What are the main categories of Design Patterns?
What is Design Patterns and why anyone should use them?
Can we create a clone of a singleton object?
Name types of Design Patterns?
What are the difference between a static class and a singleton class?
When should I use composite design pattern?
What does “program to interfaces, not implementations” mean?
What is Abstract Factory pattern?
Can you give any good explanation what is the difference between Proxy and Decorator?
What is the Chain of Responsibility pattern?
When would you use the Builder Pattern? Why not just use a Factory Pattern?
Why would I ever use a Chain of Responsibility over a Decorator?
Explain usage of Service Locator Pattern
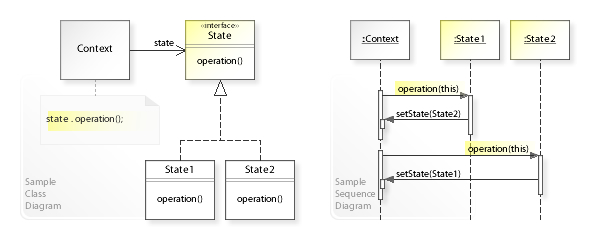
What is the difference between Strategy design pattern and State design pattern?
How is Bridge pattern is different from Adapter pattern?
Explain what is Composition over inheritance?
Could you explain the difference between Façade vs. Mediator?
Explain difference between the Facade, Proxy, Adapter and Decorator design patterns?
What is the difference between the template patterns and the strategy pattern?
What's the difference between the Dependency Injection and Service Locator patterns?
Could you explain what is the "deadly diamond of death"?
The Design patterns can be classified into three main categories:
- Creational Patterns
- Behavioral Patterns
- Functional Patterns
Patterns in programming are like recipes in cooking. They are not ready dishes, but instructions for slicing and dicing products, cooking them, serving them and so forth.
Pattern content As a rule, a pattern description consists of the following:
- a problem that the pattern solves;
- motivation for solving the the problem using the method suggested by the pattern;
- structures of classes comprising the solution;
- an example in one of the programming languages;
- a description of the nuances of pattern implementation in various contexts; relations with other patterns.
Singleton pattern comes under creational patterns category and introduces a single class which is responsible to create an object while making sure that only single object gets created. This class provides a way to access its only object which can be accessed directly without need to instantiate the object of the class.
Design patterns are a well-described solution to the most commonly encountered problems which occur during software development.
Design pattern represents the best practices evolved over a period of time by experienced software developers. They promote reusability which leads to a more robust and maintainable code.
Factory pattern is one of most used design pattern and comes under creational patterns category.
In Factory pattern, we create object without exposing the creation logic to the client and refer to newly created object using a common interface.
**Pro's**:
- Allows you to hide implementation of an application seam (the core interfaces that make up your application)
- Allows you to easily test the seam of an application (that is to mock/stub) certain parts of your application so you can build and test the other parts
- Allows you to change the design of your application more readily, this is known as loose coupling
Con's
- Makes code more difficult to read as all of your code is behind an abstraction that may in turn hide abstractions.
- Can be classed as an anti-pattern when it is incorrectly used, for example some people use it to wire up a whole application when using an IOC container, instead use Dependency Injection.
Iterator pattern is very commonly used design pattern in Java and .Net programming environment. This pattern is used to get a way to access the elements of a collection object in sequential manner without any need to know its underlying representation. Iterator pattern falls under behavioral pattern category.
Inversion of control is a broad term but for a software developer it's most commonly described as a pattern used for decoupling components and layers in the system.
For example, say your application has a text editor component and you want to provide spell checking. Your standard code would look something like this:
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor() {
this.checker = new SpellChecker();
}
}What we've done here creates a dependency between the TextEditor and the SpellChecker. In an IoC scenario we would instead do something like this:
public class TextEditor {
private IocSpellChecker checker;
public TextEditor(IocSpellChecker checker) {
this.checker = checker;
}
}You have inverted control by handing the responsibility of instantiating the spell checker from the TextEditor class to the caller.
SpellChecker sc = new SpellChecker; // dependency
TextEditor textEditor = new TextEditor(sc);Yesl, we can but the purpose of Singleton Object creation is to have single instance serving all requests.
Design patterns can be classified in three categories: Creational, Structural and Behavioral patterns.
