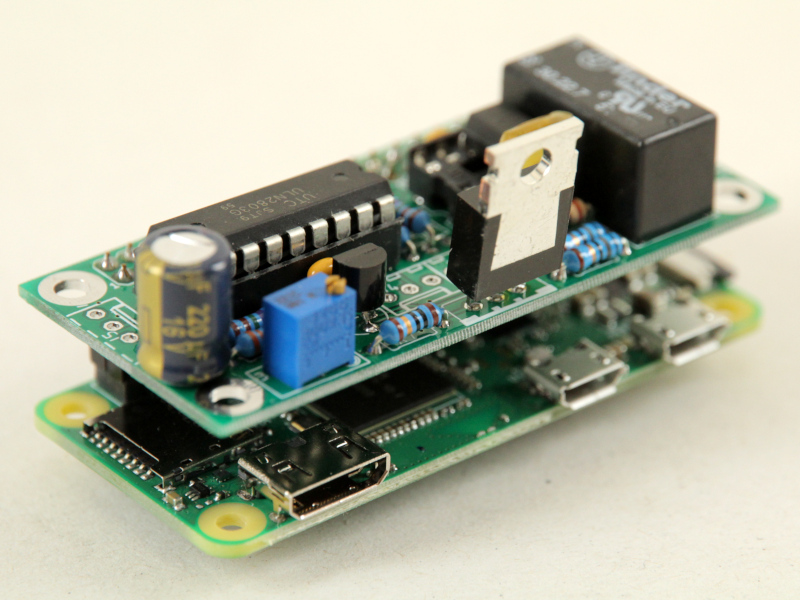
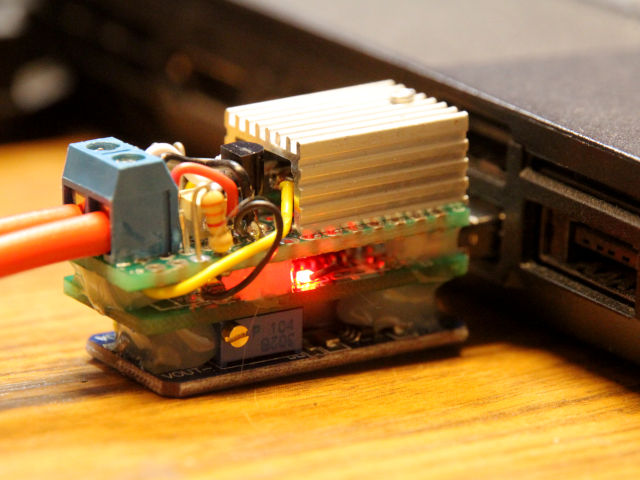
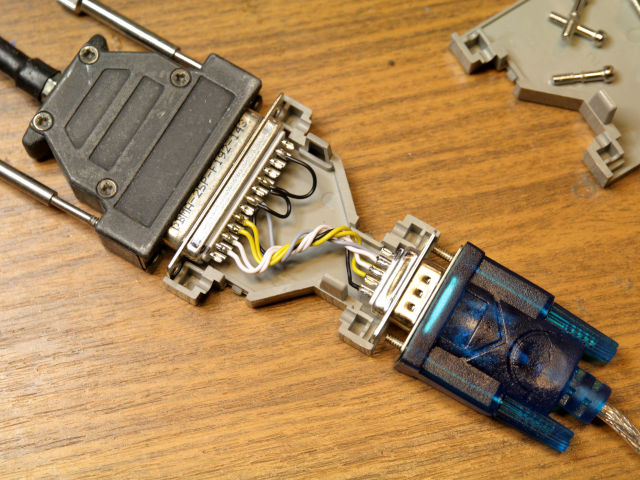
I forked the original project to adapt it to my setup:
- Raspberry Pi 4B running piTelex
- Siemens T1000 teletypewriter (with ED1000 SEU)
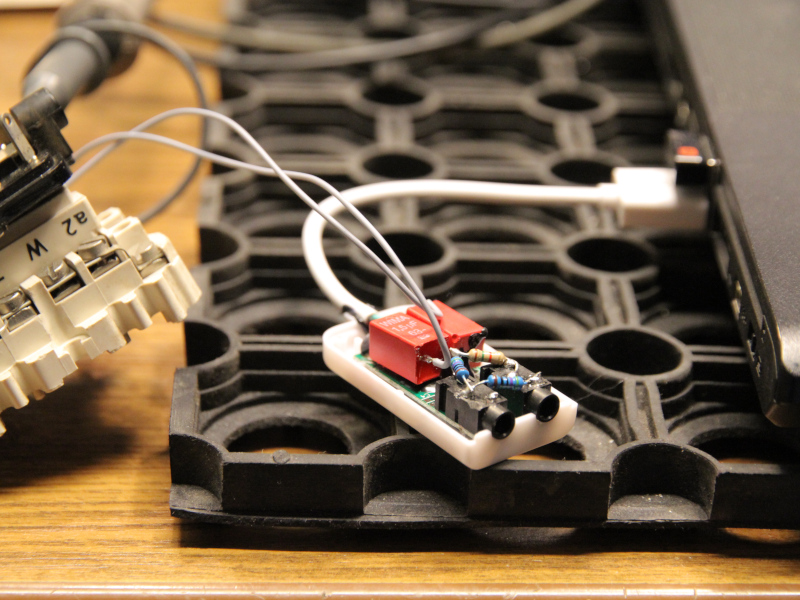
- Interface is "0d8c:0014 C-Media Electronics, Inc. Audio Adapter (Unitek Y-247A)", sold as UGREEN external USB sound card
- A Pi-Plates RELAYplate switches the TTY's mains to reduce standby power consumption
