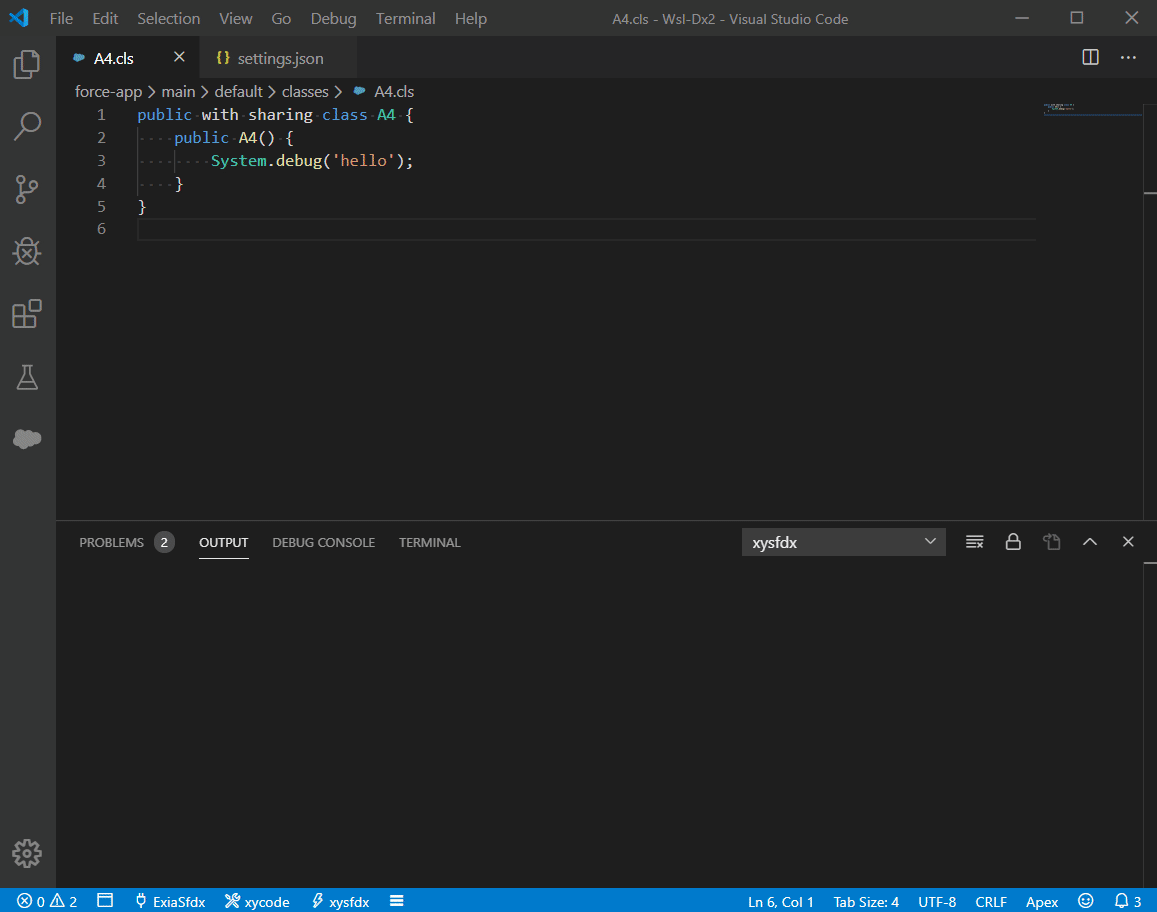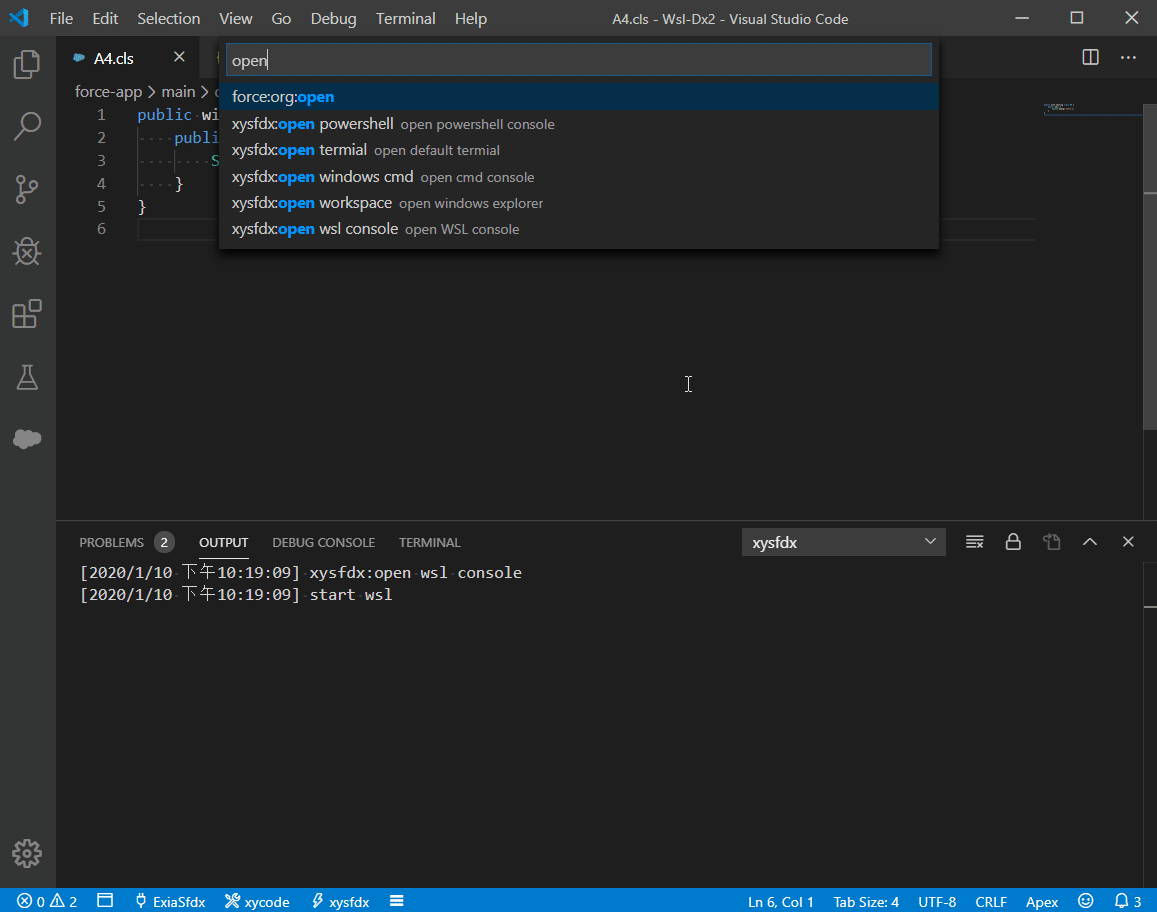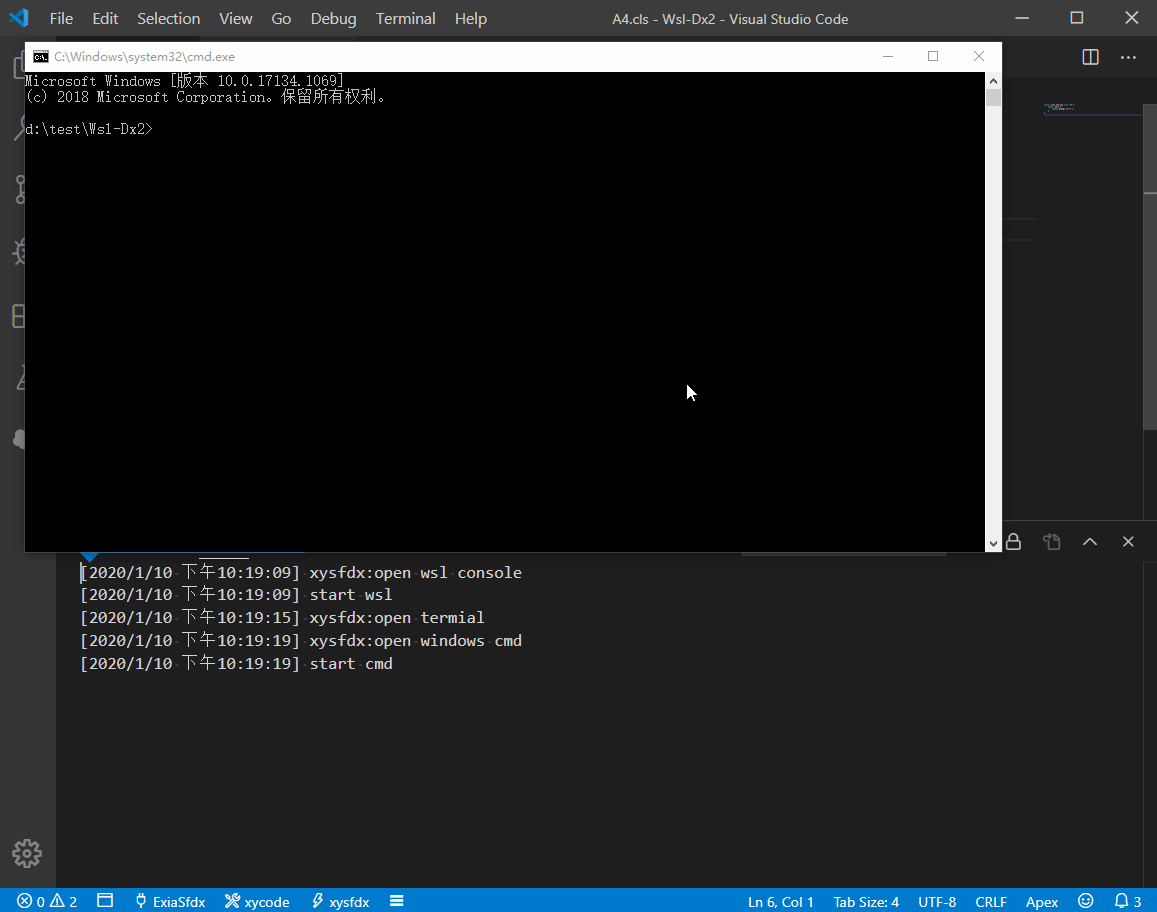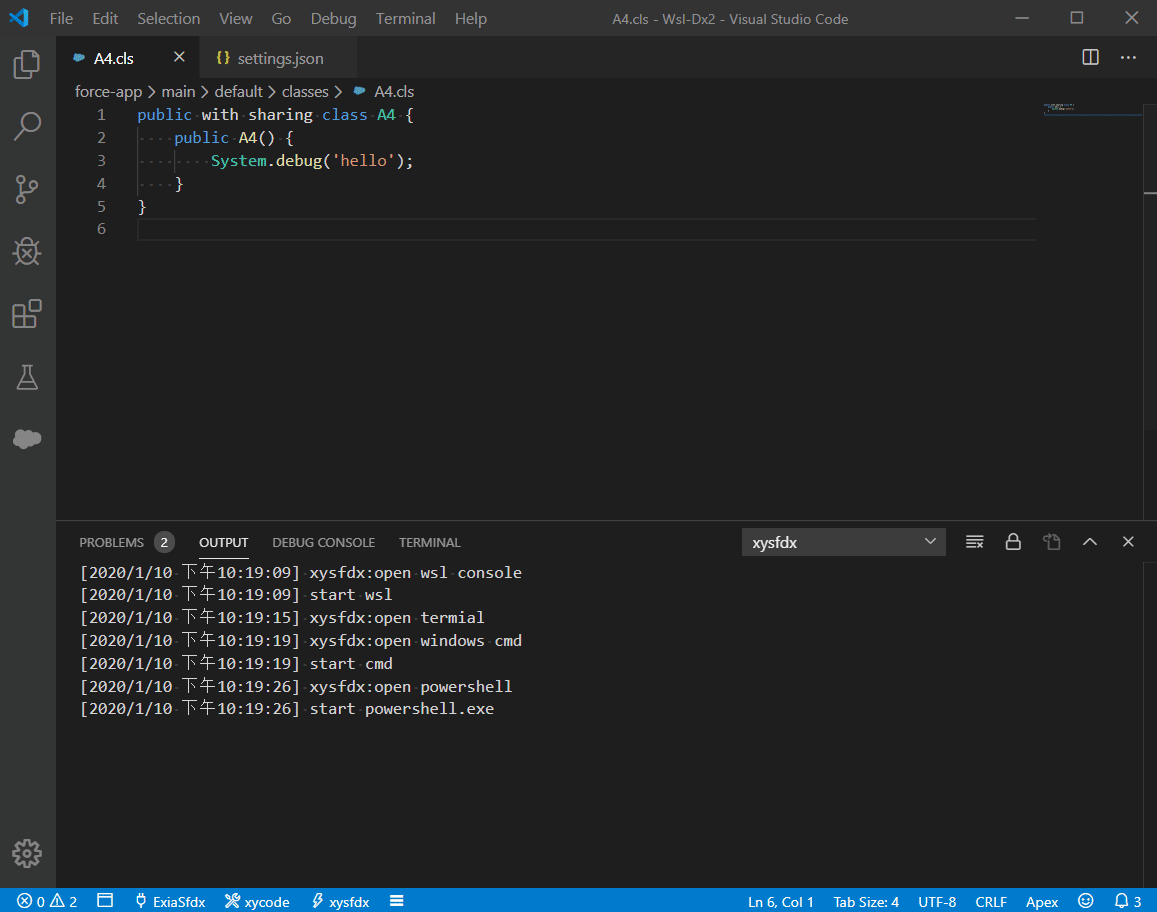
xycode is a lightweight command executor for vscode.
If you want to build a vscode extension, maybe you can use xycode first.
Project Details
Usage of xycode:
- xycode English
- xycode 日本語
- xycode 中文
- Salesforce CLI in xycode
- C Program in xycode
- Nodejs in xycode
- python in xycode
- docker in xycode
- Less than 100k.
- Shared configuration (tasks/settings) of VScode.
