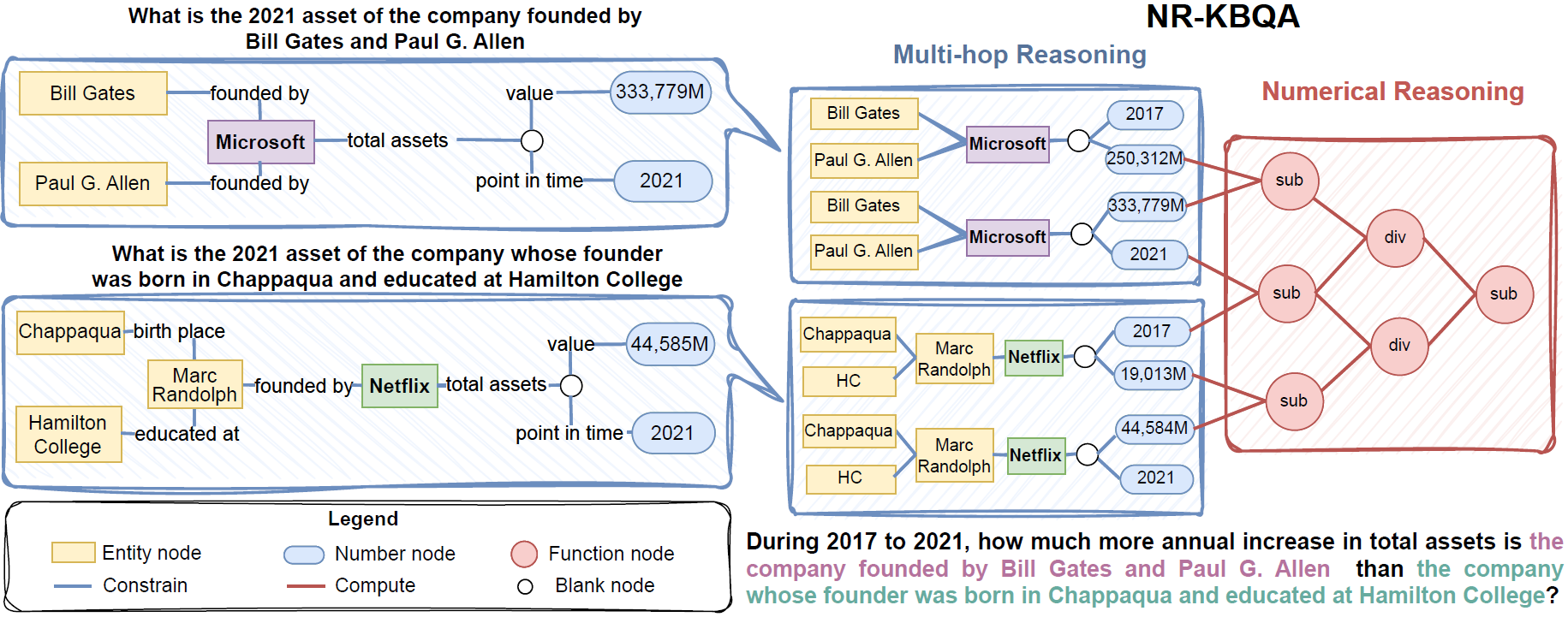
MarkQA is a large-scale dataset for question answering on knowledge bases (KBQA) on Wikidata, with 31,902 questions. Each question is annotated with answers, SPARQL, QDMR, and PyQL. It is the first dataset to focus on complex numerical reasoning in KBQA.
This is the accompanying code for the paper "MarkQA: A large scale KBQA dataset with numerical reasoning" published at EMNLP 2023. For the dataset and leaderboard, please refer to the homepage of MarkQA. The document of PyQL can be found in document of PyQL. In this repository, we provide the code for the baseline models for reproducibility and demonstrate how to work with this dataset.
The instructions for setting up a SPARQL endpoint to Wikidata for MarkQA via Virtuoso.
- OpenLink Virtuoso 7.2.6 (download from this link)
- Python 3 (required if using the provided Python script)
Our processed Virtuoso DB files are split into two files. They can be downloaded via wget and then be put together via cat:
(WARNING: 200G+ disk space is needed for the zipped file and 440G+ disk space is needed for the unzipped file)
wget https://box.nju.edu.cn/f/edd62b714b6b4fefb84e/?dl=1 -O virtuoso_db_part1
wget https://box.nju.edu.cn/f/3b0986513ff2409db5df/?dl=1 -O virtuoso_db_part2
cat virtuoso_db_part1 virtuoso_db_part2 >virtuoso_db.zip
The KB we used is a tailored version of Wikidata-2023-01-23. The original KB is not available for download therefor we suggest you use our processed KB.
We provide a Virtuoso configration file virtuoso.ini. It should be located under the same directory as the virtuoso.db file.
The virtuoso.ini can be obtained by:
wget https://box.nju.edu.cn/f/6829889a369c4b0aab6f/?dl=1 -O virtuoso.ini
To use it, first replace all virtuoso_installed_path in the file to your local Virtuoso directory. For example, if the local Virtuoso directory is /data/virtuoso-fixed, change the file via sed:
sed -i 's#virtuoso_installed_path#/data/virtuoso-fixed#g' virtuoso.ini
Then, under the same directory as the virtuoso.ini file, to start the Virtuoso service:
virtuoso-t -fd
When you see this sentence in your virtuoso.log file, your virtuoso service has been started up successfully:
INFO: Server online at 1111 (pid xxxx)
Now you can access the service via the default port 8890. Enter [ip]:8890 in a browser, you will see the virtuoso service page. You may adjust the maximum amount of RAM the service may use and other configurations in the provided virtuoso.ini file.
This repository is structured as follows:
MarkQA/
├── baselines: Baseline method of T5, GMT and QDTQA
├── dataset: Data files for training, validation, and testing.
├── environment.yaml
├── PyQL_parser.py: The implementation of PyQL.
└── readme.md
Download the data needed here and put all json files under baselines/linked_dataset_example/.
Download the huggingface t5-base model here and put all files under baselines/QDTQA/hfcache/t5-base.
chmod +x baselines/run_model_train.sh
chmod +x baselines/scripts/*
You may create a conda environment according to the configuration file environment.yaml:
conda env create -f environment.yaml
- predict_type can be set to SPARQL or PyQL
- outputs will be saved at
baselines/outputs/, its directory name starts with exp_id
conda activate QDTenv
cd baselines/
./run_model_train.sh T5 {predict_type} {exp_id} {gpu_id}
- predict_type can be set to SPARQL or PyQL
- outputs will be saved at
baselines/outputs/, its directory name starts with exp_id
conda activate QDTenv
cd baselines/
./run_model_train.sh GMT {predict_type} {exp_id} {gpu_id}
- predict_type can be set to SPARQL or PyQL
- outputs will be saved at
baselines/outputs/, its directory name starts with exp_id
conda activate QDTenv
cd baselines/
./run_model_train.sh QDTQA {predict_type} {exp_id} {gpu_id}
You may go to baselines/scripts to modify the model or training parameters freely.
@inproceedings{huang-etal-2023-markqa,
title = "{M}ark{QA}: A large scale {KBQA} dataset with numerical reasoning",
author = "Huang, Xiang and
Cheng, Sitao and
Bao, Yuheng and
Huang, Shanshan and
Qu, Yuzhong",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
month = dec,
year = "2023",
address = "Singapore",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2023.emnlp-main.633",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2023.emnlp-main.633",
pages = "10241--10259",
}