Rafay is a SaaS-first Kubernetes Operations Platform (KOP) with enterprise-class scalability, zero-trust security and interoperability for managing applications across public clouds, data centers & edge.
See Rafay documentation to learn more about the platform and how to use it.
This document will walk you through installing Kubecost on a cluster that has been provisioned or imported using the Rafay controller. The steps below describe how to create and use a custom cluster blueprint via the Rafay Web Console. The entire workflow can also be fully automated and embedded into an automation pipeline using the RCTL CLI utility or Rafay REST APIs.
You have already provisioned or imported one or more Kubernetes clusters using the Rafay controller.
Under Integrations:
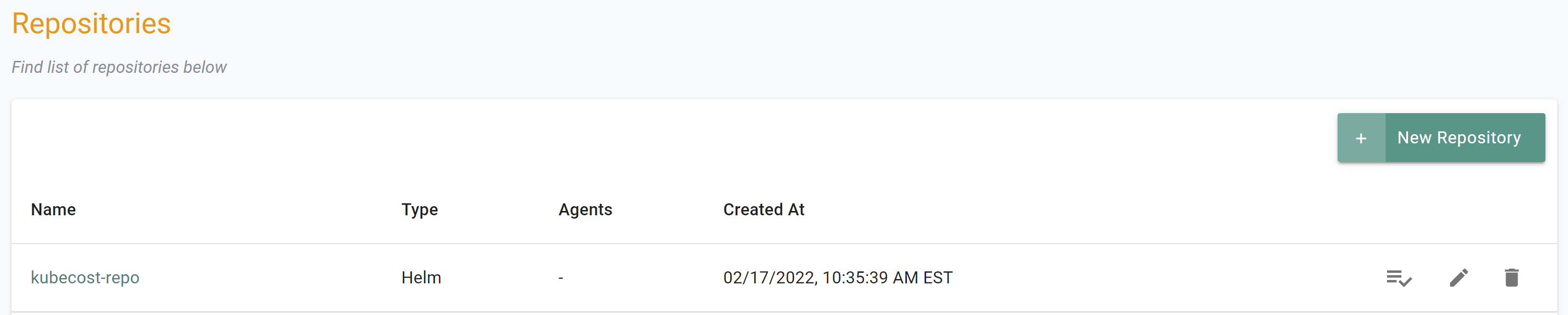
- Select Repositories and create a new repository named
kubecostof type Helm - Click Create
- Enter the endpoint value of
https://kubecost.github.io/cost-analyzer/ - Click Save
You'll need to override the default values.yaml file. Create a new file called kubecost-custom-values.yaml with the following content:
# Custom values for Kubecost
reporting:
valuesReporting: false
# Replace token with the value you get from kubecost.com/install
# after entering your email address
kubecostToken: 'token_string'- Login into the Rafay Web Console and navigate to your Project as an Org Admin or Infrastructure Admin
