-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
97 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,97 @@ | ||
| +++ | ||
| draft = false | ||
| date = 2024-09-29T17:11:31+08:00 | ||
| title = "Kubernetes CSI 简介:工作流程和原理" | ||
| description = "Kubernetes CSI 简介:工作流程和原理" | ||
| slug = "" | ||
| authors = [] | ||
| tags = ["Kubernetes"] | ||
| categories = ["Kubernetes"] | ||
| externalLink = "" | ||
| series = [] | ||
| disableComments = true | ||
| +++ | ||
|
|
||
| 本文将会以 [CSI driver - NFS](https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/csi-driver-nfs) 为例,讲述 `CSI` 驱动的工作流程和原理。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## CSI 概述 | ||
|
|
||
| `CSI` 驱动通常分为两个部分: | ||
| - `Controller plugin`: 负责存储资源的管理,如卷的创建、删除、扩容、快照等。 | ||
| - `Node plugin`: 处理节点级别的存储操作,负责在具体的节点上执行卷的挂载和卸载等任务。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| `CSI` 与 kubernetes 组件的交互: | ||
| - `Controller plugin` 与 `kube-api-server` 交互,监听存储资源的变更并执行相应操作。 | ||
| - `Node plugin` 向 `kubelet` 注册自己,而后 `kubelet` 会向其发起调用。 | ||
|
|
||
| 由于交互的通用性,为了简化 CSI 驱动程序的开发,社区提供了很多 `CSI Sidecar Containers`,包括上图中的: | ||
| - `external-provisioner`:用于卷的动态配置。监听 `PVC` 对象,向 CSI 驱动程序发起 `CreateVolume` 或 `DeleteVolume` 调用。 | ||
| - `node-driver-registrar`:负责将 CSI 驱动注册到 `kubelet`,以便后续的调用。 | ||
|
|
||
| 除此 Sidecar 之外还有: | ||
| - `external-attacher`:用于卷的 attach/detach hooks 集成。 | ||
| - `external-resizer`:用于卷的扩容。 | ||
| - `external-snapshotter`:处理卷的快照。 | ||
| - `livenessprobe`:监控 CSI 驱动程序的健康状况。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### CSI 使用过程 | ||
|
|
||
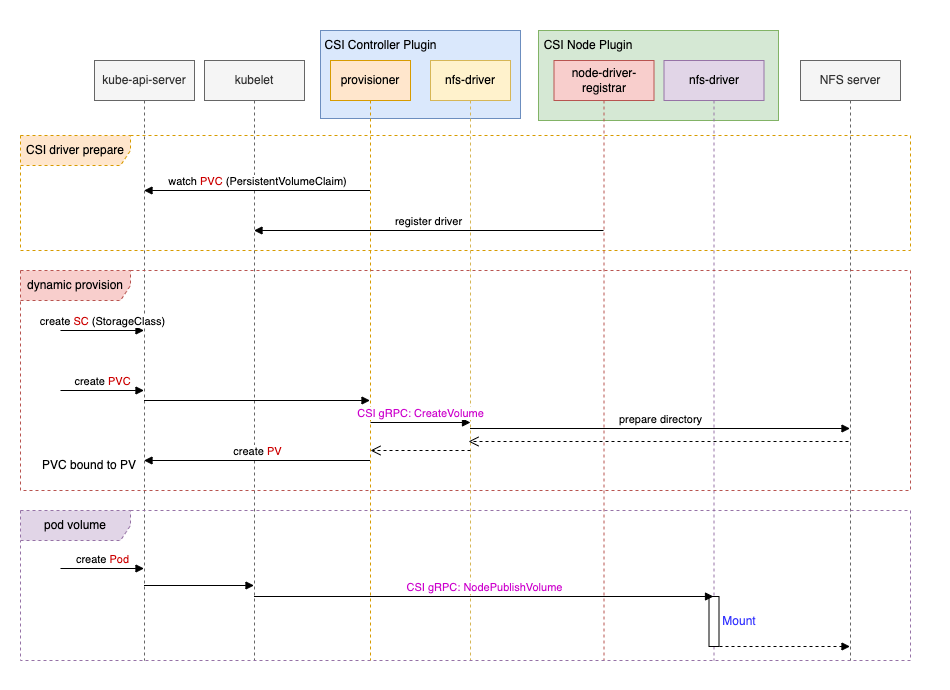
|  | ||
|
|
||
| #### 1. CSI 驱动准备阶段 | ||
|
|
||
| 确保集群中已正确安装 CSI 驱动,通常: | ||
| - `Controller plugin` 以 `Deployment` 或 `StatefulSet` 的方式部署。 | ||
| - `Node plugin` 由于是节点级别的操作,所以部署为 `DaemonSet`,每个节点运行一个 Pod。 | ||
|
|
||
| 安装完成后,`Controller plugin` 会向 `kube-api-server` 监听相关的资源对象,`Node plugin` 则会向 `kubelet` 注册自己。 | ||
