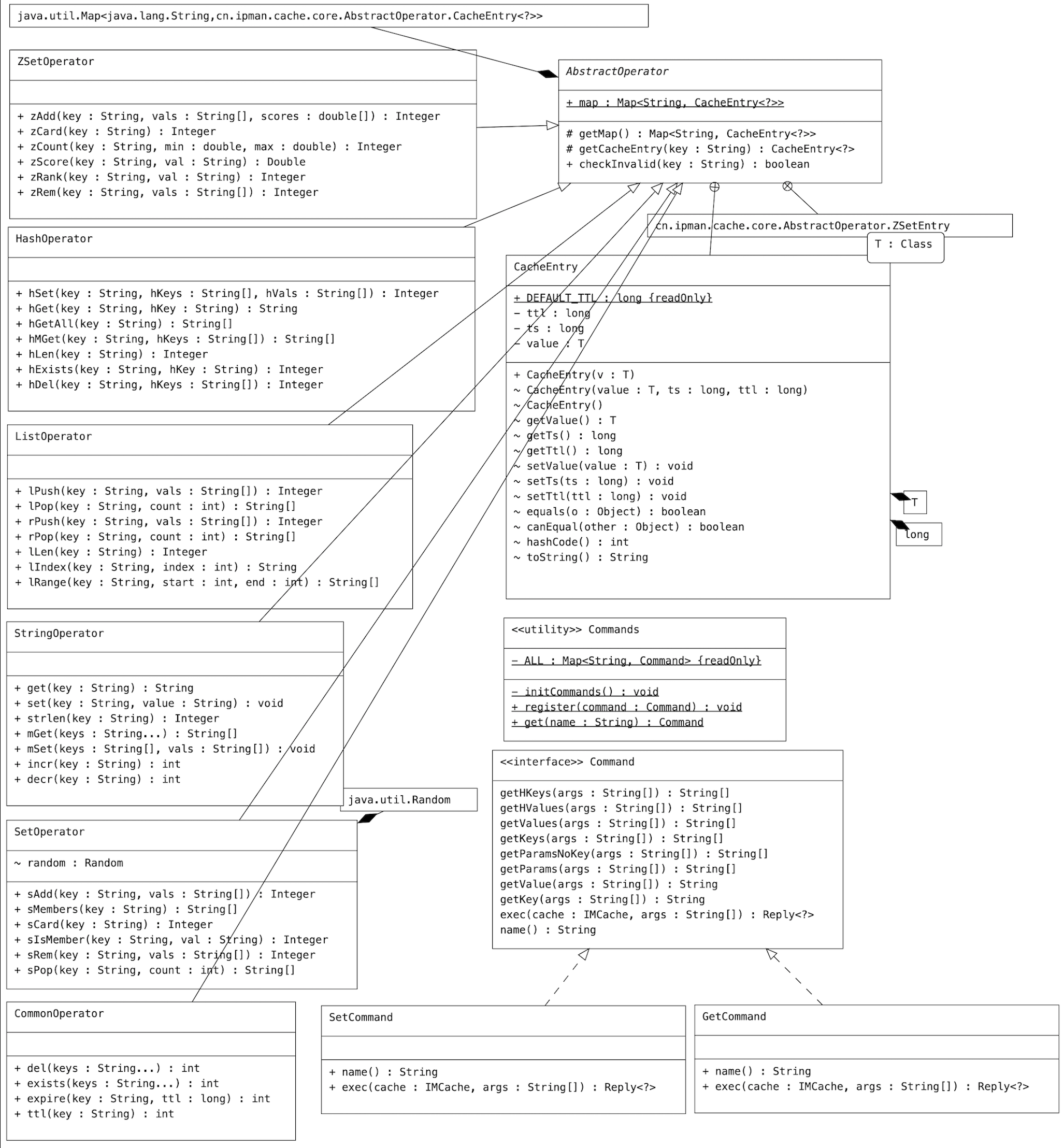
AbstractOperator 用来定义 Cache数据结构,map 要支持5种数据类型的读写(string、set、zet、list、hash),并定义创建时间和有效期,用来实现 expire命令 和 ttl命令
/**
* AbstractOperator 是一个抽象类,提供了对Cache数据的基本操作。
*/
public abstract class AbstractOperator {
// 存储缓存条目的静态映射表
public static Map<String, CacheEntry<?>> map = new HashMap<>();
// 获取当前缓存映射表
protected Map<String, CacheEntry<?>> getMap() {
return map;
}
// 根据键获取缓存条目
protected CacheEntry<?> getCacheEntry(String key) {
return map.get(key);
}
// 检查指定键是否无效(不存在或已过期)
public boolean checkInvalid(String key) {
CacheEntry<?> entry = getCacheEntry(key);
if (entry == null || entry.getValue() == null) return true;
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果键已过期,在访问时删除它
if (entry.getTtl() > 0 && (current - entry.getTs()) > entry.getTtl()) {
System.out.printf("KEY[%s] expire cause CURRENT[%d]-TS[%d] > TTL[%d] ms%n",
key, current, entry.getTs(), entry.getTtl());
map.remove(key);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class CacheEntry<T> {
private T value; // 缓存值
private long ts; // 创建时间戳
private long ttl; // 生存时间(毫秒)
public final static long DEFAULT_TTL = -1000L; // 默认生存时间
// 构造函数,初始化值和时间戳,默认生存时间
public CacheEntry(T v) {
value = v;
ts = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 创建时间戳
ttl = DEFAULT_TTL; // 默认生存时间
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class ZSetEntry {
private String value; // 有序集合中的值
private double score; // 有序集合中的分数
}
}
Reids通用性相关的指令的具体实现
**
* CommonOperator 提供了一些通用的缓存操作,如删除、检查存在、设置过期时间和获取剩余生存时间等。
*/
public class CommonOperator extends AbstractOperator {
/**
* 删除指定的键。
*
* @param keys 要删除的键
* @return 成功删除的键的数量
*/
public int del(String... keys) {
// 如果 keys 为空,返回 0;否则删除每个键并统计成功删除的数量
return keys == null ? 0 : (int) Arrays.stream(keys)
.map(map::remove).filter(Objects::nonNull).count();
}
/**
* 检查指定的键是否存在。
*
* @param keys 要检查的键
* @return 存在的键的数量
*/
public int exists(String... keys) {
// 如果 keys 为空,返回 0;否则检查每个键是否存在并统计存在的数量
return keys == null ? 0 : (int) Arrays.stream(keys)
.map(map::containsKey).filter(x -> x).count();
}
/**
* 设置指定键的过期时间。
*
* @param key 要设置过期时间的键
* @param ttl 过期时间(秒)
* @return 成功设置过期时间的键的数量(0 或 1)
*/
public int expire(String key, long ttl) {
CacheEntry<?> entry = getCacheEntry(key);
if (entry == null) return 0; // 如果键不存在,返回 0
entry.setTtl(ttl * 1000L); // 将过期时间转换为毫秒并设置
entry.setTs(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 更新时间戳
return 1;
}
/**
* 获取指定键的剩余生存时间。
*
* @param key 要获取生存时间的键
* @return 剩余生存时间(秒),键不存在返回 -2,没有设置过期时间返回 -1
*/
public int ttl(String key) {
CacheEntry<?> entry = getCacheEntry(key);
if (entry == null) return -2; // 键不存在,返回 -2
if (entry.getTtl() == CacheEntry.DEFAULT_TTL) return -1; // 没有设置过期时间,返回 -1
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long ret = (entry.getTs() + entry.getTtl() - current) / 1000; // 计算剩余生存时间(秒)
if (ret > 0) return (int) ret;
return -1; // 如果剩余生存时间小于等于 0,返回 -1
}
}
用 CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> 进行存储
/**
* HashOperator 提供了对哈希表(Hash)的操作,如设置、获取、删除哈希表中的字段等。
*/
public class HashOperator extends AbstractOperator {
/**
* 设置哈希表中一个或多个字段的值。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @param hKeys 哈希表字段的键数组
* @param hVals 哈希表字段的值数组
* @return 成功设置的字段数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer hSet(String key, String[] hKeys, String[] hVals) {
// 检查输入参数的有效性
if (hKeys == null || hKeys.length == 0) return 0;
