This plugin allows snippet, theme, and plugin CSS files to define a set of configuration options. It then allows users to see all the tweakable settings in one settings pane. Style Settings allows both toggling classes on and off the body element, as well as setting numeric, string, and color CSS variables.
This CSS Snippet can be used to adjust every CSS variable of the default Obsidian theme.
Configurable settings are defined by comments within CSS files beginning with /* @settings. These comments must contain YAML with name, id, and settings properties. Style Settings will scan for these comments in all CSS loaded by Obsidian from the snippets, themes, and plugins directories under your vault's configuration directory (%yourVault%/.obsidian/). Please see the Obsidian Docs for more information.
For example, adding this to a CSS snippet in your vault's snippets directory (%yourVault%/.obsidian/snippets):
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: my-title
title: My Settings
type: heading
level: 3
-
id: accent
title: Accent Color
type: variable-color
format: hsl-split
default: '#007AFF'
-
id: text
title: UI font
description: Font used for the user interface
type: variable-text
default: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", Roboto, Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, "Helvetica Neue", sans-serif
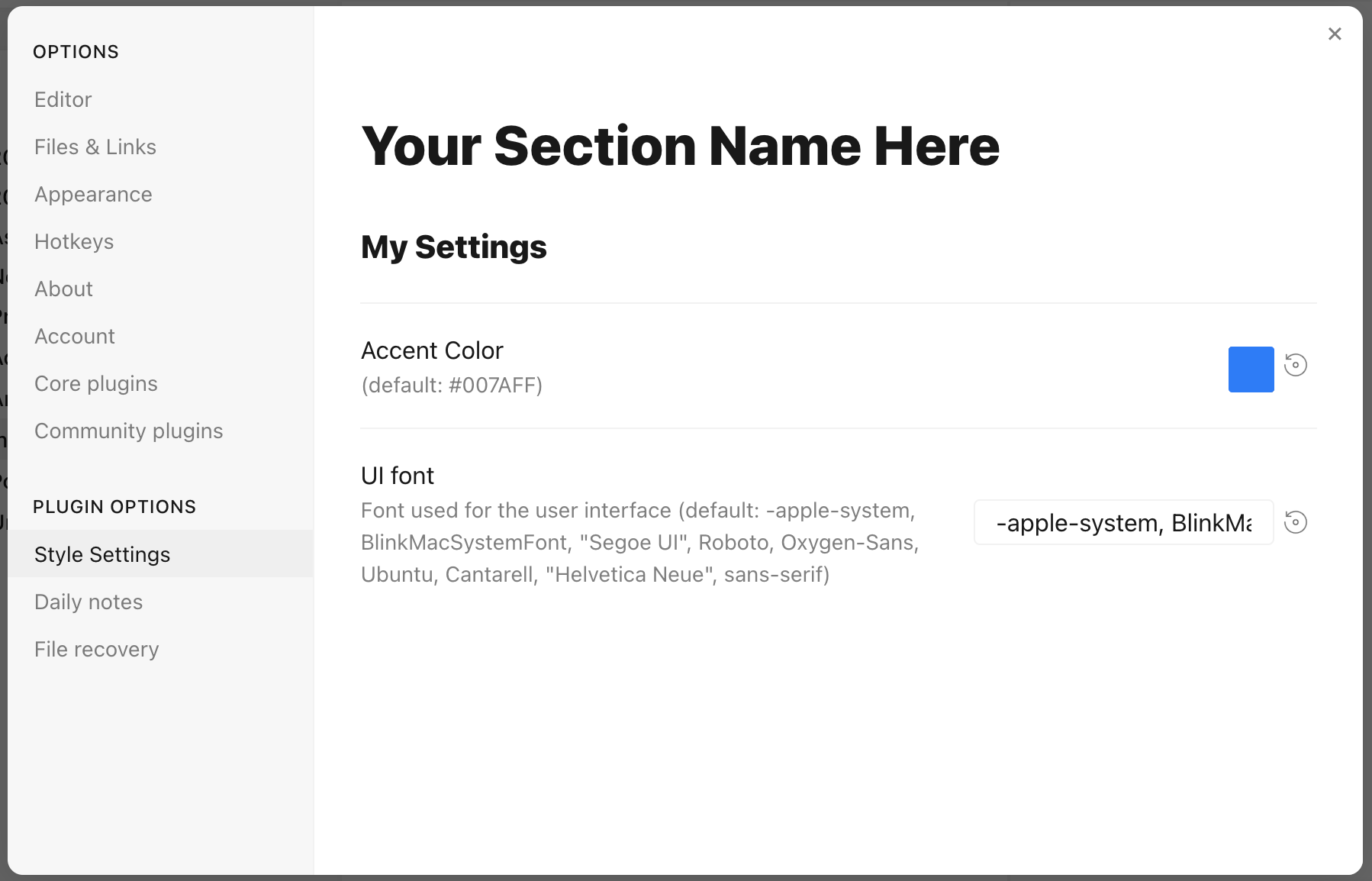
*/will result in:
Each setting definition must be separated by a dash (-). There are 7 setting types.
