次のコマンドを実行して、サンプル集をビルドします。
$ ./build_samples.bashビルドに成功するとsamples01/bin/ディレクトリに実行ファイルが生成されます。
USB通信ポートのアクセス権限を変更するため次のコマンドを実行します。
$ sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyUSB0永続的なアクセス権限を付与する場合は次のコマンドを実行します。
$ sudo usermod -aG dialout $USER
$ rebootロボットとの通信遅延を最小にするため次のコマンドを実行します。
$ sudo chmod a+rw /sys/bus/usb-serial/devices/ttyUSB0/latency_timer
$ sudo echo 1 > /sys/bus/usb-serial/devices/ttyUSB0/latency_timerSciurus17を使用する場合は、 Sciurus17入門ガイドに記載されている手順で Sciurus17制御基板の通信タイムアウト機能を解除してください。
解除しない場合はサンプル実行中のスリープ処理によって通信タイムアウト機能が働き、サーボが脱力します。
次のコマンドを実行します。 サーボモータのトルクがON / OFFします。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_onoff
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_onoff実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
CRANE-X7のトルクをON/OFFするサンプルです.
CRANE-X7(ポート:/dev/ttyUSB0 ボーレート:3000000)に接続します.
コンフィグファイル:../config/crane-x7.yamlを読み込みます.
Config file '../config/crane-x7.yaml' loaded.
arm
joint1, id:2, mode:3
joint2, id:3, mode:3
joint3, id:4, mode:3
joint4, id:5, mode:3
joint5, id:6, mode:3
joint6, id:7, mode:3
joint7, id:8, mode:3
hand
joint_hand, id:9, mode:3
ジョイントグループ:armのトルクをONにします.
10秒間スリープします.
サーボモータの制御モードが位置制御モードのとき、ロボットに触れるとトルクがONになっていることがわかります.
ジョイントグループ:armのトルクをOFFにします.
CRANE-X7との接続を解除します.RTマニピュレータC++ライブラリを使用する場合はrt_manipulators_cpp/hardware.hppをincludeします。
#include "rt_manipulators_cpp/hardware.hpp"ロボットと通信するために、rt_manipulators_cpp::Hardware(port_name)クラスのインスタンスを生成します。
インスタンスの引数には通信ポート名を入力します。
rt_manipulators_cpp::Hardware hardware("/dev/ttyUSB0");ロボットと接続するために、Hardware.connect(baudrate)を実行します。
引数には通信ボーレート(bps)を入力します。
hardware.connect(3000000);ロボットのサーボモータ構成を読み込むために、Hardware.load_config_file(file_path)を実行します。
引数にはコンフィグファイルのパスを入力します。
hardware.load_config_file("../config/crane-x7.yaml");コンフィグファイルはYAMLフォーマットで次のように作成します。
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
ジョイントグループ名(2):
joints:
- ジョイント名(4)
- ジョイント名(5)
ジョイント名(1): { id : 0, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(2): { id : 1, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(3): { id : 2, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(4): { id : 3, dynamixel: "XM540", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(5): { id : 4, dynamixel: "XM540", operating_mode: 3 }トルクをONするためにHardware.torque_on(group_name)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名を入力します。
ジョイントグループのすべてのモータのトルクがONされます。
hardware.torque_on("arm");トルクをOFFするためにHardware.torque_off(group_name)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名を入力します。
ジョイントグループのすべてのモータのトルクがFFされます。
hardware.torque_off("arm");ロボットとの接続を解除するためにHardware.disconnect()を実行します。
hardware.disconnect();次のコマンドを実行します。 サーボモータの現在角度がターミナルに表示されます。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_read_position
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_read_position実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
...
ID:2のサーボ角度は1.491029radです.
joint_handのサーボ角度は1.259398radです.
armグループの0番目のサーボ角度は1.491029radです.
armグループの1番目のサーボ角度は-0.466330radです.
armグループの2番目のサーボ角度は0.087437radです.
armグループの3番目のサーボ角度は-1.848447radです.
armグループの4番目のサーボ角度は-0.044485radです.
armグループの5番目のサーボ角度は0.233165radです.
armグループの6番目のサーボ角度は0.961806radです.