-
Creational Patterns - These design patterns provide a way to create objects while hiding the creation logic, rather than instantiating objects directly using new opreator. This gives program more flexibility in deciding which objects need to be created for a given use case.
-
Structural Patterns - These design patterns concern class and object composition. Concept of inheritance is used to compose interfaces and define ways to compose objects to obtain new functionalities.
-
Behavioral Patterns - These design patterns are specifically concerned with communication between objects.
In Template pattern, an abstract class exposes defined way(s)/template(s) to execute its methods. Its subclasses can override the method implementation as per need but the invocation is to be in the same way as defined by an abstract class. This pattern comes under behavior pattern category.
Filter pattern or Criteria pattern is a design pattern that enables developers to filter a set of objects using different criteria and chaining them in a decoupled way through logical operations. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern combines multiple criteria to obtain single criteria.
Filter design pattern is useful where you want to add filters dynamically or you are implementing multiple functionalities and most of them require different filter criteria to filter something. In that case instead of hard coding the filters inside the functionalities, you can create filter criteria and re-use it wherever required.
List<Laptop> laptops = LaptopFactory.manufactureInBulk();
AndCriteria searchCriteria = new AndCriteria(
new HardDisk250GBFilter(),
new MacintoshFilter(),
new I5ProcessorFilter());
List<Laptop> filteredLaptops = searchCriteria.meets(laptops);In Strategy pattern, a class behavior or its algorithm can be changed at run time. This type of design pattern comes under behavior pattern.
In Strategy pattern, we create objects which represent various strategies and a context object whose behavior varies as per its strategy object. The strategy object changes the executing algorithm of the context object.
Dependency injection makes it easy to create loosely coupled components, which typically means that components consume functionality defined by interfaces without having any first-hand knowledge of which implementation classes are being used.
Dependency injection makes it easier to change the behavior of an application by changing the components that implement the interfaces that define application features. It also results in components that are easier to isolate for unit testing.
In Null Object pattern, a null object replaces check of NULL object instance. Instead of putting if check for a null value, Null Object reflects a do nothing relationship. Such Null object can also be used to provide default behaviour in case data is not available.
In Null Object pattern, we create an abstract class specifying various operations to be done, concrete classes extending this class and a null object class providing do nothing implementation of this class and will be used seamlessly where we need to check null value.
In State pattern a class behavior changes based on its state. This type of design pattern comes under behavior pattern. In State pattern, we create objects which represent various states and a context object whose behavior varies as its state object changes.
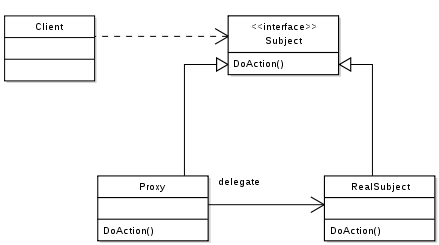
In proxy pattern, a class represents functionality of another class. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern.
In proxy pattern, we create object having original object to interface its functionality to outer world.
Builder pattern builds a complex object using simple objects and using a step by step approach. This builder is independent of other objects.
The Director class is optional and is used to make sure that the building steps are executed in the right order with the right data by the right builder. It's about validation and delegation.
Builder/Director pattern's steps invocations could be semantically presented by method chaining or so called Fluent Interface syntax.
Pizza pizza = new Pizza.Builder()
.cheese(true)
.pepperoni(true)
.bacon(true)
.build();Following are the differences between a static class and a singleton class.
- A static class can not be a top level class and can not implement interfaces where a singleton class can.
- All members of a static class are static but for a Singleton class it is not a requirement.
- A static class get initialized when it is loaded so it can not be lazily loaded where a singleton class can be lazily loaded.
- A static class object is stored in stack whereas singlton class object is stored in heap memory space.
Use the Composite Pattern when
- you want to represent part-whole hierarchies of objects.
- you want clients to be able to ignore the difference between compositions of objects and individual objects. Clients will treat all objects in the composite structure uniformly.
A common usage is a display system of graphic windows which can contain other windows and graphic elements such as images, text. The composite can be composed at run-time, and the client code can manipulate all the elements without concern for which type it is for common operations such as drawing. Another example is directories contain entries, each of which could be a directory.
Coding against interface means, the client code always holds an Interface object which is supplied by a factory.
