diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 9d18964..00e4370 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,9 +1,16 @@
-# cache-man 简易Cache框架设计概述
+# 简易Cache框架设计概述(RedisLike)
## 引言
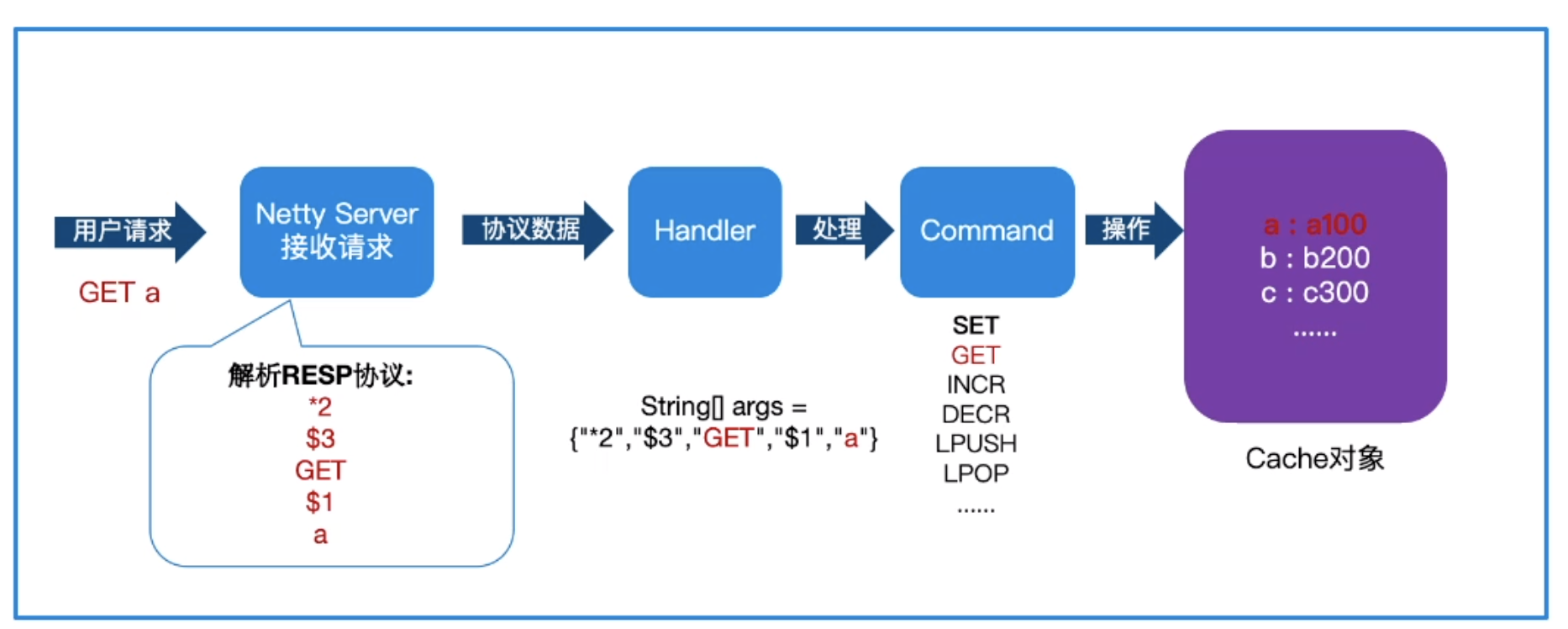
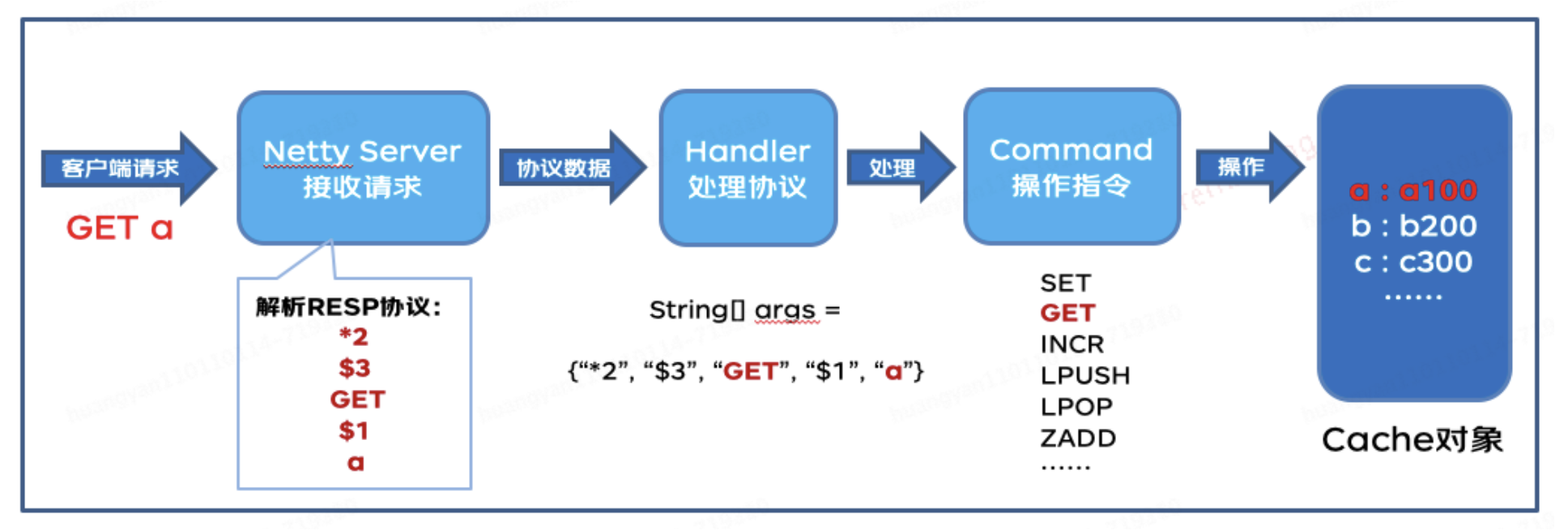
-在现代软件开发中,缓存系统作为提升应用性能的关键组件,其重要性不言而喻。`cache-man`旨在从零开始构建一个简易的Java版Redis-like缓存框架,不仅能够加深对缓存原理的理解,而且能灵活应用于实际项目中,提高数据访问速度和系统响应效率。本框架设计结合了高性能网络编程库Netty与Redis协议,以实现轻量级、高效的数据缓存解决方案。
-
+*以下只是一个非常简易的Redis版本,通过以下讲述能大致理解Redis执行原理,仅是用来学习和探讨。*
+
+
+
+在现代软件开发中,缓存系统作为提升应用性能的关键组件,其重要性不言而喻。从零开始构建一个简易的Java版Redis-like缓存框架,不仅能够加深对缓存原理的理解,而且能灵活应用于实际项目中,提高数据访问速度和系统响应效率。本框架设计结合了高性能网络编程库Netty与Redis协议,以实现轻量级、高效的数据缓存解决方案。
+
+
+
+
## 总体设计
@@ -11,9 +18,9 @@
1. **网络通信层**:基于**Netty**实现异步非阻塞的网络通信,处理客户端的连接、请求解析与响应发送。
2. **协议解析层**:实现**RESP协议解析器**,负责将接收到的网络数据包解析为可执行命令及参数。
-3. **命令处理器**:设计一系列命令处理器,对应Redis的五种基本数据结构(字符串、列表、集合、散列、有序集合)的操作。
+3. **命令处理器**:设计一系列命令处理器,对应**Redis的五种基本数据结构**(字符串、列表、集合、散列、有序集合)的操作。
4. **数据存储层**:采用内存存储机制,实现高效的数据读写操作。未来可扩展至磁盘或分布式存储。
-5. **Lua脚本支持**:集成Lua脚本引擎,允许用户提交Lua脚本进行复杂逻辑处理,进一步提升执行效率和灵活性。
+5. **Lua脚本支持**:集成**Lua脚本引擎**,允许用户提交Lua脚本进行复杂逻辑处理,进一步提升执行效率和灵活性。
### 核心特性
@@ -21,6 +28,8 @@
- **兼容性**:遵循Redis的RESP协议,易于对接现有Redis客户端。
- **灵活性**:支持基础数据类型及Lua脚本,满足多样化缓存需求。
+
+
## 核心功能实现
### 1. 网络功能(Netty实现)
@@ -39,12 +48,2034 @@
- **集合(Set)**:实现SADD/SMEMBERS/SREM等命令。
- **散列(Hash)**:实现HSET/HGET/HDEL等命令。
- **有序集合(Sorted Set)**:实现ZADD/ZRANGE/ZREM等命令。
+- **通用指令**:实现EXPIRE/TTL/EXISTS等命令
### 4. Lua脚本支持
- **脚本加载与执行**:提供接口接收Lua脚本,通过Lua引擎执行并返回结果。
-## 总结
-`cache-man`项目是一个旨在深入理解缓存机制并实践高性能网络编程的Java框架。通过整合Netty与自研的Redis协议处理逻辑,框架实现了快速响应、高并发的缓存服务。不仅覆盖了Redis的基本数据结构操作,还加入了Lua脚本支持,以增强处理复杂逻辑的能力。此框架不仅适合作为学习工具,也为开发者提供了定制化缓存解决方案的基础框架,促进在实际项目中的创新应用。
