UAV HITL Simulator brings up a set of ROS packages, config files and instructions to establish a full simulation for UAV based on PX4/Ardupilot autopilot.
The key feature is to run the simulation on a real hardware and use the actual Cyphal/DroneCAN drivers, so the autopilot knows nothing about the simulation. It covers more PX4 modules than SITL and MAVLink HITL.
Purpose
- Testing autopilot peripheral drivers (DroneCAN or Cyphal)
- Testing hardware components (actuators, payload, power and electrical systems) in pair with autopilot
- Communication Bus and Wiring Testing
- Fault Injection and Safety Measures
- Environmental and Durability Testing: Vibration Emulation, Long-Duration Endurance Runs
- Training in the development and use of drones, including creating datasets and automated testing
Recommended requirements for HITL:
- Operating System: Pure Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04 or 24.04 installation is highly recommended; WSL and VM are not recommended Operating System: A pure installation of Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04, or 24.04 is recommended; avoid WSL and VMs
- Docker: use regular Docker Engine, not Docker Desktop (because Docker Desktop relies on VM)
- Performance: for HITL part even Raspberry PI 4 is enough
Recommended requirements for 3D simulator:
- Operating System: Modern versions of Windows, Linux, and Mac.
- CPU: Aim for an Intel i7 (from 11th/12th gen). For those using AMD, any equivalent processor will suffice.
- RAM: 16GB is a recommended minimum, but more is always better for performance.
Required hardware:
- Flight controller: fmu-v5, fmu-v6c or fmu-v6x, cuav_x7pro, cuav_nora and more by request
- CAN-sniffer: Zubax Babel is recommended, but other CAN-adapters can be suitable as well
By centralizing communication through CAN and leveraging the HITL simulator, you can perform a wide range of tests that were previously complex or impractical. Let's consider them.
The HITL simulator itself is not computationally expensive. You can run it even on single-board computers like the Raspberry Pi. This feature allows the HITL simulator to be used as part of CI/CD process. Each time a developer makes a commit to the autopilot software, a the compiled binary can be deployed to a real flight controller and tested with HITL simulator. It is especially useful for developers actively working with DroneCAN/Cyphal drivers or related parts of the autopilot software.
A few examples of test scenarios for CI/CD are shown in the table below.
| Test | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Takeoff And Land | This is the simplest possible test scenario: take off, wait a few seconds, and land. It is the fastest scenario and it is intended to be triggered on every commit as part of CI. Approximate duration: 30 sec Plan: tests/ci/takeoff_and_land.plan |
| 2. Square flight | Simple quadcopter flight test. Approximate duration: 1 minute Plan: tests/ci/square.plan |
| 3. VTOL Long flight | This is the longest test scenario. It is dedicated for testing the stability. Approximate duration: 10 minutes Plan: tests/ci/sviyazhsk_vtol.plan |
Any of these scenarios can be run with 3 steps.
# 1. Upload the new firmware to the autopilot
autopilot-configurator --firmware <path_to_the_binary.px4>
# 2. Run the simulator itself with the desired protocol and airframe.
./scripts/sim.py cq
# 3. Run the test scenario. The default test scenario execution timeout is 5 minutes. For long flights you need to explicitly increase the timeout:
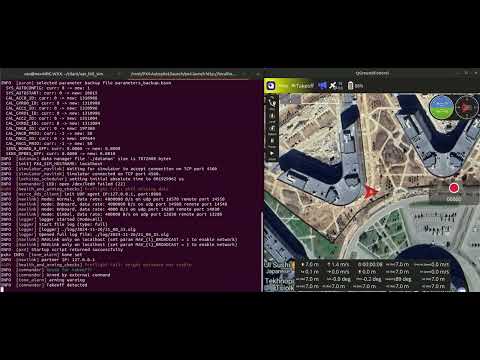
test-scenario --output flight.ulg --timeout 1000 tests/ci/sviyazhsk_vtol.planRunning the HITL simulator on a desktop unlocks advanced visualization and simulation capabilities. With tools like gui_tool, yakut, and rviz, you can monitor and interact with the simulation in real-time.
If your desktop is equipped with a modern GPU, you can further enhance the experience by integrating a 3D simulator. This setup is ideal for testing complex scenarios such as delivery missions or inspections and can even be used for pilot training, offering a realistic and immersive simulation environment.
The setup is as simple as possible. Just connect a CAN-sniffer and a flight controller to you Desktop via USB and connect the devices with each outher with CAN cable.
