This tool lets you interactively ping:
- One host from multiple locations (via SSH)
- Multiple hosts from one location (local machine, or remote via SSH)
- Multiple hosts from multiple locations (via SSH)
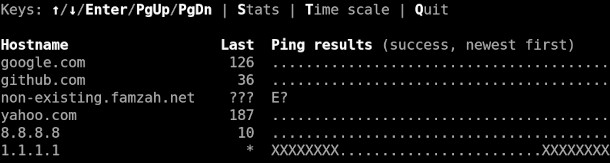
The main screen:
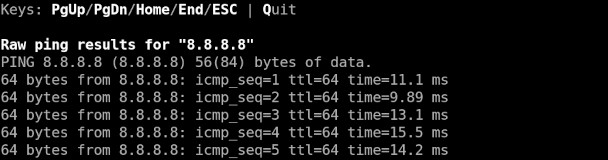
Full history of the "ping" raw output for a selected host:
The ping results are summarized in real-time and you can also observe the following statistics:
- TX_cnt: Count of sent PING requests
- RX_cnt: Count of received PING replies which are not timeouts
- XX_cnt: Count of timeouts and missing PING replies
- Loss%: Packet loss defined as the percentage of timed out and missing replies
- Avg: Average round trip time (RTT)
- Min: Minimum (best) RTT
- Max: Maximum (worst) RTT
- StDev: Population standard deviation of all RTT data
The interactive UI interface lets you visualize the RTT summary in three modes:
- Successful vs. unsuccessful PING replies
- The RTT values (ping time) as a number
- Scaled per 100 ms where "0" means an RTT between 0 and 99 ms, "1" means an RTT between 100 and 199 ms, and so on
You also have the option to review each host's "ping" command raw output. The full history is kept and you can navigate using the keys PgUp/PgDn/Home/End.
No "root" privileges are required because for each host an external process is started which uses the standard "ping" command.
You can select the statistics forwards and backwards using the lower "s" and upper "S" keys, similar to the "Vim" behavior.
pip3 install ping-multi-ext
The executable "ping-multi" is automatically added to your "~/.local/bin" directory which you should add to your "$PATH" environment, so that you can easily execute "ping-multi".
If you install the package globally using "root" privileges, then the binaries are added in "/usr/local/bin" and you should be able to use them right away with no additional setup.
Ping multiple hosts specified directly on the command-line; you can also provide just one host:
ping-multi google.com github.com
You can also use SSH to run "ping" on remote machines:
ping-multi google.com github.com github.com@[email protected]
Ping multiple hosts specified in a file; you can also add more single hosts directly as additional command-line arguments:
ping-multi -f sample.list
IPv4 CIDR masks are supported:
ping-multi 192.168.0.0/30
The usage help explains the additional command-line options:
$ ping-multi -h
usage: ping-multi [-h] [--version] [--hosts-max-width HOSTS_MAX_WIDTH] [-s {Last,Loss%,Avg,Min,Max,StDev,RX_cnt,TX_cnt,XX_cnt}] [-f FILE]
[-W SECS] [-i SECS] [-L COUNT_LIMIT] [-C]
[host ...]
Ping all hosts from FILE and HOSTs.
positional arguments:
host host to ping; you can specify this option many times
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version show program's version number and exit
--hosts-max-width HOSTS_MAX_WIDTH
maximum width of the hosts column; default=0
-s {Last,Loss%,Avg,Min,Max,StDev,RX_cnt,TX_cnt,XX_cnt}, --stat {Last,Loss%,Avg,Min,Max,StDev,RX_cnt,TX_cnt,XX_cnt}
statistic to display initially; default=Last
-f FILE, --file FILE read list of hosts from file
-W SECS, --wait SECS timeout in seconds to wait for a ping reply; default=1
-i SECS, --interval SECS
time in seconds between sending each request; default=1
-L COUNT_LIMIT, --count-limit COUNT_LIMIT
limit the number of hosts; avoids unintended bulk actions; default=600
-C, --cidr-debug debug IPv4 CIDR expansion