A frontend Framework for building data-driven applications running in the browser on top of REST/GraphQL APIs, using ES6, React and Material Design. Open sourced and maintained by ITopGun.
-
🔌 Backend Agnostic: Connects to any API (REST or GraphQL, see the list of more than 45 adapters)
-
🧩 All The Building Blocks You Need: Provides hooks and components for authentication, routing, forms & validation, datagrid, search & filter, relationships, validation, roles & permissions, rich text editor, i18n, notifications, menus, theming, caching, etc.
-
🪡 High Quality: Accessibility, responsive, secure, fast, testable
-
💻 Great Developer Experience: Complete documentation, IDE autocompletion, type safety, storybook, demo apps with source code, modular architecture, declarative API
-
👑 Great User Experience: Optimistic rendering, filter-as-you-type, undo, preferences, saved queries
-
🛠 Complete Customization: Replace any component with your own
-
☂️ Opt-In Types: Develop either in TypeScript or JavaScript
-
👨👩👧👦 Powered by MUI, react-hook-form, react-router, react-query, TypeScript and a few more
React-admin is available from npm. You can install it (and its required dependencies) using:
npm install react-admin
#or
yarn add react-adminRead the Tutorial for a 30 minutes introduction. After that, head to the Documentation, or checkout the source code of the demo for an example usage.
// in app.js
import * as React from "react";
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { Admin, Resource } from 'react-admin';
import restProvider from 'ra-data-simple-rest';
import { PostList, PostEdit, PostCreate, PostIcon } from './posts';
render(
<Admin dataProvider={restProvider('http://localhost:3000')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} edit={PostEdit} create={PostCreate} icon={PostIcon} />
</Admin>,
document.getElementById('root')
);The <Resource> component is a configuration component that allows to define sub components for each of the admin view: list, edit, and create. These components use MUI and custom components from react-admin:
// in posts.js
import * as React from "react";
import { List, Datagrid, Edit, Create, SimpleForm, DateField, TextField, EditButton, TextInput, DateInput, useRecordContext } from 'react-admin';
import BookIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Book';
export const PostIcon = BookIcon;
export const PostList = () => (
<List>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<TextField source="average_note" />
<TextField source="views" />
<EditButton />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
const PostTitle = () => {
const record = useRecordContext();
return <span>Post {record ? `"${record.title}"` : ''}</span>;
};
export const PostEdit = () => (
<Edit title={<PostTitle />}>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput disabled source="id" />
<TextInput source="title" />
<TextInput source="teaser" options={{ multiline: true }} />
<TextInput multiline source="body" />
<DateInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput source="average_note" />
<TextInput disabled label="Nb views" source="views" />
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
export const PostCreate = () => (
<Create title="Create a Post">
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="title" />
<TextInput source="teaser" options={{ multiline: true }} />
<TextInput multiline source="body" />
<TextInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput source="average_note" />
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);Yes.
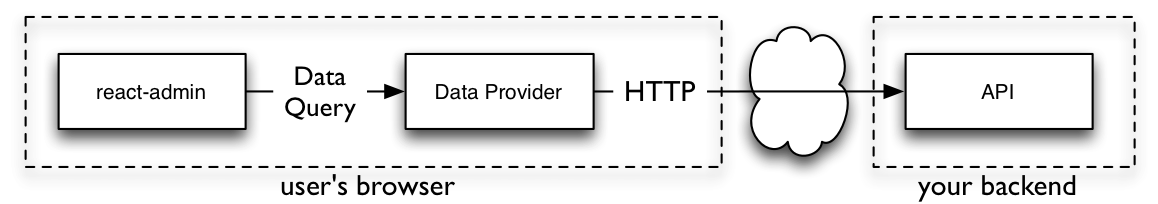
React-admin uses an adapter approach, with a concept called Data Providers. Existing providers can be used as a blueprint to design your API, or you can write your own Data Provider to query an existing API. Writing a custom Data Provider is a matter of hours.
See the Data Providers documentation for details.
React-admin is designed as a library of loosely coupled React components and hooks exposing reusable controller logic. It is very easy to replace any part of react-admin with your own, e.g. to use a custom datagrid, GraphQL instead of REST, or Bootstrap instead of Material Design.
There are several examples inside the examples folder:
simple(CodeSandbox, StackBlitz): a simple blog with posts, comments and users that we use for our e2e tests.e-commerce: (demo, source) A fictional poster shop admin, serving as the official react-admin demo.CRM: (demo, source) A customer relationship management applicationtutorial(CodeSandbox): the application built while following the tutorial.
You can run those example applications by calling:
# At the react-admin project root
make install
# or
yarn install
# Run the simple application
make run-simple
# Run the tutorial application
make build
make run-tutorial
# Run the demo application
make build
make run-demoAnd then browse to the URL displayed in your console.
Clone this repository and run make install to grab the dependencies, then make build to compile the sources from TypeScript to JS.
You can use Gitpod(An Online Open Source VS Code like IDE which is free for Open Source) for working on issues and making PRs. With a single click it will launch a workspace and automatically clone the repo, run make install and make start so that you can start straight away.
Using yarn link, you can have your project use a local checkout of the react-admin package instead of npm. This allows you to test react-admin changes in your app:
# Register your local react-admin as a linkable package
$ cd /code/path/to/react-admin/packages/react-admin && yarn link
# Replace the npm-installed version with a symlink to your local version
$ cd /code/path/to/myapp/ && yarn link react-admin
# If you run into issues with React red-screen, then you need to register your app's version of React as a linkable package
$ cd /code/path/to/myapp/node_modules/react && yarn link
# And then replace the npm-installed version of React with a symlink to your app's node_modules version
$ cd /code/path/to/react-admin/ && yarn link react
# Rebuild the packages with the same version of React
$ cd /code/path/to/react-admin/ && make build
# Return to your app and ensure all dependencies have resolved
$ cd /code/path/to/myapp/ && yarn install
# Start your app
$ yarn startAutomated tests are also crucial in our development process. You can run all the tests (linting, unit and functional tests) by calling:
make testUnit tests use jest, so you should be able to run a subset of tests, or run tests continuously on change, by passing options to
yarn jestBesides, tests related to the modified files are run automatically at commit using a git pre-commit hook. This means you won't be able to commit your changes if they break the tests.
When working on the end-to-end tests, you can leverage cypress runner by starting the simple example yourself (make run-simple or yarn run-simple) and starting cypress in another terminal (make test-e2e-local or yarn test-e2e-local).
If you have coding standards problems, you can fix them automatically using prettier by calling
make prettierHowever, these commands are run automatically at each commit so you shouldn't have to worry about them.
If you want to contribute to the documentation, install jekyll, then call
make docAnd then browse to http://localhost:4000/
=======
- ✔️React Material Admin - React Material Admin — Material-UI Dashboard
- 🚀 React Native Starter - A powerful react native starter template that bootstraps development of your mobile application
- 🔥 React Dashboard - React Dashboard - isomorphic admin dashboard template with GraphQL
- ❤️ Saleor Commerce - A modular, high performance, headless e-commerce platform built with Python, GraphQL, Django, and React.
- 💥 Ant Design - An enterprise-class UI design language and React UI library.
- 🎧 RadioWanjy - Radios from 471 Arabic and foreign radios.