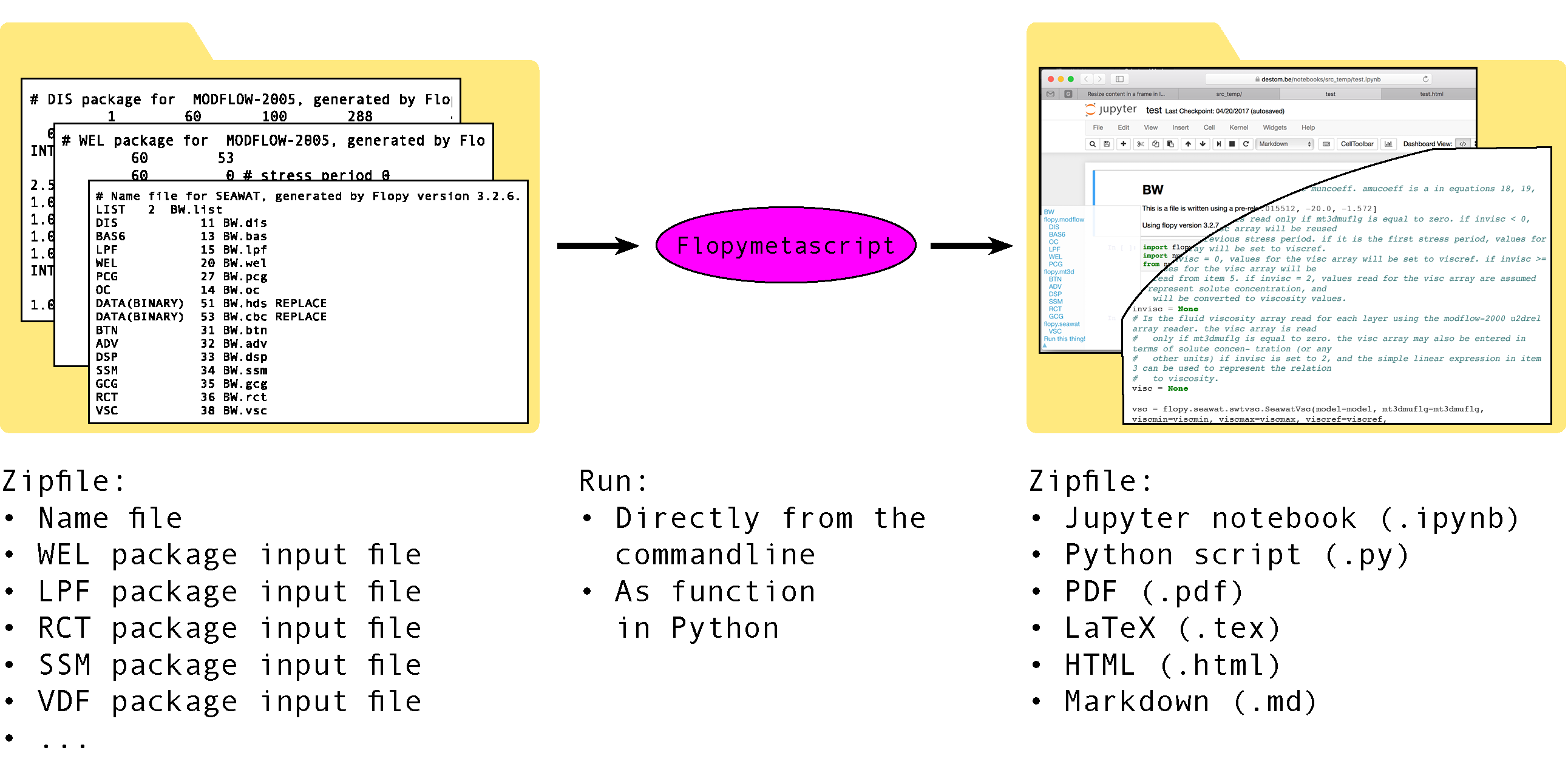
Converts a zip with MODFLOW input files to a zip containing Flopy script in different formats. This Flopy (Python) script can generate the intitial MODFLOW input files.