...サーボモータの現在角度を取得するため、
コンフィグファイルのジョイントグループにsync_read:positionを追加します。
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
sync_read:
- position
ジョイントグループ名(2):
joints:
- ジョイント名(4)
- ジョイント名(5)
sync_read:
- positionサーボモータの現在情報を読み取るため、Hardware.sync_read(group_name)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名を入力します。
この関数を実行すると、ロボットとの通信が発生します。
hardware.sync_read("arm");サーボモータの現在角度を取得するため、Hardware.get_position(id, position)を実行します。
引数にはサーボモータのIDと、角度(radian)の格納先を入力します。
double position;
hardware.get_position(2, position);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
double position;
hardware.get_position("joint1", position);ジョイントグループの現在角度を一括で取得する場合は、Hardware.get_positions(group_name, positions)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、角度の格納先を入力します。
std::vector<double> positions;
hardware.get_positions("arm", positions);次のコマンドを実行します。 CRANE-X7は垂直姿勢に移行し、ハンドを開閉します。 Sciurus17は胴体が正面を向く姿勢に移行し、右ハンドを開閉します。
安全のためロボットの周りに物や人を近づけないでください。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_write_position
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_write_position実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
...
armグループのサーボ最大加速度を0.5pi rad/s^2、最大速度を0.5pi rad/sに設定します.
handグループのサーボ最大加速度を0.5pi rad/s^2、最大速度を0.5pi rad/sに設定します.
arm、handグループのサーボ位置制御PIDゲインに(800, 0, 0)を書き込みます.
armグループのサーボ目標角度に0.0 radを書き込みます.
5秒後にX7が垂直姿勢へ移行するため、X7の周りに物や人を近づけないで下さい.
5秒間スリープして動作完了を待ちます.
ID:5のサーボ目標角度に-2.094395 radを書き込みます.
5秒間スリープして動作完了を待ちます.
joint_handジョイントのサーボ目標角度に0.523599 radを書き込みます.
5秒間スリープして動作完了を待ちます.
joint_handジョイントのサーボ目標角度に0.000000 radを書き込みます.
5秒間スリープして動作完了を待ちます.
arm、handグループのサーボ位置制御PIDゲインに(5, 0, 0)を書き込み、脱力させます.
10秒間スリープします.
CRANE-X7との接続を解除します.サーボモータに目標角度を書き込むため、
コンフィグファイルのジョイントグループにsync_write:positionを追加します。
ジョイントのoperating_modeは3に設定します.
コンフィグファイル読み込み時に、サーボモータ内部のパラメータであるOperating Modeに
3 (位置制御モード)が書き込まれます.
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
sync_write:
- position
ジョイントグループ名(2):
joints:
- ジョイント名(4)
- ジョイント名(5)
sync_write:
- position
ジョイント名(1): { id : 0, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(2): { id : 1, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(3): { id : 2, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(4): { id : 3, dynamixel: "XM540", operating_mode: 3 }
ジョイント名(5): { id : 4, dynamixel: "XM540", operating_mode: 3 }サーボモータの最大動作加速度を設定するため、Hardware.write_max_acceleration_to_group(group_name, acceleration)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、加速度(radian / second^2)を入力します。
hardware.write_max_acceleration_to_group("arm", 0.5 * M_PI);サーボモータの最大動作速度を設定するため、Hardware.write_max_velocity_to_group(group_name, velocity)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、速度(radian / second)を入力します。
hardware.write_max_velocity_to_group("arm", 0.5* M_PI);サーボモータの位置制御PIDゲインを設定するため、Hardware.write_position_pid_gain_to_group(group_name, p, i, d)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、PIDゲインを入力します。
hardware.write_position_pid_gain_to_group("arm", 800, 0, 0);指定したサーボモータにPIDゲインを設定する場合は、Hardware.write_position_pid_gain(id, p, i, d)を実行します。
hardware.write_position_pid_gain(2, 800, 0, 0);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
hardware.write_position_pid_gain("joint1", 800, 0, 0);サーボモータの目標角度を設定するため、Hardware.set_position(id, position)を実行します。
引数にはサーボモータのIDと、目標角度(radian)を入力します。
設定した目標角度をサーボモータへ書き込むためには、Hardware.sync_write()を実行します。
double position = 0.0;
hardware.set_position(2, position);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
double position = 0.0;
hardware.set_position("joint1", position);ジョイントグループの目標角度を一括で設定する場合は、Hardware.set_positions(group_name, positions)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、目標角度を入力します。
std::vector<double> positions(7, 0.0);
hardware.get_positions("arm", positions);サーボモータへ目標値を書き込むため、Hardware.sync_write(group_name)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名を入力します。
この関数を実行すると、ロボットとの通信が発生します。
hardware.sync_write("arm");次のコマンドを実行します。 CRANE-X7は、肘の現在角度に合わせてハンドを開閉します。 Sciurus17は、右肘の現在角度に合わせて右ハンドを開閉します。
安全のためロボットの周りに物や人を近づけないでください。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_thread
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_thread実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
handジョイントグループのトルクをONにします.