+
+
+
+
+# 代码实现概述
+
+## 安装核心依赖
+
+1. **Spring Boot**:用于管理 Cache 框架的生命周期,通过`ApplicationListener`初始化或优雅地关闭`CacheServer`。
+2. **Netty 4**:作为`CacheServer`,监听 6379 端口以模拟 Redis 服务,负责 Redis RESP 协议的编解码。
+3. **luaj-jse**:作为 Lua 解释器,仅用于模拟执行`EVAL`命令,通过 Lua 脚本操作`CacheServer`的具体指令。
+
+```
+
+ org.springframework.boot
+ spring-boot-starter
+
+
+
+ io.netty
+ netty-all
+ 4.1.104.Final
+
+
+
+ org.luaj
+ luaj-jse
+ 3.0.1
+ test
+
+```
+
+
+
+## CacheServer生命周期设计
+
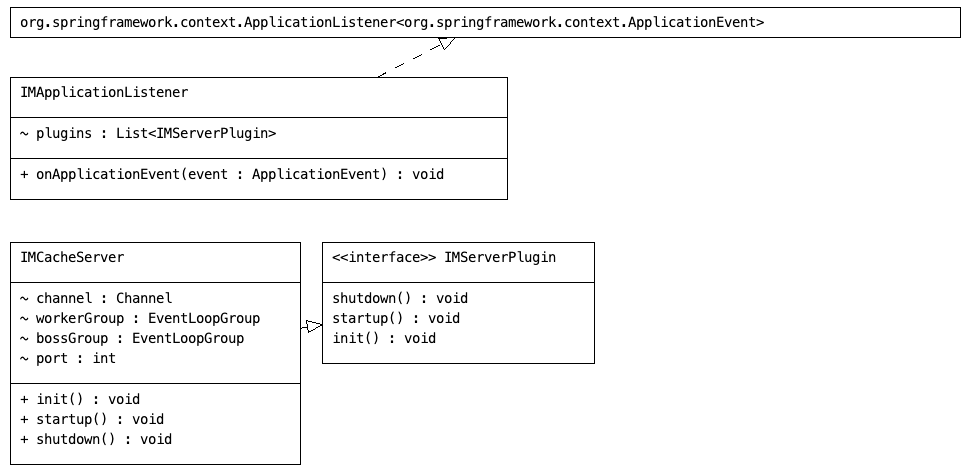
+IMApplicationListener:插件入口点类,负责在Spring应用启动和关闭时管理插件的生命周期
+
+IMServerPlugin:插件接口的用途,即定义Netty服务器的生命周期
+
+IMCacheServer:实现了IMServerPlugin接口,用来实现初始化、启动、关闭Netty
+
+
+
+首先,定义一个`IMServerPlugin`接口作为服务器插件
+
+```
+// IMServerPlugin:插件接口的用途,即定义Netty服务器的生命周期
+public interface IMServerPlugin {
+ void init(); // 初始化netty
+ void startup(); // 启动netty
+ void shutdown(); // 关停netty
+}
+```
+
+
+
+将实现`Server`接口的类注入到 Spring 容器中,使用 Netty 模拟 Redis 启动一个 TCP 服务,监听端口为 6379(编解码和处理器的细节将在后续讲解)。
+
+```
+/**
+ * 实现了IMServerPlugin接口,用来实现初始化、启动、关闭Netty
+ */
+@Component
+public class IMCacheServer implements IMServerPlugin {
+
+ // 服务器端口号
+ int port = 6379;
+ // boss 线程组,用于接受客户端连接
+ EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
+ // worker 线程组,用于处理客户端IO操作
+ EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
+ // 服务器通道
+ Channel channel;
+
+ @Override
+ public void init() {
+ // 初始化 boss 线程组,指定线程工厂
+ bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new DefaultThreadFactory("redis-boss"));
+ // 初始化 worker 线程组,指定线程工厂
+ workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16, new DefaultThreadFactory("redis-work"));
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public void startup() {
+ try {
+ // 创建 ServerBootstrap 对象,用于配置服务器
+ ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
+ b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 连接队列大小
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // 关闭Nagle,即时传输
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 支持长连接
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true) // 共享端口
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 32 * 1024) // 操作缓冲区的大小
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32 * 1024) // 发送缓冲区的大小
+ .childOption(EpollChannelOption.SO_REUSEPORT, true)
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
+ .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
+
+ // 配置 ServerBootstrap
+ b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
+ .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
+ .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
+ @Override
+ protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
+ // 添加解码器和处理器到管道
+ ch.pipeline().addLast(new IMCacheDecoder());
+ ch.pipeline().addLast(new IMCacheHandler());
+ }
+ });
+
+ channel = b.bind(port).sync().channel();
+ System.out.println("开启netty redis服务器,端口为 " + port);
+ channel.closeFuture().sync();
+ } catch (Exception e) {
+ throw new RuntimeException(e);
+ } finally {
+ bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
+ workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
+ }
+ }
+
+ // clonse server
+ @Override
+ public void shutdown() {
+ if (this.channel != null) {
+ this.channel.close();
+ this.channel = null;
+ }
+ if (this.bossGroup != null) {
+ this.bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
+ this.bossGroup = null;
+ }
+ if (this.workerGroup != null) {
+ this.workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
+ this.workerGroup = null;
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+通过`Spring事件机制` 注入所有`IMServerPlugin`实现,并监听应用的启动和停止事件。在应用启动后,初始化并启动Netty服务
+
+```
+/**
+ * 插件入口点类,负责在Spring应用启动和关闭时管理插件的生命周期
+ */
+@Component
+public class IMApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
+
+ // 自动注入所有实现了 IMServerPlugin 接口的插件
+ @Autowired
+ List plugins;
+
+ /**
+ * 处理应用程序事件的方法。
+ *
+ * @param event 应用程序事件
+ */
+ @Override
+ public void onApplicationEvent(@NonNull ApplicationEvent event) {
+ // 如果事件是 ApplicationReadyEvent(应用启动完成事件)
+ if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent) {
+ // 遍历所有插件,依次初始化并启动
+ for (IMServerPlugin plugin : plugins) {
+ plugin.init(); // 初始化插件
+ plugin.startup(); // 启动插件
+ }
+ // 如果事件是 ContextClosedEvent(应用上下文关闭事件)
+ } else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
+ // 遍历所有插件,依次关闭
+ for (IMServerPlugin plugin : plugins) {
+ plugin.shutdown(); // 关闭插件
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+下面测试下Server启动后, 用 **redis-cli** 或 **telnet 127.0.0.1 6379** 去连接测试
+
+redis-cli
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## CacheServer实现编解码
+
+由于 Netty 服务器本质上处理的是字节数据(`Byte`),为了便于后续程序处理,需要自定义解码器将字节数据转换为字符串。虽然 Netty 本身提供了对 Redis 的默认编解码实现(如 `RedisDecoder`、`RedisEncoder`),但编写自定义解码器有助于更好地理解和控制数据处理过程。
+
+
+
+IMCacheDecoder:将 Netty 接收到的二进制流(ByteBuf in)解码为字符串,并输出到管道(List