栈的特点是后入先出
根据这个特点可以临时保存一些数据,之后用到依次再弹出来,常用于 DFS 深度搜索
队列一般常用于 BFS 广度搜索,类似一层一层的搜索
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
思路:用两个栈实现,一个最小栈始终保证最小值在顶部
type MinStack struct {
min []int
stack []int
}
/** initialize your data structure here. */
func Constructor() MinStack {
return MinStack{
min: make([]int, 0),
stack: make([]int, 0),
}
}
func (this *MinStack) Push(x int) {
min := this.GetMin()
if x < min {
this.min = append(this.min, x)
} else {
this.min = append(this.min, min)
}
this.stack = append(this.stack, x)
}
func (this *MinStack) Pop() {
if len(this.stack) == 0 {
return
}
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
this.min = this.min[:len(this.min)-1]
}
func (this *MinStack) Top() int {
if len(this.stack) == 0 {
return 0
}
return this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
}
func (this *MinStack) GetMin() int {
if len(this.min) == 0 {
return 1 << 31
}
min := this.min[len(this.min)-1]
return min
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* obj.Push(x);
* obj.Pop();
* param_3 := obj.Top();
* param_4 := obj.GetMin();
*/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation
波兰表达式计算 > 输入:
["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]> 输出: 9解释:
((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
思路:通过栈保存原来的元素,遇到表达式弹出运算,再推入结果,重复这个过程
func evalRPN(tokens []string) int {
if len(tokens)==0{
return 0
}
stack:=make([]int,0)
for i:=0;i<len(tokens);i++{
switch tokens[i]{
case "+","-","*","/":
if len(stack)<2{
return -1
}
// 注意:a为被除数,b为除数
b:=stack[len(stack)-1]
a:=stack[len(stack)-2]
stack=stack[:len(stack)-2]
var result int
switch tokens[i]{
case "+":
result=a+b
case "-":
result=a-b
case "*":
result=a*b
case "/":
result=a/b
}
stack=append(stack,result)
default:
// 转为数字
val,_:=strconv.Atoi(tokens[i])
stack=append(stack,val)
}
}
return stack[0]
}给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。 s = "3[a]2[bc]", 返回 "aaabcbc". s = "3[a2[c]]", 返回 "accaccacc". s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef", 返回 "abcabccdcdcdef".
思路:通过栈辅助进行操作
func decodeString(s string) string {
if len(s) == 0 {
return ""
}
stack := make([]byte, 0)
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
switch s[i] {
case ']':
temp := make([]byte, 0)
for len(stack) != 0 && stack[len(stack)-1] != '[' {
v := stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
temp = append(temp, v)
}
// pop '['
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
// pop num
idx := 1
for len(stack) >= idx && stack[len(stack)-idx] >= '0' && stack[len(stack)-idx] <= '9' {
idx++
}
// 注意索引边界
num := stack[len(stack)-idx+1:]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-idx+1]
count, _ := strconv.Atoi(string(num))
for j := 0; j < count; j++ {
// 把字符正向放回到栈里面
for j := len(temp) - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
stack = append(stack, temp[j])
