SharePoint is a browser-based collaborative content management platform developed by Microsoft.
Where,
- Content Management means, The process of sharing and managing information, such as files, images, and videos, in an organized manner.
- Collaborative means, Multiple people can work together by sharing and editing content easily.
- Browser-Based means, There is no need to install additional software to use SharePoint. It can be accessed easily using browsers like Chrome, Safari, or Edge.
Simply, it is a platform to share and manage information, such as files, images, and videos in an organized way, so that multiple people can work together by sharing this information using browsers like Chrome or Safari.
- Store and Manage Files: Keep all your important documents, images, and videos in one organized place where they are easy to find and share.
- Teamwork: Help people work together on projects by sharing files and collaborating in real-time, no matter where they are.
- Automate Work: Make work easier by setting up automatic workflows for tasks like getting approvals or sending reminders.
- Publish Content: Easily share news, updates, or important information with your whole team or organization.
- Company Website: Create internal websites to share company news, events, and important resources with employees.
- Connect with Other Tools: Work smoothly with other Microsoft apps like Word, Excel, and Teams, or even other software you use.
- Keep Data Safe: Make sure important information is protected and only accessible to the right people.
SharePoint was created by Microsoft in 2001 as a way to help people share and manage files easily. Since then, it has become a powerful tool that many companies use for collaboration and content management.
- 2001: The first version of SharePoint was released, mainly for storing and managing documents.
- 2003: It became better, allowing teams to work together more easily and connect with Microsoft Office programs.
- 2007: New features were added, like automating tasks and making it easier to organize and search for content.
- 2010: SharePoint included social features (like networking), better connections with Office, and options for using it in the cloud.
- 2013: The user experience improved with a more modern look, smarter search options, and better integration with other Microsoft services.
- 2016: Focused on helping companies use both cloud and on-site setups together smoothly.
- 2019: Introduced a friendlier design, more support for mobile devices, and more cloud-based features.
- Today: SharePoint Online is part of Microsoft 365 and is widely used for secure collaboration and managing information in the cloud.
We know that, sharepoint is a content management platform.
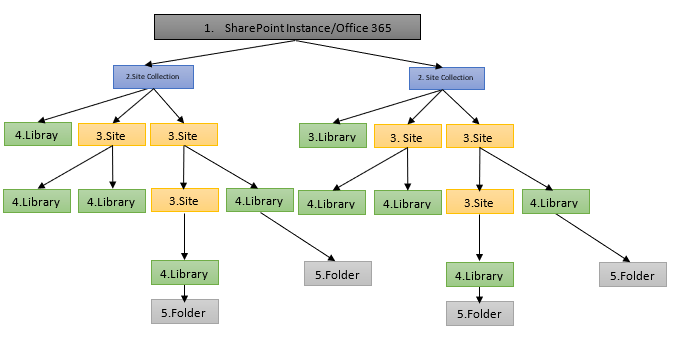
This below pictures shows that, how content in sharepoint envorironment is organized hierarchically.
Basically, Sharepoint has five layers
A SharePoint Instance is the entire environment where all the information, websites, and resources for an organization are managed and stored. It's like the main system or "container" that includes all the sites and content your organization uses in SharePoint or Office 365.
Examples:
- Company Example:
- If "Tech Corp" is a company using SharePoint, the SharePoint Instance is everything that Tech Corp owns and manages in SharePoint, like all the data, documents, and sites used by every department, such as HR, Sales, and Engineering.
- School Example:
- For a university using SharePoint, the SharePoint Instance is where the entire school's data is managed. It would include separate sections (or site collections) for different departments like "Admissions," "Faculty Resources," and "Student Projects."
In simple terms, the SharePoint Instance is the complete setup where all the websites, files, and resources for an organization live and can be accessed.
Definition:
A Site Collection is a group of related websites within SharePoint. Each site collection can contain multiple sites that share common settings, like permissions and themes, but each site within a collection has its own unique purpose and content.
Example:
- Company Example:
- In a company like "Tech Corp," there might be separate site collections for different departments, such as:
- One for "Human Resources" with different sites for "Employee Policies," "Recruitment," and "Training Programs."
- Another for "Sales" with sites for "Sales Reports," "Customer Contacts," and "Marketing Materials."
- In a company like "Tech Corp," there might be separate site collections for different departments, such as:
- School Example:
- In a university, there could be site collections for various faculties or departments:
- One for the "Engineering Faculty" with sites like "Student Projects," "Course Materials," and "Faculty Resources."
- Another for the "Admissions Department" with sites for "Application Forms," "Accepted Students," and "Admissions Events."