if (hVals == null || hVals.length == 0) return 0;
if (hKeys.length != hVals.length) throw new RuntimeException("hKeys and hVals must be same length");
// 获取或创建哈希表缓存条目
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new CacheEntry<>(new LinkedHashMap<>());
map.put(key, entry);
}
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
// 设置哈希表字段的值
for (int i = 0; i < hKeys.length; i++) {
exist.put(hKeys[i], hVals[i]);
}
return hKeys.length;
}
/**
* 获取哈希表中指定字段的值。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @param hKey 哈希表字段的键
* @return 字段的值,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String hGet(String key, String hKey) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return exist.get(hKey);
}
/**
* 获取哈希表中所有字段的键值对。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @return 所有字段的键值对数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] hGetAll(String key) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return exist.entrySet().stream()
.flatMap(e -> Stream.of(e.getKey(), e.getValue()))
.toArray(String[]::new);
}
/**
* 获取哈希表中多个字段的值。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @param hKeys 哈希表字段的键数组
* @return 字段的值数组,如果不存在则返回空数组
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] hMGet(String key, String[] hKeys) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return hKeys == null ? new String[0] : Arrays.stream(hKeys)
.map(exist::get).toArray(String[]::new);
}
/**
* 获取哈希表中字段的数量。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @return 字段的数量,如果不存在则返回 0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer hLen(String key) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return exist.size();
}
/**
* 检查哈希表中是否存在指定字段。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @param hKey 哈希表字段的键
* @return 如果字段存在返回 1,否则返回 0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer hExists(String key, String hKey) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return exist.containsKey(hKey) ? 1 : 0;
}
/**
* 删除哈希表中一个或多个字段。
*
* @param key 哈希表的键
* @param hKeys 要删除的字段键数组
* @return 成功删除的字段数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer hDel(String key, String[] hKeys) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashMap<String, String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashMap<String, String> exist = entry.getValue();
return hKeys == null ? 0 : (int) Arrays.stream(hKeys)
.map(exist::remove).filter(Objects::nonNull).count();
}
}
用 CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> 进行存储
/**
* ListOperator 提供了对列表(List)的操作,如从左/右推入、弹出元素,获取列表长度和元素等。
*/
public class ListOperator extends AbstractOperator {
/**
* 从左侧推入一个或多个值到列表中。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param vals 要推入的值数组
* @return 推入的值的数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer lPush(String key, String[] vals) {
// 获取或创建列表缓存条目
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new CacheEntry<>(new LinkedList<>());
map.put(key, entry);
}
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
// 从左侧推入值
Arrays.stream(vals).forEach(exist::addFirst);
return vals.length;
}
/**
* 从左侧弹出指定数量的值。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param count 要弹出的值的数量
* @return 弹出的值数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] lPop(String key, int count) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
// 计算实际弹出的数量
int len = Math.min(count, exist.size());
String[] ret = new String[len];