}
}
default:
stack = append(stack, s[i])
}
}
return string(stack)
}利用栈进行 DFS 递归搜索模板
boolean DFS(int root, int target) {
Set<Node> visited;
Stack<Node> s;
add root to s;
while (s is not empty) {
Node cur = the top element in s;
return true if cur is target;
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {
if (next is not in visited) {
add next to s;
add next to visited;
}
}
remove cur from s;
}
return false;
}给定一个二叉树,返回它的中序遍历。
// 思路:通过stack 保存已经访问的元素,用于原路返回
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
result := make([]int, 0)
if root == nil {
return result
}
stack := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
for len(stack) > 0 || root != nil {
for root != nil {
stack = append(stack, root)
root = root.Left // 一直向左
}
// 弹出
val := stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
result = append(result, val.Val)
root = val.Right
}
return result
}给你无向连通图中一个节点的引用,请你返回该图的深拷贝(克隆)。
func cloneGraph(node *Node) *Node {
visited:=make(map[*Node]*Node)
return clone(node,visited)
}
// 1 2
// 4 3
// 递归克隆,传入已经访问过的元素作为过滤条件
func clone(node *Node,visited map[*Node]*Node)*Node{
if node==nil{
return nil
}
// 已经访问过直接返回
if v,ok:=visited[node];ok{
return v
}
newNode:=&Node{
Val:node.Val,
Neighbors:make([]*Node,len(node.Neighbors)),
}
visited[node]=newNode
for i:=0;i<len(node.Neighbors);i++{
newNode.Neighbors[i]=clone(node.Neighbors[i],visited)
}
return newNode
}给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
思路:通过深度搜索遍历可能性(注意标记已访问元素)
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
var count int
for i:=0;i<len(grid);i++{
for j:=0;j<len(grid[i]);j++{
if grid[i][j]=='1' && dfs(grid,i,j)>=1{
count++
}
}
}
return count
}
func dfs(grid [][]byte,i,j int)int{
if i<0||i>=len(grid)||j<0||j>=len(grid[0]){
return 0
}
if grid[i][j]=='1'{
// 标记已经访问过(每一个点只需要访问一次)
grid[i][j]=0
return dfs(grid,i-1,j)+dfs(grid,i,j-1)+dfs(grid,i+1,j)+dfs(grid,i,j+1)+1
}
return 0
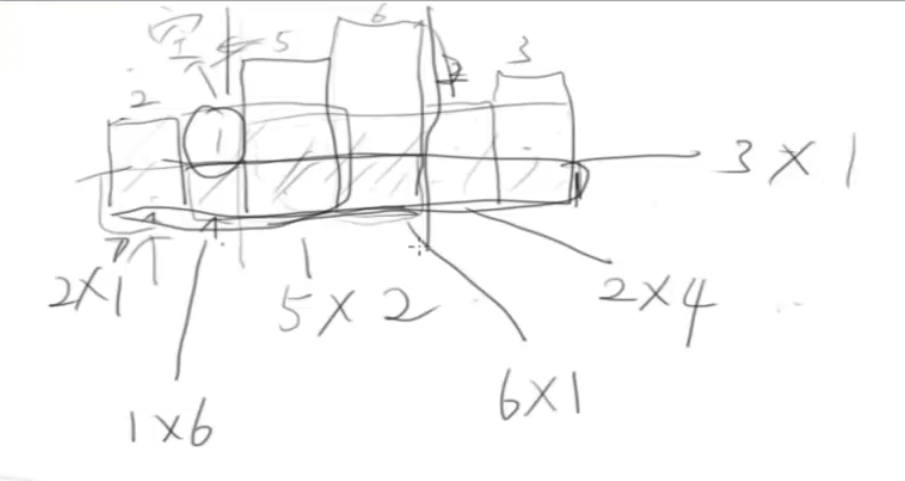
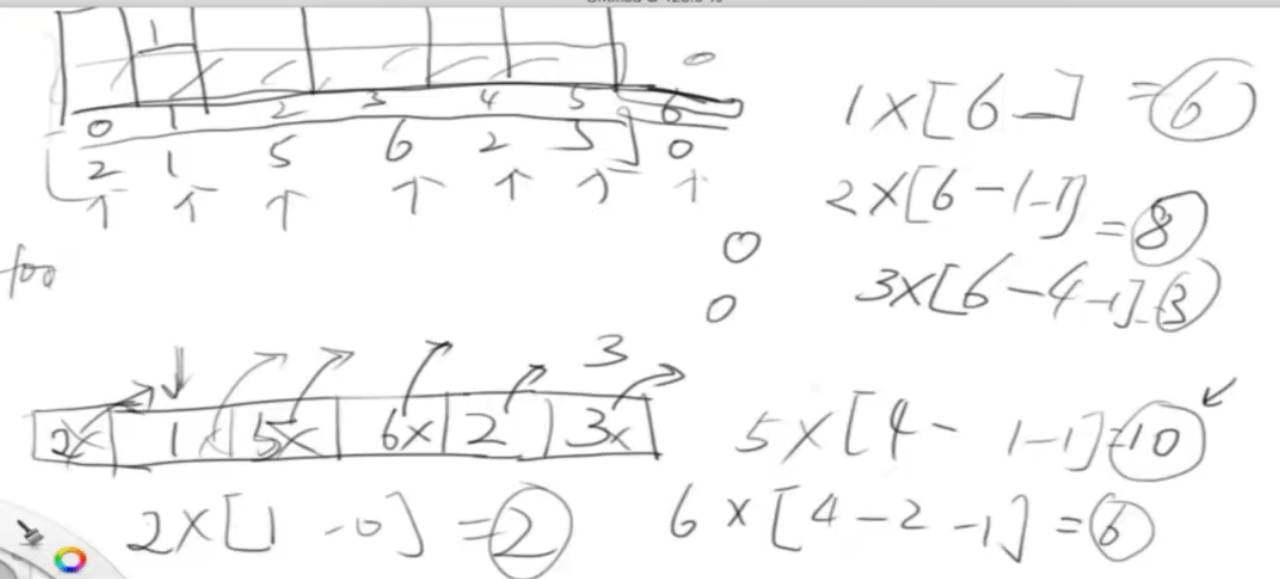
}largest-rectangle-in-histogram
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。 求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
思路:求以当前柱子为高度的面积,即转化为寻找小于当前值的左右两边值
用栈保存小于当前值的左的元素
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
if len(heights) == 0 {
return 0
}
stack := make([]int, 0)
max := 0
for i := 0; i <= len(heights); i++ {
var cur int
if i == len(heights) {
cur = 0
} else {
cur = heights[i]
}
// 当前高度小于栈,则将栈内元素都弹出计算面积
for len(stack) != 0 && cur <= heights[stack[len(stack)-1]] {
pop := stack[len(stack)-1]
stack = stack[:len(stack)-1]
h := heights[pop]
// 计算宽度
w := i
if len(stack) != 0 {
peek := stack[len(stack)-1]
w = i - peek - 1
}
max = Max(max, h*w)
}
// 记录索引即可获取对应元素
stack = append(stack, i)
}
return max
}
func Max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}常用于 BFS 宽度优先搜索
使用栈实现队列
type MyQueue struct {
stack []int
