PlexRBACJS provides APIs to add support for role and claim based security. It supports both static and instance based security.
- Role based security
- Roles can be inherited
- Claim based security, where claims define permittable actions and can be associated with principals or roles, which are in turn associated to principals.
- Instance based security using dynamic context and regular expressions.
- Roles and claims can be assigned within a range of time period.
- Resource accountings, where you can track usage by users and use them as part of instance based security.
- There are two implementations: flow based implementation that uses relational database and vanilla JS that uses Redis.
- 0.1
- MIT
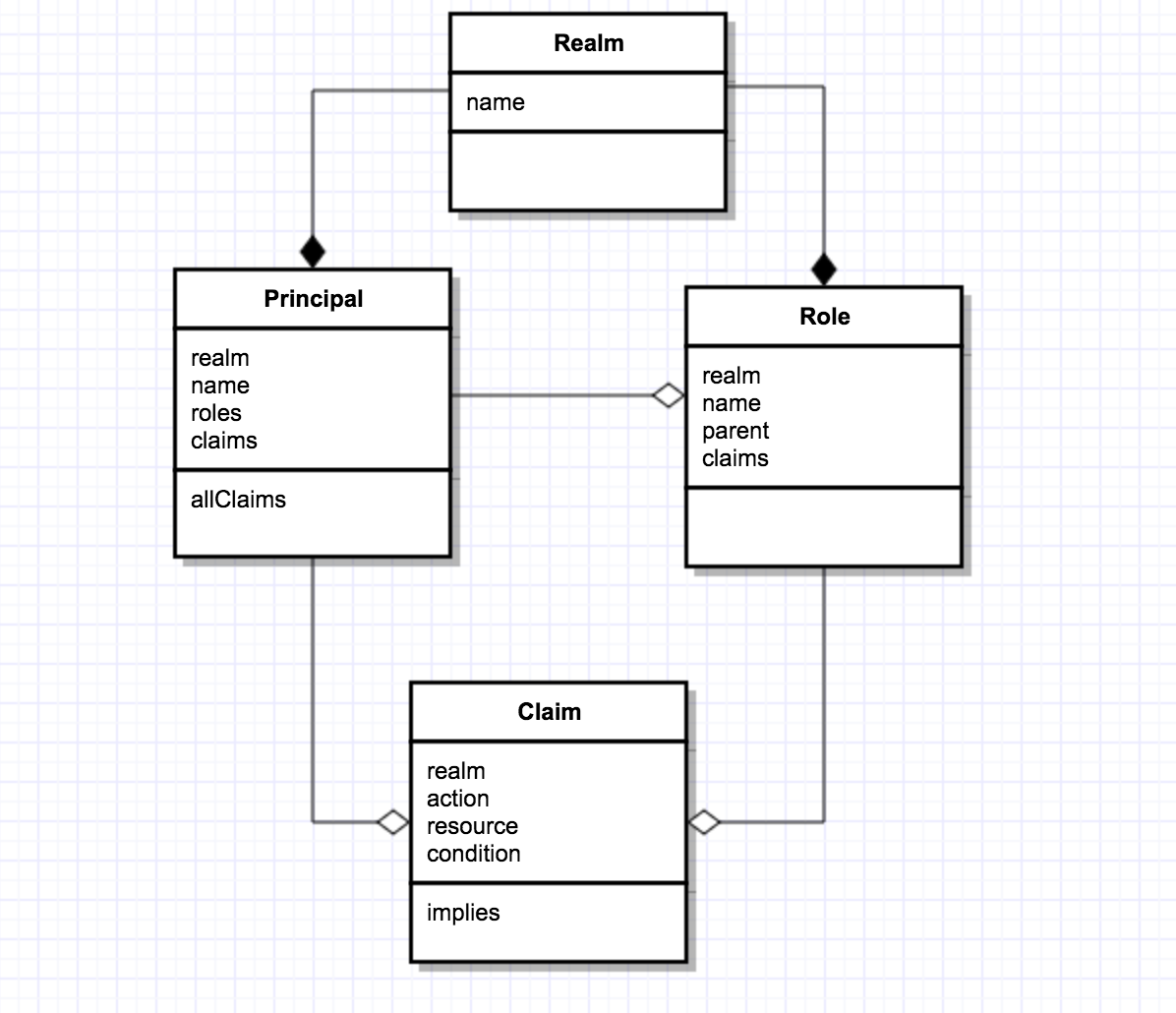
The realm defines domain of security, e.g. you may have have different security policies for different applications that can be applied by creating realm for each application.
A principal represents an identity and can be represented by user or an application.
A role represents job title or function. A principal belongs to one or more roles. One of key feature of PlexRBACJS is that roles support inheritance where a role can have one or more roles. Roles can be assigned for a predefined duration of time to principals.
A claim defines permission and consists of three parts: operation, resource and condition, where operation is a "verb" that describes action and resource represents "object" that is acted upon, and condition is an optional component that describes dynamic condition that must be checked. The claims can be assigned to roles or principal. The condition contains a Javascript based logical expressions and provides access to runtime request parameters. PlexRBACJS allows regular expressions for both operations and target, so you can define operations like "(read|write|create|delete)" or "read*", etc. Finally, claim can be assigned for a duration of time so that they are not permanent.
PlexRBACJS consists of following layers
This layer defines core classes that are part of the RBAC based security realm such as:
- Realm – - The realm allows you to support multiple applications or security realms.
- Principal – The principal represents an identity and can be mapped to users defined in an application.
- Role – A role represents job title or function.
- Claim – A claim is composed of operation, target and a condition that is used for dynamic or instance based security.
- SecurityError – Upon a claim failure, you can choose to store them in the database using SecurityError.
This layer is responsible for accessing or storing above objects in the database. PlexRBACJS uses Sqlite by default but it can be easily mapped to other databases. Following are list of repositories supported by PlexRBAC:
* RealmRepository – provides database access for Realms.
* ClaimRepository – provides database access for Claims.
* PrincipalRepository – provides database access for Principals.
* RoleRepository – provides database access for Roles.
This layer defines SecurityManager for validating authorization policies.
This layer proivdes evaluation engine for supporting instance based security.
This layer defines REST services such as:
* RealmService – this service provides REST APIs for accessing Realms.
* PrincipalService – this service provides REST APIs for accessing Principals.
* RoleService – this service provides REST APIs for accessing Roles.
* ClaimService – this service provides REST APIs for accessing Claims.
* SecurityService – this service provides REST APIs for authorizing claims.
This layer provides caching security claims to improve performance.
Please send questions or suggestions to bhatti AT plexobject.com.
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.86.9736&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/rbac/documents/design_implementation/Intro_role_based_access.htm
- http://hissa.nist.gov/rbac/poole/ir5820/ir5820s31.htm
- http://www.coresecuritypatterns.com/patterns.htm
- http://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/SHIRO/Index
- http://www.secs.oakland.edu/~kim2/papers/FASE04.pdf
- http://www.mecs-press.net/ijmecs/ijmecs-v3-n5/IJMECS-V3-N5-7.pdf
- http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/rbac/documents/design_implementation/pp-rbac-fin.pdf