-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
image search system with client model
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
155 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
155 changes: 155 additions & 0 deletions
155
content/posts/engineering/image-search-use-client-model.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,155 @@ | ||
| +++ | ||
| draft = false | ||
| date = 2024-07-04T14:44:38+08:00 | ||
| title = "以图搜图架构优化:使用客户端模型提取图像特征" | ||
| description = "以图搜图架构优化:使用客户端模型提取图像特征" | ||
| slug = "" | ||
| authors = [] | ||
| tags = ["Engineering"] | ||
| categories = ["Engineering"] | ||
| externalLink = "" | ||
| series = [] | ||
| disableComments = true | ||
| +++ | ||
|
|
||
| ## 序言 | ||
|
|
||
| 以图搜图系统指的是从图像内容提取特征向量,然后使用向量数据库进行向量数据的插入、删除、相似性检索等操作,进而提供根据图像内容搜索出具有相似内容的其它图像的功能。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 系统架构 | ||
|
|
||
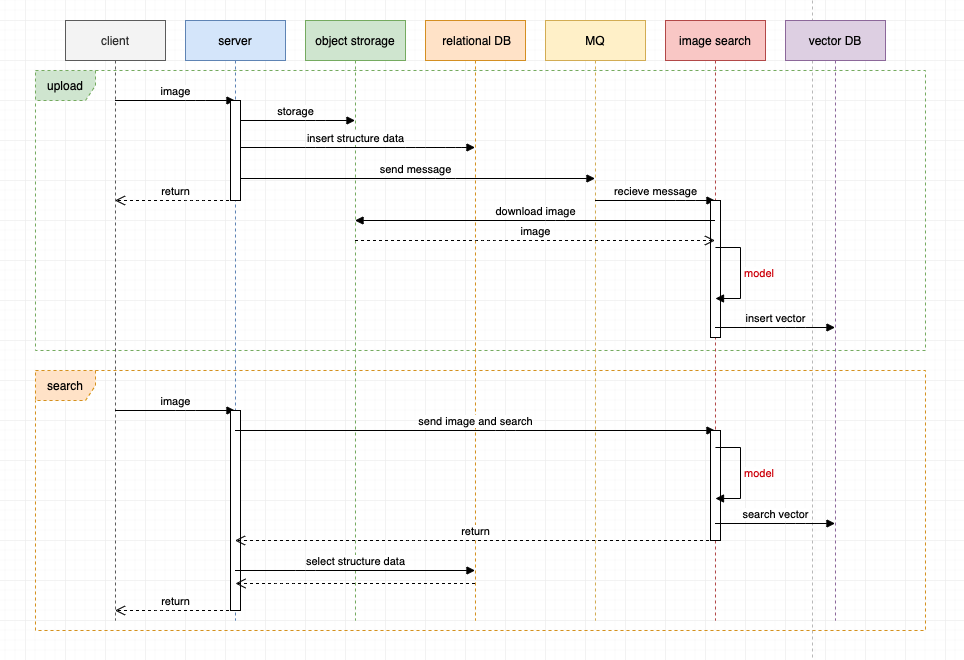
| 典型的搜图系统整体架构时序图如下: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 图像上传过程: | ||
| 1. 客户端上传图像到服务端。 | ||
| 1. 服务端存储图像至对象存储、插入结构化数据至关系型数据库、发送消息至 MQ 消息队列。 | ||
| 1. 服务端对客户端请求返回响应。 | ||
| 1. 图像搜索服务接受 MQ 的消息,下载图像内容,使用特定模型提取图像特征向量,然后将特征向量插入到向量数据库。 | ||
|
|
||
| 这里使用 MQ 的主要原因有: | ||
| - 异步快速响应,因为提取图像特征比较耗时,如果是同步的过程则会对客户端体验不友好。 | ||
| - 解耦服务、服务异构,提取图像特征属于计算机视觉领域,编程语言生态基本是 Python ,而后端服务则常见于 Java、Golang、Node.js 等,这在架构上就要求服务异构和解耦。 | ||
| - 削峰填谷,由于用户上传图像具有波峰波谷的天然特性,使用 MQ 可以使下游图像计算保持平稳。 | ||
|
|
||
| 图像搜索过程: | ||
| 1. 客户端上传图像到服务端。 | ||
| 1. 服务端发起调用并将图像传递到图像搜索服务,图像搜索服务提取图像特征向量,然后查询向量数据库进行相似性搜索,最后返回向量搜索结果。 | ||
| 1. 服务端根据向量搜索结果查询结构化数据,整合数据,最后响应。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们可以看到以上系统中,比较耗时的有两部分: | ||
| 1. 图像传递链路长:客户端 -> 服务端 -> 对象存储 -> 图像搜索服务。 | ||