read/writeスレッドを起動します.
5秒後にX7のハンドが開くので、ハンドに触れないでください.
armグループの0番目のサーボ角度は-1.070719radです.
armグループの1番目のサーボ角度は-1.632156radです.
armグループの2番目のサーボ角度は0.897379radです.
armグループの3番目のサーボ角度は-2.686000radです.
armグループの4番目のサーボ角度は-0.684155radです.
armグループの5番目のサーボ角度は1.141282radです.
armグループの6番目のサーボ角度は-0.954136radです.
handグループの0番目のサーボ角度は-0.007670radです.
armグループの0番目のサーボ角度は-1.070719radです.
armグループの1番目のサーボ角度は-1.632156radです.
armグループの2番目のサーボ角度は0.897379radです.
armグループの3番目のサーボ角度は-2.686000radです.
armグループの4番目のサーボ角度は-0.684155radです.
...サーボモータのデータを読み書きするスレッドを起動するため、Hardware.start_thread(group_names, update_cycle_ms)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、スレッドの更新周期(msec)を入力します。
スレッド内ではHardware.sync_read()とHardware.sync_write()が実行されます。
更新周期を短くする場合は通信設定を参考にUSB通信ポートの遅延を最小にしてください。
std::vector<std::string> group_names = {"arm", "hand"};
hardware.start_thread(group_names, std::chrono::milliseconds(10));スレッドを停止する場合は、Hardware.stop_thread()を実行します。
hardware.stop_thread();次のコマンドを実行します。サーボモータの現在角度、速度、電流、入力電圧、温度がターミナルに表示されます。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_read_present_values
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_read_present_values実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
...
サーボモータの電流値を観察しやすくするため、
5秒後にhandグループのトルクがONします.
arm: index, position[rad], velocity[rad/s], current[A], voltage[V], temperature[deg]
0, 0.619728, 0.000000, 0.000000, 12.200000, 32
1, 1.561592, 0.000000, 0.000000, 12.100000, 32
2, -1.965029, 0.000000, -0.002690, 12.000000, 32
3, -2.442097, 0.000000, -0.008070, 11.800000, 32
4, -1.922078, -0.023981, 0.000000, 11.700000, 34
5, 1.217981, -0.071942, 0.000000, 11.700000, 35
6, -0.358952, -0.023981, -0.008070, 11.700000, 35
hand: index, position[rad], velocity[rad/s], current[A], voltage[V], temperature[deg]
0, 0.354350, 0.000000, 0.040350, 11.700000, 37
ID:9: position[rad], velocity[rad/s], current[A], voltage[V], temperature[deg]
0.354350, 0.000000, 0.040350, 11.700000, 37
joint_hand: position[rad], velocity[rad/s], current[A], voltage[V], temperature[deg]
0.354350, 0.000000, 0.040350, 11.700000, 37
...サーボモータの現在値を取得するため、
コンフィグファイルのジョイントグループにsync_read:{position, velocity, current, voltage, temperature}を追加します。
読み取りたいデータ項目をsync_readに追加してください。
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
sync_read:
- position
- velocity
- current
- voltage
- temperature
ジョイントグループ名(2):
joints:
- ジョイント名(4)
- ジョイント名(5)
sync_read:
- current
- temperature サーボモータの現在情報を読み取るため、Hardware.sync_read(group_name)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名を入力します。
この関数を実行すると、ロボットとの通信が発生します。
hardware.sync_read("arm");サーボモータの速度を取得するため、Hardware.get_velocity(id, velocity)を実行します。
引数にはサーボモータのIDと、速度(radian / second)の格納先を入力します。
double velocity;
hardware.get_velocity(2, velocity);サーボモータの電流(ampere)は、Hardware.get_current(id, current)で取得できます。
double current;
hardware.get_current(2, current);サーボモータの入力電圧(volt)は、Hardware.get_voltage(id, voltage)で取得できます。
double voltage;
hardware.get_voltage(2, voltage);サーボモータの温度(degree Celsius)は、Hardware.get_temperature(id, temperature)で取得できます。
int8_t temperature;
hardware.get_temperature(2, temperature);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
double velocity;
double current;
double voltage;
int8_t temperature;
hardware.get_velocity("joint1", velocity);
hardware.get_current("joint1", current);
hardware.get_voltage("joint1", voltage);
hardware.get_temperature("joint1", temperature);ジョイントグループの現在値を一括で取得することも可能です。
std::vector<double> velocities;
std::vector<double> currents;
std::vector<double> voltages;
std::vector<int8_t> temperatures;
hardware.get_velocities("arm", velocities);
hardware.get_currents("arm", currents);
hardware.get_voltages("arm", voltages);
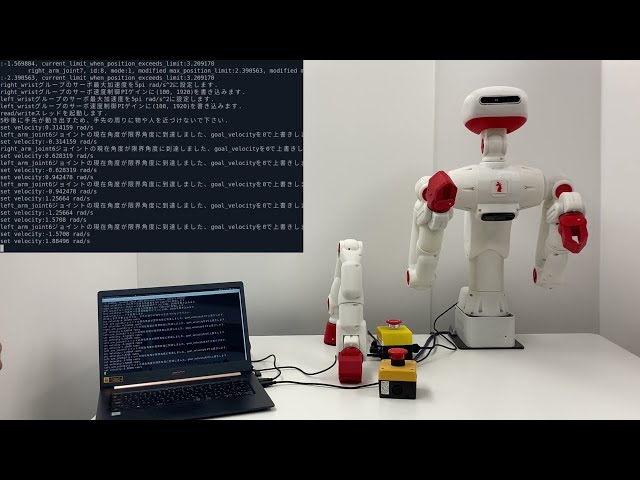
hardware.get_temperatures("arm", temperatures);次のコマンドを実行します。 CRANE-X7は前腕を回転させます。前腕が浮くようにCRANE-X7の腕を持ち上げて下さい
Sciurus17は両腕の手首を回転させます。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_write_velocity
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_write_velocity実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
...
wristグループのサーボ最大加速度を5pi rad/s^2に設定します.
wristグループのサーボ速度制御PIゲインに(100, 1920)を書き込みます.
read/writeスレッドを起動します.
5秒後に手先が動き出すため、手先の周りに物や人を近づけないで下さい.
set velocity:0.314159 rad/s
set velocity:-0.314159 rad/s
...
set velocity:2.82743 rad/s
joint5ジョイントの現在角度が限界角度に到達しました、goal_velocityを0で上書きします.
joint6ジョイントの現在角度が限界角度に到達しました、goal_velocityを0で上書きします.
...
スレッドを停止します.
wristグループにはvelocityのsync_writeが設定されています.
安全のため, stop_thread()関数内で目標速度 0 rad/sを書き込みます.
CRANE-X7との接続を解除します.
wristグループにはvelocityのsync_writeが設定されています.
安全のため, disconnect()関数内で目標速度 0 rad/sを書き込みます.サーボモータに目標速度を書き込むため、
コンフィグファイルのジョイントグループにsync_write:velocityとsync_read:positionを追加します.
sync_read:positionは可動範囲超過を検出するために必要です.
