As you can see in the above gif how the sentiment meter change according to the sentences. Every single day of life humans use sentiment analysis 88% of the time, like for guessing the emotions of a person by what he/she is saying, or for making decisions whether to watch a movie by reading the reviews online or whether the email received is a fake one saying that you've won a lottery of $10000000 and for many other things.
So in this world of technology where Machine learning, Artificial intelligence is the new electricity, teaching the machines how to react for various emotions in the real life is the coolest thing in my opinion.
Wikipedia states sentiment analysis as
"Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining or emotion AI) refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis, computational linguistics, and biometrics to systematically identify, extract, quantify, and study affective states and subjective information."
Sentiment analysis is the biggest boon for businesses as it can understand the customer reviews and make some predictions which is beneficial for the businees to improve where the customer has not liked a certain service and improve in future.
Some basic use cases of sentiment analysis are:
- Spam Email detection.
- Movie reviews analysis.
- Emotions analysis of text data
- Harmful tweets classification and many more
Some of the existing approaches to solve the sentiment analysis are knowledge based, statistical methods and hybrid approach. In knowledge based approach it uses the knowledge in the sentence by checking for the words like happy, sad, angry, etc. It also can detect some not so obvious sentiments from the sentences. In statistical methods, many machine learning algorithms like latent sentiment analysis, SVM, bag of words, deep learning (neural netowrks),etc. are used and in hybrid approach as you can guess by it's name both the aprroaches are used together to solve a complex problem and to gain higher accuraccy. In Machine learning and Deep learning community there is always a need to achieve the human level performance or atleast make accuracy near to the human level, for example of emotion detection in a sentence, lets say on a scale of 1 to 10 human level performance is 10 so the sentiment analysis should achieve approaximately 10 or near to 10 performance then it's a best fit for the problem, if the sentiment analysis is 5 then it'd make no sense.
Another visual of how the sentiments analysis might look.
A very basic task in sentiment analysis is to classify the polarity of a given text i.e to check whether the sentence has a positive or negative or a neutral impact. In advanced sentiment analysis it checks for beyond polarity that means it checks for various words like "angry", "happy" and "sad" for better understanding of the emotion.
For this article we'll be using basic python and some libraries.
I've used TextBlob library of python to do basic classification of sentiments in a given sentence.
You can install TextBlob by
pip install textblob
Here's how the classification of the polarity of a given text would look like in python
from textblob import TextBlob
string = TextBlob('I have been to the PVR cinemas Gold the experience there was quite good,I would recommend it to you as well.' ) #this line creates a textblob object which can be used in many ways for sentiment analysis
print('Polarity of the sentence -'+str(string.sentiment.polarity))
Output: Polarity of the sentence - 0.0
The second task to do in sentiment analysis is subjectivity/objectivty what it means is, it classifies the sentence into one of two classes objective or subjective. In some sentences the polarity classification might not help because the subjectivity of words and phrases may depend on their context and an objective document may contain subjective sentences.
The only takeaway from subjectivity/objectivity is that machine can determine the sentence context and it's relativity to the previous words and keep overall meaning intact.
Using the string used above to get the subjectivity
print(string.sentiment.subjectivity)
output: 0.0
This gives output as zero because the sentence stands alone as an opinion so using polarity classification is best. Another example where we get subjectivity value is:
testimonial = TextBlob("Self driving cars are amazingly simple to use")
print(testimonial.sentiment)
ouput: Sentiment(polarity=0.0, subjectivity=0.35714285714285715)
Here you can see that the subjectivity value is a non-zero value which means the sentence is not a polarity based classification sentence.
Another way is a feature based or aspect based that is it determines the opinions from the sentences and try and make intuition about that sentence. These sentences are usually reviews from the customers about various services or products they've used or experienced. This approach is usually used to gain insights on how a particular product or a service is doing and to get better or do changes in delivering those products/ services. It is also used with recommender systems together and when both are in action they provide better user experience. Recommender systems are another topic of machine learning but for now we'll focus on sentiment analysis.
