Note
The main branch currently contains the atomic deployments alpha preview.
For the lastest stable release, check out thev0.xbranch.Please see our blog post "The road to Atomic Deployments"
or watch the latest release review for more information:
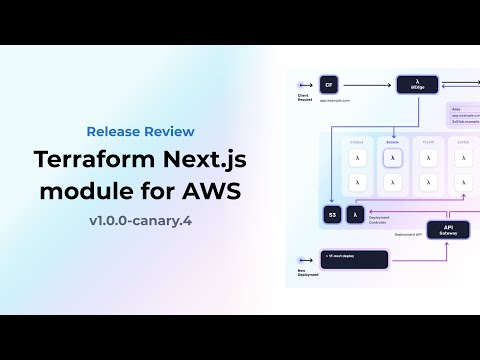
A zero-config Terraform module for self-hosting Next.js sites serverless on AWS Lambda.
Some features are still under development, here is a list of features that are currently supported and what we plan to bring with the next releases:
- ✅ Supports any version of Next.js
- ✅ Terraform
v0.15+ - ✅ Unlimited parallel deployments of Next.js apps (atomic deployments)
- ✅ Static, SSG, Lambda and API pages (with dynamic routes)
- ✅ Automatic expiration of old static assets
- ✅ Rewrites & Redirects
- ✅ Image Component & Image Optimization support
- 🚧 Incremental Static Regeneration
- ⛔️ Middleware (Not supported by Lambda@Edge / CloudFront functions)
The Next.js Terraform module is designed as a full stack AWS app. It relies on multiple AWS services and connects them to work as a single application:
You should have the following tools installed:
Note: Additionally we assume here that you already have a public Route53 Hosted Zone associated with your AWS account.
This is a requirement in the preview phase of atomic deployments, where each deployment gets a unique subdomain assigned. It will change once atomic deployments become generally available.
The Terraform module contains the system that is later used for creating new deployments and managing the aliases (domains) for your Next.js app(s). Creating the Terraform stack is only required on initial setup and creates the global resources (CloudFront distributions, DynamoDB tables, S3 storage) that is used for handling incoming requests to your website.
Create a new main.tf file in an empty folder (or add it to your existing Terraform stack) and add the following content:
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.0"
}
}
}
# Main region where the resources should be created in
# Should be close to the location of your viewers
provider "aws" {
region = "us-west-2"
}
# Provider used for creating the Lambda@Edge function which must be deployed
# to us-east-1 region (Should not be changed)
provider "aws" {
alias = "global_region"
region = "us-east-1"
}
###########
# Variables
###########
variable "custom_domain" {
description = "Your custom domain"
type = string
default = "example.com"
}
# Assuming that the ZONE of your domain is already available in your AWS account (Route 53)
# https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/AboutHZWorkingWith.html
variable "custom_domain_zone_name" {
description = "The Route53 zone name of the custom domain"
type = string
default = "example.com."
}
########
# Locals
########
locals {
# A wildcard domain(ex: *.example.com) has to be added when using atomic deployments:
aliases = [var.custom_domain, "*.${var.custom_domain}"]
}
#######################
# Route53 Domain record
#######################
# Get the hosted zone for the custom domain
data "aws_route53_zone" "custom_domain_zone" {
name = var.custom_domain_zone_name
}
# Create a new record in Route 53 for the domain
resource "aws_route53_record" "cloudfront_alias_domain" {
for_each = toset(local.aliases)
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.custom_domain_zone.zone_id
name = each.key
type = "A"
alias {
name = module.tf_next.cloudfront_domain_name
zone_id = module.tf_next.cloudfront_hosted_zone_id
evaluate_target_health = false
}
}
##########
# SSL Cert
##########
# Creates a free SSL certificate for CloudFront distribution
# For more options (e.g. multiple domains) see:
# https://registry.terraform.io/modules/terraform-aws-modules/acm/aws/
module "cloudfront_cert" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/acm/aws"
version = "~> 3.0"
domain_name = var.custom_domain
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.custom_domain_zone.zone_id
subject_alternative_names = slice(local.aliases, 1, length(local.aliases))
wait_for_validation = true
tags = {
Name = "CloudFront ${var.custom_domain}"
}
# CloudFront works only with certs stored in us-east-1
providers = {
aws = aws.global_region
}
}
##########################
# Terraform Next.js Module
##########################
module "tf_next" {
source = "milliHQ/next-js/aws"
version = "1.0.0-canary.4"
cloudfront_aliases = local.aliases
cloudfront_acm_certificate_arn = module.cloudfront_cert.acm_certificate_arn
deployment_name = "atomic-deployments"
enable_multiple_deployments = true
multiple_deployments_base_domain = "*.${var.custom_domain}"
providers = {
aws.global_region = aws.global_region
}
}
#########
# Outputs
#########
output "api_endpoint" {
value = module.tf_next.api_endpoint
}
output "api_endpoint_access_policy_arn" {
value = module.tf_next.api_endpoint_access_policy_arn
}To create the resources in your AWS account, run the following commands:
terraform init # Only needed on the first time running Terraform
terraform plan # (Optional) See what resources Terraform will create
terraform apply # Create the resources in your AWS account
> Apply complete!