It should work for all packages of MODFLOW, MT3D, and SEAWAT. For a complete list, see the Packages with default values and the load supported packages on the Flopy website.
The flopyparser is continously tested with several benchmark modflow models. This ensures that the generated python scripts contain valid code and produce the same heads and flow as the benchmark input files.
The software is available under MIT license. The author has absolutely no convidense in that the software is correct and is not responsible for the content and consequences of malicious scripts. I you find it useful, please consider donating to charity (be creative in choosing which one) and send me a note (or create and close an issue). Thanks! The author is not affiliated with the modflow family nor with Flopy. This converter/generator uses the Flopy load function. Any errors/mistakes in the Flopy load functions propagate silently in to the generated script.
- You are coming from a different modeling environment and want to start using Flopy
- Clean up your flopy script/notebook
- Add a description (and default value) to your parameters
- Check someone else's MODFLOW input files / Flopy script
- Check homework assignments
- Start from scratch by adding your own packages
- Returns .ipynb, py, tex, html, markdown, and rst file of your MODFLOW input files
- Consistent and clean markup is used
- All the parameters are defined explicitely
- A description is loaded and interpreted from the flopy package directly. The same description as in the docs (modflowpy.github.io/flopydoc/) is used.
- Makes use of smart broadcasting to reduce the size of the arrays printed to the script.
Enter in the terminal,
$ pip install https://github.com/bdestombe/python-flopy-parser/archive/master.zipThe $-sign should be omitted, and only refers to that the command is to be entered in the bash-commandline. The flopyparser package added to system's $PATH and is reachable from any directory. Check if everything works by typing in any directory,
$ flopyparser --helpUninstall with,
$ pip uninstall flopyparserTry this first,
$ flopyparser --outbytesfile output.zip --inbytesfile input.zip --logfile log.txtinput.zip is a zip-file that contains MODFLOW input files and a single .nam file. Its content is processed and written to output.zip. Some logging is written to log.txt.
Might be of interest when using flopyparser as webservice.
$ openssl base64 -in input.zip -out input.zip.b64
$ flopyparser --outbytesfile output.zip --inbase64file input.zip.b64Here, in the first line input.zip is encoded to base64 and is used in the second line as input file for flopyparser.
$ flopyparser --outbytesfile output.zip --inbase64file - < input.zip.b64The content of input.zip.b64 is streamed/piped to flopyparser
$ openssl base64 -in input.zip | flopyparser --outbytesfile output.zip --inbase64file -The same as what is done previously, however input.zip is encoded and instead of writing it to a file, it is passed as stdin to the inbase64file argument of flopyparser.
$ openssl base64 -in input.zip | flopyparser --outbase64file utput.zip --inbase64file - --logfile -The log file is printed to stdout.
You cannot send both outbase64file and logfile to stdout. They will be mixed and the resulting output file is not readable.
from flopyparser.flopyparser import process
inbytesfn = 'input.zip' # Dont forget the b flag when opening the file
outbytesfn = 'output.zip'. # Dont forget the b flag when opening the file
logfn = 'log.txt'
with open(inbytesfn, 'rb') as inbytesfh, \
open(outbytesfn, 'wb') as outbytesfh, \
open(logfn, 'w') as logfh:
process(inbytesfile=inbytesfile,
outbytesfile=outbytesfile,
logfile=logfile)This example loads a name-file and overwrites the dis and bas6 package with the default parameter values. If dis and bas6 were not loaded with the name file, they are added. Extra options are now accessible, such as print_descr for printing the parameter description (bool), width for the desired line width of the produced script (int, number of characters), use_yapf to use Google's package to format the produced code (bool, conversion becomes slow).
from flopyparser.model import Model
mp = Model(load_nam='path_to_namfile.nam', add_pack=['dis', 'bas6'])
fn = 'path_to_jupyter_notebook.ipynb'
mp.write_script_model2string(fn=fn,
print_descr=True,
width=99,
use_yapf=True)