Any instance returned by the factory would be of type Interface which any factory candidate class must have implemented. This way the client program is not worried about implementation and the interface signature determines what all operations can be done.
This approach can be used to change the behavior of a program at run-time. It also helps you to write far better programs from the maintenance point of view.
Abstract Factory patterns work around a super-factory which creates other factories. This factory is also called as factory of factories. This type of design pattern comes under creational pattern as this pattern provides one of the best ways to create an object.
In Abstract Factory pattern an interface is responsible for creating a factory of related objects without explicitly specifying their classes. Each generated factory can give the objects as per the Factory pattern.
Pros:
- Follows the Open/Closed Principle.
- Allows building families of product objects and guarantees their compatibility.
- Avoids tight coupling between concrete products and code that uses them.
- Divides responsibilities between multiple classes.
Cons:
- Increases overall code complexity by creating multiple additional classes.
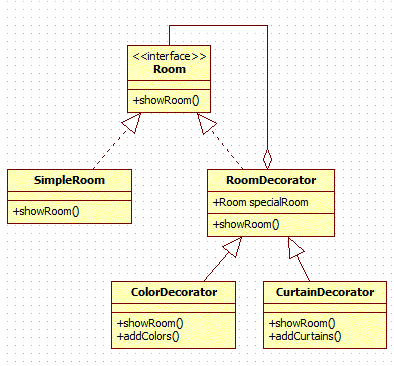
Decorator pattern allows a user to add new functionality to an existing object without altering its structure. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern acts as a wrapper to existing class.
This pattern creates a decorator class which wraps the original class and provides additional functionality keeping class methods signature intact.
Prototype pattern refers to creating duplicate object while keeping performance in mind. This pattern involves implementing a prototype interface which tells to create a clone of the current object.
The Prototype pattern is used when creation of object directly is costly. For example, an object is to be created after a costly database operation. We can cache the object, returns its clone on next request and update the database as and when needed thus reducing database calls.
Memento pattern is used to restore state of an object to a previous state. Memento pattern falls under behavioral pattern category.
Memento pattern uses three actor classes:
- Memento contains state of an object to be restored.
- Originator creates and stores states in Memento objects and
- Caretaker object is responsible to restore object state from Memento.
Decorator Pattern focuses on dynamically adding functions to an object, while Proxy Pattern focuses on controlling access to an object.
Adapter pattern works as a bridge between two incompatible interfaces. This pattern involves a single class which is responsible to join functionalities of independent or incompatible interfaces (adaptees).
A real life example could be a case of card reader which acts as an adapter between memory card and a laptop. You plugin the memory card into card reader and card reader into the laptop so that memory card can be read via laptop.
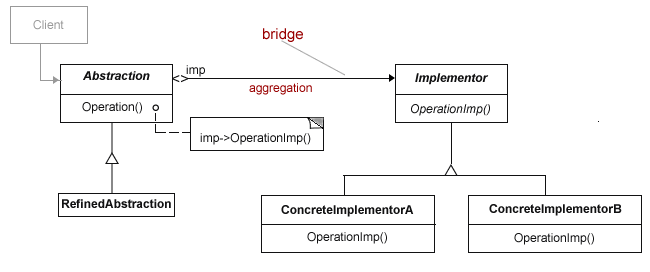
Bridge pattern is used when we need to decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern decouples implementation class and abstract class by providing a bridge structure between them.
The bridge pattern is useful when both the class and what it does vary often. The class itself can be thought of as the abstraction and what the class can do as the implementation. The bridge pattern can also be thought of as two layers of abstraction.
This pattern involves an interface which acts as a bridge which makes the functionality of concrete classes independent from interface implementer classes. Both types of classes can be altered structurally without affecting each other.
The example of bridge pattern implementation is when:
----Shape---
/ \
Rectangle Circle
/ \ / \
BlueRectangle RedRectangle BlueCircle RedCirclerefactored to:
----Shape--- Color
/ \ / \
Rectangle(Color) Circle(Color) Blue Redor in general when:
A
/ \
Aa Ab
/ \ / \
Aa1 Aa2 Ab1 Ab2refactored to:
A N
/ \ / \
Aa(N) Ab(N) 1 2As the name suggests, the chain of responsibility pattern creates a chain of receiver objects for a request. This pattern decouples sender and receiver of a request based on type of request. This pattern comes under behavioural patterns.