Here's a small example on a yelp review using just our Textblob.
def sentiment_analysis(sentence):
#initialize the positive and negative varibles
p=0
n=0
#Split the entire stirng into space separated words and add it to a list-
words = [word for word in yelp_review.split(' ')]
#Make the splitted words list to a textblob
word_blob = [TextBlob(x) for x in words]
#iterate through the all the textblobs created and
search for positive/neg polarity
for x in word_blob:
if x.sentiment.polarity > 0:
p+=1
elif x.sentiment.polarity<0:
n+=1
#confirm the positive/ negative effect of the review
if n < p:
print("It was a positive review")
else:
print("It negative review")
#input sentence --> can change to different sentences to check multiple test cases
yelp_review = '''This was a convenient and interesting place.
All I needed to do was to open a matrix barcode in Amazon Go app and scan it at an entrance gate.
That's it. I picked up what I wanted and got out of the gate without any physical payment process. Very quick.
I visited it with my family. I scanned my code and my son went through the gate.
Then, I scanned again and my wife went through. Last, I scanned again and I went through.
Then, they could select items on their own, and their payments were sent to my account. Very interesting.
If you need a bag, you need to register it on the app. This was the only thing I had to do inside the store.
You can have a fork, a spoon, a napkin and so on outside of the gates. There are a space to eat in the store.Very convenient.
I hope they will have more and more items in a store, and stores outside the big cities.'''
sentiment_analysis_assignment1(yelp_review)
output: It was a positive review
This was the basic overview of basic sentiment analysis using just python and textblob. Let's see what the bigger picture is, Natural Language Processing is the bigger picture. As the name suggests Natural language processing is the technology which understands the human language and can interact in various ways with human. Now that smart devices like amazon echo, google home or even the apple homepod have emerged which uses the assistant in the backend which is trained using the natural language processing so that it can understand the human spoken sentences and generate responses for him with lowest latency and accuracy.
