Input image on the left is detected as the target image on the right after the mask has been applied.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The purpose of this library is to create adversarial attacks against the FaceNet face recognizer. This is the preliminary work towards creating a more robust physical attack using a mask that a person could wear over their face.
For more details, please check out my research poster.
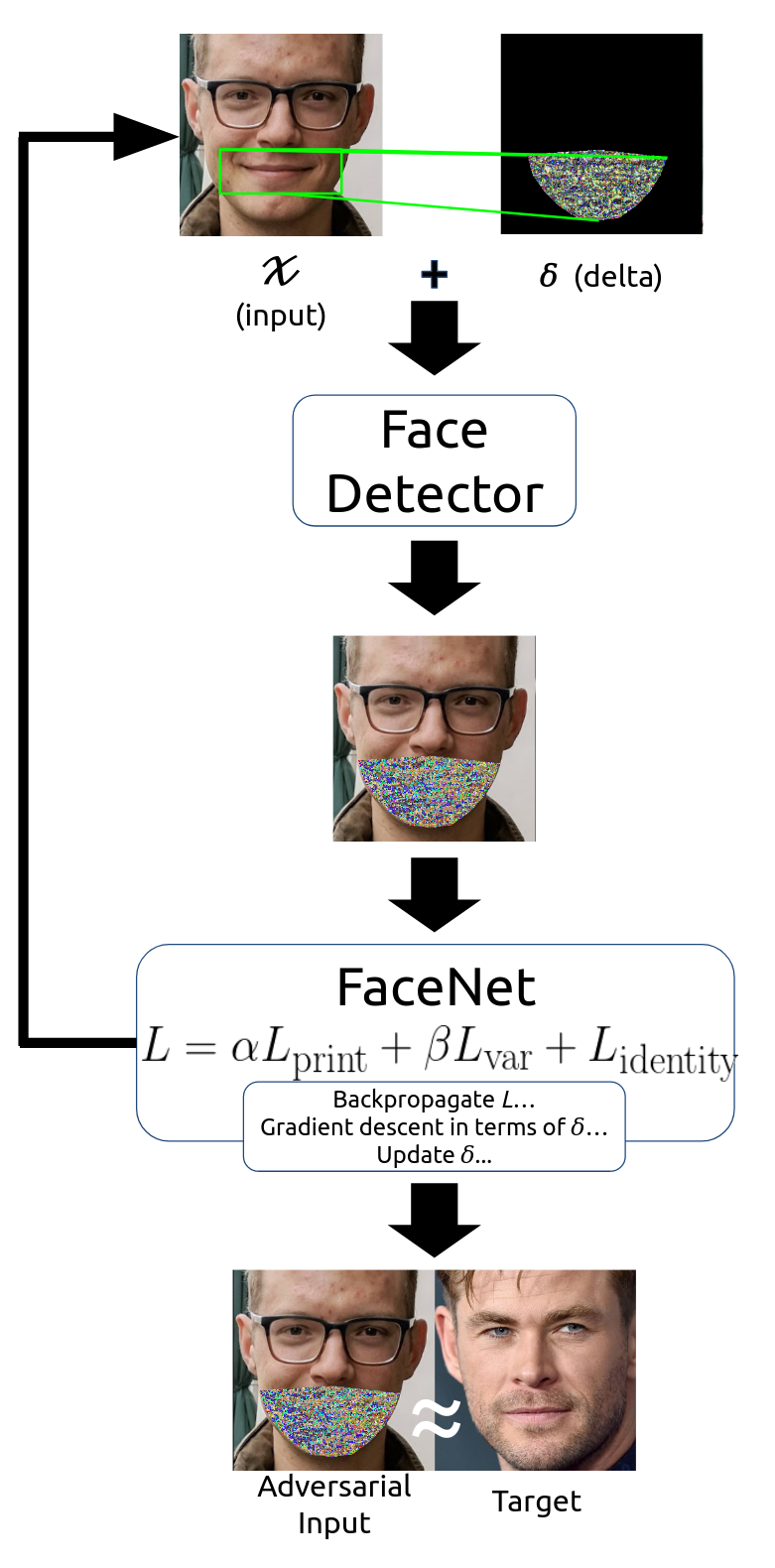
The current pipeline consists of an aligned input image with a calculated mask. This is then fed into a face detector using dlib's histogram of oriented gradients detector to test whether the face is still detected. This is then passed to FaceNet where which ouputs a face embedding and a loss which is then calculated and propagated back. This perturbs the input mask which generates enough of a disturbance to affect the loss.
The loss function maximizes the Euclidean distance between the inputs' true identity and minimizes the distance between the adversarial input and the target image.
An image of this process can be seen below.
This project works on Linux (Ubuntu 20.04). Windows and Mac are not supported but may work.
- Create a virtual environment
conda create -n facial_recognition python=3.8.5
conda activate facial_recognition- Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/392781/FaceOff.git
- Install the required libraries
pip install -r requirements.txt- Install FaceOff from inside the folder where
setup.pyis located
pip install -e .- Import and use!
from FaceOff.AFR import load_data, AttackFor training instructions look at example.py to get started in less than 30 lines.
Please cite FaceOff if used in your research:
@misc{FaceOff,
author = {Ronaldas Paulius Lencevicius},
howpublished = {GitHub},
title = {Face-Off: Steps towards physical adversarial attacks on facial recognition},
URL = {https://github.com/392781/FaceOff},
month = {Aug}
year = {2019},
}- Sharif, Mahmood, et al. "Accessorize to a crime: Real and stealthy attacks on state-of-the-art face recognition." Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. ACM, 2016.
- Wang, Mei, and Weihong Deng. "Deep face recognition: A survey." arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.06655 (2018).
- MacDonald, Bruce. “Fooling Facial Detection with Fashion.” Towards Data Science, Towards Data Science, 4 June 2019, towardsdatascience.com/fooling-facial-detection-with-fashion-d668ed919eb.
- Thys, Simen, et al. "Fooling automated surveillance cameras: adversarial patches to attack person detection." Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. 2019.
Used the PyTorch FaceNet implementation by Tim Esler