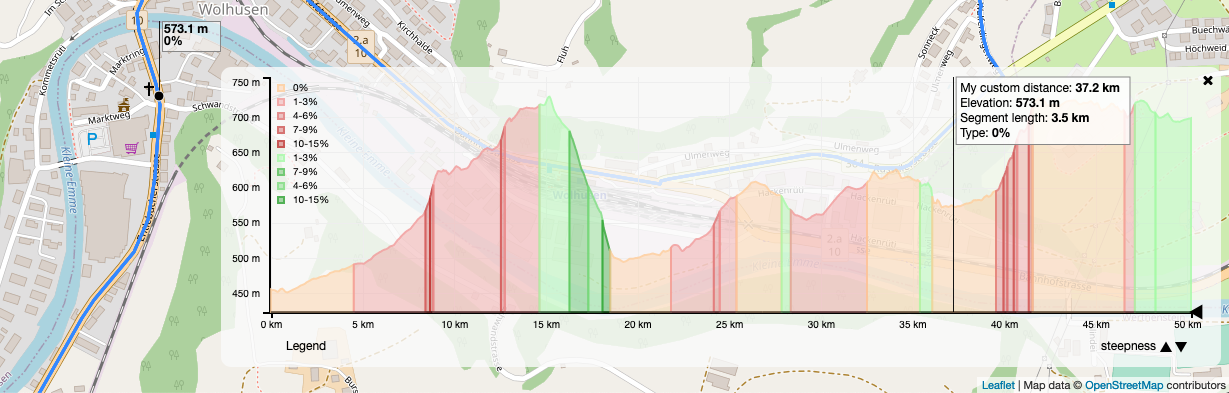
This plugin is inspired by MrMufflon/Leaflet.Elevation. You may use this plugin to view an interactive height profile of linestring segments using d3js. The input data may consist of different types of attributes you wish to display.
Supported Browsers:
- Chrome
- Firefox
- Opera
Prerequisite: node (version >=8)
or use nvm to install specific node versions
Install Leaflet.Heightgraph and dependencies with npm.
npm install leaflet.heightgraph
You can import the required libraries in the head of your index.html file
<link rel="stylesheet" href="node_modules/leaflet/dist/leaflet.css" />
<script src="node_modules/leaflet/dist/leaflet.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="src/L.Control.Heightgraph.css"/>
<script type="text/javascript" src="src/L.Control.Heightgraph.js"></script>When using NPM you can require all needed libraries like this.
require('leaflet');
require('leaflet.heightgraph');
After importing Leaflet correctly, ES 6 Module import is possible as well:
<script type="module">
import 'leaflet.heightgraph'
</script>The stylesheet can alternatively be imported in a style tag:
<style>
@import "../node_modules/leaflet.heightgraph/dist/L.Control.Heightgraph.min.css";
</style>Initialize the heightgraph, add it to your Leaflet map object and add your Data to the heightgraph object.
let hg = L.control.heightgraph();
hg.addTo(map);
hg.addData(geojson);
L.geoJson(geojson).addTo(map);Input data has to be of type GeoJSON-Format. This must consist of feature collection(s) corresponding to a certain attribute which could be e.g. surface or gradient information.
Each FeatureCollection comprises a certain attribute in its properties
(e.g. 'summary': 'steepness') and has a list of LineString features.
These should have coordinates including height values and the attributeType
which corresponds to the certain type of attribute within this segment
(in this case it could be an index of steepness) declared in its properties.
Notice that the list of coordinates has to start with the last coordinate
of the previous LineString.
const FeatureCollections = [{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[8.6865264, 49.3859188, 114.5],
[8.6864108, 49.3868472, 114.3],
[8.6860538, 49.3903808, 114.8]
]
},
"properties": {
"attributeType": "3"
}
}, {
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[8.6860538, 49.3903808, 114.8],
[8.6857921, 49.3936309, 114.4],
[8.6860124, 49.3936431, 114.3]
]
},
"properties": {
"attributeType": "0"
}
}],
"properties": {
"Creator": "OpenRouteService.org",
"records": 2,
"summary": "Steepness"
}
}];These additional options can be set to customize your heightgraph. Use them by passing an options object to the heightgraph during creation e.g.:
let options = {
position: "topleft"
}
let hg = L.control.heightgraph(options);You can choose between "bottomright", "bottomleft", "topright" and "topleft"
for the position on the map.
