-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 254
Getting a Feature Class into HDFS
There are extra steps if you are using a VM - bolded below
This tutorial will take a feature class and export it to HDFS. The opposite direction, moving tables from HDFS to a feature is here.
-
If you have not already done so, download the Geoprocessing Toolbox and follow the given Instructions.
-
You will now use tools from the geoprocessing toolbox to move your table to a feature class. We recommend building a model using model builder. Drag two tools from your toolbox into the model:
Features to JSONandCopy to HDFS.
-
Start hive in your terminal and add the appropriate jars (similar to the sample example):
hive add jar gis-tools-for-hadoop/samples/lib/esri-geometry-api.jar gis-tools-for-hadoop/samples/lib/spatial-sdk-hadoop.jar; -
Double click on the
Features to JSONtool in your model.
||| |---------|----------|----------| |Input Features (Box 1) : | This is the input feature you would like to send to HDFS| |Output JSON (Box 2) : | This is a temporary output you name, end with .json| |JSON type (optional) (Box 3) :| Choose UNENCLOSED_JSON| |Formatted JSON (optional) (Box 4) : | Do not select this option|
Run this tool.
The JSON type must match the input type as decided in Step 10 here
-
Open the .json file in a text editor (right click> edit!) you just generated (if you forget where, just double click the tool you ran).
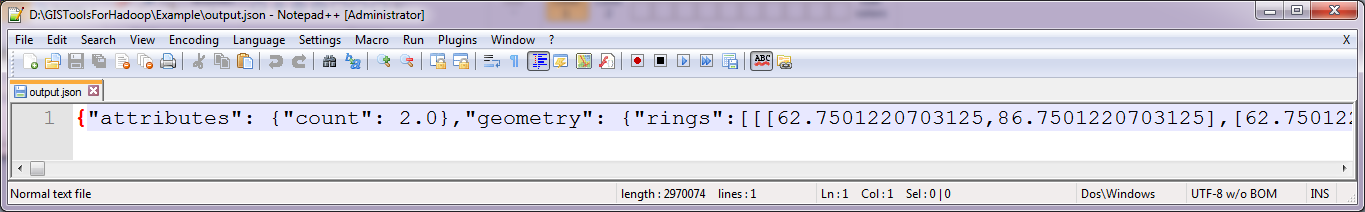
In the file look at the attributes - these will be the attribute names you use when generating your table. In this example we will have "count" and "geometry".
-
Generate an empty table to save your feature class to, in this case the table is named
input_ex, make sure to create the columns with the names found in Step 5:DROP TABLE input_ex; CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE input_ex(count int, geometry binary) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'com.esri.hadoop.hive.serde.EsriJsonSerDe' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'com.esri.json.hadoop.UnenclosedEsriJsonInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat'; -
In hive type:
describe formatted table_name;, wheretable_nameis the table you generated in Step 6 (i.e.describe formatted input_ex;).


Double click on the
Copy to HDFStool.||Standalone Cluster|VM| |---------|----------|------|--| |Input local file (Box 1): | This is your .json file from your first tool|<- same| |HDFS server name ( Box 2):| This is your namenode, you can find this information using the
describe formattedcommand above|localhost(although write down namenode)| |HDFS TCP port number (Box 3)| Accept the default|accept default| |HDFS username (Box 4):| In the terminal type:whoami[exit hive first], or in the describe command underowner|same, will berootif using hortonworks| |HDFS remote file (Box 4):| Use everything after and including the single slash from the location (above), and add a file name and .json|<- same|
VM Steps: You need to add your VM as localhost. Follow these steps and add the line 127.0.0.1 sandbox.hortonworks.com to the file and save. If you aren't using Hortonworks - this is the namenode you found for box 1 above.
Run this tool.
- In hive your table will now be populated with the features. You can check by doing a simple select statement:
SELECT * from input_ex limit 2;