All settings definitions must have these parameters:
id: A unique id for the setting parametertitle: The name of the settingdescription(optional): a description of the settingtype: The type of setting. Can be one of:heading: a heading element for organizing settingsclass-toggle: a switch to toggle classes on thebodyelementclass-select: a dropdown menu of predefined options to add classes on thebodyelementvariable-text: a text-based CSS variablevariable-number: a numeric CSS variablevariable-number-slider: a numeric CSS variable represented by a slidervariable-select: a text-based CSS variable displayed as a dropdown menu of predefined optionsvariable-color: a color CSS variable with corresponding color picker
headings can be used to organize and group settings into collapsable nested sections. Along with the required attributes, headings must contain a level attribute between 1 and 6, and can optionally contain a collapsed attribute:
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: this-is-a-heading
title: My Heading
type: heading
level: 2
collapsed: true
*/info-text displays arbitrary informational text to users. The description may contain markdown if markdown is set to true.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: my-info-text
title: Information
description: "This is *informational* text"
type: info-text
markdown: true
*/class-toggles will toggle a css class on and off of the body element, allowing CSS themes and snippets to toggle features on and off. The id of the setting will be used as the class name. The default parameter can optionally be set to true. class-toggle also supports the addCommand property. When set to true a command will be added to obsidian to toggle the class via a hotkey or the command palette.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: my-css-class
title: My Toggle
description: Adds my-css-class to the body element
type: class-toggle
*/class-select creates a dropdown of predefined options for a CSS variable. The id of the setting will be used as the variable name.
- When
allowEmptyisfalse, adefaultoption must be specified. - When
allowEmptyistrue, thedefaultattribute is optional, and may be set tonone.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: theme-variant
title: Theme variant
description: Variations on a theme
type: class-select
allowEmpty: false
default: my-class
options:
- my-class
- my-other-class
- and-yet-another
*/Options may also be given a label:
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: theme-variant
title: Theme variant
description: Variations on a theme
type: class-select
allowEmpty: false
default: my-class
options:
-
label: My Class
value: my-class
-
label: My Other Class
value: my-other-class
*/variable-text represents any text based CSS value. The id of the setting will be used as the variable name. The output will be wrapped in quotes if quotes is set to true. variable-text settings require a default attribute.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: text
title: UI font
description: Font used for the user interface
type: variable-text
default: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", Roboto, Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, "Helvetica Neue", sans-serif
*/This will output the variable:
--text: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", Roboto, Oxygen-Sans, Ubuntu, Cantarell, "Helvetica Neue", sans-serif;
Using quotes:
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: icon
title: Bullet Icon
description: Text used in bullet points
type: variable-text
default: •
quotes: true
*/This will output the variable:
--icon: '•'
variable-number represents any numeric CSS value. The id of the setting will be used as the variable name. variable-number settings require a default attribute. Optionally, a format attribute can be set. This value will be appended to the number. Eg format: px will result in 42px
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: line-width
title: Line width
description: The maximum line width in rem units
type: variable-number
default: 42
format: rem
*/This will output the variable:
--line-width: 42rem;
variable-number-slider represents any numeric CSS value. The id of the setting will be used as the variable name. variable-number-slider settings require a default attribute, as well as these three attributes:
min: The minimum possible value of the slidermax: The maximum possible value of the sliderstep: The size of each "tick" of the slider. For example, a step of 100 will only allow the slider to move in increments of 100.