| 1. 图像特征计算比较耗时、且比较消耗服务器资源。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 使用客户端模型优化架构 | ||
|
|
||
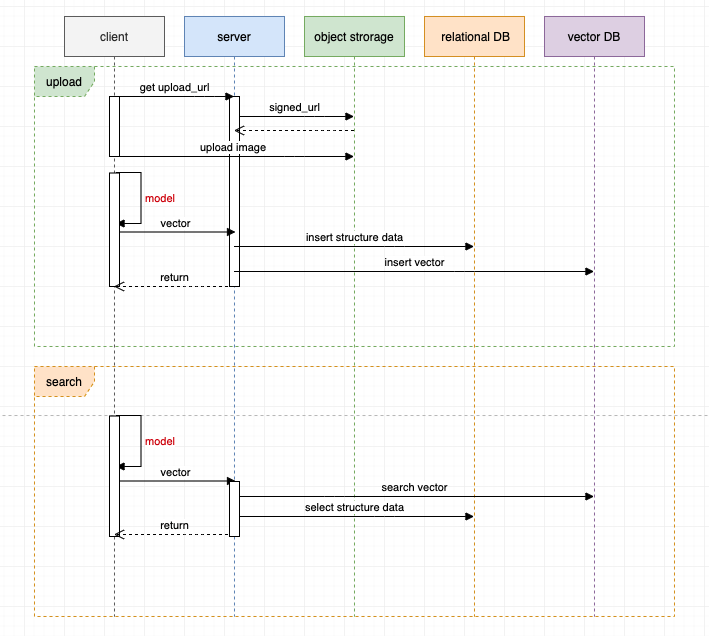
| 为了进一步优化系统架构,我们可以尝试使用客户端模型进行图像特征提取。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 图像上传过程: | ||
| 1. 客户端向服务端请求对象存储的直传地址,然后客户端直接将图像内容传递到对象存储(需要对象存储支持直传操作)。 | ||
| 1. 客户端进行本地计算,提取图像特征向量,然后传递特征向量和结构化数据给服务端。 | ||
| 1. 服务端对结构化数据和向量数据分别插入到不同的数据库,完成响应。 | ||
|
|
||
| 图像搜索过程: | ||
| 1. 客户端进行本地计算,提取图像特征向量,然后传递特征向量和结构化数据给服务端。 | ||
| 1. 服务端分别进行向量检索和结构化数据查询,整合数据,完成响应。 | ||
|
|
||
| 优化后的架构: | ||
| - 图像传递链路短,只有客户端 -> 对象存储。 | ||
| - 图像特征计算卸载到了客户端完成,服务器不需要再消耗计算资源。 | ||
| - 减少了 MQ 和图像搜索服务这两个构件,架构更加简单、复杂度降低。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 客户端模型的可行性和约束 | ||
|
|
||
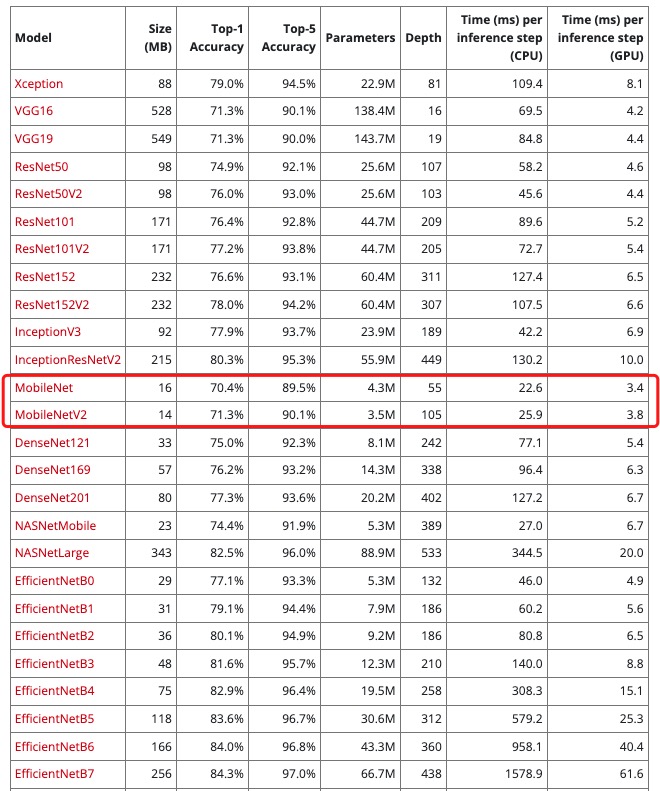
| 客户端相比于服务端具有硬件资源有限、且不可扩展的特点,因此这就要求客户端使用的模型要更小、计算消耗更少。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 我们根据上图中的模型对比可以看到 mobilenet 这种模型更符合我们的需求(模型的名字就能看出来)。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 示例 | ||
|
|
||
| 以下给出一个前端使用 mobilenet 完成图像特征提取的示例: | ||
|
|
||
| ```html | ||
| <!DOCTYPE html> | ||
| <html lang="en"> | ||
| <head> | ||
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> | ||
| <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs"></script> | ||
| <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow-models/mobilenet"></script> | ||
| </head> | ||
| <body> | ||
| <input type="file" id="imageInput"> | ||
| <button onclick="extractFeatures()">Extract Features</button> | ||
| <pre id="result"></pre> | ||
|
|
||
| <script> | ||
| let model; | ||
| async function loadModel() { | ||
| if (!model) { | ||
| // 加载模型时 mobilenet 会去 storage.googleapis.com 下载 | ||
| model = await mobilenet.load({version: 2, alpha: 1.0}); | ||
| } | ||
| return model; | ||
| } | ||
| function preprocessImage(image) { | ||
