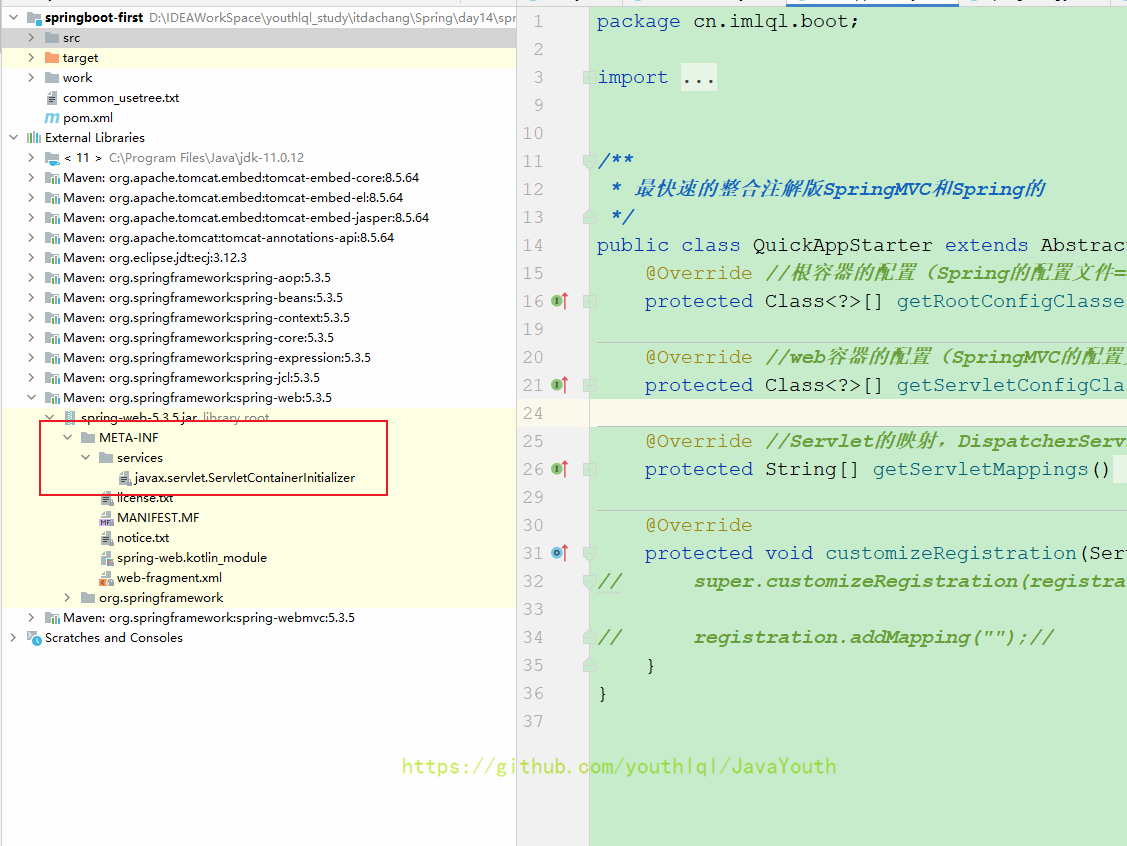
springboot-first
├── common_usetree.txt
├── pom.xml
├── springboot-first.iml
├── src/
| ├── main/
| | ├── java/
| | | └── cn/
| | | └── imlql/
| | | └── boot/
| | | ├── config/
| | | | ├── SpringConfig.java
| | | | └── SpringMVCConfig.java
| | | ├── controller/
| | | | └── HelloController.java
| | | ├── Main.java
| | | ├── QuickAppStarter.java
| | └── resources/
| └── test/
| └── java/
└── work/
└── Tomcat/
└── localhost/
└── boot/<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-first</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.tomcat.embed/tomcat-embed-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<version>8.5.64</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.tomcat.embed/tomcat-embed-jasper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<version>8.5.64</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>package cn.imlql.boot;
import org.apache.catalina.Context;
import org.apache.catalina.LifecycleException;
import org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws LifecycleException {
//自己写Tomcat的启动源码
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
tomcat.setPort(8888);
tomcat.setHostname("localhost");
tomcat.setBaseDir(".");
// user.dir代表当前工作目录
Context context = tomcat.addWebapp("/boot", System.getProperty("user.dir") + "/src/main");
tomcat.start();//启动tomcat 注解版MVC利用Tomcat SPI机制
tomcat.getServer().await(); //服务器等待
}
}package cn.imlql.boot;
import cn.imlql.boot.config.SpringConfig;
import cn.imlql.boot.config.SpringMVCConfig;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
/**
* 最快速的整合注解版SpringMVC和Spring的
*/
public class QuickAppStarter extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override //根容器的配置(Spring的配置文件===Spring的配置类)
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
@Override //web容器的配置(SpringMVC的配置文件===SpringMVC的配置类)
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{SpringMVCConfig.class};
}
@Override //Servlet的映射,DispatcherServlet的映射路径
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
// super.customizeRegistration(registration);
// registration.addMapping("");//
}
}@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.boot",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = Controller.class)
})
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
//Spring的父容器
}@ComponentScan(value = "cn.imlql.boot",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type= FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = Controller.class)
},useDefaultFilters = false)
public class SpringMVCConfig {
//SpringMVC的子容器,能扫描的Spring容器中的组件
}package cn.imlql.boot.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
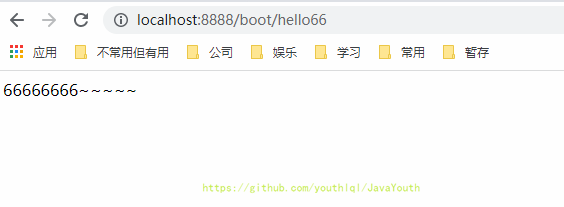
@GetMapping("/hello66")
public String hello(){
return "66666666~~~~~";
}
}- 我们看到上面很神奇的效果,我们自己写代码做到了类似SpringBoot的效果,不需要配置本地tomcat,直接就把Web应用启动起来了。
- 这里只是简单的捋一下,详细过程在前面讲过
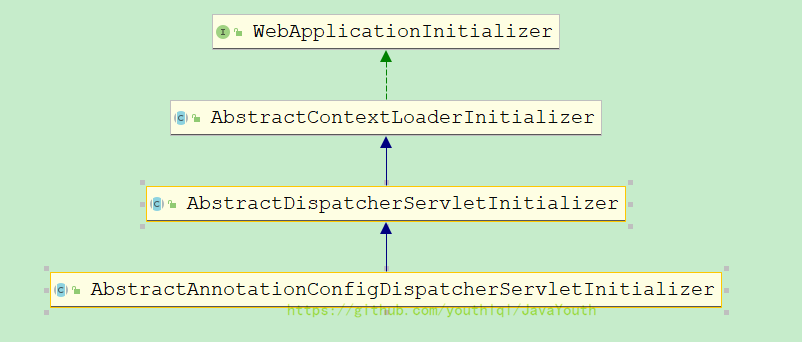
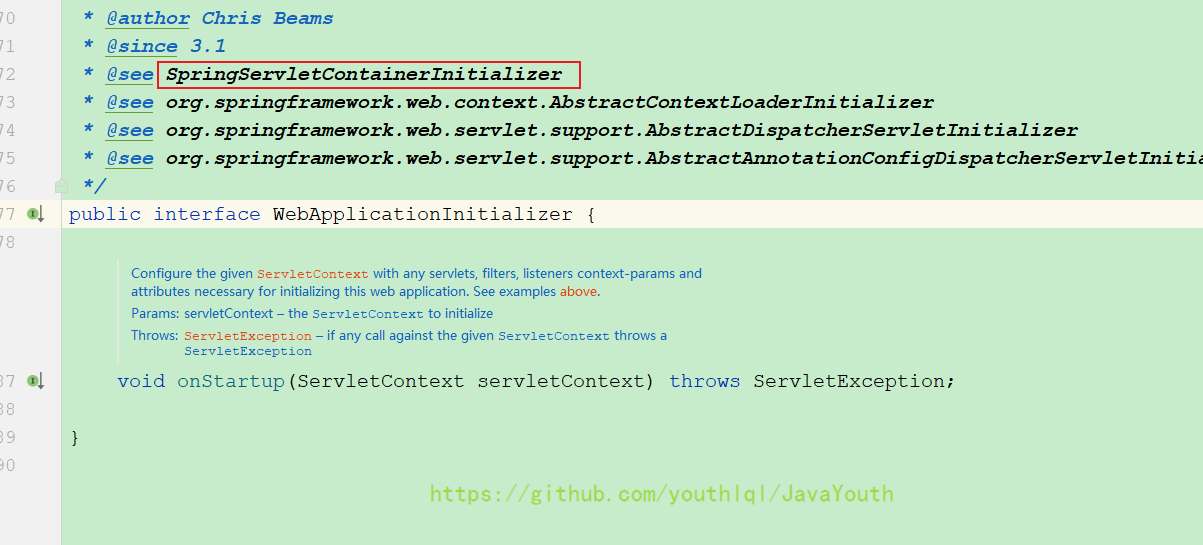
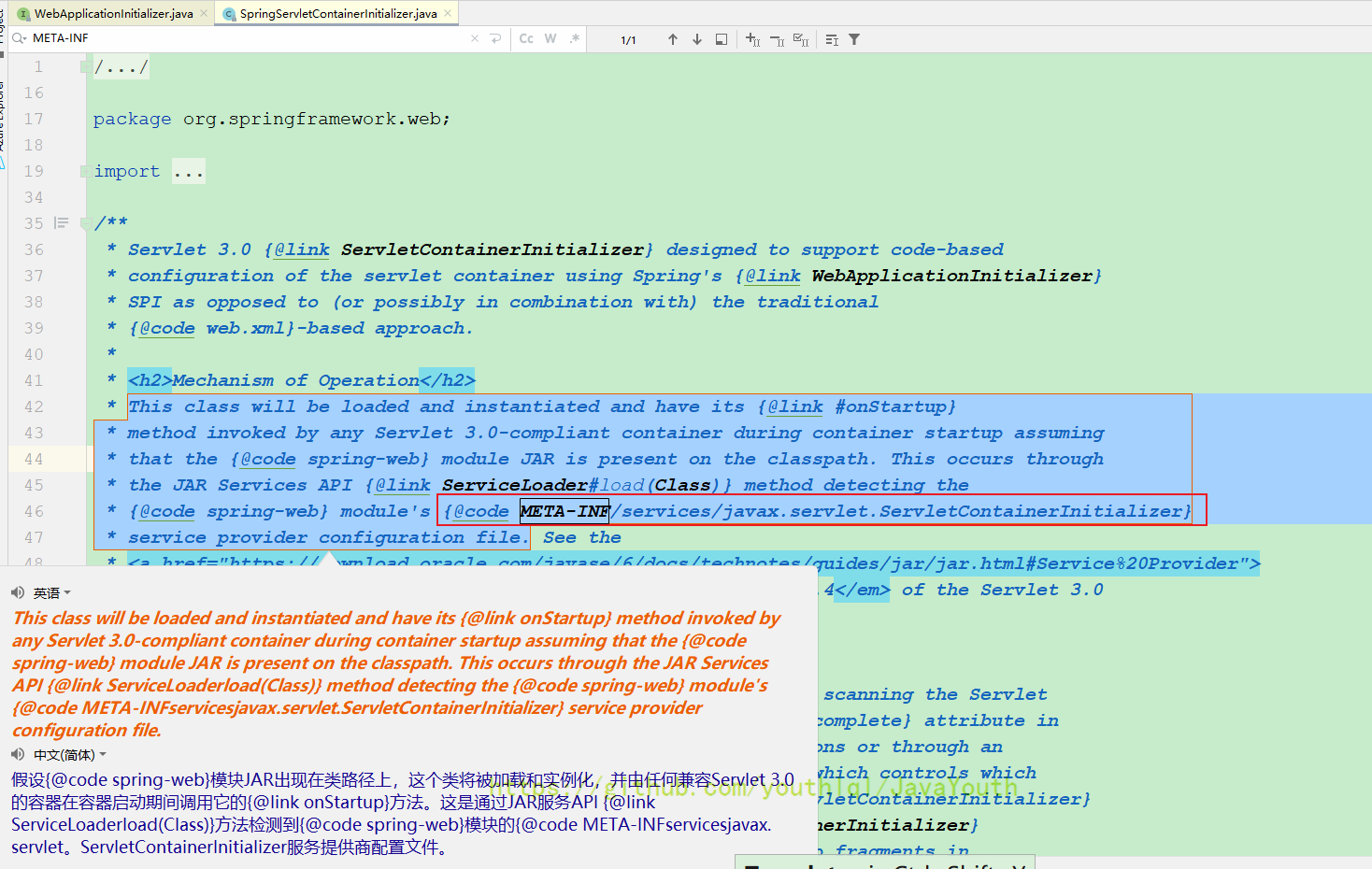
我们的QuickAppStarter实现了
利用Java的SPI加载META-INF/services下的实现类
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
/**
* Delegate the {@code ServletContext} to any {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* implementations present on the application classpath.