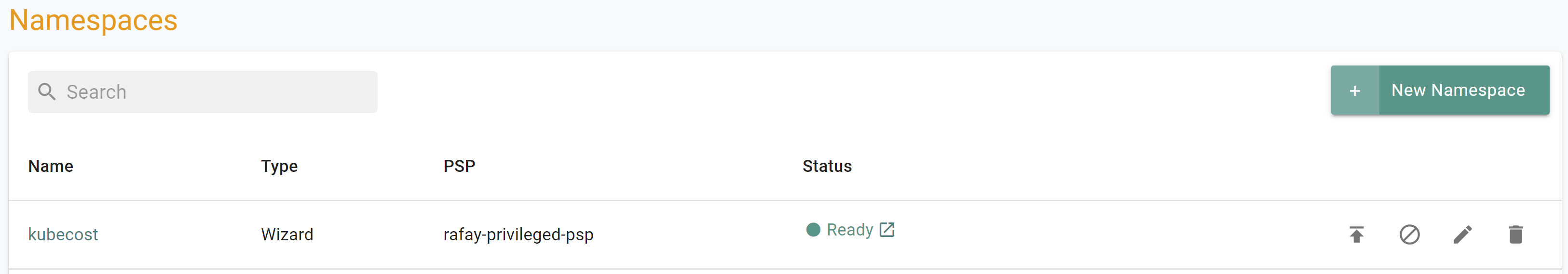
- Under Infrastructure, select Namespaces and create a new namespace called
kubecost, and select type Wizard
- Click Save & Go to Placement
- Select the cluster/s that the namespace will be added to. Select Save & Go To Publish
- Click Publish to publish the namespace to the selected cluster(s)
- Once the namespace has been published, Click Exit
- Under Infrastructure, select Clusters
- Click on the
kubectlbutton on the cluster to open a virtual terminal - Verify that the
kubecostnamespace has been created by running the following command:
$ kubectl get ns kubecost
NAME STATUS AGE
kubecost Active 44mFrom the Web Console:
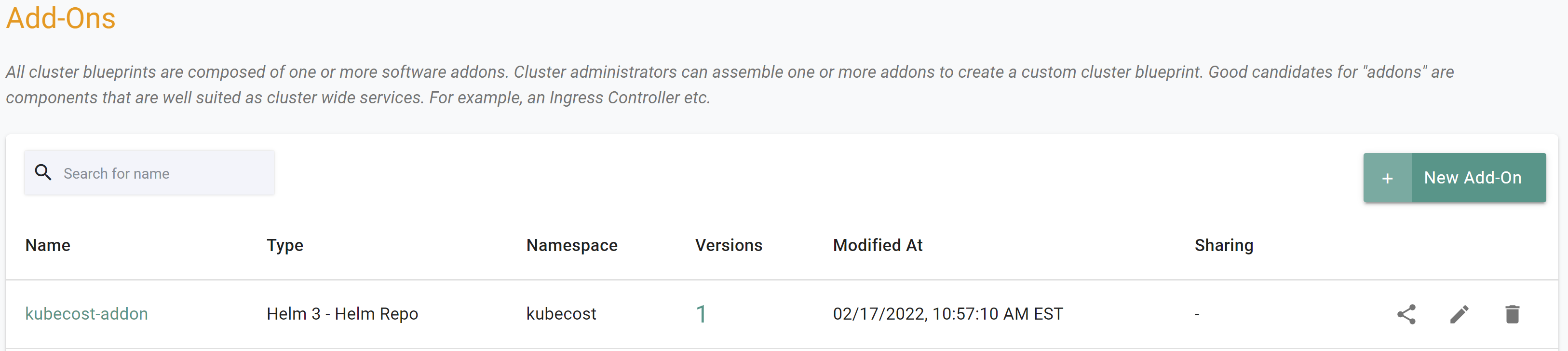
- Select Add-ons and Create a new add-on called
kubecost - Select Bring your own
- Select
Helm 3for type - Select Pull files from repository
- Select
Helmfor the repository type - Select
kubecostfor the namespace - Click Create
- Create a new version of the add-on
- Select New Version
- Provide a version name such as
v1 - Select
kubecostfor the repository - Enter
cost-analyzerfor the chart name - Upload the
kubecost-custom-values.yamlfile that was previously created - Click Save Changes
Once you've created the Kubecost add-on, use it in assembling a custom cluster blueprint. You can add other add-ons to the same custom blueprint.
