-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 729
Powering GSM module
Some GSM modules come without integrated power converter, so it may require some specific power supply.
For example this cheap SIM800L module:
Operating Voltage - 3.6V to 4.2V
Operating Current - up to 2A
Since we don't get standard voltage regulators at this voltage, we need to use adjustable voltage regulators. Here are some options to correctly power your GSM module.
WARNING:
One should be very careful to not to disconnect the GND before the VCC and always connect GND before VCC. Otherwise it can use the low voltage serial pins as ground and can destroy the module instantly.
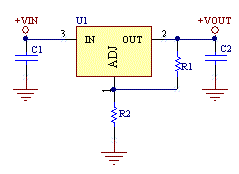
One of the cheapest options, is to use LM317 or LM338. Here is the resistor value calculator

This is much more efficient than a liner voltage regulator. Any 2A-rated DC-DC converter would do.


Cool, those batteries voltage is generally in the range of 3.7V - 4.2V (3.7V nominal and 4.2V when charging).

With a 5V power supply, we can use a 1N4007 diode, as it has a 0.7V drop.

If you use a bench power supply, never turn it off/on when it's still connected to your board. The PSU's output is very unstable when it's being turned on/off, and can destroy your modem. First turn on the supply, when it has settled to the desired voltage, connect the modem. To turn off the supply, first disconnect the modem, then turn off the power supply.
If you like TinyGSM library - give it a star, or fork it and contribute!