- In a university, there could be site collections for various faculties or departments:
In short, a Site Collection is a way to organize SharePoint sites by grouping related ones together, making it easier to manage and share information across different parts of an organization.
Definition:
A Site in SharePoint is a specific website within a Site Collection. Each site serves a particular purpose and contains content that is related to that purpose. Sites allow teams or departments to organize and collaborate on specific tasks or projects.
Example:
- Company Example:
- In a company like "Tech Corp," within the "Human Resources" site collection, you might have different sites for different purposes:
- Employee Policies site: Stores company policies and employee guidelines.
- Recruitment site: Manages hiring processes, candidate resumes, and job descriptions.
- Training Programs site: Provides resources and schedules for employee training sessions.
- In a company like "Tech Corp," within the "Human Resources" site collection, you might have different sites for different purposes:
- School Example:
- In a university, within the "Engineering Faculty" site collection, there might be different sites such as:
- Student Projects site: For storing and sharing student project reports.
- Course Materials site: For posting lectures, assignments, and reading materials for students.
- Faculty Resources site: For faculty members to share resources, schedules, and announcements.
- In a university, within the "Engineering Faculty" site collection, there might be different sites such as:
In simple terms, a Site is a specific space within SharePoint that allows teams or departments to focus on their work, collaborate, and store relevant content in an organized way.
Definition:
A Library in SharePoint is a place within a site where documents, files, and other content are stored. It is similar to a folder or file storage system on your computer, but it provides additional features like version control, metadata, and sharing options to better organize and manage documents.
Example:
- Company Example:
- In a company like "Tech Corp," within the "Recruitment" site, you might have libraries such as:
- Job Descriptions library: Stores all job role descriptions in the company.
- Candidate Resumes library: Stores resumes of all job candidates.
- In a company like "Tech Corp," within the "Recruitment" site, you might have libraries such as:
- School Example:
- In a university, within the "Student Projects" site, there might be libraries such as:
- Project Reports library: Stores reports and documents for student projects.
- Presentations library: Stores slides and materials for student presentations.
- In a university, within the "Student Projects" site, there might be libraries such as:
In simple terms, a Library is a storage space within a site where related documents and files are kept, making it easier to organize, track, and share content.
In SharePoint, both Lists and Libraries are used to store information, but they are designed for different types of content. A List is used to store structured data like tasks, contacts, or calendar events, while a Library is specifically designed to store documents and files.
Key Differences:
- List:
- A List stores structured data in rows and columns (similar to a table in a database or spreadsheet).
- Used to track things like tasks, contacts, or events.
- Items in a list can contain text, numbers, dates, and more.
- Example: A Task List to track work assignments, or a Contact List with names, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Library:
- A Library stores files (documents, spreadsheets, presentations, etc.) and provides tools for document management like versioning, check-out, and sharing.
- Used primarily for storing and managing documents.
- Items in a library are typically files that can be opened, edited, and shared.
- Example: A Document Library to store files like Word documents, Excel spreadsheets, or PowerPoint presentations.
Example to Illustrate:
- Company Example:
- In a company like "Tech Corp," a Task List could be used in the "Projects" site to manage tasks for different teams, whereas a Document Library could be used in the same site to store all project-related documents.
- School Example:
- In a university, a Contact List might be used to store student details, while a Document Library could store lecture slides, project reports, and other educational materials.
In summary, a List is for managing data in a structured format, while a Library is for storing and managing files and documents.
Company Document Management System Structure for "Contoso Ltd."
-
SharePoint Instance/Office 365
- Top-level entry point for the company’s SharePoint.
- URL Example: https://contoso.sharepoint.com
- All site collections, departments, and resources will branch out from here.
-
Site Collections (Major areas for company divisions or purposes)
- Two main site collections are created to represent the primary divisions:
- HR Division: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR
- Finance Division: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance
-
Sites (Sub-divisions or projects within each division)
- HR Site Collection:
- Employee Policies: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Policies
- Recruitment: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Recruitment
- Training: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Training
- Finance Site Collection:
- Accounts Payable: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AP
- Accounts Receivable: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AR
- Financial Reports: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/Reports
-
Libraries (Document libraries for storing files)
- HR Division:
- Employee Handbook: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Policies/Handbook
- Training Materials: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Training/Materials
- Interview Questions: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Recruitment/Questions
- Finance Division:
- Invoices: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AP/Invoices
- Expense Reports: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AR/Reports
- Annual Financials: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/Reports/Annual
-
Folders (Sub-categories under each library for better organization)
- HR Division:
- In Employee Handbook:
- General Policies: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Policies/Handbook/General
- Safety Guidelines: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Policies/Handbook/Safety
- In Training Materials:
- Online Courses: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Training/Materials/OnlineCourses
- Classroom Training: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/HR/Training/Materials/Classroom
- Finance Division:
- In Invoices:
- 2024 Invoices: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AP/Invoices/2024
- 2023 Invoices: https://contoso.sharepoint.com/sites/Finance/AP/Invoices/2023
- In Annual Financials:
A SharePoint list is an online tool to store and organize information in rows and columns, like a table.