* <p>Because this class declares @{@code HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)},
* Servlet 3.0+ containers will automatically scan the classpath for implementations
* of Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} interface and provide the set of all
* such types to the {@code webAppInitializerClasses} parameter of this method.
* <p>If no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are found on the classpath,
* this method is effectively a no-op. An INFO-level log message will be issued notifying
* the user that the {@code ServletContainerInitializer} has indeed been invoked but that
* no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations were found.
* <p>Assuming that one or more {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected,
* they will be instantiated (and <em>sorted</em> if the @{@link
* org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is present or
* the {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been
* implemented). Then the {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)}
* method will be invoked on each instance, delegating the {@code ServletContext} such
* that each instance may register and configure servlets such as Spring's
* {@code DispatcherServlet}, listeners such as Spring's {@code ContextLoaderListener},
* or any other Servlet API componentry such as filters.
* @param webAppInitializerClasses all implementations of
* {@link WebApplicationInitializer} found on the application classpath
* @param servletContext the servlet context to be initialized
* @see WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)
* @see AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
*/
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = Collections.emptyList();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
initializers = new ArrayList<>(webAppInitializerClasses.size());
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says... 所有的非接口非抽象的WebApplicationInitializer实现类
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) //集合负责保存满足上面条件的类
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
//下面会遍历所有满足要求的WebApplicationInitializer,调用他们的onStartup
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext); //所有的 WebApplicationInitializer 的 onStartup
}
}
}- 其中@HandlesTypes注解表示可以处理的类,在
onStartup方法中,可以通过Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses获取得到。 - @HandlesTypes属于sun公司对Servlet定义的规范,包括tomcat,jetty等服务器都对它有不同的实现
- tomcat的具体实现咱们这里不深究,可以肯定的是一定用到了Java的SPI,如下。
ServiceLoader<DataSaveService> load = ServiceLoader.load(WebApplicationInitializer.class);- tomcat具体对于@HandlesTypes一定是和上面类似甚至是一样的代码来加载WebApplicationInitializer的实现
因为咱们的QuickAppStarter继承的AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer也属于WebApplicationInitializer,所以它就会被加载
-
tomcat会遵循sun公司的规范给每一个Servlet创建对象
-
所以DispatcherServlet肯定也会创建对象
-
Servlet的规范
- Servlet创建对象
- Servlet调用Init初始化
- 每次请求调用service处理
- tomcat停止的时候调用destroy进行销毁
-
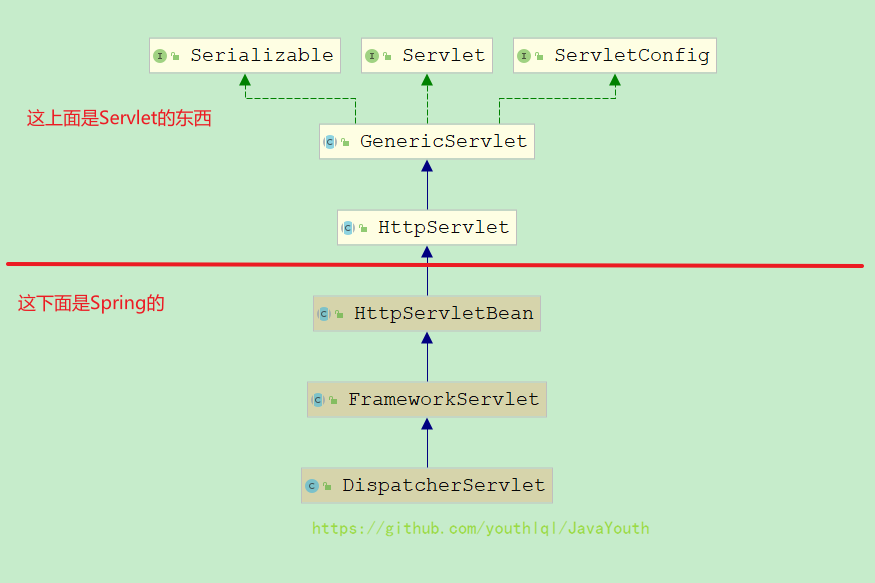
Serlvet是被谁调用开始初始化的属于tomcat的源码,我们这里不研究
- spring-web中有一个叫DispatcherServlet的类,很明显他是一个Servlet,所以tomcat启动的时候就会加载它,加载它的话当然是从父类一层一层加载的
- 也就是说是从Servlet最顶层开始一层一层往下面调用
- 最终我们发现FrameworkServlet里有一个核心方法
/** 追踪看web应用启动做了什么。
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); //初始化WebIOC容器,那我们想一下大概率是在这里启动的IOC容器
initFrameworkServlet(); //这又是留给子类的
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}-
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();没错,看名字就知道是从这里开始启动Web容器的。 -
然后我们就自己搭建了一个MySpringBoot项目,我们这个项目和SpringBoot官方的区别就是官方帮我们封装了很多自动配置类,帮我们给容器中放了很多组件,使得我们感觉开发更方便了。
为什么 @SpringBootApplication +SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSourceApplication.class, args);能把Spring+SpringMVC+Tomcat+其他场景都整合进来
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootSourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSourceApplication.class, args);
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.atuigu.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-source</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-source</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>- 首先是在Maven依赖上的支持,spring-boot-starter-xxx的这种依赖内部又导入了很多的依赖,包括上面说的嵌入式tomcat,以及Spring,SpringMVC
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
//......
}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}这个注解的功能就相当于@Configuration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
//......
}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
//......
