This repository contains the attack reproduction artifacts for the paper "AtomicDisk: A Secure Virtual Disk for TEEs against Eviction Attacks", which has been accepted by FAST'25. You can reproduce the attack by following the instructions in this documentation.
sudo docker pull occlum/occlum:0.30.1-test-ubuntu22.04
git clone [email protected]:Fischer0522/EvictionAttack.git {src_path}
sudo docker run -it --device /dev/sgx/enclave --device /dev/sgx/provision --name "occlum-0.31.0-rc-dev" --net=host -v "{src_path}:/root" occlum/occlum:0.30.1-rc-ubuntu22.04
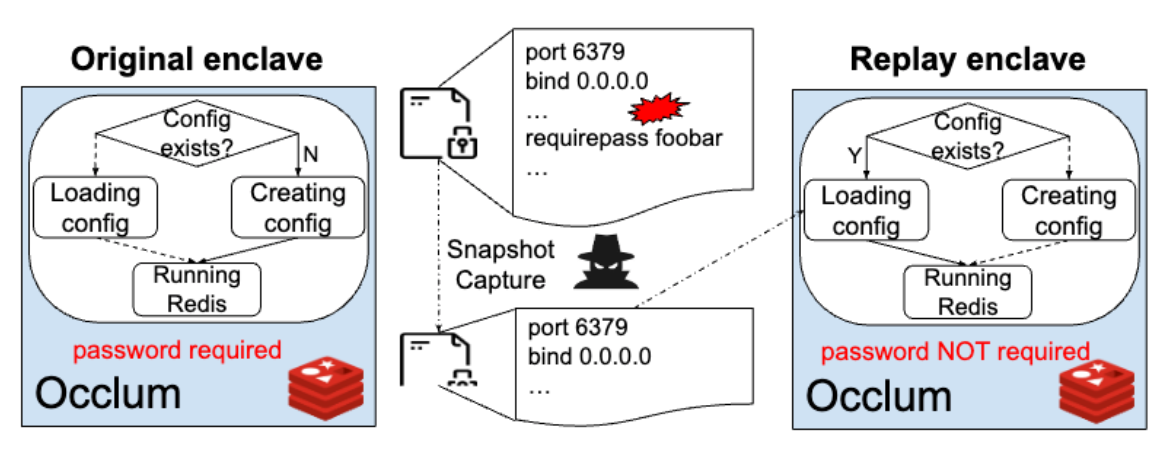
A simple snapshot demo is provided in the ./simple_snapshot directory. In this demo, we set up a C++ program as the entry point of the Occlum enclave. The program performs a single operation: writing 20,000 lines of content to redis.conf. When it triggers an SGX-PFS eviction, the program pauses briefly to allow an attacker to capture a snapshot, then proceeds to write the remaining content to redis.conf (the pause is implemented to make reproduction easier).
The following bash scripts are provided for capturing and restoring snapshots:
take_snapshot_step_1.sh: Captures the snapshot when SGX-PFS performs an eviction. Execute this script whengen_filetriggers an eviction. It copies the entire run directory.take_snapshot_step_2.sh: Execute this aftergen_filecompletes. It copies the metadata file.restore_snapshot.sh: Replaces the original run directory with the snapshot and metadata file. The script then displays the content of redis.conf, which will show approximately 3,000 lines, representing a vulnerable state of the configuration.
In the /redis_snapshot directory, we demonstrate the eviction attack on Redis. Here, gen_conf serves as the entry point of the Occlum enclave. Similar to gen_file in the simple snapshot demo, it reads content from redis.conf.source and writes it to redis.conf, simulating the initialization of the configuration file. To reproduce the eviction attack, execute take_snapshot_step_1.sh when gen_conf triggers the SGX-PFS eviction, and run take_snapshot_step_2.sh after the program exits.
After program completion, you can start a Redis server using the redis.conf:
cd occlum_instance
occlum run /bin/redis-server /redis.conf
When connecting to the server using redis-cli, you'll receive an (error) NOAUTH Authentication required message if you haven't executed restore_snapshot.sh. After executing the restore script and restarting the Redis server, you can connect without any authentication requirements.
It is straightforward to exploit the snapshots to attack more applications.
Many popular databases (e.g., MongoDB and Cassandra)
rely on similar configuration-based authentication mechanisms.
The adversary can exploit this vulnerability by capturing configuration snapshots
where critical authentication directives are missing or set to default value
(e.g., authentication in MongoDB, authenticator in Cassandra),
then leverage the same eviction attack to circumvent authentication controls.
A more interesting direction, which we leave for future work,
is how to exploit the snapshots that involve multiple files.
See more details in Attack Demo and our upcoming paper on FAST'25