Tool 1. CAN bus analysis tools: gui_tool, yakut
If you run a HITL simulator, you can then run both yakut, gui_tool and any other similar tools at any time. It allows you analyse the CAN bus in real time.
| DroneCAN: gui_tool | Cyphal: yakut |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Tool 2. RVIZ for a flight visualization
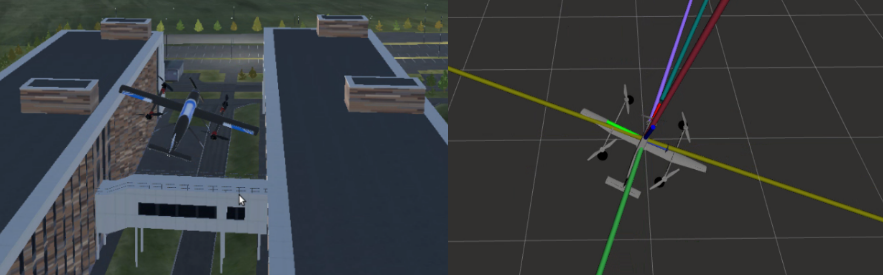
With RVIZ you can visualise the vehicle orientation, vectors of the applied forces, torques, speed and more.
How to run:
./scripts/sim.py rviz vtol_T_300Tool 3. 3D-simulator
Simulator3d is a digital environment that replicates the world as closely as a robot or UAV would perceive it, with all interactions being facilitated through the same API formats these robots would use in reality. It is avaliable on GitHub: ZilantRobotics/Simulator3d.
Test scenarios
| Test scenario | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Delivery or Last Mile Aerologistics Scenarios. Testing and optimization of cargo delivery processes using unmanned aerial vehicles. 1. Delivery from KazanExpress to the Yard. 4 minutes. Plan: kazanexpress_to_yard.plan 2. Delivery from KazanExpress to the Technopark. 6 minutes. Plan: kazanexpress_to_technopark.plan |
 |
Construction Inspection. 1. Quadcopter. 3:40. Plan: technopark.plan 2. VTOL. Structure scan of the northest techonopark. 9:25. Plan: technopark_structure_scan.plan 3. VTOL. Survey of all technoparks in the town. 28:00. technopark_survey_half_town.plan 3. VTOL. Survey of all the town. 44:40. technopark_survey_full_town.plan |
 |
Fault scenarios. Evaluation of the behavior and response of UAV to various types of failures during flight. 1. Using /uav/scenario ROS topic run or stop a specific event, for example disable differential pressure sensor (as shown on the example), gnss, ESC feedback or turn off ICE. Please, check scenarios.hpp for details 2. In Cyphal you can disable/enable any port in real time |
How to run:
Download the simulator before the first usage:
# 1. Download Simulator3d in Downloads directory.
cd Downloads
wget https://github.com/ZilantRobotics/Simulator3d/releases/download/v0.1.19/ZilantSimulator-Linux64-0.1.19.zip
# 2. Unzip it and make it executable
unzip ZilantSimulator-Linux64-0.1.19.zip
chmod +x ZilantSimulator.x86_64Run it:
# 1. Run the Simulator3d itself
./ZilantSimulator.x86_64
# 2. Run rosbridge and sim interface nodes
./scripts/docker.sh i
roslaunch innopolis_vtol_dynamics 3d_sim.launchKey points in 3D simulation
| Yard | Delivery point | Technopark office parking | Buildings |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Connect the HITL simulator to a particular component of a vehicle or almost to the whole system. Use actual UAV hardware to simulate real-world operations without physical flight.
An example of connection to the whole system is show below.
Example of testing scenarios:
- Power and Electrical System Verification:
- Load Testing: Simulate various flight profiles that cause different current draws on ESCs and motors.
- Battery and Power Module Evaluation: Emulate different battery states-of-charge, voltage sags, or current spikes
- Thermal Management Assessment:
- Thermal Stress Scenarios: By simulating prolonged hover or aggressive maneuvers, the electronics may heat up.
- Communication Bus and Wiring Testing:
- Bus Utilization and Noise: By simulating high CAN communication traffic engineers can evaluate if cables, connectors, and bus termination are correct.
- Fault Injection and Safety Measures:
- Fail-Safe Triggers: Simulate sensor failures, GPS dropouts, or communications errors and observe the hardware’s ability to detect and respond via built-in fail-safes, including checking the reaction of power relays, backup power lines, or redundant components.