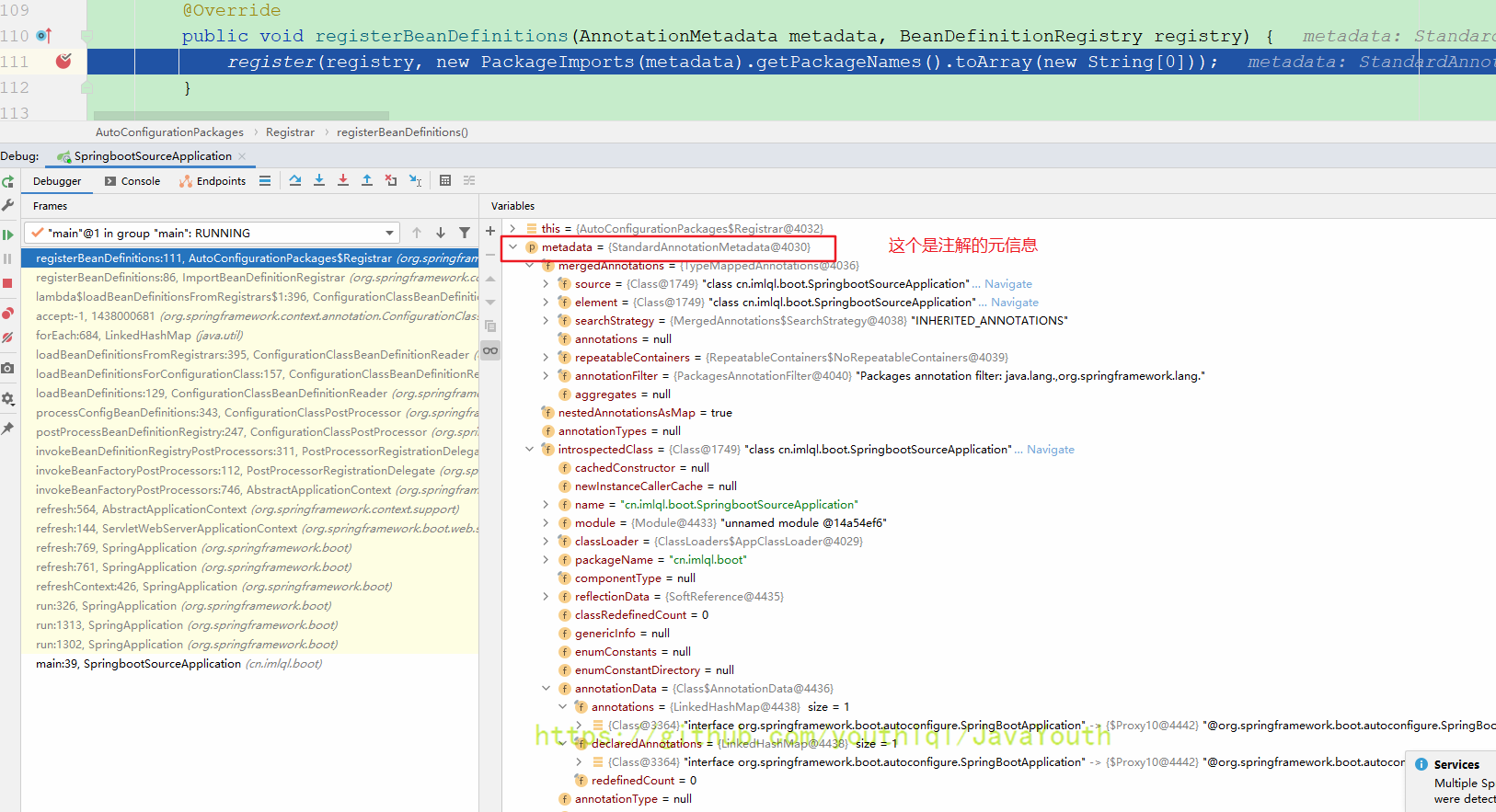
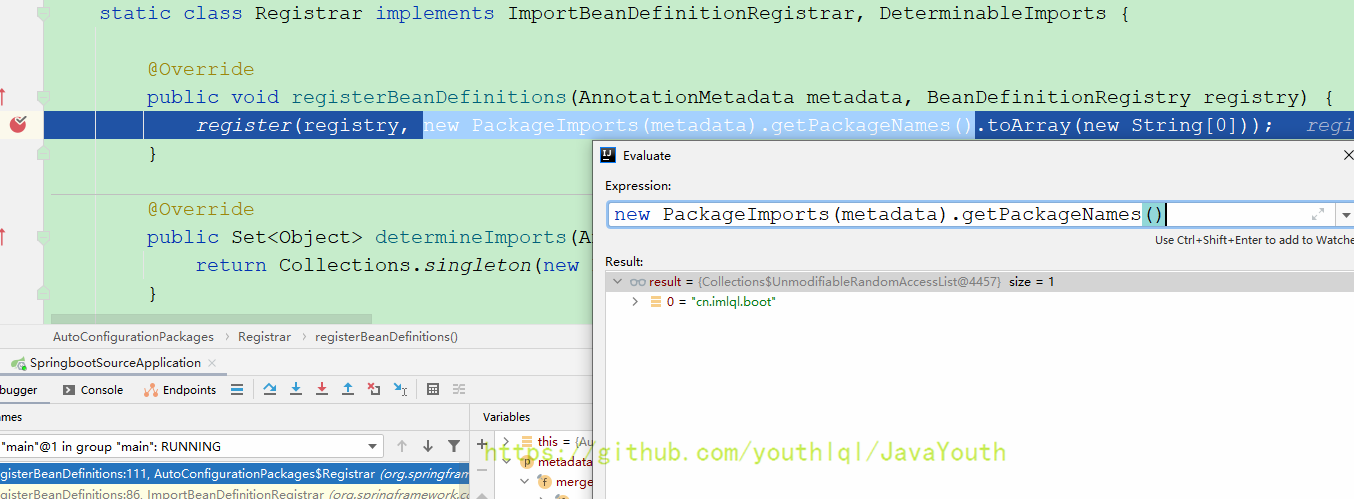
}static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}这里就是得到要注册哪些包下的信息,F7进入此方法。从这里你也能知道SpringBoot默认导的包是SpringbootXXXApplication所在的那个包层级
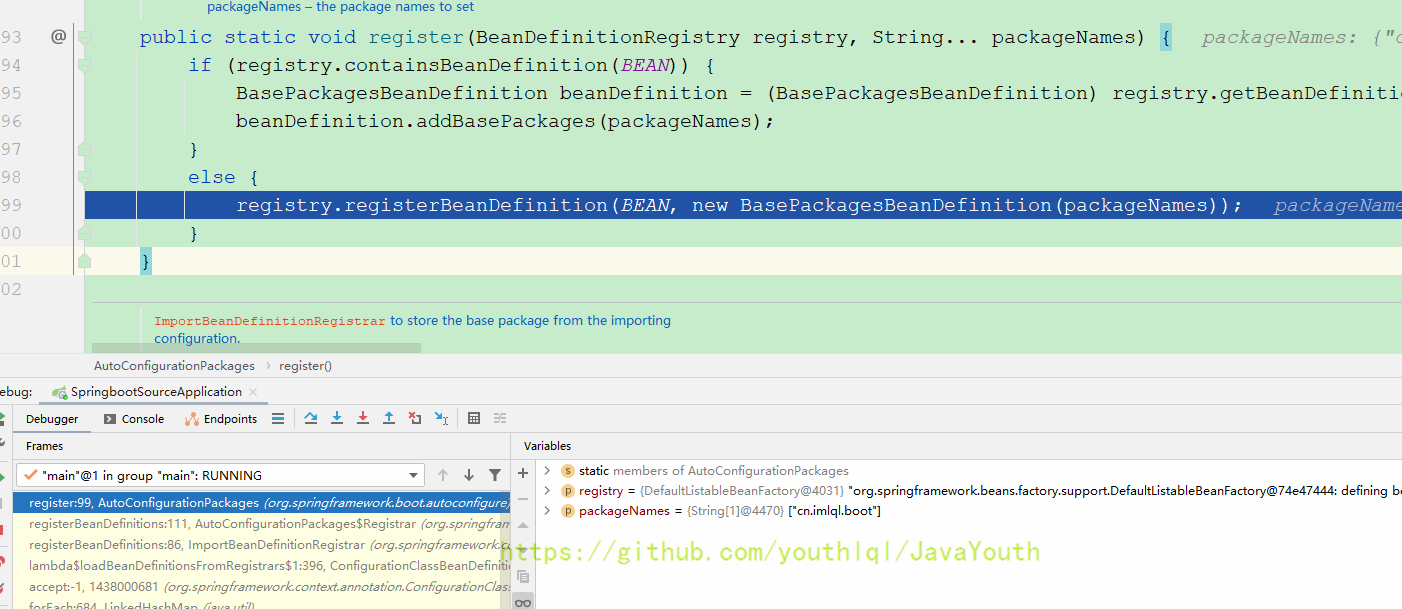
public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String... packageNames) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN)) {
BasePackagesBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (BasePackagesBeanDefinition) registry.getBeanDefinition(BEAN);
beanDefinition.addBasePackages(packageNames);
}
else {
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN, new BasePackagesBeanDefinition(packageNames));
}
}
private static final String BEAN = AutoConfigurationPackages.class.getName();static final class BasePackagesBeanDefinition extends GenericBeanDefinition {
private final Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
BasePackagesBeanDefinition(String... basePackages) {
setBeanClass(BasePackages.class);
setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
addBasePackages(basePackages);//就是要指定最终要扫哪些包
}
@Override
public Supplier<?> getInstanceSupplier() {
return () -> new BasePackages(StringUtils.toStringArray(this.basePackages));
}
private void addBasePackages(String[] additionalBasePackages) {
this.basePackages.addAll(Arrays.asList(additionalBasePackages));
}
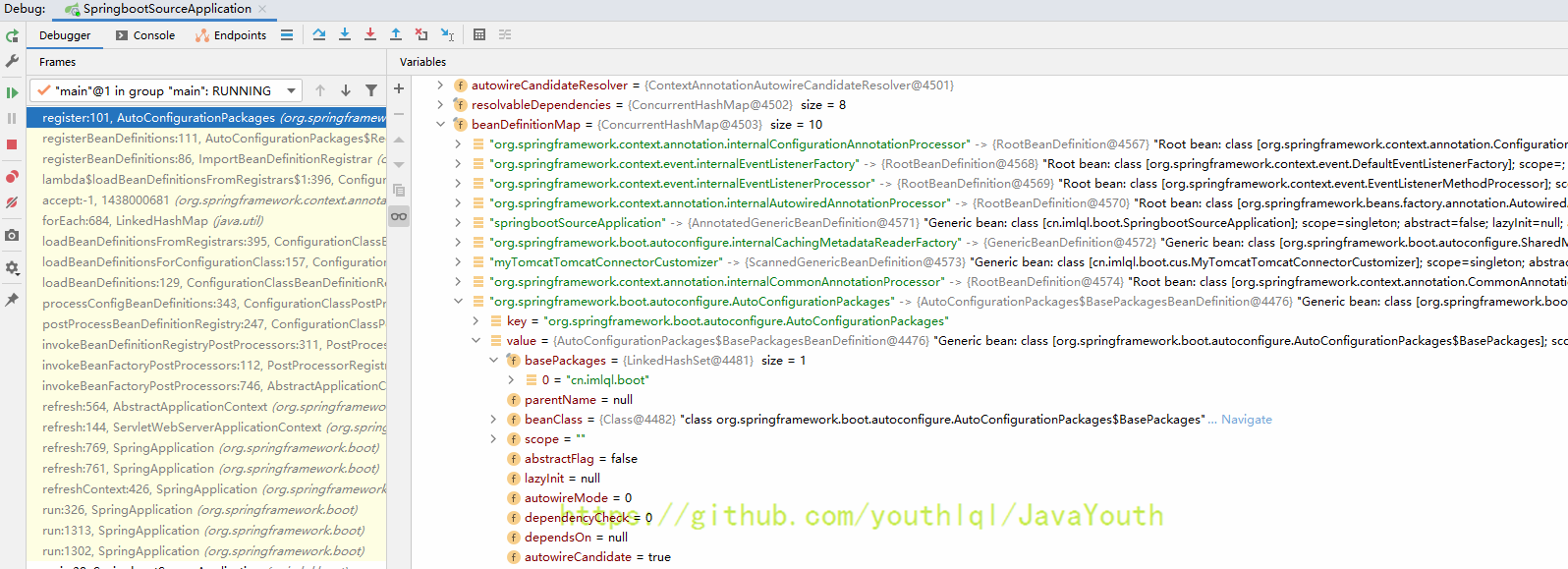
}此时beanDefinitionMap已经有了AutoConfigurationPackages,当处理到这个Bean的时候,最终发现这是个包导入的组件,最终就会导入这个包里面的组件
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
//......