Features of a SharePoint List
- Store Data: Save information like text, numbers, dates, and files in rows and columns.
- Customizable Columns: Define what kind of data you want in each column, such as text, choices, or dates.
- Collaboration: Share the list with others so your team can work on it together.
- Filtering and Sorting: Quickly find the information you need by applying filters or sorting columns.
- Custom Views: Display data in different ways, like grouping by status or showing only completed tasks.
- Permissions: Control who can see or edit the list.
- Track Changes: See who made changes and what was updated.
- Templates: Use pre-made templates to quickly create lists for tasks, issues, or events.
- Integration: Link your list with other tools like Excel, Power Automate, or Power Apps for automation and analysis.
- Mobile Access: View and update lists on the go using a phone or tablet.
- Create a List from Scratch
- Step 1: Go to your SharePoint site.
- Step 2: Click on the gear icon in the top-right corner and select Site contents.
- Step 3: Click New and then choose List.
- Step 4: Give your list a name, and then click Create.
- Step 5: Add columns to your list based on the type of information you want to store.
- Use a List Template
- Step 1: Go to your SharePoint site.
- Step 2: Click on the gear icon and select Site contents.
- Step 3: Click New, then choose List.
- Step 4: Choose a pre-built template, such as a Task List, Issue Tracking, or Contact List.
- Step 5: Name your list and click Create. The template will automatically set up useful columns for you.
- Create a List from an Existing Excel File
- Step 1: Open your SharePoint site.
- Step 2: Go to Site contents and click New, then choose List.
- Step 3: Choose the option to Import from Excel.
- Step 4: Upload your Excel file, and SharePoint will automatically create columns based on your data.
- Step 5: Name your list and click Create.
- Create a List from Power Apps
- Step 1: Open Power Apps and create a new app.
- Step 2: Choose to create a data source and select SharePoint.
- Step 3: Choose your SharePoint site and then select Create a list.
- Step 4: Customize the fields in your list and save it to your SharePoint site.
- Create a List Using Power Automate (Flow)
- Step 1: Open Power Automate and create a new flow.
- Step 2: Choose a trigger to start the flow, such as a new item added or a specific action.
- Step 3: Add the action Create item and select the SharePoint list you want to work with.
- Step 4: Configure the flow to automatically create a list item based on the action that triggered it.
In SharePoint, columns define the type of data you can store in a list. These columns can be configured in various ways depending on the type of data you need to store (e.g., text, numbers, dates). Below is a detailed explanation of each column data type, along with multiple examples to show how they can be used effectively.
1. Single Line of Text
- Description: This column type is used for storing short strings of text, such as names, titles, or short descriptions. It allows for just a single line of text per item.
- Example Use Cases:
- Employee Name: Stores the names of employees.
- Project Title: Stores the title of a project.
- Product Code: Stores unique product identifiers.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Employee Name
Value: John Doe - Column Name: Project Title
Value: "Website Redesign"
- Column Name: Employee Name
2. Multiple Lines of Text
- Description: Used for longer text, this column allows multiple lines of input, which is ideal for comments, descriptions, or notes. You can choose whether the text is plain or formatted.
- Example Use Cases:
- Job Description: Stores detailed job roles and responsibilities.
- Comments: Used to collect feedback or comments on a specific task or item.
- Project Description: A description of a project that may span multiple lines.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Job Description
Value: "Responsible for managing the team, handling client communication, and ensuring timely project delivery." - Column Name: Comments
Value: "The task is progressing well, but we need more information from the client to complete it."
- Column Name: Job Description
3. Choice
- Description: This column allows you to create a drop-down menu of predefined options. You can allow users to select only one option or multiple options from the list.
- Example Use Cases:
- Status: Indicates the current state of a project or task (e.g., Active, Inactive, On Hold).
- Priority Level: Specifies the priority of a task or request (e.g., High, Medium, Low).
- Department: Allows the user to select a department from a list of options.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Status
Choices: Active, Inactive, On Hold
Value: Active - Column Name: Priority Level
Choices: High, Medium, Low
Value: Medium
- Column Name: Status
4. Number
- Description: Stores numeric values, including integers or decimals. You can also set minimum and maximum values, and define whether the number should be displayed as a whole number or with decimal points.