>
> Outputs:
>
> api_endpoint = "https://<api-id>.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com"
> api_endpoint_access_policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:policy/access-api"The api_endpoint is later used by the CLI tool to create new deployments.
With the api_endpoint_access_policy_arn AWS policy you can create new users (and assign that policy) that only can use the CLI tool tf-next but cannot access other resources inside of your AWS account.
After the successful deployment your Next.js app is publicly available at the CloudFront subdomain from the cloudfront_domain_name output.
For building and deploying Next.js apps to the system we created a CLI tool called tf-next.
It is a npm package that can be installed with:
npm i -g tf-next@canaryNext, we need to build the Next.js so that it can run in a serverless environment (with AWS Lambda).
This is archived by running tf-next build in the same directory where your Next.js app is located (Right where your package.json or next.config.js files are located):
tf-next build
> All serverless functions created in: 20.791ms
> 1752924 total bytes
> Build successful!
Now deploy the Next.js app by running tf-next deploy from the same directory.
The deploy command communicates through a secured (and authenticated with your AWS credentials) API with the Terraform module.
To tell the command where to deploy the app, an additional --endpoint flag must be provided, which should use the value from the api_endpoint output from the terraform apply step:
tf-next deploy --endpoint https://<api-id>.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
> Available at: https://3edade7a2bf7bb0343699af6b851bbfa.example.com/
The preview deployment can now be accessed by the displayed url.
To make the deployment available from a more readable url, you can use the tf-next alias subcommand:
tf-next alias set my-app.example.com 3edade7a2bf7bb0343699af6b851bbfa.example.com
> Available at: https://my-app.example.com/
For a full list of available commands that can be used with tf-next, check the command reference.
- Atomic Deployments
Each deployment gets a unique url from where it can be previewed. - Complete
Complete example with SSR, API and static pages. - Static
Example that uses static pages only (No SSR). - Next Image
Images are optimized on the fly by AWS Lambda. - Existing CloudFront
Use the module together with an existing CloudFront distribution that can be fully customized. - Custom Domain
Use the module with your own domain from Route 53.
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| terraform | >= 0.15 |
| aws | >= 4.8 |
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| aws | >= 4.8 |
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cloudfront_acm_certificate_arn | ACM certificate arn for custom_domain | string |
null |
no |
| cloudfront_aliases | Aliases for custom_domain | list(string) |
[] |
no |
| cloudfront_cache_key_headers | Header keys that should be used to calculate the cache key in CloudFront. | list(string) |
[ |
no |
| cloudfront_create_distribution | Controls whether the main CloudFront distribution should be created. | bool |
true |
no |
| cloudfront_external_arn | When using an external CloudFront distribution provide its arn. | string |
null |
no |
| cloudfront_external_id | When using an external CloudFront distribution provide its id. | string |
null |
no |
| cloudfront_minimum_protocol_version | The minimum version of the SSL protocol that you want CloudFront to use for HTTPS connections. One of SSLv3, TLSv1, TLSv1_2016, TLSv1.1_2016, TLSv1.2_2018 or TLSv1.2_2019. | string |
"TLSv1" |
no |
| cloudfront_origin_request_policy | Id of a custom request policy that overrides the default policy (AllViewer). Can be custom or managed. | string |
null |
no |
| cloudfront_price_class | Price class for the CloudFront distributions (main & proxy config). One of PriceClass_All, PriceClass_200, PriceClass_100. | string |
"PriceClass_100" |
no |
| cloudfront_response_headers_policy | Id of a response headers policy. Can be custom or managed. Default is empty. | string |
null |
no |
| cloudfront_webacl_id | An optional webacl2 arn or webacl id to associate with the cloudfront distribution | string |
null |
no |
| create_image_optimization | Controls whether resources for image optimization support should be created or not. | bool |
true |
no |
| debug_use_local_packages | Use locally built packages rather than download them from npm. | bool |
false |
no |