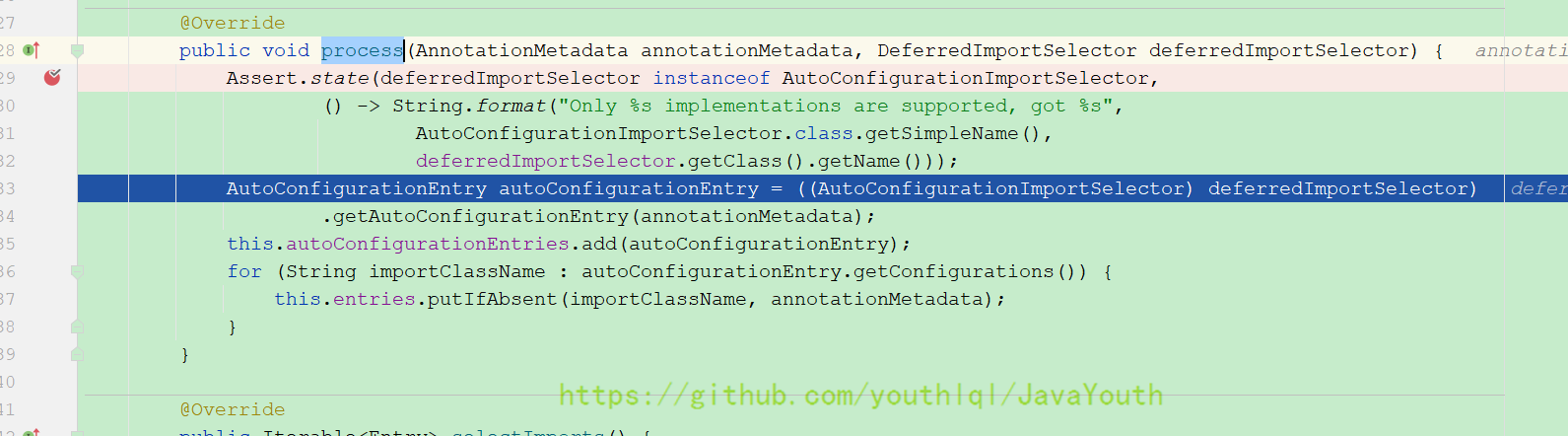
}- AutoConfigurationImportSelector是用@Import注解导进来的
- AutoConfigurationImportSelector根据它的名字很明显它是一个ImportSelector的实现类,了解ImportSelector的都应该知道它是通过
selectImports()方法来实现导入哪些组件的
F7进入此方法
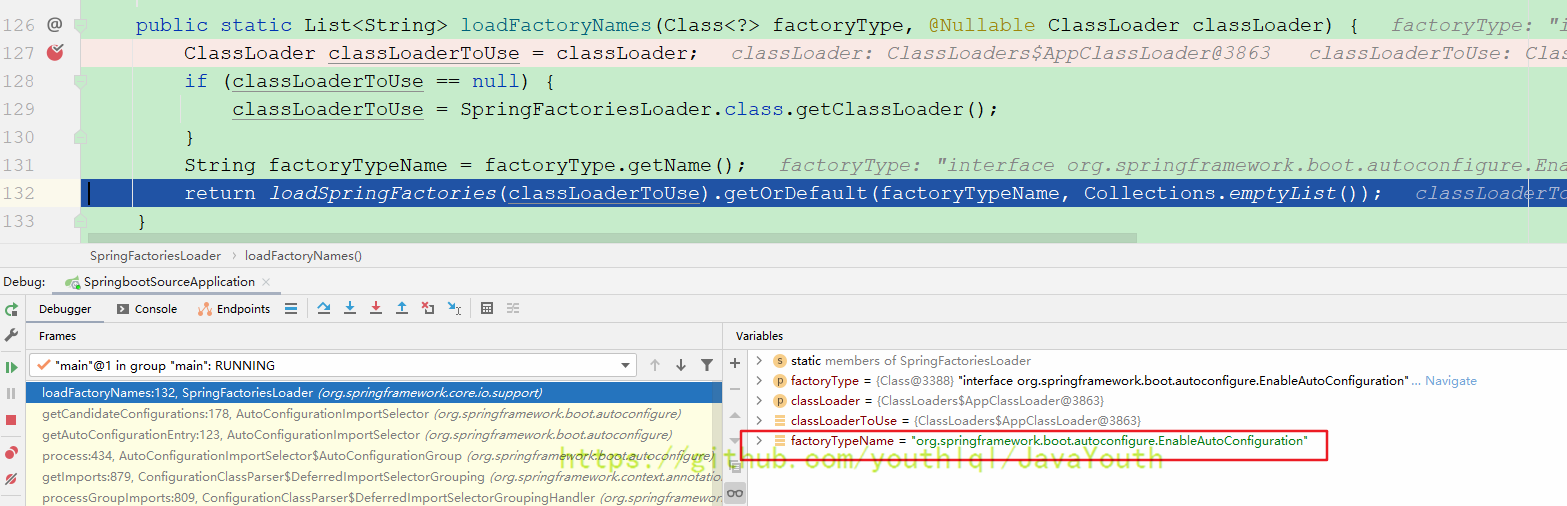
F7进入此方法
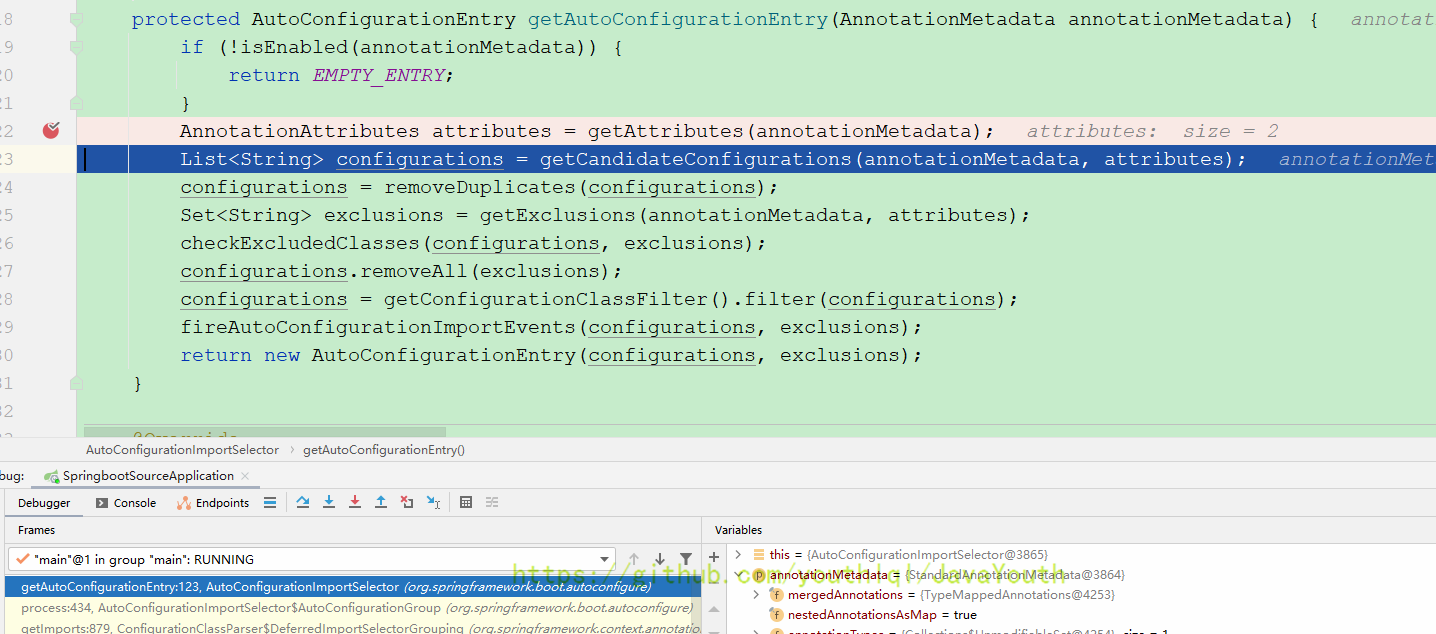
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
} public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
//加载类路径下META-INF/spring.factories的资源
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
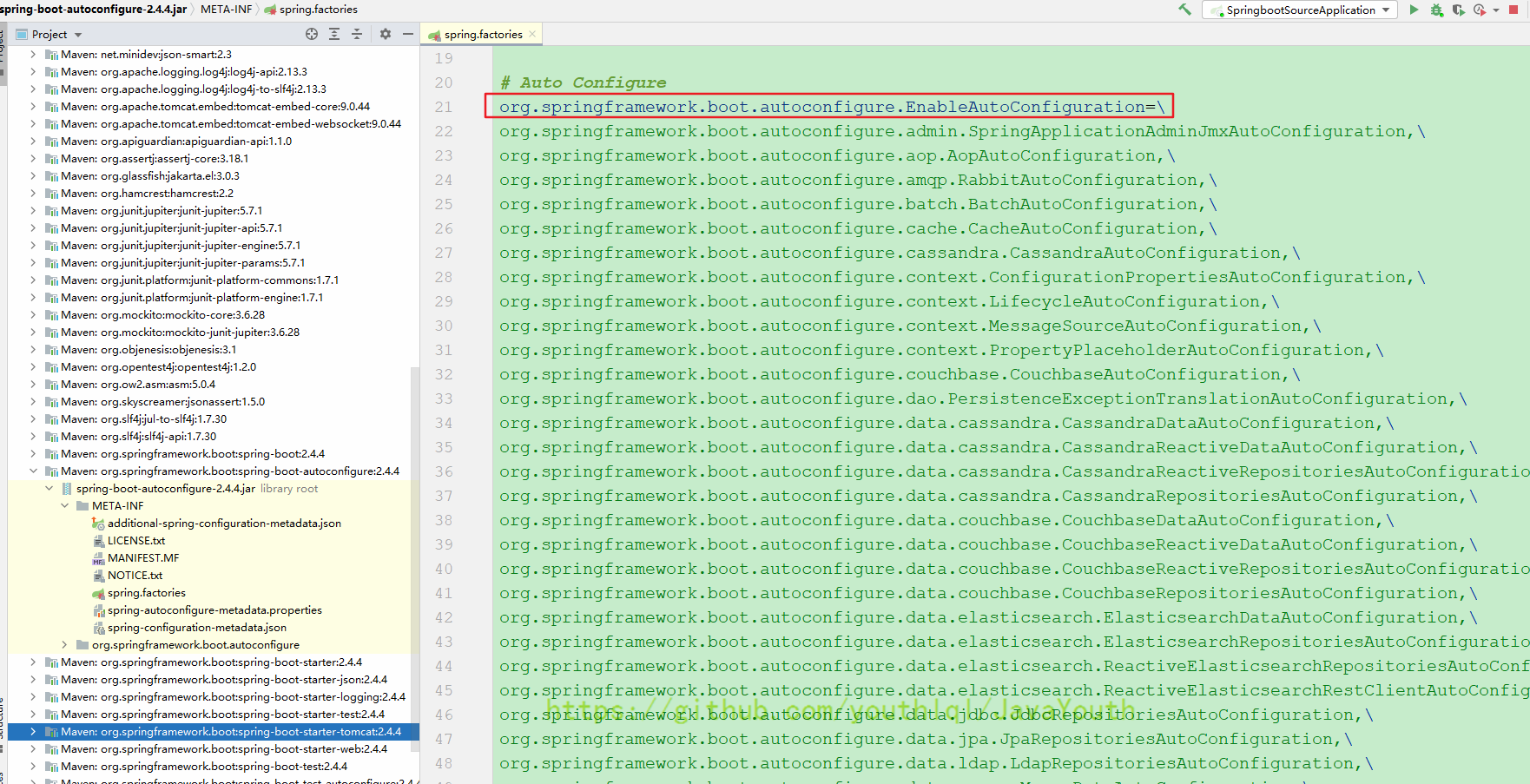
}然后咱们就要找类路径下META-INF/spring.factories,并且名字是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的资源,这有点类似于SPI机制
- 不止这个包下有spring.factories文件,可能很多第三方的starter都有,这个包下的这些类只是Spring能想到的常用的组件。
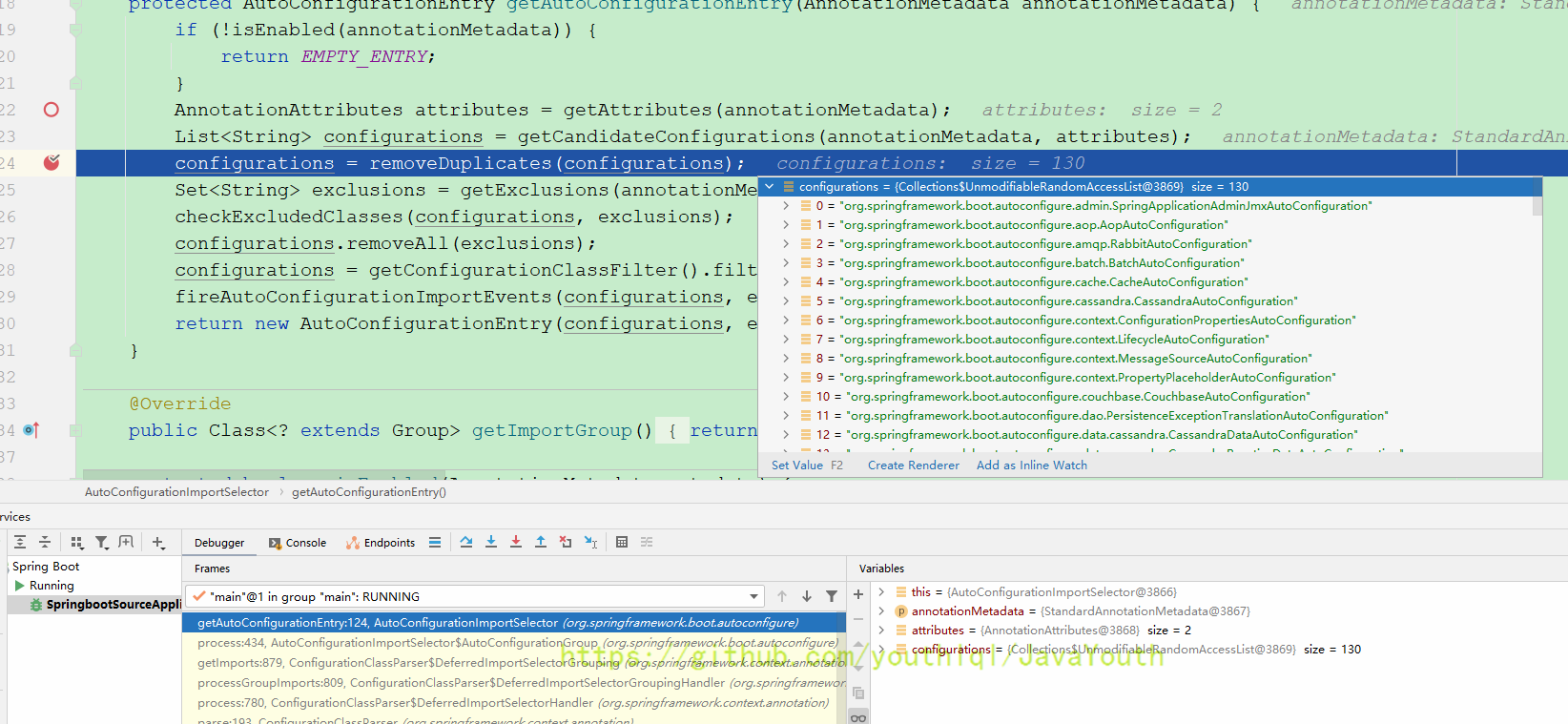
- 自此这130个组件会先被放到List里,但不一定全部导入
- 然后这里会有一个过滤
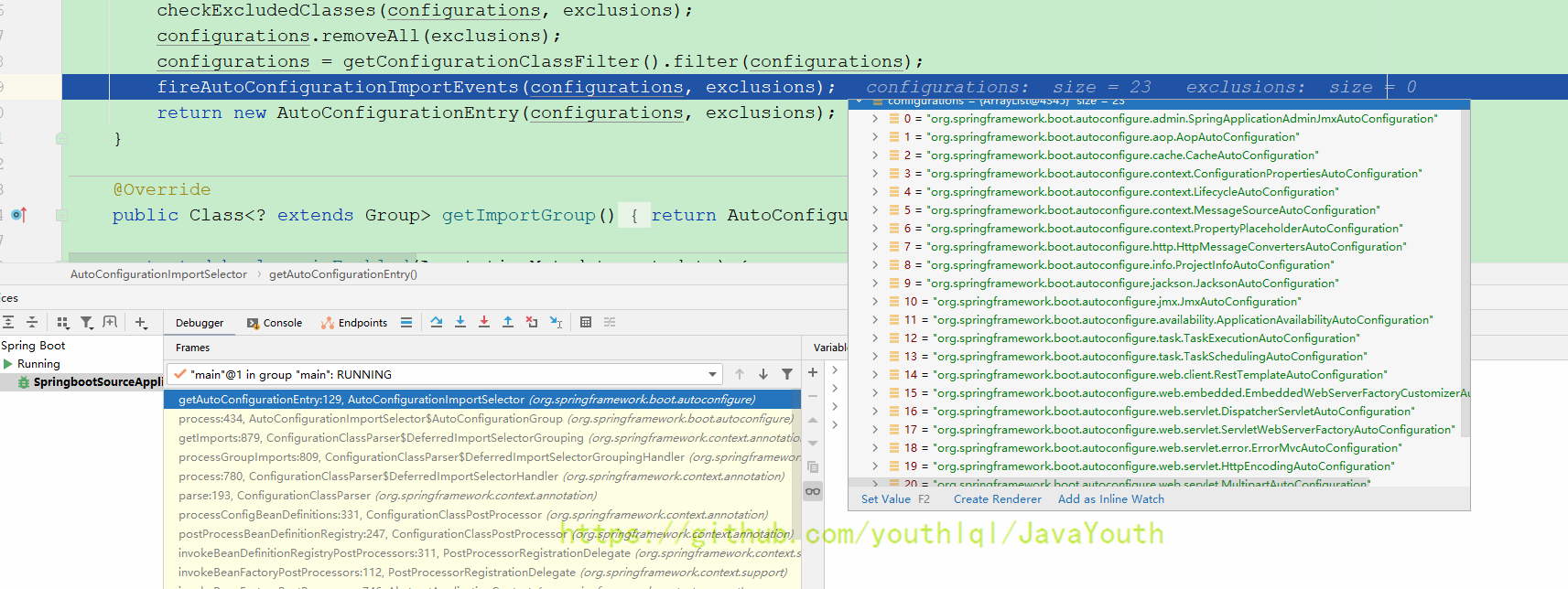
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
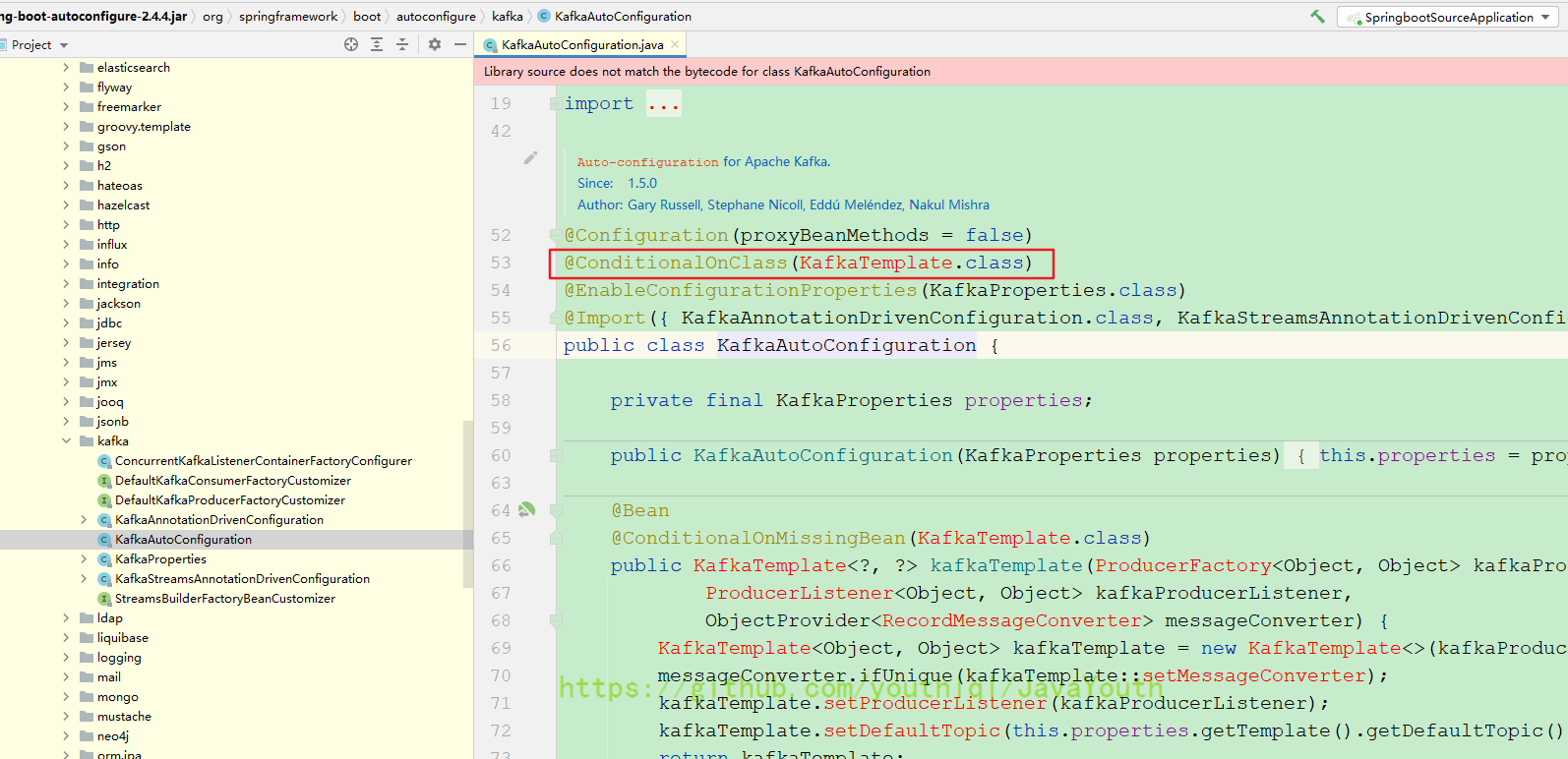
- 最终这里只会有23个组件被放到容器中,为什么这里要过滤?看下面的@ConditionalOnClass注解,当容器中有KafkaTemplate这个类时才会导入KafkaAutoConfiguration,而KafkaTemplate这个类只有导入了kafka相关jar包才会有。意思就是你只有在maven中导入了相关jar包,才会给你自动配置
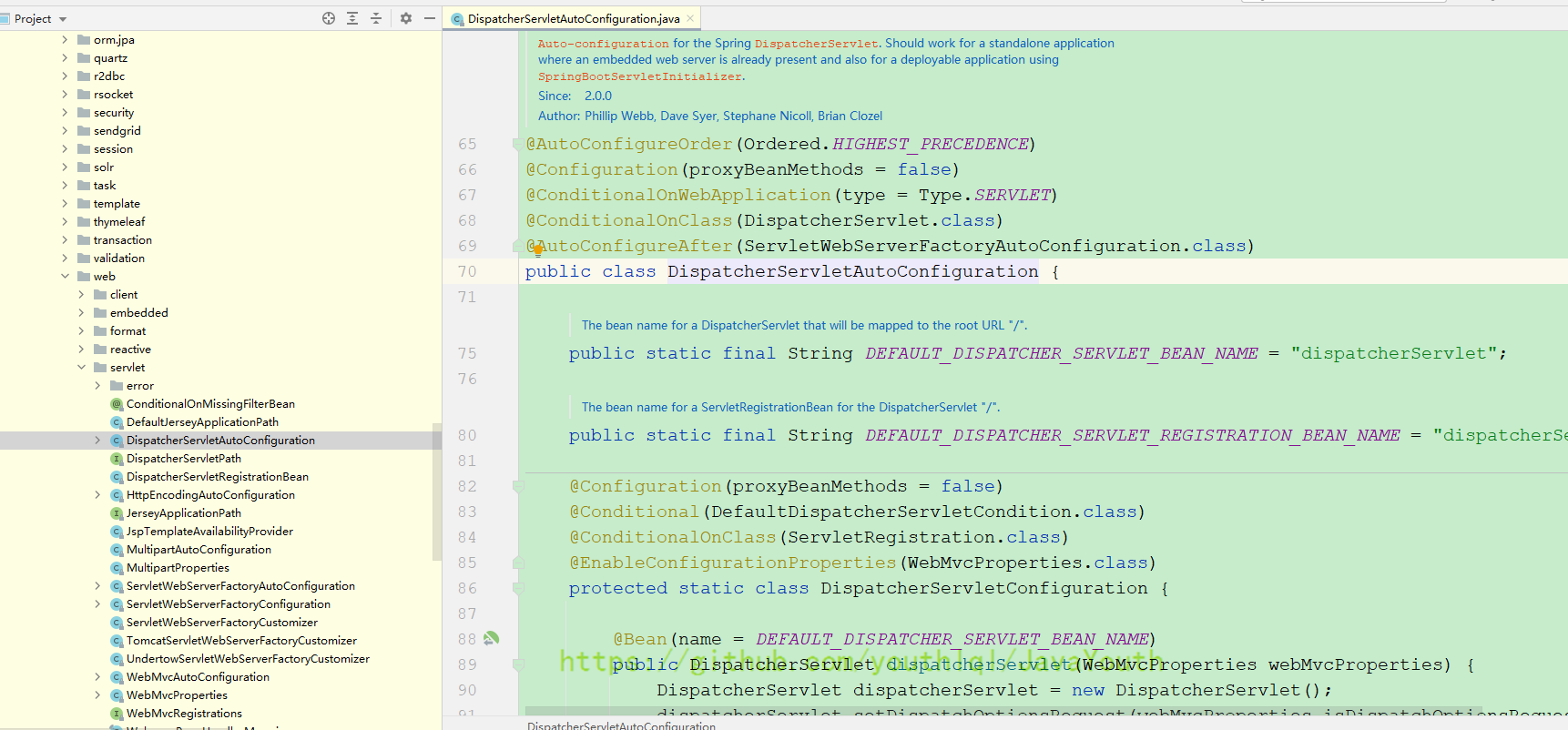
还有下面这个SpringMvc的,当你有DispatcherServlet这个类的时候,才会给你自动配置web相关的东西。而有DispatcherServlet类就代表你导入了web的相关依赖
- 在刚开始的时候我们自己实现的简易SpringBoot是利用SPI机制启动的Web容器
- 其实我们还要一个方法就是自己创建一个DispatcherServlet注册到Tomcat里,然后Tomcat就会调用Servlet相关初始化,最终调用到FrameworkServlet类里调用的
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();,进而启动Web容器。在SpringBoot里使用的就是这种方式启动Web容器
