
Emotions are all over the place
Inside Out 2 (2024) by Pixar Animation Studios
This repository consists of a curated list of resources related to emotion recognition.
It serves as a comprehensive guide for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in understanding and advancing the technologies behind detecting emotions with a primary focus on audio, while also extending to the integration of visual data.
- Gan, C., Zheng, J., Zhu, Q., Cao, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2024). "A survey of dialogic emotion analysis: Developments, approaches and perspectives", Pattern Recognition, 156, 110794. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110794
A survey of methods and datasets in dialogic emotion analysis based on natural language processing from 2017 to 2024 - G. Hu, Y. Xin, W. Lyu, H. Huang, C. Sun, Z. Zhu, L. Gui, and R. Cai, “Recent Trends of Multimodal Affective Computing: A Survey from NLP Perspective”, arXiv, Sep. 11, 2024.
A survey presenting recent trends in multimodal affective computing from an NLP perspective covering four tasks: multimodal sentiment analysis, multimodal emotion recognition in conversation, multimodal aspect-based sentiment analysis, and multimodal multi-label emotion recognition - I. Saadi, D. W. cunningham, A. Taleb-Ahmed, A. Hadid, and Y. E. Hillali, “Driver’s facial expression recognition: A comprehensive survey”, Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 242, p. 122784, May 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122784.
A comprehensive survey from 2018 to 2024 on recognizing facial expressions of drivers - H. H. Mustafa, N. R. Darwish, and H. A. Hefny, “Automatic Speech Emotion Recognition: a Systematic Literature Review”, International Journal of Speech Technology, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 267–285, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1007/s10772-024-10096-7.
A systematic literature review on Automatic Speech Emotion Recognition from 2011 to 2023 - H. Barakat, O. Turk, and C. Demiroglu, “Deep learning-based expressive speech synthesis: a systematic review of approaches, challenges, and resources”, EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, vol. 2024, no. 1, p. 11, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.1186/s13636-024-00329-7.
A systematic review of the literature on expressive speech synthesis models published within the last 5 years, with a particular emphasis on approaches based on deep learning - S. K. Khare, V. Blanes-Vidal, E. S. Nadimi, and U. R. Acharya, “Emotion recognition and artificial intelligence: A systematic review (2014–2023) and research recommendations”, Information Fusion, vol. 102, p. 102019, 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102019.
A systematic review of emotion recognition from different input signals (e.g., physical, physiological)
- J. de Lope and M. Graña, “An ongoing review of speech emotion recognition”, Neurocomputing, vol. 528, pp. 1–11, Apr. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.002.
A comprehensive review of most popular datasets, and current machine learning and neural networks models for SER - A. Gandhi, K. Adhvaryu, S. Poria, E. Cambria, and A. Hussain, “Multimodal sentiment analysis: A systematic review of history, datasets, multimodal fusion methods, applications, challenges and future directions”, Information Fusion, vol. 91, pp. 424–444, Mar. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.09.025.
A review on multimodal fusion architectures
- E. H. Houssein, A. Hammad, and A. A. Ali, “Human emotion recognition from EEG-based brain-computer interface using machine learning: a comprehensive review”, Neural Computing and Applications, May 2022, doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07292-4.
Human emotion recognition using EEG-based brain signals and machine learning - K. B. Bhangale and M. Kothandaraman, “Survey of Deep Learning Paradigms for Speech Processing”, Wireless Personal Communications, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11277-022-09640-y.
Machine learning techniques for speech processing - S. Saganowski, “Bringing Emotion Recognition Out of the Lab into Real Life: Recent Advances in Sensors and Machine Learning”, Electronics, vol. 11, no. 3, Art. no. 3, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.3390/electronics11030496.
Advancements in sensors and machine learning methods and techniques
- T. M. Wani, T. S. Gunawan, S. A. A. Qadri, M. Kartiwi, and E. Ambikairajah, “A Comprehensive Review of Speech Emotion Recognition Systems”, IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 47795–47814, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3068045.