- Integrated with system command and work with vscode.
- Support Docker development.
- express
- flask
- jekyll
- Support c lang.
- Support vbs.
- Support dotnet core.
- Support go language.
- Support python.
- Support ruby.
- Support gradle.
- Support npm/nodejs/express/vue.
- Support prettier, format source automatically.
- Support Heroku development.
- Support git command.
- Support sfdx, it is a Rapid development tool for Salesforce SFDX Development. Metadata diff with server, retrieve standard sobject...
- Support Wenyan 文言文編程語言.
- Support hexo/mkdoc blog.
- Support WSL Develope.
- TODO : a calculator.
run xycode: download config, and select config file.
Please download config From xycode-config.
And copy the configs to Home directory( ~/.xycode or %USERPROFILE%/.xycode)
use
ctrl+shift+p, searchxycode: open config directory
create json file in below
- Windows user:
%USERPROFILE%/.xycode - Linux/Mac user:
~/.xycode
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "label name, required",
"description": "description, not required",
"command": "your command, required",
// cwd is not required
"cwd": "path of current working directory",
// filetypes is not required
// "filetypes": [".py"],
// if you not need the command , please set it true
// "inActive": false,
// show the message in termial, default show in channel.
// "termial": { name?: string, shellPath?: string, shellArgs?: string[] | string };
// before run the command, you can set some check.
"beforeTriggers": [
{
"type": "buildin",
"fn": "CheckFileExist",
"params": ["${project_directory}/${project_name}"]
}
],
// after ran the command, you can do something.