In this pattern, normally each receiver contains reference to another receiver. If one object cannot handle the request then it passes the same to the next receiver and so on. The chain of responsibility is an object oriented version of the if ... else if ... else if ....... else ... endif idiom, with the benefit that the condition–action blocks can be dynamically rearranged and reconfigured at runtime.
Observer pattern (also known as Publish-Subscribe Pattern) is used when there is one-to-many relationship between objects such as if one object is modified, its dependent objects are to be notified automatically. Observer pattern falls under behavioral pattern category.
An object with a one-to-many relationship with other objects who are interested in its state is called the subject or publisher. The observers are notified whenever the state of the subject changes and can act accordingly. The subject can have any number of dependent observers which it notifies, and any number of observers can subscribe to the subject to receive such notifications.
Observer pattern uses two actor classes:
- The Observer (os Subscriber) abstract class provides an
update()method which will be called by the subject to notify it of the subject’s state change. - The Subject (or Publisher) class is also an abstract class and defines four primary methods:
attach(),detach(),setState(), andnotify()
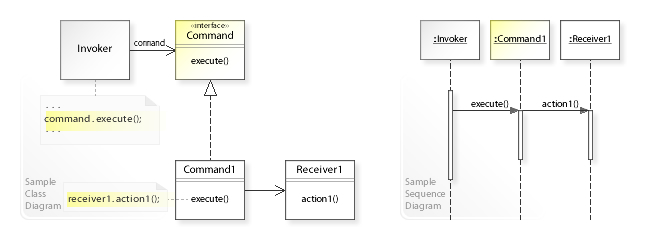
Command pattern is a data driven design pattern and falls under behavioural pattern category. A request is wrapped under an object as command and passed to invoker object. Invoker object looks for the appropriate object which can handle this command and passes the command to the corresponding receiver which executes the command.
Interpreter pattern provides a way to evaluate language grammar or expression. This type of pattern comes under behavioral pattern. This pattern involves implementing an expression interface which tells to interpret a particular context.
This class diagram means that an AbstractExpression is either a TerminalExpression or a NonTerminalExpression. If its a NonTerminalExpression, it is itself an aggregation of one or several AbstractExpression.
Any mechanism for interpreting formal languages suites this pattern perfectly, it can be anything: from a simple calculator to a C# parser.
Facade pattern hides the complexities of the system and provides an interface to the client using which the client can access the system. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern adds an interface to existing system to hide its complexities.
This pattern involves a single class which provides simplified methods required by client and delegates calls to methods of existing system classes.
Mediator pattern is used to reduce communication complexity between multiple objects or classes. This pattern provides a mediator class which normally handles all the communications between different classes and supports easy maintenance of the code by loose coupling. Mediator pattern falls under behavioral pattern category.
The builder pattern is a good choice when designing classes whose constructors or static factories would have more than a handful of parameters.
Consider a restaurant. The creation of "today's meal" is a factory pattern, because you tell the kitchen "get me today's meal" and the kitchen (factory) decides what object to generate, based on hidden criteria.
The builder appears if you order a custom pizza. In this case, the waiter tells the chef (builder) "I need a pizza; add cheese, onions and bacon to it!" Thus, the builder exposes the attributes the generated object should have, but hides how to set them.
The key difference is that a Decorator adds new behaviour that in effect widens the original interface. It is similar to how normal extension can add methods except the "subclass" is only coupled by a reference which means that any "superclass" can be used.
The Chain of Responsibility pattern can modify an existing behaviour which is similar to overriding an existing method using inheritance. You can choose to call super.xxx() to continue up the "chain" or handle the message yourself.
Flyweight pattern is primarily used to reduce the number of objects created and to decrease memory footprint and increase performance. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern provides ways to decrease object count thus improving the object structure of application.
Flyweight pattern tries to reuse already existing similar kind objects by storing them and creates new object when no matching object is found.
The service locator pattern is a design pattern used in software development to encapsulate the processes involved in obtaining a service with a strong abstraction layer. This pattern uses a central registry known as the “service locator” which on request returns the information necessary to perform a certain task. The ServiceLocator is responsible for returning instances of services when they are requested for by the service consumers or the service clients.