- Environmental and Durability Testing:
- Vibration Emulation: Although you aren’t using real propellers, you can introduce simulated vibration profiles through test stands or external actuators. This allows checking if connectors remain tight under conditions similar to real flight.
- Long-Duration Endurance Runs: Run the drone hardware in a simulated “mission” environment for hours, verifying long-term reliability, potential component drift, or intermittent connection issues that only appear after extended usage.
SITL mode is out of the scope of the interests of this simulator. But anyway, it happens that you need to test something and you don't have the required hardware in your hand. So, you can run the flight stack and the dynamics on your PC:
Run the HITL dynamics as usual, but choose MAVLink mode, for example:
./scripts/sim.py mq # mq stands for PX4 Mavlink QuadcopterRun the PX4 flight stack. You can either build and run it according to PX4 official instructions, or use our Dockerfile to build and ru neverything in a single command:
./scripts/sim.py px4-sitl irisThe simulator is distributed as a Docker image. To simplify the interraction with Docker, a ./scripts/sim.py script was written. The script configures all the necessary Docker flags, performs automatic firmware upload, configuration, creates a CAN interface, and generally provides a simple interface to interact with the simulator.
Step 1. Clone repository with submodules
git clone https://github.com/ZilantRobotics/innopolis_vtol_dynamics.git --recursiveWhenever you pull this repository, don't forget to update submodules:
git submodule update --init --recursiveStep 2. Install requirements and Build/pull the docker image
pip install -r requirements.txtTo build docker image, type:
./scripts/sim.py b # b stands for buildStep 3. Connect everything together for HITL
You should skip this step if you want to run PX4 MAVLink SITL mode. Please follow docs/px4/mavlink for details.
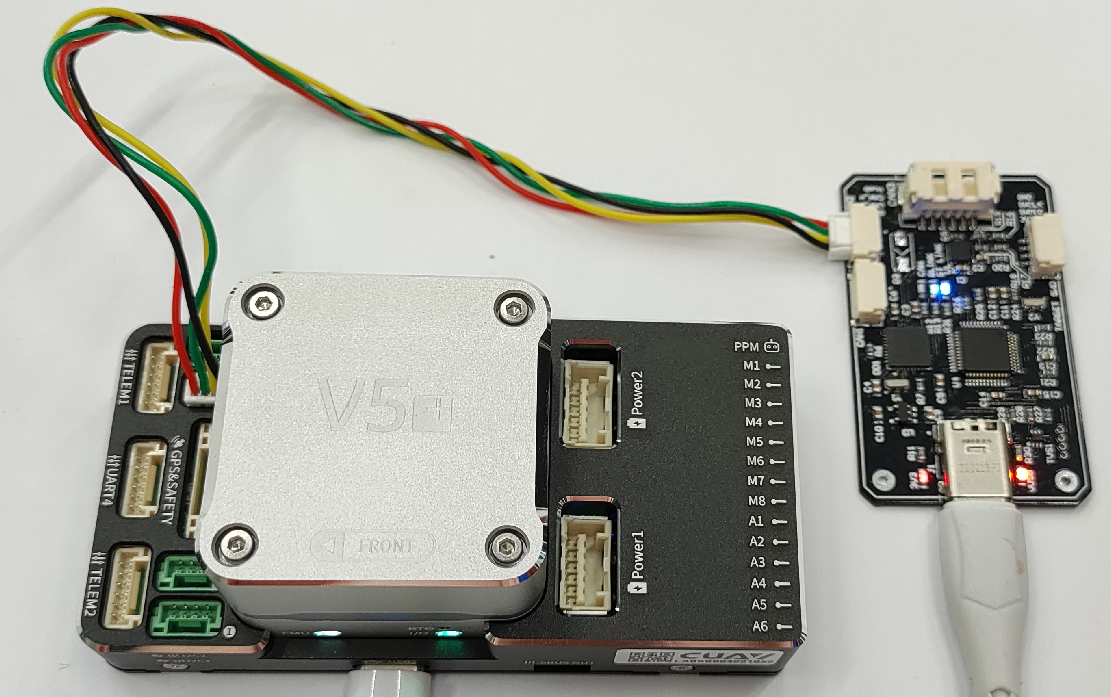
Typically we use CUAV v5+ and RL-programmer-sniffer, but it might be anything else.