"afterTriggers": [
{
"type": "buildin",
"fn": "SwitchFolder",
"params": ["${project_directory}/${project_name}"]
}
]
}
],
"variables": {
"apex_template": {
"label": "sfdc apex template",
"description": "",
"value": [
"DefaultApexClass",
"ApexException",
"ApexUnitTest",
"InboundEmailService"
]
},
"base_metadata": {
"label": "default sfdc metadata",
"description": "",
"value": "ApexClass, ApexPage, ApexComponent, ApexTrigger"
}
}
}- ${HOME} - Home directory
- ${file} - the current opened file
- ${relativeFile} - the current opened file relative to workspaceFolder
- ${relativeFileDirname} - the current opened file's dirname relative to workspaceFolder
- ${fileBasename} - the current opened file's basename
- ${fileBasenameNoExtension} - the current opened file's basename with no file extension
- ${workspaceFolder} - the path of the folder opened
- ${workspaceFolderBasename} - the name of the folder opened in Sublime without any slashes (/)
- ${fileDirname} - the current opened file's dirname
- ${fileExtname} - the current opened file's extension
- ${YYYYMMDD} - current date
- ${YYYYMMDD_HHmm} - current datetime
- ${TMPDIR} - Temp directory
- ${XYCODE_PATH} - XYCODE Extension path
Windows Only Predefined variables:
- ${wslHOME} - WSL Home directory
- ${wslTMPDIR} - WSL Temp directory
- ${wslFile} - the current opened wsl file path
- ${wslWorkspaceFolder} - the wsl path of the folder opened
- ${wslFileDirname} - the current opened file's wsl dirname
- Mkdirs - make directory
- SwitchFolder - switch project folder
- OpenFile - open file
- CopyFile - copy file
- CheckFileExist - check file exist
- Diff - diff file
- input - Custom Input String
- select - Select List
- multiselect - Multiple Select List
- openFolderDailog - Folder Path Selector
- singleFileDailog - File Path Selector
- multiFilesDailog - Mutliple File Paths Selector
use |wslpath to change the windows path to wsl path
example :
- get the wsl path of folder:
echo ${openFolderDailog:project_directory|wslpath} - get the wsl path of current file:
echo ${file|wslpath}
echo user input
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:user-input",
"description": "echo user input",
"command": "echo ${input:project_directory}"
}
],
"variables": {}
}if you want to set the default value, please define the variable:
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:user-input",
"description": "echo user input",
"command": "echo ${input:project_directory}"
}
],
"variables": {
"project_directory": {
"label": "project directory",
"value": "${HOME}/test-project"
}
}
}echo user select
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:user-select",
"description": "echo user select",
"command": "echo ${select:dotnet_template}"
}
],
"variables": {
"dotnet_template": {
"label": "dotnet core template",
"value": [
"console",
"classlib",
"wpf",
"wpflib",
"wpfcustomcontrollib",
"wpfusercontrollib",
"winforms"
]
}
}
}echo files path, you can use separator to control the result string.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:multiselect",
"description": "echo user multiselect",
"command": "echo ${multiselect:METADATA}"
}
],
"variables": {
"METADATA": {
"label": "sfdc metadata",
"separator": ",",
"value": [
"ApexClass",
"ApexComponent",
"ApexPage",
"ApexTestSuite",
"ApexTrigger"
]
}
}
}echo directory path
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:folder-path",
"description": "echo directory",
"command": "echo ${openFolderDailog:project_directory}"
}
],
"variables": {}
}single file dailog, you can use filters to control the file type.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:file-path",
"description": "echo single file path",
"command": "echo ${singleFileDailog:package_xml}"
}
],
"variables": {
"package_xml": {
"label": "sfdc package.xml path",
"filters": { "package.xml": ["xml"] },
"value": "./manifest/package.xml"
}
}
}Mutliple File Paths Selector
- use
filtersto control the file type. - use
separatorto control the result string.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:files-paths",
"description": "echo files paths",
"command": "echo ${multiFilesDailog:sfdcsourcesfiles}"
}
],
"variables": {
"sfdcsourcesfiles": {
"label": "sfdc sources files",
"separator": ",",
"value": ""
}
}
}change the shellPath, you can run command in wsl/bash/powershell ... or other termial
{
"label": "run command in wsl",
"termial": {
"name": "xycode",
"shellPath": "wsl.exe"
},
"command": "pwd"
}After you save file in vscode,
It will use yapf to format code and run python code automatically.
