nTimetools is a suite of console tools developed to work with timestamps in Windows. NTFS stores timestamps with 100-nanosecond level of precision. However, most live response forensic tools as well as timestomping tools are only able to provide up to 1 second level of precision. nTimetools (n is short for nano) comprises 2 tools that allow both forensic analysts as well as red teamers to modify and verify file timestamps up to 100-nanosecond precision.
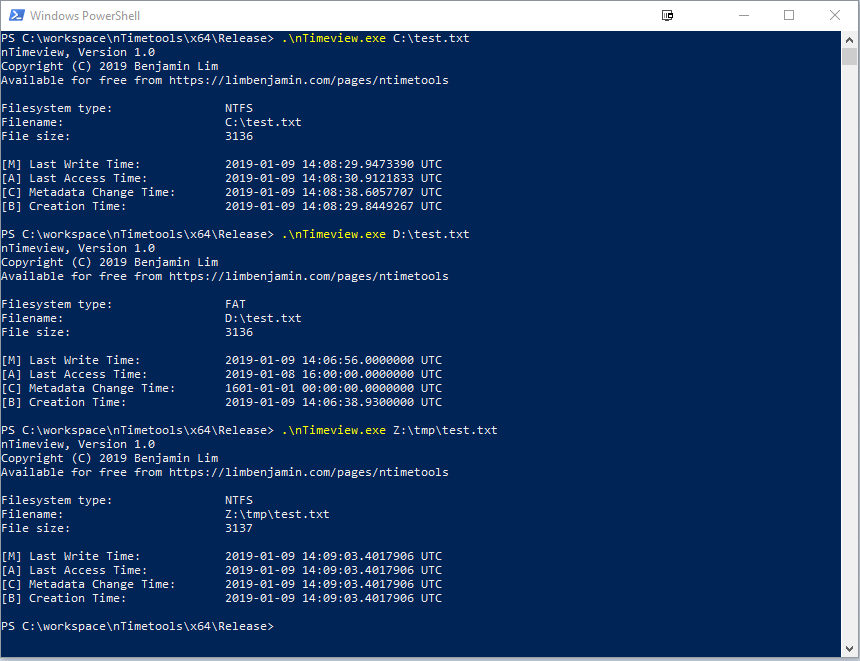
- nTimeview allows forensic analysts to view the MACB timestamps of files on a live system. It uses the undocumented NtQueryInformationFile API. As such, it works on NTFS/FAT and even mapped drives. It does not require privileged access. This is particularly useful in the case of mapped drives as the current user does not usually have privileged access on a mapped drive in enterprise settings. It is also oftentimes not possible to take the mapped drive offline due to other connected users.
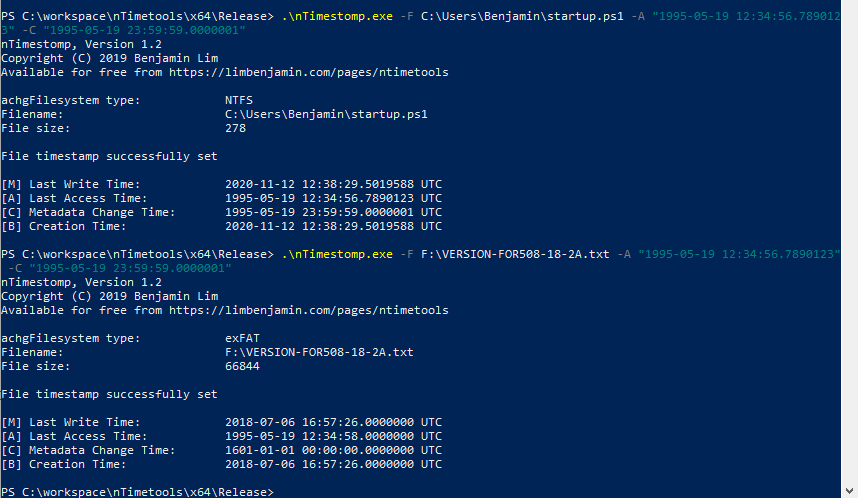
- nTimestomp allows red teamers to timestomp MACB timestamps of files with 100-nanosecond level precision. Forensic analysts are usually taught to spot 0s in the millisecond position as evidence that timestomping has occurred. nTimestomp will allow your files to blend in on cursory inspection. It uses the same undocumented NtSetInformationFile API which means privileged access is not neccessary and files on NTFS/FAT and mapped drives can also be timestomped.
The syntax for nTimestomp is nTimestomp.exe -F F:\VERSION-FOR508-18-2A.txt -M "1995-05-19 12:34:56.7890123" -A "1995-05-19 12:34:56.7890123" -C "1995-05-19 23:59:59.0000001" -B "1995-05-19 23:59:59.0000001" The separator for the nanoseconds portion is a dot and not a colon. The date format is YYYY-MM-DD. Filename is a required argument, any combination of -M -A -C -B is accepted, current timestamp will be retained if that argument is not specified.
FAT does not keep track of metadata change time, hence the null value. The difference in timestamps is due to the level of precision of FAT timestamps. Also, creation timestamps on mounted drives cannot be modified to due API limitations.
nTimeview_v1.0_64bit - SHA1() = 7b0506dca02e7a3dd9ba4fcbe4f4ff45008d31c8
nTimestomp_v1.2_64bit - SHA1() = 1175837865ab8282f1905b66c7417efdd8a56259
Joakim Schicht (jschicht) has an excellent set of tools out there, MftRcrd and SetMace, that work with timestamps of up to 100-nanosecond precision. These tools work in a different way. The raw device is mounted and the MFT is parsed and read from. The advantage of doing so is that $FILE_NAME timestamps can also be read. This allows a more in-depth check for signs of timestomping. However, the downside of using raw device mounting is that it will only work on NTFS filesystems and it requires privileged access. For SetMace, due to restrictions placed in recent version of Windows on writing to a raw device, it will only work on non system drives.
The software is distributed "as is". No warranty of any kind is expressed or implied. You use at your own risk. The author will not be liable for data loss, damages, loss of profits or any other kind of loss while using or misusing this software.
The Licensee is allowed to freely redistribute the software subject to the following conditions.
- The Software may be installed and used by the Licensee for any legal purpose.
- The Licensee will not charge money or fees for the software product, except to cover distribution costs.
- The Licensor retains all copyrights and other proprietary rights in and to the Software.
- Use within the scope of this License is free of charge and no royalty or licensing fees shall be paid by the Licensee.
Create an issue on github
nTimestomp v1.1 (10/02/19) - Modified help example to have only 7 digits for nanosecond field.
nTimestomp v1.2 (14/09/21) - Consistency in order of MACB arguments. Added flags for arguments.