I try to keep my changes generic and well-documented, in the hopes that most commits will be suitable for upstream. If there should be a specific issue with my modifications, feel free to create an issue.
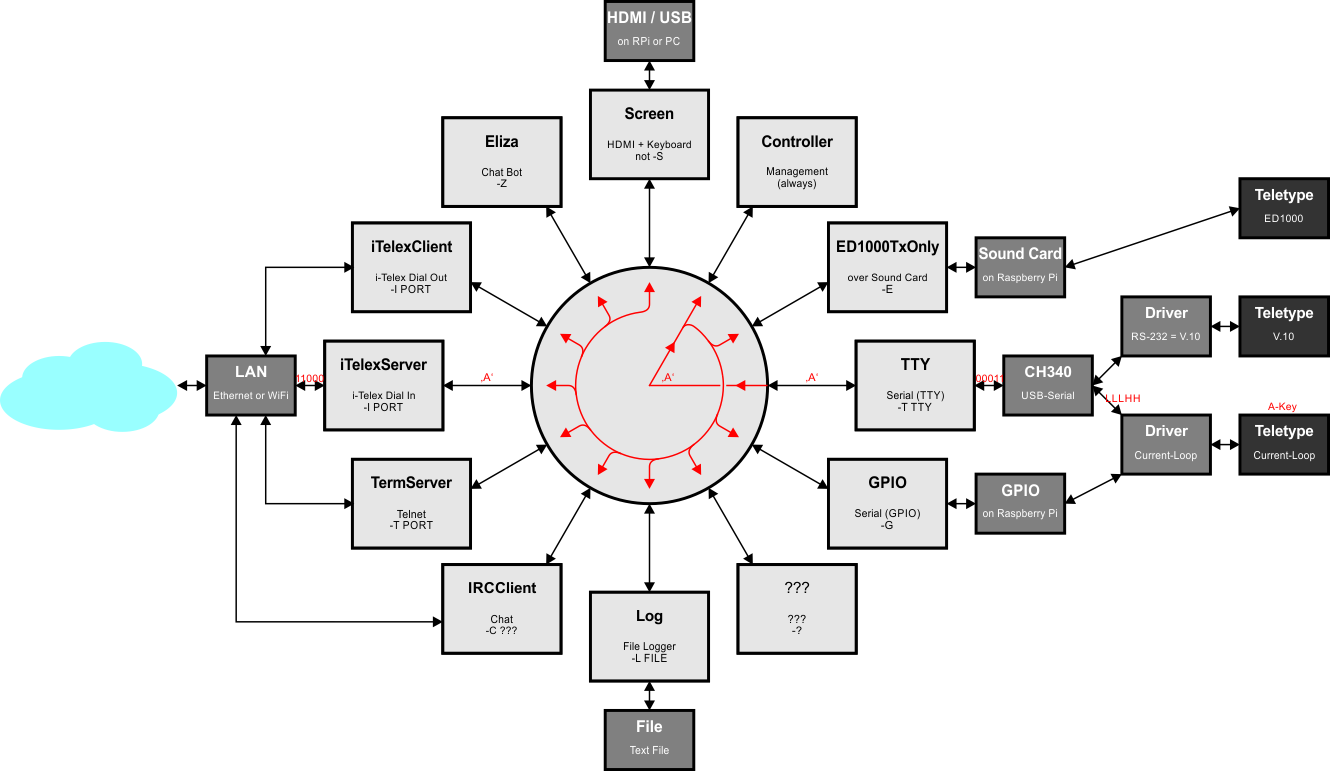
The goal is to connect a historic telex device (teletype) with TW39 protocol on a current loop to a modern Windows/Linux-PC (over USB) or a Raspberry Pi (over GPIO) with minimal hardware.