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet;
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
//这里就是DispatcherServlet在自动配置之前,先自动配置ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean name for a DispatcherServlet that will be mapped to the root URL "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
/**
* The bean name for a ServletRegistrationBean for the DispatcherServlet "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServletRegistration";
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10)
private static class DefaultDispatcherServletCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
// ......
}
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10)
private static class DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
// ......
}
}@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)- 这里就是最关键的,@AutoConfigureAfter注解看名字就能大概明白是什么意思,这里就是DispatcherServlet在自动配置之前,先自动配置ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class, //这里是最核心的
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class, //这里都是嵌入式服务器
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class, //这里都是嵌入式服务器
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class }) //这里都是嵌入式服务器
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
// ......
} @Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
return;
}
//给容器中注册一个服务器的后置处理器
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor",
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class,
WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor::new);
registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor",
ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor.class, ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor::new);
}package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
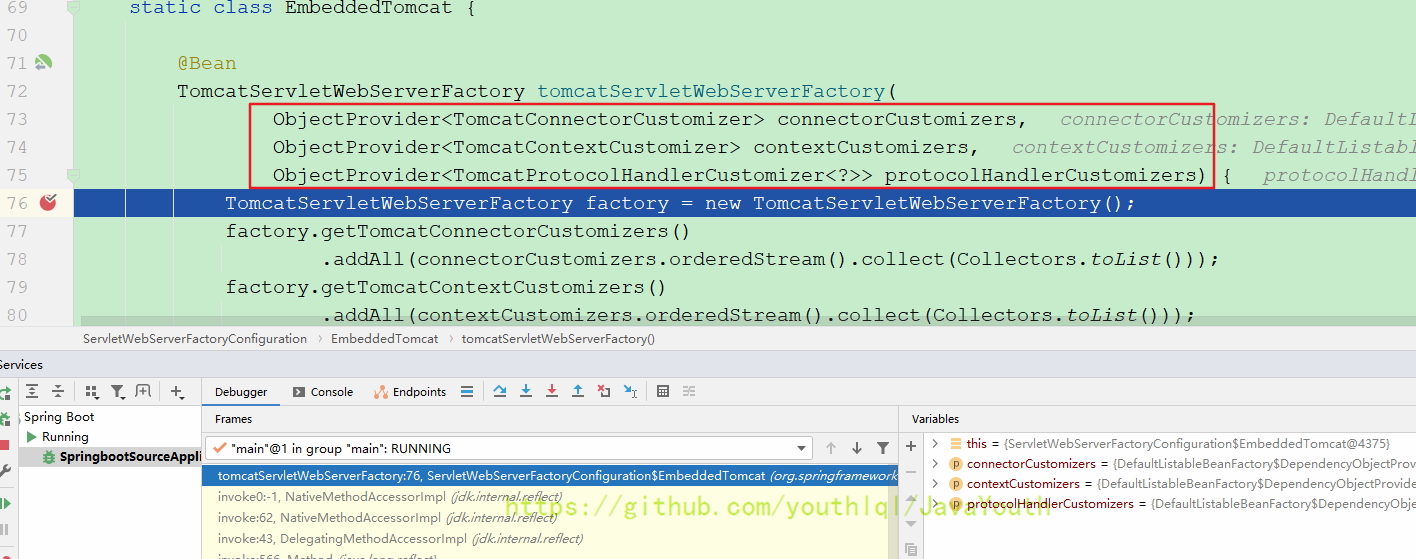
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<TomcatConnectorCustomizer> connectorCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatContextCustomizer> contextCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?>> protocolHandlerCustomizers) {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getTomcatConnectorCustomizers()
.addAll(connectorCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
factory.getTomcatContextCustomizers()
.addAll(contextCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
factory.getTomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizers()
.addAll(protocolHandlerCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
return factory;
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Jetty is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
JettyServletWebServerFactory JettyServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<JettyServerCustomizer> serverCustomizers) {
JettyServletWebServerFactory factory = new JettyServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getServerCustomizers().addAll(serverCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
return factory;
}
}
/**
* Nested configuration if Undertow is being used.