ジョイントのoperating_modeは1に設定します.
コンフィグファイル読み込み時に、サーボモータ内部のパラメータであるOperating Modeに
1 (速度制御モード)が書き込まれます.
ジョイントのpos_limit_marginは、
サーボモータ内部に設定された可動範囲(Max/Min Position Limit)から、
どれくらいの角度余裕(radian)を設けるかというパラメータです.
サーボモータが速度制御モードの時、サーボモータ内部の角度制限機能が動作しません。
そのため、Hardwareクラスのスレッド内部で、
サーボモータの現在角度を観察し、可動範囲を超える場合は目標速度0 radian / secondを書き込む処理を実施しています.
安全のためサーボモータ内部の可動範囲パラメータ(Max/Min Position Limit)が適切に設定されているかご確認ください。
サーボモータの現在角度が可動範囲の限界値付近にあるとき、
目標速度0 radian / secondを書き込んでも回転速度が下がりきらず、
現在角度が可動範囲を超える場合があります.
安全ため、コンフィグファイルのpos_limit_marginに0以上の数値を設定し、
可動範囲を狭くしてください.
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
sync_write:
- velocity
sync_read:
- position
ジョイント名(1): { id : 0, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5}
ジョイント名(2): { id : 1, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5}
ジョイント名(3): { id : 2, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5}サーボモータの速度制御PIゲインを設定するため、Hardware.write_velocity_pi_gain_to_group(group_name, p, i)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、PIゲインを入力します。
hardware.write_velocity_pi_gain_to_group("arm", 100, 1920);指定したサーボモータにPIゲインを設定する場合は、Hardware.write_velocity_pi_gain(id, p, i)を実行します。
hardware.write_velocity_pi_gain(2, 100, 1920);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
hardware.write_velocity_pi_gain("joint1", 100, 1920);サーボモータに目標速度を書き込む準備として、
Hardware.start_thread(group_names, update_cycle_ms)を実行し、スレッドを起動します。
std::vector<std::string> group_names = {"arm", "hand"};
hardware.start_thread(group_names, std::chrono::milliseconds(10));サーボモータの目標速度を設定するため、Hardware.set_velocity(id, velocity)を実行します。
引数にはサーボモータのIDと、目標速度(radian / second)を入力します。
double velocity = 3.14;
hardware.set_velocity(2, velocity);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
double velocity = 0.0;
hardware.set_velocity("joint1", velocity);ジョイントグループの目標速度を一括で設定する場合は、Hardware.set_velocities(group_name, velocities)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、目標速度を入力します。
std::vector<double> velocities(7, 3.14);
hardware.get_velocities("arm", velocities);速度制御時は、安全のためHardware.stop_thread()とHardware.disconnect()の内部で
目標速度0 radian / secondが書き込まれます。
hardware.stop_thread();
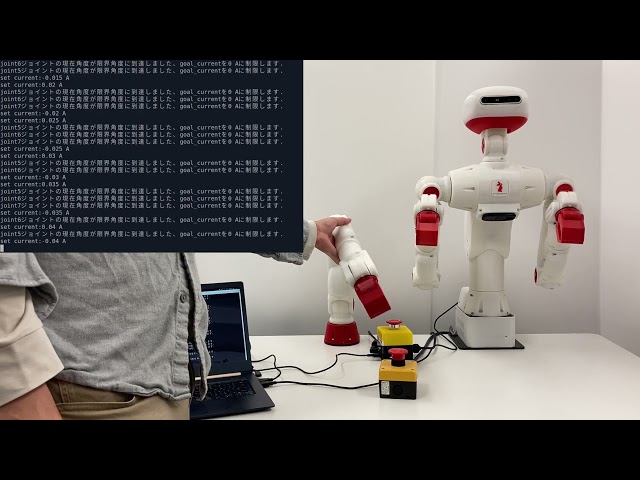
hardware.disconnect();次のコマンドを実行します。 CRANE-X7は前腕を回転させます。前腕が浮くようにCRANE-X7の腕を持ち上げて下さい
Sciurus17は両腕の手首を回転させます。
# CRANE-X7の場合
$ cd bin/
$ ./x7_write_current
# Sciurus17の場合
$ ./s17_write_current実行結果(CRANE-X7の場合)
...
read/writeスレッドを起動します.