int index = 0;
while (index < len) {
ret[index++] = exist.pollFirst();
}
return ret;
}
/**
* 从右侧推入一个或多个值到列表中。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param vals 要推入的值数组
* @return 推入的值的数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer rPush(String key, String[] vals) {
// 获取或创建列表缓存条目
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new CacheEntry<>(new LinkedList<>());
map.put(key, entry);
}
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
// 从右侧推入值
if (vals.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
exist.addAll(List.of(vals));
return vals.length;
}
/**
* 从右侧弹出指定数量的值。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param count 要弹出的值的数量
* @return 弹出的值数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] rPop(String key, int count) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
// 计算实际弹出的数量
int len = Math.min(count, exist.size());
String[] ret = new String[len];
int index = 0;
while (index < len) {
ret[index++] = exist.removeLast();
}
return ret;
}
/**
* 获取列表的长度。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @return 列表的长度,如果不存在则返回 0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer lLen(String key) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return 0;
return exist.size();
}
/**
* 获取列表中指定索引的值。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param index 索引
* @return 列表中指定索引的值,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String lIndex(String key, int index) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
if (index >= exist.size()) return null;
return exist.get(index);
}
/**
* 获取列表中指定范围的值。
*
* @param key 列表的键
* @param start 起始索引
* @param end 结束索引
* @return 指定范围的值数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] lRange(String key, int start, int end) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedList<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedList<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
int size = exist.size();
if (start >= size) return null;
if (end >= size) {
end = size - 1;
}
// 计算实际返回的长度
int len = Math.min(size, end - start + 1);
String[] ret = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ret[i] = exist.get(start + i);
}
return ret;
}
}
用 CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> 进行存储
/**
* SetOperator 提供了对集合(Set)的操作,如添加、移除、检查成员、获取所有成员等。
*/
public class SetOperator extends AbstractOperator {
/**
* 向集合中添加一个或多个值。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @param vals 要添加的值数组
* @return 成功添加的值的数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer sAdd(String key, String[] vals) {
// 获取或创建集合缓存条目
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new CacheEntry<>(new LinkedHashSet<>());
map.put(key, entry);
}
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (vals == null || vals.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
exist.addAll(Arrays.asList(vals));
return vals.length;
}
/**
* 获取集合中的所有成员。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @return 集合中的所有成员数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] sMembers(String key) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
return exist.toArray(String[]::new);
}
/**
* 获取集合的基数(成员数量)。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @return 集合的基数,如果不存在则返回 0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer sCard(String key) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return 0;
