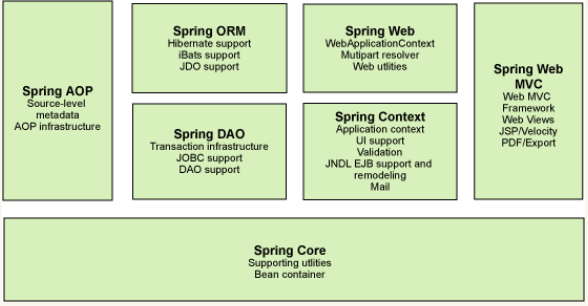
Spring是一个轻量级的开发框架,旨在提高开发人员的开发效率以及系统的可维护性。是为Java应用程序提供基础性服务的一套框架,目的是用于简化企业应用程序的开发,它使得开发者只需要关心业务需求。常见的配置方式有三种:基于XML配置,基于注解的配置,基于Java的配置。
- Spring Core:核心类库,提供IOC服务
- Spring Context:提供框架式的Bean访问方式,以及企业级功能;
- Spring AOP:AOP服务
- Spring DAO:对JDBC的抽象,简化了数据访问异常的处理
- Spring ORM:对现有的ORM框架的支持
- Spring Web:提供了基本的面向Web的综合特性,例如多方文件上传
- Spring MVC:提供面向Web应用的Model-View-Controller实现
在Spring中,那些组成应用程序的主体及由Spring IOC容器所管理的对象,被称之为bean。简单地讲,bean就是由IOC容器初始化、装配及管理的对象,除此之外,bean就与应用程序中的其他对象没有什么区别了。
一个java对象不一定是spring bean,但是spring bean一定是java对象,并且java对象没有生命周期,而spring bean是有生命周期的。
常见的有两种:singleton和prototype
1、singleton
容器初始化的时候创建,只会创建一次
2、prototype
获取bean的时候才会被创建,会创建多次
后面会专门对bean的生命周期进行更全面的分析。
beanDefinition是怎么被扫描进beanDefinitionMap中的?
首先看下面这段测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(App.class);
}然后进入AnnotationConfigAppcationContext的构造方法:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}在执行这个构造方法之前,会去执行父类GenricApplication的构造方法:
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}在该构造方法中,创建了一个DefaultListbleBeanFactory,那么就是说子类AnnotationConfigAppcationContext也会拥有父类的这个beanFactory。
回到它的构造方法,此时debug,代码还没执行完register(componentClasses)方法,此时的beanFactory中的beanDefinitionMap中会有如下beanDefinition:
这5个beanDefinition是spring开天辟地的5个beanDefinition(最新版本只有4个了,有一个已经过期),由spring放进beanDefinitionMap中。
当执行完register(componentClasses)方法后:
可以看到,此时多了一个beanDefinition叫app,它是我们自己定义的加了@ComponentScan注解的bean,通过构造函数传入。
接下来我们看实现了beanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类的执行时机。上面执行完register方法后,beanDefinition就被扫描进了beanDefinitonMap中,然后继续执行构造函数中的refresh方法。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}这个方法里面有12个核心方法,我们先来看invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)这个方法,通过它的名字可以看出是执行BeanFactoryPostProcessors(注意后面加了s,表示复数),当执行完这个方法后:
此时beanDefinitonMap中多了两个beanDefinition,y是加了@Component注解的类,另外一个是自定义实现了beanFactoryPostProcessors接口的类
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* 执行时机:扫描完成之后,也就是类变成BeanDefinition之后,在实例化之前
* @param beanFactory
* @throws BeansException
*/
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("-----beanFactoryPostProcessor-----");
}
}此时控制台输出:-----beanFactoryPostProcessor-----
**而其实将beanDefinition放入bdmap中的是这个方法中的第一个invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,它调用的是spring开天辟地5个bean中的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor重写的方法 **,具体会在后面的容器扫描原理中分析。
总结:调用invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors会执行以下步骤:
1、执行所有需要被执行的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,它会执行spring内置的子类BeanFactoryPostProcessor,完成了扫描ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(这是前面说的开天辟地的5个bd之一)
2、执行程序员提供的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
具体的实现和顺序见后面的扫描原理。
首先是BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* 在所有的 BeanDefinition 加载完成后,实例化 Bean 对象之前,提供修改 BeanDefinition 属性的机制
*
* @param beanFactory
* @throws BeansException
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}在 Spring 源码中有这样一段描述 Allows for custom modification of an application context's bean definitions,adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying bean factory. 其实也就是说这个接口是满足于在所有的 BeanDefinition 加载完成后,实例化 Bean 对象之前,提供修改 BeanDefinition 属性的机制。
BeanPostProcessor:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 在 Bean 对象执行初始化方法之前,执行此方法
*
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* 在 Bean 对象执行初始化方法之后,执行此方法
*
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}在 Spring 源码中有这样一段描述 Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.也就是提供了修改新实例化 Bean 对象的扩展点。