default: position: "bottomright"
The width of the expanded heightgraph display in pixels.
default: width: 800
The height of the expanded heightgraph display in pixels.
default: height: 280
The margins define the distance between the border of the heightgraph
and the actual graph inside. You are able to specify margins for top,
right, bottom and left in pixels.
default:
margins: {
top: 10,
right: 30,
bottom: 55,
left: 50
}
Boolean value that defines if the heightgraph should be expanded on creation.
default: true
Boolean value that defines if the expand controls (i.e. toggle and close) should be visible. To be set to false when the heightgraph is embedded in another component and that controls when and how the heightgraph is expanded.
default: true
Function to be called if the heightgraph is expanded or reduced. The state of
the heightgraph is passed as an argument. It is true when expanded and
false when reduced.
default: undefined
example:
expandCallback: function(expanded){
console.log("Expanded: " + expanded)
}You may add a mappings object to customize the colors and labels in the height graph.
Without adding custom mappings the segments and labels within the graph will be displayed in random colors.
Each key of the object must correspond to the summary key in properties within the FeatureCollection.
default: undefined
Example:
colorMappings.Steepness = {
'3': {
text: '1-3%',
color: '#F29898'
},
'0': {
text: '4-6%',
color: '#E07575'
}
};You can customize the highlight style when using the horizontal line to
find parts of the route above an elevation value.
Use any Leaflet Path options
as value of the highlightStyle parameter.
default: highlightStyle:{color: 'red'}
Example:
highlightStyle = {
weight: 10,
opacity: 0.8,
color: 'orange'
}Allows customizing the style of the height graph.
You may specify the element presentation attributes in the form of a JavaScript object.
Note that in case of conflict the mappings attributes take precedence over the graphStyle attributes.
default: graphStyle: {}
Example:
graphStyle: {
opacity: 0.8,
'fill-opacity': 0.5,
'stroke-width': '2px'
};You can change the labels of the heightgraph info field by passing translations
for distance, elevation, segment_length, type and legend.
default:
translation: {
distance: "Distance",
elevation: "Elevation",
segment_length: "Segment length",
type: "Type",
legend: "Legend"
}
Overwrite automatic tick handling for x axis and specify the tick frequency in the x axis of the graph. Corresponds approximately to
2 to the power of value ticks.
default: xTicks: 3
Overwrite automatic tick handling for y axis and specify the tick frequency in the y axis of the graph. Corresponds approximately to
2 to the power of value ticks.
default: yTicks: 3
The following methods are available on a created L.control.heightgraph instance,
represented by hg in the examples.
Used together with mapMouseoutHandler.
Takes a mousemove event as input hg.mapMousemoveHandler(event) to show
the current position on the heightgraph when hovering over the respective
geometry on the map.
The marker on the map can be disabled by passing an object with properties
showMapMarker:false as second argument. showMapMarker is true by default.
hg.mapMousemoveHandler(mousemoveEvent, {showMapMarker: false})Check example.js for an implementation example.
Used together with mapMousemoveHandler.
Responsible for removing the created markers again.
You can pass a timeout in milliseconds to delay the removal.
The default timeout is 1000.
hg.mapMouseoutHandler(0)Check example.js for an implementation example.
Use this to resize the heightgraph container including the graph to the
specified extent by passing an object including defined width and height
properties in pixel values:
hg.resize({width: 1000, height: 300})# clone the repository
$ git clone https://github.com/GIScience/Leaflet.Heightgraph.git
# install dependencies using a node-version >= 8
$ npm install
# start development server
$ npm startYou can create run configurations for different tasks:
- open
Run -> Edit Configurations... - click
+to add a new configuration and choose the npm template - give the Configuration a name e.g.
Dev - choose
startas command - press
OK
Debug jasmine tests with karma in WebStorm
- open
Run -> Edit Configurations... - click
+to add a new configuration and choose the karma template - give the Configuration a name e.g.
Test - press
OK
Run karma with coverage
- once you have a karma task configured just click the run with coverage button
- analyse coverage in Webstorm or Browser (open ./coverage/html/index.html)