- Example Use Cases:
- Quantity: Stores the number of items in stock.
- Total Sales: Records the total sales amount for a specific period.
- Rating: Allows users to rate something on a numeric scale (e.g., 1 to 5).
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Quantity
Value: 150 - Column Name: Total Sales
Value: 124,500.75
- Column Name: Quantity
5. Currency
- Description: This column type is used to store monetary values. It allows you to format the number with a currency symbol (like $, €, £) and specify decimal places for accuracy.
- Example Use Cases:
- Salary: Stores the salary of employees.
- Invoice Amount: The total cost on an invoice.
- Budget: Records the budget allocated for a project.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Salary
Value: $65,000.00 - Column Name: Invoice Amount
Value: €1,250.50
- Column Name: Salary
6. Date and Time
- Description: This column stores dates and optionally times. You can choose whether to store the time along with the date and whether the time should be displayed in 12-hour or 24-hour format.
- Example Use Cases:
- Start Date: The start date of a project.
- Due Date: The deadline for a task.
- Event Date: The date of an event or meeting.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Start Date
Value: 2024-11-21 (2024-11-21 09:00 AM if time is also included) - Column Name: Due Date
Value: 2024-12-15
- Column Name: Start Date
7. Lookup
- Description: This column allows you to reference data from another SharePoint list. It is useful for relating data between two lists, like referencing a customer from a "Customers" list in an "Orders" list.
- Example Use Cases:
- Department: Looks up department names from a department list.
- Customer: Looks up customer names from a customer list.
- Project Manager: References project managers stored in another list.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Department
Value: HR (from a "Departments" list) - Column Name: Project Manager
Value: Sarah Smith (from a "Employees" list)
- Column Name: Department
8. Yes/No
- Description: Stores a boolean value. Typically, this is represented as "Yes" or "No" (or "True" or "False"). It is ideal for binary decisions or options, such as confirming whether a task is completed.
- Example Use Cases:
- Active Employee: Indicates whether an employee is currently active or not.
- Completed: Shows whether a task is marked as completed.
- Accepted: Indicates whether a proposal has been accepted.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Active Employee
Value: Yes - Column Name: Completed
Value: No
- Column Name: Active Employee
9. Person or Group
- Description: This column allows you to store the name of a person or group. It can pull data from the SharePoint User Profile, including email and contact details.
- Example Use Cases:
- Project Manager: Refers to the manager of a project.
- Assigned To: Refers to the person who is assigned to a task.
- Created By: Displays the person who created an item in the list.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Project Manager
Value: John Doe - Column Name: Assigned To
Value: Emily Davis
- Column Name: Project Manager
10. Hyperlink or Picture
- Description: This column stores URLs or image links. It is useful for referencing websites, online resources, or linking to documents.
- Example Use Cases:
- Website: A link to a relevant website.
- Document: A link to a document stored online.
- Logo: A link to an image, like a company logo.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Website
Value: https://www.example.com - Column Name: Logo
Value: https://www.example.com/logo.png
- Column Name: Website
11. Calculated
- Description: A calculated column lets you perform mathematical or text operations on other columns within the same list. This can include operations like summing values, concatenating text, or calculating dates.
- Example Use Cases:
- Total Price: Calculate the total price from quantity and unit price.
- Full Name: Concatenate first name and last name to form a full name.
- Days Left: Calculate how many days are left until a project’s due date.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Total Price
Formula: [Quantity] * [Unit Price]
Value: 250 (calculated from 25 * $10) - Column Name: Full Name
Formula: [First Name] & " " & [Last Name]
Value: "John Doe"
- Column Name: Total Price
12. Managed Metadata
- Description: This column stores data that comes from a predefined taxonomy or term set. It helps with classification and tagging content using a controlled vocabulary.
- Example Use Cases:
- Product Category: Stores a category for products (e.g., Electronics, Furniture).
- Tags: Used for tagging documents or content with metadata.
- Region: Allows for the classification of data based on geographic regions.
- Example Values:
- Column Name: Product Category
Value: Electronics (from a predefined taxonomy) - Column Name: Region
Value: North America
- Column Name: Product Category
Conclusion
SharePoint columns are highly flexible and customizable, and you can mix and match them to fit your specific needs. Depending on the type of data you need to store, you can use text, numbers, dates, people, links, or even calculated values to make your SharePoint lists powerful tools for organizing and managing data. Let me know if you need help setting up any of these column types!