Our ambition is also to support all telex features as AT/ST buttons and pulse dialing for handling the teletype like in the good old days.
One part of the project is the hardware to adapt the current loop for TW39 to modern logic level ports. The 5V or 3.3V TTL lines can be connected directly to an USB-serial-adapter or the GPIO pins of a Raspberry Pi.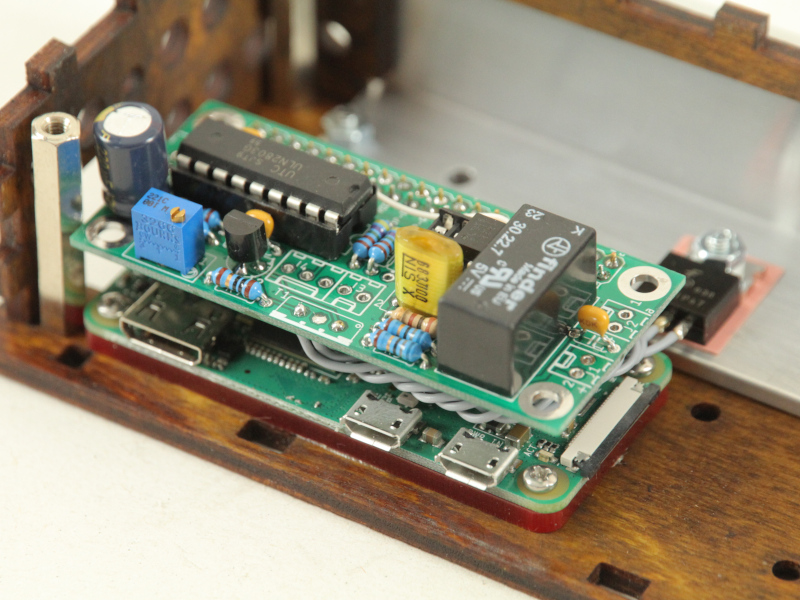 
As side effect teletypes with V.10 interface (like TeKaDe FS200Z / FS220Z) can also be connected to a USB-to-RS232-adapter with a simple DIY adapter cable. The V.10 interface control lines are completely handled by the software (No FAG200 is needed).
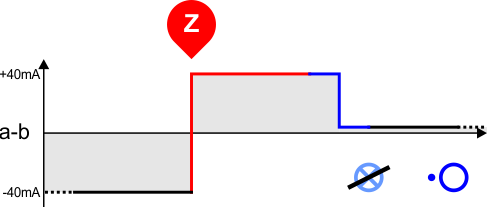
Another playground is the ED1000 interface used by (more) modern teletypes (like Siemens T1000, T1200 or SEL Lo2000, Lo3000). It is based on frequency-shift-keying (FSK) and is handled by a USB sound card, a few passive components and a lot of software.
The other part is the Python software to send and receive the serial data (50 baud, 5 data-bits) and decode the "Baudot-Murray-Code" character set (also called "CCITT-2" or "ITA2") to ASCII.
With the characters arrived in the PC / RPi the data can be routed to an internet services like i-Telex, Telnet, eMail, RSS or IRC. The teletype can also be (miss-) used as a steampunk printer or keyboard.
The software supports also a connection to another telex device in the i-Telex Network over TCP/IP.
For building the hardware and implementing the software it was important to understand the protocols and timings. So, another objective was to pick up the pieces of information a bring it into an understandable form.
For more informations see the WIKI pages
The software and hardware are in use by about 10 teletype stations and working fine.
- 2020-09: Moved non-source-code folders to new project piTelex.supplement
- 2020-09: Merged Björns rework of i-Telex protocol handling and ED1000 workflow
- 2020-08: Merged Björns fork (https://github.com/b-schliessmann/piTelex) with TNS, ED1000 and i-Telex-connection rework
- 2020-08: Added device module CLI for commands over teletype
- 2020-07: Merged Dirks device module for Twitter (https://github.com/dirkenstein/piTelex)