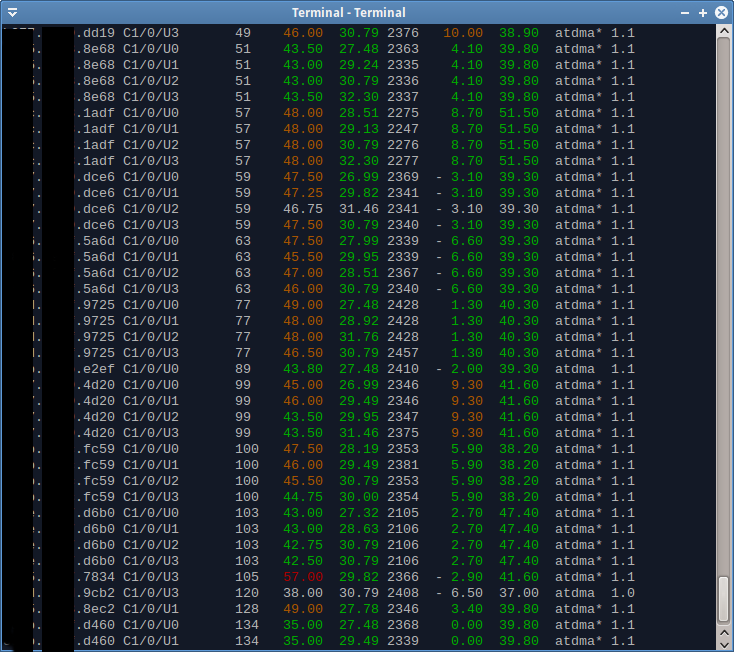
tel provides the following:
- Use a simple, single command to connect to multiple network device types.
- Create aliases for hard to type router names or commands.
- Handles terminal-related issues, such as proper backspace.
- clogin-style CLI arguments (via -c and -x).
- Color highlighting.
- Optional global config that supports multiple users.
- Keepass and Keyring support
- Handles automatic logins for text-based user interfaces common on older networking devices.
- Highly customizable
On cisco, logout is logout or exit. On zhone it's exit. On dlink it's logout. Casa, logout. allied telesis, logout. hatteras, logout or exit. On mikrotik, it's /quit.
On UNIX, depending on the shell, logout or exit might work.
Many devices come up with their own unique way of logging out. Having to figure out if it's logout, quit, /quit, exit, etc. Can be tiring if you're switching between devices all day.
UNIX has a shortcut that works in all shells. Ctrl-D is end of file. That will logout/exit any shell you're using, and also works in many applications to stop what you're doing and quit.
The tel script aliases Ctrl-D to run whichever logout command is used for the device you connect to.
Dlink, and many other platforms have a broken backspace. This script detects dlink and aliases backspace to the right sequence. Casa has a Cisco-like CLI, but doesn't support Ctrl-Z. This will add Ctrl-Z.
common tasks can be automated and even advanced commands can be scripted through Perl's Expect.pm. Most of that is available directly in the telrc files without modifying the code in tel. See the COMMANDS file for examples.
Example: tel -c 'show ver; show ip int br' sw1-cisco-device
Example:
cat <<EOF>commands.txt
conf t
int vlan2
description Hello
end
wr
EOF
tel -x commands.txt sw1-cisco-device
Administrators may control login settings for multiple users via the global config file. This is useful if you have a NOC where 10 people may need to login all the time and your telrc config file has complicated business logic in it, but you don't want to update each person’s home directory each time a change is made to it.
- The global config file is stored in /etc/telrc
- Per-user configs are stored in $HOME/.telrc2
Please read the COMMANDS file for an in-depth command list, with examples.
Take the dottelrc.sample and copy it to /etc/telrc, then edit it to suit your site’s needs. This is a baseline configuration that everyone on a jump host can use. It's actually a perl file so advanced scripting is possible. See the COMMANDS file for descriptions of some of the options and examples of their use.
Once you've done that you may need to install a couple of things to get it running. Here is the easy route if you're running a debian-based OS:
sudo apt-get install libmodule-install-perl libtest-most-perl libexpect-perl libio-stty-perl make
Now you can run the usual build commands to install:
- perl Makefile.PL
- make
- make install
A far easier way to install is to use cpanminus if you're comfortable with it, now that the app is on CPAN:
-
curl -L https://cpanmin.us | perl - App::cpanminus
-
cpanm App::Tel
When you've installed and are ready to use the app, you can instruct your users to run "mktelrc". This will prompt them for the username and password they use for routers, then write them to a .telrc2 file in their home directory.
This file should be only readable by the user for security reasons, although the very act of storing passwords for your routers in a file means you are already defeating some security. I advise you to only run this on a heavily firewalled box that is only used to allow users to access routers.
Obviously, if the router supports real ssh keys or any other secure authentication you should let the login be handled by that. This script can still provide value without the need to login for you.
You may want to download File::KeePass, Passwd::Keyring::Auto, Passwd::Keyring::Gnome, Crypt::PWSafe3, or GnuPG::Interface. If any of these are installed they will be used to provide additional features. Some setup may be required. Please see the COMMANDS file for more information.
If you've worked at a NOC at any point in time you’ve probably made a script like this one. It's probably written in Expect and probably sends your username and password to log you in. You might have different variants for different types of devices, or different things you need to do to a device.
This script aims to replace all of those and provide an easy to use interactive client for most of the CLI I've encountered.
I've been working on this off-and-on for 14 years. It started out in expect and now is written in perl/Expect.pm.
After posting this to reddit I found some people had similar ideas and had made progress on some things, but some have taken different directions. Here are the projects I know about:
-
A comment in http://www.reddit.com/r/networking/comments/2bxehw/coloring_cli/ references a python expect implementation. Here is a screenshot with some example code http://i.imgur.com/1slyPkK.png
-
This thread gives a few ideas that I'll list below http://www.reddit.com/r/networking/comments/2hy2dj/cisco_cli_colorization/
-
Cisco nx-os supports CLI coloring directly with "terminal color"
-
Cisco embedded event manager can be used to colorize output in recent IOS versions. You need to write scripts on each of the devices you connect with.
-
SecureCRT or MacOS iTerm2 can highlight sections by regex, if you prefer doing it at the terminal emulator level
-
If you want to do it at the ssh protocol level, there is https://github.com/mxtommy/Cisco-SSH-Client
-
Sending a "#" to the router via -c will match that as a prompt if that is what your prompt is set for. clear_accum doesn't fix this.. need to put more thought into it.
-
See ISSUES for a complete list of currently existing bugs
Please let me know about bugs or feature requests via github. Submit patches when possible to fix or enhance something, or to improve the testing.
I decided to put it on CPAN with the "tel" name despite it being pretty generic. If you've been running the script a while you may have left over library files in <perl_location>/Expect/Tel/. These are now unused and safe to remove. You might run "make uninstall" on the old release before installing the new version.