5秒後に手先が動き出すため、手先の周りに物や人を近づけないで下さい.
set current:0.005 A
set current:-0.005 A
set current:0.01 A
set current:-0.01 A
...
set current:-0.035 A
joint6ジョイントの現在角度が限界角度に到達しました、goal_currentを0.02917 Aに制限します.
joint5ジョイントの現在角度が限界角度に到達しました、goal_currentを0.02917 Aに制限します.
set current:0.04 A
...
スレッドを停止します.
wristグループにはcurrentのsync_writeが設定されています.
安全のため, stop_thread()関数内で目標電流 0 Aを書き込みます.
CRANE-X7との接続を解除します.
wristグループにはcurrentのsync_writeが設定されています.
安全のため, disconnect()関数内で目標速度 0 Aを書き込みます.サーボモータに目標電流を書き込むため、
コンフィグファイルのジョイントグループにsync_write:currentとsync_read:positionを追加します.
sync_read:positionは可動範囲超過を検出するために必要です.
ジョイントのoperating_modeは0に設定します.
コンフィグファイル読み込み時に、サーボモータ内部のパラメータであるOperating Modeに
0 (電流制御モード)が書き込まれます.
ジョイントのpos_limit_marginは、
サーボモータ内部に設定された可動範囲(Max/Min Position Limit)から、
どれくらいの角度余裕(radian)を設けるかというパラメータです.
サーボモータが電流制御モードの時、サーボモータ内部の角度制限機能が動作しません。
そのため、Hardwareクラスのスレッド内部で、
サーボモータの現在角度を観察し、可動範囲を超える場合は目標電流値を制限する処理(制限値は後述のcurrent_limit_marginで調整可能)を実施しています.
安全のためサーボモータ内部の可動範囲パラメータ(Max/Min Position Limit)が適切に設定されているかご確認ください。
ジョイントのcurrent_limit_marginは、
サーボモータ内部に設定された電流制限(Current Limit)から、
どれくらいの電流余裕(A)を設けるかというパラメータです.
サーボモータの現在角度が可動範囲を超える場合、
目標電流値が[Current Limit] - [current_limit_margin]に制限されます。
joint_groups:
ジョイントグループ名(1):
joints:
- ジョイント名(1)
- ジョイント名(2)
- ジョイント名(3)
sync_write:
- current
sync_read:
- position
ジョイント名(1): { id : 0, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5, current_limit_margin: 1.0}
ジョイント名(2): { id : 1, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5, current_limit_margin: 1.0}
ジョイント名(3): { id : 2, dynamixel: "XM430", operating_mode: 1, pos_limit_margin: 0.5, current_limit_margin: 1.0}サーボモータに目標電流を書き込む準備として、
Hardware.start_thread(group_names, update_cycle_ms)を実行し、スレッドを起動します。
std::vector<std::string> group_names = {"arm", "hand"};
hardware.start_thread(group_names, std::chrono::milliseconds(10));サーボモータの目標電流を設定するため、Hardware.set_current(id, current)を実行します。
引数にはサーボモータのIDと、目標電流(A)を入力します。
double current = 0.1;
hardware.set_current(2, current);ジョイント名で指定することも可能です。
double current = -0.1;
hardware.set_current("joint1", current);ジョイントグループの目標電流を一括で設定する場合は、Hardware.set_currents(group_name, currents)を実行します。
引数にはジョイントグループ名と、目標電流を入力します。
std::vector<double> currents(7, 0.0);
hardware.get_currents("arm", currents);電流制御時は、安全のためHardware.stop_thread()とHardware.disconnect()の内部で
目標電流0 Aが書き込まれます。
目標電流値が0 Aになると、ロボットが脱力します。
脱力によってロボットが人や物にぶつからないように支えてください。
hardware.stop_thread();
hardware.disconnect();