In this summary I will try to collect the basics and important terminology surrounding the course. Hopefully it will help when writing the report. The end goal would be for this summary to be the only necessary source in order to complete the course.
Here are some links for where you will find specific course materials and software. I will also go showcase some of the assignments to be completed during the run of this course.
This is the current Course Admin:
Name: Kirsten "Kirre" Rassmus-Gröhn
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone: 046 - 222 03 50
Here are some helpful links for the course:
- Moodle Here you will find all course material for your course.
- Course Page This is the course page.
- Android Studio Here you can download Android Studio if you don't already have it.
- JDK This is the programming language you all will be using.
- GitHub This is really important for version handling, you don't have to use GitHub but it is recommended since it is so easy tracking versions of your project and for working together in a team.
Here is a list of some authors with helpful literature:
- Norman
- Preece, Rogers, Sharp
- Arvola
This is the programming tools you will need for the project:
- Java Development Kit
- Android Studio
- GitHub
You are to create an app for the android using java with non-traditional interaction. You will be in a team of four where the other team-members will be chosen for you by course admin. If you miss an obligatory event contact course admin to get an assignment since deadline will be one week from missed occassion. In parallell to the app you will also write a report that describes the design process and your decisions.
You will need the following equipment which you may also have access to in school or borrow from course admin:
- A computer
- Android phone
The laid out guide-lines are:
- Tuition once a week with your mentor.
- Brainstorming event with the group.
- Presentation of conceptual idea.
- Presentation of work in progress.
- Showcase fair with everyones products.
For every occassion your group will have to bring an android phone where you can test your app. You will also have to show your progress while discussing progress, problems, fears and future plans.
As a start you will have a workshop for setting up the enviroment in Android Studio and testing the individual assignment "Hello Sensor". This assignment is only pass or fail.
All code should be put on GitHub, where your mentor is to be invited as well. All borrowed code has to be referenced, and it is desirable in this project since you will be able to focus more on the design rather than function.
The presentation of the work in progress is supposed to be like an elevator pitch. It is desirable to use powerpoint as an aid during the presentation. You should also send the slides one day before the presentation.
You are as mentioned to write an report where you describe your design process. You will find the template on Moodle.
The report consists of:
- Theory
- Method
- Explanation of motivation of design decisions
- Explanation of the prototype
Keep the report updated everytime you work on the project.
You will leave feedback on eachothers reports.
You will also write an A4 paper of your individual experience from the project, it should be around 450-750 words.
These are the content titles:
- My greatest contribution to the project.
- My project members greatest contribution to the project.
- What I've learned from the project. (Most important part)
This part is meant to jugg a bit of your memory from past terminology from previous courses.
The most basic definition of prototype is, “A simulation or sample version of a final product, which is used for testing prior to launch.” The goal of a prototype is to test products (and product ideas) before sinking lots of time and money into the final product.
Prototypes have four main qualities:
- Representation — The actual form of the prototype, i.e., paper and mobile, or HTML and desktop.
- Precision — The fidelity of the prototype, meaning its level of detail, polish, and realism.
- Interactivity — The functionality open to the user, e.g., fully functional, partially functional, or view-only
- Evolution — The lifecycle of the prototype. Some are built quickly, tested, thrown away, and then replaced with an improved version (this is known as “rapid prototyping”). Others may be built and improved upon, ultimately evolving into the final product.
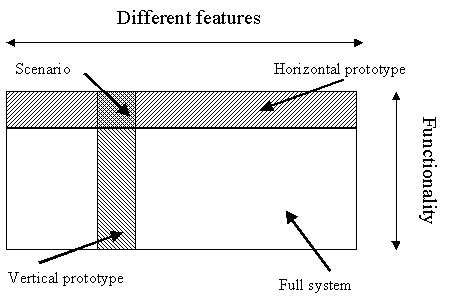
There are generally two types of prototypes:
- Horisontal prototype - Lots of functions but low on details.
- Vertical prototype - Few functions but high on details.
LoFi-prototype is an example of a primarily horistonal prototype, while HiFi-prototype is a lot closer to the finished product and is usually a lot more of a vertical prototype high on detail.
T-prototype is an example of a vertical and horisontal prototype where you showcase what intended features are, but really only go into depth of a few. The more functions with high detail the more "legs" the T-prototype has.
A common problem with developing a product is a two-way road.
- The designer just understands a small part of the users problem.
- The user overestimates the designer’s understanding of the problem.
By integrating the user in all the parts of the design process you will be much more likely to develop a successfull product.
Here are some great buzz-words to use for the report: Understanding, users, tasks, enviroments, evaluation, iterative(rework many times), user experience (Look, feel and usability), multidiciplinary (a diverse team in thinking and knowledge.
You will find the instructions for the first assignment on Moodle, but I will go through everything here as well. There will be a workshop for you if you feel you get stuck and need help.
This section will help you getting started with the assignment.
If you don't want to follow my instructions below on how to initialize Android Studio and your first project you can just watch this video instead. It will start on 1.35 since this is where the real walkthrough starts.
This this section will help you set up Android Studio for the assignment. You can skip this part if you already have Android Studio and connected it with your Git-account.
- Go to this webpage and download and install Android Studio.
- Open Android Studio. If this is the first time you open the application you will have to configure some settings first. I will guide you through the process:
- They will ask if you want to share your data in order to "improve" their program. I personally never send any data anywhere if I can chose not to, but do feel free to send user data if you don't mind.
- Next you will have to decide how you want to initialize Android Studio. You can chose between Standard and Custom, the only difference is that Custom will allow you to decide how much RAM to allocate when running emulator instances. Standard is recommended if you don't have any preferences.
- Next they will ask you to pick a theme, I went with Darcula (black theme FTW).
- Now you will be able to pick SDK components, tick in the "Android Virutal Device" if you want an emulator in order to test your app directly on the computer in Android Studio. You will also be able to pick installation folder for the SDK components further down.
- If you chose custom and have a system that can run the emulator in accelerated performance mode you will be able to chose how much RAM you want to allocate for the emulator instances. Just go with the recommended if you don't know that you are doing.
- Go to "File" in the top left corner and chose on Mac: "Other Settings" -> "Preferences for New Projects". And on other systems: "Settings..."
- Go to "Version Control" -> "Git". Here you should check that the path to your installed Git directory is shown in the box for "Path to Git executable". This is usually "Auto-detected". If you press the "Test"-button you will see if your Git is configured correctly in Android Studio.
- In the same window, go to the section "GitHub". Press "Add account". Let the Server/Host stay as "github.com". Write in your account information for GitHub then press "Login" and "Apply". You should see your account displayed in the window.
This is a quick explanation on how to connect an existing project in Android Studio to a repository on your GitHub. You can skip this part if you already know how to or if you just want to start on the assignment "Hello Sensor" instead.
- In the top menu, pick "VCS" -> "Import into Version Control" -> "Share Project on GitHub".
- Fill in the necessary information and press "Share".
- A menu will pop-up allowing you to decide what files you want to commit and add to your new respository. You can also write your commit message in the bottom of the window. Press "OK" when done.
- Now you can easily just press the buttons near the top of the window in order to commit and pull changes from your repository. You can just as easily use the terminal (which I prefer and recommend that you learn how to use).
Now you will begin creating your app, I will try to guide you through the process.
- Create a new project by clicking on "File" -> "New" -> "New Project". Choose an "Empty Activity" and press "Next".
- For name you can choose whatever, a suitible name can be "Hello Sensor". Make sure the language chosen is Java since this is one of the criteria for the project.