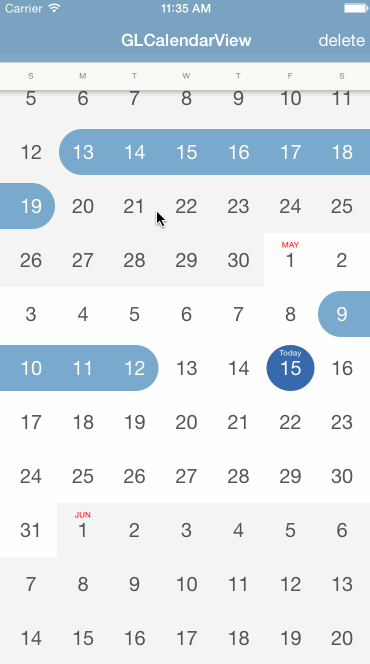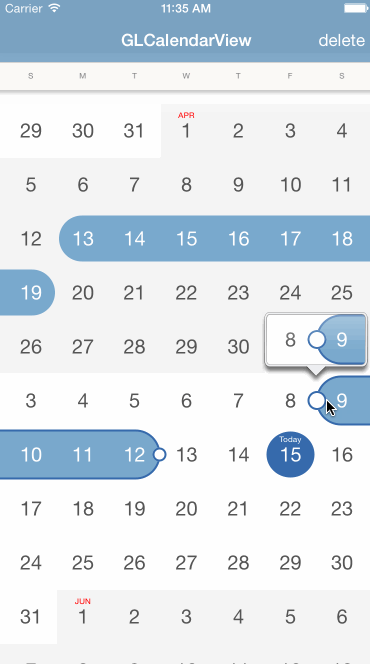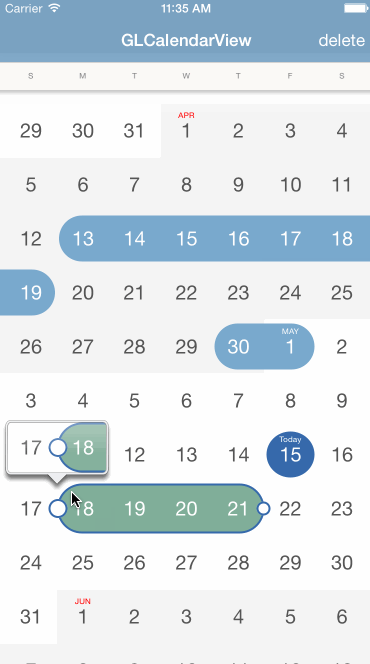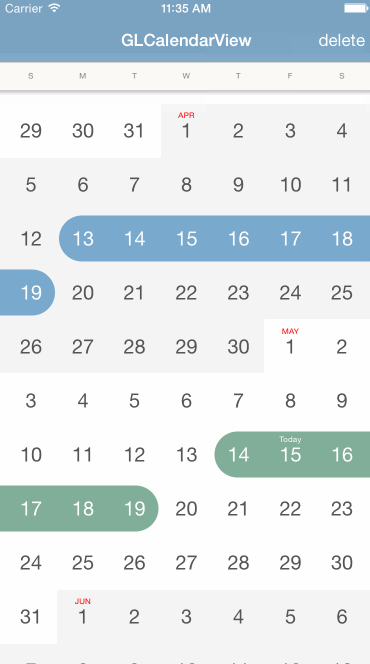
With CocoaPods you can simply add GLCalendarView in your Podfile:
pod "GLCalendarView", "~> 1.0.0"
You can copy all the files under the Sources folder into your project.
- Init the view by placing it in the storyboard or programmatically init it and add it to your view controller.
- In
viewDidLoad, set thefirstDateandlastDateof the calendarView. - In
viewWillAppear, set up the model data and call[self.calendarView reload];to refresh the calendarView.
