ServiceControl is the monitoring brain in the Particular Service Platform. It collects data on every single message flowing through the system (Audit Queue), errors (Error Queue), as well as additional information regarding sagas, endpoints heartbeats and custom checks (Control Queue). The information is then exposed to ServicePulse and ServiceInsight via an HTTP API and SignalR notifications.
The current version of ServiceControl can be downloaded from https://particular.net/downloads.
Documentation for ServiceControl is located on the Particular Docs website at following address:
https://docs.particular.net/servicecontrol/
- Enable Windows Feature .NET Framework 3.5 support, which is needed to support the Wix components in the ServiceControl installer.
- If not using Visual Studio, you may need to install .NET 4.0 SDK according to https://stackoverflow.com/a/45509430
- Follow the Coding and design guidelines
Testing using the CI workflow depends on the following secrets, which must be defined for both Actions and Dependabot secrets. The Particular values for these secrets are stored in the secure note named ServiceControl Repo Secrets.
LICENSETEXT: Particular Software license textAWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: For testing SQSAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: For testing SQSAWS_REGION: For testing SQS
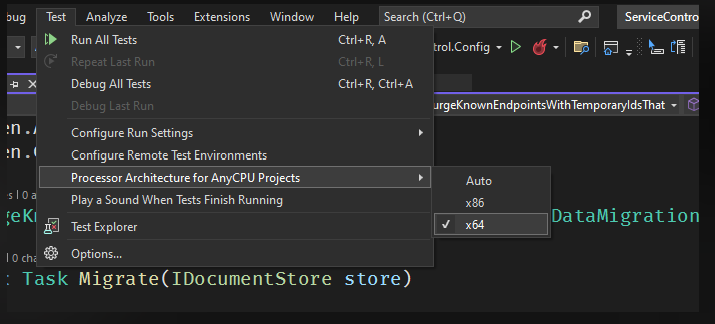
The tests need to be run in x64 otherwise an exception about RavenDB (Voron) not being supported in 32bit mode will be thrown. The ServiceControl.runsettings file in each test project should automatically ensure that tests are run in 64 bit mode. For reference, there is also a setting in Visual Studio that can be used to ensure test execution is using x64 only:
ًBy default integration tests use MSMQ transport to run. This can be overridden by renaming the _connection.txt file in the root of the solution to connection.txt and updating the transport type and connection string.
Only the first 3 lines of this file are read with the following information:
- First line is the Transport name
- Second line is the ServiceControl Transport type information (implementation of
ITransportIntegrationinterface) - Third line is the connection string
To change the tests to use LearningTransport, rename the file and change the content to this:
LearningTransport
ConfigureEndpointLearningTransport
c:\Temp\ServiceControlTemp
NOTE: The following instructions are provided to ease development stages only. To run container images in production refer to the ones available on Docker Hub.
Docker images are built by the ServiceControl.DockerImages project. The project is not automatically built when building the solution to keep the overall build time under control. To build Docker images explicitly build that project using the IDE or MSBuild from the command line.
NOTE: The project will build Docker images for all supported transports. To build images for a subset of the transports, edit the .csproj file and comment out, or delete the not needed transport definitions in the SupportedTransport ItemGroup.
Once the images are built, the instances can be started by first running the init container to provision the required queues and databases (using RabbitMQ Conventional topology as an example):
docker run --name servicecontrol.init -e "ServiceControl/ConnectionString=host=[connectionstring]" -e 'ServiceControl/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' -v C:/ServiceControl/:c:/data/ particular/servicecontrolrabbitdirect.init
docker run --name servicecontrol.monitoring.init -e "Monitoring/ConnectionString=[connectionstring]" -e 'ServiceControl/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' particular/servicecontrolrabbitconventional.monitoring.init
docker run --name servicecontrol.audit.init -e "ServiceControl.Audit/ConnectionString=host=[connectionstring]" -e 'ServiceControl/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' -v C:/ServiceControl.Audit/:c:/data/ particular/servicecontrolrabbitdirect.audit.init
That will create the required queues and the database for ServiceControl and ServiceControl.Audit. To run the containers now that everything is provisioned, first run the audit container:
docker run --name servicecontrol.audit -p 44444:44444 -e "ServiceControl.Audit/ConnectionString=host=[connectionstring]" -e 'ServiceControl.Audit/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' -e 'ServiceControl.Audit/ServiceControlQueueAddress=Particular.ServiceControl' -v C:/ServiceControl.Audit/:c:/data/ -d particular/servicecontrolrabbitdirect.audit
Then grab its IP address using docker inspect, and specify it using the ServiceControl/RemoteInstances environment variable when starting the servicecontrol container.
docker run --name servicecontrol -p 33333:33333 -e "ServiceControl/ConnectionString=host=[connectionstring]" -e 'ServiceControl/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' -e 'ServiceControl.Audit/ServiceControlQueueAddress=Particular.ServiceControl' -e "ServiceControl/RemoteInstances=[{'api_uri':'http://172.28.XXX.XXX:44444/api'}]" -v C:/ServiceControl:c:/data/ -d particular/servicecontrolrabbitdirect
ServiceControl will now run in a docker container.
To run a ServiceControl Monitoring instance:
docker run --name servicecontrol.monitoring -p 33633:33633 -e "Monitoring/ConnectionString=host=[connectionstring]" -e 'Monitoring/LicenseText=[licensecontents]' -d particular/servicecontrolrabbitdirect.monitoring
- RabbitMQ can either be installed on the host or run in another Docker container. In either case, the ServiceControl connection strings will need to refer to the host IP address.
- The special DNS name
host.docker.internaldoes not work on Docker Desktop for Windows, and it also doesn't support host networks. To get the IP address of the host for the connection string environment variables, useipconfigand find the IP address of the vEthernet adapter Docker is using, e.g.
Ethernet adapter vEthernet (nat):
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::c12a:27cf:ad50:8b7b%41
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 172.29.144.1
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.240.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
- RabbitMQ's default
guestaccount cannot be used, since authentication will fail when ServiceControl is running in a docker container. - The ServiceControl docker images are currently Windows based images while the RabbitMQ docker image is Linux based. As such, these cannot be managed by docker-compose on a single Windows host.
- Refer to here for more in depth documentation on running ServiceControl docker images (including on how to mount the license file rather than pass it in as an environment variable)