| const tensor = tf.browser.fromPixels(image) | ||
| .resizeNearestNeighbor([224, 224]) | ||
| .toFloat() | ||
| .expandDims(); | ||
| return tensor.div(255.0); | ||
| } | ||
| async function extractFeatures() { | ||
| const input = document.getElementById('imageInput'); | ||
| if (input.files.length === 0) { | ||
| alert('Please select an image file first.'); | ||
| return; | ||
| } | ||
| const model = await loadModel(); | ||
| const timeStart = Date.now(); | ||
| const file = input.files[0]; | ||
| const reader = new FileReader(); | ||
| reader.onload = async function (e) { | ||
| const image = new Image(); | ||
| image.src = e.target.result; | ||
| image.onload = async function () { | ||
| const processedImage = preprocessImage(image); | ||
| const features = model.infer(processedImage, false); // 去掉最后的全连接层 | ||
| const featuresArray = await features.array(); | ||
| document.getElementById('result').textContent = JSON.stringify(featuresArray, null, 2); | ||
| console.log(`Extract feature spend: ${Date.now() - timeStart} ms`);; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| reader.readAsDataURL(file); | ||
| } | ||
| </script> | ||
| </body> | ||
| </html> | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
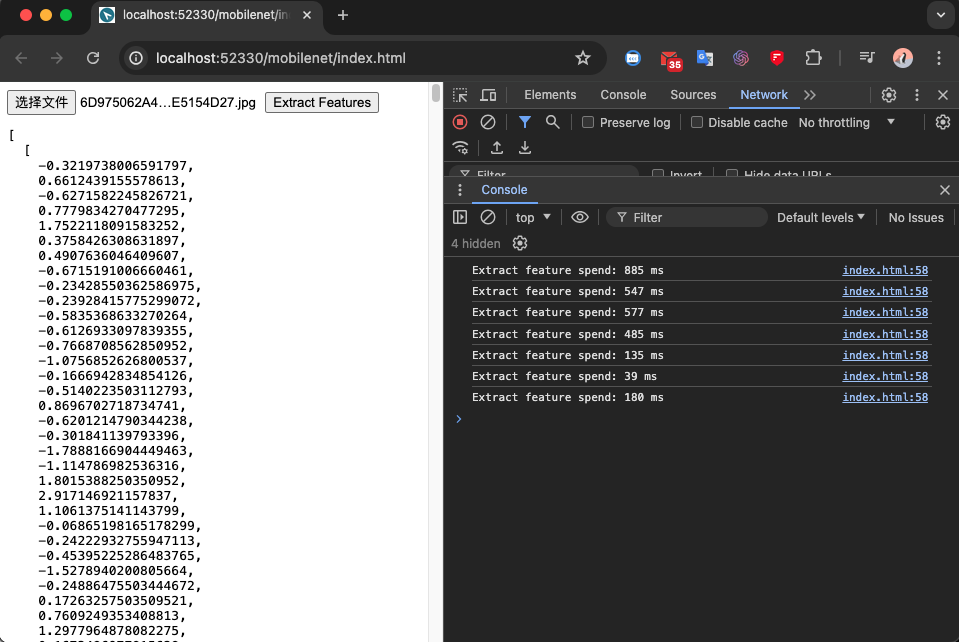
| 然后在我的笔记本电脑简单测试的结果: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 从上图可以看到,在我的客户端处理一张图像可以在一秒内完成,当然实际耗时取决于硬件资源和图像大小。 | ||
|
|
||
| 最后,如果你对此类主题感兴趣,可以阅读我的[其它相关文章](https://lingxu.pages.dev/categories/engineering/)。 | ||
|
|
||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| 参考资料: | ||
|
|
||
| - *https://keras.io/api/applications/* | ||
| - *https://www.tensorflow.org/js/models* | ||
| - *https://github.com/tensorflow/tfjs-models/tree/master/mobilenet* |