SER systems' varied design components/methodologies, databases - E. Lieskovska, M. Jakubec, R. Jarina, and M. Chmulik, “A Review on Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning and Attention Mechanism”, Electronics, vol. 10, p. 1163, May 2021, doi: 10.3390/electronics10101163.
Extensive comparison of Deep Learning architectures, mainly on the IEMOCAP benchmark database - Md. Shah Fahad, A. Ranjan, J. Yadav, and A. Deepak, “A survey of speech emotion recognition in natural environment”, Digital Signal Processing, vol. 110, p. 102951, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102951.
A comprehensive survey of SER in the natural environment, various issues of SER in the natural environment, databases, feature extraction, and models - S. P. Yadav, S. Zaidi, A. Mishra, and V. Yadav, “Survey on Machine Learning in Speech Emotion Recognition and Vision Systems Using a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)”, Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 1753–1770, May 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11831-021-09647-x.
A survey of deep learning algorithms in speech and vision applications and restrictions - P. Koromilas and T. Giannakopoulos, “Deep Multimodal Emotion Recognition on Human Speech: A Review”, Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 17, Art. no. 17, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.3390/app11177962.
A comprehensive review of the latest advancements in multimodal speech emotion recognition methods.
Russell's circumplex model of affect [1] is a model of human emotion that posits that all emotions can be represented as points on a two-dimensional space, with one dimension representing valence (pleasantness vs. unpleasantness) and the other dimension representing arousal (activation vs. deactivation). Valence refers to the positive and negative degree of emotion and arousal refers to the intensity of emotion. Most categorical emotions used in SER databases are based on this model
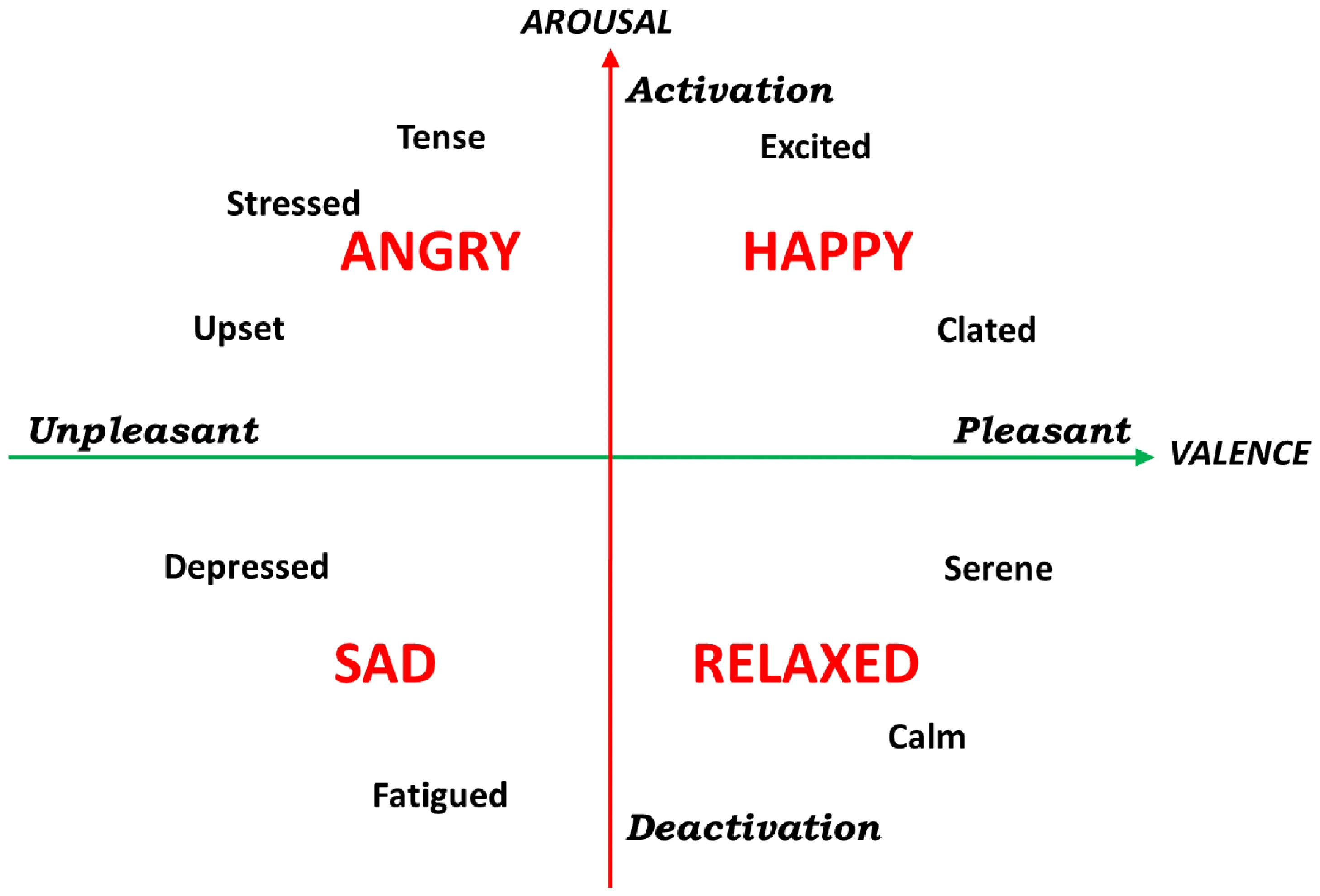
[1] Russell, J. A. (1980). A circumplex model of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(6), 1161–1178. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0077714
[2] Valenza, G., Citi, L., Lanatá, A. et al. Revealing Real-Time Emotional Responses: a Personalized Assessment based on Heartbeat Dynamics. Sci Rep 4, 4998 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04998
| Dataset | Lang | Size | Type | Emotions | Modalities | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AffectNet | N/A | ~450.000 subjects | Natural | Continuous valence/arousal values and categorical emotions: anger, contempt, disgust, fear, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise | Visual | 425x425 |
| Belfast Naturalistic Database | Spanish | 127 multi-cultural speakers of 298 emotional clips | Natural | Amusement, anger, disgust, fear, frustration, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual |
N/A |
| Berlin Database of Emotional Speech (Emo-DB) | German | 5 male and 5 female speakers, with more than 500 utterances | Acted | Anger, boredom, disgust, fear/anxiety, happiness, neutral, sadness | Audio | Audio: 48kHz, downsampled to 16kHz Formats:.wav |