return exist.size();
}
/**
* 检查给定的值是否是集合的成员。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @param val 要检查的值
* @return 如果是成员返回 1,否则返回 0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer sIsMember(String key, String val) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
return exist.contains(val) ? 1 : 0;
}
/**
* 从集合中移除一个或多个值。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @param vals 要移除的值数组
* @return 成功移除的值的数量
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer sRem(String key, String[] vals) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
return vals == null ? 0 : (int) Arrays.stream(vals)
.map(exist::remove).filter(x -> x).count();
}
// 随机数生成器
Random random = new Random();
/**
* 随机移除并返回集合中的一个或多个值。
*
* @param key 集合的键
* @param count 要移除的值的数量
* @return 移除的值数组,如果不存在则返回 null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String[] sPop(String key, int count) {
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null; // 检查键是否无效
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<String>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashSet<String> exist = entry.getValue();
if (exist == null) return null;
// 计算实际移除的数量
int len = Math.min(count, exist.size());
String[] ret = new String[len];
int index = 0; // sPop 是随机移除
while (index < len) {
String[] array = exist.toArray(String[]::new);
String obj = array[random.nextInt(exist.size())];
exist.remove(obj);
ret[index++] = obj;
}
return ret;
}
}
用 CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> 进行存储
/**
* ZSetOperator 提供了对集合(ZSet)的操作,如添加、Rank、取分、删除等操作
*/
public class ZSetOperator extends AbstractOperator {
// 添加元素到有序集合中
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer zAdd(String key, String[] vals, double[] scores) {
// 如果值数组为空或长度为0,返回0
if (vals == null || vals.length == 0) return 0;
// 如果分数数组为空或长度为0,返回0
if (scores == null || scores.length == 0) return 0;
// 如果值数组和分数数组长度不一致,抛出运行时异常
if (vals.length != scores.length) throw new RuntimeException("vals和scores的长度必须相同");
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
// 如果缓存中没有该键,创建一个新的有序集合并放入缓存
entry = new CacheEntry<>(new LinkedHashSet<>());
map.put(key, entry);
}
// 获取当前键对应的有序集合
LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry> exist = entry.getValue();
// 将所有值和对应的分数添加到有序集合中
for (int i = 0; i < vals.length; i++) {
exist.add(new ZSetEntry(vals[i], scores[i]));
}
// 返回有序集合的大小
return exist.size();
}
// 获取有序集合的基数(元素数量)
public Integer zCard(String key) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0;
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<?> entry = map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<?> exist = (LinkedHashSet<?>) entry.getValue();
// 返回有序集合的大小
return exist.size();
}
// 计算分数在指定范围内的元素数量
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer zCount(String key, double min, double max) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0;
// 如果最小值大于最大值,抛出运行时异常
if (min > max) throw new RuntimeException("min必须小于max");
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry> exist = entry.getValue();
// 计算分数在指定范围内的元素数量
return (int) exist.stream()
.filter(x -> x.getScore() >= min && x.getScore() <= max)
.count();
}
// 获取指定元素的分数
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Double zScore(String key, String val) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null;
// 如果值为空,返回null
if (val == null) return null;