Here's a small visual to make the bigger picture of natural language processing clearer.
In NLP the optimal way to build a system is to use deep learning models to train the data. Most commonly tokenization of the sentences is done in NLP so that it splits text into tokens and using these tokens we can perform various tasks.Machine learning models take vectors (arrays of numbers) as input. When working with text, the first thing we must do come up with a strategy to convert strings to numbers (or to "vectorize" the text) before feeding it to the model. There are different strategies to convert the strings to numbers. Some of the majorly used strategies are:
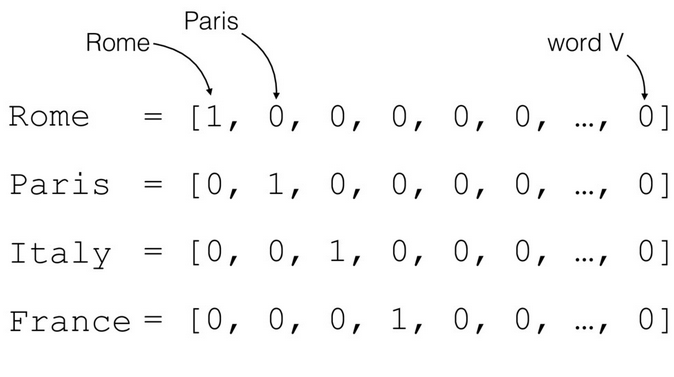
- One hot encode: This is a technique that produces as many vectors as many categories are there. for example
-
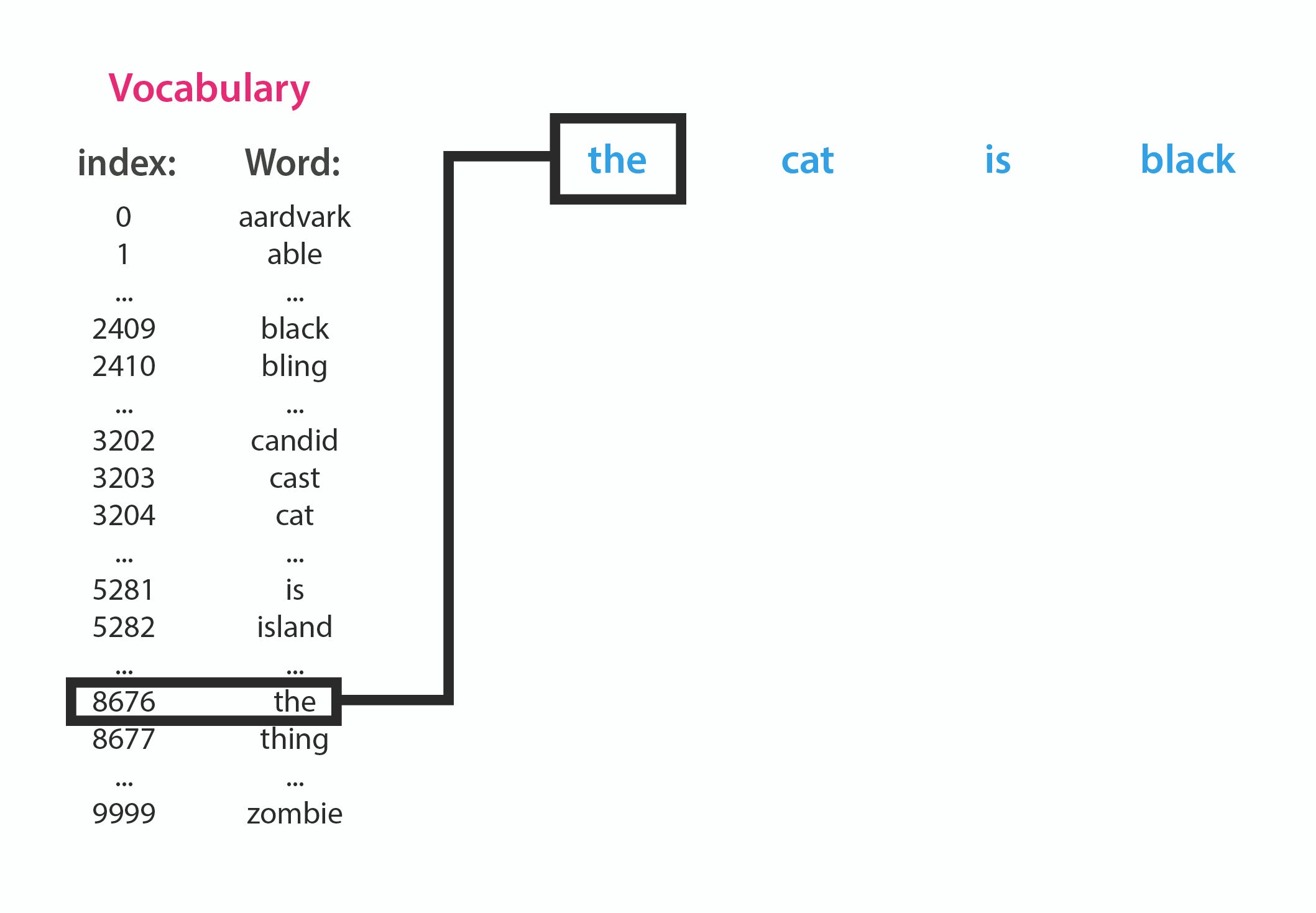
Encode each word with a unique number- In this approach we encode by assigning each word a unique number in this way we can generate the sequence of the sentences. Let's say in the above example we assign paris as 3, Rome as 2, Italy as 4, France as 1 then in a sentence "In our Europe tour iteneary we have Paris, France and Rome" we can get a sequence of [6,7,8,9,11,23,3,1,5,2] assuming that other characters have been assigned with those numbers encoding. This was just an example of how sequencing would look like.
-
Word Embeddings - This strategy is the optimal and efficient to use dense neural networks because in some cases there could be same encodings for different words like for example 'cat' and 'mat' could have same one-hot encoding 'listen' and 'silent' will have same encoding since it has same letters in it. So for this word embeddings is the optimal one. We do not have to specify this encoding by hand. An embedding is a dense vector of floating point values.
This were the strategies to convert the string/ text data to number vector for our neural network model training.