| CMU Multimodal Opinion Sentiment and Emotion Intensity (CMU-MOSEI) | English | 1000 gender-balanced YouTube speakers, 23500 sentences | Natural | Sentiment: Negative, weakly negative, neutral, weakly positive, positive Emotions: Anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual Text |
N/A |
| CaFE |
French (Canadian) | 12 actors, 6 males, and 6 females, 6 sentences | Acted | Anger, disgust, fear, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise in two different intensities | Audio | Audio: 192kHz and 48kHz Formats:.aiff |
CREMA-D  |
English | 91 actors,48 males, and 43 females, 12 sentences | Acted | Anger, disgust, fear, happy, neutral and sad / Emotional Intensity | Audio Visual |
Audio: 16kHz Formats:.wav,.mp3,.flv |
EmoV-DB  |
English (North American), French (Belgian) |
4 English, (2 males, and 2 females) and 1 French (male) | Acted | Amused, anger, disgust, neutral, and sleepiness | Audio | Audio: 16kHz Formats: wav |
EMOVIE  |
Chinese (Mandarin) | 9,754 utterances from television programs and movies | Natural | Emotion Polarity (-1, -0.5, 0, 0.5 and 1) | Audio | Audio: 22.05kHz Formats: wav |
ESD  |
English (North American), Chinese (Mandarin) | 10 English (5 males, 5 females) and 10 Chinese (5 males, 5 females) speakers, 700 utterances | Acted | Anger, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise | Audio Text |
Audio: 16kHz Formats: wav |
Interactive Emotional Motion Capture (USC-IEMOCAP)  |
English | A 12h multimodal and multispeaker (5 males and 5 females) database | Acted Elicited |
Anger, frustration, happiness, neutral, sadness as well as dimensional labels such as valence, activation and dominance | Audio Visual |
Audio: 48kHz Video: 120 fps |
| MELD: Multimodal EmotionLines Dataset | English | More than 13000 utterances from multiple speakers | Natural | Anger, disgust, fear, joy, neutral, non-neutral, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual Text |
Audio: 16bit PCM Formats: .wav |
| OMG-Emotion | English | 10 hours of YouTube videos around 1min long | Natural | Continuous valence/arousal values and categorical emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual Text |
N/A |
| RESD (Russian Emotional Speech Dialogs) | Russian | 3.5 hours of live speech | Natural | Anger, disgust, fear, enthusiasm, happiness, neutral and sadness | Audio | Audio: 16 or 44.1kHz Formats: .wav |
| Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS) |
English (North American) | A database of emotional speech and song of 12 males and 12 females | Acted | Anger, disgust, calmness, fear, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual |
Audio: 48kHz - 16bit Video: 720p Formats: .wav,.mp4 |
| SEMAINE | English | 95 sessions of human-agent interactions | Natural | 4D Emotional space | Audio Visual Text |
N/A |
Surrey Audio-Visual Expressed Emotion (SAVEE)  |
English | 4 male speakers x 480 utterances | Acted | Anger, disgust, fear, happiness, neutral, sadness, surprise | Audio Visual |
Audio: 44.1kHz - mono - 16bit Video: 256p - 60fps Formats: .wav, .avi |
| SUSAS | English | Speech under stress corpus with more than 16000 utterances from 32 speakers (13 females, 19 males) | Acted | Ten stress styles such as speaking style, single tracking task, and Lombard effect domain | Audio | 8kHz, 8bit PCM |
| Database | Year | Type | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
VGGSound  |
2020 | more than 210k videos for 310 audio classes | N/A, 10sec long |
AudioSet  |