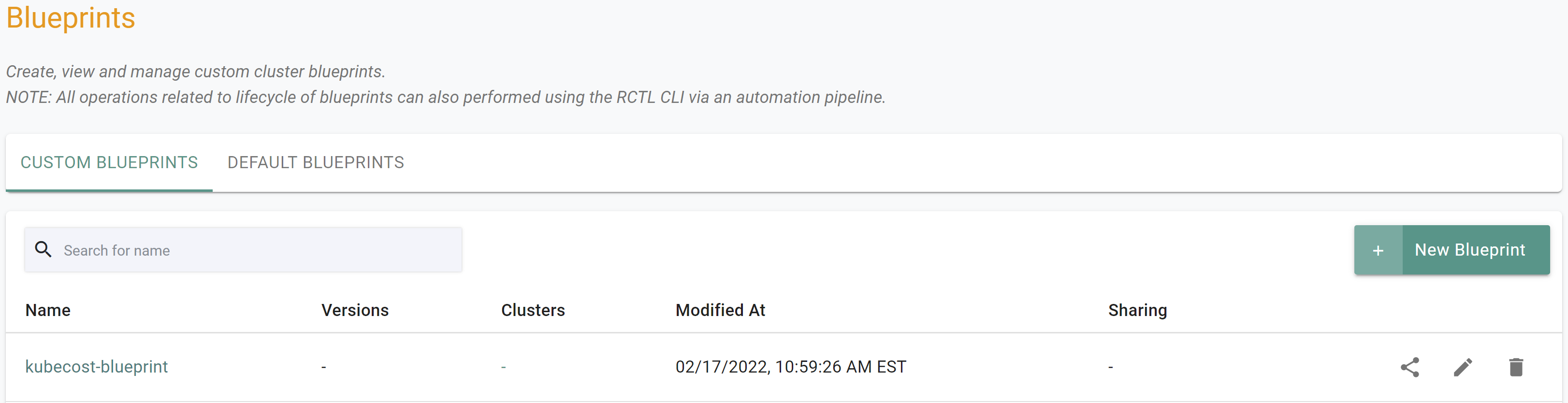
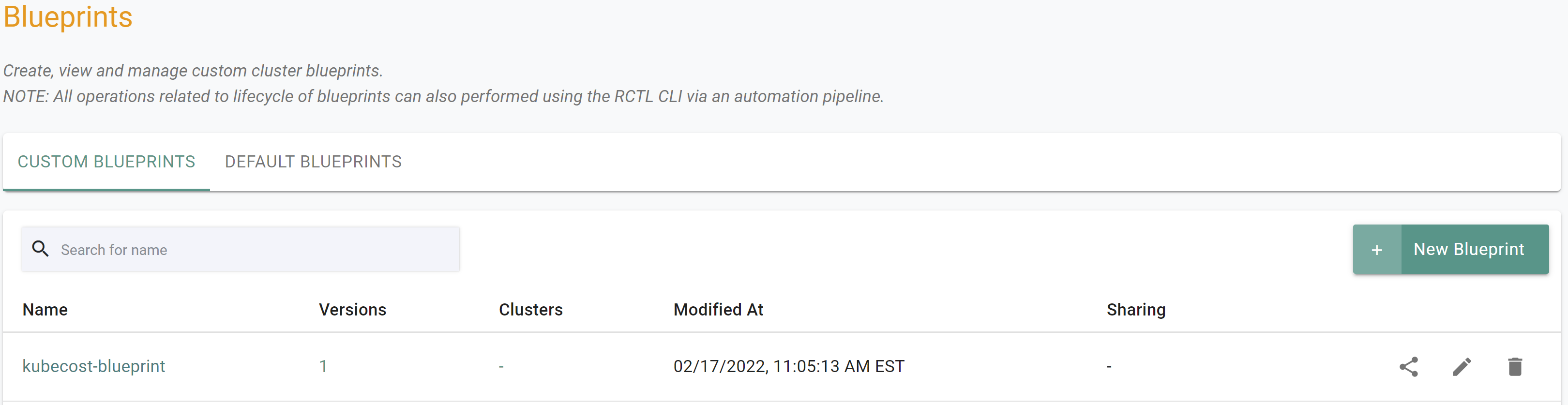
- Under Infrastructure, select Blueprints
- Create a new blueprint and give it a name such as
kubecost - Click Save
- Create a new version of the blueprint
- Select New Version
- Provide a version name such as
v1 - Under Add-Ons, select the
kubecostAdd-on and the version that was previously created - Click Save Changes
You may now apply this custom blueprint to a cluster.
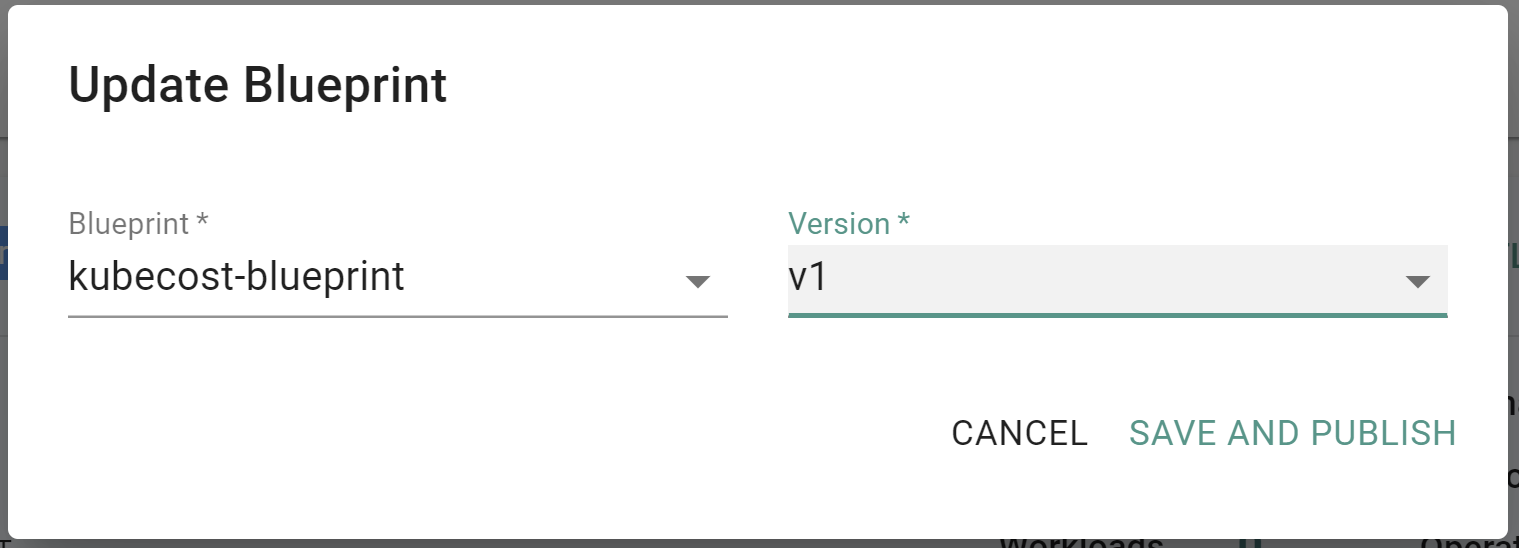
- Click on Options for the target cluster in the Web Console
- Select Update Blueprint and select the
kubecostblueprint and version you created previously - Click on Save and Publish
This will start the deployment of the Add-ons configured in the kubecost blueprint to the targeted cluster. The blueprint sync process can take a few minutes. Once complete, the cluster will display the current cluster blueprint details and whether the sync was successful or not.
You can optionally verify whether the correct resources have been created on the cluster. Click on the kubectl button on the cluster to open a virtual terminal.
Then, verify the pods in the kubecost namespace. Run kubectl get pod -n kubecost, and check that the output is similar to the example below.
$ kubectl get pod -n kubecost