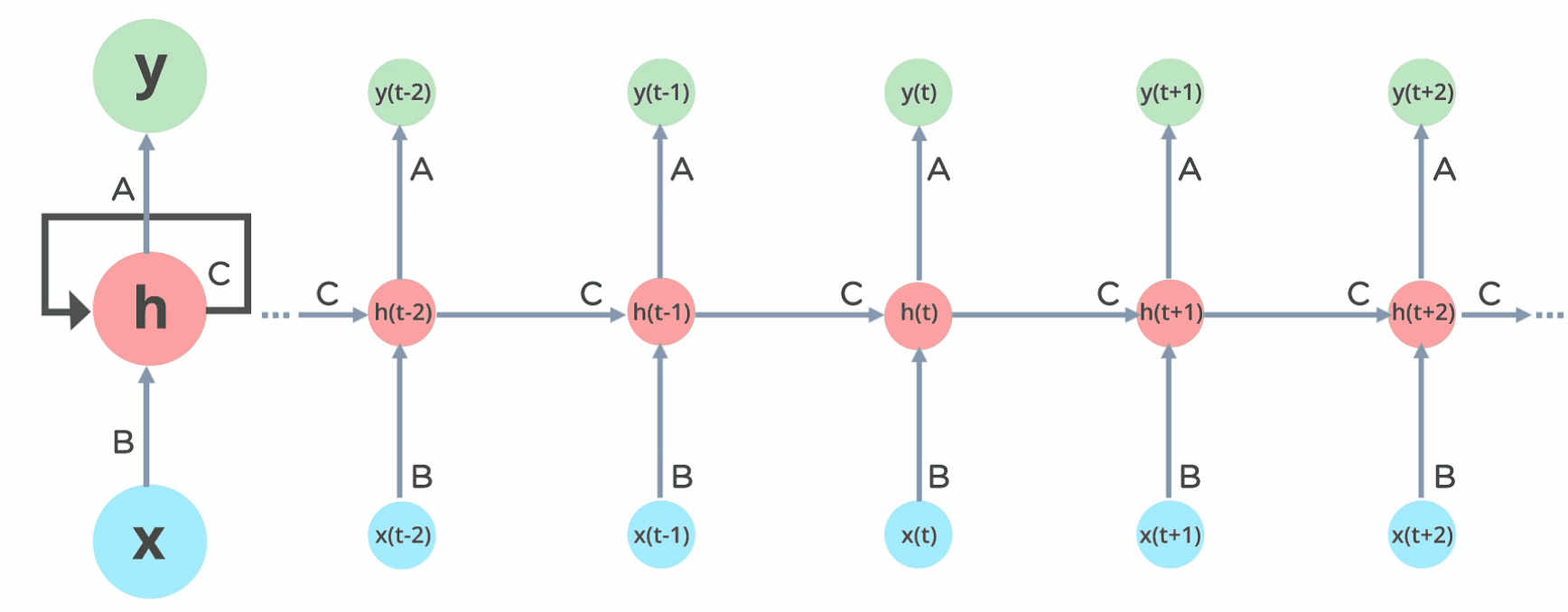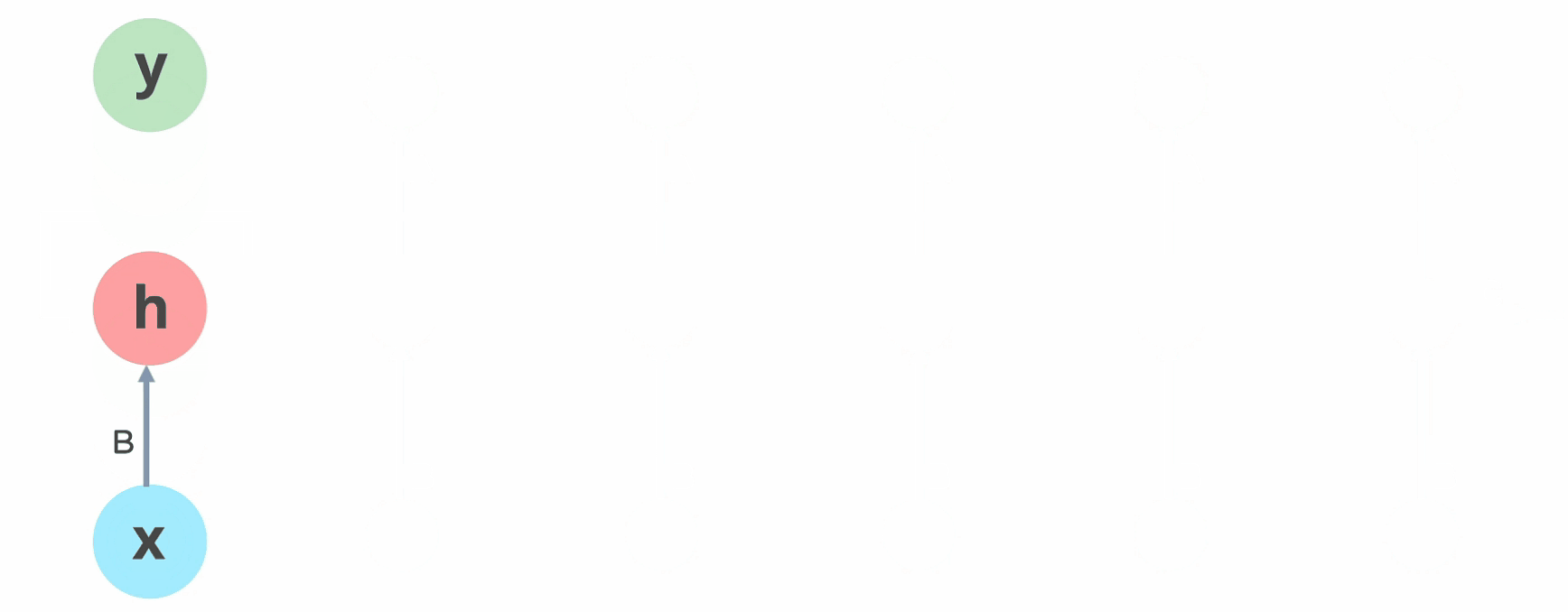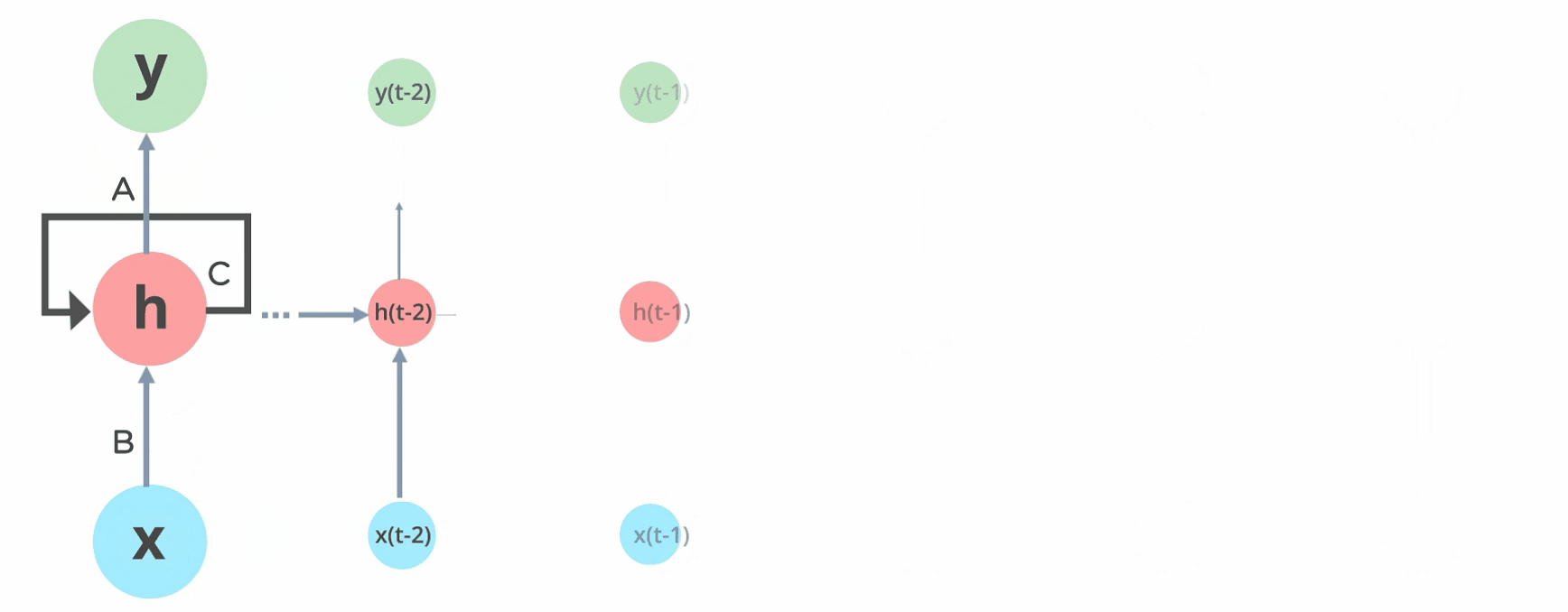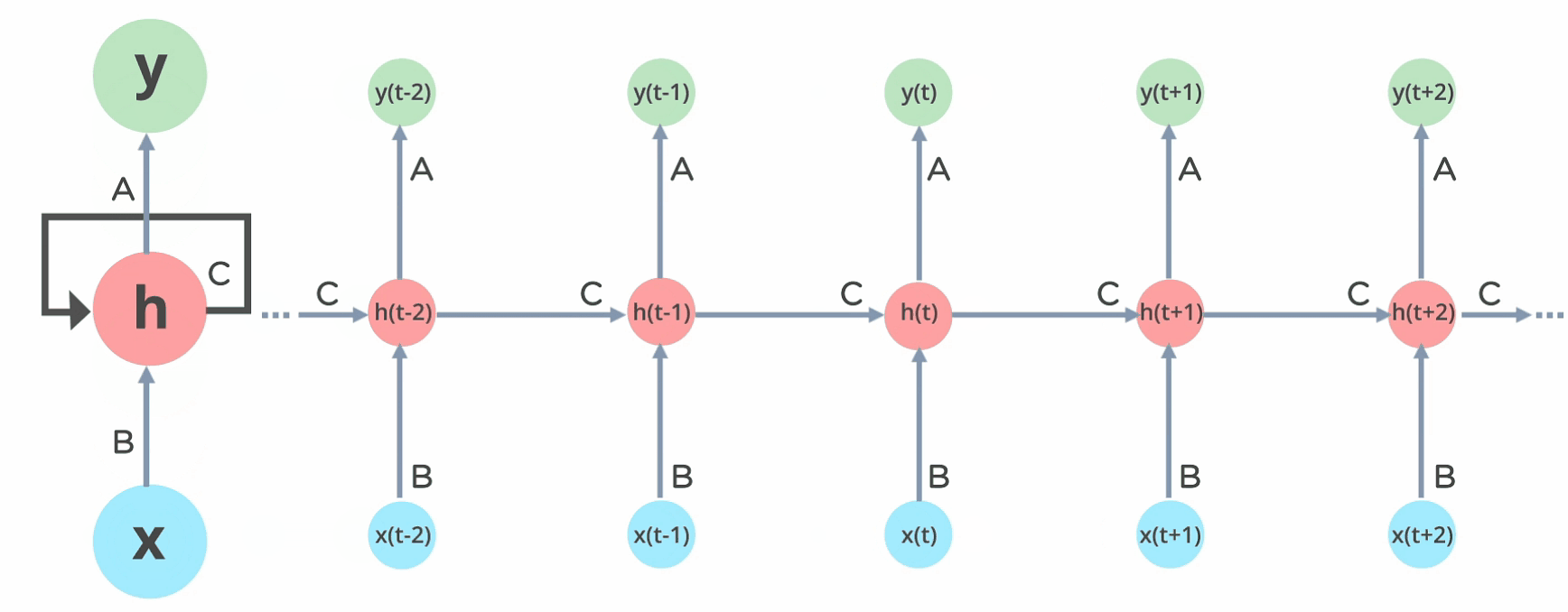
The neural network architecture used for NLP is Recurrent neural network because of it's robustness and it's feature to support the time series makes it more appealing in NLP to not only for sentiment analysis but also to generate texts.
Here's how the recurrent network works. For the in-depth about RNN, about how the activations are calculated and how the previous states are taken for consideration of further calculations you can always refer to this RNN article
But for now we'll make a basic sentiment analysis using a basic neural network. We'll build a sarcasm detector by training a neural network using sarcasm detection in news headline dataset. We will use tensorflow for this. There are two ways to use tensorflow, you can install tensorflow on your local machine by
pip install tensorflow
Here's Tensorflow's GPU guide if you have CUDA based GPU which will make the training much more faster.
or you can use the google's colab notebooks which has almost every deep learning libraries pre-installed in it.
For this we will need to
-
Tokenize the text. [Tokenizer class allows to vectorize a text corpus, by turning each text into either a sequence of integers (each integer being the index of a token in a dictionary) or into a vector where the coefficient for each token could be binary, based on word count]
-
Then use fit_on_texts function to fit the vocabulary size of the training sentences
-
Then create sequences of the tokens created in the previous step and outputs a python array of numberes with sequences of the tokens that represent the sentence numnerically in our defined way.