An example of a connection is shown in the picture below.
All default parameters expect that you use CAN1 on the autopilot side.
Step 4. Run the container in force mode
In --force mode the script automatically upload the required firmware and parameters corresponded
to the specified mode, create SLCAN and run the container with required docker flags.
To run force mode you need to install autopilot-tools python package: pip install autopilot-tools.
To get the list of all supported modes, just type:
./scripts/sim.py --helpTo run PX4 Cyphal quadcopter, type:
./scripts/sim.py cq # cq = px4_v1_15_0_cyphal_quadcopterTo run PX4 Dronecan VTOL, type:
./scripts/sim.py dv # cq = dronecan_vtolTroubleshooting:
- If your sniffer connection is not found or something else is missing, it will exit in a few seconds.
If something doesn't work, please open an issue.
Step 5. Run ground control station
Here 2 options are suggested.
- You can run QGroundControl or MissionPlanner to have manual flight
- (soon) You can run a script to run one of the test scenario in automatic mode.
Step 6. (optional) 3D Simulator
# 1. Run the Simulator3d itself
./ZilantSimulator.x86_64
# 2. Run rosbridge and sim interface nodes
./scripts/docker.sh i
roslaunch innopolis_vtol_dynamics 3d_sim.launchYou can obrain the actual list of the suported modes by typing ./scripts/sim.py --help.
Well, here is our main targets:
| Target | DroneCAN | Cyphal | MAVLink SITL |
|---|---|---|---|
| PX4 v1.15 Quadcopter | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported |
| PX4 v1.15 Quadplane VTOL | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported | ✅ Supported |
| PX4 v1.15 Plane | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported |
| ArduPilot v4.5.7 Copter | ✅ Supported | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported |
| ArduPilot v4.5.7 Plane | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported |
| ArduPilot v4.5.7 QuadPlane | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported | ❌ Not Supported |
New modes will be extended step by step.
VTOL HITL Dynamics Simulator is designed to be modular. It is divided into the following main components:
UAV dynamicsis the main node that handles actuator commands from the communicator, performs dynamics simulation, and publishes vehicle and sensors states.Communicatoris the set of nodes that communicate with thePX4 flight stackin HITL (via Cyphal/DroneCAN) and SITL (via MAVLink) modes.inno_sim_interfaceis a bridge for interaction with3D-Simulatorthrough ROS.
The design of the simulator is shown below.
- Create a new command in configs/vehicles/ folder.
- Once you create a new yaml file, the command should appear in
./scripts/sim.py --help
- Once you create a new yaml file, the command should appear in
- Create a dynamics properties in configs/dynamics/ directory
- Use either existed multirotor or VTOL dynamics as template
- Keep your autopilot configuration parameters in configs/ directory
- It can be used either as a hint for manual further configuration or in an auto configuration script
- [will be automoted soon] Add a command in scripts/run_sim.sh.
Check the video below.
Docs:
Outdated manual instructions:
- PX4 Cyphal manual configuration instructions
- PX4 DroneCAN manual configuration instructions
- ArduPilot manual configuration instructions
| Version | ReleaseDate | Major changes |
|---|---|---|
| v0.10.0 | In progress... | Add ArduPilot: Quadcopter and Plane support |
| v0.9.0 | Dec 08, 2024 | Add px4_fmu-v6c, px4_fmu-v6x, cuav_x7pro, cuav_nora support beside fmu-v5 |
| v0.8.0 | Jun 10, 2024 | Update PX4 from v1.14 to v1.15 |
| v0.7.0 | Oct 31, 2023 | Update PX4 from v1.13 to v1.14 |
| v0.6.0 | Jul 16, 2023 | Add Octorotor dynamics, fault scenarios and Cyphal ESC feedback |
| v0.5.0 | May 17, 2023 | Add Cyphal PX4 v1.13.0 quadcopter, update DroneCAN PX4 from v1.12.1 to v1.13.0 |
| v0.4.0 | May 16, 2022 | Add Cyphal/DroneCAN custom version of Ardupilot |
| v0.3.0 | Aug 25, 2021 | Add Docker |
| v0.2.0 | Aug 17, 2021 | Update to public DroneCAN PX4 v1.12.1 |
| v0.1.0 | Mar 18, 2021 | First public release for private custom version of DroneCAN PX4 v1.11.2, only CUAV V5+, SITL and HITL modes |