back []int
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
func Constructor() MyQueue {
return MyQueue{
stack: make([]int, 0),
back: make([]int, 0),
}
}
// 1
// 3
// 5
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
for len(this.back) != 0 {
val := this.back[len(this.back)-1]
this.back = this.back[:len(this.back)-1]
this.stack = append(this.stack, val)
}
this.stack = append(this.stack, x)
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
for len(this.stack) != 0 {
val := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
this.back = append(this.back, val)
}
if len(this.back) == 0 {
return 0
}
val := this.back[len(this.back)-1]
this.back = this.back[:len(this.back)-1]
return val
}
/** Get the front element. */
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
for len(this.stack) != 0 {
val := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
this.back = append(this.back, val)
}
if len(this.back) == 0 {
return 0
}
val := this.back[len(this.back)-1]
return val
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return len(this.stack) == 0 && len(this.back) == 0
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* obj.Push(x);
* param_2 := obj.Pop();
* param_3 := obj.Peek();
* param_4 := obj.Empty();
*/二叉树层次遍历
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
// 通过上一层的长度确定下一层的元素
result := make([][]int, 0)
if root == nil {
return result
}
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
queue = append(queue, root)
for len(queue) > 0 {
list := make([]int, 0)
// 为什么要取length?
// 记录当前层有多少元素(遍历当前层,再添加下一层)
l := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < l; i++ {
// 出队列
level := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
list = append(list, level.Val)
if level.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, level.Left)
}
if level.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, level.Right)
}
}
result = append(result, list)
}
return result
}给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵,找出每个元素到最近的 0 的距离。 两个相邻元素间的距离为 1
// BFS 从0进队列,弹出之后计算上下左右的结果,将上下左右重新进队列进行二层操作
// 0 0 0 0
// 0 x 0 0
// x x x 0
// 0 x 0 0
// 0 0 0 0
// 0 1 0 0
// 1 x 1 0
// 0 1 0 0
// 0 0 0 0
// 0 1 0 0
// 1 2 1 0
// 0 1 0 0
func updateMatrix(matrix [][]int) [][]int {
q:=make([][]int,0)
for i:=0;i<len(matrix);i++{
for j:=0;j<len(matrix[0]);j++{
if matrix[i][j]==0{
// 进队列
point:=[]int{i,j}
q=append(q,point)
}else{
matrix[i][j]=-1
}
}
}
directions:=[][]int{{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,0}}
for len(q)!=0{
// 出队列
point:=q[0]
q=q[1:]
for _,v:=range directions{
x:=point[0]+v[0]
y:=point[1]+v[1]
if x>=0&&x<len(matrix)&&y>=0&&y<len(matrix[0])&&matrix[x][y]==-1{
matrix[x][y]=matrix[point[0]][point[1]]+1
// 将当前的元素进队列,进行一次BFS
q=append(q,[]int{x,y})
}
}
}
return matrix
}- 熟悉栈的使用场景
- 后入先出,保存临时值
- 利用栈 DFS 深度搜索
- 熟悉队列的使用场景
- 利用队列 BFS 广度搜索