-
Then pad the sequences with zeros incase any sequence is short, as it may happen because all sentences are not of the same size. This was basic neural network for sentiment analysis which after training will be able to classify whether a sentence is sarcastic or not.
-
Then build and compile a model with an embedding layer, a Global Average pooling 1d layer, Dense layer, Dense layer (for output).
VADER stands for **V**alence **A**ware **D**ictionary and s**E**ntiment **R**easoner, it is a lexicon and rule-based sentiment analysis tool.
**VADER** is specially modelled and trained to determine the sentiments on the social media texts to determine any harmful or negative activity specifically. Here's how VADER is different from basic sentiment analysis.
To use Vader you can install vader simply by running this command in your command prompt: ``pip install vaderSentiment`` After successful installation you're good to go and use VADER for sentiment analysis.
Next we need to import Vader in order to use its features:
from vaderSentiment.vaderSentiment import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer
sentence = 'The latest Batman movie looks amazing by just it's teaser and I'm really excited for it'
Here we need to first initialize the class by creating an object of the class SentimentIntensityAnalyzer
object = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer()
Now unlike Textblob this class function returns a sentiment dictionary so if we need to print a specific value we need to first access it.
out_dict = object.polarity_scores(sentence)
print("Overall sentiment dictionary is : ", out_dict)
This will print out the overall sentiment dictionary returned by the function.
To see the single sentiments we can do this:
print("sentence was rated as ", out_dict['neg']*100,"% Negative")
print("sentence was rated as ", out_dict['neu']*100,"% Neutral")
print("sentence was rated as ", outt_dict['pos']*100,"% Positive")
So this is the most basic use case of VADER and how it can be used. VADER is a self sufficient beast to analyze different sentiments from the text data, so it best performs on social media data and even works better for other domains.
Other use cases of VADER could be
In the paper VADER: A Parsimonious Rule-based Model for Sentiment Analysis of Social Media Text by sir C.J. Hutto and Eric Gilbert the entire idea behind VADER is explained and how it works. There's also a github repository here's the link for it if you want to go ahead and try VADER for some other problem.
There is google's BERT NLP framework which is a mind-blowing work which has a lot of potential in it which has gained a lot of attention of modern NLP problems and to solve them by using BERT.
Okay so what is BERT?
As of internet definition
"BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. It is designed to pre-train deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context. As a result, the pre-trained BERT model can be fine-tuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models for a wide range of NLP tasks"
For more Advanced sentiment analysis BERT is used or even to fine tune the current working RNN models or other dense networks.
Here's the architecture of the BERT network
Some facts and features to know about BERT from internet-
- BERT is a transformer based architecture.
- BERT is a language model.
- BERT has over-performed human beings performance.
- BERT has been used to solve problems lilke sentiment analysis and QNA (questions and answers)
- BERT can be used to fine tune the RNN models used for the NLP problems.
- BERT is pre-trained on a large corpus of unlabelled text including the entire Wikipedia(that’s 2,500 million words!) and Book Corpus (800 million words).
- BERT is a “deeply bidirectional” model. Bidirectional means that BERT learns information from both the left and the right side of a token’s context during the training phase.
I've not implemented BERT here because it needs neural network model on which it could be used to fine tune the model and pump up the accuracy.
Here's a paper you could read regarding to BERT link
So that's it,
Thank you for staying till here and I hope you had a good time reading this and probably learnt something just like the neural network!
You can always contact me at my social media handles:



Mail me at: [email protected]
If you're more into reading the behind the scenes and about how the NLP actually is in action in real life problems here are some papers you might want to check it out.
Extra readings for curious minds In "The general inquirer: A computer approach to content analysis." paper from MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (1966) it shows the hints towards quantifying patterns in text and psychological research that could examine a person's psychological state based on analysis of their verbal behaviour.
"Sentiment Extraction from Consumer Reviews for Providing Product Recommendations" in this paper the research shows sentiment extraction from customer reviews and building an intuition to recommend a product to user base of similarlikes/ dislikes.
Sentiment analysis of citations using sentence structure-based features](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P11-3015.pdf)
All the images and gifs have been used from google image search and the links to them are in the source incase you need. Some facts and lines are taken from few articles on the wikipedia.com and one of them(facts and features of BERT) is from analyticsvidhya.com