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry> exist = entry.getValue();
// 查找并返回指定元素的分数
return exist.stream()
.filter(x -> x.getValue().equals(val))
.map(ZSetEntry::getScore)
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
// 获取指定元素的排名
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer zRank(String key, String val) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return -1;
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return -1;
LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry> exist = entry.getValue();
// 获取指定元素的分数
Double source = zScore(key, val);
if (source == null) return -1;
// 计算并返回比指定元素分数小的元素数量,即排名
return (int) exist.stream().filter(x -> x.getScore() < source).count();
}
// 从有序集合中移除指定元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Integer zRem(String key, String[] vals) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0;
// 从缓存中获取当前键对应的有序集合
CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>> entry = (CacheEntry<LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry>>) map.get(key);
if (entry == null) return 0;
LinkedHashSet<ZSetEntry> exist = entry.getValue();
// 如果值数组为空,返回0;否则,移除指定元素并返回移除的数量
return vals == null ? 0 : (int) Arrays.stream(vals)
.map(x -> exist.removeIf(y -> y.getValue().equals(x)))
.filter(x -> x)
.count();
}
}
用 CacheEntry<String> 进行存储
public class StringOperator extends AbstractOperator {
// 获取指定键的值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String get(String key) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return null;
// 从缓存中获取键对应的条目
CacheEntry<String> cacheEntry = (CacheEntry<String>) map.get(key);
// 条目不存在则返回 null
if (cacheEntry == null) return null;
// 返回条目中的值
return cacheEntry.getValue();
}
// 设置指定键的值
public void set(String key, String value) {
// 将新的缓存条目放入缓存中
map.put(key, new CacheEntry<>(value));
}
// 获取指定键的值的长度
public Integer strlen(String key) {
// 检查键是否无效
if (checkInvalid(key)) return 0;
// 获取键的值,如果值为 null 则长度为 0
return get(key) == null ? 0 : get(key).length();
}
// 获取多个键的值
public String[] mGet(String... keys) {
// 如果键数组为 null,则返回空数组
if (keys == null) return new String[0];
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历所有键
for (String key : keys) {
// 如果键有效,则获取其值并添加到返回列表中
if (!checkInvalid(key)) {
ret.add(this.get(key));
}
}
// 将列表转换为数组并返回
return ret.toArray(new String[0]);
}
// 设置多个键的值
public void mSet(String[] keys, String[] vals) {
// 如果键数组为 null 或长度为 0,则直接返回
if (keys == null || keys.length == 0) return;
// 遍历所有键和对应的值,逐个设置
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
set(keys[i], vals[i]);
}
}
// 将指定键的值递增 1
public int incr(String key) {
// 获取键的值
String str = get(key);
int val = 0;
try {
// 如果值不为 null,则将其解析为整数
if (str != null) {
val = Integer.parseInt(str);
}
// 值递增 1
val++;
// 将新值设置回缓存中
set(key, String.valueOf(val));
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
// 如果值无法解析为整数,则抛出异常
throw nfe;
}
// 返回递增后的值
return val;
}
// 将指定键的值递减 1
public int decr(String key) {
// 获取键的值
String str = get(key);
int val = 0;
try {
// 如果值不为 null,则将其解析为整数
if (str != null) {
val = Integer.parseInt(str);
}
// 值递减 1
val--;
// 将新值设置回缓存中
set(key, String.valueOf(val));
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
// 如果值无法解析为整数,则抛出异常
throw nfe;
}
// 返回递减后的值
return val;
}
}
在 Redis 中执行 Lua 脚本通常使用EVAL或EVALSHA命令。以下是如何在 Redis 中执行 Lua 脚本的示例:
EVAL命令用于执行 Lua 脚本。它的基本语法如下:
EVAL script numkeys key [key ...] arg [arg ...]
