A clean and scalable template to kickstart your AutoML project 🚀⚡🔥
Currently uses dev version of Hydra.
Suggestions are always welcome!
You can refer to Wiki for more details.
Hyperbox目前支持:
- 神经架构搜索(Neural Architecture Search, NAS):基于微软的NNI框架设计并做了改进,涉及的核心模块包括
hyperbox.mutables和hyperbox.mutator。另外hyperbox.networks重新实现了很多NAS论文中的搜索空间。 - 超参优化(Hyperparameters Optimization, HPO):基于
hydra和optuna库实现 - 自动数据增强(Auto Data Augmentation, ADA):基于
Kornia库实现
- 安装
安装方式有两种:
- 第一种是pip安装
pip install hyperbox- 第二种是源码安装
git clone https://github.com/marsggbo/hyperbox.git
cd hyperbox
python setup.py develop # 建议已开发者模式安装
python install -r requirements.txt- Quick Start
python -m hyperbox.run experiment=example_random_nas +trainer.fast_dev_run=True
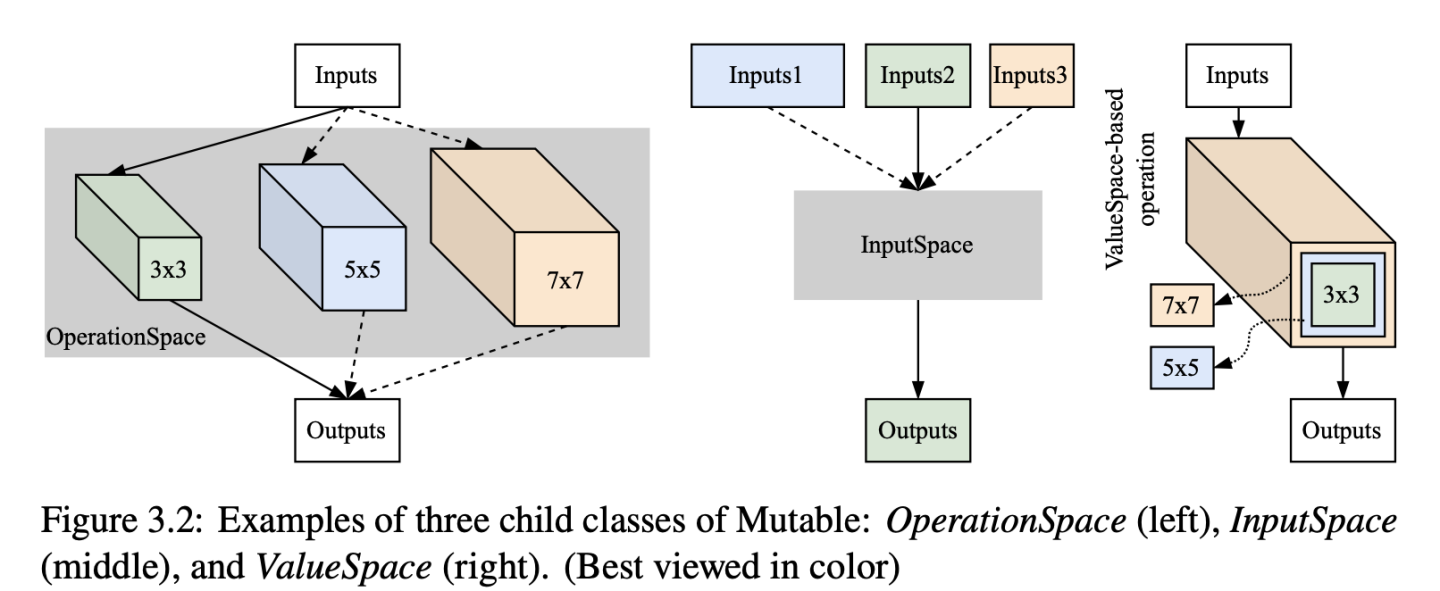
目前hyperbox支持实现上面三种搜索模块,这已经能够覆盖现有的大多数模型结构了。hyperbox.networks中十几个常见的NAS搜索空间。下面我们可以看看图中三种不同搜索空间的代码实现示例
- 图左代码实现示例:候选操作搜索
这个其实就是相当于在某一层中我们有若干个候选操作,我们想从中选择出最适合的一个,OperationSpace就是这个用途
import torch.nn as nn
from hyperbox . mutables . spaces import OperationSpace
op1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride =1, padding=1)
op2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride =1, padding=2)
op3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=16, kernel_size=7, stride =1, padding=3)
ops = OperationSpace(candidates=[op1, op2, op3], key=’conv_op’, mask=[1, 0, 0])可以看到OperationSpace有三个重要的参数:
candidates:很显然就是一个list,每个元素是一个Pytorch的nn.Modulekey:可以理解成是一个唯一识别码,如果两个可搜索模块重名了,那么它们二者的搜索结果会一样,这个需要特别注意mask: 默认为None,表示当前模块需要搜索;否则,可以传入list或者dict来之指明选择哪一个操作- one-hot格式的list,长度需要和
candidates一样。上面mask=[1, 0, 0]表示选择第一个操作,即3x3卷积 - dict(字典),即
{key: value},其中的key和value可以有很多组,并且value也必须是list。不过其中必须包含一组{'conv_op': [0, 1, 0]}。
- one-hot格式的list,长度需要和
如无特殊说明,后面两种模块也遵循这种设计。
- 图中代码实现示例:输入节点搜索
除了从多个候选操作中选择一个,很多情况我们也想从模型前面几层的输出中选择一个或者若干作为当前层的输入,这个时候可以用InputSpace
import torch
from hyperbox.mutables.spaces import InputSpace
in1 = torch.rand(2, 64)
in2 = torch.rand(2, 32)
in3 = torch.rand(2, 16)
inputs = [in1, in2, in3]
skipconnect = InputSpace(n_candidates=3, n_chosen=1, key=’sc’, mask=[0, 1, 0])
out = skipconnect([ in1 , in2 , in3 ])
assert out is in2
>>> True- 图右代码实现示例:细腻度(Finegrained)操作搜索
以上两个模块都是参考的微软NNI框架实现的,不过他们仅支持搜索完整的操作,很多时候我们也许像搜索更加细腻度的操作,就像图右所示,我们想搜索不同卷积核大小,不过它们就像人生无常,大肠包小肠一样地重叠在一起了,现有的框架大都不支持这个。Hyperbox实现了ValueSpace,然后override了pytorch的所有卷积操作(Conv1d/2d/3d)、线性层(Linear)和batchnorm。只要传入的参数是ValueSpace,hyperbox就能够对这个参数进行搜索,我们看看下面的例子
from hyperbox.mutables.spaces import ValueSpace
from hyperbox.mutables.ops import Conv2d, Linear
# convolution
ks = ValueSpace([3, 5, 7], key=’kernelSize’, mask=[0, 1, 0])
cout = ValueSpace([16, 32, 64], key=’channelOut’, mask=[0, 1, 0])