* **Service Locator**: The Service Locator abstracts the API lookup services, vendor dependencies, lookup complexities, and business object creation, and provides a simple interface to clients. This reduces the client’s complexity. In addition, the same client or other clients can reuse the Service Locator. * **InitialContext**: The InitialContext object is the start point in the lookup and creation process. Service providers provide the context object, which varies depending on the type of business object provided by the Service Locator’s lookup and creation service. * **ServiceFactory**: The ServiceFactory object represents an object that provides life cycle management for the BusinessService objects. The ServiceFactory object for enterprise beans is an EJBHome object. * **BusinessService**: The BusinessService is a role that is fulfilled by the service the client is seeking to access. The BusinessService object is created or looked up or removed by the ServiceFactory. The BusinessService object in the context of an EJB application is an enterprise bean.
The difference simply lies in that they solve different problems:
- The State pattern deals with what (state or type) an object is (in) -- it encapsulates state-dependent behavior, whereas
- the Strategy pattern deals with how an object performs a certain task -- it encapsulates an algorithm.
The constructs for achieving these different goals are however very similar; both patterns are examples of composition with delegation.
The intent of the Adapter pattern is to make one or more classes' interfaces look the same as that of a particular class.
The Bridge pattern is designed to separate a class's interface from its implementation so you can vary or replace the implementation without changing the client code.
Composition over inheritance (or composite reuse principle) in object-oriented programming (OOP) is the principle that classes should achieve polymorphic behavior and code reuse by their composition (by containing instances of other classes that implement the desired functionality) rather than inheritance from a base or parent class. It is more natural to build business-domain classes out of various components than trying to find commonality between them and creating a family tree.
One common drawback of using composition instead of inheritance is that methods being provided by individual components may have to be implemented in the derived type, even if they are only forwarding methods.
Some languages, notably Go, use type composition exclusively.
- The facade only exposes the existing functionality from a different perspective.
- The mediator "adds" functionality because it combines different existing functionality to create a new one.
- Adapter adapts a given class/object to a new interface. In the case of the former, multiple inheritance is typically employed. In the latter case, the object is wrapped by a conforming adapter object and passed around. The problem we are solving here is that of non-compatible interfaces.
- Facade is more like a simple gateway to a complicated set of functionality. You make a black-box for your clients to worry less i.e. make interfaces simpler.
- Proxy provides the same interface as the proxied-for class and typically does some housekeeping stuff on its own. (So instead of making multiple copies of a heavy object X you make copies of a lightweight proxy P which in turn manages X and translates your calls as required.) You are solving the problem of the client from having to manage a heavy and/or complex object.
- Decorator is used to add more gunpowder to your objects (note the term objects -- you typically decorate objects dynamically at runtime). You do not hide/impair the existing interfaces of the object but simply extend it at runtime
The main difference between the two is when the concrete algorithm is chosen.
-
With the Template method pattern this happens at compile-time by subclassing the template. Each subclass provides a different concrete algorithm by implementing the template's abstract methods. When a client invokes methods of the template's external interface the template calls its abstract methods (its internal interface) as required to invoke the algorithm.
-
In contrast, the Strategy pattern allows an algorithm to be chosen at runtime by containment. The concrete algorithms are implemented by separate classes or functions which are passed to the strategy as a parameter to its constructor or to a setter method. Which algorithm is chosen for this parameter can vary dynamically based on the program's state or inputs.
- With the ServiceLocator, the class is still responsible for creating its dependencies. It just uses the service locator to do it.
- Service locators hide dependencies - you can't tell by looking at an object whether it hits a database or not (for example) when it obtains connections from a locator.
- With DI, the class is given it's dependencies. It neither knows, nor cares where they come from.
One important result of this is that the DI example is much easier to unit test -- because you can pass it mock implementations of its dependent objects. You could combine the two -- and inject the service locator (or a factory), if you wanted.
The diamond problem (sometimes referred to as the "deadly diamond of death") is an ambiguity that arises when two classes B and C inherit from A, and class D inherits from both B and C. If there is a method in A that B and C have overridden, and D does not override it, then which version of the method does D inherit: that of B, or that of C?
If a structure D embeds two structures B and C which both have a method F(), thus satisfying an interface A, the compiler will complain about an "ambiguous selector" if D.F() is called, or if an instance of D is assigned to a variable of type A. B and C's methods can be called explicitly with D.B.F() or D.C.F().