script是 Lua 脚本的内容。numkeys是键的数量。key [key ...]是键列表。arg [arg ...]是参数列表。
Lua 脚本:共3个,1个是简单的 Set 命令、1个是简单的先 exists 再 get 命令,1个是原子操作,先 get 比较大小,再mset更新值
--[[
脚本说明:基于逻辑删除数据
脚本入参:eval/evalsha 脚本内容/sha1 1 keyName
脚本返回值:返回OK
--]]
local dk = '{'..KEYS[1]..'}d'
redis.call("set",dk,1)
return "OK"
--[[
脚本说明:基于获取数据,如果数据被逻辑删除则返回nil
脚本入参:eval/evalsha 脚本内容/sha1 1 keyName
脚本返回值:返回数据项
--]]
local dk = '{'..KEYS[1]..'}d'
if(redis.call('exists', dk)==1) then
return nil
else
return redis.call("get",KEYS[1])
end
--[[
脚本说明:基于版本更新数据,如果版本小于等于当前版本则不处理,如果写入数据则同时清理逻辑删除标记
脚本入参:eval/evalsha 脚本内容/sha1 1 keyName newVersion newValue
脚本返回值:更新成功则返回OK,否则返回nil
--]]
local dk = '{'..KEYS[1]..'}d'
local vk = '{'..KEYS[1]..'}v'
if(redis.call('exists', vk)==1) then
local ov = redis.call("get",vk)
if (tonumber(ov) < tonumber(ARGV[1])) then
redis.call("mset",vk,ARGV[1],KEYS[1],ARGV[2])
redis.call("del",dk)
return "OK"
end
else
redis.call("mset",vk,ARGV[1],KEYS[1],ARGV[2])
redis.call("del",dk)
return "OK"
end
return nil
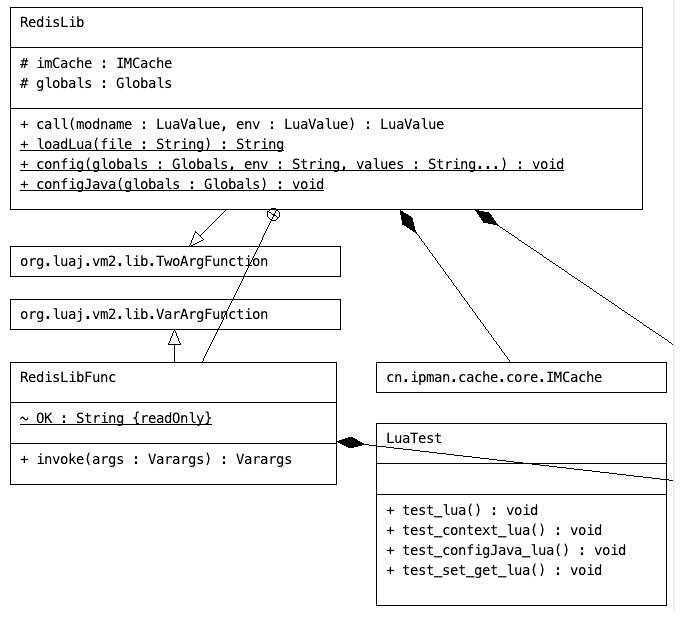
通过 RedisLib类读取 Lua 脚本,再通过 LuaTest类 进行单元测试,目标是查看是否能正常解析 Lua脚本,并调用上述 IMCache类 执行指令操作,如:GET、SET等等
RedisLib类 主要干2件事,1是加载 Lua脚本到内存中。2是通过TwoArgFunction的call方法 调用 IMCache 执行具体的操作指令,如:GET、SET等
/**
* RedisLib 类用于将 Redis 命令集成到 Lua 环境中
*/
public class RedisLib extends TwoArgFunction {
// Lua 全局变量
protected Globals globals;
// IMCache 实例,用于缓存操作
protected IMCache imCache = new IMCache();
@Override
public LuaValue call(LuaValue modname, LuaValue env) {
// 初始化全局变量
globals = env.checkglobals();
// 创建一个新的 Lua 表
LuaTable redis = new LuaTable();
// 在表中设置 "call" 方法为 RedisLibFunc
redis.set("call", new RedisLibFunc());
// 将 redis 表设置到 Lua 环境中
env.set("redis", redis);
// 将 redis 表加载到 Lua 包中
env.get("package").get("loaded").set("redis", redis);
return redis;
}
// 内部类,用于实现具体的 Redis 命令
class RedisLibFunc extends VarArgFunction {
// 常量 OK 表示操作成功
static final String OK = "OK";
@Override
public Varargs invoke(Varargs args) {
// 获取参数数量
int n = args.narg();
// 获取命令、键和值
String cmd = args.arg(1).toString();
String key = args.arg(2).toString();
String value = n > 2 ? args.arg(3).toString() : null;
// 根据命令执行相应操作
if ("SET".equalsIgnoreCase(cmd)) {
imCache.set(key, value);
return valueOf(OK);
} else if ("GET".equalsIgnoreCase(cmd)) {
return valueOf(imCache.get(key));
} else if ("DEL".equalsIgnoreCase(cmd)) {
return valueOf(imCache.del(key));
} else if ("MSET".equalsIgnoreCase(cmd)) {
for (int i = 2; i < n; i += 2) {
imCache.set(args.arg(i).toString(), args.arg(i + 1).toString());