2017 | 2.1 million sound clips from YouTube videos, 632 audio event classes | N/A, 10sec long |
| UrbanSound8K |
2014 | Urban sound excerpts | sampling rate may vary from file to file, duration<=4sec |
ESC-50  |
2000 | Environmental audio recordings | 44.1kHz, mono, 5sec long |
| Database | Year | Description |
|---|---|---|
Real Acoustic Fields (RAF)  |
2024 | An audio-visual room acoustics dataset and benchmark |
Room Impulse Responses Datasets  |
2023 | A list of publicly available room impulse response datasets and scripts to download them |
- C++
- MATLAB
- Audio Toolbox | Provides tools for audio processing, speech analysis, and acoustic measurement
- Covarep |
| A Cooperative Voice Analysis Repository for Speech Technologies
- Python Libraries
- Aubio |
| Free, open source library for audio and music analysis * Librosa |
| A Python package for music and audio analysis
- OpenSoundscape |
| A Python utility library for analyzing bioacoustic data
- Parselmouth |
| A Pythonic interface to the Praat software
- PyAudioAnalysis |
| A Python library that provides a wide range of audio-related functionalities focusing on feature extraction, classification, segmentation, and visualization issues
- Pydub |
| Manipulate audio with a simple and easy high-level interface
- SoundFile |
| A python library for audio IO processing
- Aubio |
- Audacity |
| Free, open source, cross-platform audio software
- AudioGPT |
| Solve AI tasks with speech, music, sound, and talking head understanding and generation in multi-round dialogues, which empower humans to create rich and diverse audio content with unprecedented ease (paper)
- ESPNet |
| ESPnet is an end-to-end speech processing toolkit covering end-to-end speech recognition, text-to-speech, speech translation, speech enhancement, speaker diarization, and spoken language understanding
- Kaldi |
| Kaldi is an automatic speech recognition toolkit
- NVIDIA NeMo |
| NVIDIA NeMo is a conversational AI toolkit built for researchers working on automatic speech recognition (ASR), natural language processing (NLP), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS)
- S3PRL |
| A toolkit targeting for Self-Supervised Learning for speech processing. It supports three major features: i) Pre-training, ii) Pre-trained models (Upstream) collection, and iii) Downstream Evaluation
- SpeechBrain |
| A PyTorch speech and all-in-one conversational AI toolkit
- Audiomentations - A Python library for audio data augmentation
- torch-audiomentations - Fast audio data augmentation in PyTorch
- Audio/Speech
- Visual
Various performance metrics can be used to evaluate a SER system, such as
- Accuracy, Weighted Accuracy
- Recall, Unweighted Average Recall, Weighted Average Recall
- Precision
- F1 score, Weighted F1-score
- Mean Absolute Error
- Root Mean Square Error
- Average Recognition Rate
List
| Name | Impact Factor | Review Method | First-decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontiers in Computer Science | 1.039 | Peer-review | 13w |
| International Journal of Speech Technology | 1.803 | Peer-review | 61d |
| Machine Vision and Applications | 2.012 | Peer-review | 44d |
| Applied Accoustics | 2.639 | Peer-review | 7.5w |
| Applied Sciences | 2.679 | Peer-review | 17.7d |
| Multimedia Tools and Applications | 2.757 | Peer-review | 99d |
| IEEE Sensors | 3.301 | Peer-review | 60d |