{
"tasks": [],
"variables": {},
"onSaveEvents": [
{
"label": "format python code",
"description": "format python code",
"filetypes": [".py"],
"inActive": false,
"command": "yapf \"${file}\" --style \"google\" -i"
},
{
"label": "run python file",
"description": "run python file",
"filetypes": [".py"],
"inActive": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"command": "python \"${file}\""
}
]
}use Prettier to pretty code .
{
"tasks": [],
"variables": {},
"onSaveEvents": [
{
"label": "pretty code.",
"description": "Prettier is an opinionated code formatter.",
"filetypes": [".json", ".javascript", ".js", ".md", ".css", ".vue"],
"inActive": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"command": "prettier --write \"${file}\" --single-quote=true --end-of-line=lf --arrow-parens=always --tab-width=4"
}
]
}{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "hello:echo:wsl-folder-path",
"description": "echo directory",
"options": {
"shell": "C:\\Windows\\System32\\bash.exe"
},
"command": "echo ${openFolderDailog:project_directory|wslpath}"
}
],
"variables": {}
}{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "console: WSL",
"description": "open WSL",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "cd ${workspaceFolder} && start wsl"
},
{
"label": "console: cmd",
"description": "open cmd",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "start cmd"
},
{
"label": "console: Cmder",
"description": "open Cmder",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "Cmder.exe /single ${workspaceFolder}"
},
{
"label": "console: bash",
"description": "open bash",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "cd ${workspaceFolder} && start bash"
},
{
"label": "console: mintty.exe",
"description": "open mintty.exe",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "start /b mintty.exe /bin/bash --login"
}
],
"variables": {}
}open directory in windows explorer or sublime.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "windows: explorer",
"description": "open explorer",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "start explorer ${workspaceFolder}"
},
{
"label": "windows: open home directory",
"description": "open home directory",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "start explorer ${HOME}"
},
{
"label": "sublime",
"description": "open sublime",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "\"C:\\Program Files\\Sublime Text 3\\sublime_text.exe\" \"${openFolderDailog:project_directory}\""
},
{
"label": "sublime:open this workspace",
"description": "open sublime",
"notShowProcess": true,
"command": "\"C:\\Program Files\\Sublime Text 3\\sublime_text.exe\" \"${workspaceFolder}\""
}
],
"variables": {}
}add docker to your json file in ~/.xycode,
then each task in this json config file will run in docker container.
{
"tasks": [
{
"description": "use docker run command!",
"label": "docker:run js",
"command": "node ${file}",
"dockerOptions": {
"openTTY": false
}
}
],
"variables": {},
"docker": {
"dockerContainer": "${lowercaseWorkspaceName}_sfdx_1"
}
}more example about docker:
define a dynamic variable, the value of var is the script result.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "docker:base:attach docker shell",
"termial": {
"name": "docker"
},
"description": "open default termial",
"command": "docker exec -it \"${select:docker_container_names}\" /bin/sh -c \"[ -e /bin/bash ] && /bin/bash || /bin/sh\""
}
],
"variables": {
"docker_container_names": {
"label": "docker container name",
"scripttype": "shell",
"script": "docker container ls --format=\"{{.Names}}\" --all",
"datatype": "array",
"separator": "\n"
}
}
}shortkey: ctrl+shift+i
Require commands which you set in your config file in ~/.xycode/*.json
This extension contributes the following settings:
xycode.maxBuffer: The maxBuffer option specifies the largest number of bytes allowed on stdout or stderr.
None
Release Notes:
Initial release of Xycode.
Enjoy it!