conv = Conv2d(3 , cout , ks , stride =1, padding=2, bias=False)
print([x.shape for x in conv.parameters()])
>>> [torch.Size([32, 3, 5, 5])]
# linear
cout = ValueSpace([10, 100], key=’channelOut1’)
isBias = ValueSpace([0, 1], key=’bias’) # 0: False, 1: True
linear = Linear(10, cout , bias=isBias)
print([x.shape for x in linear.parameters()])
>>> [ torch.Size ([100 , 10]) , torch.Size ([100]) ]- Random Search Algorithm
RandomMutator前面介绍hyperbox.mutables时,我们可以看到都有显式地指明一个参数,即mask=...。但很多时候其实我们不知道模型应该长什么样,所以保持默认值mask=None即可。
之后,可以用到hyperbox.mutator来对设计的搜索空间进行搜索。可以看看下面的代码示例:
from hyperbox.mutator import RandomMutator
from hyperbox.networks.ofa import OFAMobileNetV3
net = OFAMobileNetV3(mask=None)
rm = RandomMutator(net)
rm.reset() # search a subnet
arch: dict = rm._cache # arch of a subnet
print(arch)
subnet1 = OFAMobileNetV3(mask=arch) # initialize a subnet, which has smaller parameters than `net`
subnet2 = net.build_subnet(mask_arch)OFAMobileNetV3是Once-for-all (OFA)论文中用到的搜索空间,此时mask=None表示模型处于待搜索状态- 第5行,模型
net作为参数传给了RandomMutator,在RandomMutator初始化的时候它会对net中所有的模块遍历一遍,如果发现了hyperbox.mutables模块就会记录下。每次模型forward的时候,正常的nn.Module模块没有变化,而hyperbox.mutables的forward会受到Mutator的控制。比如一个OperationSpace的mask搜索结构是[0,1,0],那么Mutator会自动激活第二个操作参与到的forward计算,另外两个不会参与运算。 - 第6行:
.reset()是调用搜索算法,看看RandomMutator源码应该就能知道是什么作用了 - 第7行:每次调用
reset()就会采样得到一个新的子网,该子网的结构用字典表示,存储在_cache这个属性中 - 第10行和11行:这两行显示了两种生成子模型的方法,建议使用第二种,因为它能够自动继承Supernet的权重到子网的对应位置。第一种会随机初始化权重。
class RandomMutator(Mutator):
def __init__(self, model, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(model)
def reset(self):
... # 一些预处理操作
self._cache = self.sample_search()
return self._cache
def sample_search(self):
result = dict()
for mutable in self.mutables:
if isinstance(mutable, OperationSpace):
gen_index = torch.randint(high=mutable.length, size=(1, ))
result[mutable.key] = F.one_hot(gen_index, num_classes=mutable.length).view(-1).bool()
mutable.mask = result[mutable.key].detach()
elif isinstance(mutable, InputSpace):
if mutable.n_chosen is None:
result[mutable.key] = torch.randint(high=2, size=(mutable.n_candidates,)).view(-1).bool()
else:
perm = torch.randperm(mutable.n_candidates)
mask = [i in perm[:mutable.n_chosen] for i in range(mutable.n_candidates)]
result[mutable.key] = torch.tensor(mask, dtype=torch.bool) # pylint: disable=not-callable
mutable.mask = result[mutable.key].detach()
elif isinstance(mutable, ValueSpace):
gen_index = torch.randint(high=mutable.length, size=(1, ))
result[mutable.key] = F.one_hot(gen_index, num_classes=mutable.length).view(-1).bool()
mutable.mask = F.one_hot(gen_index, num_classes=mutable.length).view(-1).bool()
return result超参调优和自动数据增强见下一篇文章介绍
Hyperbox框架还有很多可以完善的地方,对框架开发感兴趣的小伙伴可以扫码入群,有问题也可以在群里讨论。