Optionally, a format attribute can be set. This value will be appended to the number. Eg format: px will result in 42px
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: line-width
title: Line width
description: The maximum line width in rem units
type: variable-number-slider
default: 42
min: 10
max: 100
step: 1
*/This will output the variable:
--line-width: 42;
variable-select creates a dropdown of predefined options for a CSS variable. The id of the setting will be used as the variable name. variable-select settings require a default attribute as well as a list of options.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: text
title: UI font
description: Font used for the user interface
type: variable-select
default: Roboto
options:
- Roboto
- Helvetica Neue
- sans-serif
- Segoe UI
*/Options can optionally be given a label:
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: text
title: UI font
description: Font used for the user interface
type: variable-select
default: Roboto
options:
-
label: The best font
value: Roboto
-
label: The next best font
value: Helvetica Neue
*/This will output the variable:
--text: Roboto;
variable-color creates a color picker with a variety of output format options. A default attribute is required in hex or rgb format. Note: hex color values must be wrapped in quotes. A format attribute is also required.
Optional parameters:
- Setting
opacitytotruewill enable opacity support in all output formats. - A list of alternate output formats can be supplied via the
alt-formatsetting
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: accent
title: Accent Color
type: variable-color
opacity: false
format: hex
alt-format:
-
id: accent-rgb
format: rgb
default: '#007AFF'
*/This will output the variable:
--accent: #007AFF;
--accent-rgb: rgb(0, 123, 255);
variable-themed-color is identical to variable-color except that it generates two color pickers for a light and dark variant.
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: accent
title: Accent Color
type: variable-themed-color
format: hex
opacity: false
default-light: '#007AFF'
default-dark: '#2DB253'
*/This will output the variables:
body.theme-light.css-settings-manager { --accent: #007AFF; }
body.theme-dark.css-settings-manager { --accent: #2DB253; }
There are 8 formatting options:
hex
--accent: #007AFF;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent: #007AFFFF;
rgb
--accent: rgb(0, 122, 255);
When opacity is set to true:
--accent: rgba(0, 122, 255, 1);
rgb-values
--accent: 0, 122, 255;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent: 0, 122, 255, 1;
rgb-split
--accent-r: 0;
--accent-g: 122;
--accent-b: 255;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent-r: 0;
--accent-g: 122;
--accent-b: 255;
--accent-a: 1;
hsl
--accent: hsl(211, 100%, 50%);
When opacity is set to true:
--accent: hsla(211, 100%, 50%, 1);
hsl-values
--accent: 211, 100%, 50%;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent: 211, 100%, 50%, 1;
hsl-split
--accent-h: 211;
--accent-s: 100%;
--accent-l: 50%;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent-h: 211;
--accent-s: 100%;
--accent-l: 50%;
--accent-a: 1;
hsl-split-decimal
--accent-h: 211;
--accent-s: 1;
--accent-l: 0.5;
When opacity is set to true:
--accent-h: 211;
--accent-s: 1;
--accent-l: 0.5;
--accent-a: 1;
color-gradient outputs a fixed number of colors along a gradient between two existing color variables. A format attribute is also required. Note: The to variable must be set in style settings for the gradient to be generated. Also, gradients will only be generated using colors defined under the current style settings id.
Parameters:
from: The starting color, or color that will be at step 0to: The ending color, or color that will be at step 100step: The increment at which to output a CSS variable. For example, settingstepto10will output--var-0,--var-10,--var-20, etc...format: Can be one of:hsl,rgb, orhex;pad?: When set, the number section of the variable will be padded with0's until it contains this number of digits. For example, settingpadto3andstepto10will output--var-000,--var-010,--var-020
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: color-base
type: color-gradient
from: color-base-00
to: color-base-100
step: 5
pad: 2
format: hex
*/Plugins can specify a style setting config in the plugin's CSS. Plugins must call app.workspace.trigger("parse-style-settings") when the plugin loads in order for Style Settings to be notified of CSS changes.
Translations for titles and descriptions can be supplied for each language Obsidian supports by using one of the following postfixes:
en: English
zh: 简体中文
zh-TW: 繁體中文
ru: Pусский
ko: 한국어
it: Italiano
id: Bahasa Indonesia
ro: Română
pt-BR: Portugues do Brasil
cz: čeština
de: Deutsch
es: Español
fr: Français
no: Norsk
pl: język polski
pt: Português
ja: 日本語
da: Dansk
uk: Український
sq: Shqip
tr: Türkçe (kısmi)
hi: हिन्दी (आंशिक)
nl: Nederlands (gedeeltelijk)
ar: العربية (جزئي)
For example:
/* @settings
name: Your Section Name Here
id: a-unique-id
settings:
-
id: my-css-class
title: My Toggle
title.de: Mein Toggle
title.ko: 내 토글
description: Adds my-css-class to the body element
description.de: Fügt my-css-class zum body-Element hinzu
description.ko: my-css-class를 body 요소에 추가합니다.
type: class-toggle
*/