To display some ranges in the calendar view, construct some GLCalendarDateRange objects, set them as the model of the calendar view
NSDate *today = [NSDate date];
NSDate *beginDate = [GLDateUtils dateByAddingDays:-23 toDate:today];
NSDate *endDate = [GLDateUtils dateByAddingDays:-18 toDate:today];
GLCalendarDateRange *range = [GLCalendarDateRange rangeWithBeginDate:beginDate endDate:endDate];
range.backgroundColor = COLOR_BLUE;
range.editable = YES;
range.binding = yourModelObject // you can bind your model to the range
self.calendarView.ranges = [@[range1] mutableCopy];
[self.calendarView reload];For the binding field, it helps in that you can bind the actual model to the range, thus you can easily retrieve the corresponding model from the range later. For example, if you are building a trip app, you probably has a Trip class, you can bind the Trip instance to the range, and if the range gets updated in the calendar view, you can easily get the Trip instance from it and do some further updates.
The calendar view will handle all the user interactions including adding, updating, or deleting a range, you just need to implement the delegate protocol to listen for those events:
@protocol GLCalendarViewDelegate <NSObject>
- (BOOL)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView canAddRangeWithBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate;
- (GLCalendarDateRange *)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView rangeToAddWithBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate;
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView beginToEditRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range;
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView finishEditRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range continueEditing:(BOOL)continueEditing;
- (BOOL)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView canUpdateRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range toBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate endDate:(NSDate *)endDate;
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView didUpdateRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range toBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate endDate:(NSDate *)endDate;
@endSample implementation:
- (BOOL)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView canAddRangeWithBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate
{
// you should check whether user can add a range with the given begin date
return YES;
}
- (GLCalendarDateRange *)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView rangeToAddWithBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate
{
// construct a new range object and return it
NSDate* endDate = [GLDateUtils dateByAddingDays:2 toDate:beginDate];
GLCalendarDateRange *range = [GLCalendarDateRange rangeWithBeginDate:beginDate endDate:endDate];
range.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
range.editable = YES;
range.binding = yourModel // bind your model to the range instance
return range;
}
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView beginToEditRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range
{
// save the range to a instance variable so that you can make some operation on it
self.rangeUnderEdit = range;
}
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView finishEditRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range continueEditing:(BOOL)continueEditing
{
// retrieve the model from the range, do some updates to your model
id yourModel = range.binding;
self.rangeUnderEdit = nil;
}
- (BOOL)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView canUpdateRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range toBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate endDate:(NSDate *)endDate
{
// you should check whether the beginDate or the endDate is valid
return YES;
}
- (void)calenderView:(GLCalendarView *)calendarView didUpdateRange:(GLCalendarDateRange *)range toBeginDate:(NSDate *)beginDate endDate:(NSDate *)endDate
{
// update your model if necessary
id yourModel = range.binding;
}
GLCalendarView 's appearance is fully customizable, you can adjust its look through the appearance api(generally your should config it in the AppDelegate), check the header file to see all customizable fields:
[GLCalendarView appearance].rowHeight = 54;
[GLCalendarView appearance].padding = 6;
[GLCalendarView appearance].weekDayTitleAttributes = @{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:8], NSForegroundColorAttributeName:[UIColor grayColor]};
[GLCalendarView appearance].monthCoverAttributes = @{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:30]};
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].dayLabelAttributes = @{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:20], NSForegroundColorAttributeName:UIColorFromRGB(0x555555)};
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].monthLabelAttributes = @{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:8]};
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].editCoverBorderWidth = 2;
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].editCoverBorderColor = UIColorFromRGB(0x366aac);
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].editCoverPointSize = 14;
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].todayBackgroundColor = UIColorFromRGB(0x366aac);
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].todayLabelAttributes = @{NSFontAttributeName:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:20]};
[GLCalendarDayCell appearance].rangeDisplayMode = RANGE_DISPLAY_MODE_CONTINUOUS;You can clone the project and investigate the demo for more detailed usage~