| deployment_name | Identifier for the deployment group (only lowercase alphanumeric characters and hyphens are allowed). | string |
"tf-next" |
no |
| enable_multiple_deployments | Controls whether it should be possible to run multiple deployments in parallel (requires multiple_deployments_base_domain). | bool |
false |
no |
| image_optimization_lambda_memory_size | Amount of memory in MB the worker Lambda Function for image optimization can use. Valid value between 128 MB to 10,240 MB, in 1 MB increments. | number |
2048 |
no |
| lambda_attach_policy_json | Whether to deploy additional lambda JSON policies. If false, lambda_policy_json will not be attached to the lambda function. (Necessary since policy strings are only known after apply when using Terraforms data.aws_iam_policy_document) | bool |
false |
no |
| lambda_attach_to_vpc | Set to true if the Lambda functions should be attached to a VPC. Use this setting if VPC resources should be accessed by the Lambda functions. When setting this to true, use vpc_security_group_ids and vpc_subnet_ids to specify the VPC networking. Note that attaching to a VPC would introduce a delay on to cold starts | bool |
false |
no |
| lambda_policy_json | Additional policy document as JSON to attach to the Lambda Function role | string |
null |
no |
| lambda_role_permissions_boundary | ARN of IAM policy that scopes aws_iam_role access for the lambda | string |
null |
no |
| multiple_deployments_base_domain | Default wildcard domain where new deployments should be available. Should be in the form of *.example.com. | string |
null |
no |
| tags | Tag metadata to label AWS resources that support tags. | map(string) |
{} |
no |
| tags_s3_bucket | Tag metadata to label AWS S3 buckets. Overrides tags with the same name in input variable tags. | map(string) |
{} |
no |
| vpc_security_group_ids | The list of Security Group IDs to be used by the Lambda functions. lambda_attach_to_vpc should be set to true for these to be applied. | list(string) |
[] |
no |
| vpc_subnet_ids | The list of VPC subnet IDs to attach the Lambda functions. lambda_attach_to_vpc should be set to true for these to be applied. | list(string) |
[] |
no |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| api_endpoint | API endpoint that is used by the CLI. |
| api_endpoint_access_policy_arn | ARN of the policy that grants access to the API endpoint. |
| cloudfront_custom_error_response | Preconfigured custom error response the CloudFront distribution should use. |
| cloudfront_default_cache_behavior | Preconfigured default cache behavior the CloudFront distribution should use. |
| cloudfront_default_root_object | Preconfigured root object the CloudFront distribution should use. |
| cloudfront_domain_name | Domain of the main CloudFront distribution (When created). |
| cloudfront_hosted_zone_id | Zone id of the main CloudFront distribution (When created). |
| cloudfront_ordered_cache_behaviors | Preconfigured ordered cache behaviors the CloudFront distribution should use. |
| cloudfront_origins | Preconfigured origins the CloudFront distribution should use. |
| upload_bucket_id | n/a |
Under the hood this module uses a lot of Vercel's build pipeline. So issues that exist on Vercel are likely to occur on this project too.
-
Stack deletion (
terraform destroy) fails on first run (terraform-provider-aws#1721)This is intentional because we cannot delete a Lambda@Edge function (Used by proxy module) in a synchronous way. It can take up to an hour for AWS to unbind a Lambda@Edge function from it's CloudFront distribution even when the distribution is already destroyed.
Workaround:
After running the initial
terraform destroycommand (that failed) wait ~1 hour and run the command again. This time it should run successfully and delete the rest of the stack. -
Initial apply fails with error message
Error: error creating Lambda Event Source Mapping(#138)There is some race condition when the permissions are created for the static deployment Lambda. This should only happen on the first deployment.
Workaround:
You should be able to run
terraform applyagain and the stack creation would proceed without this error.
Contributions are welcome!
If you want to improve this module, please take a look at our contributing guidelines to get started.
This project is maintained by milliVolt infrastructure.
We build custom infrastructure solutions for any cloud provider.
Apache-2.0 - see LICENSE for details.
Note: All sample projects in
examples/*are licensed as MIT to comply with the official Next.js examples.

