This repository contains a Poisson solver using the Portable, Extensible Toolkit for Scientific Computation (PETSc). The solver utilizes a structured grid and the Krylov Subspace Methods (KSP) for solving the discretized Poisson equation in two dimensions.1
The Poisson equation is a fundamental partial differential equation that appears in many fields of science and engineering, such as electrostatics, mechanical engineering, and thermal dynamics. This solver employs PETSc's distributed array (DMDA) for grid management and its linear system solvers for finding the solution.2
- PETSc installed on your system
- A C compiler, such as GCC
- An MPI implementation for parallel execution
To compile the Poisson solver, run the following command in the terminal:
make poisson.cTo run the Poisson solver with a custom grid size and visualize the grid layout, use the following command in your terminal:
-da_grid_x 9 -da_grid_y 9 -dm_view draw -draw_pause 10The Poisson solver is structured into several key components to efficiently solve the Poisson equation on a structured grid using PETSc. Below is an overview of the main parts of the code:
-
main: This is the entry point of the program. It initializes the PETSc environment, sets up the grid, matrix, and vectors, and then solves the Poisson equation. It also computes the error norm between the computed solution and the exact solution, and finally, it cleans up the PETSc objects before terminating. -
formMatrix(DM da, Mat A): This function is responsible for forming the system matrixAfor the discretized Poisson equation. It iterates over the grid points to fill the matrix based on the finite difference approximation of the Laplacian operator. -
formExact(DM da, Vec uexact): This function computes the exact solution of the Poisson equation for validation purposes. It fills the vectoruexactwith the values of the analytical solution evaluated at each grid point. -
formRHS(DM da, Vec b): This function computes the right-hand side (RHS) of the Poisson equation, which represents the source term. It fills the vectorbwith the values of the function defining the source term evaluated at each grid point.
The solver utilizes PETSc's DMDA for managing the structured grid and KSP for solving the linear system. The DMDALocalInfo structure is used to access information about the grid, such as the number of grid points in each direction and the starting indices for the local portion of the grid.
To run the solver and further explore its capabilities, see the Running the Solver section.
For more detailed information on PETSc's linear solvers and other features are in PETSc KSP Documentation.
The PETSc framework provides extensive customization for solving linear systems, allowing users to tailor the solver to their specific needs. Below are some of the additional command-line options you can use when running the Poisson solver:
-
Solver and Preconditioner Options:
-ksp_type <type>: Specifies the type of Krylov subspace method to use (e.g.,cg,gmres).-pc_type <type>: Sets the type of preconditioner (e.g.,none,jacobi,ilu).
-
Grid Customization:
-da_grid_x <Nx>: Sets the number of grid points in the x-direction.-da_grid_y <Ny>: Sets the number of grid points in the y-direction.
-
Visualization and Debugging:
-ksp_view: Displays detailed information about the Krylov solver configuration.-ksp_monitor: Monitors the convergence of the solver at each iteration.-log_view: Outputs a detailed performance log upon completion.
-
Example: Running with a Custom Solver and Preconditioner
./poisson -da_grid_x 9 -da_grid_y 9 -ksp_type gmres -pc_type ilu -ksp_monitor
After running the Poisson solver, the program outputs the following information:
on 9 x 9 grid: error |u-uexact|_inf = 0.000763959
 |
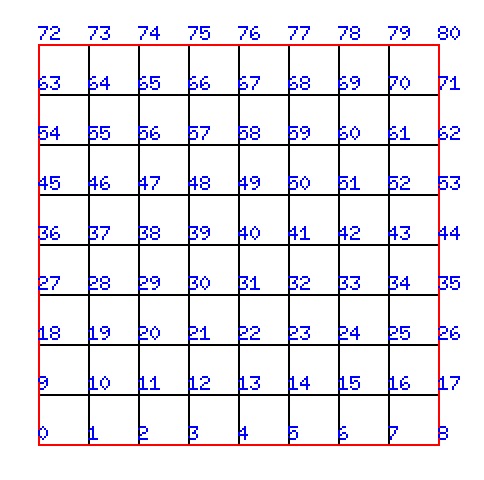 |
| Mesh without Coordinates | Mesh with Coordinates |