*/
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedUndertow {
@Bean
UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory(
ObjectProvider<UndertowDeploymentInfoCustomizer> deploymentInfoCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<UndertowBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers) {
UndertowServletWebServerFactory factory = new UndertowServletWebServerFactory();
factory.getDeploymentInfoCustomizers()
.addAll(deploymentInfoCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
factory.getBuilderCustomizers().addAll(builderCustomizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
return factory;
}
@Bean
UndertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer undertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new UndertowServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
}
}ServletWebServerFactory:服务器工厂,我们可以自己放Serlvet容器,我们自己放了就会用我们自己的
XXXProvider的意思就是这些方法的参数都是从容器中拿,如果你自定义了,就用自定义的
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
} @Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
StartupStep createWebServer = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.boot.webserver.create");
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
//最终在这里调用了TomcatServletWebServerFactory#getWebServer()
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
createWebServer.end();
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
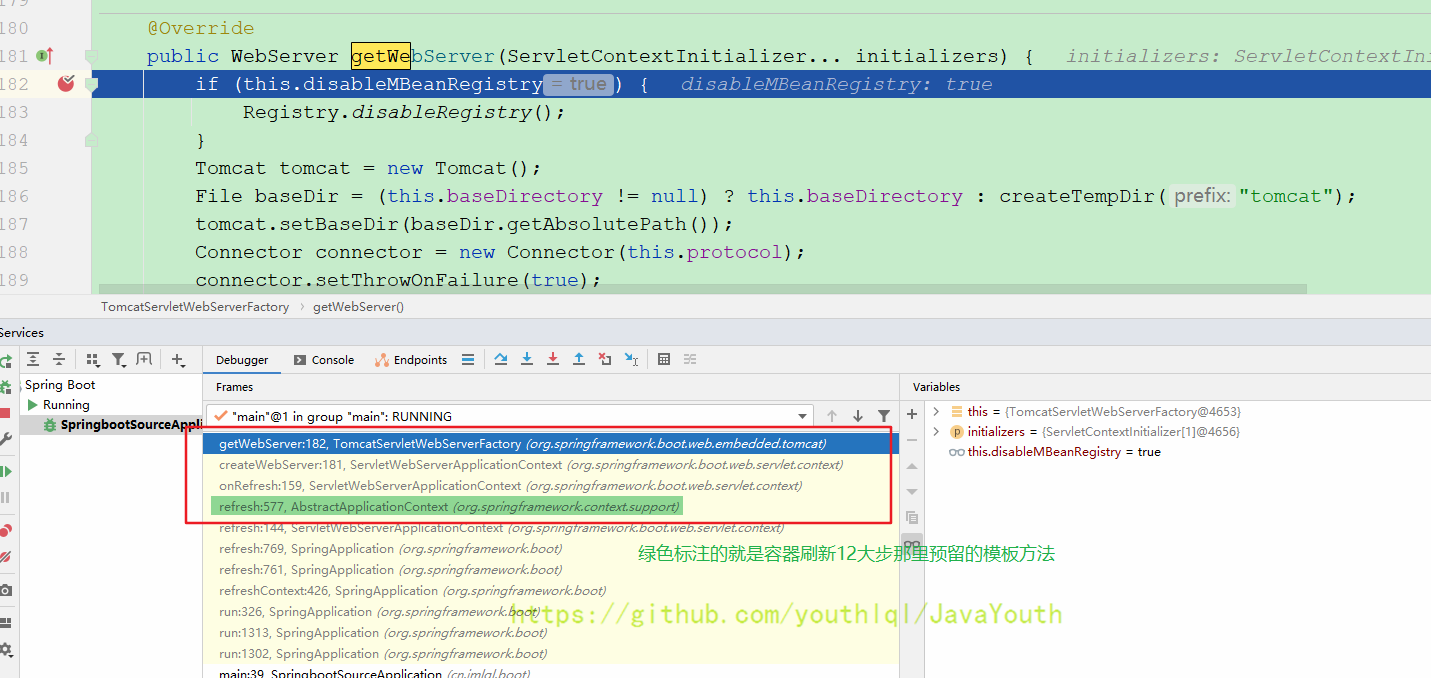
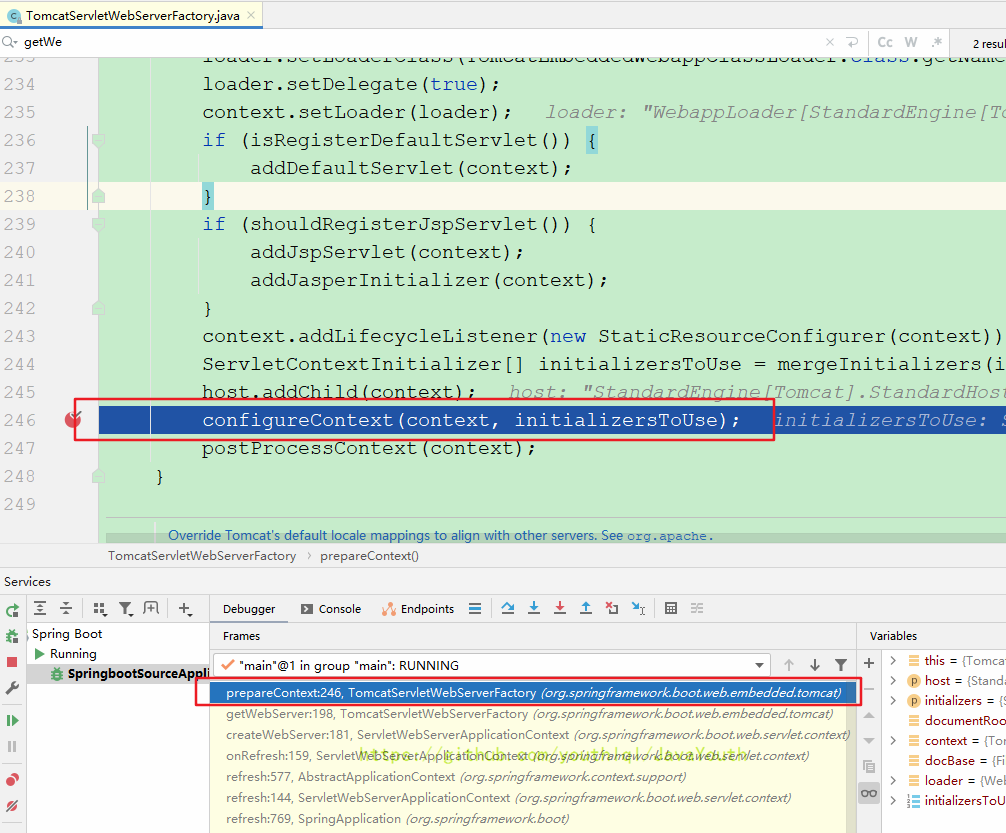
}注意看ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers);这一步就是Tomcat启动加载DispatcherServlet的时机
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet;
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
/**
* The bean name for a DispatcherServlet that will be mapped to the root URL "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServlet";
/**
* The bean name for a ServletRegistrationBean for the DispatcherServlet "/".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME = "dispatcherServletRegistration";
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DefaultDispatcherServletCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(MultipartResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = DispatcherServlet.MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME)
public MultipartResolver multipartResolver(MultipartResolver resolver) {
// Detect if the user has created a MultipartResolver but named it incorrectly
return resolver;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional(DispatcherServletRegistrationCondition.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRegistration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebMvcProperties.class)
@Import(DispatcherServletConfiguration.class)
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
//注意看DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
// ......
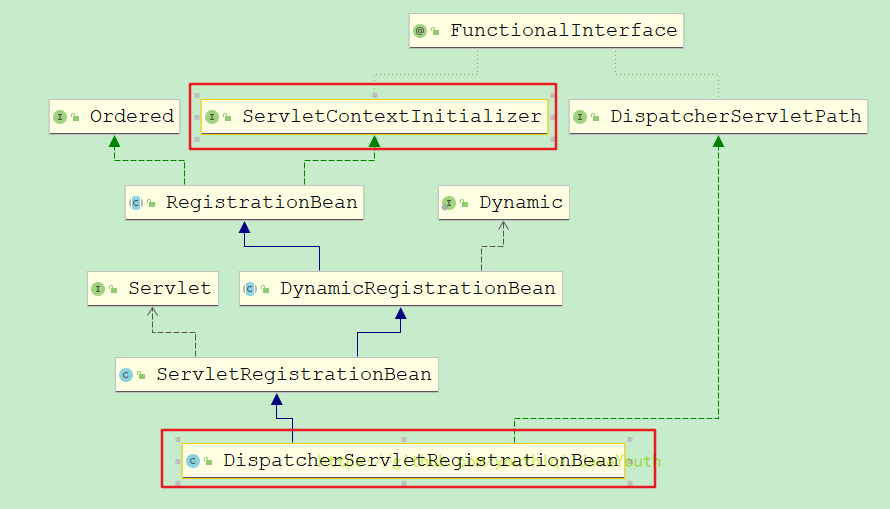
}我们发现DispatcherServletRegistrationBean它是一个ServletContextInitializer
F7进入上面说的这个configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
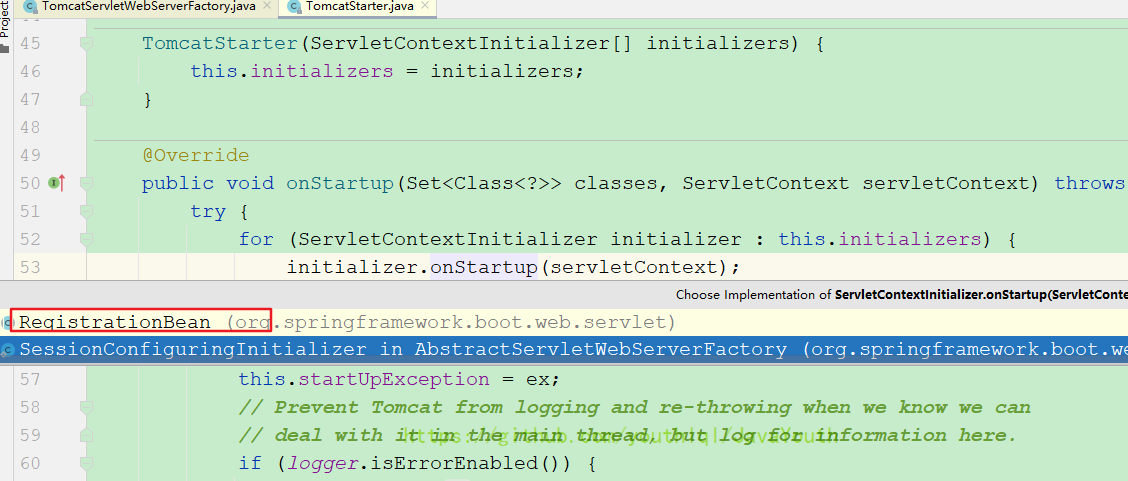
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers);//注意在这里把这些ServletContextInitializer给了TomcatStarter
// ......