| IEEE Access | 3.367 | Binary Peer-review | 4-6w |
| Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience | 3.633 | Peer-review | 40d |
| IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing | 3.919 | Peer-review | N/A |
| Neurocomputing | 5.719 | Peer-review | 74d |
| IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing | 10.506 | Peer-review | N/A |
2023
| Name | Date | Location | More |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE / CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) | June 2023 | Canada | |
| International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing (ICASSP) | June 2023 | Greece | |
| International Speech Communication Association - Interspeech (ISCA) | August 2023 | Ireland | |
| European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO) | September 2023 | Finland | ➖ |
| Workshop on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) | September 2023 | Finland | |
| IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA) | October 2023 | USA | ➖ |
| International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR) | November 2023 | Italy |
2024
| Name | Date | Location | More |
|---|---|---|---|
| International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, & Signal Processing (ICASSP) | April 2024 | Seoul, Korea | |
| IEEE / CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR) | June 2024 | Seattle, WA, USA | |
| International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) | July 2024 | Vienna, Austria | ➖ |
| European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO) | August 2024 | Lyon, France | ➖ |
| International Speech Communication Association - Interspeech (ISCA) | September 2024 | Kos, Greece | ➖ |
| Workshop on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) | October 2024 | Tokyo, Japan | |
| ACM International Conference on Multimedia | October 2024 | Melbourne, Australia | ➖ |
| International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR) | November 2024 | San Fransisco, CA, USA | ➖ |
| Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) | December 2024 | Vancouver, Canada | ➖ |
- Deep Learning for Audio (HSE University)
- Deep Learning for Audio (University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign)
- Dive into Deep Learning
- Introduction to Speech Processing, 2nd Edition, Aalto University
- Mastering Audio - The Art and the Science, Robert A. Katz
- Spectral Audio Signal Processing, Julius O. Smith III
- The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing, Steven W. Smith
Audio/Speech
- Awesome Speaker Diarization
- Casual Conversations Dataset
- Music Emotion Recognition Datasets
- Project TaRSila speech datasets for Brazilian Portuguese language
- SER Datasets
- Voice Datasets
- ✨❔
Visual/Face
- Awesome-SOTA-FER a curated list of facial expression recognition in both 7-emotion classification and affect estimation
- FG 2024 experience the cutting edge of progress in facial analysis, gesture recognition, and biometrics with this repository
- ✨❔
|
A picture(s) is worth a thousand words! A 2-min visual example of how we communicate emotions, our perceptions, the role of subjectivity and what is effective listening. Are emotions consistent? What about the dynamics of the context to our decisions and emotional wellness? |

from Inside Out (2015) by Pixar Animation Studios |





