}
return valueOf((n - 1) / 2);
} else if ("EXISTS".equalsIgnoreCase(cmd)) {
return valueOf(imCache.exists(key));
}
return valueOf(OK);
}
}
// 加载 Lua 脚本文件
public static String loadLua(String file) {
return Strings.join(IOUtil.readLines(Objects.requireNonNull(RedisLib.class.getResourceAsStream(file))), '\n');
}
// 配置 Lua 全局变量
public static void config(Globals globals, String env, String... values) {
LuaValue[] array = new LuaValue[values.length];
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
array[i] = LuaValue.valueOf(values[i]);
}
globals.set(env, LuaValue.listOf(array));
}
// 配置 Java 打印功能到 Lua 环境
public static void configJava(Globals globals) {
globals.set("printJava", new VarArgFunction() {
@Override
public Varargs invoke(Varargs args) {
int n = args.narg();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.println(args.arg(i).toString());
}
return NIL;
}
});
}
}
Lua脚本测试类如下:
/**
* LuaTest 类用于测试 Lua 脚本在 Java 环境中的执行
*/
public class LuaTest {
@Test
public void test_lua() {
// 初始化 Lua 全局环境
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
// 加载并执行简单的 Lua 脚本,返回 1
LuaValue script = globals.load("return 1");
LuaValue value = script.call();
// 验证脚本返回值是否为 1
assertEquals(1, value.toint());
// 加载并执行 Lua 脚本,使用 string.match 匹配字符串
LuaValue script2 = globals.load("local f,v = string.match('123:abcd', '(%d+):(%a+)') return {f,v}");
LuaValue value2 = script2.call();
// 验证返回值是否为表
assertTrue(value2.istable());
LuaTable table = (LuaTable) value2;
// 验证表的长度是否为 2
assertEquals(2, table.length());
// 验证表中的第一个值是否为 "123"
LuaValue f = table.get(1);
assertEquals("123", f.toString());
// 验证表中的第二个值是否为 "abcd"
LuaValue v = table.get(2);
assertEquals("abcd", v.toString());
}
@Test
public void test_context_lua() {
// 初始化 Lua 全局环境
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
// 创建 LuaValue 数组并设置到全局变量 KEYS
LuaValue[] array = new LuaValue[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
array[i] = LuaValue.valueOf("k" + i);
}
globals.set("KEYS", LuaValue.listOf(array));
// 加载并执行 Lua 脚本,返回 KEYS[1] 的值
LuaValue script = globals.load("return KEYS[1]");
LuaValue value = script.call();
// 验证返回值是否为 "k0"
assertEquals("k0", value.toString());
}
@Test
public void test_configJava_lua() {
// 初始化 Lua 全局环境
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
// 配置 Java 打印功能到 Lua 环境
RedisLib.configJava(globals);
// 设置 KEYS 和 ARGV 全局变量
RedisLib.config(globals, "KEYS", "tag1");
RedisLib.config(globals, "ARGV", "101", "value101");
// 加载并执行 Lua 脚本,打印 KEYS 和 ARGV 的值并返回 ARGV 的长度