for (TomcatContextCustomizer customizer : this.tomcatContextCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(context);
}
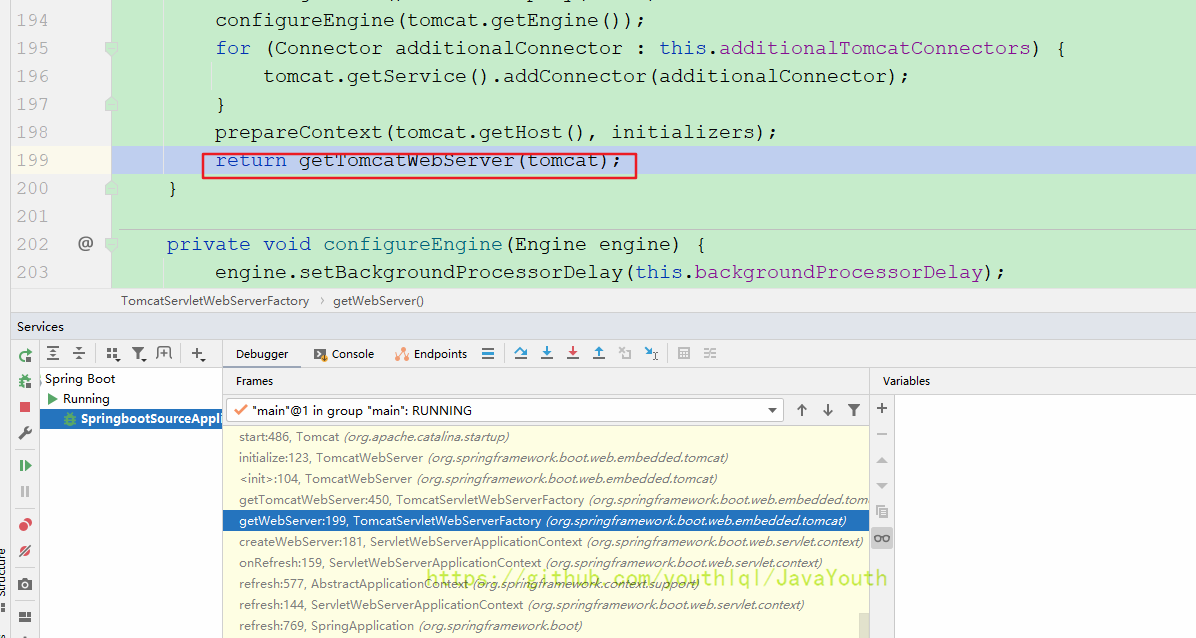
}然后返回到getWebServer调用最后一步
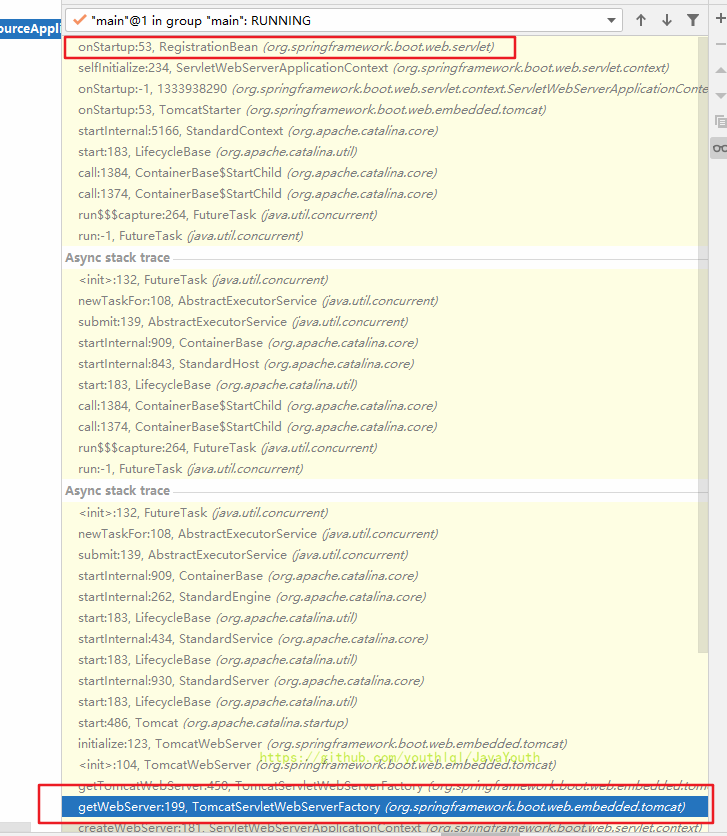
最终初始化会调用到onStartup()
TomcatStarter(ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
this.initializers = initializers;
}
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> classes, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
try {
for (ServletContextInitializer initializer : this.initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
this.startUpException = ex;
// Prevent Tomcat from logging and re-throwing when we know we can
// deal with it in the main thread, but log for information here.
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Error starting Tomcat context. Exception: " + ex.getClass().getName() + ". Message: "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
}
}F7进入,省略到一些不重要的方法
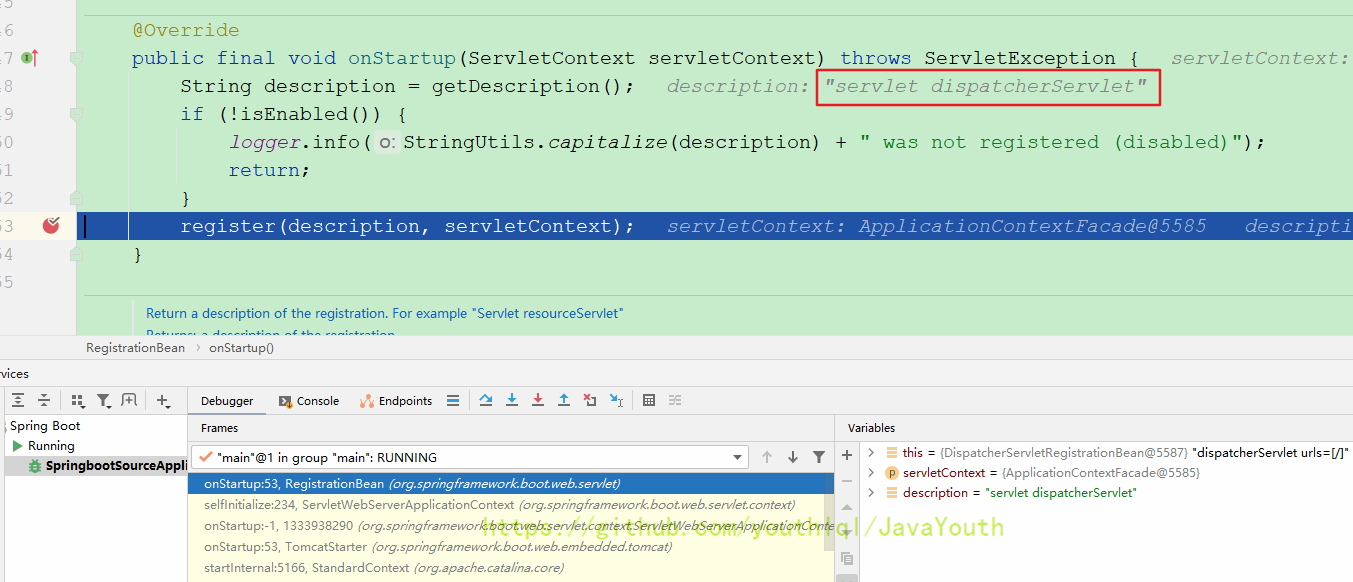
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(registration);
}servletContext这个就是tomcat容器
-
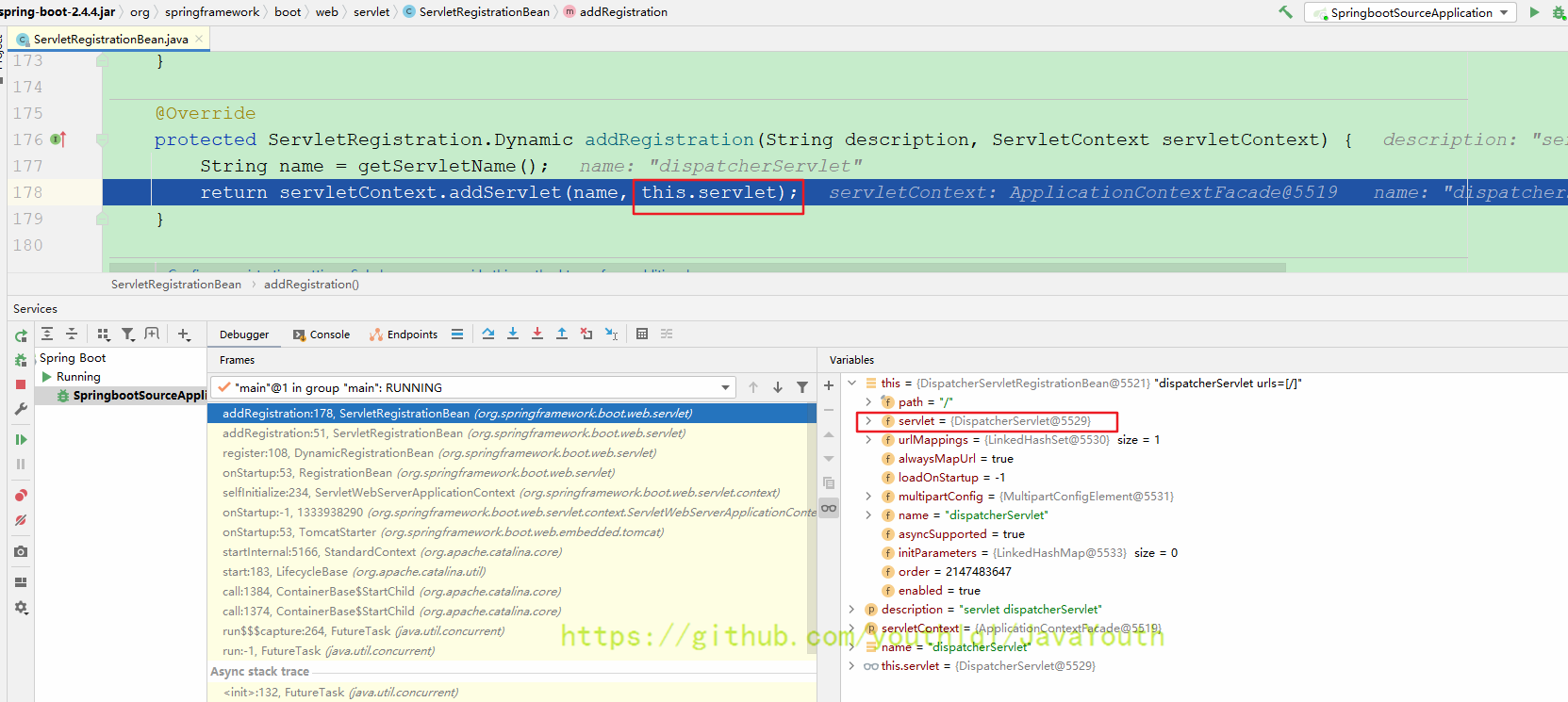
ServletRegistration.Dynamic#addRegistration()将dispatcherServlet放入tomcat容器中
-
然后Tomcat启动之后自然就调用Servelt初始化,进而调到了dispatcherServlet,然后就是之前讲过的初始化web容器。
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
得到下面的结论
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootSourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSourceApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean //所有的xxxRegistrationBean都是允许我们注册原生的Servlet组件进去,
//利用 ServletContextInitializer在Tomcat启动完成以后进行回调的机制
ServletRegistrationBean<HelloServlet> registrationBean(){
ServletRegistrationBean<HelloServlet> registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new HelloServlet());
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/he66");
return registrationBean;
}
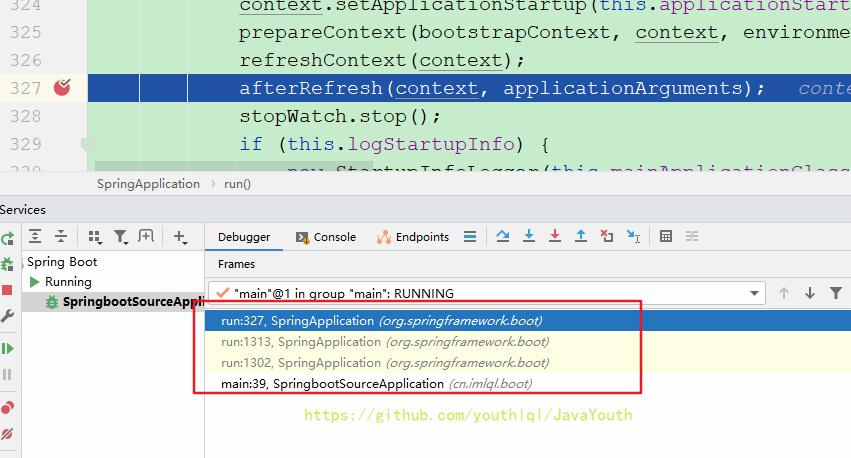
} public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建容器
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新容器
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}就是这样很简单