|
|
||
| #### 2. 卷的动态配置 | ||
|
|
||
| 集群管理员创建 `StorageClass` 对象来声明存储类型。 | ||
|
|
||
| 用户创建 `PVC` 对象并指定 `StorageClass`,此时 `Controller plugin` 中的: | ||
| - `provisioner` 监听到 `PVC` 创建后,向 `nfs-driver` 发起 gRPC `CreateVolume` 调用。 | ||
| - `nfs-driver` 向 NFS server 准备好共享存储目录。 | ||
| - 最后,`provisioner` 创建 `PV`。至此,`PVC` 与 `PV` 完成了绑定。 | ||
|
|
||
| #### 3. 创建 Pod 并使用卷 | ||
|
|
||
| 用户创建 Pod 并使用卷。 | ||
|
|
||
| `kube-api-server` 接受到请求,`kube-scheduler` 将 Pod 调度到节点上。 | ||
|
|
||
| 该节点上的 `kubelet` 向 `Node plugin` 发起 gRPC `NodePublishVolume` 调用,由 `Node plugin` 中的 `nfs-driver`(具体的 CSI 驱动程序)完成文件目录的挂载。 | ||
|
|
||
| 至此,Pod 中的应用程序便可以使用挂载好的文件目录了,就像使用本地文件系统一样。 | ||
|
|
||
| 然而,Pod 中的应用程序实际操作的是 NFS 远程共享目录,这又是怎么做到的? | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
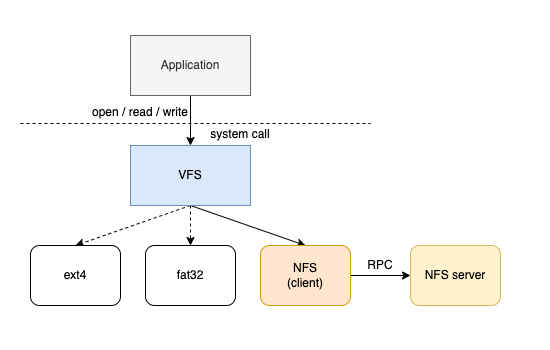
| ## Linux VFS | ||
|
|
||
| Linux 在实际的文件系统之上,其实还有一层 `VFS`(virtual filesystem)虚拟文件系统。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| `VFS` 是一个抽象层,它允许应用程序通过统一的系统调用来操作不同类型的文件系统。无论是本地文件系统还是远程文件系统(如 `NFS`),操作都经过 `VFS` 中转。对于挂载了 `NFS` 目录的系统,`VFS` 会将相应的系统调用转交给 `NFS` 客户端,`NFS` 客户端则使用 RPC 网络通信与 `NFS` 服务器进行交互。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 总结 | ||
|
|
||
| 除了 `NFS` 之外,`CephFS` 等其他分布式存储系统也采用了类似的工作原理和流程。 | ||
|
|
||
| `CSI` 定义了标准化的 `gRPC` 协议,以及 CSI 驱动的交互过程和架构,使得各种存储系统可以通过统一的接口集成到 Kubernetes 中。 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| (关注我,无广告,专注于技术,不煽动情绪) | ||
|
|
||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| 参考资料: | ||
|
|
||
| - *https://github.com/container-storage-interface/spec/blob/master/spec.md* | ||
| - *https://kubernetes-csi.github.io/docs/introduction.html* | ||
| - *https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/csi-driver-nfs* | ||
| - *https://www.starlab.io/blog/introduction-to-the-linux-virtual-filesystem-vfs-part-i-a-high-level-tour* |