LuaValue script = globals.load("printJava('#KEYS='..#KEYS,'ARGV[1]='..ARGV[1],'ARGV[2]='..ARGV[2]) return #ARGV");
LuaValue value = script.call();
// 验证返回值是否为 "2"
assertEquals("2", value.toString());
}
@Test
public void test_set_get_lua() {
// 1. 初始化 Lua 全局环境
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
// 2. 加载 RedisLib 库
globals.load(new RedisLib());
// 3. 设置 Lua 全局变量 KEYS 和 ARGV
RedisLib.config(globals, "KEYS", "tagA");
RedisLib.config(globals, "ARGV", "1", "value01");
// 4. 加载并执行设置键值的 Lua 脚本
LuaValue setScript = globals.load(RedisLib.loadLua("/lua/tag_set.lua"));
LuaValue setValue = setScript.call();
// 验证返回值是否为 "OK"
assertEquals("OK", setValue.toString());
// 5. 加载并执行获取键值的 Lua 脚本
LuaValue getScript = globals.load(RedisLib.loadLua("/lua/tag_get.lua"));
LuaValue getValue = getScript.call();
// 验证返回值是否为 "value01"
assertEquals("value01", getValue.toString());
// 6. 修改 ARGV 的值但保持版本不变,执行设置脚本并验证返回值是否为 nil
RedisLib.config(globals, "ARGV", "1", "value02");
setValue = setScript.call();
assertTrue(setValue.isnil());
// 7. 修改 ARGV 的值和版本,执行设置脚本并验证返回值是否为 "OK"
RedisLib.config(globals, "ARGV", "2", "value02");
setValue = setScript.call();
assertEquals("OK", setValue.toString());
// 8. 执行获取脚本并验证返回值是否为 "value02"
getValue = getScript.call();
assertEquals("value02", getValue.toString());
}
}
String类型

Hash类型

List类型

Set类型

ZSet类型

关于Jedis配置和工具类的代码就不展开了,下面是核心的测试代码,启动cache server后通过jedis客户端进行测试
@SpringBootTest(classes = {CacheTestJedisApplication.class})
class CacheTestJedisApplicationTests {
static ApplicationContext context1;
@Autowired
JedisUtil jedisUtil;
@BeforeAll
@SneakyThrows
static void init() {
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
System.out.println(" ============ 6379 ============= ");
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
System.out.println(" ================================ ");
context1 = SpringApplication.run(CacheServerApplication.class);
}
@Test
void test_set_get() {
jedisUtil.set("test", "test", 0);
Assertions.assertEquals("test", jedisUtil.get("test", 0));
Assertions.assertEquals(1L, jedisUtil.del(0, "test"));
}
@Test
void test_set_get_expire() throws InterruptedException {
jedisUtil.set("test", "test", 0);
jedisUtil.expire("test", 1, 0);
Thread.sleep(2000L);
Assertions.assertNull(jedisUtil.get("test", 0));
}
@AfterAll
static void destroy() {
System.out.println(" =========== close spring context ======= ");
SpringApplication.exit(context1, () -> 1);
}
}

以上只是一个单机版本、没有HA的简易RedisLike版本,主要是能够加深对Redis缓存使用及原理的理解。