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kubecost-cost-analyzer-8544c4bbd4-gx4nl 3/3 Running 0 6m23s
kubecost-grafana-768655466d-vlsmq 3/3 Running 0 6m23s
kubecost-kube-state-metrics-f99c657b5-mh5mt 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
kubecost-prometheus-node-exporter-26fwv 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
kubecost-prometheus-node-exporter-zfkvw 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
kubecost-prometheus-server-5cc6745978-z98f8 2/2 Running 0 6m23sIn order to access the Kubecost UI, you'll need to enable access to the frontend application using port-forward. To do this, download and use the Kubeconfig with the KubeCTL CLI (../../accessproxy/kubectl_cli/)
kubectl port-forward --namespace kubecost deployment/kubecost-cost-analyzer 9090
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9090 -> 9090
Forwarding from [::1]:9090 -> 9090
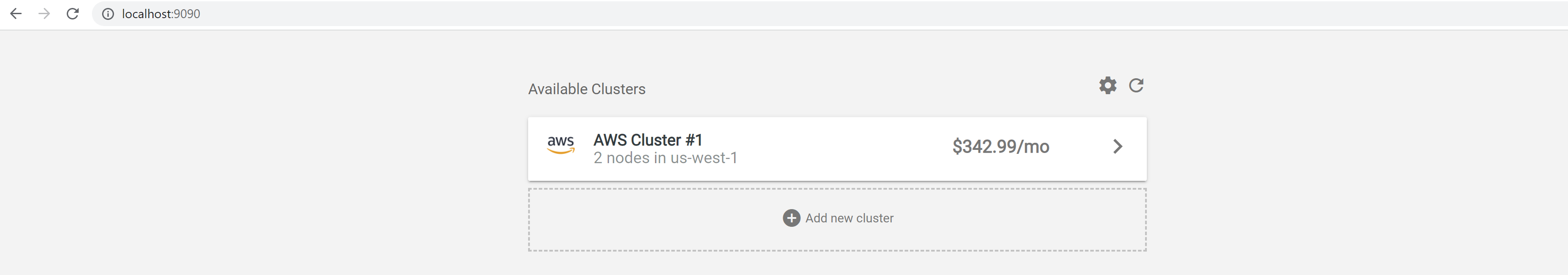
Handling connection for 9090You can now access the Kubecost UI by visiting http://localhost:9090 on your browser.
Et voilà! You have successfully created a custom cluster blueprint with the kubecost add-on and applied to a cluster. Use this blueprint on as many clusters as you require.
You can find this same guide as well as the guides for how to create or import a cluster using the Rafay controller on the Rafay documentation site.
Edit this doc on GitHub